Esophageal Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicle miR-21-5p Contributes to EMT of ESCC Cells by Disorganizing Macrophage Polarization
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
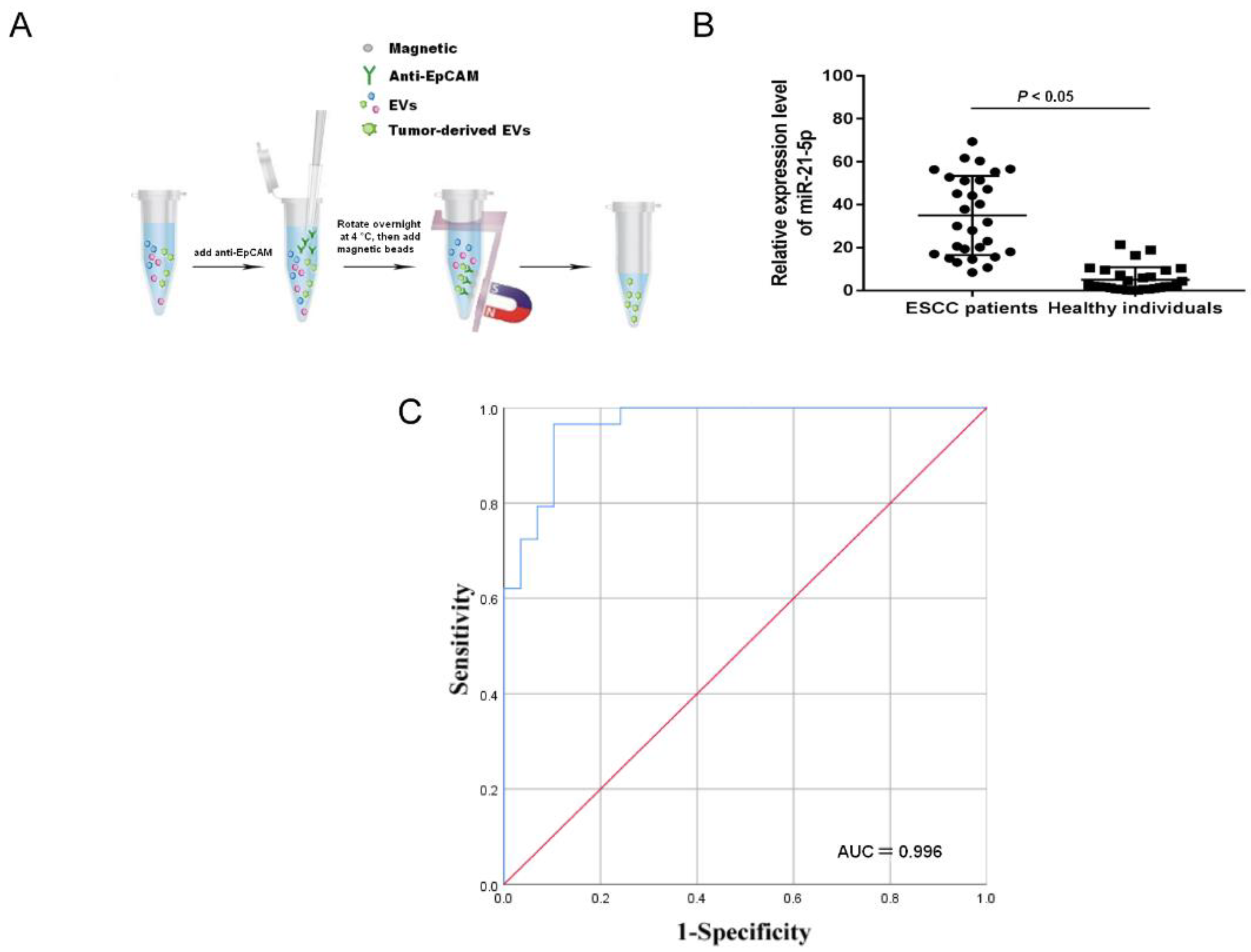
2.1. Upregulation of Tumor-Derived EVs-miR-21-5p Correlates with ESCC Progression
2.2. EVs-miR-21-5p Secreted by ESCC Cells Are Taken Up by PMA-Treated Macrophages
2.3. EVs-miR-21-5p Secreted by EC109 or EC9706 Cells Promote Polarization of M2 Macrophages
2.4. EVs-miR-21-5p Activate Polarization of M2 Macrophages via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT/STAT6 Axis
2.5. EVs-miR-21-5p Regulates Migration, Invasion, and Expression of EMT-Related Genes in EC109 and EC9706 Cells
2.6. M2 Macrophage-Derived EVs-miR-21-5p Mediates the Expression of EMT-Associated Genes in Esophageal Cancer Cells through Modulation of TGF-β Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical Samples and Ethical Statement
4.2. Isolation of Plasma EVs
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Macrophage Differentiation and Polarization
4.5. Cell EVs Isolation and Identification
4.6. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. Cy3-Labeled EVs-miR-21-5p Transfer Assay
4.9. Flow Cytometry
4.10. Cell Transfection
4.11. Luciferase Activity Assay
4.12. Western Blotting
4.13. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
4.14. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| ESCC | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) |
| EpCAM | Cell adhesion molecule |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| OR | Odds ratio |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Zheng, R.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zou, X.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Wei, K.; et al. Cancer survival in China, 2003–2005: A population-based study. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1921–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alsop, B.R.; Sharma, P. Esophageal Cancer. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 45, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.; McCormack, V.; Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Arnold, M.; Camargo, M.C.; Dar, N.A.; Dawsey, S.M.; Etemadi, A.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Fleischer, D.E.; et al. International cancer seminars: A focus on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanmee, T.; Ontong, P.; Konno, K.; Itano, N. Tumor-Associated Macrophages as Major Players in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2014, 6, 1670–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruytinx, P.; Proost, P.; Van Damme, J.; Struyf, E. Chemokine-Induced Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Conditions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalen, F.J.; Stevendaal, M.; Fennemann, F.L.; Verdoes, M.; Ilina, O. Molecular Repolarisation of Tumour-Associated Macrophages. Molecules 2018, 24, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porcheray, F.; Viaud, S.; Rimaniol, A.C.; Leone, C.; Samah, B.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; Dormont, D.; Gras, G. Macrophage activation switching: An asset for the resolution of inflammation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 142, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.N.; Yang, T.; Li, L.J.; Sun, L.N.; Hou, Y.Z.; Hu, X.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Tian, H.L.; Zhao, Q.J.; Peng, J.X.; et al. TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disease. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, G.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Huang, C.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B.; Su, L.; Qiu, Z. Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-301a Mediates M2 Macrophage Polarization via PTEN/PI3Kgamma to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4586–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sica, A.; Larghi, P.; Mancino, A.; Rubino, L.; Porta, C.; Totaro, M.G.; Rimoldi, M.; Biswas, S.K.; Allavena, P.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage polarization in tumour progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2008, 18, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, B.; Lam, E.W.; Sun, Y. Extracellular vesicles in the tumor microenvironment: Therapeutic resistance, clinical biomarkers, and targeting strategies. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 1318–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Thakur, B.K.; Weiss, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Peinado, H.; Lyden, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Cell-to-Cell Mediators of Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mateescu, B.; Kowal, E.J.; van Balkom, B.W.; Bartel, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Buzas, E.I.; Buck, A.H.; de Candia, P.; Chow, F.W.; Das, S.; et al. Obstacles and opportunities in the functional analysis of extracellular vesicle RNA—An ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1286095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Hung, F.Y.; Chang, W.A.; Jian, S.F.; Lin, Y.S.; Pan, Y.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Kuo, P.L. Hypoxic Lung-Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA-103a Increases the Oncogenic Effects of Macrophages by Targeting PTEN. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madhavan, B.; Yue, S.; Galli, U.; Rana, S.; Gross, W.; Muller, M.; Giese, N.A.; Kalthoff, H.; Becker, T.; Buchler, M.W.; et al. Combined evaluation of a panel of protein and miRNA serum-exosome biomarkers for pancreatic cancer diagnosis increases sensitivity and specificity. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2616–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimachi, K.; Matsumura, T.; Hirata, H.; Uchi, R.; Ueda, M.; Ueo, H.; Shinden, Y.; Iguchi, T.; Eguchi, H.; Shirabe, K.; et al. Identification of a bona fide microRNA biomarker in serum exosomes that predicts hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sica, A.; Schioppa, T.; Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P. Tumour-associated macrophages are a distinct M2 polarised population promoting tumour progression: Potential targets of anti-cancer therapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aras, S.; Zaidi, M.R. TAMeless traitors: Macrophages in cancer progression and metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, J.; Liu, R.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Expression profiling of exosomal miRNAs derived from human esophageal cancer cells by Solexa high-throughput sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 15530–15551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gires, O.; Pan, M.; Schinke, H.; Canis, M.; Baeuerle, P.A. Expression and function of epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM: Where are we after 40 years? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 969–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Hao, Y.; He, C.; Li, L.; Zhu, G. Exosome-orchestrated hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Yu, X.; Mao, X.; Jin, F. PTBP1 promotes the growth of breast cancer cells through the PTEN/Akt pathway and autophagy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 8930–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.R.; Chen, M.; Pandolfi, P.P. The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: New modes and prospects. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xia, J.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.; Ma, T.; Li, J. The role of PTEN in regulation of hepatic macrophages activation and function in progression and reversal of liver fibrosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 317, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, S.; Ten Dijke, P. Targeting TGF-beta Signaling in Cancer. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derynck, R.; Budi, E.H. Specificity, versatility, and control of TGF-beta family signaling. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaav5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harding, C.V.; Heuser, J.E.; Stahl, P.D. Exosomes: Looking back three decades and into the future. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahyazadeh Mashhadi, S.M.; Kazemimanesh, M.; Arashkia, A.; Azadmanesh, K.; Meshkat, Z.; Golichenari, B.; Sahebkar, A. Shedding light on the EpCAM: An overview. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12569–12580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohtar, M.A.; Syafruddin, S.E.; Nasir, S.N.; Low, T.Y. Revisiting the Roles of Pro-Metastatic EpCAM in Cancer. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Bussel, M.T.J.; Pluim, D.; Bol, M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Brandsma, D. EpCAM-based assays for epithelial tumor cell detection in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 137, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.; Bernard, V.; San Lucas, F.A.; Allenson, K.; Capello, M.; Kim, D.U.; Gascoyne, P.; Mulu, F.C.; Stephens, B.M.; Huang, J.; et al. Surfaceome profiling enables isolation of cancer-specific exosomal cargo in liquid biopsies from pancreatic cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, H.; Shao, H.; Park, Y.I.; Peterson, V.M.; Castro, C.M.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. Label-free detection and molecular profiling of exosomes with a nano-plasmonic sensor. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Ni, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Exosomes from nicotine-stimulated macrophages accelerate atherosclerosis through miR-21-3p/PTEN-mediated VSMC migration and proliferation. Theranostics 2019, 9, 6901–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Yue, R.; Ma, J.; Li, W.; Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Hu, Z.; Lv, C.; Xu, X.; et al. Nitidine chloride exerts anti-inflammatory action by targeting Topoisomerase I and enhancing IL-10 production. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Fan, T.; Liu, M.; Shi, X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Z. Down-regulation of Rictor enhances cell sensitivity to PI3K inhibitor LY294002 by blocking mTORC2-medicated phosphorylation of Akt/PRAS40 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Sozzani, S.; Locati, M.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A. Macrophage polarization: Tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffell, B.; Coussens, L.M. Macrophages and Therapeutic Resistance in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taylor, D.D.; Gercel-Taylor, C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 110, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowits, G.; Gercel-Taylor, C.; Day, J.M.; Taylor, D.D.; Kloecker, G.H. Exosomal microRNA: A diagnostic marker for lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2009, 10, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.H.; Zhai, R.N.; Hua, B.Y.; Bao, L.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.P.; Yao, W.; Fan, H.; Hao, C.F. miR-let-7d attenuates EMT by targeting HMGA2 in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19355–19364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Kano, M.; Murakami, K.; Toyozumi, T.; Suito, H.; Takahashi, M.; Sekino, N.; Shiraishi, T.; Kamata, T.; Ryuzaki, T.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes influence the cell cycle and cell migration of human esophageal cancer cell lines. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4348–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Yang, P.; Qi, Y.; Jin, L.; Zhao, A.; Ding, M.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Hao, C. Transcriptome analysis reveals a protective role of liver X receptor alpha against silica particle-induced experimental silicosis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, P.; Liu, M.; Xie, M.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Yin, J.; Liu, R. Novel-miR-4885 Promotes Migration and Invasion of Esophageal Cancer Cells Through Targeting CTNNA2. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 38, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| miRNA | Number of Samples | β | SE | Wald | p-Value | OR | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21-5p | 36 | 0.293 | 0.083 | 12.365 | <0.001 | 1.340 | 1.138–1.578 |
| miRNA | AUC | 95% CI | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cut-Off |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21-5p | 0.966 | 0.881–0.996 | 0.966 | 0.897 | 10.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.; Yang, P.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, M.; Duan, X.; Liu, R. Esophageal Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicle miR-21-5p Contributes to EMT of ESCC Cells by Disorganizing Macrophage Polarization. Cancers 2021, 13, 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164122
Song J, Yang P, Li X, Zhu X, Liu M, Duan X, Liu R. Esophageal Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicle miR-21-5p Contributes to EMT of ESCC Cells by Disorganizing Macrophage Polarization. Cancers. 2021; 13(16):4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164122
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jing, Peiyan Yang, Xiuwen Li, Xinyi Zhu, Mengxin Liu, Xuexin Duan, and Ran Liu. 2021. "Esophageal Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicle miR-21-5p Contributes to EMT of ESCC Cells by Disorganizing Macrophage Polarization" Cancers 13, no. 16: 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164122
APA StyleSong, J., Yang, P., Li, X., Zhu, X., Liu, M., Duan, X., & Liu, R. (2021). Esophageal Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicle miR-21-5p Contributes to EMT of ESCC Cells by Disorganizing Macrophage Polarization. Cancers, 13(16), 4122. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164122







