Antithetic hTERT Regulation by Androgens in Prostate Cancer Cells: hTERT Inhibition Is Mediated by the ING1 and ING2 Tumor Suppressors
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Retroviral Transduction
2.2. RNA-Sequencing and Transcriptome Analysis
2.3. Generation of Spheroids and Immunostaining
2.4. Senescence-Associated Beta-Galactosidase (SA β-Gal) Staining of Spheroids
2.5. Reporter Gene Assay
2.6. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR)
| β-Actin: | fwd: | CACCACACCTTCTACAATGAGC |
| rev: | CACAGCCTGGATAGCAACG | |
| RPL13a: | fwd: | GTATGCTGCCCCACAAAACC |
| rev: | TGTAGGCTTCAGACGCACGAC | |
| TBP: | fwd: | GGCGTGTGAAGATAACCCAAGG |
| rev: | CGCTGGAACTCGTCTCACT | |
| KLK3: | fwd: | GAGGCTGGGAGTGCGAGAAG |
| rev: | TTGTTCCTGATGCAGTGGGC | |
| hTERT: | fwd: | CGGAAGAGTGTCTGGAGCAA |
| rev: | GGATGAAGCGGAGTCTGGA |
2.7. Antibodies and Western Blot Analyses
2.8. Ex Vivo Treatment of Prostate Cancer Samples
2.9. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
2.10. Primer Pairs for Human Genes Used for qPCR Analysis
2.11. KLK3, PSA ARE I
2.12. Primer Pairs for hTERT Used for Nested-PCR Analysis with Sequence 5′→3′
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Molecular Profiling on Transcriptomics Level Reveals Repression of hTERT Expression by SAL
3.2. Repression of hTERT by SAL in PCa Tumor Samples Ex Vivo and in Spheroids
3.3. Androgen-Mediated Repression and Activation of hTERT Expression Is Time- and Concentration-Dependent
3.4. Identification of a Positive Androgen Response Element in the Distal hTERT Promoter
3.5. Identification of a Negative Androgen Response Element in the Proximal hTERT Promoter
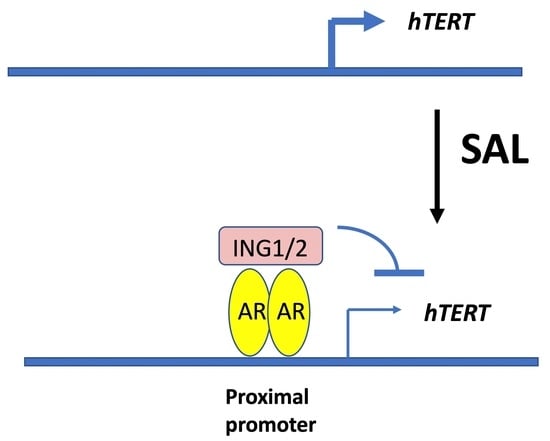
3.6. The Tumor Suppressor ING1 and ING2 Mediate AR-Regulated Transrepression of hTERT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AR | androgen receptor |
| ADT | androgen deprivation therapy |
| BAT | bipolar androgen therapy |
| ChIP | chromatin immuno-precipitation |
| CRPC | castration-resistant PCa |
| DHT | dihydrotestosterone |
| hTERT | human telomerase reverse transcriptase catalytic subunit |
| ING1/2 | inhibitor of growth 1 and 2 |
| LAL | low androgen levels |
| nARE | negative androgen response element |
| pARE | positive androgen response element |
| PCa | prostate cancer |
| R1881 | methyltrienolone |
| SAL | supraphysiological androgen level |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; David, F.; Baniahmad, A. Androgen Receptor-Dependent Mechanisms Mediating Drug Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teply, B.A.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Sullivan, R.; Rifkind, I.; Bruns, A.; Spitz, A.; DeCarli, M.; Sinibaldi, V.; Pratz, C.F.; et al. Bipolar androgen therapy in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer after progression on enzalutamide: An open-label, phase 2, multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denmeade, S.R. Bipolar androgen therapy in the treatment of prostate cancer. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 16, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leone, G.; Buttigliero, C.; Pisano, C.; Di Stefano, R.F.; Tabbò, F.; Turco, F.; Vignani, F.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Di Maio, M.; Tucci, M. Bipolar androgen therapy in prostate cancer: Current evidences and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2020, 152, 102994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, J.T.; Brennen, W.N.; Denmeade, S.R. Serial bipolar androgen therapy (sBAT) using cyclic supraphysiologic testosterone (STP) to treat metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, S311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmana, G.; Baniahmad, A. Interference with the androgen receptor protein stability in therapy-resistant prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1775–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roediger, J.; Hessenkemper, W.; Bartsch, S.; Manvelyan, M.; Huettner, S.S.; Liehr, T.; Esmaeili, M.; Foller, S.; Petersen, I.; Grimm, M.-O.; et al. Supraphysiological androgen levels induce cellular senescence in human prostate cancer cells through the Src-Akt pathway. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moehren, U.; Papaioannou, M.; Reeb, C.A.; Grasselli, A.; Nanni, S.; Asim, M.; Roell, D.; Prade, I.; Farsetti, A.; Baniahmad, A. Wild-type but not mutant androgen receptor inhibits expression of the hTERT telomerase subunit: A novel role of AR mutation for prostate cancer development. FASEB J. 2007, 22, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dotzlaw, H.; Moehren, U.; Mink, S.; Cato, A.C.; Iñiguez Lluhí, J.A.; Baniahmad, A. The amino terminus of the human AR is target for corepressor action and antihormone agonism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groner, A.C.; Brown, M. Role of steroid receptor and coregulator mutations in hormone-dependent cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Qi, Y.; Ge, Y.; Duplessis, T.; Rowan, B.G.; Ip, C.; Cheng, H.; Rennie, P.S.; Horikawa, I.; Lustig, A.J.; et al. Telomerase as an Important Target of Androgen Signaling Blockade for Prostate Cancer Treatment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, C.; Armbruster, B.N.; Price, D.T.; Counter, C.M. In Vivo Regulation of hTERT Expression and Telomerase Activity by Androgen. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iczkowski, K.A.; Huang, W.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Pantazis, C.G.; Stevens, G.R.; Montironi, R. Androgen ablation therapy for prostate carcinoma suppresses the immunoreactive telomerase subunit hTERT. Cancer 2004, 100, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, A.K.; Sommerfeld, H.J.; Coffey, D.S. Telomerase is activated in the prostate and seminal vesicles of the castrated rat. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 5743–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teske, E.; Naan, E.; van Dijk, E.; Van Garderen, E.; Schalken, J. Canine prostate carcinoma: Epidemiological evidence of an increased risk in castrated dogs. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2002, 197, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Nayak, S.; Kakar, R.; Chaudhari, U.K.; Joshi, D.; Vundinti, B.R.; Fernandes, G.; Barai, R.S.; Kholkute, S.D.; Sachdeva, G. A triad of telomerase, androgen receptor and early growth response 1 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esmaeili, M.; Pungsrinont, T.; Schaefer, A.; Baniahmad, A. A novel crosstalk between the tumor suppressors ING1 and ING2 regulates androgen receptor signaling. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, M.; Jennek, S.; Ludwig, S.; Klitzsch, A.; Kraft, F.; Melle, C.; Baniahmad, A. The tumor suppressor ING1b is a novel core-pressor for the androgen receptor and induces cellular senescence in prostate cancer cells. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, A.; Al Shueili, B.; Yang, Y.; Nabbi, A.; Fink, D.; Riabowol, K. Biological Functions of the ING Proteins. Cancers 2019, 11, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, G.H.; Helbing, C.; Wagner, M.J.; Sensen, C.W.; Riabowol, K. Phylogenetic Analysis of the ING Family of PHD Finger Proteins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 22, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pungsrinont, T.; Baniahmad, A. Cellular senescence by the epigenetic regulators Inhibitor of Growth. Aging Sci. 2016, 4, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.; He, Q.-Y. ReactomePA: An R/Bioconductor package for reactome pathway analysis and visualization. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Pungsrinont, T.; Ženata, O.; Neubert, L.; Vrzal, R.; Baniahmad, A. Interleukin-23 Represses the Level of Cell Senescence Induced by the Androgen Receptor Antagonists Enzalutamide and Darolutamide in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells. Horm. Cancer 2020, 11, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessenkemper, W.; Roediger, J.; Bartsch, S.; Houtsmuller, A.B.; van Royen, M.; Petersen, I.; Grimm, M.-O.; Baniahmad, A. A Natural Androgen Receptor Antagonist Induces Cellular Senescence in Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1831–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handa, R.J.; Pak, T.R.; Kudwa, A.E.; Lund, T.D.; Hinds, L. An alternate pathway for androgen regulation of brain function: Activation of estrogen receptor beta by the metabolite of dihydrotestosterone, 5α-androstane-3β,17β-diol. Horm. Behav. 2008, 53, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, E.M.; Pendlebury, D.F.; Nandakumar, J. Structural biology of telomeres and telomerase. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Richardson, M.; Reddy, V.; Menon, M.; Barrack, E.R.; Reddy, G.P.-V.; Kim, S.-H. Structural and functional association of androgen receptor with telomeres in prostate cancer cells. Aging 2013, 5, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-H.; Richardson, M.; Chinnakannu, K.; Bai, V.U.; Menon, M.; Barrack, E.R.; Reddy, G.P.-V. Androgen Receptor Interacts with Telomeric Proteins in Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10472–10476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosaad, E.; Chambers, K.F.; Futrega, K.; Clements, J.A.; Doran, M.R. The Microwell-mesh: A high-throughput 3D prostate cancer spheroid and drug-testing platform. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.H.E.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E.-L. Androgen receptor: Structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jesus, B.B.; Blasco, M.A. Telomerase at the intersection of cancer and aging. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.; DePinho, R.A. Telomerase extracurricular activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12520–12522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monsen, R.C.; DeLeeuw, L.; Dean, W.L.; Gray, R.D.; Sabo, T.M.; Chakravarthy, S.; Chaires, J.B.; O’Trent, J. The hTERT core promoter forms three parallel G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 5720–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misiti, S.; Nanni, S.; Fontemaggi, G.; Cong, Y.-S.; Wen, J.; Hirte, H.W.; Piaggio, G.; Sacchi, A.; Pontecorvi, A.; Bacchetti, S.; et al. Induction of hTERT Expression and Telomerase Activity by Estrogens in Human Ovary Epithelium Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 3764–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanni, S.; Narducci, M.; Della Pietra, L.; Moretti, F.; Grasselli, A.; De Carli, P.; Sacchi, A.; Pontecorvi, A.; Farsetti, A. Signaling through estrogen receptors modulates telomerase activity in human prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Chen, S.; Ng, P.; Bubley, G.J.; Nelson, P.S.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Marck, B.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Simon, N.; Wang, H.; et al. Intratumoral De Novo Steroid Synthesis Activates Androgen Receptor in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer and Is Upregulated by Treatment with CYP17A1 Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6503–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gecgel, K.K.; Muduroglu, M.; Erdogan, S. Inhibition of telomerase potentiates enzalutamide efficiency of androgen-sensitive human prostate cancer cells. J. BUON Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2018, 22, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Doyon, Y.; Cayrou, C.; Ullah, M.; Landry, A.J.; Côté, V.; Selleck, W.; Lane, W.S.; Tan, S.; Yang, X.J.; Côté, J. ING tumor suppressor proteins are critical regulators of chromatin acetylation required for genome expres-sion and perpetuation. Mol. Cell 2006, 21, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Primary Antibody | Manufacturer/Catalog No. | Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-androgen receptor, polyclonal, and rabbit | Merck, 06-680 | 1:15 |
| Anti-ING1, polyclonal, rabbit | Sigma Aldrich, SAB1410716-100UG | 1:20 |
| Anti-ING2, polyclonal, rabbit | Proteintech, 11560-1-AP | 1:10 |
| Anti-rabbit IgG, HRP-conjugated | Cell Signaling, 70,745 | 1:100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartsch, S.; Mirzakhani, K.; Neubert, L.; Stenzel, A.; Ehsani, M.; Esmaeili, M.; Pungsrinont, T.; Kacal, M.; Rasa, S.M.M.; Kallenbach, J.; et al. Antithetic hTERT Regulation by Androgens in Prostate Cancer Cells: hTERT Inhibition Is Mediated by the ING1 and ING2 Tumor Suppressors. Cancers 2021, 13, 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164025
Bartsch S, Mirzakhani K, Neubert L, Stenzel A, Ehsani M, Esmaeili M, Pungsrinont T, Kacal M, Rasa SMM, Kallenbach J, et al. Antithetic hTERT Regulation by Androgens in Prostate Cancer Cells: hTERT Inhibition Is Mediated by the ING1 and ING2 Tumor Suppressors. Cancers. 2021; 13(16):4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164025
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartsch, Sophie, Kimia Mirzakhani, Laura Neubert, Alexander Stenzel, Marzieh Ehsani, Mohsen Esmaeili, Thanakorn Pungsrinont, Merve Kacal, Seyed Mohammad Mahdi Rasa, Julia Kallenbach, and et al. 2021. "Antithetic hTERT Regulation by Androgens in Prostate Cancer Cells: hTERT Inhibition Is Mediated by the ING1 and ING2 Tumor Suppressors" Cancers 13, no. 16: 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164025
APA StyleBartsch, S., Mirzakhani, K., Neubert, L., Stenzel, A., Ehsani, M., Esmaeili, M., Pungsrinont, T., Kacal, M., Rasa, S. M. M., Kallenbach, J., Damodaran, D., Ribaudo, F., Grimm, M.-O., Neri, F., & Baniahmad, A. (2021). Antithetic hTERT Regulation by Androgens in Prostate Cancer Cells: hTERT Inhibition Is Mediated by the ING1 and ING2 Tumor Suppressors. Cancers, 13(16), 4025. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164025