MicroRNA and Other Non-Coding RNAs in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Cancers
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
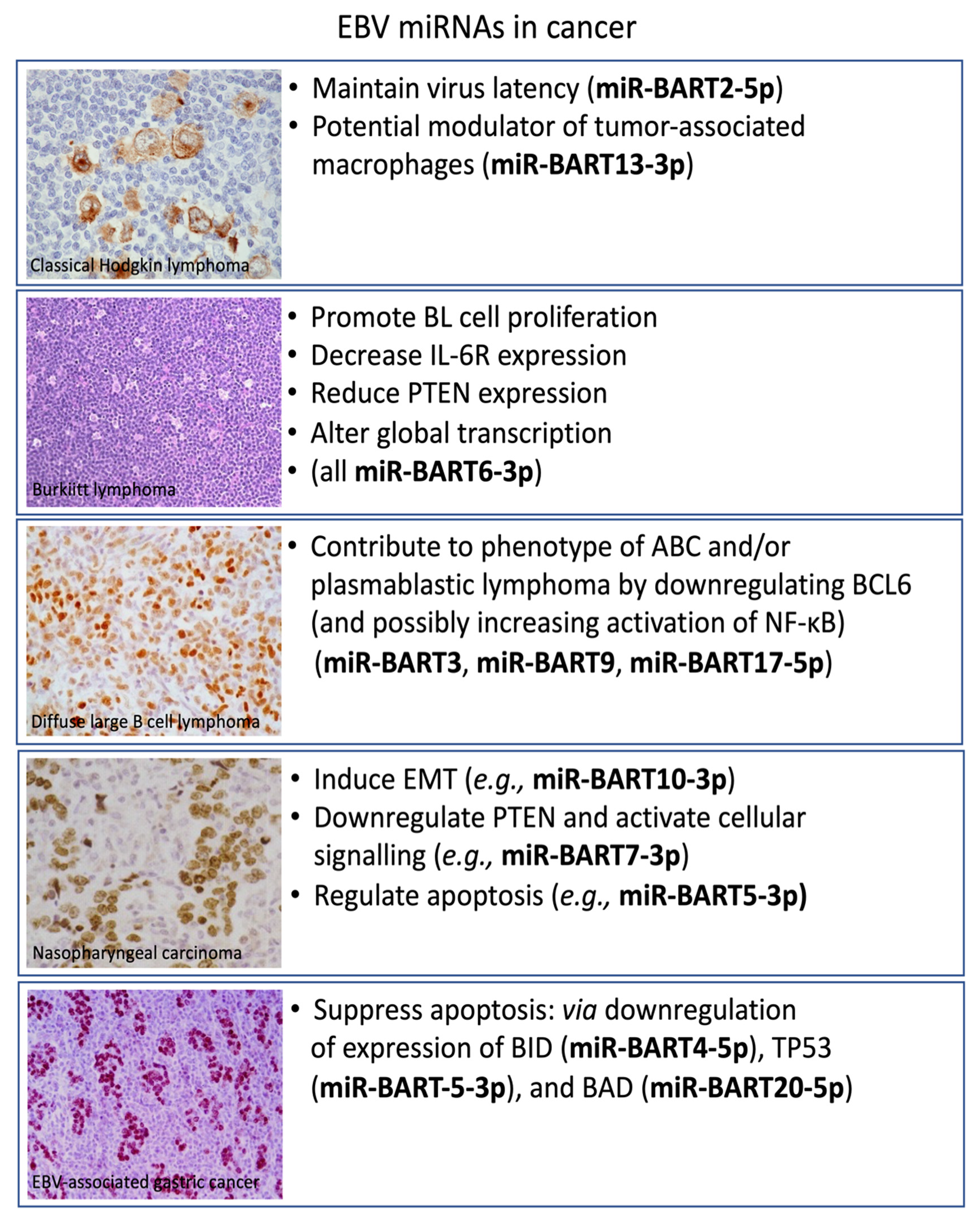
2. Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
| miRNA/ncRNA | Putative Role | Clinical Potential | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25-miRNA | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [72] |
| has-miR-21 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [73] |
| has-miR-30e/d | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [73] |
| has-miR-92b | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [73] |
| has-miR-124a | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [74] |
| 18-lncRNA | Oncogene | Prognostic biomarker | [78] |
| FLJ42351 | Oncogene | Diagnostic biomarker | [75] |
| LINC00116 | Oncogene | Diagnostic biomarker | [76] |
| LINC00461 | Oncogene | Diagnostic biomarker | [76] |
| lncRNA H19 | Oncogene | Prognostic biomarker | [79] |
3. Burkitt Lymphoma
| miRNA/ncRNA | Putative Role | Clinical Potential | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-17 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [90] |
| hsa-miR-21 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [94] |
| hsa-miR-23a | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [123] |
| has-miR-10a-5p | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [107] |
| MCM3AP-AS1 | Oncogene | Prognostic biomarker | [121] |
| DLEU1 | Tumor suppressor | Prognostic biomarker | [122] |
4. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
| miRNA/ncRNA | Putative Role | Clinical Potential | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-155 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [155,156] |
| hsa-miR-221/222 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [129] |
| hsa-miR-146a | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [156] |
| hsa-miR-146b | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [157] |
| hsa-miR-18a | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [158] |
| hsa-miR-21 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [159] |
| hsa-miR-181a | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [129,160] |
| hsa-miR-222 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [129] |
| 19-lncRNA | Oncogene | Prognostic biomarker | [123] |
| 17-lncRNA | Oncogene | Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker | [144] |
| 6-lncRNA | Oncogene | Prognostic biomarker | [146] |
| NAALADL2-AS2 | Oncogene | Diagnostic biomarker | [141] |
| NON-HSAT120161 | Oncogene | Diagnostic biomarker | [141] |
| PEG10 | Oncogene | Prognostic biomarker | [154] |
| HOTAIR | Oncogene | Prognostic biomarker | [149] |
| NEAT1 | Oncogene | Prognostic biomarker | [150] |
| NONHSAG026900 | Tumor suppressor | Prognostic biomarker | [151] |
5. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
| miRNA/ncRNA | Putative Role | Clinical Potential | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| BART5-5p | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [171] |
| BART9-3p | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [172,173] |
| BART1 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [175] |
| BART8-3p | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [177] |
| BART2-5P | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [180] |
| BART8-3p | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [181] |
| BART10-3p | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [182] |
| BART19-3p | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [183] |
6. Gastric Carcinoma
| miRNA/ncRNA | Putative Role | Clinical Potential | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| BART4-5p | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [206] |
| BART5-5p | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [213] |
| BART20-5p | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [214] |
| BART10-3p | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [210] |
| BART22 | OncomiR | Prognostic biomarker | [210] |
| hsa-miR-196a | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [211] |
| hsa-miR-196b | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [211] |
| hsa-miR-185 | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [211] |
| hsa-miR-let-7i | OncomiR | Diagnostic biomarker | [211] |
| SNHG8 | Oncogene | Diagnostic biomarker | [212] |
7. Role of ncRNA in Immune Evasion
8. Clinical Potential of miRNAs and Other Non-Coding RNAs
9. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Elgui Oliveira, D.; Müller-Coan, B.G.; Pagano, J.S. Viral carcinogenesis beyond malignant transformation: EBV in the progression of human cancers. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krump, N.A.; You, J. Molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis in humans. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.W.; Jiang, S.; Gewurz, B.E. Epstein-Barr virus LMP1-mediated oncogenicity. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01718-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenson, H.B. Epstein-Barr virus. Pediatr. Rev. 2011, 32, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smatti, M.K.; Al-Sadeq, D.W.; Ali, N.H.; Pintus, G.; Abou-Saleh, H.; Nasrallah, G.K. Epstein-barr virus epidemiology, serology, and genetic variability of LMP-1 oncogene among healthy population: An update. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.J. Epstein–Barr virus and cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2019, 14, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.H. EBV and human cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidry, J.T.; Birdwell, C.E.; Scott, R.S. Epstein–Barr virus in the pathogenesis of oral cancers. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Longnecker, R. Epithelial cell infection by Epstein–Barr virus. FEMS MicroBiol. Rev. 2019, 43, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tugizov, S.M.; Berline, J.W.; Palefsky, J.M. Epstein-Barr virus infection of polarized tongue and nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rowe, M. Epstein-Barr virus infection of polarized epithelial cells via the basolateral surface by memory B cell-mediated transfer infection. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Qu, J.; Peng, Q.; Gan, R. Molecular mechanisms of EBV-driven cell cycle progression and oncogenesis. Med. MicroBiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.F.; Rosales, C.; Lopez-Nieva, P.; Grana, O.; Ballestar, E.; Ropero, S.; Espada, J.; Melo, S.A.; Lujambio, A.; Fraga, M.F.; et al. The dynamic DNA methylomes of double-stranded DNA viruses associated with human cancer. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.S.; Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus latent genes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Nanbo, A.; Sun, L.; Lin, Z. Extracellular vesicles in Epstein-Barr virus’ life cycle and pathogenesis. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laichalk, L.L.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. Terminal differentiation into plasma cells initiates the replicative cycle of Epstein-Barr virus in vivo. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusch, J.A.; Nawandar, D.M.; Wright, K.L.; Kenney, S.C.; Mertz, J. Cellular differentiation regulator BLIMP1 induces Epstein–Barr virus lytic reactivation in epithelial and B cells by activating transcription from both the R and Z promoters. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, J.G.; Steitz, J.A. Localization of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs by in situ hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 9006–9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, P.A.; Sharp, N.A.; Clemens, M.J. Expression of genes for the Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs EBER-1 and EBER-2 in Daudi Burkitt’s lymphoma cells: Effects of interferon treatment. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 3169–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.C.; Mann, R.B.; Charache, P.; Hayward, S.D.; Staal, S.; Lambe, B.C.; Ambinder, R.F. Detection of EBV gene expression in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin’s disease. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 46, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, M.R.; Andrews, N.C.; Miller, G.; Steitz, J.A. Two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus and complexed with protein are precipitated by antibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toczyski, D.P.; Matera, A.G.; Ward, D.C.; Steitz, J.A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) small RNA EBER1 binds and relocalizes ribosomal protein L22 in EBV-infected human B lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3463–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, M.J.; Laing, K.G.; Jeffrey, I.W.; Schofield, A.; Sharp, T.V.; Elia, A.; Matys, V.; James, M.C.; Tilleray, V.J. Regulation of the interferon-inducible eIF-2 alpha protein kinase by small RNAs. Biochimie 1994, 76, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorovic, G.; Boulden, E.A.; Bosshard, R.; Elgueta Karstegl, C.; Skalsky, R.; Cullen, B.R.; Gujer, C.; Rämer, P.; Münz, C.; Farrell, P.J. Epstein–Barr viruses (EBVs) deficient in EBV-encoded RNAs have higher levels of latent membrane protein 2RNAexpression in lymphoblastoid cell lines and efficiently establish persistent infections in humanized mice. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11711–11714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Moss, W.N.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. EBV noncoding RNA binds nascent RNA to drive host PAX5 to viral DNA. Cell 2015, 160, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheimar, A.; Kaufer, B.B. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNAs (EBERs) complement the loss of herpesvirus telomerase RNA (vTR) in virus-induced tumor formation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA-cancer connection: The beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7390–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis; Function and Role in Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, M.D.; Lund, A.H. MicroRNA and cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Croce, C.M. miRNA profiling of cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2013, 23, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eis, P.S.; Tam, W.; Sun, L.; Chadburn, A.; Li, Z.; Gomez, M.F.; Lund, E.; Dahlberg, J.E. Accumulation of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3627–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashita, Y.; Osada, H.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yamada, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tomida, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Kawahara, K.; Sekido, Y.; Takahashi, T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9628–9632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, L.; Braaten, T.; Al-Shibli, K.; Lund, E.; Busund, L.T.R. Differential expression of the miR-17-92 cluster and miR-17 family in breast cancer according to tumor type; results from the Norwegian Women and Cancer (NOWAC) study. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Diederichs, S.; Wang, W.; Böing, S.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; Tidow, N.; Brandt, B.; Buerger, H.; Bulk, E.; et al. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8031–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Yang, M.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. MALAT-1: A long non-coding RNA and its important 3’ end functional motif in colorectal cancer metastasis. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.B. MicroRNA (miRNA) in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Stein, H.; Banks, P.M.; Chan, J.K.; Cleary, M.L.; Delsol, G.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Falini, B.; Gatter, K.C.; et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: A proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994, 84, 1361–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathas, S.; Hartmann, S.; Küppers, R. Hodgkin lymphoma: Pathology and biology. Semin. Hematol. 2016, 53, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küppers, R. The biology of Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargou, R.C.; Emmerich, F.; Krappmann, D.; Bommert, K.; Mapara, M.Y.; Arnold, W.; Royer, H.D.; Grinstein, E.; Greiner, A.; Scheidereit, C.; et al. Constitutive nuclear factor-B-RelA activation is required for proliferation and survival of Hodgkin’s disease tumor cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2961–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, M.; Löser, P.; Mathas, S.; Krappmann, D.; Dörken, B.; Scheidereit, C. Constitutive NF-κB maintains high expression of a characteristic gene network; including CD40; CD86; and a set of antiapoptotic genes in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells. Blood 2001, 97, 2798–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilger, E.; Kieser, A.; Baumann, M.; Hammerschmidt, W. Epstein-Barr virus-mediated B-cell proliferation is dependent upon latent membrane protein 1; which simulates an activated CD40 receptor. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 1700–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, E.M.; Pallesen, G.; Niedobitek, G.; Crocker, J.; Brooks, L.; Rickinson, A.B.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus and Hodgkin’s disease: Transcriptional analysis of virus latency in the malignant cells. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grässer, F.A.; Murray, P.G.; Kremmer, E.; Klein, K.; Remberger, K.; Feiden, W.; Reynolds, G.; Niedobitek, G.; Young, L.S.; Mueller-Lantzsch, N. Monoclonal antibodies directed against the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1): Immunohistologic detection of EBNA1 in the malignant cells of Hodgkin’s disease. Blood 1994, 84, 3792–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.G.; Young, L.S.; Rowe, M.; Crocker, J. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the Epstein–Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein in paraffin sections of Hodgkin’s disease. J. Pathol. 1992, 166, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedobitek, G.; Kremmer, E.; Herbst, H.; Whitehead, L.; Dawson, C.W.; Niedobitek, E.; von Ostau, C.; Rooney, N.; Grässer, F.A.; Young, L.S. Immunohistochemical detection of the Epstein-Barr Virus-encoded latent membrane protein 2A in Hodgkin’s disease and infectious mononucleosis. Blood 1997, 90, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.G.; Young, L.S. An etiological role for the Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, G.J.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. Tonsillar memory B cells; latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus; express the restricted pattern of latent genes previously found only in Epstein-Barr virus-associated tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12250–12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, G.J.; Hochberg, D.; Thorley-Lawson, A.D. The expression pattern of Epstein-Barr virus latent genes in vivo is dependent upon the differentiation stage of the infected B cell. Immunity 2000, 13, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; Babcock, G.J. A model for persistent infection with Epstein-Barr virus: The stealth virus of human B cells. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 1433–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, D.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Catalina, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. Demonstration of the Burkitt’s lymphoma Epstein-Barr virus phenotype in dividing latently infected memory cells in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Pegtel, M.; Hopmans, E.; Murray, P.; Middeldorp, J.; Shapiro, M.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. A novel persistence associated EBV miRNA expression profile is disrupted in neoplasia. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navari, M.; Etebari, M.; Ibrahimi, M.; Leoncini, L.; Piccaluga, P.P. Pathobiologic roles of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs in human lymphomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoroso, R.; Fitzsimmons, L.; Thomas, W.A.; Kelly, G.L.; Rowe, M.; Bell, A.I. Quantitative studies of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs provide novel insights into their Regulation. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 996–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Sekizuka, T.; Uehara, T.; Hishima, T.; Mine, S.; Fukumoto, H.; Sato, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Kuroda, M.; Katano, H. Next-generation sequencing of miRNAs in clinical samples of Epstein–Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphomas. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Lin, X.; Shumilov, A.; Bernhardt, K.; Feederle, R.; Poirey, R.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Pereira, B.; Almeida, R.; Delecluse, H.J. The biological properties of different Epstein-Barr virus strains explain their association with various types of cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 10238–10254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, S.C.; Ranjbar, B.; Laursen, M.B.; Falgreen, S.; Bilgrau, A.E.; Bødker, J.S.; Jørgensen, L.K.; Primo, M.N.; Schmitz, A.; Ettrup, M.S.; et al. High miR-34a expression improves response to doxorubicin in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Exp. Hematol. 2016, 44, 238–246.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delecluse, S.; Yu, J.; Bernhardt, K.; Haar, J.; Poirey, R.; Tsai, M.H.; Kiblawi, R.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Schnitzler, P.; Zeier, M.; et al. Spontaneous lymphoblastoid cell lines from patients with Epstein-Barr virus infection show highly variable proliferation characteristics that correlate with the expression levels of viral microRNAs. PLoS ONE 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, S.; Pfuhl, T.; Mamiani, A.; Ehses, C.; Roemer, K.; Kremmer, E.; Jäker, C.; Höck, J.; Meister, G.; Grässer, F.A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA miR-BART2 downregulates the viral DNA polymerase BALF5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrzalikova, K.; Vockerodt, M.; Leonard, S.; Bell, A.; Wei, W.; Schrader, A.; Wright, K.L.; Kube, D.; Rowe, M.; Woodman, C.B.; et al. Downregulation of BLIMP1α by the EBV oncogene; LMP-1; disrupts the plasma cell differentiation program and prevents viral replication in B cells: Implications for the pathogenesis of EBV-associated B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2011, 117, 5907–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fachko, D.; Ivanov, N.S.; Skinner, C.M.; Skalsky, R.L. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs regulate B cell receptor signal transduction and lytic reactivation. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vockerodt, M.; Morgan, S.L.; Kuo, M.; Wei, W.; Chukwuma, M.B.; Arrand, J.R.; Kube, D.; Gordon, J.; Young, L.S.; Woodman, C.B.; et al. The Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein; latent membrane protein-1; reprograms germinal centre B cells towards a Hodgkin’s Reed-Sternberg-like phenotype. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Grujil, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, H.; Yamakawa, N.; Imadome, K.I.; Yahata, T.; Kotaki, R.; Ogata, J.; Kakizaki, M.; Fujita, K.; Lu, J.; Yokoyama, K.; et al. Role of exosomes as a proinflammatory mediator in the development of EBV-associated lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2552–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.L.; Scott, D.W.; Hong, F.; Kahl, B.S.; Fisher, R.I.; Bartlett, N.L.; Advani, R.H.; Buckstein, R.; Rimsza, L.M.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Tumor-associated macrophages predict inferior outcomes in classic Hodgkin lymphoma: A correlative study from the E2496 Intergroup trial. Blood 2012, 120, 3280–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, A.; Gaya, A.; Martinez, A.; Urbano-Ispizua, A.; Pons, A.; Balagué, O.; Gel, B.; Abrisqueta, P. Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Artells, R.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiling in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Espiridion, B.; Martin-Moreno, A.M.; Montalban, C.; Figueroa, V.; Vega, F.; Younes, A.; Medeiros, L.J.; Alvés, F.J.; Canales, M.; Estévez, M.; et al. MicroRNA signatures and treatment response in patients with advanced classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiab, M.B.; Ziadi, S.; Ksiaa, F.; Louhichi, T.; Gacem, R.B.; Zineb, A.B.; Amara, K.; Hachana, M.; Trimeche, M. Methylation of miR124a-1, miR124a-2, and miR124a-3 in Hodgkin lymphoma. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayari, M.; Kok, K.; Kortman, G.; Sietzema, J.; de Jong, D.; Terpstra, M.; Visser, L.; Diepstra, A.; Kluiver, J.; Van den Berg, A. Long non-coding RNAs are commonly deregulated in Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2013, 122, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayari, M.M.; Winkle, M.; Kortman, G.; Sietzema, J.; de Jong, D.; Terpstra, M.; Mestdagh, P.; Kroese, F.G.; Visser, L.; Diepstra, A.; et al. Long noncoding RNA expression profiling in normal B-cell subsets and Hodgkin lymphoma reveals Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cell-specific long noncoding RNAs. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2462–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.B.; Yan, X.H.; Tian, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.L.; Sheng, Y.X.; Dong, L.; Zhang, W.L. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 regulates Hodgkin’s lymphoma cell proliferation and invasion via miR-448 mediated regulation of DCLK1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 24, 6219–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, J.; Lin, W.; Li, B.; Guo, Y. Construction of relapse-related lncRNA-mediated ceRNA networks in Hodgkin lymphoma. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 16, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Sui, M. Long non-coding RNA H19 promotes proliferation of Hodgkin’s lymphoma via AKT pathway. J. Buon 2018, 23, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar]
- Magrath, I. Epidemiology: Clues to the pathogenesis of Burkitt lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 156, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah-Yunes, S.A.; Murphy, D.J.; Noy, A. HIV-associated Burkitt lymphoma. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e594–e600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucci, E.; Onnis, A.; Cocco, M.; De Falco, G.; Imperatore, F.; Giuseppina, A.; Costanzo, V.; Cerino, G.; Mannucci, S.; Cantisani, R.; et al. B-cell differentiation in EBV-positive Burkitt lymphoma is impaired at posttranscriptional level by miRNA-altered expression. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertus, J.L.; Kluiver, J.; Weggemans, C.; Harms, G.; Reijmers, R.M.; Swart, Y.; Kok, K.; Rosati, S.; Schuuring, E.; van Imhoff, G.; et al. MiRNA profiling in B non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A MYC-related miRNA profile characterizes Burkitt lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosio, M.R.; Mundo, L.; Gazaneo, S.; Picciolini, M.; Vara, P.S.; Sayed, S.; Ginori, A.; Lo Bello, G.; Del Porro, L.; Navari, M.; et al. MicroRNAs sequencing unveils distinct molecular subgroups of plasmablastic lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107356–107373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oduor, C.I.; Kaymaz, Y.; Chelimo, K.; Otieno, J.A.; Ong’echa, J.M.; Moormann, A.M.; Bailey, J.A. Integrative microRNA and mRNA deep-sequencing expression profiling in endemic Burkitt lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, G.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Fuligni, F.; Onnis, A.; Bellan, C.; Rocca, B.J.; Navari, M.; Etebari, M.; Mundo, L.; Gazaneo, S.; et al. Burkitt lymphoma beyond MYC translocation: N-MYC and DNA methyltransferases dysregulation. BMC Cancer 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenze, D.; Leoncini, L.; Hummel, M.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Amato, T.; De Falco, G.; Githanga, J.; Horn, H.; Nyagol, J.; et al. The different epidemiologic subtypes of Burkitt lymphoma share a homogenous micro RNA profile distinct from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wake, L.; Liu, C.; Deffenbacher, K.; Lachel, C.M.; Wang, C.; Rohr, J.; et al. Global microRNA expression profiling uncovers molecular markers for classification and prognosis in aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaina, M.C.; Faccion, R.S.; Mazzoccoli, L.; Rezende, L.M.; Queiroga, E.; Bacchi, C.E.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Klumb, C.E. miR-17-92 cluster components analysis in Burkitt lymphoma: Overexpression of miR-17 is associated with poor prognosis. Ann. Hematol. 2016, 95, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhu, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Bai, J.; Xu, N. c-Myc suppressed E-cadherin through miR-9 at the post-transcriptional level. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 37, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onnis, A.; De Falco, G.; Antonicelli, G.; Onorati, M.; Bellan, C.; Sherman, O.; Sayed, S.; Leoncini, L. Alteration of MicroRNAs Regulated by c-Myc in Burkitt Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, V.B.; Rong, N.H.; Han, J.; Yang, Q.; Aris, V.; Soteropoulos, P.; Petrelli, N.J.; Dunn, S.P.; Krueger, L.J. MicroRNA let-7a downregulates MYC and reverts MYC-induced growth in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9762–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H. MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-155 promote the progression of Burkitt’s lymphoma by the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bornkamm, G.W. Epstein-Barr virus and the pathogenesis of Burkitt’s lymphoma: More questions than answers. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panea, R.I.; Love, C.L.; Shingleton, J.R.; Reddy, A.; Bailey, J.A.; Moormann, A.M.; Otieno, J.A.; Ong’echa, J.M.; Oduor, C.I.; Schroeder, K.M.S.; et al. The whole-genome landscape of Burkitt lymphoma subtypes. Blood 2019, 134, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, M.; Rowe, D.T.; Gregory, C.D.; Young, L.S.; Farrell, P.J.; Rupani, H.; Rickinson, A.B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 2743–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, F.; Ambrosio, M.; Mundo, L.; Laginestra, M.; Fuligni, F.; Rossi, M.; Zairis, S.; Gazaneo, S.; De Falco, G.; Lazzi, S.; et al. Distinct viral and mutational spectrum of endemic Burkitt lymphoma. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, G.L.; Long, H.M.; Stylianou, J.; Thomas, W.A.; Leese, A.; Bell, A.I.; Bornkamm, G.W.; Mautner, J.; Rickinson, A.B.; Rowe, M. An Epstein-Barr Virus Anti-Apoptotic Protein Constitutively Expressed in Transformed Cells and Implicated in Burkitt Lymphomagenesis: The Wp/BHRF1 Link. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, G.L.; Milner, A.E.; Baldwin, G.S.; Bell, A.I.; Rickinson, A.B. Three restricted forms of Epstein-Barr virus latency counteracting apoptosis in c-myc-expressing Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14935–14940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, R.J.; Shannon-Lowe, C.D.; Fitzsimmons, L.; Bell, A.I.; Rowe, M. Unexpected patterns of Epstein-Barr virus transcription revealed by a high throughput PCR array for absolute quantification of viral Mrna. Virology 2015, 474, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruf, I.K.; Rhyne, P.W.; Yang, C.; Cleveland, J.L.; Sample, J.T. Epstein-Barr virus small RNAs potentiate tumorigenicity of Burkitt lymphoma cells independently of an effect on apoptosis. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10223–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Hur, D.Y.; Hong, S.W.; Kim, J.H. EBV-encoded EBNA1 regulates cell viability by modulating miR34a-NOX2-ROS signaling in gastric cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onnis, A.; Navari, M.; Antonicelli, G.; Morettini, F.; Mannucci, S.; De Falco, G.; Vigorito, E.; Leoncini, L. Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 induces expression of the cellular microRNA hsa-miR-127 and impairing B-cell differentiation in EBV-infected memory B cells. New insights into the pathogenesis of Burkitt lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanbo, A.; Takada, K. The role of Epstein–Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) in oncogenesis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2002, 12, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Chen, J.N.; Huang, J.T.; Gong, L.P.; Shao, C.K. The roles of EBV-encoded microRNAs in EBV-associated tumors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 135, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduor, C.I.; Movassagh, M.; Kaymaz, Y.; Chelimo, K.; Otieno, J.; Ong’echa, J.M.; Moormann, A.M.; Bailey, J.A. Human and Epstein-Barr virus miRNA profiling as predictive biomarkers. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, Z.L.; Kuzembayeva, M.; Sengupta, S.; Sugden, B. The microRNAs of Epstein-Barr Virus are expressed at dramatically differing levels among cell lines. Virology 2009, 386, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereide, D.T.; Seto, E.; Chiu, Y.F.; Hayes, M.; Tagawa, T.; Grundhoff, A.; Hammerschmidt, W.; Sugden, B. Epstein-Barr virus maintains lymphomas via its miRNAs. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, H.P. EBV-BART-6-3p and cellular microRNA197 compromise the immune defense of host cells in EBV-positive Burkitt lymphoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Bu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, S. Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-BamHI-A Rightward Transcript (BART)-6 and Cellular MicroRNA-142 Synergistically Compromise Immune Defense of Host Cells in EBV-Positive Burkitt Lymphoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 4114–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccaluga, P.P.; Navari, M.; De Falco, G.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Lazzi, S.; Fuligni, F.; Bellan, C.; Rossi, M.; Sapienza, M.R.; Laginestra, M.A.; et al. Virus-encoded microRNA contributes to the molecular profile of EBV-positive Burkitt lymphomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, M.R.; Navari, M.; Di Lisio, L.; Leon, E.A.; Onnis, A.; Gazaneo, S.; Mundo, L.; Ulivieri, C.; Gomez, G.; Lazzi, S.; et al. The Epstein Barr-encoded BART-6-3p microRNA affects regulation of cell growth and immuno response in Burkitt lymphoma. Infect. Agent Cancer 2014, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, K.J.; Rabinowitz, G.S.; Yario, T.A.; Luna, J.M.; Darnell, R.B.; Steitz, J.A. EBV and human microRNAs co-target oncogenic and apoptotic viral and human genes during latency. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2207–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhai, X.W.; Wang, H.S.; Qian, X.W.; Miao, H.; Zhu, X.H. Circulating microRNA-21; microRNA-23a; and microRNA-125b as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of Burkitt lymphoma in children. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 4992–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doose, G.; Haake, A.; Bernhart, S.H.; López, C.; Duggimpudi, S.; Wojciech, F.; Bergmann, A.K.; Borkhardt, A.; Burkhardt, B.; Claviez, A.; et al. MINCR is a MYC-induced lncRNA able to modulate MYC’s transcriptional network in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5261–E5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; He, D. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA PVT1 inhibits the proliferation of Raji cells through cell cycle regulation. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Jin, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, W. Knockdown of long non coding RNA ANRIL inhibits the proliferation and promotes the apoptosis of Burkitt lymphoma cells through the TGF β1 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Yin, J.; Bai, Z.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z. LncRNA-ANRIL promotes gastric cancer progression by enhancing NF-kB signaling. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Sun, H.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, M.; Guo, Z.; Lv, Z.; Ren, W. Evaluation of LncRNA ANRIL Potential in Hepatic Cancer Progression. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 2019, 38, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Gong, M.; Li, Z. Knockdown of lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 Attenuates Chemoresistance of Burkitt Lymphoma to Doxorubicin Treatment via Targeting the miR-15a/EIF4E Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5845–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Luo, W.; Shah, T.; Yin, C.; O’Connell, T.; Chung, T.H.; Perkins, S.L.; Miles, R.R.; Ayello, J.; Morris, E.; et al. The effects of DLEU1 gene expression in Burkitt lymphoma (BL): Potential mechanism of chemoimmunotherapy resistance in BL. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27839–27853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Di Lisio, L.; Sánchez-Beato, M.; Gómez-López, G.; Rodríguez, M.E.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Mollejo, M.; Menárguez, J.; Martínez, M.A.; Alves, F.J.; Pisano, D.G.; et al. MicroRNA signatures in B-cell lymphomas. Blood Cancer J. 2012, 2, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Harris, N.L.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011, 117, 5019–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.; Tan, B.; Rosenwald, A.; Hurt, E.H.; Wiestner, A.; Staudt, L.M. A gene expression-based method to diagnose clinically distinct subgroups of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9991–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Elsen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Grubor, V.; Love, C.L.; Banerjee, A.; Richards, K.L.; Mieczkowski, P.A.; Dunphy, C.; Choi, W.; Au, W.Y.; Srivastava, G.; et al. Genetic heterogeneity of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, B.; Sarkozy, C. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: R-CHOP failure—what to do? Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2016, 2016, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alencar, A.J.; Malumbres, R.; Kozloski, G.A.; Advani, R.; Talreja, N.; Chinichian, S.; Briones, J.; Natkunam, Y.; Sehn, L.H.; Gascoyne, R.D.; et al. MicroRNAs are Independent Predictors of Outcome in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Patients Treated with R-CHOP. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4125–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrie, C.H.; Soneji, S.; Marafioti, T.; Cooper, C.D.; Palazzo, S.; Paterson, J.C.; Cattan, H.; Enver, T.; Mager, R.; Boultwood, J.; et al. MicroRNA expression distinguishes between germinal center B cell-like and activated B cell-like subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malumbres, R.; Sarosiek, K.A.; Cubedo, E.; Ruiz, J.W.; Jiang, X.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Tibshirani, R.; Lossos, I.S. Differentiation stage-specific expression of microRNAs in B lymphocytes and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2009, 113, 3754–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehle, A.; Hoefig, K.P.; Repsilber, D.; Thorns, C.; Ziepert, M.; Wesche, K.O.; Thiere, M.; Loeffler, M.; Klapper, W.; Pfreundschuh, M.; et al. MicroRNA signatures characterize diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and follicular lymphomas. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 732–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, G.; Sutherland, H.G.; Haupt, L.M.; Griffiths, L.R. Dysregulated MicroRNA expression profiles and potential cellular; circulating and polymorphic biomarkers in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Genes 2016, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imig, J.; Motsch, N.; Zhu, J.Y.; Barth, S.; Okoniewski, M.; Reineke, T.; Tinguely, M.; Faggioni, A.; Trivedi, P.; Meister, G.; et al. MicroRNA profiling in Epstein-Barr virus-associated B-cell lymphoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 1880–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, E.; Salinas, R.E.; Chang, C.; Zhou, T.; Linnstaedt, S.D.; Gottwein, E.; Jacobs, C.; Jima, D.; Li, Q.J.; Dave, S.S.; et al. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-induced tumor suppressor microRNA MiR-34a is growth promoting in EBV-infected B cells. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6889–6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motsch, N.; Pfuhl, T.; Mrazek, J.; Barth, S.; Grässer, F.A. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) induces the expression of the cellular microRNA miR-146a. RNA Biol. 2007, 4, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Chen, B. Evaluation of latent membrane protein 1 and microRNA-155 for the prognostic prediction of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9725–9734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, D.M.; Vargiu, P.; Montes-Moreno, S.; A León, E.; Rodríguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Lisio, L.D.; Martinez, N.; Rodríguez, R.; Mollejo, M.; Castellvi, J.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs repress BCL6 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2012, 26, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Tang, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, B.; Sun, X.; He, B.; Pan, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Serum microRNA expression profiling predict response to R-CHOP treatment in diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients. Ann. Hematol. 2014, 93, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousti, F.; Shahrisa, A.; Ansari, H.; Hajjari, M.; Tahmasebi Birgani, Y.; Mohammadiasl, J.; Tahmasebi Birgani, M. Long non-coding RNAs expression levels in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: An in silico analysis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1462–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Fang, C.; Li, X.; Geng, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. Predictive analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23228–23236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.Y.; Wu, B.; Yan, W.; Gong, Z.M.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.H.; Yang, W. Microarray expression profiles of long non-coding RNAs in germinal center-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Chen, X.; Su, P. A Pooled Analysis of The Clinical Utilities of Long Non-Coding RNA Based Molecular Signature for Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Bao, S.; Cheng, L.; Sun, J. Discovery and validation of immune-associated long non-coding RNA biomarkers associated with clinically molecular subtype and prognosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Jiang, Y.; Du, W.; Fairchild, L.; Melnick, A.; Elemento, O. Transcriptome sequencing reveals thousands of novel long non-coding RNAs in B cell lymphoma. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Cheng, L.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, M. A potential panel of six-long non-coding RNA signature to improve survival prediction of diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Hu, L.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, Q.; Tong, X. Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by targeting miR-497-5p/PIM1 axis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7395–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Qi, Q. LncRNA SNHG14/miR-5590-3p/ZEB1 positive feedback loop promoted diffuse large B cell lymphoma progression and immune evasion through regulating PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Han, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Sui, Y.; Wang, M. Elevated RNA expression of long non-coding HOTAIR promotes cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 5125–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Jiang, L.; Tseng, K.F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, R.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X. Aberrant NEAT1_1 expression may be a predictive marker of poor prognosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 23, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Fang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Liao, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, W.; et al. The long non-coding RNA NONHSAG026900 predicts prognosis as a favorable biomarker in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34374–34386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.M.; Lian, G.Y.; Song, Y.; Huang, Y.F.; Gong, Y. LncRNA MALAT1 promotes tumorigenesis and immune escape of diffuse large B cell lymphoma by sponging miR-195. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Su, L.; Jiang, J. Long Non-Coding RNA Paternally Expressed Imprinted Gene 10 (PEG10) Elevates Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Progression by Regulating Kinesin Family Member 2A (KIF2A) via Targeting MiR-101-3p. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Fan, H.; Wu, G.; Wu, J.; Feng, J. Upregulation of long noncoding RNA PEG10 associates with poor prognosis in diffuse large B cell lymphoma with facilitating tumorigenicity. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 16, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadvand, M.; Eskandari, M.; Pashaiefar, H.; Yaghmaie, M.; Manoochehrabadi, S.; Khakpour, G.; Sheikhsaran, F.; Montazer Zohour, M. Over expression of circulating miR-155 predicts prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2018, 70, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Xu, L.; Zhong, J.H.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Q.; Huang, H.H.; Chen, F.Y. Clinical and prognostic significance of miR-155 and miR-146a expression levels in formalin-fixed/paraffin-embedded tissue of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Zhu, J.; Guo, X.Y.; Wang, J.F. Low expression of microRNA-146b-5p and microRNA-320d predicts poor outcome of large B-cell lymphoma treated with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, A.; Stevenson, K.; Vanderburg, C.; Ravi, D.; McDonald, J.T.; Christie, A.L.; Shigemori, K.; Jester, H.; Weinstock, D.M.; Evens, A.M. Identification of Circulating Serum Multi-MicroRNA Signatures in Human DLBCL Models. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fu, R.; Yang, L.; Tu, W. miR-21 expression predicts prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 15019–15024. [Google Scholar]
- Kozloski, G.A.; Jiang, X.; Bhatt, S.; Ruiz, J.; Vega, F.; Shaknovich, R.; Melnick, A.; Lossos, I.S. miR-181a negatively regulates NF-κB signaling and affects activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma pathogenesis. Blood 2016, 127, 2856–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharkawy, A.; Al Zaidan, L.; Malki, A. Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignancies: Roles of viral oncoproteins in carcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.S.; Dawson, C.W. Epstein-Barr virus and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizaki, T.; Endo, K.; Ren, Q.; Wakisaka, N.; Murono, S.; Kondo, S.; Sato, H.; Furukawa, M. Oncogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2007, 34, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, J.; Liao, Q.; Yang, L.; Sun, L.Q. EBV-encoded RNA via TLR3 induces inflammation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24291–24303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, K.; Li, X.; Fan, S.; Shi, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, P. Expression of LINC00312; a long intergenic non-coding RNA; is negatively correlated with tumor size but positively correlated with lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Mol. Histol. 2013, 44, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Zeng, J.; Chao, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Deng, K.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Dai, M.; Chen, S.; et al. Serum long non-coding RNAs MALAT1; AFAP1-AS1 and AL359062 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41166–41177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Chen, G.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Chang, K.P.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, H.C. Characterization of Epstein-Barr virus miRNAome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by deep sequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, T.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Miyauchi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Kashiwabara, S.; Baba, T.; Suzuki, T. Selective stabilization of mammalian microRNAs by 3′ adenylation mediated by the cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerase GLD-2. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchenbauer, F.; Morin, R.D.; Argiropoulos, B.; Petriv, O.I.; Griffith, M.; Heuser, M.; Yung, E.; Piper, J.; Delaney, A.; Prabhu, A.L.; et al. In-depth characterization of the microRNA transcriptome in a leukemia progression model. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, E.Y.W.; Siu, K.L.; Kok, K.H.; Lung, R.W.; Tsang, C.M.; To, K.F.; Kwong, D.L.; Tsao, S.W.; Jin, D.Y. An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA targets PUMA to promote host cell survival. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Long, Y.; Chong, T.; Cai, W.; Tsang, C.M.; Zhou, X.; Lin, Y.; Ding, T.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, H.; et al. EBV-miR-BART7-3p imposes stemness in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing SMAD7. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.M.; Lyu, X.M.; Luo, W.R.; Cui, X.F.; Ye, Y.F.; Yuan, C.C.; Peng, Q.X.; Wu, D.H.; Liu, T.F.; Wang, E.; et al. EBV-miR-BART7-3p promotes the EMT and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing the tumor suppressor PTEN. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2156–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Lyu, X.; Cai, L.; Lu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yao, K.; et al. EBV-miR-BART1 is involved in regulating metabolism-associated genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 436, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lyu, X.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Cai, H.; Yao, K.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA BART1 induces tumour metastasis by regulating PTEN-dependent pathways in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Lyu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gold nano-particles (AuNPs) carrying anti-EBV-miR-BART7-3p inhibit growth of EBV-positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7838–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, J.; Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, D.; Cai, L. EBV encoded miRNA BART8-3p promotes radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by regulating ATM/ATR signaling pathway. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20190415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Yi, Y.H.; Chang, K.P.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, S.J.; Chen, H.C. The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA MiR-BART9 promotes tumor metastasis by targeting E-cadherin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zeng, Z.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; He, B.; Song, Y.; Li, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Liao, Q.; et al. EBV-miR-BART10-3p facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting BTRC. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 41766–41782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Li, L.; Xiang, Y.Q.; Lung, M.L.; Zeng, T.; Lu, J.; Tsao, S.W.; Zeng, M.S.; Yun, J.P.; Kwong, D.L.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus miRNA BART2-5p promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by suppressing RND3. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 1957–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.; He, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, W. MicroRNA expression profiling analysis in serum for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis. Gene 2020, 727, 144243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wong, T.S.; Lv, K.X.; Zhang, M.J.; Tsang, R.K.; Chan, J.Y. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)—encoded microRNAs in plasma of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck. 2019, 41, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhu, J.; He, X. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus microRNA profile reveals novel biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 27, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.; Mai, S.J.; Lin, H.X.; Zhang, M.Y.; Huang, J.L.; Hua, X.; Lin, C.; Long, Z.Q.; Lu, Z.J.; Sun, X.Q.; et al. Identification of two microRNA signatures in whole blood as novel biomarkers for diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polakovicova, I.; Jerez, S.; Wichmann, I.A.; Sandoval-Bórquez, A.; Carrasco-Véliz, N.; Corvalán, A.H. Role of microRNAs and exosomes in Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus associated gastic cancers. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizasa, H.; Nanbo, A.; Nishikawa, J.; Jinushi, M.; Yoshiyama, H. Epstein-barr virus (EBV)-associated gastric carcinoma. Viruses 2012, 4, 3420–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, J.; Yoshiyama, H.; Iizasa, H.; Kanehiro, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Nishimura, J.; Saito, M.; Okamoto, T.; Sakai, K.; Suehiro, Y.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus in gastric carcinoma. Cancers 2014, 6, 2259–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.O.; Tang, C.M.; Yu, J. Epigenetic dysregulation in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma: Disease and treatments. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 6448–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, J.; zur Hausen, A.; Klein Kranenbarg, E.; van de Velde, C.J.; Middeldorp, J.M.; van den Brule, A.J.; Meijer, C.J.; Bloemena, E. EBV-positive gastric adenocarcinomas: A distinct clinicopathologic entity with a low frequency of lymph node involvement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagi, A.; Nishikawa, J.; Shimokuri, K.; Shuto, T.; Takagi, T.; Takagi, F.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Miura, O.; Yanai, H.; et al. Clinicopathologic Characteristics of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer Over the Past Decade in Japan. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.H.; Jeng, Y.M.; Chen, K.H.; Lee, C.H.; Yuan, C.T.; Liau, J.Y. An Integrative Morphomolecular Classification System of Gastric Carcinoma with Distinct Clinical Outcomes. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genitsch, V.; Novotny, A.; Seiler, C.A.; Kröll, D.; Walch, A.; Langer, R. Epstein–Barr virus in gastro-esophageal adenocarcinomas–single center experiences in the context of current literature. Front. Oncol. 2015, 26, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Won, H.S.; Sun, S.; Hong, J.H.; Ko, Y.H. Prognostic role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Cao, M.; Duan, Y.; Bai, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Prognostic role of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in gastric cancer: A meta-analysis and experimental validation. Arch. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks, S.; Liao, X.; Chiaravalli, A.M.; Xu, X.; Camargo, M.C.; Solcia, E.; Sessa, F.; Fleitas, T.; Freeman, G.J.; Rodig, S.J.; et al. Abundant PD-L1 expression in Epstein-Barr Virus-infected gastric cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32925–32932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, K.; Chung, H.C.; Shankaran, V.; Geva, R.; Catenacci, D.; Gupta, S.; Eder, J.P.; Golan, T.; Le, D.T.; Burtness, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with PD-L1-positive advanced gastric cancer (KEYNOTE-012): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Koizumi, S.; Sugiura, M.; Tokunaga, M.; Uemura, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Tanaka, S.; Sato, E.; Osato, T. Gastric carcinoma: Monoclonal epithelial malignant cells expressing Epstein-Barr virus latent infection protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9131–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, A.; D’Arena, G.; Crispo, A.; Tecce, M.F.; Nocerino, F.; Grimaldi, M.; Rotondo, E.; D’Ursi, A.M.; Scrima, M.; Galdiero, M.; et al. Role of Viral miRNAs and Epigenetic Modifications in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Carcinogenesis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 6021934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, V.H.; O’Neil, J.D.; Wei, W.; Stewart, S.E.; Dawson, C.W.; Young, L.S. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 regulates cellular gene transcription and modulates the STAT1 and TGFbeta signaling pathways. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4135–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivachandran, N.; Sarkari, F.; Frappier, L. Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 contributes to nasopharyngeal carcinoma through disruption of PML nuclear bodies. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, G.T.; Lou, W.P.; Chow, C.; To, K.F.; Choy, K.W.; Leung, A.W.; Tong, C.Y.; Yuen, J.W.; Ko, C.W.; Yip, T.T.; et al. Constitutive activation of distinct NF-κB signals in EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, D.; Eizuru, Y.; Tokunaga, M.; Takada, K. Autocrine growth of Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric carcinoma cells mediated by an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7062–7067. [Google Scholar]
- Iwakiri, D.; Sheen, T.S.; Chen, J.Y.; Huang, D.P.; Takada, K. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA induces insulin-like growth factor 1 and supports growth of nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived cell lines. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwakiri, D.; Takada, K. Role of EBERs in the pathogenesis of EBV infection. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 107, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, A.; Sakatani, T.; Ushiku, T.; Hino, R.; Isogai, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Uozaki, H.; Takada, K.; Fukayama, M. Downregulation of MicroRNA-200 in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4719–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki-Ushiku, A.; Kunita, A.; Isogai, M.; Hibiya, T.; Ushiku, T.; Takada, K.; Fukayama, M. Profiling of Virus-Encoded MicroRNAs in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Carcinoma and Their Roles in Gastric Carcinogenesis. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5581–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Wei, L.; Peng, Q.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus microRNA miR-BART5-3p inhibits p53 expression. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01022-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquitz, A.R.; Mathur, A.; Nam, C.S.; Raab-Traub, N. The Epstein–Barr Virus BART microRNAs target the pro-apoptotic protein Bim. Virology 2011, 412, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, H.; Lee, S.K. Epstein–Barr virus miR-BART20-5p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting BAD. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Gong, L.P.; Chen, J.N.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, Y.W.; Hui, D.Y.; Zhao, X.X.; Wu, X.Y.; Shao, C.K. EBV-miR-BART10-3p and EBV-miR-BART22 promote metastasis of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma by activating the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Cell Oncol. 2020, 43, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treece, A.L.; Duncan, D.L.; Tang, W.; Elmore, S.; Morgan, D.R.; Dominguez, R.L.; Speck, O.; Meyers, M.O.; Gulley, M.L. Gastric adenocarcinoma microRNA profiles in fixed tissue and in plasma reveal cancer-associated and Epstein-Barr virus-related expression patterns. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Ji, Y.; Hu, D.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Chen, G.; Luo, X.; Zheng, X.W.; Lin, X. SNHG8 is identified as a key regulator of epstein-barr virus(EBV)-associated gastric cancer by an integrative analysis of lncRNA and mRNA expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 80990–81002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.J.; Chang, M.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.; Koo, B.K.; Yun, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Woo, J.H. Epstein–Barr virus-encoded miR-BART5-5p upregulates PD-L1 through PIAS3/pSTAT3 modulation; worsening clinical outcomes of PD-L1-positive gastric carcinomas. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.W.; Choi, Y.H.; Kwon, O.K.; Lee, S.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Yu, W.; Bae, H.I.; Seo, A.N.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.K.; et al. High level of viral microRNA-BART20-5p expression is associated with worse survival of patients with Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 14988–14994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandya, D.; Mariani, M.; He, S.; Andreoli, M.; Spennato, M.; Dowell-Martino, C.; Fiedler, P.; Ferlini, C. Epstein-Barr virus microRNA expression increases aggressiveness of solid malignancies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, L.; Peng, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Ou, C.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus miR-BART6-3p Inhibits the RIG-I Pathway. J. Innate Immun. 2017, 9, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneklaus, M.; Gerlic, M.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Rainey, A.A.; Pich, D.; McInnes, I.B.; Hammerschmidt, W.; O’Neill, L.A.; Masters, S.L. Cutting edge: miR-223 and EBV miR-BART15 regulate the NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1β production. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3795–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.T.; Lin, C.W. EBV-encoded miR-BART20-5p and miR-BART8 inhibit the IFN-γ-STAT1 pathway associated with disease progression in nasal NK-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerleider, N.; Bullard, W.; Kara, M.; Wang, X.; Roberts, C.; Renne, R.; Tibbetts, S.; Flemington, E.K. EBV miRNAs are potent effectors of tumor cell transcriptome remodeling in promoting immune escape. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, T.; Albanese, M.; Bouvet, M.; Moosmann, A.; Mautner, J.; Heissmeyer, V.; Zielinski, C.; Lutter, D.; Hoser, J.; Hastreiter, M.; et al. Epstein-Barr viral miRNAs inhibit antiviral CD4+ T cell responses targeting IL-12 and peptide processing. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2065–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanese, M.; Tagawa, T.; Bouvet, M.; Maliqi, L.; Lutter, D.; Hoser, J.; Hastreiter, M.; Hayes, M.; Sugden, B.; Martin, L.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs reduce immune surveillance by virus-specific CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6467–E6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, R.; Abe, H.; Kunita, A.; Yamashita, H.; Seto, Y.; Fukayama, M. Overexpression and gene amplification of PD-L1 in cancer cells and PD-L1 + immune cells in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer: The prognostic implications. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, J.; Hong, S.; Zhan, J.; Chen, N.; Qin, T.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhou, T.; et al. EBV-driven LMP1 and IFN-γ upregulate PD-L1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Implications for oncotargeted therapy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 12189–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Rodig, S.; Juszczynski, P.; Ouyang, J.; Sinha, P.; O’Donnell, E.; Neuberg, D.; Shipp, M.A. Constitutive AP-1 activity and EBV infection induce PD-l1 in Hodgkin lymphomas and posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders: Implications for targeted therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.Y.; Guo, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.B.; Chen, Q.Y.; Tang, L.Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.T.; Zhang, L.; Mai, H.Q. Tumor CTLA-4 overexpression predicts poor survival in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13060–13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.D.; Lu, L.X.; Xie, Y.B.; Chen, L.Z.; Feng, Q.S.; Kang, T.; Jia, W.H.; Zeng, Y.X. Clinical values of multiple Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) serological biomarkers detected by xMAP technology. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakry, J.A.; Hegde, A.M.; Durand, C.M.; Massie, A.B.; Greer, A.E.; Ambinder, R.F.; Valsamakis, A. The clinical significance of EBV DNA in the plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with or without EBV diseases. Blood 2016, 127, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y.; Le, Q.T.; Yom, S.S.; Pinsky, B.A.; Bratman, S.V.; Ng, R.H.; El Mubarak, H.S.; Chan, K.C.; Sander, M.; Conley, B.A. Current state of PCR-based Epstein-barr virus DNA testing for nasopharyngeal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djx007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, S.; Horikawa, T.; Takeshita, H.; Kanegane, C.; Kasahara, Y.; Sheen, T.S.; Sato, H.; Furukawa, M.; Yoshizaki, T. Diagnostic value of serum EBV-DNA quantification and antibody to viral capsid antigen in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komabayashi, Y.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Ueda, S.; Takahara, M.; Harabuchi, Y. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus–encoded micro-RNAs as potential biomarkers for nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zong, J.; Lin, S.; Verhoeven, R.J.; Tong, S.; Chen, Y.; Ji, M.; Cheng, W.; Tsao, S.W.; Lung, M.; et al. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs miR-BART7 and miR-BART13 as biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E301–E312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, N.; Wakisaka, N.; Kondo, S.; Aga, M.; Moriyama-Kita, M.; Ueno, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Endo, K.; Sugimoto, H.; Murono, S.; et al. Potential interest in circulating miR-BART17-5p as a post-treatment biomarker for prediction of recurrence in Epstein-Barr virus-related nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jiang, C.; Chen, J.; Xie, S.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Lung, M.; Kam, N.W.; Kwong, D.L.; Cao, S.; Guan, X.Y. Evaluation of circulating EBV microRNA BART2-5p in facilitating early detection and screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 3209–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Guo, Q.; Lin, K.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, C.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs BART7-3p and BART13-3p as novel biomarkers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramayanti, O.; Verkuijlen, S.A.W.M.; Novianti, P.; Scheepbouwer, C.; Misovic, B.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; van Weering, J.; Beckers, L.; Adham, M.; Martorelli, D.; et al. Vesicle-bound EBV-BART13-3p miRNA in circulation distinguishes nasopharyngeal from other head and neck cancer and asymptomatic EBV-infections. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2555–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.P.; Tan, G.W.; Sivanesan, V.M.; Goh, S.L.; Ng, X.J.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, W.R.; Mohidin, T.B.B.M.; Mohd Dali, N.S.; Ong, S.H.; et al. Systematic comparison of plasma EBV DNA; anti-EBV antibodies and miRNA levels for early detection and prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 2336–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.H.; Lu, L.X.; Cui, C.; Chen, M.Y.; Li, X.Z.; Jia, W.H. Epstein-Barr virus mir-bart1-5p detection via nasopharyngeal brush sampling is effective for diagnosing nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 4972–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.Y.; Gao, W.; Ho, W.K.; Wei, W.I.; Wong, T.S. Overexpression of epstein-barr virus-encoded microRNA-BART7 in undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 3201–3210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.Y.; Kok, K.H.; Tsao, S.W.; Jin, D.Y. Utility of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA promoters for driving the expression of fusion transcripts harboring short hairpin RNAs. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Pei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhi, H.; Wong, W.H.; Wei, H.; Ng, I.O.; et al. Exosomes derived from Vδ2-T cells control Epstein-Barr virus-associated tumors and induce T cell antitumor immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Tang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, M.; Xiong, W.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zeng, X.; Liao, Q.; Guo, X.; et al. Mir-216b suppresses tumor growth and invasion by targeting KRAS in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2997–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerleider, N.; Concha, M.; Lin, Z.; Roberts, C.; Wang, X.; Cao, S. The Epstein-Barr virus circRNAome. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 14, e1007206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toptan, T.; Abere, B.; Nalesnik, M.A.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Ranganathan, S.; Lee, N.; Shair, K.H.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Circular DNA tumor viruses make circular RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8737–E8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullard, W.L.; Flemington, E.K.; Renne, R.; Tibbetts, S.A. Connivance, complicity, or collusion? The role of noncoding RNAs in promoting gamma herpesvirus tumorigenesis. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Epstein-Barr virus circRNAome as host miRNA sponge regulates virus infection, cell cycle, and oncogenesis. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilala, J.; Becnel, D.; Abdelghani, R. Role of virally encoded circular RNAs in the pathogenicity of human oncogenic viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 657036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.P.; Chen, J.N.; Dong, M.; Xiao, Z.D.; Feng, Z.Y.; Pan, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Bi, Y.H.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-derived circular RNA LMP2A induces stemness in EBV-associated gastric cancer. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e49689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shuai, M.; Xia, Y. Knockdown of EBV-encoded circRNA circRPMS1 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis through sponging multiple miRNAs. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8023–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Hu, J. Long noncoding RNAs involvement in Epstein-Barr virus infection and tumorigenesis. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Notarte, K.I.; Senanayake, S.; Macaranas, I.; Albano, P.M.; Mundo, L.; Fennell, E.; Leoncini, L.; Murray, P. MicroRNA and Other Non-Coding RNAs in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Cancers. Cancers 2021, 13, 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153909
Notarte KI, Senanayake S, Macaranas I, Albano PM, Mundo L, Fennell E, Leoncini L, Murray P. MicroRNA and Other Non-Coding RNAs in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Cancers. Cancers. 2021; 13(15):3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153909
Chicago/Turabian StyleNotarte, Kin Israel, Suranga Senanayake, Imee Macaranas, Pia Marie Albano, Lucia Mundo, Eanna Fennell, Lorenzo Leoncini, and Paul Murray. 2021. "MicroRNA and Other Non-Coding RNAs in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Cancers" Cancers 13, no. 15: 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153909
APA StyleNotarte, K. I., Senanayake, S., Macaranas, I., Albano, P. M., Mundo, L., Fennell, E., Leoncini, L., & Murray, P. (2021). MicroRNA and Other Non-Coding RNAs in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Cancers. Cancers, 13(15), 3909. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153909








