Characteristics and Clinical Application of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. History of Extracellular Vesicles
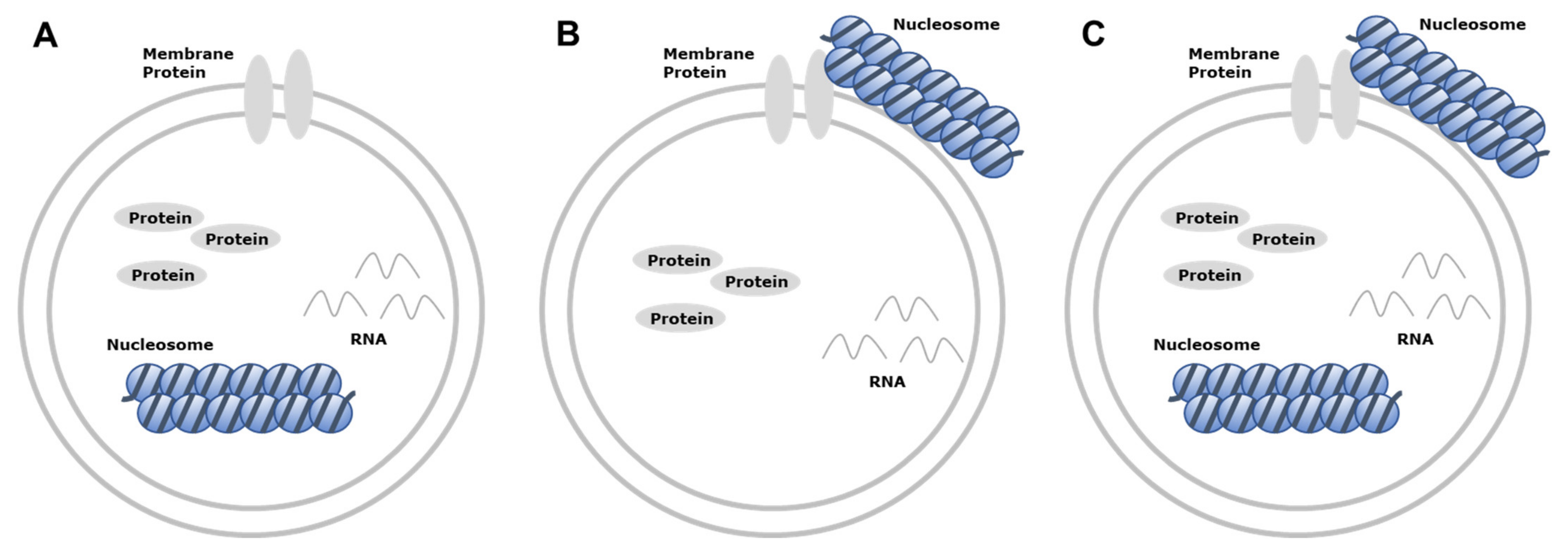
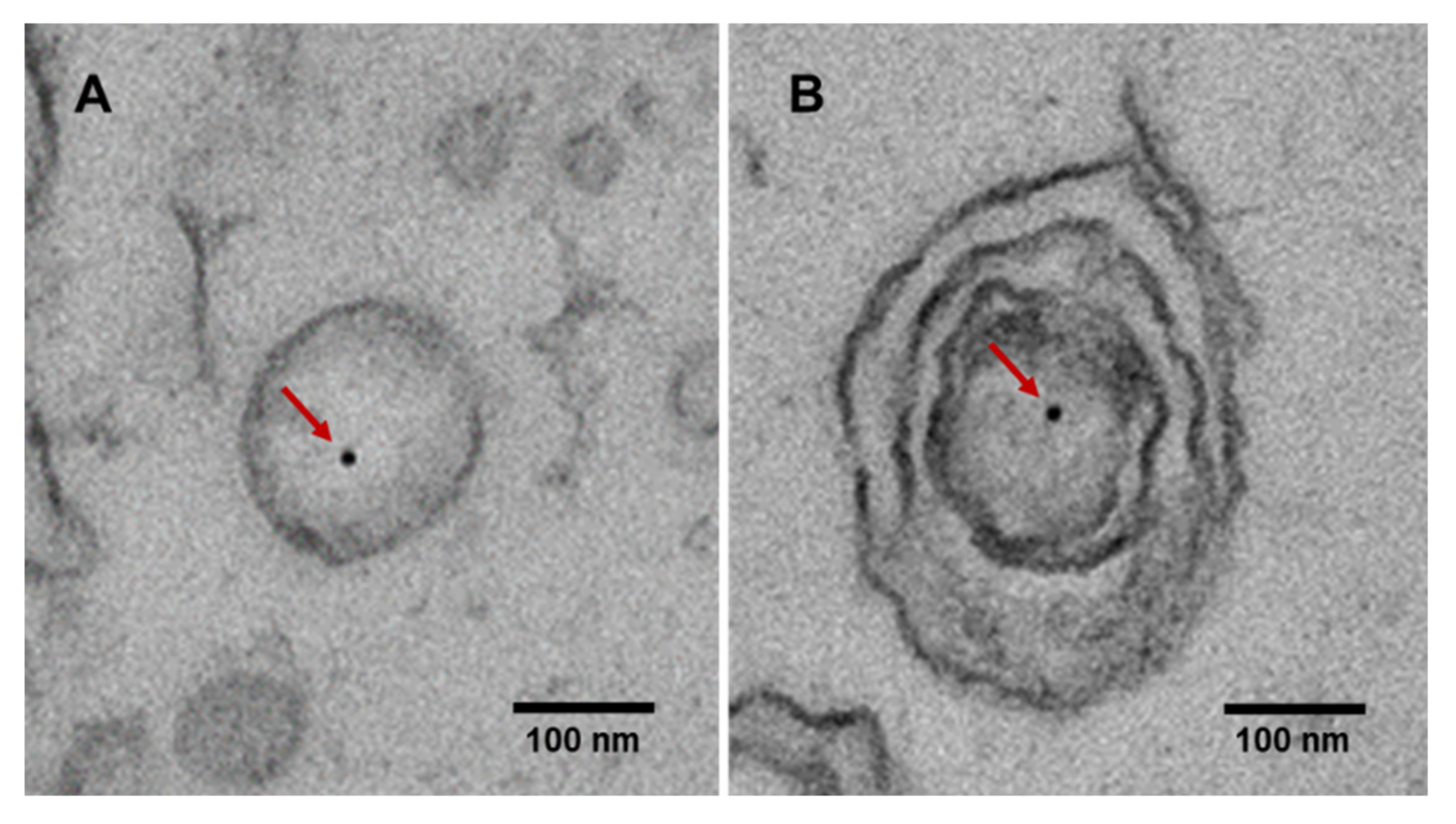
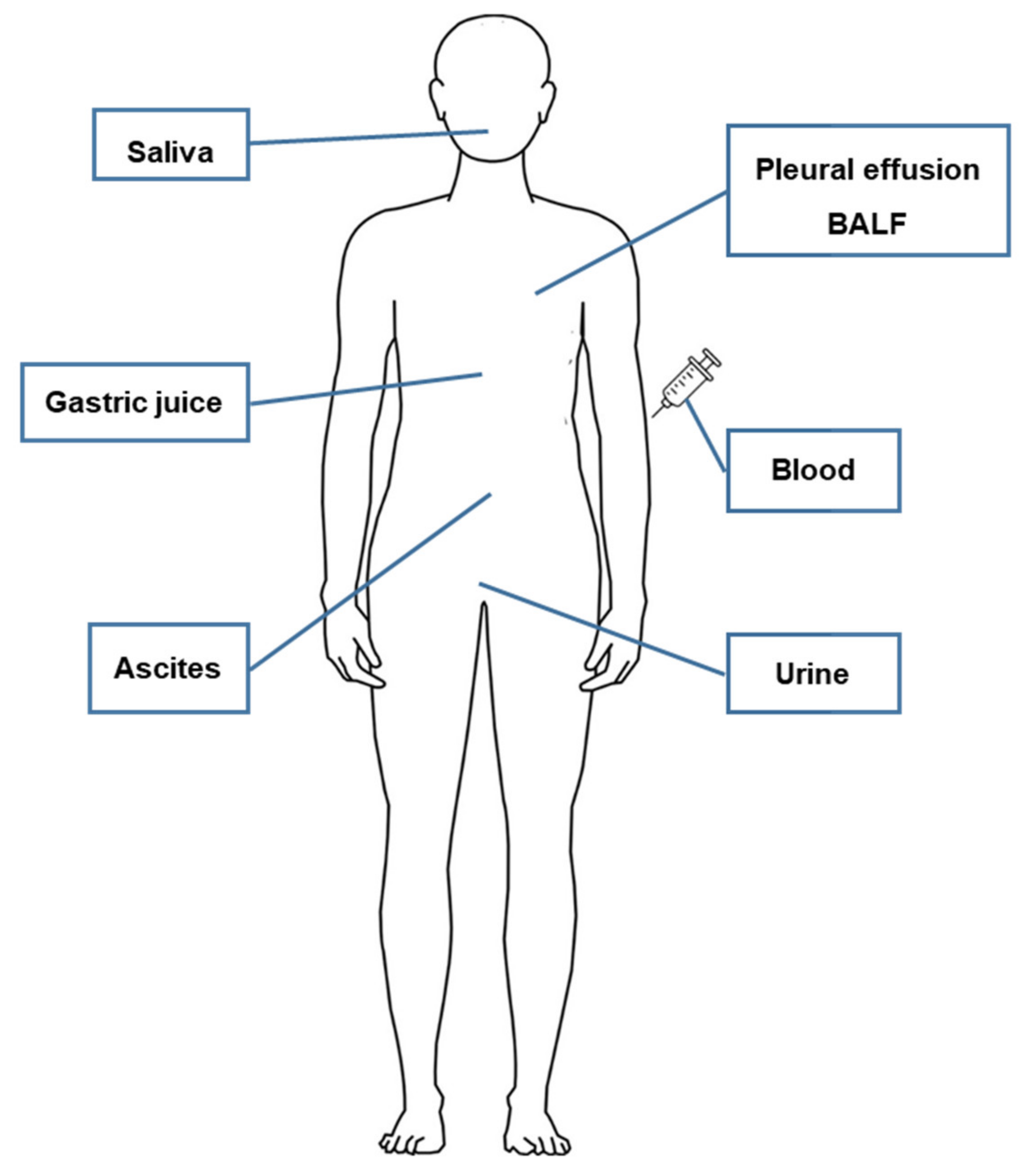
3. Characteristics of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA
4. Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA Stability and Mutant Detection
5. Methylation of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA
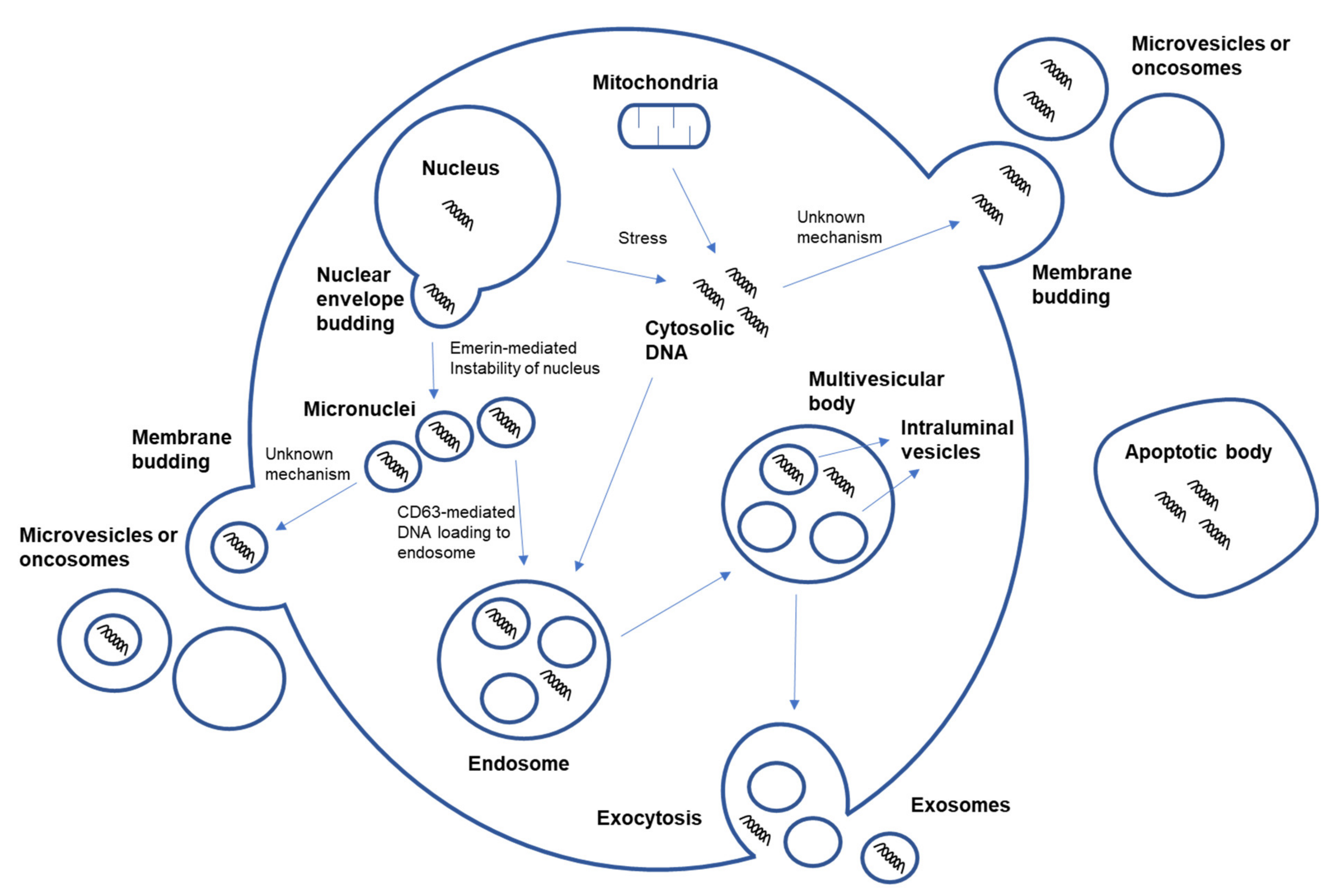
6. Mechanism of DNA Loading onto EV and Transfer of EV-Derived DNA
7. NGS Analysis Using Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA
7.1. WGS and WES
7.2. Targeted NGS
8. Challenges of Studying Extracellular Vesicles
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerber, D.E. Targeted therapies: A new generation of cancer treatments. Am. Fam. Physician 2008, 77, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farkona, S.; Diamandis, E.P.; Blasutig, I.M. Cancer immunotherapy: The beginning of the end of cancer? BMC Med. 2016, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ginsburg, G.S.; Phillips, K.A. Precision Medicine: From Science to Value. Health Aff. 2018, 37, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, A.K.; Bettegowda, C.; Zhou, S.; Papadopoulos, N.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. Applications of liquid biopsies for cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaay1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crowley, E.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Loupakis, F.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsy: Monitoring cancer-genetics in the blood. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Meo, A.; Bartlett, J.; Cheng, Y.; Pasic, M.D.; Yousef, G.M. Liquid biopsy: A step forward towards precision medicine in urologic malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, K.; Wei, F.; Wong, D.T.; Tu, M. Saliva liquid biopsy for point-of-care applications. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.S.; Jiang, B.Y.; Yang, J.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, J.Y.; Zhong, W.Z.; Tu, H.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Unique genetic profiles from cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA in leptomeningeal metastases of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer: A new medium of liquid biopsy. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, H.; Nykin, D.; Bui, N.; Quan, D.; Gomez, G.; Woodward, B.; Venkatapathy, S.; Duttagupta, R.; Fung, E.; Lippman, S.M.; et al. Cell-Free DNA from Ascites and Pleural Effusions: Molecular Insights into Genomic Aberrations and Disease Biology. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Hur, J.Y.; Kim, I.A.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, K.Y. Liquid biopsy using the supernatant of a pleural effusion for EGFR genotyping in pulmonary adenocarcinoma patients: A comparison between cell-free DNA and extracellular vesicle-derived DNA. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrugo-Ramirez, J.; Mir, M.; Samitier, J. Blood-Based Cancer Biomarkers in Liquid Biopsy: A Promising Non-Invasive Alternative to Tissue Biopsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perdomo, S.; Avogbe, P.H.; Foll, M.; Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Facciolla, V.L.; Anantharaman, D.; Chopard, P.; Calvez-Kelm, F.L.; Vilensky, M.; Polesel, J.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA detection in head and neck cancer: Evaluation of two different detection approaches. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 72621–72632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ou, Z.; Li, K.; Yang, T.; Dai, Y.; Chandra, M.; Ning, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Gao, T.; Xie, Y.; et al. Detection of bladder cancer using urinary cell-free DNA and cellular DNA. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ponti, G.; Manfredini, M.; Tomasi, A. Non-blood sources of cell-free DNA for cancer molecular profiling in clinical pathology and oncology. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 141, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hur, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Jung, M.K.; Pack, C.G.; Lee, K.Y. Extracellular vesicle-derived DNA for performing EGFR genotyping of NSCLC patients. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bunda, S.; Zuccato, J.A.; Voisin, M.R.; Wang, J.Z.; Nassiri, F.; Patil, V.; Mansouri, S.; Zadeh, G. Liquid Biomarkers for Improved Diagnosis and Classification of CNS Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quandt, D.; Dieter Zucht, H.; Amann, A.; Wulf-Goldenberg, A.; Borrebaeck, C.; Cannarile, M.; Lambrechts, D.; Oberacher, H.; Garrett, J.; Nayak, T.; et al. Implementing liquid biopsies into clinical decision making for cancer immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 48507–48520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, A.; Kirchner, T. Liquid Biopsy in Tumor Genetic Diagnosis. Dtsch. Aerzteblatt Int. 2018, 115, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilie, M.; Hofman, P. Pros: Can tissue biopsy be replaced by liquid biopsy? Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russano, M.; Napolitano, A.; Ribelli, G.; Iuliani, M.; Simonetti, S.; Citarella, F.; Pantano, F.; Dell’Aquila, E.; Anesi, C.; Silvestris, N.; et al. Liquid biopsy and tumor heterogeneity in metastatic solid tumors: The potentiality of blood samples. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, E.; Rothwell, D.G.; Brady, G.; Dive, C. Liquid Biopsy-Based Biomarkers of Treatment Response and Resistance. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, A.; Kostallari, E.; Feldstein, A.E.; Shah, V.H. Extracellular vesicles, the liquid biopsy of the future. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1292–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, B.; Xu, K.; Zheng, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zheng, S. Application of exosomes as liquid biopsy in clinical diagnosis. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, K.; Montuenga, L.M. Exosomes in Liquid Biopsy: The Nanometric World in the Pursuit of Precision Oncology. Cancers 2021, 13, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Risch, H.A. Exosomes: Potential for early detection in pancreatic cancer. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Becker, A.; Matei, I.; Huang, Y.; Costa-Silva, B.; Zheng, Y.; Hoshino, A.; Brazier, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Double-stranded DNA in exosomes: A novel biomarker in cancer detection. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.; Wu, G.; Jose, P.A.; Zeng, C. Functional transferred DNA within extracellular vesicles. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 349, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicle transfer of cancer pathogenic components. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of Extracellular Vesicles, Their Origin, Composition, Purpose, and Methods for Exosome Isolation and Analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Andaloussi, S.; Mager, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J. Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, T.L. Tumor-Derived Exosomes and Their Role in Cancer Progression. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 74, 103–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, D.D.; Gercel-Taylor, C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 110, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Wei, J.; Taron, M. Circulating MicroRNA Signatures of Tumor-Derived Exosomes for Early Diagnosis of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2009, 10, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagner, T.; Spinelli, C.; Minciacchi, V.R.; Balaj, L.; Zandian, M.; Conley, A.; Zijlstra, A.; Freeman, M.R.; Demichelis, F.; De, S.; et al. Large extracellular vesicles carry most of the tumour DNA circulating in prostate cancer patient plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1505403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahlert, C. Liquid Biopsy: Is There an Advantage to Analyzing Circulating Exosomal DNA Compared to cfDNA or Are They the Same? Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2462–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouliere, F.; Chandrananda, D.; Piskorz, A.M.; Moore, E.K.; Morris, J.; Ahlborn, L.B.; Mair, R.; Goranova, T.; Marass, F.; Heider, K.; et al. Enhanced detection of circulating tumor DNA by fragment size analysis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaat4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorgannezhad, L.; Umer, M.; Islam, M.N.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Circulating tumor DNA and liquid biopsy: Opportunities, challenges, and recent advances in detection technologies. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 1174–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Shao, Y.; Gao, L.; Yin, H.; Cui, C.; et al. DNA in serum extracellular vesicles is stable under different storage conditions. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- San Lucas, F.A.; Allenson, K.; Bernard, V.; Castillo, J.; Kim, D.U.; Ellis, K.; Ehli, E.A.; Davies, G.E.; Petersen, J.L.; Li, D.; et al. Minimally invasive genomic and transcriptomic profiling of visceral cancers by next-generation sequencing of circulating exosomes. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.E.; Park, H.Y.; Hur, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, I.A.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, K.Y. Genomic profiling of extracellular vesicle-derived DNA from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, A.J. Microvesicles and vesicles of multivesicular bodies versus “virus-like” particles. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1975, 54, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chargaff, E.; West, R. The biological significance of the thromboplastic protein of blood. J. Biol. Chem. 1946, 166, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P. The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br. J. Haematol. 1967, 13, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonucci, E. Fine structure and histochemistry of “calcifying globules” in epiphyseal cartilage. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 1970, 103, 192–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F.; Quay, S.C.; Orenstein, N.S.; Dvorak, A.M.; Hahn, P.; Bitzer, A.M.; Carvalho, A.C. Tumor shedding and coagulation. Science 1981, 212, 923–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.T.; Johnstone, R.M. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 1983, 33, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarini, M.; Guidoni, L.; Luciani, A.M.; Mariutti, G.; Rosi, A.; Viti, V. Biochemical and NMR studies on structure and release conditions of RNA-containing vesicles shed by human colon adenocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 1989, 44, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Nijman, H.W.; Stoorvogel, W.; Liejendekker, R.; Harding, C.V.; Melief, C.J.; Geuze, H.J. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj-Krzyworzeka, M.; Szatanek, R.; Weglarczyk, K.; Baran, J.; Urbanowicz, B.; Branski, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z.; Zembala, M. Tumour-derived microvesicles carry several surface determinants and mRNA of tumour cells and transfer some of these determinants to monocytes. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2006, 55, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahn, M.; Concino, M.; Gromkova, R.; Goodgal, S. DNA binding activity of vesicles produced by competence deficient mutants of Haemophilus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 87, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.E.; Maul, G.; Goodgal, S.H. Possible mechanism for donor DNA binding and transport in Haemophilus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 6370–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bomberger, J.M.; Maceachran, D.P.; Coutermarsh, B.A.; Ye, S.; O’Toole, G.A.; Stanton, B.A. Long-distance delivery of bacterial virulence factors by Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane vesicles. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitto, N.J.; Chapman, R.; Pidot, S.; Costin, A.; Lo, C.; Choi, J.; D’Cruze, T.; Reynolds, E.C.; Dashper, S.G.; Turnbull, L.; et al. Bacterial membrane vesicles transport their DNA cargo into host cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlert, C.; Melo, S.A.; Protopopov, A.; Tang, J.; Seth, S.; Koch, M.; Zhang, J.; Weitz, J.; Chin, L.; Futreal, A.; et al. Identification of double-stranded genomic DNA spanning all chromosomes with mutated KRAS and p53 DNA in the serum exosomes of patients with pancreatic cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3869–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emelyanov, A.; Shtam, T.; Kamyshinsky, R.; Garaeva, L.; Verlov, N.; Miliukhina, I.; Kudrevatykh, A.; Gavrilov, G.; Zabrodskaya, Y.; Pchelina, S.; et al. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles from cerebrospinal fluid. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konoshenko, M.; Sagaradze, G.; Orlova, E.; Shtam, T.; Proskura, K.; Kamyshinsky, R.; Yunusova, N.; Alexandrova, A.; Efimenko, A.; Tamkovich, S. Total Blood Exosomes in Breast Cancer: Potential Role in Crucial Steps of Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaj, L.; Lessard, R.; Dai, L.; Cho, Y.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Han, Y.; Ren, H.; Chen, C.; He, D.; Zhou, L.; Eisner, G.M.; Asico, L.D.; Jose, P.A.; Zeng, C. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of donor genomic DNA to recipient cells is a novel mechanism for genetic influence between cells. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 5, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.H.; Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Audemard, E.; Montermini, L.; Meehan, B.; Rak, J. Oncogenic ras-driven cancer cell vesiculation leads to emission of double-stranded DNA capable of interacting with target cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 451, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lazaro-Ibanez, E.; Lasser, C.; Shelke, G.V.; Crescitelli, R.; Jang, S.C.; Cvjetkovic, A.; Garcia-Rodriguez, A.; Lotvall, J. DNA analysis of low- and high-density fractions defines heterogeneous subpopulations of small extracellular vesicles based on their DNA cargo and topology. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1656993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malkin, E.Z.; Bratman, S.V. Bioactive DNA from extracellular vesicles and particles. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzanowska, J.; Semira, C.; Costa-Silva, B. DNA in extracellular vesicles: Biological and clinical aspects. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, S.; Tschitschko, B.; Zhong, L.; Raftery, M.J.; Cavicchioli, R. A plasmid from an Antarctic haloarchaeon uses specialized membrane vesicles to disseminate and infect plasmid-free cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grull, M.P.; Mulligan, M.E.; Lang, A.S. Small extracellular particles with big potential for horizontal gene transfer: Membrane vesicles and gene transfer agents. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro-Ibanez, E.; Sanz-Garcia, A.; Visakorpi, T.; Escobedo-Lucea, C.; Siljander, P.; Ayuso-Sacido, A.; Yliperttula, M. Different gDNA content in the subpopulations of prostate cancer extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes. Prostate 2014, 74, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sato, T.A.; Ochiya, T. Extracellular vesicles as trans-genomic agents: Emerging roles in disease and evolution. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Yoon, H.; Park, S.; Kim, J.S.; Ahn, Y.H.; Kwon, K.; Lee, D.; Kim, K.H. Urinary Exosomal and cell-free DNA Detects Somatic Mutation and Copy Number Alteration in Urothelial Carcinoma of Bladder. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, P.; Lai, A.; Salomon, C.; Ivanovski, S. Detection of Salivary Small Extracellular Vesicles Associated Inflammatory Cytokines Gene Methylation in Gingivitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, A.; Villar-Prados, A.; Oliphint, P.A.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; De Hoff, P.; Morey, R.; Liu, J.; Roszik, J.; Clise-Dwyer, K.; et al. Mechanisms of nuclear content loading to exosomes. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Morita, R.; Oikawa, R.; Matsuo, Y.; Maehata, T.; Nosho, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Itoh, F. Detection of DNA methylation of gastric juice-derived exosomes in gastric cancer. Integr. Mol. Med. 2014, 1, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.; Di, K.; He, H.; Xia, Y.; Xie, H.; Huang, R.; Liu, C.; Yang, M.; Zheng, S.; He, N.; et al. Progress in exosome associated tumor markers and their detection methods. Mol. Biomed. 2020, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, A.R.; Hayes, J.J. A brief review of nucleosome structure. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589 Pt A, 2914–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torralba, D.; Baixauli, F.; Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Fernandez-Delgado, I.; Latorre-Pellicer, A.; Acin-Perez, R.; Martin-Cofreces, N.B.; Jaso-Tamame, A.L.; Iborra, S.; Jorge, I.; et al. Priming of dendritic cells by DNA-containing extracellular vesicles from activated T cells through antigen-driven contacts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, A.; Okada, R.; Nagao, K.; Kawamata, Y.; Hanyu, A.; Yoshimoto, S.; Takasugi, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kanemaki, M.T.; Obuse, C.; et al. Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amintas, S.; Vendrely, V.; Dupin, C.; Buscail, L.; Laurent, C.; Bournet, B.; Merlio, J.P.; Bedel, A.; Moreau-Gaudry, F.; Boutin, J.; et al. Next-Generation Cancer Biomarkers: Extracellular Vesicle DNA as a Circulating Surrogate of Tumor DNA. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 622048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.A.; Hur, J.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, K.Y. Liquid biopsy using extracellular vesicle-derived DNA in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2020, 54, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Fang, L.; Bai, J.; Wang, Z. Characteristics and Changes of DNA in Extracellular Vesicles. DNA Cell Biol. 2020, 39, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Shin, S.; Kim, B.; Lee, K.A. Selecting short length nucleic acids localized in exosomes improves plasma EGFR mutation detection in NSCLC patients. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohrmann, L.; Huang, H.J.; Hong, D.S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Fu, S.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Subbiah, V.; Karp, D.D.; Naing, A.; Krug, A.; et al. Liquid Biopsies Using Plasma Exosomal Nucleic Acids and Plasma Cell-Free DNA Compared with Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Advanced Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellanos-Rizaldos, E.; Grimm, D.G.; Tadigotla, V.; Hurley, J.; Healy, J.; Neal, P.L.; Sher, M.; Venkatesan, R.; Karlovich, C.; Raponi, M.; et al. Exosome-Based Detection of EGFR T790M in Plasma from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2944–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Shin, S.; Lee, K.A. Exosome-based detection of EGFR T790M in plasma and pleural fluid of prospectively enrolled non-small cell lung cancer patients after first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Romero, N.; Madurga, R.; Rackov, G.; Palacin-Aliana, I.; Nunez-Torres, R.; Asensi-Puig, A.; Carrion-Navarro, J.; Esteban-Rubio, S.; Peinado, H.; Gonzalez-Neira, A.; et al. Polyethylene glycol improves current methods for circulating extracellular vesicle-derived DNA isolation. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyabi, N.; Abbasgholizadeh, R.; Maitra, A.; Ardekani, A.; Biswal, S.L.; Grande-Allen, K.J. Isolation and mutational assessment of pancreatic cancer extracellular vesicles using a microfluidic platform. Biomed. Microdevices 2020, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akuma, P.; Okagu, O.D.; Udenigwe, C.C. Naturally Occurring Exosome Vesicles as Potential Delivery Vehicle for Bioactive Compounds. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaram, A.; Jay, S.M. Preservation and Storage Stability of Extracellular Vesicles for Therapeutic Applications. AAPS J. 2017, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osteikoetxea, X.; Sodar, B.; Nemeth, A.; Szabo-Taylor, K.; Paloczi, K.; Vukman, K.V.; Tamasi, V.; Balogh, A.; Kittel, A.; Pallinger, E.; et al. Differential detergent sensitivity of extracellular vesicle subpopulations. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 9775–9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagala, R.; Aqil, F.; Jeyabalan, J.; Gupta, R.C. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalra, H.; Adda, C.G.; Liem, M.; Ang, C.S.; Mechler, A.; Simpson, R.J.; Hulett, M.D.; Mathivanan, S. Comparative proteomics evaluation of plasma exosome isolation techniques and assessment of the stability of exosomes in normal human blood plasma. Proteomics 2013, 13, 3354–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumeda, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Akimoto, Y.; Kawakami, H.; Tsujimoto, M.; Yanoshita, R. Characterization of Membrane Integrity and Morphological Stability of Human Salivary Exosomes. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allenson, K.; Castillo, J.; San Lucas, F.A.; Scelo, G.; Kim, D.U.; Bernard, V.; Davis, G.; Kumar, T.; Katz, M.; Overman, M.J.; et al. High prevalence of mutant KRAS in circulating exosome-derived DNA from early-stage pancreatic cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, B.; Lei, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Gu, Y.; et al. Nanoscale extracellular vesicle-derived DNA is superior to circulating cell-free DNA for mutation detection in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2379–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, C.; Eom, J.S.; Kim, M.H.; Cho, Y.K. Detection of EGFR Mutations Using Bronchial Washing-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, I.A.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, K.Y. Extracellular vesicle-based EGFR genotyping in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from treatment-naive non-small cell lung cancer patients. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulis, M.; Esteller, M. DNA methylation and cancer. Adv. Genet. 2010, 70, 27–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Locke, W.J.; Guanzon, D.; Ma, C.; Liew, Y.J.; Duesing, K.R.; Fung, K.Y.C.; Ross, J.P. DNA Methylation Cancer Biomarkers: Translation to the Clinic. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Liu, Y. DNA methylation in human diseases. Genes Dis. 2018, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Oikawa, R.; Morita, R.; Yoshida, Y.; Maehata, T.; Yasuda, H.; Itoh, F. BARHL2 Methylation Using Gastric Wash DNA or Gastric Juice Exosomal DNA is a Useful Marker For Early Detection of Gastric Cancer in an H. pylori-Independent Manner. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sina, A.A.; Lin, T.Y.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Wang, Z.; Dey, S.; Wang, J.; Behren, A.; Wuethrich, A.; Carrascosa, L.G.; Trau, M. Methylation dependent gold adsorption behaviour identifies cancer derived extracellular vesicular DNA. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavridou, M.; Strati, A.; Bournakis, E.; Smilkou, S.; Tserpeli, V.; Lianidou, E. Prognostic Significance of Gene Expression and DNA Methylation Markers in Circulating Tumor Cells and Paired Plasma Derived Exosomes in Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baris, I.C.; Hacioglu, S.; Turk, N.S.; Cetin, G.O.; Zencir, S.; Bagci, G.; Caner, V. Expression and DNA methylation profiles of EZH2-target genes in plasma exosomes and matched primary tumor tissues of the patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, C.L.; Fuh, M.M.; Kaulich, K.; Fita, K.D.; Stevic, I.; Heiland, D.H.; Welsh, J.A.; Jones, J.C.; Gorgens, A.; Ricklefs, T.; et al. Genome-wide methylation profiling of glioblastoma cell-derived extracellular vesicle DNA allows tumor classification. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Bartold, P.M.; Salomon, C.; Ivanovski, S. Salivary Outer Membrane Vesicles and DNA Methylation of Small Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers for Periodontal Status: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis-Sobreiro, M.; Chen, J.F.; Novitskaya, T.; You, S.; Morley, S.; Steadman, K.; Gill, N.K.; Eskaros, A.; Rotinen, M.; Chu, C.Y.; et al. Emerin Deregulation Links Nuclear Shape Instability to Metastatic Potential. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6086–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Harris, S.L.; Levine, A.J. The regulation of exosome secretion: A novel function of the p53 protein. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4795–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bianco, F.; Perrotta, C.; Novellino, L.; Francolini, M.; Riganti, L.; Menna, E.; Saglietti, L.; Schuchman, E.H.; Furlan, R.; Clementi, E.; et al. Acid sphingomyelinase activity triggers microparticle release from glial cells. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte-’t Hoen, E.; Cremer, T.; Gallo, R.C.; Margolis, L.B. Extracellular vesicles and viruses: Are they close relatives? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9155–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bello-Morales, R.; Lopez-Guerrero, J.A. Extracellular Vesicles in Herpes Viral Spread and Immune Evasion. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maacha, S.; Bhat, A.A.; Jimenez, L.; Raza, A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S.; Grivel, J.C. Extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication: Roles in the tumor microenvironment and anti-cancer drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yanez-Mo, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borras, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, R.; Greening, D.W.; Zhu, H.J.; Takahashi, N.; Simpson, R.J. Extracellular vesicle isolation and characterization: Toward clinical application. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Stremersch, S.; Braeckmans, K.; de Smedt, S.C.; Hendrix, A.; Wood, M.J.A.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Raemdonck, K.; Vader, P. Electroporation-induced siRNA precipitation obscures the efficiency of siRNA loading into extracellular vesicles. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, T.N.; Raiker, R.S.; Jay, S.M. Exogenous DNA Loading into Extracellular Vesicles via Electroporation is Size-Dependent and Enables Limited Gene Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3650–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanada, M.; Bachmann, M.H.; Hardy, J.W.; Frimannson, D.O.; Bronsart, L.; Wang, A.; Sylvester, M.D.; Schmidt, T.L.; Kaspar, R.L.; Butte, M.J.; et al. Differential fates of biomolecules delivered to target cells via extracellular vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1433–E1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciardiello, C.; Cavallini, L.; Spinelli, C.; Yang, J.; Reis-Sobreiro, M.; de Candia, P.; Minciacchi, V.R.; Di Vizio, D. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: New Frontiers of Cell-to-Cell Communication in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Del Conde, I.; Shrimpton, C.N.; Thiagarajan, P.; Lopez, J.A. Tissue-factor-bearing microvesicles arise from lipid rafts and fuse with activated platelets to initiate coagulation. Blood 2005, 106, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergsmedh, A.; Szeles, A.; Henriksson, M.; Bratt, A.; Folkman, M.J.; Spetz, A.L.; Holmgren, L. Horizontal transfer of oncogenes by uptake of apoptotic bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6407–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmgren, L.; Szeles, A.; Rajnavolgyi, E.; Folkman, J.; Klein, G.; Ernberg, I.; Falk, K.I. Horizontal transfer of DNA by the uptake of apoptotic bodies. Blood 1999, 93, 3956–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldenstrom, A.; Genneback, N.; Hellman, U.; Ronquist, G. Cardiomyocyte microvesicles contain DNA/RNA and convey biological messages to target cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, S.; Cornils, K.; Speiseder, T.; Badbaran, A.; Reimer, R.; Indenbirken, D.; Grundhoff, A.; Brunswig-Spickenheier, B.; Alawi, M.; Lange, C. Indication of Horizontal DNA Gene Transfer by Extracellular Vesicles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sansone, P.; Savini, C.; Kurelac, I.; Chang, Q.; Amato, L.B.; Strillacci, A.; Stepanova, A.; Iommarini, L.; Mastroleo, C.; Daly, L.; et al. Packaging and transfer of mitochondrial DNA via exosomes regulate escape from dormancy in hormonal therapy-resistant breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9066–E9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ono, R.; Yasuhiko, Y.; Aisaki, K.I.; Kitajima, S.; Kanno, J.; Hirabayashi, Y. Exosome-mediated horizontal gene transfer occurs in double-strand break repair during genome editing. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minciacchi, V.R.; Freeman, M.R.; Di Vizio, D. Extracellular vesicles in cancer: Exosomes, microvesicles and the emerging role of large oncosomes. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sisquella, X.; Ofir-Birin, Y.; Pimentel, M.A.; Cheng, L.; Abou Karam, P.; Sampaio, N.G.; Penington, J.S.; Connolly, D.; Giladi, T.; Scicluna, B.J.; et al. Malaria parasite DNA-harbouring vesicles activate cytosolic immune sensors. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Guan, X.; Zhao, J.; Shen, L.; Liu, J. Exosomal double-stranded DNA as a biomarker for the diagnosis and preoperative assessment of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, S.; Pu, D.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Zeng, P.; Su, F.; Chen, Z.; Guo, M.; Gu, Y.; et al. Detection of fetal trisomy and single gene disease by massively parallel sequencing of extracellular vesicle DNA in maternal plasma: A proof-of-concept validation. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhen, O.; Mirzai, B.; Clark, M.E.; Nguyen, B.; Salomon, C.; Erber, W.; Meehan, K. Comparison of Circulating Tumour DNA and Extracellular Vesicle DNA by Low-Pass Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals Molecular Drivers of Disease in a Breast Cancer Patient. Biomedicines 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.; Wong, N.C.; Semple, T.; Clark, M.; Wong, S.Q.; Leslie, C.; Mirzai, B.; Millward, M.; Meehan, K.; Lim, A.M. Low-coverage whole-genome sequencing of extracellular vesicle-associated DNA in patients with metastatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degli Esposti, C.; Iadarola, B.; Maestri, S.; Beltrami, C.; Lavezzari, D.; Morini, M.; De Marco, P.; Erminio, G.; Garaventa, A.; Zara, F.; et al. Exosomes from Plasma of Neuroblastoma Patients Contain Doublestranded DNA Reflecting the Mutational Status of Parental Tumor Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.; Bernard, V.; San Lucas, F.A.; Allenson, K.; Capello, M.; Kim, D.U.; Gascoyne, P.; Mulu, F.C.; Stephens, B.M.; Huang, J.; et al. Surfaceome profiling enables isolation of cancer-specific exosomal cargo in liquid biopsies from pancreatic cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontopoulou, E.; Strachan, S.; Reinhardt, K.; Kunz, F.; Walter, C.; Walkenfort, B.; Jastrow, H.; Hasenberg, M.; Giebel, B.; von Neuhoff, N.; et al. Evaluation of dsDNA from extracellular vesicles (EVs) in pediatric AML diagnostics. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugaard, I.; Kjeldsen, T.E.; Hager, H.; Hansen, L.L.; Wojdacz, T.K. The influence of DNA degradation in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue on locus-specific methylation assessment by MS-HRM. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyard, A.; Boyez, A.; Pujals, A.; Robe, C.; Tran Van Nhieu, J.; Allory, Y.; Moroch, J.; Georges, O.; Fournet, J.C.; Zafrani, E.S.; et al. DNA degrades during storage in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue blocks. Virchows Arch. 2017, 471, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabhan, J.F.; Hu, R.; Oh, R.S.; Cohen, S.N.; Lu, Q. Formation and release of arrestin domain-containing protein 1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) at plasma membrane by recruitment of TSG101 protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4146–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Kadungure, T.; Beyene, J.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Q. ARMMs as a versatile platform for intracellular delivery of macromolecules. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Lehrich, B.M.; Zheng, S.; Lu, M. Emerging methods in biomarker identification for extracellular vesicle-based liquid biopsy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescitelli, R.; Lasser, C.; Szabo, T.G.; Kittel, A.; Eldh, M.; Dianzani, I.; Buzas, E.I.; Lotvall, J. Distinct RNA profiles in subpopulations of extracellular vesicles: Apoptotic bodies, microvesicles and exosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willms, E.; Cabanas, C.; Mager, I.; Wood, M.J.A.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicle Heterogeneity: Subpopulations, Isolation Techniques, and Diverse Functions in Cancer Progression. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oksvold, M.P.; Kullmann, A.; Forfang, L.; Kierulf, B.; Li, M.; Brech, A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Smeland, E.B.; Neurauter, A.; Pedersen, K.W. Expression of B-cell surface antigens in subpopulations of exosomes released from B-cell lymphoma cells. Clin. Ther. 2014, 36, 847–862.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Freitas, D.; Kim, H.S.; Fabijanic, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Martin, A.B.; Bojmar, L.; et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmisano, G.; Jensen, S.S.; Le Bihan, M.C.; Laine, J.; McGuire, J.N.; Pociot, F.; Larsen, M.R. Characterization of membrane-shed microvesicles from cytokine-stimulated beta-cells using proteomics strategies. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.J.; Shaw, A.T. Resisting Resistance: Targeted Therapies in Lung Cancer. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA Approves First KRAS Inhibitor: Sotorasib. Cancer Discov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.A.; Yarchoan, M.; Jaffee, E.; Swanton, C.; Quezada, S.A.; Stenzinger, A.; Peters, S. Development of tumor mutation burden as an immunotherapy biomarker: Utility for the oncology clinic. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.F.; Li, G.R.; Wang, R.J.; Yi, Y.T.; Yang, L.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.P.; Peng, Y. Application of next-generation sequencing in clinical oncology to advance personalized treatment of cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2012, 31, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrati, S.; De Summa, S.; Pilato, B.; Petriella, D.; Lacalamita, R.; Tommasi, S.; Pinto, R. Next-generation sequencing: Advances and applications in cancer diagnosis. Onco-Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 7355–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Kateb, H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Steger-May, K.; Pfeifer, J.D. Identification of major factors associated with failed clinical molecular oncology testing performed by next generation sequencing (NGS). Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hagemann, I.S.; Devarakonda, S.; Lockwood, C.M.; Spencer, D.H.; Guebert, K.; Bredemeyer, A.J.; Al-Kateb, H.; Nguyen, T.T.; Duncavage, E.J.; Cottrell, C.E.; et al. Clinical next-generation sequencing in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2015, 121, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Spath, S.S.; Marjani, S.L.; Zhang, W.; Pan, X. Characterization of cancer genomic heterogeneity by next-generation sequencing advances precision medicine in cancer treatment. Precis. Clin. Med. 2018, 1, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.Q.; Li, J.; Tan, A.Y.; Vedururu, R.; Pang, J.M.; Do, H.; Ellul, J.; Doig, K.; Bell, A.; MacArthur, G.A.; et al. Sequence artefacts in a prospective series of formalin-fixed tumours tested for mutations in hotspot regions by massively parallel sequencing. BMC Med. Genom. 2014, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zill, O.A.; Greene, C.; Sebisanovic, D.; Siew, L.M.; Leng, J.; Vu, M.; Hendifar, A.E.; Wang, Z.; Atreya, C.E.; Kelley, R.K.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Next-Generation Sequencing in Pancreatobiliary Carcinomas. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.T.; Janku, F.; Jung, B.; Hou, C.; Madwani, K.; Alden, R.; Razavi, P.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Shen, R.; Isbell, J.M.; et al. Ultra-deep next-generation sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA in patients with advanced lung cancers: Results from the Actionable Genome Consortium. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.P.; Cheng, H.; Guo, X.; Levy, B.; Halmos, B. Circulating Tumor DNA in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Primer for the Clinician. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustanovich, A.; Schwartz, R.; Peretz, T.; Grinshpun, A. Life and death of circulating cell-free DNA. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zareba, L.; Szymanski, J.; Homoncik, Z.; Czystowska-Kuzmicz, M. EVs from BALF-Mediators of Inflammation and Potential Biomarkers in Lung Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2021, 22, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Source of EV (Sample Size) | EV Type (Size) | Isolation Method of EV | Methylation Analysis (Gene) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Murine melanoma cell B16-F10 | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | Dot blot analysis | [26] |
| Gastric juice from patients with gastric cancer (n = 20) | Exosome (30–100 nm) | ExoQuick-TC | Bisulfite pyrosequencing (SOX17) | [73] |
| Gastric juice, gastric cancer (n = 20), and non-gastric cancer (n = 10) | Exosome | ExoQuick-TC | Bisulfite pyrosequencing (BARHL2) | [102] |
| Serum; normal (n = 7), breast cancer (n = 5), and melanoma (n = 4) | EV (30–250 nm) | Total Exosome isolation reagent | ELISA-based global DNA methylation analysis and microelectrode device | [103] |
| Saliva from patients with gingivitis (n = 7) and healthy individuals (n = 5) | Small EV (<200 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration or size exclusion chromatography | Quantitative methylation-specific PCR (IL−6, TNF-α, IL−1β, IL−8, and IL−10) | [71] |
| Plasma from patients with prostate cancer (n = 62) and healthy individuals (n = 10) | Exosome | exoRNeasy Maxi kit | Real-time methylation-specific PCR (GSTP1, RASSF1A, and SLFN11) | [104] |
| Plasma from patients with lymphoma (n = 21) and healthy individuals (n = 21) | Exosome (40–120 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | Methylation-specific PCR (CDKN1A, CDKN1B, CDKN2A, and CDKN2B) or dot blot analysis | [105] |
| Glioblastoma stem-like cell (n = 8) | EV | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration or size exclusion chromatography | Infinium methylation EPIC arrays | [106] |
| Saliva from patients with gingivitis (n = 7) and periodontitis (n = 8) and healthy individuals (n = 7) | Small EV (<200 nm) | Size exclusion chromatography | Global DNA methylation assay | [107] |
| Donor Cells | Recipient Cells | EV Type (Size) | Isolation Method of EV | Method of EV Transfer | Effect of EV DNA Transfer | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV-carrying transformed lymphoid cells | Human fibroblast, macrophage, or bovine aortic endothelial cell | Apoptotic body | Co-culture | EBV-DNA and gDNA transfer to recipient cells via apoptotic bodies | [124] | |
| H-ras and c-myc transformed rat embryonic fibroblasts | Mouse embryonic fibroblast | Apoptotic body | Co-culture | Oncogenes of donor cell (H-ras and c-myc) cause transformation of the recipient cells via apoptotic bodies | [123] | |
| Mouse cardiomyocytes HL-1 | Fibroblasts NIH 3T3 | Microvesicle | Differential ultracentrifugation | Incubation of fibroblasts with EV | EV DNA transfer to fibroblasts | [125] |
| AT1 receptor transfected HEK293 cells or VSMC or leukemia cells, K562 | HEK293 or human neutrophil | EV (30–1000 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation | Incubation of HEK293 or human neutrophils with EVs | AT1 receptor or BCR/ABL hybrid gene transfer via EV and expression on recipient cells | [61] |
| H-ras transformed rat epithelial cells, RAS-3 | Rat fibroblasts RAT-1 | EV (100 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | Incubation of fibroblasts with EVs | Transfer of oncogenes of donor cells to recipient cells via EV | [62] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana-plasmid-transduced hMSC | hMSC | Small EV (50–150 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation | Incubation of hMSC with EVs | Horizontal plant DNA transfer to eukaryotic cells via EV | [126] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Human adenocarcinoma A549 | OMV (~20 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation, filtration, and density gradient ultracentrifugation | Incubation of lung epithelial cells with OMV | OMV-derived DNA is detected in the nuclear fraction of epithelial cell | [56] |
| Murine cancer-associated fibroblasts from xenograft | Hormonal therapy-naïve breast cancer cell | EV (~140 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation | Injecting mCAF EV into tumor-bearing mouse or incubation of breast cancer cells with EV | Transfer of therapy resistance to therapy-sensitive cells via mtDNA from EV in vivo and in vitro | [127] |
| NGS Type | Source of EV (Sample Size) | EV Type (Size) | Isolation Method of EV | Mean Depth | Subjects of Comparison | Number of Targeted Genes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WGS | Plasma of healthy humans (n = 30) | EV | Differential ultracentrifugation | [61] | |||
| WGS | Serum of patients with pancreatic cancer (n = 2) | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | 4× | CNV of tumor DNA and exoDNA | [57] | |
| WGS | Murine melanoma cells, B16-F10 | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | CNV of exoDNA | [26] | ||
| WGS | Human H-ras transformed rat intestinal epithelial cells, RAS-3 | EV (100 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | ~7× | CNV of EV DNA | [62] | |
| WGS | Pleural effusion (n = 1) and plasma (n = 2) of patients with pancreaticobiliary cancer | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | 12–35× | CNV, SNV, gene fusions, and mutational signature of tumor DNA (tissue) and exoDNA | [40] | |
| WGS | Human bone marrow-derived MSC (n = 2) | Small EV (50–150 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation | CNV of EV DNA | [126] | ||
| WGS | Malaria parasite-infected human red blood cells | EV (50–350 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation, filtration, and density gradient ultracentrifugation | CNV of malaria gDNA and EV DNA | [130] | ||
| WGS | Human fibroblasts, TIG-3 | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation, filtration, and density gradient ultracentrifugation | RPKM of genomic DNA and EV DNA | [78] | ||
| WGS | Urine of patients with urothelial bladder carcinoma (n = 9) | Exosome | ExoQuick-TC | 0.6× | CNV of tumor DNA and urinary DNA (cfDNA and exoDNA) | [70] | |
| WGS | Serum of patients with pheochromocytoma and paragangliomas and rat cells, PC12 | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation | SNP of tumor DNA and exoDNA | [131] | ||
| WGS | Human prostate cancer cells, PC3 | Large EV (1.0–5.5 μm) | Differential ultracentrifugation and density gradient ultracentrifugation | ~1.4× | CNV and genomic rearrangements of gDNA and EV DNA | [35] | |
| WGS | Human erythroleukemic cells, TF-1, and mast cells, HMC-1 | Small EV (~120 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation and density gradient ultracentrifugation | 9.25–15.88 × | CNV of EV DNA | [63] | |
| WGS | Plasma and ascites of patients with ovarian cancer (n = 3) and human ovarian cancer cells, OVCAR-5 | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | 20× | CNV and SNV of tumor DNA (tissue) and exoDNA (plasma and ascites) | [72] | |
| WGS | Maternal plasma (n = 20) | EV (30–50 nm) | ExoQuick | 0.25× | cfDNA and EV DNA | [132] | |
| WGS | Plasma of patients with breast cancer (n = 1, serial samples (X3)) | EV (30–600 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation | 1× | CNV of tumor DNA (FFPE), ctDNA, and EV DNA | [133] | |
| WGS | Plasma of patients with tongue base squamous cell carcinoma (n = 3) and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (n = 2) | EV (215 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation | 0.5–1× | CNV of tumor DNA (FFPE) and EV DNA | [134] | |
| WES | Pleural effusion (n = 1) and plasma (n = 2) of patients with pancreaticobiliary cancer | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration | 133–490× | SNV and mutational signature of tumor DNA (tissue) and exoDNA | [40] | |
| WES | Plasma of patients with neuroblastoma (n = 19) | Exosome | Exo-RNeasy serum/plasma midi kit | 110× | SNV and TMB of tumor DNA (FFPE) and exoDNA (plasma) | [135] | |
| Targeted NGS | Plasma of patients with advanced cancers (n = 43) | Exosome | ExoLution Plus Isolation kit | SNV of tumor DNA (tissue) and exoNA | 3 | [83] | |
| Targeted NGS | Urine of patients with urothelial bladder carcinoma (n = 9) | Exosome | ExoQuick-TC | 102–4909× | SNV of tumor DNA (tissue), cfDNA, and exoDNA | 9 | [70] |
| Targeted NGS | Plasma of PDAC patients | Exosome | Differential ultracentrifugation and cancer-specific exosome capture | SNV of tumor DNA (tissue) and exoDNA | 275 | [136] | |
| Targeted NGS | BALF of patients with lung adenocarcinoma (n = 20) | EV (207.0 ± 48.3 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation | 190–755× | SNV of tumor DNA (FFPE) and EV DNA | 375 | [41] |
| Targeted NGS | Plasma of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (n = 4) | EV (30–150 nm) | Differential ultracentrifugation | SNV of tumor DNA and EV DNA | 54 | [137] | |
| Targeted NGS | Glioblastoma stem-like cells (n = 8) | EV | Differential ultracentrifugation and filtration or size exclusion chromatography | SNV of tumor DNA (tissue and cell) and exoDNA | 47 | [106] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hur, J.Y.; Lee, K.Y. Characteristics and Clinical Application of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA. Cancers 2021, 13, 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153827
Hur JY, Lee KY. Characteristics and Clinical Application of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA. Cancers. 2021; 13(15):3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153827
Chicago/Turabian StyleHur, Jae Young, and Kye Young Lee. 2021. "Characteristics and Clinical Application of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA" Cancers 13, no. 15: 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153827
APA StyleHur, J. Y., & Lee, K. Y. (2021). Characteristics and Clinical Application of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived DNA. Cancers, 13(15), 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153827






