A Real-World, Observational, Prospective Study to Assess the Molecular Epidemiology of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations upon Progression on or after First-Line Therapy with a First- or Second-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The ‘LUNGFUL’ Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. EGFR Mutation Testing
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Study Objectives
2.5. Relevant Definitions
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Sample Size
3. Results
3.1. Patient Disposition and Characteristics at Enrollment
3.2. NSCLC Disease Characteristics at Initial NSCLC Diagnosis, at First-Line EGFR-TKI Treatment Initiation, and at the Time of Progression in the First-Line Setting
3.3. NSCLC Management from Initial Diagnosis until the End of First-Line Treatment for Advanced Disease
3.4. Response Rates and Patterns of Disease Progression in the First-Line Treatment Setting
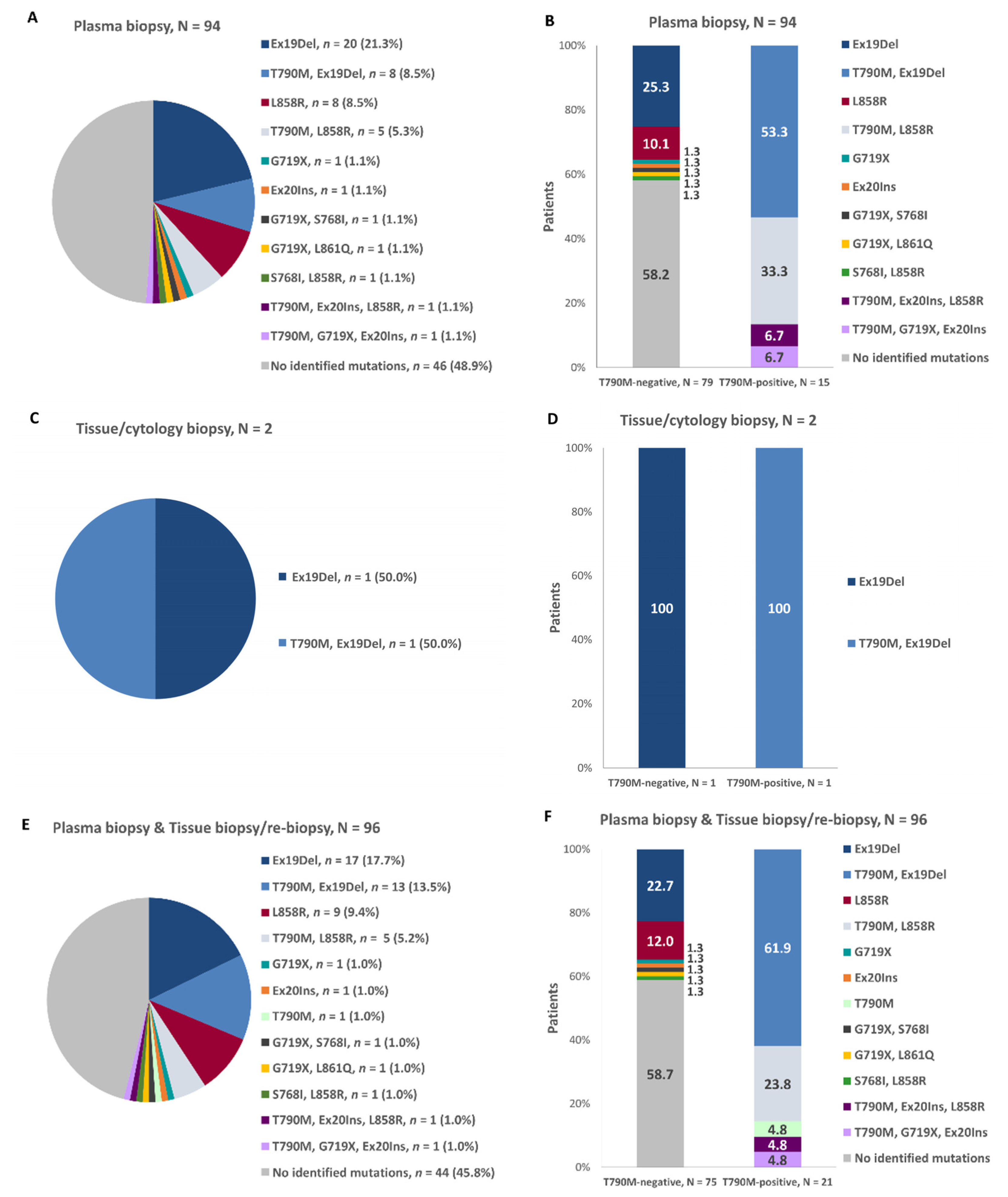
3.5. EGFR Gene Mutation Profile Prior to EGFR-TKI Treatment Initiation and at Disease Progression in the First-Line Setting
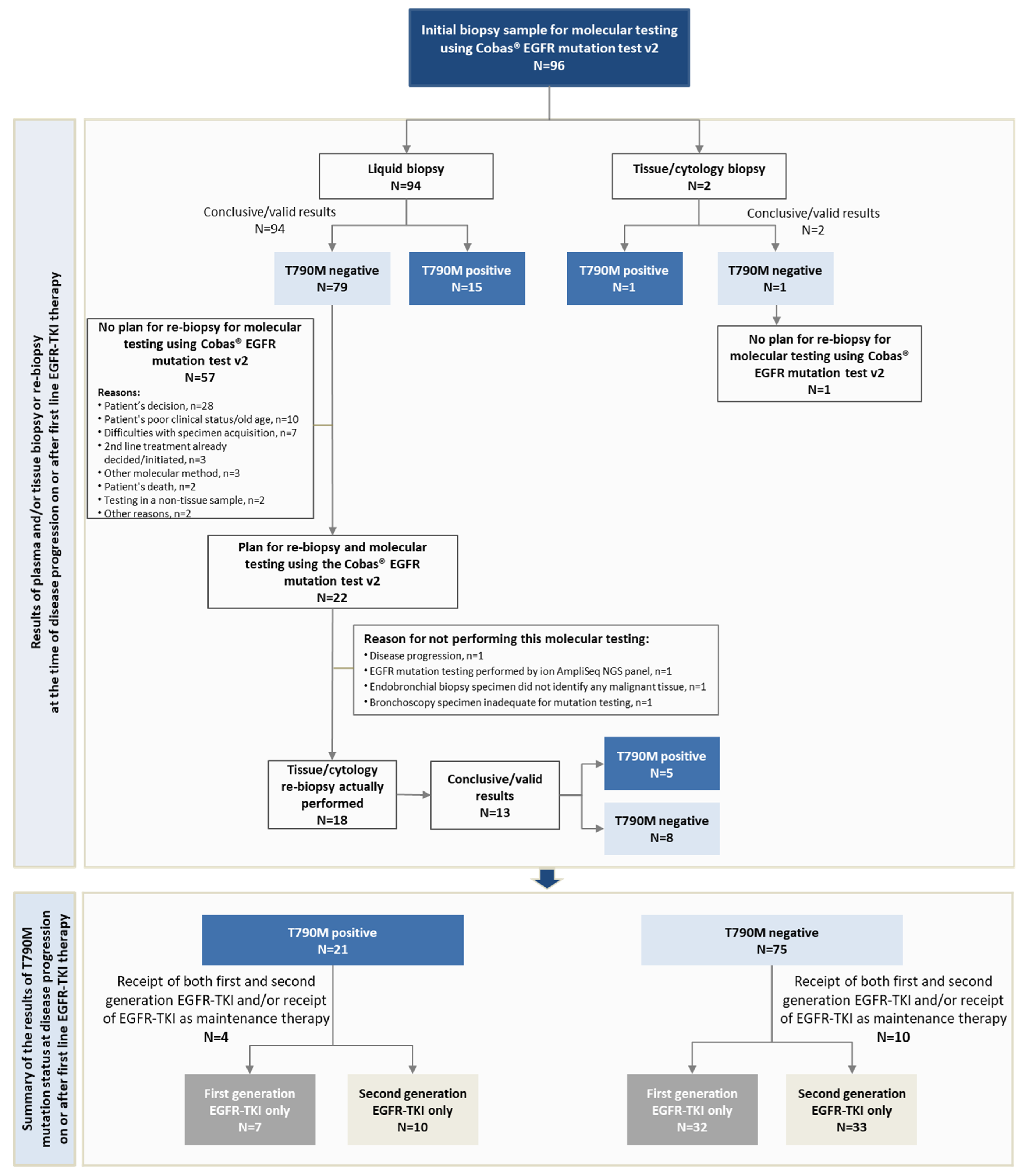
3.6. T790M-Mediated Primary and Secondary Resistance Rates to First-Line EGFR-TKI and Patterns of Progression in T790M-Positive and T790M-Negative Patients
3.7. Association of Patient and Clinicopathological Characteristics with EGFR-T790M Status
3.8. Deaths and Study Withdrawal
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer. Estimated Number of New Cases in 2018. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/ (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- World Cancer Research Fund International. Lung Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/cancer-trends/lung-cancer-statistics (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Maemondo, M.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Updated overall survival results from a randomized phase III trial comparing gefitinib with carboplatin-paclitaxel for chemo-naive non-small cell lung cancer with sensitive EGFR gene mutations (NEJ002). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, J.C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Boyer, M.; Mok, T.; Hirsh, V.; Yang, J.C.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): A phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Tan, E.H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Hirsh, V.; Boyer, M.; Yang, J.C.; Mok, T.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Overall survival data from the phase IIb LUX-Lung 7 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Lee, M.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Improvement in Overall Survival in a Randomized Study That Compared Dacomitinib with Gefitinib in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and EGFR-Activating Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Shaw, A.T. Emerging paradigms in the development of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Cho, B.C.; Shim, H.S.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, S.K.; Chang, J.; Kim, D.J.; Kim, J.H. Prediction for response duration to epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR mutated never smoker lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2014, 83, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, B.P.; Rao, P.; Becker, D.J.; Becker, K. Attacking a Moving Target: Understanding Resistance and Managing Progression in EGFR-Positive Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Oncology 2016, 30, 601–612. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Chu, H.; Yao, Y. Intrinsic resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with activating EGFR mutations. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 3711–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakely, C.M.; Bivona, T.G. Resiliency of lung cancers to EGFR inhibitor treatment unveiled, offering opportunities to divide and conquer EGFR inhibitor resistance. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cortot, A.B.; Janne, P.A. Molecular mechanisms of resistance in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinomas. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2014, 23, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Arcila, M.E.; Sima, C.S.; Riely, G.J.; Chmielecki, J.; Kris, M.G.; Pao, W.; Ladanyi, M.; Miller, V.A. Acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutant lung cancer: Distinct natural history of patients with tumors harboring the T790M mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M.; Nakagawa, K. First- and Second-Generation EGFR-TKIs Are All Replaced to Osimertinib in Chemo-Naive EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.G.; Liu, Y.N.; Tsai, M.F.; Chang, Y.L.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, P.C.; Yang, J.C.; Wen, Y.F.; Shih, J.Y. The mechanism of acquired resistance to irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor-afatinib in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12404–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, G.; Tsai, C.M.; Shepherd, F.A.; Bazhenova, L.; Lee, J.S.; Chang, G.C.; Crino, L.; Satouchi, M.; Chu, Q.; Hida, T.; et al. Osimertinib for pretreated EGFR Thr790Met-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AURA2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, S.W.; Su, W.C.; Horn, L.; et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsies: Genotyping circulating tumor DNA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwapisz, D. The first liquid biopsy test approved. Is it a new era of mutation testing for non-small cell lung cancer? Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Niederst, M.J.; Karlovich, C.A.; Wakelee, H.A.; Neal, J.W.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fulton, L.; Hata, A.N.; Lockerman, E.L.; Kalsy, A.; et al. Heterogeneity Underlies the Emergence of EGFRT790 Wild-Type Clones Following Treatment of T790M-Positive Cancers with a Third-Generation EGFR Inhibitor. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina Diaz, I.; Nocon, A.; Mehnert, D.H.; Fredebohm, J.; Diehl, F.; Holtrup, F. Performance of Streck cfDNA Blood Collection Tubes for Liquid Biopsy Testing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnostics, R. Cobas Mutation Test v2. Available online: https://diagnostics.roche.com/global/en/products/params/cobas-egfr-mutation-test-v2.html (accessed on 8 June 2021).
- FDA. Cobas®EGFR Mutation Test v2 Indication. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/cobas-egfr-mutation-test-v2 (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- FDA. SUMMARY OF SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS DATA (SSED) cobas® EGFR Mutation Test v2. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf15/p150044b.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2021).
- Gandara, D.R.; Li, T.; Lara, P.N.; Kelly, K.; Riess, J.W.; Redman, M.W.; Mack, P.C. Acquired resistance to targeted therapies against oncogene-driven non-small-cell lung cancer: Approach to subtyping progressive disease and clinical implications. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bao, Y.; Yin, W.; Liu, L.; Liu, R.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Shuai, J. Poor Prognosis with Coexistence of EGFR T790M Mutation and Common EGFR-Activating Mutation in Non- Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 9621–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Miller, V.A.; Robson, M.E.; Azzoli, C.G.; Pao, W.; Ladanyi, M.; Arcila, M.E. Screening for germline EGFR T790M mutations through lung cancer genotyping. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Yu, C.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Yang, C.H.; Shih, J.Y.; Yang, P.C. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on “uncommon” epidermal growth factor receptor mutations of unknown clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3812–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linardou, H.; Kotoula, V.; Kouvatseas, G.; Mountzios, G.; Karavasilis, V.; Samantas, E.; Kalogera-Fountzila, A.; Televantou, D.; Papadopoulou, K.; Mavropoulou, X.; et al. Genotyping KRAS and EGFR Mutations in Greek Patients with Non-small-cell Lung Cancer: Incidence, Significance and Implications for Treatment. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2019, 16, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochmair, M.J.; Buder, A.; Schwab, S.; Burghuber, O.C.; Prosch, H.; Hilbe, W.; Cseh, A.; Fritz, R.; Filipits, M. Liquid-Biopsy-Based Identification of EGFR T790M Mutation-Mediated Resistance to Afatinib Treatment in Patients with Advanced EGFR Mutation-Positive NSCLC, and Subsequent Response to Osimertinib. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.C.; Chooback, N.; Ho, C.; Melosky, B. Outcome Differences between First- and Second-generation EGFR Inhibitors in Advanced EGFR Mutated NSCLC in a Large Population-based Cohort. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e576–e583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L.; Lv, D. Detection of plasma T790M mutation after the first generation EGFR-TKI resistance of non-small cell lung cancer in the real world. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosaki, K.; Satouchi, M.; Kurata, T.; Yoshida, T.; Okamoto, I.; Katakami, N.; Imamura, F.; Tanaka, K.; Yamane, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Re-biopsy status among non-small cell lung cancer patients in Japan: A retrospective study. Lung Cancer 2016, 101, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, E.; Tsoulos, N.; Tsantikidi, K.; Metaxa-Mariatou, V.; Stamou, P.E.; Kladi-Skandali, A.; Kapeni, E.; Tsaousis, G.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Petrakis, D.; et al. Clinical feasibility of NGS liquid biopsy analysis in NSCLC patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jung, H.A.; Lee, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K.; Sun, J.M. Comprehensive evaluation of the clinical utility of plasma EGFR test in non-small cell lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to first-line EGFR inhibitors. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, C. Comparison of cross-platform technologies for EGFR T790M testing in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 100801–100818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.; Yang, J.C.; Janne, P.A.; Thress, K.S.; Yu, K.; Hodge, R.; Weston, S.; Dearden, S.; Patel, S.; Cantarini, M.; et al. EGFR Mutation Analysis for Prospective Patient Selection in Two Phase II Registration Studies of Osimertinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.S.; Park, C.H.; Lee, S.; Park, H.S. Clinicopathological parameters for circulating tumor DNA shedding in surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR or KRAS mutation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.O.; Oh, I.J.; Kho, B.G.; Park, H.Y.; Chang, J.S.; Park, C.K.; Shin, H.J.; Lim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Kim, Y.I.; et al. Feasibility of re-biopsy and EGFR mutation analysis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlovich, C.; Goldman, J.W.; Sun, J.M.; Mann, E.; Sequist, L.V.; Konopa, K.; Wen, W.; Angenendt, P.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.; et al. Assessment of EGFR Mutation Status in Matched Plasma and Tumor Tissue of NSCLC Patients from a Phase I Study of Rociletinib (CO-1686). Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2386–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thress, K.S.; Brant, R.; Carr, T.H.; Dearden, S.; Jenkins, S.; Brown, H.; Hammett, T.; Cantarini, M.; Barrett, J.C. EGFR mutation detection in ctDNA from NSCLC patient plasma: A cross-platform comparison of leading technologies to support the clinical development of AZD9291. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Delmonte, A.; Hsia, T.C.; Laskin, J.; Kim, S.W.; He, Y.; Tsai, C.M.; et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation analysis in tissue and plasma from the AURA3 trial: Osimertinib versus platinum-pemetrexed for T790M mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2020, 126, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntzifa, A.; Kroupis, C.; Haliassos, A.; Lianidou, E. A pilot plasma-ctDNA ring trial for the Cobas(R) EGFR Mutation Test in clinical diagnostic laboratories. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, e97–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Si, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M. Re-biopsy status among Chinese non-small-cell lung cancer patients who progressed after icotinib therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 7513–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.S.; Yom, S.S.; Tsao, M.S.; Pass, H.I.; Kelly, K.; Peled, N.; Yung, R.C.; Wistuba, I.I.; Yatabe, Y.; Unger, M.; et al. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Consensus Statement on Optimizing Management of EGFR Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Status in 2016. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 946–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, S.; Yang, J.C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Yu, K.; Patel, S.; Weston, S.; Hodge, R.; Cantarini, M.; Janne, P.A.; Mitsudomi, T.; et al. Plasma ctDNA Analysis for Detection of the EGFR T790M Mutation in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, N.; Azuma, K.; Sakai, K.; Hattori, S.; Kawahara, A.; Ishii, H.; Tokito, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Yamada, K.; Nishio, K.; et al. Association of EGFR Exon 19 Deletion and EGFR-TKI Treatment Duration with Frequency of T790M Mutation in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, R.; Kenmotsu, H.; Serizawa, M.; Koh, Y.; Wakuda, K.; Ono, A.; Taira, T.; Naito, T.; Murakami, H.; Isaka, M.; et al. Frequency of EGFR T790M mutation and multimutational profiles of rebiopsy samples from non-small cell lung cancer developing acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Japanese patients. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, J.S.; Su, K.Y.; Yang, T.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Hsu, K.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Tsai, C.R.; Yu, S.L.; Chang, G.C. The emergence of T790M mutation in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma patients having a history of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI: Focus on rebiopsy timing and long-term existence of T790M. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 48059–48069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Patient Enrollment Characteristics | Value (Mean or Median or %) |
|---|---|
| Age (N = 96), median (IQR), years | 67.8 (57.6–74.9) |
| ≤65 years, n (%) | 39 (40.6) |
| >65 and ≤75 years, n (%) | 33 (34.4) |
| >75 years, n (%) | 24 (25.0) |
| Females (N = 96), n (%) | 65 (67.7) |
| Caucasian (N = 96), n (%) | 96 (100.0) |
| BMI (N = 77), mean (SD), kg/m2 | 26.3 (4.8) |
| Obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) (N = 77), n (%) | 17 (22.1) |
| Smoking status (N = 96) | |
| Former smokers, n (%) | 33 (34.4) |
| Pack-years, median (IQR) | 16.0 (10.0–40.0) |
| Current smokers, n (%) | 8 (8.3) |
| Pack-years, median (IQR) | 17.5 (11.3–47.5) |
| ECOG performance status (N = 96), n (%) | |
| 0 | 51 (53.1) |
| 1 | 29 (30.2) |
| 2 | 12 (12.5) |
| 3 | 4 (4.2) |
| Medical/Surgical history and comorbidities (excluding surgeries for NSCLC) (N = 96), n (%) | 51 (53.1) |
| Comorbidities (N = 96), n (%) | 43 (44.8) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 21 (21.9) |
| Hypothyroidism, n (%) | 11 (11.5) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 10 (10.4) |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 10 (10.4) |
| Age at initial diagnosis (N = 96), median (IQR), years | 66.8 (55.5–73.4) |
| Specimen used for documentation/confirmation of the initial diagnosis (N = 96), n (%) | |
| Histological | 69 (71.9) |
| Cytological | 14 (14.6) |
| Histological and cytological | 13 (13.5) |
| NSCLC stage at initial disease diagnosis (N = 96), n (%) | |
| I: IB | 1 (1.0): 1 (1.0) |
| II: IIA, IIB | 5 (5.2): 4 (4.2), 1 (1.0) |
| III: IIIA, IIIB, IIIC, Locally advanced (unspecified stage) | 15 (15.6): 8 (8.3), 5 (5.1), 1 (1.0), 1 (1.0) |
| IV | 75 (78.1) |
| Primary tumor histological classification (N = 95), n (%) | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 91 (95.8) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 3 (3.2) |
| Adenosquamous carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma-predominant | 1 (1.1) |
| Age at index diagnosis with advanced NSCLC (N = 96), median (IQR), years | 66.8 (56.3–73.4) |
| Age at EGFR-TKI treatment initiation (N = 96), median (IQR), years | 66.9 (56.4–73.5) |
| NSCLC stage at index diagnosis (N = 96), n (%) | |
| III: IIIB, IIIC, Locally advanced (unspecified stage) | 9 (9.4): 6 (6.3), 1 (1.0), 2 (2.1) |
| IV | 87 (90.6) |
| Criteria used for NSCLC staging at index diagnosis (N = 96), n (%) | |
| AJCC/UICC 6th edition | 1 (1.0%) |
| AJCC/UICC 7th edition | 35 (36.5%) |
| AJCC/UICC 8th edition | 57 (59.4%) |
| Unknown | 3 (3.1%) |
| Assays used for EGFR mutation testing prior to initiation of first-line EGFR-TKI (N = 96), n (%) | |
| cobas® EGFR Mutation Test v2 | 37 (38.5) |
| Other cobas® tests | 12 (12.5) |
| Next-generation sequencing | 28 (29.2) |
| Other assays | 15 (15.6) |
| Unspecified assay | 4 (4.2) |
| Sample used for EGFR mutation testing prior to initiation of first-line EGFR-TKI (N = 96), n (%) | |
| Tumor tissue | 80 (83.3) |
| Cytology sample | 9 (9.4) |
| Plasma | 7 (7.3) |
| EGFR mutations identified prior to initiation of first-line EGFR-TKI (N = 96), n (%) | |
| Exon 19 deletion | 56 (58.3) |
| L858R | 26 (27.1) |
| Exon 20 insertion | 6 (6.3) |
| G719X | 5 (5.2) |
| S768I | 3 (3.1) |
| L861Q | 2 (2.1) |
| T790M | 2 (2.1) |
| Other mutations (E709-T710>D, R776S, R836C, V765M) | 4 (4.2) |
| Exon 19 unspecified mutation | 1 (1.0) |
| First-Line Treatment for the Index NSCLC Diagnosis (N = 96) | n (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| First generation EGFR-TKI without preceding chemotherapy | 35 (36.5) | |
| First generation EGFR-TKI with preceding chemotherapy | 4 (4.2) | |
| Second generation EGFR-TKI without preceding chemotherapy | 41 (42.7) | |
| Second generation EGFR-TKI with preceding chemotherapy | 2 (2.1) | |
| Both a first- and a second-generation EGFR-TKI | 5 (5.2) | |
| First- and/or second-generation EGFR-TKI as maintenance therapy after receipt of platinum-based chemotherapy | 9 (9.4) | |
| Best response in the first-line treatment setting, n (%) | ||
| Confirmed and not confirmed responses (N = 92) | Only confirmed responses (N = 61) | |
| Complete response | 7 (7.6) | 5 (8.2) |
| Partial response | 40 (43.5) | 21 (34.4) |
| Stable disease | 25 (27.2) | 15 (24.6) |
| Progressive disease | 20 (21.7) | 20 (32.8) |
| Primary and secondary resistance in the first-line treatment setting, n (%) | ||
| Confirmed and not confirmed responses (N = 92) | Only confirmed responses (N = 61) | |
| Primary resistance | 25 (27.2) | 22 (36.1) |
| Secondary resistance | 67 (72.8) | 39 (63.9) |
| Prior to First-Line EGFR-TKI Initiation | at Disease Progression on or after First-Line EGFR-TKI |
|---|---|
| Exon 19 deletion, n = 13 | T790M, Exon 19 deletion, n = 12 |
| T790M, n = 1 | |
| L858R, n = 5 | T790M, L858R, n = 5 |
| G719X, n = 1 | T790M, G719X, Exon 20 insertion, n = 1 |
| Exon 20 insertion, L858R, n = 1 | T790M, Exon 20 insertion, L858R, n = 1 |
| T790M, Exon19 unspecified mutation, n = 1 | T790M, Exon 19 deletion, n = 1 |
| Patient Characteristics | T790M-Positive | T790M-Negative | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | p-Value | ||
| Age at the time of biopsy collection upon disease progression on or after first-line EGFR-TKI treatment (N = 96) | >65 years | 13 (61.9) | 44 (58.7) | 0.790 |
| ≤65 years | 8 (38.1) | 31 (41.3) | ||
| Smoking status at enrollment (N = 96) | Ever-smoker | 10 (47.6) | 31 (41.3) | 0.607 |
| Never-smoker | 11 (52.4) | 44 (58.7) | ||
| Sex (N = 96) | Male | 5 (23.8) | 26 (34.7) | 0.350 |
| Female | 16 (76.2) | 49 (65.3) | ||
| ECOG performance status at enrollment (N = 96) | ≥2 | 7 (33.3) | 9 (12.0) | 0.026 |
| 0–1 | 14 (66.7) | 66 (88.0) | ||
| Generation of first-line EGFRI-TKI (N = 82) † | First-generation | 7 (41.2) | 32 (49.2) | 0.555 |
| Second-generation | 10 (58.8) | 33 (50.8) | ||
| Exon 19 deletion prior to initiation of first-line EGFR-TKI (N = 96) | No | 8 (38.1) | 32 (42.7) | 0.707 |
| Yes | 13 (61.9) | 43 (57.3) | ||
| L858R mutation prior to initiation of first-line EGFR-TKI (N = 96) | No | 15 (71.4) | 55 (73.3) | 0.862 |
| Yes | 6 (28.6) | 20 (26.7) | ||
| Exon 19 deletion and/or L858R mutation prior to initiation of first-line EGFR-TKI (N = 96) | No | 2 (9.5) | 12 (16.0) | 0.463 |
| Yes | 19 (90.5) | 63 (84.0) | ||
| Exon 20 insertion prior to initiation of first-line EGFR-TKI (N = 96) | No | 19 (90.5) | 65 (86.7) | 0.643 |
| Yes | 2 (9.5) | 10 (13.3) | ||
| Type of biopsy to determine T790M status (N = 96) | Plasma-based liquid | 15 (71.4) | 74 (98.7) | 0.002 |
| Tissue | 6 (28.6) | 1 (1.3) | ||
| Tissue biopsy/re-biopsy collection site (N = 17) | Metastatic site | 3 (50.0) | 4 (36.4) | 0.587 |
| Site of the primary tumor | 3 (50.0) | 7 (63.6) | ||
| Time elapsed between EGFR-TKI initiation in the first-line setting and first documented disease progression (N = 82) † | <10 months | 3 (17.6) | 32 (49.2) | 0.027 |
| ≥10 months | 14 (82.4) | 33 (50.8) | ||
| Time from first documentation of disease progression in the first-line setting to biopsy collection for EGFR mutation analysis with the cobas® EGFR Mutation Test v2 (N = 96) | <1 month | 11 (52.4) | 53 (70.7) | 0.121 |
| ≥1 month | 10 (47.6) | 22 (29.3) | ||
| Best response to first-line EGFR-TKI based on confirmed and not confirmed responses (N = 92) | PD | 1 (4.8) | 19 (26.8) | 0.060 |
| CR/PR/SD | 20 (95.2) | 52 (73.2) | ||
| Type of resistance to first-line EGFR-TKI based on confirmed and not confirmed responses (N = 92) | Primary resistance | 2 (9.5) | 23 (32.4) | 0.054 |
| Secondary resistance | 19 (90.5) | 48 (67.6) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mountzios, G.; Koumarianou, A.; Bokas, A.; Mavroudis, D.; Samantas, E.; Fergadis, E.G.; Linardou, H.; Katsaounis, P.; Athanasiadis, E.; Karamouzis, M.V.; et al. A Real-World, Observational, Prospective Study to Assess the Molecular Epidemiology of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations upon Progression on or after First-Line Therapy with a First- or Second-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The ‘LUNGFUL’ Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 3172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133172
Mountzios G, Koumarianou A, Bokas A, Mavroudis D, Samantas E, Fergadis EG, Linardou H, Katsaounis P, Athanasiadis E, Karamouzis MV, et al. A Real-World, Observational, Prospective Study to Assess the Molecular Epidemiology of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations upon Progression on or after First-Line Therapy with a First- or Second-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The ‘LUNGFUL’ Study. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133172
Chicago/Turabian StyleMountzios, Giannis, Anna Koumarianou, Alexandros Bokas, Dimitrios Mavroudis, Epaminondas Samantas, Evangelos Georgios Fergadis, Helena Linardou, Panagiotis Katsaounis, Elias Athanasiadis, Michalis V. Karamouzis, and et al. 2021. "A Real-World, Observational, Prospective Study to Assess the Molecular Epidemiology of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations upon Progression on or after First-Line Therapy with a First- or Second-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The ‘LUNGFUL’ Study" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133172
APA StyleMountzios, G., Koumarianou, A., Bokas, A., Mavroudis, D., Samantas, E., Fergadis, E. G., Linardou, H., Katsaounis, P., Athanasiadis, E., Karamouzis, M. V., Pentheroudakis, G., Lampaki, S., Froudarakis, M. E., Perdikouri, E.-I. A., Somarakis, A., Papageorgiou, F., Paparepa, Z., Nikolaou, A., & Syrigos, K. N. (2021). A Real-World, Observational, Prospective Study to Assess the Molecular Epidemiology of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations upon Progression on or after First-Line Therapy with a First- or Second-Generation EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in EGFR Mutation-Positive Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The ‘LUNGFUL’ Study. Cancers, 13(13), 3172. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133172








