The Ability of Metabolomics to Discriminate Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes Depends on the Stage of the Disease and the Type of Material Studied
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics and Samples Collection
2.2. Tissue and Plasma Samples Preparation
2.3. Lung Tissue and Plasma Metabolic Fingerprinting
2.4. LC-MS Data Treatment and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Metabolite Identification
3. Results
3.1. Quality Assurance of Metabolomics Data
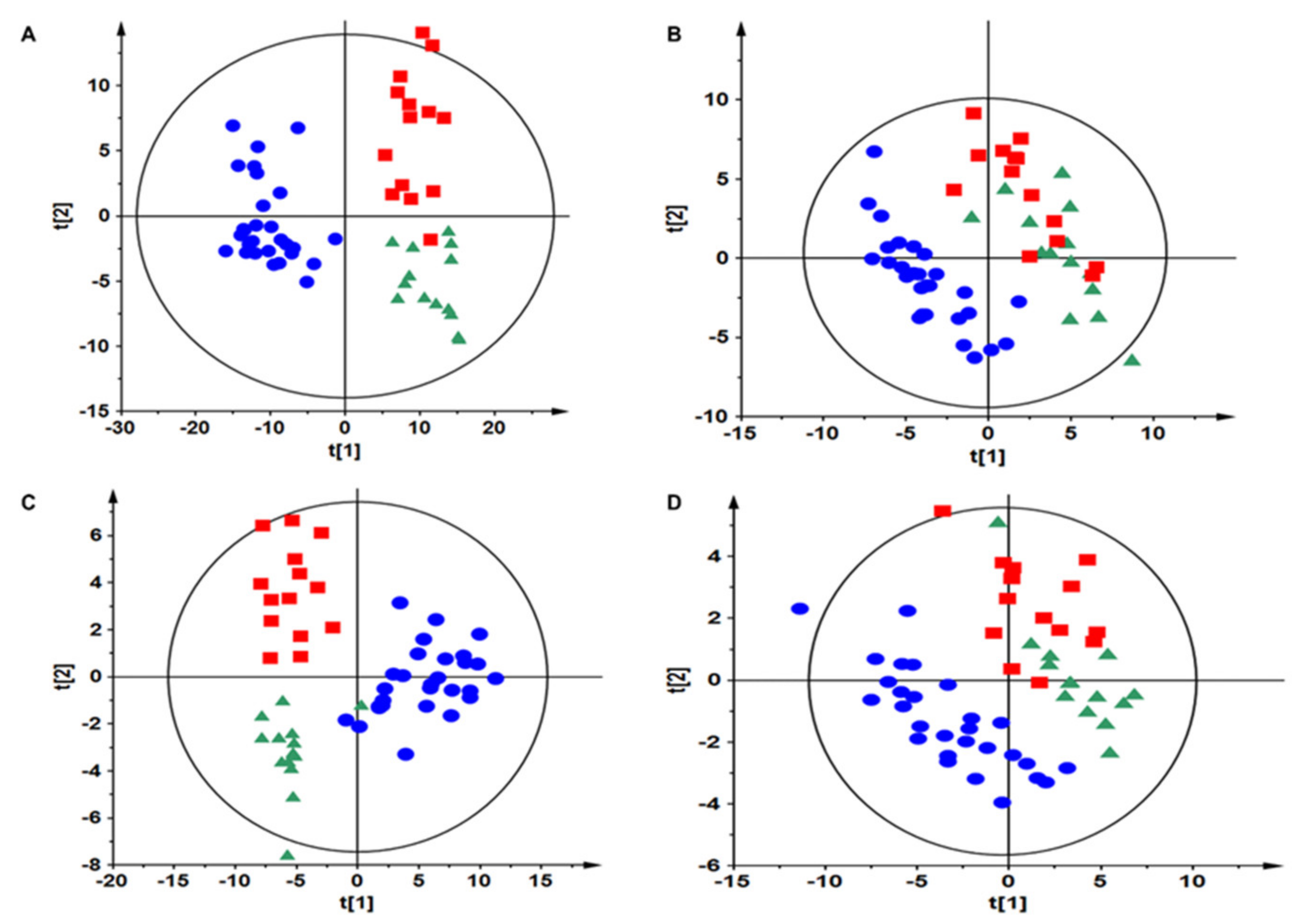
3.2. Samples Classification
3.3. Metabolomics of Tissue Samples
3.4. Metabolomics of Plasma Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Adenocarcinoma |
| ALK | Tyrosine kinase receptor |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CID | Collision-induced dissociation |
| cMYC | C-myc protein |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic acid |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EML4-ALK | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic acid |
| ESI− | Electrospray ionization negative |
| ESI+ | Electrospray ionization positive |
| ETrE | Eicosatrienoic acid |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| GPL | Glycerophospholipids |
| GP-NAE | Glycerophospho (N-acyl) ethanolamines |
| HILIC | Hydrophilic interactions chromatography |
| KRAS | GTPase KRas |
| LCC | Large cell cancer |
| LC-MS | Liquide chromatography mass spectrometry |
| LPEAT2 | Lysophosphatidylethanolamine acyltransferase 2 |
| LysoPC | Lysophosphatidylcholines |
| LysoPE | Lysophosphatidylethanolamines |
| LysoPI | Lysophosphatidylinositols |
| NAA | N-acetyl aspartate |
| NRF2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholines |
| PCA | Principal components analysis |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamines |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| QC | Quality control |
| ROS1 | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase ROS |
| RP | Reversed-phase chromatography |
| SCC | Squamous cell cancer |
| SM | Sphingomyelin |
| TCA cycle | Tricarboxylic acid cycle |
| TMA | Trimethylamine |
| TNM | Tumor, node, metastasis classification |
| TP53 | Tumor protein p53 |
| VIP | Variable importance into projection values |
References
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Lung Cancers: Molecular Characterization, Clonal Heterogeneity and Evolution, and Cancer Stem Cells. Cancers 2018, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Fillmore, C.M.; Hammerman, P.S.; Kim, C.F.; Wong, K.K. Non-small-cell lung cancers: A heterogeneous set of diseases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Huang, L.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niemira, M.; Collin, F.; Szalkowska, A.; Bielska, A.; Chwialkowska, K.; Reszec, J.; Niklinski, J.; Kwasniewski, M.; Kretowski, A. Molecular Signature of Subtypes of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer by Large-Scale Transcriptional Profiling: Identification of Key Modules and Genes by Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA). Cancers 2020, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calvayrac, O.; Pradines, A.; Pons, E.; Mazières, J.; Guibert, N. Molecular biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, E.G.; Southam, A.D. Monitoring cancer prognosis, diagnosis and treatment efficacy using metabolomics and lipidomics. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, C.; Jin, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Xia, Y.; Shu, Y.; Guo, R. Cortisol, cortisone, and 4-methoxyphenylacetic acid as potential plasma biomarkers for early detection of non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2018, 33, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Shahjaman, M.; Mollah, M.N.H.; Islam, S.M.S.; Hoque, M.A. Serum and Plasma Metabolomic Biomarkers for Lung Cancer. Bioinformation 2017, 13, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Zhong, J.; Li, L.; Min, L.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Dai, L. Simultaneous quantification of serum monounsaturated and polyunsaturated phosphatidylcholines as potential biomarkers for diagnosing non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchades-Carrasco, L.; Jantus-Lewintre, E.; Pérez-Rambla, C.; García-García, F.; Lucas, R.; Calabuig, S.; Blasco, A.; Dopazo, J.; Camps, C.; Pineda-Lucena, A. Serum metabolomic profiling facilitates the non-invasive identification of metabolic biomarkers associated with the onset and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12904–12916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Zheng, C.; Wu, L. Targeted metabolomics for serum amino acids and acylcarnitines in patients with lung cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahrmann, J.F.; Kim, K.; DeFelice, B.C.; Taylor, S.L.; Gandara, D.R.; Yoneda, K.Y.; Cooke, D.T.; Fiehn, O.; Kelly, K.; Miyamoto, S. Investigation of metabolomic blood biomarkers for detection of adenocarcinoma lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hori, S.; Nishiumi, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Shinohara, M.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Kotani, Y.; Hatano, N.; Maniwa, Y.; Nishio, W.; Bamba, T.; et al. A metabolomic approach to lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2011, 74, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, A.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Zhong, J.; Min, L.; Dai, L. Metabolomic profiling of human serum in lung cancer patients using liquid chromatography/hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, J.; Higashiyama, M.; Imaizumi, A.; Nakayama, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Daimon, T.; Yamakado, M.; Imamura, F.; Kodama, K. Possibility of multivariate function composed of plasma amino acid profiles as a novel screening index for non-small cell lung cancer: A case control study. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, T.W.; Lane, A.N.; Higashi, R.M.; Farag, M.A.; Gao, H.; Bousamra, M.; Miller, D.M. Altered regulation of metabolic pathways in human lung cancer discerned by (13)C stable isotope-resolved metabolomics (SIRM). Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kami, K.; Fujimori, T.; Sato, H.; Sato, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Ohashi, Y.; Sugiyama, N.; Ishihama, Y.; Onozuka, H.; Ochiai, A.; et al. Metabolomic profiling of lung and prostate tumor tissues by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fahrmann, J.F.; Grapov, D.D.; Wanichthanarak, K.; DeFelice, B.C.; Salemi, M.R.; Rom, W.N.; Gandara, D.R.; Phinney, B.S.; Fiehn, O.; Pass, H.; et al. Integrated Metabolomics and Proteomics Highlight Altered Nicotinamide- and Polyamine Pathways in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Grapov, D.; Fahrmann, J.F.; DeFelice, B.; Rom, W.N.; Pass, H.I.; Kim, K.; Nguyen, U.; Taylor, S.L.; Gandara, D.R.; et al. Metabolomic markers of altered nucleotide metabolism in early stage adenocarcinoma. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niklinski, J.; Kretowski, A.; Moniuszko, M.; Reszec, J.; Michalska-Falkowska, A.; Niemira, M.; Ciborowski, M.; Charkiewicz, R.; Jurgilewicz, D.; Kozlowski, M.; et al. Systematic biobanking, novel imaging techniques, and advanced molecular analysis for precise tumor diagnosis and therapy: The Polish MOBIT project. Adv. Med. Sci. 2017, 62, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciborowski, M.; Kisluk, J.; Pietrowska, K.; Samczuk, P.; Parfieniuk, E.; Kowalczyk, T.; Kozlowski, M.; Kretowski, A.; Niklinski, J. Development of LC-QTOF-MS method for human lung tissue fingerprinting. A preliminary application to nonsmall cell lung cancer. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniluk, U.; Daniluk, J.; Kucharski, R.; Kowalczyk, T.; Pietrowska, K.; Samczuk, P.; Filimoniuk, A.; Kretowski, A.; Lebensztejn, D.; Ciborowski, M. Untargeted Metabolomics and Inflammatory Markers Profiling in Children With Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis-A Preliminary Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciborowski, M.; Teul, J.; Martin-Ventura, J.L.; Egido, J.; Barbas, C. Metabolomics with LC-QTOF-MS permits the prediction of disease stage in aortic abdominal aneurysm based on plasma metabolic fingerprint. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil-de-la-Fuente, A.; Godzien, J.; Saugar, S.; Garcia-Carmona, R.; Badran, H.; Wishart, D.S.; Barbas, C.; Otero, A. CEU Mass Mediator 3.0: A Metabolite Annotation Tool. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godzien, J.; Ciborowski, M.; Martínez-Alcázar, M.P.; Samczuk, P.; Kretowski, A.; Barbas, C. Rapid and Reliable Identification of Phospholipids for Untargeted Metabolomics with LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3204–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berker, Y.; Vandergrift, L.A.; Wagner, I.; Su, L.; Kurth, J.; Schuler, A.; Dinges, S.S.; Habbel, P.; Nowak, J.; Mark, E.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy-based Metabolomic Biomarkers for Typing, Staging, and Survival Estimation of Early-Stage Human Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocha, C.M.; Barros, A.S.; Goodfellow, B.J.; Carreira, I.M.; Gomes, A.; Sousa, V.; Bernardo, J.; Carvalho, L.; Gil, A.M.; Duarte, I.F. NMR metabolomics of human lung tumours reveals distinct metabolic signatures for adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno, P.; Jimenez-Jimenez, C.; Garrido-Rodriguez, M.; Calderon-Santiago, M.; Molina, S.; Lara-Chica, M.; Priego-Capote, F.; Salvatierra, A.; Munoz, E.; Calzado, M.A. Metabolomic profiling of human lung tumor tissues—Nucleotide metabolism as a candidate for therapeutic interventions and biomarkers. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1778–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Agouza, I.M.; Eissa, S.S.; El Houseini, M.M.; El-Nashar, D.E.; Abd El Hameed, O.M. Taurine: A novel tumor marker for enhanced detection of breast cancer among female patients. Angiogenesis 2011, 14, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, S.; Zhang, X.L.; Wan, H.F.; Xia, Y.Q.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yang, X.H.; Wan, F.S. Effect of taurine on cell proliferation and apoptosis human lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5473–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velasquez, M.T.; Ramezani, A.; Manal, A.; Raj, D.S. Trimethylamine N-Oxide: The Good, the Bad and the Unknown. Toxins 2016, 8, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, C.W.H.; Law, B.M.H.; Waye, M.M.Y.; Chan, J.Y.W.; So, W.K.W.; Chow, K.M. Trimethylamine-N-oxide as One Hypothetical Link for the Relationship between Intestinal Microbiota and Cancer—Where We Are and Where Shall We Go? J. Cancer 2019, 10, 5874–5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Hooi, S.C.; Jiang, Y.M.; Lu, G.D. Fatty acid activation in carcinogenesis and cancer development: Essential roles of long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Sui, C.; Meng, F.; Ma, P.; Jiang, Y. The omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid inhibits proliferation and progression of non-small cell lung cancer cells through the reactive oxygen species-mediated inactivation of the PI3K /Akt pathway. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eggers, L.F.; Muller, J.; Marella, C.; Scholz, V.; Watz, H.; Kugler, C.; Rabe, K.F.; Goldmann, T.; Schwudke, D. Lipidomes of lung cancer and tumour-free lung tissues reveal distinct molecular signatures for cancer differentiation, age, inflammation, and pulmonary emphysema. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, T.W.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Kang, W.Y.; Arnold, S.; Higashi, R.M.; Liu, J.; Lane, A.N. Exosomal lipids for classifying early and late stage non-small cell lung cancer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1037, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Ahmed, R.; Huang, G.; Reid, J.; Mandal, R.; Maksymuik, A.; Sitar, D.S.; Tappia, P.S.; Ramjiawan, B.; et al. A High-Performing Plasma Metabolite Panel for Early-Stage Lung Cancer Detection. Cancers 2020, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ros-Mazurczyk, M.; Jelonek, K.; Marczyk, M.; Binczyk, F.; Pietrowska, M.; Polanska, J.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Jassem, J.; Rzyman, W.; Widlak, P. Serum lipid profile discriminates patients with early lung cancer from healthy controls. Lung Cancer 2017, 112, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.E.; Lespi, P.; Di Luca, M.; Bustos, C.; Marra, F.A.; de Alaniz, M.J.; Marra, C.A. A reliable biomarker derived from plasmalogens to evaluate malignancy and metastatic capacity of human cancers. Lipids 2008, 43, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messias, M.C.F.; Mecatti, G.C.; Priolli, D.G.; de Oliveira Carvalho, P. Plasmalogen lipids: Functional mechanism and their involvement in gastrointestinal cancer. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Dai, M.; Ai, J.; Li, Y.; Mahon, B.; Dai, S.; Deng, Y. Plasma lipidomics profiling identified lipid biomarkers in distinguishing early-stage breast cancer from benign lesions. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36622–36631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.M.; Cravatt, B.F. Endocannabinoid biosynthesis proceeding through glycerophospho-N-acyl ethanolamine and a role for alpha/beta-hydrolase 4 in this pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26465–26472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, J.; Gouveia-Figueira, S.; Alhouayek, M.; Fowler, C.J. Effects of tumour necrosis factor α upon the metabolism of the endocannabinoid anandamide in prostate cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyszniak, M.; Tabarkiewicz, J.; Łuszczki, J.J. Endocannabinoid system as a regulator of tumor cell malignancy—Biological pathways and clinical significance. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 4323–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lou, T.F.; Sethuraman, D.; Dospoy, P.; Srivastva, P.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.; Ma, X.; Chen, P.H.; Huffman, K.E.; Frink, R.E.; et al. Cancer-Specific Production of N-Acetylaspartate via NAT8L Overexpression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Potential as a Circulating Biomarker. Cancer Prev. Res. 2016, 9, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Chen, H.; Ai, J.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Borgia, J.A.; Yang, J.S.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, B.; Gu, W.; et al. Global lipidomics identified plasma lipids as novel biomarkers for early detection of lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107899–107906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, N.; Pang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Pan, H.; Zuo, X.; Guan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Cui, Z.; et al. An Updated Overview of Metabolomic Profile Changes in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Metabolites 2019, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinkla, S.; van Eijk, L.T.; Fuchs, B.; Schiller, J.; Joosten, I.; Brock, R.; Pickkers, P.; Bosman, G.J. Inflammation-associated changes in lipid composition and the organization of the erythrocyte membrane. BBA Clin. 2016, 5, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Hanash, S.; DeFelice, B.; Miyamoto, S.; Barnett, M.; Zhao, Y.; Goodman, G.; Feng, Z.; Gandara, D.; Fiehn, O.; et al. Diacetylspermine Is a Novel Prediagnostic Serum Biomarker for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Has Additive Performance With Pro-Surfactant Protein B. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3880–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Sakaguchi, K.; Horio, H.; Hiramatsu, K.; Moriya, S.; Takahashi, K.; Kawakita, M. Urinary N1, N12-diacetylspermine is a non-invasive marker for the diagnosis and prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaira, K.; Oriuchi, N.; Imai, H.; Shimizu, K.; Yanagitani, N.; Sunaga, N.; Hisada, T.; Tanaka, S.; Ishizuka, T.; Kanai, Y.; et al. Prognostic significance of L-type amino acid transporter 1 expression in resectable stage I-III nonsmall cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, B.; You, W.; Xue, S.; Qin, H.; Jiang, H. The membrane bile acid receptor TGR5 drives cell growth and migration via activation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, C.E.; Bergmann, A. The Sound of Silence: Signaling by Apoptotic Cells. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 114, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raynor, A.; Jantscheff, P.; Ross, T.; Schlesinger, M.; Wilde, M.; Haasis, S.; Dreckmann, T.; Bendas, G.; Massing, U. Saturated and mono-unsaturated lysophosphatidylcholine metabolism in tumour cells: A potential therapeutic target for preventing metastases. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eto, M.; Shindou, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Tamura-Nakano, M.; Shimizu, T. Lysophosphatidylethanolamine acyltransferase 2 (LPEAT2) incorporates DHA into phospholipids and has possible functions for fatty acid-induced cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, C.; Fortin, S. Docosahexaenoic Acid Monoglyceride Increases Carboplatin Activity in Lung Cancer Models by Targeting EGFR. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6015–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogretmen, B. Sphingolipid metabolism in cancer signalling and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieberich, E.; Wang, G. Sphingolipid in Lung Cancer Pathogenesis and Therapy; InTech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]





| Type of Biological Material | Patients Characteristic | Squemous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) | Adenocarcinoma (ADC) | Large Cell Carcinoma (LCC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue | Age (mean) | 64.45 ± 8.02 | 64.77 ± 8.44 | 64.58 ± 6.43 |
| BMI (mean) | 25.4 ± 3.48 | 25.4 ± 3.59 | 25.5 ± 2.83 | |
| Male | 39 | 23 | 10 | |
| Female | 15 | 10 | 2 | |
| pTNM: I A | 7 | 8 | 0 | |
| I B | 7 | 6 | 0 | |
| II A | 13 | 6 | 2 | |
| II B | 18 | 7 | 7 | |
| III A | 9 | 6 | 3 | |
| Plasma | Age (mean) | 65.61 ± 6.52 | 64.16 ± 6.91 | 64.57 ± 5.62 |
| BMI (mean) | 27.4 ± 4.48 | 26.0 ± 3.41 | 24.9 ± 1.78 | |
| Male | 21 | 20 | 6 | |
| Female | 12 | 12 | 1 | |
| pTNM: I A | 10 | 10 | 0 | |
| I B | 9 | 10 | 0 | |
| II A | 3 | 4 | 0 | |
| II B | 7 | 6 | 6 | |
| III A | 4 | 2 | 1 | |
| Control group | ||||
| Plasma | Number of patients | 20 | ||
| Age (mean) | 61.5 ± 12.06 | |||
| Male | 13 | |||
| Female | 7 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalczyk, T.; Kisluk, J.; Pietrowska, K.; Godzien, J.; Kozlowski, M.; Reszeć, J.; Sierko, E.; Naumnik, W.; Mróz, R.; Moniuszko, M.; et al. The Ability of Metabolomics to Discriminate Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes Depends on the Stage of the Disease and the Type of Material Studied. Cancers 2021, 13, 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133314
Kowalczyk T, Kisluk J, Pietrowska K, Godzien J, Kozlowski M, Reszeć J, Sierko E, Naumnik W, Mróz R, Moniuszko M, et al. The Ability of Metabolomics to Discriminate Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes Depends on the Stage of the Disease and the Type of Material Studied. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133314
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalczyk, Tomasz, Joanna Kisluk, Karolina Pietrowska, Joanna Godzien, Miroslaw Kozlowski, Joanna Reszeć, Ewa Sierko, Wojciech Naumnik, Robert Mróz, Marcin Moniuszko, and et al. 2021. "The Ability of Metabolomics to Discriminate Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes Depends on the Stage of the Disease and the Type of Material Studied" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133314
APA StyleKowalczyk, T., Kisluk, J., Pietrowska, K., Godzien, J., Kozlowski, M., Reszeć, J., Sierko, E., Naumnik, W., Mróz, R., Moniuszko, M., Kretowski, A., Niklinski, J., & Ciborowski, M. (2021). The Ability of Metabolomics to Discriminate Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes Depends on the Stage of the Disease and the Type of Material Studied. Cancers, 13(13), 3314. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133314








