Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated T- and NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases: A Review of Clinical and Pathological Features
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
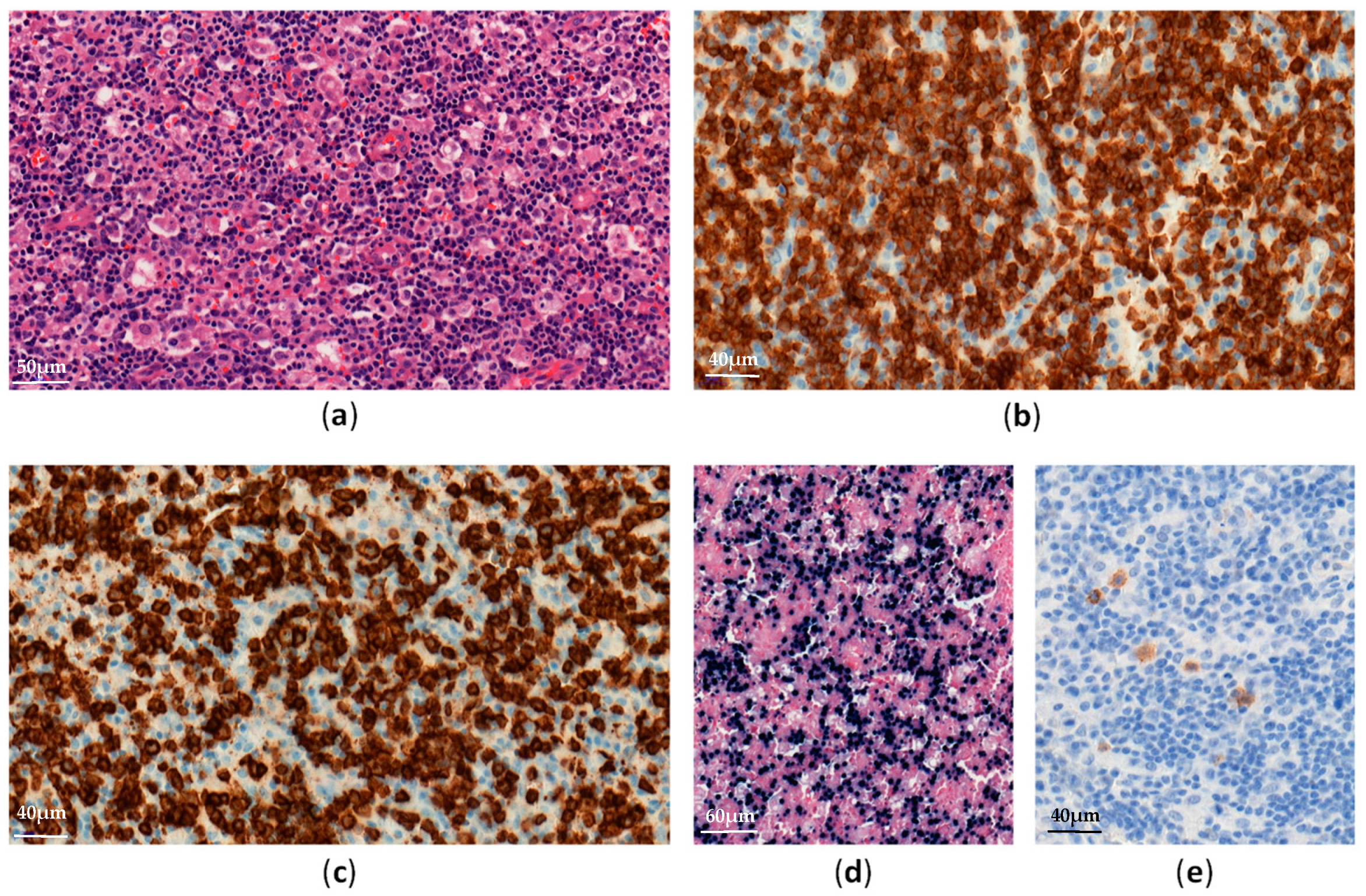
2. EBV-Positive Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
3. Chronic Active EBV Infection, Systemic Form
4. Chronic Active EBV Infection, Cutaneous Form
4.1. Hydroavacciniforme-Like Lymphoproliferative Disorder
4.2. Severe Mosquito Bite Allergy
5. Systemic EBV-Positive T-Cell Lymphoma of Childhood
6. Extra-Nodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type
7. Aggressive NK-Cell Leukemia
8. Primary EBV-Positive Nodal T-Cell or NK-Cell Lymphoma
9. Differential Diagnoses
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, L.S.; Rickinson, A.B. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.; Kis, L.L.; Klein, G. Epstein–Barr virus infection in humans: From harmless to life endangering virus–lymphocyte interactions. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, J.; Young, L.; Martin, B.; Chatman, T.; Kieff, E.; Rickinson, A.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus types 1 and 2 differ in their EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, and EBNA-3C genes. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4084–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Ito, Y.; Kawabe, S.; Gotoh, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Kojima, S.; Naoe, T.; Esaki, S.; Kikuta, A.; Sawada, A.; et al. EBV-associated T/NK–cell lymphoproliferative diseases in nonimmunocompromised hosts: Prospective analysis of 108 cases. Blood 2012, 119, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingeroth, J.D.; Weis, J.J.; Tedder, T.F.; Strominger, J.L.; Biro, P.A.; Fearon, D.T. Epstein-Barr virus receptor of human B lymphocytes is the C3d receptor CR2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4510–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trempat, P.; Tabiasco, J.; Andre, P.; Faumont, N.; Meggetto, F.; Delsol, G.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Fournie, J.-J.; Vivier, E.; Brousset, P. Evidence for Early Infection of Nonneoplastic Natural Killer Cells by Epstein-Barr Virus. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11139–11142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabiasco, J.; Vercellone, A.; Meggetto, F.; Hudrisier, D.; Brousset, P.; Fournié, J.-J. Acquisition of viral receptor by NK cells through immunological synapse. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 1950 2003, 170, 5993–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukas, C.D.; Lambris, J.D. Expression of CR2/EBV receptors on human thymocytes detected by monoclonal antibodies. Eur. J. Immunol. 1988, 18, 1299–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henter, J.-I.; Horne, A.; Aricó, M.; Egeler, R.M.; Filipovich, A.H.; Imashuku, S.; Ladisch, S.; McClain, K.; Webb, D.; Winiarski, J.; et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 48, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, R.A. Epstein–Barr Virus and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, G.E. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1983, 140, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, G.E.; Lehmberg, K. Hemophagocytic syndromes—An update. Blood Rev. 2014, 28, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.A.; Madden, L.; Kitchen, B.J.; Mody, R.; McClimon, B.; Jordan, M.B.; Bleesing, J.J.; Zhang, K.; Filipovich, A.H. XIAP deficiency: A unique primary immunodeficiency best classified as X-linked familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and not as X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. Blood 2010, 116, 1079–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canna, S.W.; de Jesus, A.A.; Gouni, S.; Brooks, S.R.; Marrero, B.; Liu, Y.; DiMattia, M.A.; Zaal, K.J.M.; Sanchez, G.A.M.; Kim, H.; et al. An activating NLRC4 inflammasome mutation causes autoinflammation with recurrent macrophage activation syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-J.; Wang, H.-S.; Ju, X.-L.; Xiao, P.-F.; Xiao, Y.; Xue, H.-M.; Shi, H.-Y.; Gao, Y.-J.; Jia, G.-C.; Li, X.-R.; et al. Clinical presentation and outcome of pediatric patients with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in China: A retrospective multicenter study: XU ET AL. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, E. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Children: Pathogenesis and Treatment. Front. Pediatr. 2016, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, Y.; Yachie, A. Cell type specific infection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in EBV-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and chronic active EBV infection. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 44, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogawa, K.; Sato, H.; Asano, T.; Ohga, S.; Kudo, K.; Morimoto, A.; Ohta, S.; Wakiguchi, H.; Kanegane, H.; Oda, M.; et al. Prognostic factors of Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children: Report of the Japan Histiocytosis Study Group. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Ko, Y.; Kimura, H.; Jaffe, E. EBV–positive T-cell and NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases of childhood. In WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues; WHO IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.I.; Jaffe, E.S.; Dale, J.K.; Pittaluga, S.; Heslop, H.E.; Rooney, C.M.; Gottschalk, S.; Bollard, C.M.; Rao, V.K.; Marques, A.; et al. Characterization and treatment of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus disease: A 28-year experience in the United States. Blood 2011, 117, 5835–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Kwong, Y.-L. EBV Viral Loads in Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Response Assessment. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Hoshino, Y.; Hara, S.; Sugaya, N.; Kawada, J.-I.; Shibata, Y.; Kojima, S.; Nagasaka, T.; Kuzushima, K.; Morishima, T. Differences between T cell-type and natural killer cell-type chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H. Pathogenesis of chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection: Is this an infectious disease, lymphoproliferative disorder, or immunodeficiency? Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.Y.; Montes-Mojarro, I.A.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated T and NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Cohen, J.I. Chronic Active Epstein–Barr Virus Disease. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Morishima, T.; Kanegane, H.; Ohga, S.; Hoshino, Y.; Maeda, A.; Imai, S.; Okano, M.; Morio, T.; Yokota, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, A. Chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection: A bi-faceted disease with inflammatory and neoplastic elements. Immunol. Med. 2018, 41, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Murata, T.; Sato, Y.; Muramatsu, H.; Murakami, N.; Okuno, T.; Yoshida, K.; Ito, Y.; Sawada, A.; Ohshima, K.; et al. Genetic Background of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Disease. Blood 2017, 130, 1468. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, Z.-H.; Yan, Z.-X.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Pan, C.-M.; Hu, Y.; Cai, C.-P.; Dong, Y.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Young, R.M.; Ceribelli, M.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Wright, G.; Shaffer, A.L.; Hodson, D.J.; Buras, E.; et al. Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis and therapeutic targets from structural and functional genomics. Nature 2012, 490, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, Y.; Murata, T.; Sato, Y.; Muramatsu, H.; Ito, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Okuno, T.; Murakami, N.; Yoshida, K.; Sawada, A.; et al. Defective Epstein–Barr virus in chronic active infection and haematological malignancy. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, S.; Nakamura, H. Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection: Is It Immunodeficiency, Malignancy, or Both? Cancers 2020, 12, 3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugaya, N.; Kimura, H.; Hara, S.; Hoshino, Y.; Kojima, S.; Morishima, T.; Tsurumi, T.; Kuzushima, K. Quantitative analysis of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-specific CD8+ T cells in patients with chronic active EBV infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuge, I.; Morishima, T.; Kimura, H.; Kuzushima, K.; Matsuoka, H. Impaired cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to Epstein-Barr virus-infected NK cells in patients with severe chronic active EBV infection. J. Med. Virol. 2001, 64, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohshima, K.; Kimura, H.; Yoshino, T.; Kim, C.W.; Ko, Y.H.; Lee, S.-S.; Peh, S.-C.; Chan, J.K.C.; CAEBV Study Group. Proposed categorization of pathological states of EBV-associated T/natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorder (LPD) in children and young adults: Overlap with chronic active EBV infection and infantile fulminant EBV T-LPD. Pathol. Int. 2008, 58, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, G.; Man, I.; Kemmett, D. Hydroa vacciniforme: A clinical and follow-up study of 17 cases. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2000, 42, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Ridaura, C.; Nagl, F.; Sáez-de-Ocariz, M.; Durán-McKinster, C.; Ruiz-Maldonado, R.; Alderete, G.; Grube, P.; Lome-Maldonado, C.; Bonzheim, I.; et al. Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoma: A chronic EBV+ lymphoproliferative disorder with risk to develop a systemic lymphoma. Blood 2013, 122, 3101–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Hur, K.; Ohn, J.; Kim, T.M.; Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Mun, J.-H. Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder in Korea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Barrionuevo, C.; Garcia, J.; Martínez, M.T.; Pajares, R.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Casavilca, S.; Montes, J.; Bravo, F.; Zaharia, M.; et al. EBV-associated cutaneous NK/T-cell lymphoma: Review of a series of 14 cases from peru in children and young adults. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.I.; Manoli, I.; Dowdell, K.; Krogmann, T.A.; Tamura, D.; Radecki, P.; Bu, W.; Turk, S.-P.; Liepshutz, K.; Hornung, R.L.; et al. Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder: An EBV disease with a low risk of systemic illness in whites. Blood 2019, 133, 2753–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Li, M.; Rao, H. Clinicopathological categorization of hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder: An analysis of prognostic implications and treatment based on 19 cases. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 14, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, L. Hydroa vacciniforme-like lymphoproliferative disorder: A study of clinicopathology and whole-exome sequencing in Chinese patients. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 99, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, H. Hypersensitivity to mosquito bites: A unique pathogenic mechanism linking Epstein-Barr virus infection, allergy and oncogenesis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 45, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Kumar, S.; Fend, F.; Reyes, E.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Kingma, D.W.; Sorbara, L.; Raffeld, M.; Straus, S.E.; Jaffe, E.S. Fulminant EBV+ T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder following acute/chronic EBV infection: A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Blood 2000, 96, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, M.; Ishida, M.; Hodohara, K.; Okuno, H.; Nakanishi, R.; Yoshida, T.; Okabe, H. Systemic Epstein-Barr virus-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disease of childhood: Report of a case with review of the literature. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.C.; Cohen, D.N.; Greig, B.; Yenamandra, A.; Vnencak-Jones, C.; Thompson, M.A.; Kim, A.S. The ambiguous boundary between EBV-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and systemic EBV-driven T cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5738–5749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.-M.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W.-Y.; Wang, M.; Li, H.-F.; Lizaso, A.; Liu, W.-P. Somatic mutations in KMT2D and TET2 associated with worse prognosis in Epstein-Barr virus-associated T or natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorders. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, W.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Intragumtornchai, T.; Nakamura, S.; Kim, W.-S.; Sng, I.; Vose, J.; Armitage, J.O.; Liang, R. International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project Clinical differences between nasal and extranasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: A study of 136 cases from the International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood 2009, 113, 3931–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, P.; Zhao, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.Q.; Fang, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.Y.; et al. A clinical study of 115 patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Clin. Oncol. R Coll. Radiol. 2008, 20, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harabuchi, Y.; Takahara, M.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Kumai, T. Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type: Basic Science and Clinical Progress. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Suh, C.; Park, Y.H.; Ko, Y.H.; Bang, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, D.H.; Huh, J.; Oh, S.Y.; Kwon, H.-C.; et al. Extranodal Natural Killer T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal-Type: A Prognostic Model From a Retrospective Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harabuchi, Y.; Takahara, M.; Kishibe, K.; Moriai, S.; Nagato, T.; Ishii, H. Nasal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma: Clinical, histological, virological, and genetic features. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 14, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guan, P.; Shan, T.; Ye, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Pan, L.; et al. CD30 expression and survival in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16547–16556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, S.; Feng, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Zuo, Z.; Lin, P.; Konoplev, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Vega, F.; Medeiros, L.J.; et al. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: A report of 73 cases at MD Anderson Cancer Center. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhuang, J.-Y.; Chang, S.-T.; Weng, S.-F.; Pan, S.-T.; Chu, P.-Y.; Hsieh, P.-P.; Wei, C.-H.; Chou, S.-C.; Koo, C.-L.; Chen, C.-J.; et al. Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type in Taiwan: A relatively higher frequency of T-cell lineage and poor survival for extranasal tumors. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Lee, T.; Young Kang, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, W.; Ko, Y.-H. Nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphomas are more frequently T rather than NK lineage based on T-cell receptor gene, RNA, and protein studies: Lineage does not predict clinical behavior. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.H.; Ree, H.J.; Kim, W.S.; Choi, W.H.; Moon, W.S.; Kim, S.W. Clinicopathologic and genotypic study of extranodal nasal-type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and natural killer precursor lymphoma among Koreans. Cancer 2000, 89, 2106–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, W.-Y.; Pang, A.; Choy, C.; Chim, C.-S.; Kwong, Y.-L. Quantification of circulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA in the diagnosis and monitoring of natural killer cell and EBV-positive lymphomas in immunocompetent patients. Blood 2004, 104, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mel, S.; Hue, S.S.-S.; Jeyasekharan, A.D.; Chng, W.-J.; Ng, S.-B. Molecular pathogenic pathways in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosialos, G.; Birkenbacht, M.; Yalamanchill, R.; Arsdale, T.V.; Ware, C.; Kleff, E. The Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell 1995, 80, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara, M.; Kis, L.L.; Nagy, N.; Liu, A.; Harabuchi, Y.; Klein, G.; Klein, E. Concomitant increase of LMP1 and CD25 (IL-2-receptor alpha) expression induced by IL-10 in the EBV-positive NK lines SNK6 and KAI3. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aozasa, K.; Takakuwa, T.; Hongyo, T.; Yang, W.-I. Nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma: Epidemiology and pathogenesis. Int. J. Hematol. 2008, 87, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, Y.; Tagawa, H.; Suzuki, R.; Karnan, S.; Karube, K.; Ohshima, K.; Muta, K.; Nawata, H.; Morishima, Y.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia: Different genomic alteration patterns of aggressive NK-cell leukemia and extranodal Nk/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2005, 44, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.-B.; Selvarajan, V.; Huang, G.; Zhou, J.; Feldman, A.L.; Law, M.; Kwong, Y.-L.; Shimizu, N.; Kagami, Y.; Aozasa, K.; et al. Activated oncogenic pathways and therapeutic targets in extranodal nasal-type NK/T cell lymphoma revealed by gene expression profiling. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, B.; Lin, B.; Lee, P.T.; Chung, T.-H.; Tan, J.; Bi, C.; Lee, X.T.; Selvarajan, V.; Ng, S.-B.; et al. EZH2 phosphorylation by JAK3 mediates a switch to noncanonical function in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvarajan, V.; Osato, M.; Nah, G.S.S.; Yan, J.; Chung, T.-H.; Voon, D.C.-C.; Ito, Y.; Ham, M.F.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Shimizu, N.; et al. RUNX3 is oncogenic in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and is transcriptionally regulated by MYC. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, G.C.; Tan, S.Y.; Tang, T.; Poon, S.L.; Allen, G.E.; Tan, L.; Chong, S.C.; Ong, W.S.; Tay, K.; Tao, M.; et al. Janus kinase 3-activating mutations identified in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, J.; Lee, S.; Kwak, S.H.; Park, K.S.; Yoo, H.Y.; Kim, W.S.; et al. Genetic alterations of JAK/STAT cascade and histone modification in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17764–17776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Cui, B.-W.; Wang, N.; Dai, Y.-T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.-F.; Zhong, H.-J.; Cheng, S.; Ou-Yang, B.-S.; Hu, Y.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Characterization of Natural Killer T Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 403–419.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobashi, A.; Tsuyama, N.; Asaka, R.; Togashi, Y.; Ueda, K.; Sakata, S.; Baba, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Hatake, K.; Takeuchi, K. Frequent BCOR aberrations in extranodal NK/T-Cell lymphoma, nasal type. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2016, 55, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Mojarro, I.A.; Chen, B.-J.; Ramirez-Ibarguen, A.F.; Quezada-Fiallos, C.M.; Pérez-Báez, W.B.; Dueñas, D.; Casavilca-Zambrano, S.; Ortiz-Mayor, M.; Rojas-Bilbao, E.; García-Rivello, H.; et al. Mutational profile and EBV strains of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type in Latin America. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xia, Y.; Feng, L.-N.; Chen, J.-R.; Li, H.-M.; Cui, J.; Cai, Q.-Q.; Sim, K.S.; Nairismägi, M.-L.; Laurensia, Y.; et al. Genetic risk of extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasserjian, R.P.; Harris, N.L. NK-cell lymphomas and leukemias: A spectrum of tumors with variable manifestations and immunophenotype. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 127, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, F. Aggressive NK-Cell Leukemia. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufva, O.; Kankainen, M.; Kelkka, T.; Sekiguchi, N.; Awad, S.A.; Eldfors, S.; Yadav, B.; Kuusanmäki, H.; Malani, D.; Andersson, E.I.; et al. Aggressive natural killer-cell leukemia mutational landscape and drug profiling highlight JAK-STAT signaling as therapeutic target. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, N.; Ling, S.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J.; Hao, L.; Luo, H.; Hu, X.; Sheng, L.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies deregulated JAK/STAT-MYC-biosynthesis axis in aggressive NK-cell leukemia. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Asano, N.; Miyata-Takata, T.; Takata, K.; Elsayed, A.A.; Satou, A.; Takahashi, E.; Kinoshita, T.; Nakamura, S. T-cell receptor (TCR) phenotype of nodal Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma (CTL): A clinicopathologic study of 39 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, J.-H.; Sung, J.-Y.; Han, J.H.; Ko, Y.-H. Epstein-Barr virus–positive nodal T/NK-cell lymphoma: An analysis of 15 cases with distinct clinicopathological features. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.-B.; Chung, T.-H.; Kato, S.; Nakamura, S.; Takahashi, E.; Ko, Y.-H.; Khoury, J.D.; Yin, C.C.; Soong, R.; Jeyasekharan, A.D.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated primary nodal T/NK-cell lymphoma shows a distinct molecular signature and copy number changes. Haematologica 2018, 103, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, S.S.-S.; Oon, M.L.; Wang, S.; Tan, S.-Y.; Ng, S.-B. Epstein–Barr virus-associated T- and NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases: An update and diagnostic approach. Pathology 2020, 52, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouly, F.; Baccard, M.; Rybojad, M.; Lebbé, C.; Morinet, F.; Morel, P. Aggressive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma associated with the presence of Epstein-Barr virus. 2 cases. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 1996, 123, 574–576. [Google Scholar]
- Novelli, M.; Merlino, C.; Ponti, R.; Bergallo, M.; Quaglino, P.; Cambieri, I.; Comessatti, A.; Sidoti, F.; Costa, C.; Corino, D.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas: Evaluation of the Viral Presence and Significance in Skin and Peripheral Blood. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulc, P.; N’Guyen, J.M.; Dréno, B. Prognostic factors in Sézary syndrome: A study of 28 patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 149, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.L.; Grogg, K.L.; Macon, W.R.; Dogan, A.; Feldman, A.L. Clinicopathologic features of B-Cell lineage neoplasms with aberrant expression of CD3: A study of 21 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Nakamura, N.; Kamata, H.; Kotani, S.; Ohsaka, M.; Kajita, S.; Miyazaki, K.; Ohtani, S.; Nakayama, M.; et al. CD3- and CD4-positive plasmablastic lymphoma: A literature review of Japanese plasmablastic lymphoma cases. Intern. Med. Tokyo Jpn. 2010, 49, 1801–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Lau, S.; Raghavan, R.I.; Rowsell, E.H.; Said, J.; Weiss, L.M.; Huang, Q. CD3-positive Large B-cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courville, E.L.; Sohani, A.R.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Zukerberg, L.R.; Harris, N.L.; Ferry, J.A. Diverse clinicopathologic features in human herpesvirus 8-associated lymphomas lead to diagnostic problems. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 142, 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropf, J.; Gerges, M.; Perez, A.P.; Ellis, A.; Mathew, M.; Ayesu, K.; Ge, L.; Carlan, S.J. T Cell Primary Effusion Lymphoma in an HIV-Negative Man with Liver Cirrhosis. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e919032-1–e919032-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Disease Entity | Age Group | Phenotype | Histology | Molecular Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV-HLH | Pediatrics, adolescents | T CD8+ > NK | Lymphohistiocytic infiltrates Hemophagocytosis EBV+ cells with slight or no atypia | +/− Predisposing genetic conditions: mutations in PRF1, UNC13D, STX11, STXBP2, SH2D1A, XIAP/BIRC4 genes. |
| CAEBV, systemic form | Pediatrics, adolescents | T CD4+ > CD8+ > NK | Non-destructive inflammatory lesions Scattered small-sized EBV+ cells | +/− Predisposing genetic conditions: HLA 26 and 52 loci [23]. Chromosomal abnormalities noted in few cases [3]. Alterations in NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways [25]. Recurrent mutations involving DDX3X, KMT2D, BCOR/BCORL1, KDM6A and TET2 genes [26]. Intragenic deletions in EBV genome [29]. |
| CAEBV, cutaneous forms: -HV-LPD | Pediatrics, adolescents | T CD8+ | Non-specific inflammatory changes Small or medium-sized EBV+ cells | Mutations in STAT3, IKBKB, ELF3, CHD7 and KMT2D genes reported in one study [40]. |
| -SMBA | Pediatrics, adolescents | NK | Polymorphic infiltrate Extensive necrosis, angiodestruction Large atypical EBV+ cells | Chromosomal abnormalities noted in rare cases [3]. |
| STCLC | Pediatrics, adolescents | T CD8+ (primary) T CD4+ (post CAEBV) | Proliferation of bland EBV+ cells +/− Admixed atypical cells | Chromosomal abnormalities associated with poor outcomes [44]. Recurrent mutations involving KMT2D, MFHAS1, STAT3, EP300, ITPKB, DDX3X NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 genes [45]. |
| ENKTL | Adults | NK | Proliferation of EBV+ atypical cells Angiocentricity, angiodestruction Necrosis | Cytogenetic aberrations: 6q16–27 and 17p15–22 deletions; 1q21–q44, 2q and 7q gains [62]. Mutations in TP53, FAS, BCOR, STAT3, STAT5B, JAK3, DDX3X genes. Alterations in epigenetic regulators (KMT2D, KMT2C, ASXL3, ARID1A and EP300) [27,61,66,67,68,69,70]. Gene expression: cell cycle/apoptosis, NFKB, NOTCH and JAK/STAT pathways deregulations, MYC, RUNX3 and EZH2 overexpression [63,64,65]. |
| ANKL | Adults | NK | Patchy or diffuse destructive monotonous EBV+ infiltrates +/− Necrosis, hemophagocytosis | Cytogenetic aberrations: 1q23.1–24.2 and 1q31.3 gains; 7p15.1–p22.3 and 17p13.1 losses [62]. Recurrent mutations involving STAT3 and STAT5B genes, RAS-MAPK pathways, TP53, DDX3X, BCOR, TET2, CREBBP and MLL2 [45,74,75]. |
| Nodal TNKL * | Adults, the elderly | T CD8+ > γδ or NK | Monomorphic or pleomorphic EBV+ cells proliferation +/− Necrosis, angiodestruction | Loss of 14q11.2 (TCRA loci) Gene expression: upregulation of PD-L1 and T-cell related genes (CD2, CD8, CD3G, CD3D, TRAC, LEF1); downregulation of CD56 [78]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syrykh, C.; Péricart, S.; Lamaison, C.; Escudié, F.; Brousset, P.; Laurent, C. Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated T- and NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases: A Review of Clinical and Pathological Features. Cancers 2021, 13, 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133315
Syrykh C, Péricart S, Lamaison C, Escudié F, Brousset P, Laurent C. Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated T- and NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases: A Review of Clinical and Pathological Features. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133315
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyrykh, Charlotte, Sarah Péricart, Claire Lamaison, Frédéric Escudié, Pierre Brousset, and Camille Laurent. 2021. "Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated T- and NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases: A Review of Clinical and Pathological Features" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133315
APA StyleSyrykh, C., Péricart, S., Lamaison, C., Escudié, F., Brousset, P., & Laurent, C. (2021). Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated T- and NK-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases: A Review of Clinical and Pathological Features. Cancers, 13(13), 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133315







