The Landscape of lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Translational Perspective
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. LncRNAs in the Hallmarks of HCC
2.1. Activating Invasion and Metastasis
2.2. Sustaining Proliferative Signaling
2.3. Deregulating Cell Metabolism
2.4. Self-Renewal and Maintenance of Cancer Stem Cells
2.5. Resisting Cell Death
2.6. Enabling Replicative Immortality
2.7. Inducing Angiogenesis
2.8. Tumor-Promoting Inflammation and Avoiding Immune Destruction
3. Concluding Remarks
3.1. Molecular Mechanisms of lncRNAs Relevant for HCC
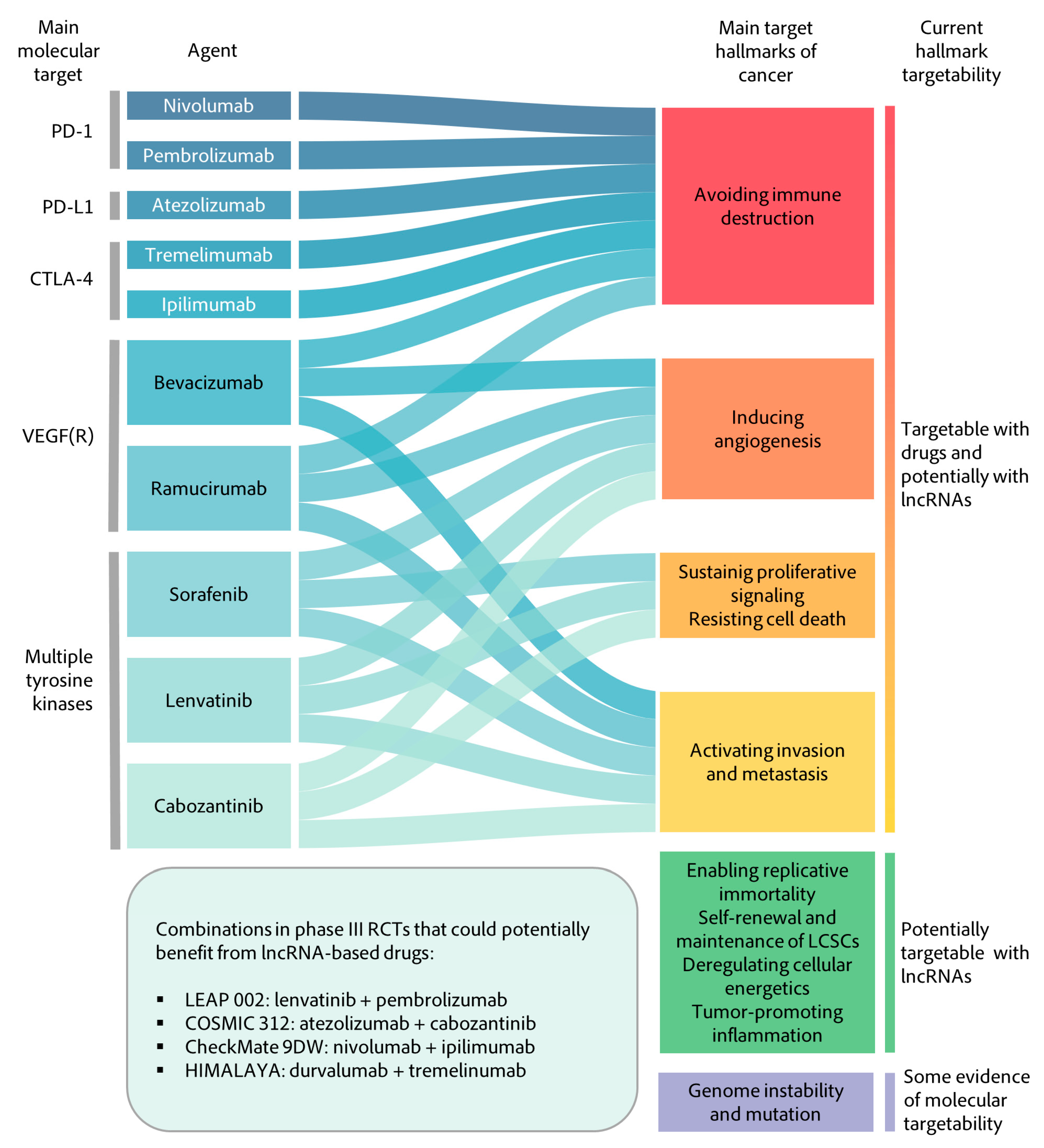
3.2. Therapeutic Implications
3.3. Biomarker Potential
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSC | Cancer stem cells |
| CTNNBIP1 | Catenin beta interacting protein 1 |
| CUL4 | Cullin 4A |
| DNA | Desoxiribonucleic acid |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of zeste 2 polycomb repressive complex 2 |
| FBXW7 | F-box and WD repeat domain-containing 7 |
| GTPases | Guanosine triphosphate (GTP) hydrolase |
| HDAC1 | Histone deacetylase 1 |
| JAK2 | Janus kinase 2 |
| m6A | N6-methyladenosine |
| MBNL3 | Muscleblind-like splicing regulator 3 |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NOP2 | NOP2 nucleolar protein |
| p300 | Histone acetyltransferase p 300 |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| SHP1 | Tyrosine phosphatase SHP1 |
| SLUG | Snail family transcription repressor 2 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| TWIST | Twist family BHLH transcription factor 1 |
| UTR | Untranslated region |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 477–491.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; Lampertico, P.; Nahon, P. Epidemiology and surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: New trends. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y.; Artaman, A.; et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, D.; Villanueva, A.; Friedman, S.L.; Llovet, J.M. Liver Cancer Cell of Origin, Molecular Class, and Effects on Patient Prognosis. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, J.U.; Andersen, J.B.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Functional and genetic deconstruction of the cellular origin in liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee, European Association for the Study of the L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Roccarina, D.; Thorburn, D.; Davidson, B.R.; Tsochatzis, E.; Gurusamy, K.S. Management of people with early- or very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estfan, B.; Byrne, M.; Kim, R. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 36, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Edeline, J.; Cattan, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Palmer, D.; Verslype, C.; Zagonel, V.; Fartoux, L.; Vogel, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): A non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J. Endpoints in clinical trials for liver cancer and their value in evidence-based clinical decision making: An unresolved Gordian knot. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatica, A.; Bozzoni, I. Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, R.J.; Pheasant, M.; Mattick, J.S. The relationship between non-protein-coding DNA and eukaryotic complexity. BioEssays 2007, 29, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Bajic, V.B.; Zhang, Z. On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, B.; Prats-Mari, L.; Unfried, J.P.; Fortes, P. LncRNAs in the Type I Interferon Antiviral Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unfried, J.P.; Fortes, P. SMIM30, a tiny protein with a big role in liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1010–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, J.D.; Wei, Y.; Khavari, P.A. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unfried, J.P.; Serrano, G.; Suárez, B.; Sangro, P.; Ferretti, V.; Prior, C.; Boix, L.; Bruix, J.; Sangro, B.; Segura, V.; et al. Identification of Coding and Long Noncoding RNAs Differentially Expressed in Tumors and Preferentially Expressed in Healthy Tissues. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5167–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, M.M.; Matboli, M.; Sallam, M.; Montasser, I.F.; Saad, A.S.; El-Tawdi, A.H. Investigation of long noncoding RNAs expression profile as potential serum biomarkers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Res. 2016, 168, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Yang, C.; Huang, R.; Han, C.; Yu, T.; Huang, K.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Zhu, G.; Su, H.; et al. Identification of Potential Prognostic Long Non-Coding RNA Biomarkers for Predicting Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1854–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.-X.; Zhang, X.; Miao, R.-C.; Xiang, X.-H.; Fu, Y.-N.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Liu, C.; Qu, K. Six-long non-coding RNA signature predicts recurrence-free survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, F.H.; Au, S.L.; Wei, L.; Fan, D.N.; Lee, J.M.; Wong, C.C.; Ng, I.O.; Wong, C.-M. Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP is frequently up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and is targeted by tumour suppressive miR-125b. Liver Int. 2014, 35, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wang, T.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Q.; Chen, K. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Regulation, Functions, and Underlying Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unfried, J.P.; Fortes, P. LncRNAs in HCV Infection and HCV-Related Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero, E.; Barriocanal, M.; Prior, C.; Unfried, J.P.; Segura, V.; Guruceaga, E.; Enguita, M.; Smerdou, C.; Gastaminza, P.; Fortes, P. Long noncoding RNA EGOT negatively affects the antiviral response and favors HCV replication. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1013–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriocanal, M.; Prior, C.; Suarez, B.; Unfried, J.P.; Razquin, N.; Hervás-Stubbs, S.; Sangro, B.; Segura, V.; Fortes, P. Long Noncoding RNA EGOT Responds to Stress Signals to Regulate Cell Inflammation and Growth. J. Immunol. 2021, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytle, N.K.; Barber, A.G.; Reya, T. Stem cell fate in cancer growth, progression and therapy resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chan, T.H.M.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, L.; Huang, J.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Dong, S.; Tang, K.H.; Xie, D.; et al. CHD1L promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis in mice and is associated with these processes in human patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1178–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, L.; Huang, W.; Tian, D.; Zhu, H.; Qi, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Fan, D.; Nie, Y.; et al. Overexpression of forkhead box C1 promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2012, 57, 610–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-D.; Chen, W.-M.; Qi, F.-Z.; Xia, R.; Sun, M.; Xu, T.-P.; Yin, L.; Zhang, E.-B.; De, W.; Shu, Y.-Q. Long non-coding RNA ANRIL is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and regulates cell apoptosis by epigenetic silencing of KLF2. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yao, B.; Liang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Dou, C.; Xu, M.; Liu, Q.; Tu, K. Long non-coding RNA CASC2 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through CASC2/miR-367/FBXW7 axis. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, M.; Groß, M.; Goyal, A.; Polycarpou Schwarz, M.; Miersch, T.; Ernst, A.; Leupold, J.; Patil, N.; Warnken, U.; Allgayer, H.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA Cancer Susceptibility 9 and RNA Binding Protein Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein L Form a Complex and Coregulate Genes Linked to AKT Signaling. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.-X.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Tao, Q.-F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.-L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.-G.; Xu, Q.-G.; et al. Long noncoding RNADANCRincreases stemness features of hepatocellular carcinoma by derepression ofCTNNB1. Hepatology 2016, 63, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Shen, W.; Xia, M.; Chen, C.; Xiang, D.; Ning, B.; Cui, X.; Li, H.; Li, X.; et al. Long non-coding RNA DILC regulates liver cancer stem cells via IL-6/STAT3 axis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, D.; Chiodo, L.; Alfano, V.; Floriot, O.; Cottone, G.; Paturel, A.; Pallocca, M.; Plissonnier, M.-L.; Jeddari, S.; Belloni, L.; et al. Hepatitis B protein HBx binds the DLEU2 lncRNA to sustain cccDNA and host cancer-related gene transcription. Gut 2020, 69, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-F.; Guo, Y.-J.; Zhao, C.-X.; Yuan, S.-X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.-N.; Zhou, W.-P.; Sun, S.-H. Hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx)-related long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) down-regulated expression by HBx (Dreh) inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by targeting the intermediate filament protein vimentin. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1882–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Hao, X.-Y.; Yan, X.; Liao, H.; Chen, X.; Xie, K.; et al. KIAA1429 contributes to liver cancer progression through N6-methyladenosine-dependent post-transcriptional modification of GATA3. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, C.; Ungerleider, N.; Chen, W.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Kwon, H.; Ma, W.; Wu, T. A Transforming Growth Facto β and H19 Signaling Axis in Tumor Initiating Hepatocytes That Regulates Hepatic Carcinogenesis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conigliaro, A.; Costa, V.; Dico, A.L.; Saieva, L.; Buccheri, S.; Dieli, F.; Manno, M.; Raccosta, S.; Mancone, C.; Tripodi, M.; et al. CD90+ liver cancer cells modulate endothelial cell phenotype through the release of exosomes containing H19 lncRNA. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, P.; Luo, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, W.; Du, Y.; Ye, B.; Wang, D.; He, L.; et al. LncRNA HAND2 AS1 promotes liver cancer stem cell self renewal via BMP signaling. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Gu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Lian, Q.; Lv, G.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.-C.T.; et al. Recurrently deregulated lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Jiang, B.; Yuan, X.; Qiu, Y.; Peng, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Super-Enhancer–Associated Long Noncoding RNA HCCL5 Is Activated by ZEB1 and Promotes the Malignancy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, L.; Huo, X.-S.; Yuan, J.-H.; Xu, D.; Yuan, S.-X.; Zhu, N.; Zhou, W.-P.; Yang, G.-S.; Wang, Y.-Z.; et al. Long noncoding RNA high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma facilitates tumor growth through enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in humans. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.-H.; Yin, C.; Chen, S.-J.; Wen, L.-Z.; Ding, K.; Lei, S.-J.; Liu, J.-P.; Wang, J.; Chen, K.-X.; Jiang, H.-L.; et al. The HNF1α-regulated lncRNA HNF1A-AS1 reverses the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by enhancing the phosphatase activity of SHP-1. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Peng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Wu, C.; Fan, Q.; Wei, S.; Li, H.; Liu, J. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes exosome secretion by regulating RAB35 and SNAP23 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.-M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, W.-M.; Lu, Y.-F.; Hu, B.-G.; Wang, H.; Liang, W.-C.; Wang, S.-S.; Ko, C.-H.; Waye, M.M.-Y.; et al. Hotair mediates hepatocarcinogenesis through suppressing miRNA-218 expression and activating P14 and P16 signaling. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xing, Z.; Mani, S.K.K.; Bancel, B.; Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F.; Tran, E.; Merle, P.; Andrisani, O. RNA helicase DEAD box protein 5 regulates Polycomb repressive complex 2/Hox transcript antisense intergenic RNA function in hepatitis B virus infection and hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quagliata, L.; Matter, M.; Piscuoglio, S.; Arabi, L.; Ruiz, C.; Procino, A.; Kovac, M.; Moretti, F.; Makowska, Z.; Boldanova, T.; et al. Long noncoding RNA HOTTIP/HOXA13 expression is associated with disease progression and predicts outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Hepatology 2014, 59, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, N.; Miao, M.; Jiao, B.; Chen, H. The noncoding RNA HOXD-AS1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis and apoptosis phenotype in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Huo, X.; Yang, X.-R.; He, J.; Cheng, L.; Wang, N.; Deng, X.; Jingyuan, F.; Wang, N.; Wang, C.; et al. STAT3-mediated upregulation of lncRNA HOXD-AS1 as a ceRNA facilitates liver cancer metastasis by regulating SOX4. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämmerle, M.; Gutschner, T.; Uckelmann, H.; Ozgur, S.; Fiskin, E.; Gross, M.; Skawran, B.; Geffers, R.; Longerich, T.; Breuhahn, K.; et al. Posttranscriptional destabilization of the liver-specific long noncoding RNA HULC by the IGF2 mRNA-binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1). Hepatology 2013, 58, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Song, T.; Cai, X.; Sun, B.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Long Noncoding RNA HULC Modulates Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Hepatoma Cells through an miR-9–Mediated RXRA Signaling Pathway. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Wu, M.; Meng, Q.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, Q.; Pu, H.; Gui, X.; et al. Long noncoding RNA HULC accelerates liver cancer by inhibiting PTEN via autophagy cooperation to miR15a. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Qiao, Y.; Zhan, Q. Long noncoding RNA HULC modulates the phosphorylation of YB-1 through serving as a scaffold of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and YB-1 to enhance hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1612–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Ni, P.; Gu, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, N.; Sun, F.; Fan, Q. CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5366–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Liu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, L.; Shi, J.; Xu, G.; Li, N.; Cheng, K.; Wu, M.; Cheng, S.; et al. ICAM-1–Related Noncoding RNA in Cancer Stem Cells Maintains ICAM-1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Yang, F.; Yuan, J.-H.; Zhang, L.; Bi, H.-S.; Zhou, C.-C.; Liu, F.; Wang, F.; Sun, S.-H. Long noncoding RNAs associated with liver regeneration 1 accelerates hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration by activating Wnt/β-Catenin signaling. Hepatology 2013, 58, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zhu, X.; Qin, F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Linc00210 drives Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation and liver tumor progression through CTNNBIP1-dependent manner. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Gong, C.; Wu, P.; Battaglia-Hsu, S.-F.; Feng, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, H.; Guo, D.; Yao, Y.; Chen, B.; et al. LINC00662 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via altering genomic methylation profiles. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2191–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhao, J.; Huan, L.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; He, X. Inflammation Induced Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA (LINC00665) Increases Malignancy Through Activating the Double Stranded RNA–Activated Protein Kinase/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1666–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Chen, Z.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Cao, M.; Cai, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. M6A-mediated upregulation of LINC00958 increases lipogenesis and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, H.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Mao, C.; Liu, S. Peptide SMIM30 promotes HCC development by inducing SRC/YES1 membrane anchoring and MAPK pathway activation. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, M.; Groß, M.; Holler, J.M.; Coggins, S.A.; Patil, N.; Leupold, J.H.; Munschauer, M.; Schenone, M.; Hartigan, C.R.; Allgayer, H.; et al. The lncRNA lincNMR regulates nucleotide metabolism via a YBX1-RRM2 axis in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Luo, Y.; Liu, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S. A p53/lnc Ip53 Negative Feedback Loop Regulates Tumor Growth and Chemoresistance. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, Y.; Huang, G.; Ye, B.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; Du, Y.; He, L. lnc-β-Catm elicits EZH2-dependent β-catenin stabilization and sustains liver CSC self-renewal. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, G.; Liu, B.; Ye, B.; Du, Y.; Gao, G.; Tian, Y.; He, L.; et al. LncBRM initiates YAP1 signalling activation to drive self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Deng, L.; Ji, J.; Xie, Y.; Wang, K.; Jia, W.; Chu, W.-M.; Sun, B. The long noncoding RNA lnc-EGFR stimulates T-regulatory cells differentiation thus promoting hepatocellular carcinoma immune evasion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, P.; Lu, T.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Ye, B.; Liu, B.; Yang, L.; Wang, J.; et al. The long non-coding RNA LncHDAC2 drives the self-renewal of liver cancer stem cells via activation of Hedgehog signaling. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.-M.; Huan, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. An LTR Retrotransposon-Derived Long Noncoding RNA lncMER52A Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Binding p120-Catenin. Cancer Res. 2019, 80, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Yang, F.; Wang, F.; Ma, J.-Z.; Guo, Y.-J.; Tao, Q.-F.; Liu, F.; Pan, W.; Wang, T.-T.; Zhou, C.-C.; et al. A Long Noncoding RNA Activated by TGF-β Promotes the Invasion-Metastasis Cascade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Liu, X.-N.; Wang, T.-T.; Pan, W.; Tao, Q.-F.; Zhou, W.-P.; Wang, F.; Sun, S.-H. The MBNL3 splicing factor promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing PXN expression through the alternative splicing of lncRNA-PXN-AS1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Z.; Huang, L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Zhai, W.-J.; Zhu, P.-P.; Gao, Y. LncSox4 promotes the self-renewal of liver tumour-initiating cells through Stat3-mediated Sox4 expression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, L.; Du, Y.; Zhu, P.; Huang, G.; Luo, J.; Yan, X.; Ye, B.; Li, C.; Xia, P.; et al. The Long Noncoding RNA lncTCF7 Promotes Self-Renewal of Human Liver Cancer Stem Cells through Activation of Wnt Signaling. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 16, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Kuang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuang, S. Lnc UCID Promotes G1/S Transition and Hepatoma Growth by Preventing DHX9 Mediated CDK6 Down regulation. Hepatology 2019, 70, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakar, P.; Shilo, A.; Mogilevsky, A.; Stein, I.; Pikarsky, E.; Nevo, Y.; Benyamini, H.; Elgavish, S.; Zong, X.; Prasanth, K.V.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development by SRSF1 Upregulation and mTOR Activation. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakar, P.; Stein, I.; Saragovi, A.; Winkler, R.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Berger, M.; Pikarsky, E.; Karni, R. Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Regulates Cancer Glucose Metabolism by Enhancing mTOR-Mediated Translation of TCF7L2. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2480–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Tong, X.; Yang, W.; Xu, Q.; Huang, D.; et al. A novel lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-194-5p/FOXA1 axis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liang, L.; Dong, Q.; Huan, L.; He, J.; Li, B.; Yang, C.; Jin, H.; Wei, L.; Yu, C.; et al. Long noncoding RNA miR503HG, a prognostic indicator, inhibits tumor metastasis by regulating the HNRNPA2B1/NF-κB pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2814–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, G.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Ju, S.; Cheng, W.; et al. Metabolism induced tumor activator 1 ( MITA1 ), an Energy Stress–Inducible Long Noncoding RNA, Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, D.; Wu, W.; Wu, S.; Qian, J.; Hao, Y.; Yan, F.; Zhu, P.; Wu, J.; Huang, G.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Hepatocarcinogenesis via lncRNA–MUF Interaction with ANXA2 and miR-34a. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6704–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.-X.; Yang, F.; Yang, Y.; Tao, Q.-F.; Zhang, J.; Huang, G.; Wang, R.-Y.; Yang, S.; Huo, X.-S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Long noncoding RNA associated with microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes angiogenesis and serves as a predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma patients’ poor recurrence-free survival after hepatectomy. Hepatology 2012, 56, 2231–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, Y.; Song, R.; Yang, G.; Han, J.; Lan, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1-modulated abnormal lipolysis via ATGL drives hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, W.; Fang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, N.; He, X.; et al. A hMTR4 PDIA3P1 miR 125/124 TRAF6 Regulatory Axis and Its Function in NF kappa B Signaling and Chemoresistance. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1660–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.-C.; Yang, F.; Yuan, S.-X.; Ma, J.-Z.; Liu, F.; Yuan, J.-H.; Bi, F.-R.; Lin, K.-Y.; Yin, J.-H.; Cao, G.-W.; et al. Systemic genome screening identifies the outcome associated focal loss of long noncoding RNA PRAL in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2016, 63, 850–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Tu, X.; Li, H.; Cao, P.; Chen, X.; Song, J.; Han, H.; Li, Y.; Guo, B.; Yang, L.; et al. Long Noncoding RNA p53 Stabilizing and Activating RNA Promotes p53 Signaling by Inhibiting Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein K deSUMOylation and Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2020, 71, 112–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L.; Tseng, Y.-W.; Wu, J.-C.; Chen, G.-Y.; Lin, K.-C.; Hwang, S.-M.; Hu, Y.-C. Suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma by baculovirus-mediated expression of long non-coding RNA PTENP1 and MicroRNA regulation. Biomaterials 2015, 44, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.-Q.; Yang, X.-W.; Chen, Y.-B.; Zhang, D.-W.; Jiang, X.-F.; Xue, P. Exosomal miR-21 regulates the TETs/PTENp1/PTEN pathway to promote hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.-L.; Cao, S.-W.; Ou, Q.-S.; Yang, B.; Zheng, S.-H.; Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.-W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q. The long non-coding RNA PTTG3P promotes cell growth and metastasis via up-regulating PTTG1 and activating PI3K/AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, J.-H.; Wang, S.-B.; Yang, F.; Yuan, S.-X.; Ye, C.; Yang, N.; Zhou, W.-P.; Li, W.-L.; Sun, S.-H. Oncofetal long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and stem cell-like property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilizing NOP2. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yu, Q.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, P.; Ma, X.; Huang, H.; Dong, D.; et al. An Insertion/Deletion Polymorphism within RERT-lncRNA Modulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 6163–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Yuan, K.; Yan, X.; Xu, L.; Liao, H.; Hao, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Xie, K.; et al. LncRNA SNHG10 Facilitates Hepatocarcinogenesis and Metastasis by Modulating Its Homolog SCARNA13 via a Positive Feedback Loop. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3220–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-D.; Chen, W.-M.; Qi, F.-Z.; Sun, M.; Xu, T.-P.; Ma, P.; Shu, Y.-Q. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 is up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell growth and apoptosis by epigenetically silencing of KLF2. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Wu, M.-H.; Huang, Y.-H.; Yeh, C.-T.; Cheng, M.-L.; Chi, H.-C.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Chung, I.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, K.-H. Taurine up-regulated gene 1 functions as a master regulator to coordinate glycolysis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Ye, F.; Liang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, K.; Chen, L.; Ding, Y. A novel lncRNA uc.134 represses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inhibiting CUL4A-mediated ubiquitination of LATS1. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, D.; Guo, X.; Xie, L.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Liu, L. The Long Intergenic Noncoding RNA UFC1, a Target of MicroRNA 34a, Interacts With the mRNA Stabilizing Protein HuR to Increase Levels of β-Catenin in HCC Cells. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 415–426.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xie, J.; Shen, C.; Cheng, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Shen, B.; Peng, C.; et al. Amplification of Long Noncoding RNA ZFAS1 Promotes Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Subramanyam, D.; Blelloch, R.; Derynck, R. Regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal and mesenchymal–epithelial transitions by microRNAs. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Baker, D.; Dijke, P.T. TGF-β-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-W.; Hsu, S.-C.; Xia, W.; Cao, X.; Shih, J.-Y.; Wei, Y.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Hung, M.-C. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cooperates with Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 to Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Cells via Up-regulation of TWIST Gene Expression. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9066–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.S.; Li, X.-Y.; Lee, I.; Choi, H.-S.; Kang, S.E.; Cha, S.Y.; Ryu, J.K.; Yoon, D.; Fearon, E.R.; et al. A p53/miRNA-34 axis regulates Snail1-dependent cancer cell epithelial mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 195, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Poon, R.T.; Yuen, A.P.; Ling, M.T.; Kwok, W.K.; Wang, X.H.; Wong, Y.C.; Guan, X.Y.; Man, K.; Chau, K.L.; et al. Twist Overexpression Correlates with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis through Induction of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5369–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werfel, T.A.; Elion, D.L.; Rahman, B.; Hicks, D.J.; Sanchez, V.; Gonzales-Ericsson, P.I.; Nixon, M.J.; James, J.L.; Balko, J.M.; Scherle, P.A.; et al. Treatment-Induced Tumor Cell Apoptosis and Secondary Necrosis Drive Tumor Progression in the Residual Tumor Microenvironment through MerTK and IDO1. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, S.; Gosens, R.; Wieland, T.; Schmidt, M. Paving the Rho in cancer metastasis: Rho GTPases and beyond. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 183, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheau, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Costache, R.; Caruntu, C.; Mihai, G.L.; Didilescu, A.C.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Xie, J.; Shen, C.; Cheng, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhan, Q.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Shen, B.; et al. miR-150-5p Inhibits Hepatoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Targeting MMP14. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taras, D.; Blanc, J.-F.; Rullier, A.; Dugot-Senant, N.; Laurendeau, I.; Vidaud, M.; Rosenbaum, J. Pravastatin reduces lung metastasis of rat hepatocellular carcinoma via a coordinated decrease of MMP expression and activity. J. Hepatol. 2007, 46, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, L. MMP16 promotes tumor metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 72197–72204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouissou, S.; Nault, J.-C. Advances in molecular classification and precision oncology in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaposi-Novak, P.; Libbrecht, L.; Woo, H.G.; Lee, Y.-H.; Sears, N.C.; Conner, E.A.; Factor, V.M.; Roskams, T.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Central Role of c-Myc during Malignant Conversion in Human Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, K.; Imbeaud, S.; Letouzé, E.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Calderaro, J.; Rebouissou, S.; Couchy, G.; Meiller, C.; Shinde, J.; Soysouvanh, F.; et al. Exome sequencing of hepatocellular carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential therapeutic targets. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Electronic address wbe, Cancer Genome Atlas Research N. Comprehensive and Integrative Genomic Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 1327–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.W.H.; Peng, H.; Yang, H.; Kurniawidjaja, S.; Panthaki, P.; Zheng, Y.; Mato, J.M.; Lu, S.C. S-Adenosylmethionine and methylthioadenosine inhibit β-catenin signaling by multiple mechanisms in liver and colon cancer. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvisi, D.F.; Simile, M.M.; Ladu, S.; Pellegrino, R.; De Murtas, V.; Pinna, F.; Tomasi, M.L.; Frau, M.; Virdis, P.; De Miglio, M.R.; et al. Altered methionine metabolism and global DNA methylation in liver cancer: Relationship with genomic instability and prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.-Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, Z.-R.; Ding, C.-H.; Lei, S.-J.; Liu, J.-P.; Yin, C.; Hu, P.-F.; Ding, J.; Chen, W.-S.; et al. SHP-1 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocarcinogenesis and HCC Progression. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4680–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Barrena, M.G.; Arechederra, M.; Colyn, L.; Berasain, C.; Avila, M.A. Epigenetics in hepatocellular carcinoma development and therapy: The tip of the iceberg. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Meng, J.; Su, R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, X.; Xia, Q. Epitranscriptomics in liver disease: Basic concepts and therapeutic potential. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 664–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O.; Wind, F.; Negelein, E. The Metabolism of Tumors in the Body. J. Gen. Physiol. 1927, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, M.; Groß, M.; Goyal, A.; Polycarpou-Schwarz, M.; Miersch, T.; Ernst, A.-S. The lncRNA CASC9 and RNA binding protein HNRNPL form a complex and co-regulate genes linked to AKT signaling. Hepatology 2017, 777, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Nio, K.; Yamashita, T.; Kaneko, S. The evolving concept of liver cancer stem cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Heo, J.; Libbrecht, L.; Chu, I.-S.; Kaposi-Novak, P.; Calvisi, D.F.; Mikaelyan, A.; Roberts, L.R.; Demetris, A.J.; Sun, Z.; et al. A novel prognostic subtype of human hepatocellular carcinoma derived from hepatic progenitor cells. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.; Sfakianakis, I.; Krupp, M.; Staib, F.; Gerhold-Ay, A.; Victor, A.; Binder, H.; Blettner, M.; Maass, T.; Thorgeirsson, S.; et al. Genetic signatures shared in embryonic liver development and liver cancer define prognostically relevant subgroups in HCC. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lecerf, C.; Peperstraete, E.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. Propagation and Maintenance of Cancer Stem Cells: A Major Influence of the Long Non-Coding RNA H19. Cells 2020, 9, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheiss, C.S.; Laggai, S.; Czepukojc, B.; Hussein, U.K.; List, M.; Barghash, A.; Tierling, S.; Hosseini, K.; Golob-Schwarzl, N.; Pokorny, J.; et al. The long non-coding RNA H19 suppresses carcinogenesis and chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Stress 2017, 1, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Peng, Y.; He, W.; Huang, C. The role of long noncoding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Han, S.; Wu, G.; Latchoumanin, O.; Zhou, G.; Hebbard, L.; George, J.; Qiao, L. Dysregulated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for tumorigenesis, disease progression, and liver cancer stem cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, W.P.; Thomas, A.; Kaina, B. DNA damage and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lee, S.; Shin, D.-J.; Tran, M.; Wang, L. Long noncoding RNA H19 interacts with polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1 to reprogram hepatic lipid homeostasis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1768–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhry, H.; Harris, A.L. Advances in Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Biology. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.-S.; Wong, C.-M. Decoding the Roles of Long Noncoding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojic, L.; Lun, A.T.L.; Mangei, J.; Mascalchi, P.; Quarantotti, V.; Barr, A.; Bakal, C.; Marioni, J.C.; Gergely, F.; Odom, D.T. Specificity of RNAi, LNA and CRISPRi as loss-of-function methods in transcriptional analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 5950–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q. Nusinersen as a Therapeutic Agent for Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Yonsei Med. J. 2020, 61, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Farbiak, L.; Johnson, L.T.; Dilliard, S.A.; Siegwart, D.J. Selective organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles for tissue-specific mRNA delivery and CRISPR–Cas gene editing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Feng, X.; Li, H.; Qiu, C.; Yi, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J. Long Non-coding RNA FENDRR Acts as a miR-423-5p Sponge to Suppress the Treg-Mediated Immune Escape of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 17, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Wood, J.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Involvement of Extracellular Vesicle Long Noncoding RNA (linc-VLDLR) in Tumor Cell Responses to Chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Ye, Y.; Chan, L.-C.; Li, Y.; Liang, K.; Lin, A.; Egranov, S.D.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, W.; Gong, J.; et al. Oncogenic lncRNA downregulates cancer cell antigen presentation and intrinsic tumor suppression. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 835–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xue, Y.; Han, Y.; Lin, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Q.; Cao, X. The STAT3-Binding Long Noncoding RNA lnc-DC Controls Human Dendritic Cell Differentiation. Science 2014, 344, 310–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iii, C.F.S.; Tossberg, J.T.; Guo, Y.; Collier, S.P.; Crooke, P.S.; Aune, T.M. Expression and functions of long noncoding RNAs during human T helper cell differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Aiello, D.; Atianand, M.K.; Ricci, E.P.; Gandhi, P.; Hall, L.L.; Byron, M.; Monks, B.; Henry-Bezy, M.; Lawrence, J.B.; et al. A Long Noncoding RNA Mediates Both Activation and Repression of Immune Response Genes. Science 2013, 341, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, J.A.; Wapinski, O.L.; Yang, Y.W.; Bureau, J.-F.; Gopinath, S.; Monack, D.M.; Chang, H.Y.; Brahic, M.; Kirkegaard, K. The NeST Long ncRNA Controls Microbial Susceptibility and Epigenetic Activation of the Interferon-γ Locus. Cell 2013, 152, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Chang, H.; Yang, W.; Lu, Y.; Hu, J.; Jin, S. A novel IFNα-induced long noncoding RNA negatively regulates immunosuppression by interrupting H3K27 acetylation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-J.; Zhu, C.-C.; Xu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, W.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Z.-Z. The lncRNA UCA1 promotes proliferation, migration, immune escape and inhibits apoptosis in gastric cancer by sponging anti-tumor miRNAs. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningarhari, M.; Caruso, S.; Hirsch, T.Z.; Bayard, Q.; Franconi, A.; Védie, A.-L.; Noblet, B.; Blanc, J.-F.; Amaddeo, G.; Ganne, N.; et al. Telomere length is key to hepatocellular carcinoma diversity and telomerase addiction is an actionable therapeutic target. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heesch, S.; Witte, F.; Schneider-Lunitz, V.; Schulz, J.F.; Adami, E.; Faber, A.B.; Kirchner, M.; Maatz, H.; Blachut, S.; Sandmann, C.-L.; et al. The Translational Landscape of the Human Heart. Cell 2019, 178, 242–260.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingenberg, M.; Matsuda, A.; Diederichs, S.; Patel, T. Non-coding RNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanisms, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukowati, C.; Cabral, L.; Tiribelli, C.; Pascut, D. Circulating Long and Circular Noncoding RNA as Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tools of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicine 2021, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, R.; Yoshida, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Mine, N.; Kondo, Y.; Omata, M. Diagnostic accuracy of tumor markers for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review. Hepatol. Int. 2007, 2, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulitsky, I. Evolution to the rescue: Using comparative genomics to understand long non-coding RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Cho, S.W.; Birk, H.S.; Malatesta, M.; He, D.; Attenello, F.J.; Villalta, J.E.; Cho, M.Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. CRISPRi-based genome-scale identification of functional long noncoding RNA loci in human cells. Science 2017, 355, eaah7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bester, A.C.; Lee, J.; Chavez, A.; Lee, Y.-R.; Nachmani, D.; Vora, S.; Victor, J.; Sauvageau, M.; Monteleone, E.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. An Integrated Genome-wide CRISPRa Approach to Functionalize lncRNAs in Drug Resistance. Cell 2018, 173, 649–664.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangro, B.; Sarobe, P.; Hervás-Stubbs, S.; Melero, I. Advances in immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


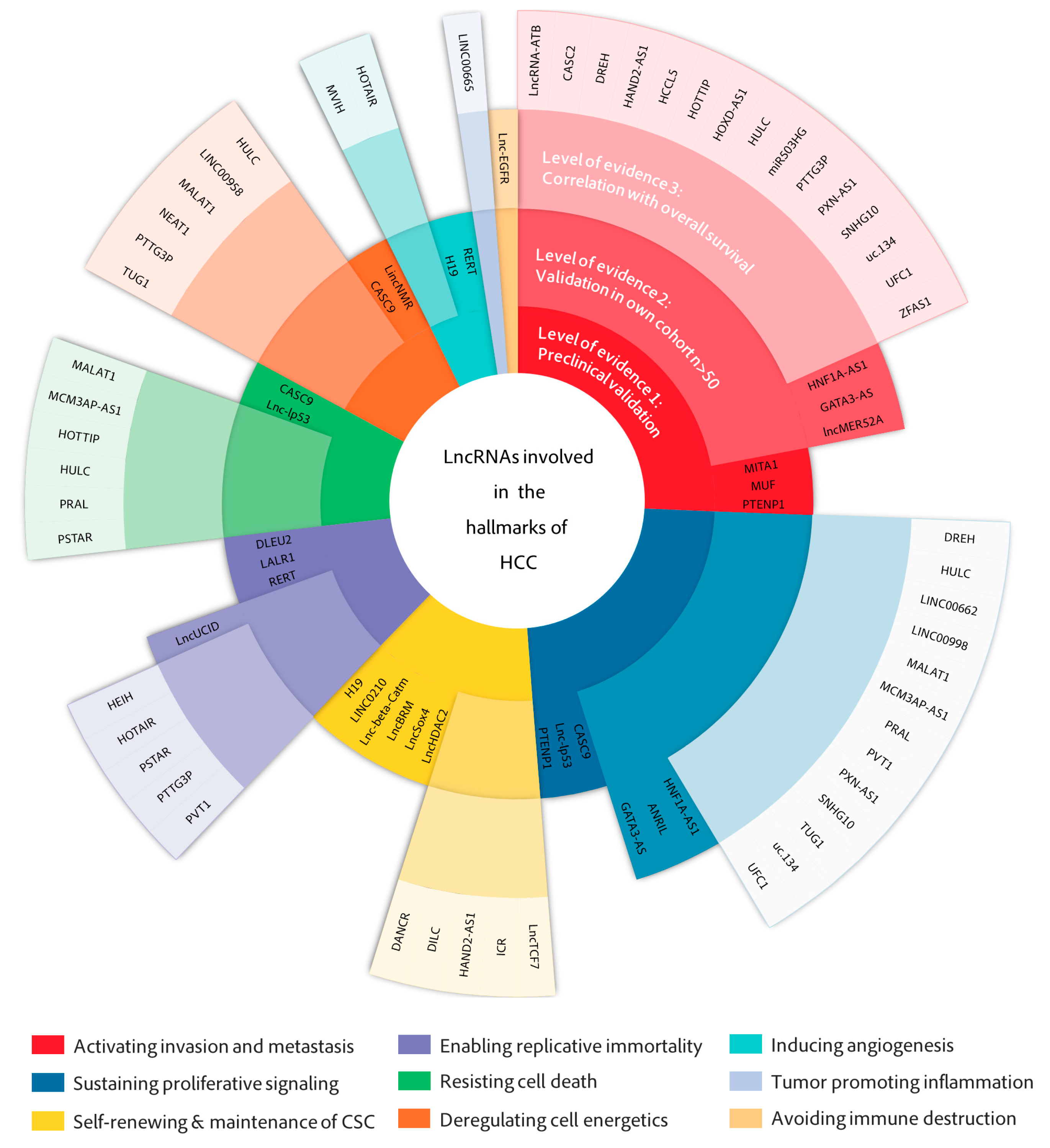
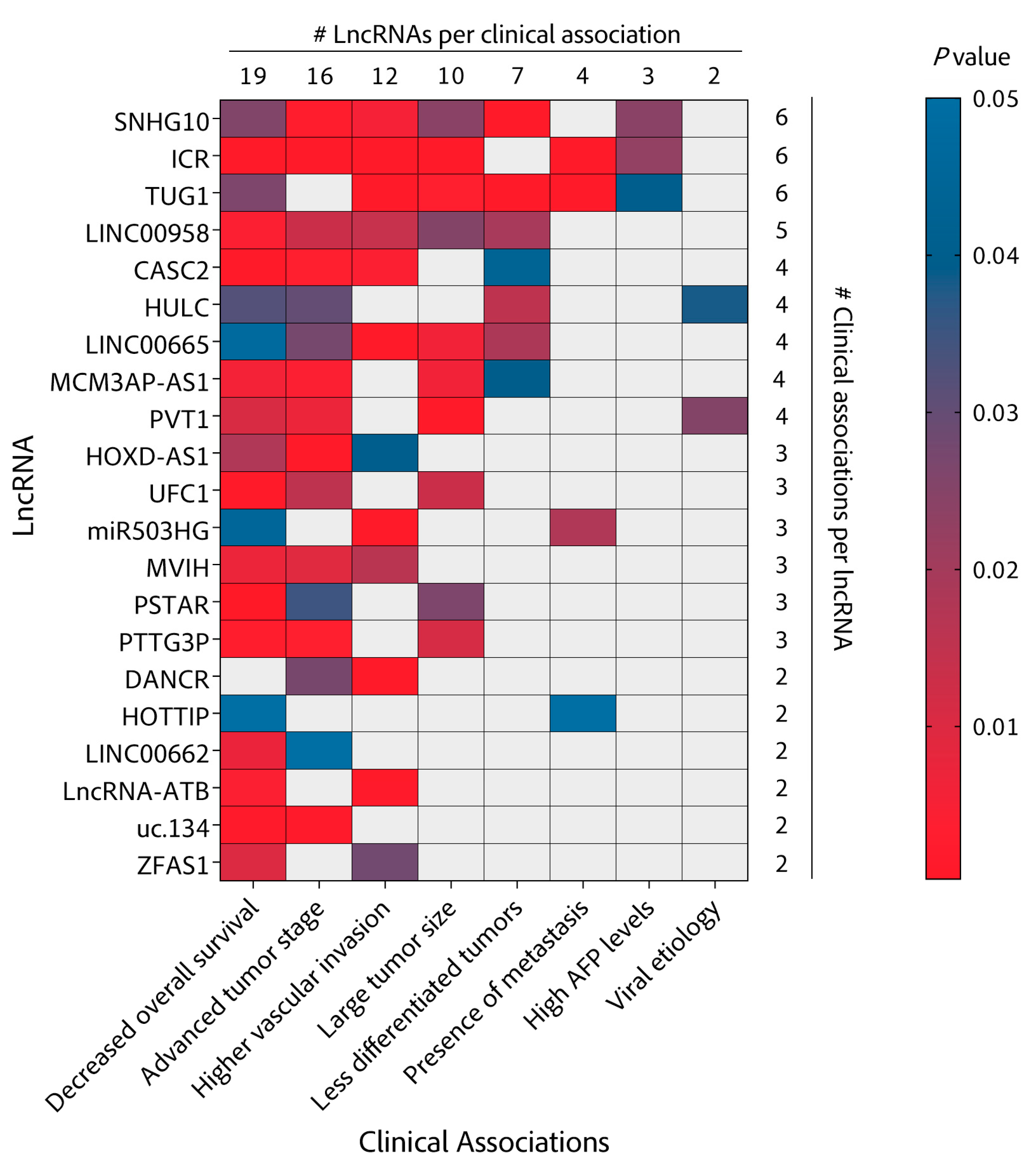
| LncRNA | Biochemistry | Pre-Clinical | Clinical | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target | Detail | Cell Type | Model | Own Cohort (n > 50) | OS (p Value) | |
| ANRIL [39] | ↑PRC2 | Epigenetically represses KLF2 by binding PRC2 and recruiting it to KLF2 promoter | HepG2 | SC | 77 | |
| CASC2 [40] | ↓miR-367 | Sponges miR-367 and prevents targeting of FBXW7 | MHCC-97H, Hep-3B | M | 75 | p < 0.001 |
| CASC9 [41] | ↑HNRNPL | Regulates AKT function and DNA damage sensing | HLE | CAM | No HCC tissues | |
| DANCR [42] | ↑CTNNB1 | Associates with CTNNB1 and blocks the repressing effect of miR-214, 0320a and 199a on CTNNB1 | SMMC7721 | SC, OT | 135 | p = 0.0003 |
| DILC [43] | ↓IL-6 | Binds to IL-6 promoter, preventing NF-κB binding and inhibits IL-6 transcription, IL-6/STAT3 signaling and LCSC expansion | LM3 | SC | 195 | p = 0.019 |
| DLEU2 [44] | ↑DLEU2-HBx | DLEU2-HBx association with target host promoters relieves EZH2 and leads to transcriptional activation | No animal model | No HCC tissues | ||
| DREH [45] | ↓Vimentin | Binds and represses vimentin to change normal cytoskeleton structure and inhibit tumor metastasis | Hepa1-6 | SC, OT, M | 100 | p = 0.039 |
| GATA3-AS [46] | ↓GATA3 | Interacts with KIAA1429 for binding to GATA3 pre-mRNA, competitively preventing binding of HuR and promoting the degradation of GATA3 pre-mRNA | SK-Hep1, HCCLM3 | SC, M | 70 | Not with lncRNA but KIAA1429 |
| H19 [47,48] | ↑VEGF, ICAM | CSC-like CD90+-derived exosomes contain high levels of H19 which induces angiogenesis in endothelial cells | No animal model | No exosomes | ||
| ↑TGF-β | TGF-β inhibits expression of Sox2 TF and Sox2-mediated activation of H19 in TICs | TICs | OT | No HCC tissues | ||
| HAND2-AS1 [49,50] | ↑INO80 | Recruits the INO80 chromatin-remodeling complex to the promoter of BMPR1A, inducing its expression and activation of BMP signaling | HUH7, patient-derived samples | SC, DEN | 60 | p < 0.05 from TCGA |
| Screening of recurrently deregulated lncRNAs enriched in co-expressed clusters of genes related to cell adhesion | No animal model | No HCC tissues | ||||
| HCCL5 [51] | Transcriptionally driven by ZEB1 via a super-enhancer. Activated by TGF-β. Upregulates EMT genes | SMMC-7721 | SC | 196 | p < 0.05 from TCGA | |
| HEIH [52] | ↓EZH2 | Binds to EZH2, inhibiting EZH2 targets such as p15, p16, p21 and p57 | HUH7, SMMC-7721 | SC | 50/107/85 | p = 0.014 |
| HNF1A-AS1 [53] | ↑SHP-1 | Interacts with SHP-1, increasing phosphatase activity | HUH7, MHCC-LM3 | SC, M | 277 | Not with lncRNA but HNF1 |
| HOTAIR [54,55,56] | ↑RAB35, VAMP3-SNAP23 and p-SNAP23 | Promotes MVB fusion by regulating the location and phosphorylation of SNAP23 to form the SNARE complex | No animal model | No exosomes | ||
| ↑SUZ12 | Together with DDX5, regulates SUZ12 stability and PRC2-mediated gene repression of EpCAM, pluripotency genes and HBV cccDNA-encoded genes. | No tumor: hepatocyte-specific Hnf4a-null mice | 52 | |||
| ↑miR218 | Activates P16Ink4a and P14ARF signaling, increasing miR-218 expression and suppressing Bmi-1, resulting in inhibition of P14 and P16 | HepG2 | SC | No HCC tissues | ||
| HOTTIP [57] | ↑WDR5 | Upregulates oncogenic transcription factors such as HOXA13 | HepG2 | SC | 52 | |
| HOXD-AS1 [58,59] | ↓miR-130a-3p | Binds miR-130a-3p and prevents SOX4 miRNA-mediated degradation, thus activating the expression of EZH2 and MMP2 | HUH7 | M | 120 | p = 0.0179 |
| ↓miR19a | Upregulates Rho GTPase ARHGAP11A by competitively binding to microRNA-19a | HCCLM3 | SC, M | 60 | Not with lncRNA but ARHGAP11A | |
| HULC [60,61,62,63,64] | ↑p-YB1 | Promotes the phosphorylation of YB-1 and release from silenced oncogene mRNAs | No animal model | 41 | p = 0.032 | |
| ↓IGF2BP1 | Acts as an adaptor protein of the CCR4-NOT that destabilizes HULC | No animal model | 60 | |||
| ↓miR-15a | Inhibits PTEN through miR-15a/P62, activating AKT-PI3K-mTOR | Hep3B | SC | 30 | ||
| ↓miR-9 | Promotes methylation of miR-9 promoter and suppresses targeting of PPARA, which activates the ACSL1 promoter and lipogenesis | HepG2, HUH7 | SC | 60 | ||
| ↓miR-372 | Inhibits miR-372, derepresses PRKACB, which induces CREB phosphorylation and HULC transcription in an auto regulatory loop | No animal model | 14 | |||
| ICR [65] | ↑ICAM-1 | Increases the stability of ICAM-1 mRNA through RNA duplex formation | HUH7 | SC | 245/372 | p < 0.001 |
| LALR1 [66] | ↑CTCF | Recruits CTCF to repress AXIN1 promoter, increasing cyclin D1 expression through Wnt/β-catenin activation | Liver transfection | No HCC tissues | ||
| LINC00210 [67] | CTNNBIP1 | Interacts with CTNNBIP1 and blocks its inhibitory role in Wnt/β-catenin activation. | Liver TICs | SC | 5 | |
| LINC00662 [68] | ↑AHCY ↓MAT1A | Regulates MAT1A and AHCY that influence SAM and SAH levels to maintain genomic hypomethylation | HCCLM9 | SC, M | 70 | p = 0.0071 |
| LINC00665 [69] | ↑PKR | Interacts with PKR, enhances its activation and blocks degradation, resulting in a positive regulation of NF-κB | HUH7 | SC | 50/122 | p = 0.0472 |
| LINC00958 [70] | ↓miR-3619-5p | Sponges miR-3619-5p to upregulate HDGF expression, facilitating lipogenesis and progression | Primary HCC cells | SC, OT | 80 | p = 0.0039 |
| LINC00998 [71] | ↑SRC/YES1 | Codes for the SMIM30 micropeptide that binds SRC/YES1, to drive anchoring and phosphorylation, activating MAPK pathway | HUH7 | SC | 369/160 | p = 0.00014 |
| LINCNMR [72] | ↑YBX1 | Binds YBX1 which regulates RRM2, TYMS and TK1 expression binding to their promoter regions | HLE | CAM | No HCC tissues | |
| Lnc lp53 [73] | ↑HDAC1, p300 | Interacts with HDAC1 and p300 to prevent HDAC1 degradation and attenuate p300 activity, resulting in increased CDKN1A and PUMA | SK-N-SH | SC | No HCC tissues | |
| Lnc-beta-Catm [74] | ↑EZH2 | Associates with β-catenin and EZH2, promoting β-catenin, methylation and reduced ubiquitination, thus promoting its stability, leading to activation of Wnt–β-catenin | Primary HCC cells | SC | No HCC tissues | |
| LncBRM [75] | ↓miR-150 | Binds miR-150 and abrogates its tumor-suppressive function by inhibiting ZEB1, MMP14 and MMP16 | Primary HCC cells | SC | 6 | Not with lncRNA but YAP1 |
| Lnc-EGFR [76] | ↑EGFR | Binds to EGFR inhibiting its interaction with c-CBL and blocking its ubiquitination and sustaining its activity | DCs, CD4+, CD8+ T cells and 97H | SC | 125 | |
| LNCHDAC2 [77] | NuRD or ↓PTCH1 | In liver CSCs, recruits the NuRD onto PTCH1 promoter to inhibit expression, and activation of Hedgehog signaling | SC | 3/6 | Not with lncRNA but HDAC | |
| lncMER52A [78] | ↑ p120-catenin | Stabilizes p120-catenin and triggers the activation of Rho GTPase and p120-ctn/Rac1/Cdc42 axis | HUH7 | M | 120 | p > 0.05 |
| LncRNA-ATB [79] | ↓miR-200 | Sponges miR-200s family derepressing ZEB1 and ZEB2 | SMMC-7721, HCCLM6 | OT | 86 | p = 0.004 |
| ↑IL-11 | Binds and stabilizes IL-11 mRNA, causing autocrine IL-11 induction and STAT3 signaling-mediated colonization | |||||
| lncRNA-PXN-AS1 [80] | ↑PXN mRNA | MBNL3 induces lncRNA-PXN-AS1 exon 4 inclusion, which allows PXN-AS1 to bind to PXN mRNA preventing its degradation | SMMC-7721, QSG-7701, HUH7 | SC | 279 | 0.0402 |
| LncSox4 [81] | ↑STAT3 | Interacts with and recruits Stat3 to the Sox4 promoter to initiate the expression of Sox4 | Primary HCC cells | SC | No HCC tissues | |
| lncTCF7 [82] | ↑SWI/SNF | Recruits SWI/SNF complex and together they activate TCF7 expression. TCF7 activates Wnt signaling, priming LCSC self-renewal | HEP3B, HUH7 | SC | 37 | p < 0.05 |
| LncUCID [83] | ↓DHX9 | Enhances CDK6 expression by competitively binding to DHX9 and sequestering DHX9 from CDK6-3’UTR | QGY-7703 | SC | 139 | |
| MALAT1 [84,85] | ↑Wnt | Through SRSF1, regulates alternative splicing of effector genes (↑RPS6KB1, TEAD1, mTORC1, ↓ BIM, BIN1 ↑Cyclin D1) | PHM-1 | SC | 35 | |
| Prevents gluconeogenesis and promotes glycolysis | No animal model | No HCC tissues | ||||
| MCM3AP-AS1 [86] | ↓miR-194-5p | Targets miR-194-5p and subsequently promotes FOXA1 expression | Hep3B | SC | 80 | p = 0.0054 |
| miR503HG [87] | ↓ HNRNPA2B1 | Interacts with HNRNPA2B1 and promotes its degradation, decreasing the stability of p52 and p65 mRNA and suppressing the NF-κB signaling | HUH7, SMMC-7721 | OT | 93 | p = 0.045 |
| MITA1 [88] | Promotes EMT, partially by increasing Slug transcription | SK-Hep1 | M | No HCC tissues | ||
| MUF [89] | ↓miR-34a | Works as a ceRNA for miR-34a, leading to Snail1 upregulation and EMT | SMMC-7721 | SC,M | No HCC tissues | |
| ↑ANXA2 | Binds Annexin A2 (ANXA2) and activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling | |||||
| MVIH [90] | ↓PGK1 | Prevents PGK1 secretion | HCCLM3 | SC, OT, M | 40/215/65 | p = 0.007 |
| NEAT1 [91] | ↑miR-124-3p | Binds miR-124-3p to regulate ATGL expression | HUH7, MHCC-LM3 | SC, OT | 29/40 | p = 0.0236 |
| PDIA3P1 [92] | ↓miR-125a/b/miR-124 | Binds to miR-125a/b/miR-124 and relieves their repression over TRAF6, leading to activation of NF-κB pathway | QGY-7703 | SC | 347 | |
| PRAL [93] | ↑HSP90, p53 | Stem-loop motifs at the 5’end of lncRNA-PRAL facilitate union of HSP90 and p53, inhibiting MDM2-dependent p53 ubiquitination, resulting in enhanced p53 stability | SMMC-7721 | SC | 56/189/102/80 | p = 0.035 (c.2) p = 0.027 (c.3) |
| PSTAR [94] | ↑hnRNPK | Binds to hnRNPK and enhances its SUMOylation and interaction between hnRNPK and p53, resulting in accumulation and transactivation of p53 | HepG2 | SC, OT | 38/127/136 | p = 0.0003 |
| PTENP1 [95,96] | ↓miR-17, 19b and 20a” | Decoys oncomiRs miR-17, miR-19b and miR-20a, preventing targeting of PTEN, PHLPP and autophagy genes ULK1, ATG7 and p62 | Mahlavu | SC | No HCC tissues | |
| ↑miR-21 | Exosomes increase miR-21 and downregulate PTEN, PTENP1 and TETs, promoting tumor growth | SNU-449 | SC | No HCC tissues | ||
| PTTG3P [97] | ↑PTTG1 | Upregulates PTTG1, activates PI3K/AKT signaling and its downstream signals | HepG2 | SC | 90 | p = 0.002 |
| PVT1 [98] | ↑NOP2 | Increases stability of nucleolar protein NOP2 | SMMC-7721 | SC | 89 | p = 0.0104 |
| RERT [99] | ↑EGLN2 | rs10680577 affects RERT-lncRNA structure and subsequently EGLN2 expression | No animal model | |||
| SNHG10 [100] | ↓miR-150-5p | Sponges miR-150-5p and interacts with RPL4 mRNA to increase the expression and activity of c-Myb. Enhanced SNHG10, SCARNA13 and SOX9 expression. | SNU-387 and HCCLM3 | SC, OT | 64 | p = 0.0255 |
| TUG1 [101,102] | ↑PRC2 | Epigenetically represses KLF2 transcription by binding PRC2 and recruiting it to KLF2 promoter region | HepG2 | SC | 77 | |
| ↑miR-455-3p | Induces miR-455-3p, which targets the 3’UTR of AMPKβ2, which downregulates HK2 promoting glycolysis and metastasis | SK-Hep1 | M | 239/242 | p = 0.026 (c.1); p = 0.039 (c.2) | |
| uc.134 [103] | ↑CUL4 | Binds to CUL4A, inhibits its nuclear export and ubiquitination of LATS1. Increases p-YAP to silence its target genes | MHCC97-H and HCCLM3 | SC, M | 170 | p < 0.001 |
| UFC1 [104] | ↑HuR | Interacts with HuR to increase levels of β-catenin mRNA and protein | SK-Hep1, BEL-7402 | SC | 131 | p < 0.001 |
| ZFAS1 [105] | ↓miR-150 | Binds miR-150 and abrogates its tumor-suppressive function over ZEB1, MMP14 and MMP16 | HUH7 | SC, M | 113 | p < 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Unfried, J.P.; Sangro, P.; Prats-Mari, L.; Sangro, B.; Fortes, P. The Landscape of lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Translational Perspective. Cancers 2021, 13, 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112651
Unfried JP, Sangro P, Prats-Mari L, Sangro B, Fortes P. The Landscape of lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Translational Perspective. Cancers. 2021; 13(11):2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112651
Chicago/Turabian StyleUnfried, Juan Pablo, Paloma Sangro, Laura Prats-Mari, Bruno Sangro, and Puri Fortes. 2021. "The Landscape of lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Translational Perspective" Cancers 13, no. 11: 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112651
APA StyleUnfried, J. P., Sangro, P., Prats-Mari, L., Sangro, B., & Fortes, P. (2021). The Landscape of lncRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Translational Perspective. Cancers, 13(11), 2651. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112651








