Circulating miRNAs as Novel Non-Invasive Biomarkers to Aid the Early Diagnosis of Suspicious Breast Lesions for Which Biopsy Is Recommended
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
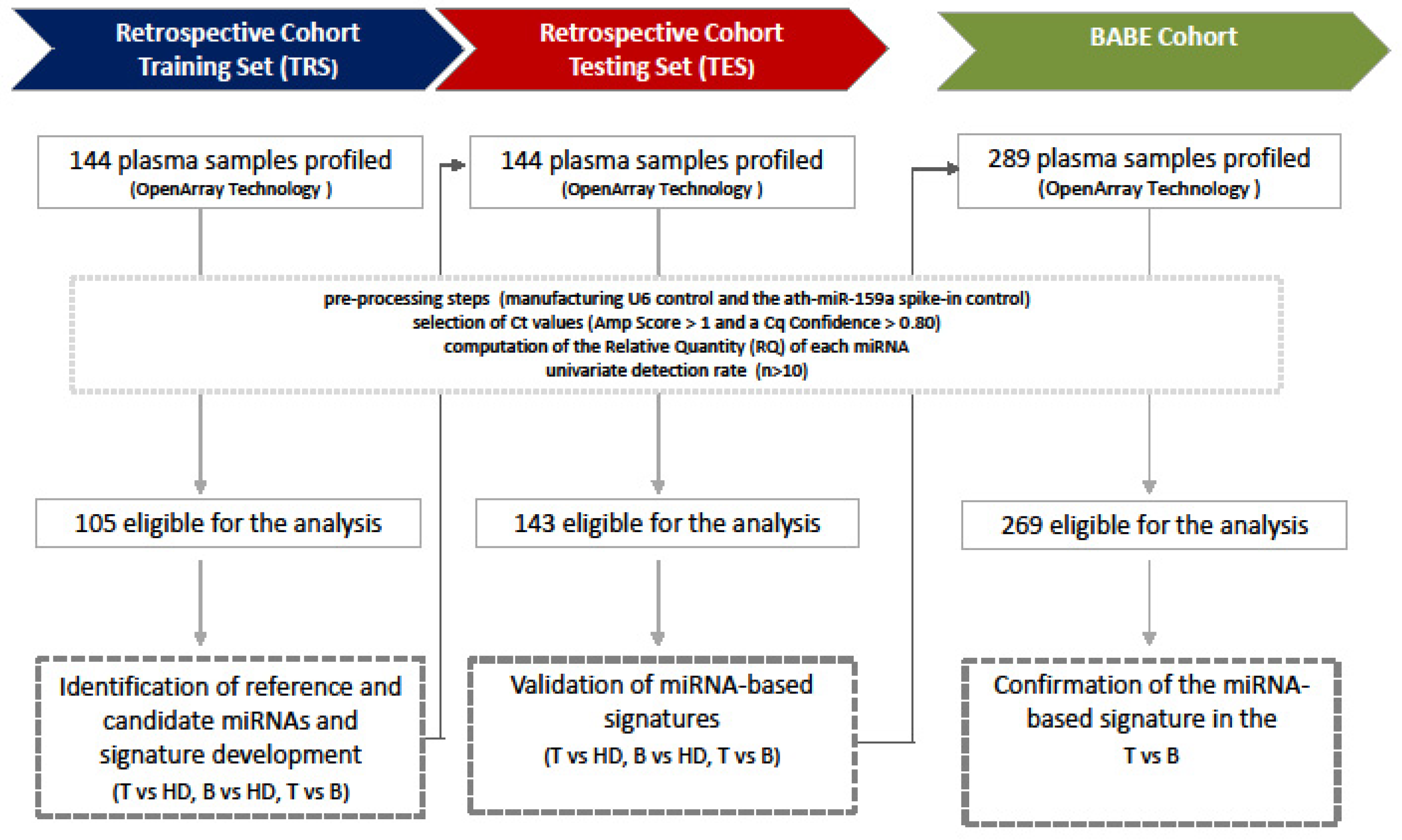
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasma Samples
2.2. Blood Collection, Plasma Separation, and RNA Extraction
2.3. miRNA Profile
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Preprocessing Step
2.4.2. Retrospective Cohort Analysis
2.4.3. BABE Cohort Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Retrospective Cohort Analysis
3.2. BABE Cohort Analysis
3.3. BABE-FU Cohort Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mendelson, E.B.; Baum, J.; Berg, W.; Merritt, C.; Rubin, E. ACR BIRADS Ultrasound. In ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, 4th ed.; ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson, E.B. ACR BIRADS Ultrasound. In ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System, 5th ed.; ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Guan, X.; Fan, Z.; Ching, L.M.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, W.M.; Liu, D.X. Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Detection of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. microRNAs in cancer: Small molecules with a huge impact. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5848–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: Diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, F.J.; Talhouk, R.; Zgheib, N.K.; Tfayli, A.; El Sabban, M.; El Saghir, N.S.; Boulos, F.; Jabbour, M.N.; Chalala, C.; Boustany, R.M.; et al. microRNA Expression in Ethnic Specific Early Stage Breast Cancer: An Integration and Comparative Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16829–16978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Qin, W.; Atasoy, U.; Sauter, E.R. Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer and healthy subjects. BMC Res. Notes 2009, 2, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heneghan, H.M.; Miller, N.; Kelly, R.; Newell, J.; Kerin, M.J. Systemic miRNA-195 differentiates breast cancer from other malignancies and is a potential biomarker for detecting noninvasive and early stage disease. Oncologist 2010, 15, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asaga, S.; Kuo, C.; Nguyen, T.; Terpenning, M.; Giuliano, A.E.; Hoon, D.S. Direct serum assay for microRNA-21 concentrations in early and advanced breast cancer. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, C.; Rack, B.; Muller, V.; Janni, W.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating microRNAs as blood-based markers for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, E.J.; Santarpia, L.; Kim, J.; Esteva, F.J.; Moretti, E.; Buzdar, A.U.; Di Leo, A.; Le, X.F.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Park, S.T.; et al. Plasma microRNA 210 levels correlate with sensitivity to trastuzumab and tumor presence in breast cancer patients. Cancer 2012, 118, 2603–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuk, K.; Zucknick, M.; Heil, J.; Madhavan, D.; Schott, S.; Turchinovich, A.; Arlt, D.; Rath, M.; Sohn, C.; Benner, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma as early detection markers for breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Hu, C. Circulating microRNA-92a and microRNA-21 as novel minimally invasive biomarkers for primary breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, G.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Qi, J.; Li, J. Serum microRNA-155 as a potential biomarker to track disease in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.; Liaw, C.S.; Ji, S.M.; Tan, H.H.; Wong, C.Y.; Thike, A.A.; Tan, P.H.; Ho, G.H.; Lee, A.S. Identification of circulating microRNA signatures for breast cancer detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4477–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuk, K.; Zucknick, M.; Madhavan, D.; Schott, S.; Golatta, M.; Heil, J.; Marmé, F.; Turchinovich, A.; Sinn, P.; Sohn, C.; et al. Plasma microRNA panel for minimally invasive detection of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zearo, S.; Kim, E.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.T.; Sidhu, S.B.; Robinson, B.G.; Soon, P.S. MicroRNA-484 is more highly expressed in serum of early breast cancer patients compared to healthy volunteers. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sochor, M.; Basova, P.; Pesta, M.; Dusilkova, N.; Bartos, J.; Burda, P.; Pospisil, V.; Stopka, T. Oncogenic microRNAs: miR-155, miR-19a, miR-181b, and miR-24 enable monitoring of early breast cancer in serum. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, E.K.; Li, R.; Shin, V.Y.; Jin, H.C.; Leung, C.P.; Ma, E.S.; Pang, R.; Chua, D.; Chu, K.M.; Law, W.L.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as specific biomarkers for breast cancer detection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mar-Aguilar, F.; Mendoza-Ramirez, J.A.; Malagon-Santiago, I.; Espino-Silva, P.K.; Santuario-Facio, S.K.; Ruiz-Flores, P.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C.; Reséndez-Pérez, D. Serum circulating microRNA profiling for identification of potential breast cancer biomarkers. Dis. Markers 2013, 34, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J. Analysis of miR-205 and miR-155 expression in the blood of breast cancer patients. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 25, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodahl, A.R.; Lyng, M.B.; Binder, H.; Cold, S.; Gravgaard, K.; Knoop, A.S.; Ditzel, H.J. Novel circulating microRNA signature as a potential non-invasive multi-marker test in ER-positive early-stage breast cancer: A case control study. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamam, R.; Hamam, D.; Alsaleh, K.A.; Kassem, M.; Zaher, W.; Alfayez, M.; Aldahmash, A.; Alajez, N.M. Circulating microRNAs in breast cancer: Novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimomura, A.; Shiino, S.; Kawauchi, J.; Takizawa, S.; Sakamoto, H.; Matsuzaki, J.; Ono, M.; Takeshita, F.; Niida, S.; Shimizu, C.; et al. Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosse, S.A.; Muller, V.; Steinbach, B.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating cell-free cancer-testis MAGE-A RNA, BORIS RNA, let-7b and miR-202 in the blood of patients with breast cancer and benign breast diseases. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Steinbach, B.; Muller, V.; Pantel, K. Diagnostic potential of PTEN-targeting miR-214 in the blood of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 134, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Loke, S.Y.; Tan, V.K.; Quek, S.T.; Jagmohan, P.; Tang, Y.C.; Madhukumar, P.; Tan, B.K.; Yong, W.S.; Sim, Y.; et al. Development of a microRNA Panel for Classification of Abnormal Mammograms for Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhani, S.R.; Ellis, I.O.; Schnitt, S.J.; Tan, P.H.; Van de Vijver, M.J. WHO Classification of Tumours. In WHO Classification of Tumours of the Breast, 4th ed.; WHO Classification of Tumours of the Breast; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-92-832-2433-4. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzamiglio, S.; Zanutto, S.; Ciniselli, C.M.; Belfiore, A.; Bottelli, S.; Gariboldi, M.; Verderio, P. A methodological procedure for evaluating the impact of hemolysis on circulating microRNAs. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verderio, P.; Bottelli, S.; Ciniselli, C.M.; Pierotti, M.A.; Gariboldi, M.; Pizzamiglio, S. NqA: An R-based algorithm for the normalization and analysis of microRNA quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 461, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanutto, S.; Ciniselli, C.M.; Belfiore, A.; Lecchi, M.; Masci, E.; Delconte, G.; Primignani, M.; Tosetti, G.; Dal, F.M.; Fazzini, L.; et al. Plasma miRNA-based signatures in CRC screening programs. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Cosimo, S.; Appierto, V.; Pizzamiglio, S.; Tiberio, P.; Iorio, M.V.; Hilbers, F.; De Azambuja, E.; de la Pena, L.; Izquierdo, M.A.; Huober, J.; et al. Plasma microRNA levels for predicting therapeutic response to neoadjuvant treatment in HER2-positive breast cancer: Results from the NeoALTTO trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verderio, P.; Bottelli, S.; Pizzamiglio, S.; Ciniselli, C.M. Developing miRNA signatures: A multivariate prospective. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr. Regression Modeling Strategies with Applications to Linear Models, Logistic Regression, and Survival Analysis, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-387-95232-2. [Google Scholar]
- Moons, K.G.; Donders, A.R.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Harrell, F.E. Penalized maximum likelihood estimation to directly adjust diagnostic and prognostic prediction models for overoptimism: A clinical example. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestdagh, P.; Van Vlierberghe, P.; De Weer, A.; Muth, D.; Westermann, F.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. A novel and universal method for microRNA RT-qPCR data normalization. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiodoni, C.; Cancila, V.; Renzi, T.A.; Perrone, M.; Tomirotti, A.M.; Sangaletti, S.; Botti, L.; Dugo, M.; Milani, M.; Bongiovanni, L.; et al. Transcriptional Profiles and Stromal Changes Reveal Bone Marrow Adaptation to Early Breast Cancer in Association with Deregulated Circulating microRNAs. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Li, B.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, A.M.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, K.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Cross-platform genomic identification and clinical validation of breast cancer diagnostic biomarkers. Aging 2021, 13, 4258–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Canto, L.M.; Marian, C.; Willey, S.; Sidawy, M.; Da Cunha, P.A.; Rone, J.D.; Li, X.; Gusev, Y.; Haddad, B.R. MicroRNA analysis of breast ductal fluid in breast cancer patients. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, M.N.; Kim, M.S.; Adil, M.; Patil, A.H.; Lu, Y.; Mitchell, C.J.; Leal-Rojas, P.; Xu, J.; Kumar, M.; Dawson, V.L.; et al. Toward the human cellular microRNAome. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Rie, D.; Abugessaisa, I.; Alam, T.; Arner, E.; Arner, P.; Ashoor, H.; Astrom, G.; Babina, M.; Bertin, N.; Burroughs, A.M.; et al. An integrated expression atlas of miRNAs and their promoters in human and mouse. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juzenas, S.; Venkatesh, G.; Hubenthal, M.; Hoeppner, M.P.; Du, Z.G.; Paulsen, M.; Rosenstiel, P.; Senger, P.; Hofmann-Apitius, M.; Keller, A.; et al. A comprehensive, cell specific microRNA catalogue of human peripheral blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 9290–9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aparicio-Puerta, E.; Jaspez, D.; Lebron, R.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; Marchal, J.A.; Hackenberg, M. liqDB: A small-RNAseq knowledge discovery database for liquid biopsy studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D113–D120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Otsubo, T.; Shimada, S.; Yuasa, Y. Involvement of epigenetically silenced microRNA-181c in gastric carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Qiao, Q.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z. miR-625 down-regulation promotes proliferation and invasion in esophageal cancer by targeting Sox2. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Retrospective Cohort (n = 100) | BABE Cohort (n = 125) | BABE FU Cohort (n = 29) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | ||
| Histology | IDC a | 74 (74) | 87 (69) | 17 (59) |
| ILC b | 10 (10) | 18 (15) | 5 (18) | |
| IDC + ILC | 5 (5) | 1 (1) | 1 (3) | |
| In situ c | 3 (3) | 8 (6) | 4 (14) | |
| IDC mixed d | 3 (3) | 4 (3) | 1 (3) | |
| Special Types e | 5 (1) | 6 (5) | 1 (3) | |
| Normal Tissue | - | 1 (1) | - | |
| IHC Histotype f | Luminal A | 17 (17) | 34 (27) | 12 (41) |
| Luminal B | 45 (45) | 60 (48) | 12 (41) | |
| Luminal HER2 | 11 (11) | 5 (4) | - | |
| HER2 | 5 (5) | 7 (6) | 1 (3) | |
| Triple-Negative | 19 (19) | 5 (4) | - | |
| In situ | 3 (3) | 8 (6) | 4 (15) | |
| Not determined | - | 6 (5) | - | |
| Grade | I | 8 (8) | 14 (11) | 3 (11) |
| II | 43 (43) | 72 (58) | 21 (72) | |
| III | 49 (49) | 38 (30) | 5 (17) | |
| Not determined | - | 1 (1) | - | |
| Tumor Size g | T1 | 68 (68) | 101 (81) | 27 (93) |
| T2 | 32 (32) | 21 (17) | 2 (7) | |
| Not determined | - | 3 (2) | - | |
| Lymph node | Negative | 62 (62) | 83 (66) | 22 (76) |
| Positive | 38 (38) | 24 (19) | 7 (24) | |
| Not determined | - | 18 (15) | - | |
| ER h | Positive | 74 (74) | 105 (84) | 26 (90) |
| Negative | 26 (26) | 14 (11) | 3 (10) | |
| Not determined | - | 6 (5) | - | |
| PgR h | Positive | 63 (63) | 95 (76) | 19 (66) |
| Negative | 36 (36) | 24 (19) | 10 (34) | |
| Not determined | 1 (1) | 6 (5) | - | |
| HER2 i | Positive | 17 (17) | 14 (11) | 2 (7) |
| Negative | 83 (83) | 105 (84) | 27 (93) | |
| Not determined | - | 6 (5) | - | |
| Ki-67 l | Positive | 79 (79) | 79 (63) | 13 (45) |
| Negative | 19 (19) | 36 (29) | 16 (55) | |
| Not determined | 2 (2) | 10 (8) | - | |
| Age | Median (interquartile range) | 59 (49–72) | 55 (48–70) | 56 (50–72) |
| T vs. HD | miRNA | #T | #HD | KW-p Value | Direction |
| hsa-miR-423-5p-002340 | 31 | 45 | 0.0003 | up | |
| hsa-miR-21-000397 | 29 | 46 | 0.0006 | up | |
| hsa-miR-148a-000470 | 30 | 46 | 0.0011 | up | |
| hsa-miR-218-000521 | 31 | 42 | 0.0037 | up | |
| dme-miR-7-000268 | 24 | 37 | 0.0046 | up | |
| hsa-miR-324-3p-002161 | 31 | 45 | 0.0067 | up | |
| hsa-miR-502-3p-002083 | 30 | 46 | 0.0067 | up | |
| hsa-miR-625-002431 | 27 | 45 | 0.0081 | down | |
| hsa-miR-18a-002422 | 31 | 46 | 0.0120 | up | |
| hsa-miR-142-5p-002248 | 31 | 46 | 0.0127 | down | |
| hsa-miR-301b-002392 | 21 | 43 | 0.0148 | down | |
| hsa-miR-186-002285 | 31 | 46 | 0.0153 | down | |
| hsa-miR-370-002275 | 16 | 43 | 0.0155 | up | |
| hsa-miR-548c-5p-002429 | 20 | 35 | 0.0182 | up | |
| hsa-miR-181c-000482 | 30 | 44 | 0.0190 | down | |
| mmu-miR-134-001186 | 18 | 43 | 0.0237 | down | |
| B vs. HD | miRNA | #B | #HD | KW-p Value | Direction |
| hsa-miR-128a-002216 | 26 | 45 | 0.0008 | down | |
| hsa-miR-24-000402 | 27 | 46 | 0.0009 | down | |
| hsa-miR-598-001988 | 26 | 45 | 0.0013 | down | |
| hsa-miR-27a-000408 | 28 | 46 | 0.0027 | down | |
| hsa-miR-133a-002246 | 27 | 46 | 0.0028 | down | |
| hsa-miR-30c-000419 | 28 | 46 | 0.0048 | down | |
| hsa-miR-320-002277 | 28 | 46 | 0.0051 | up | |
| hsa-miR-148b-000471 | 27 | 46 | 0.0068 | down | |
| hsa-miR-204-000508 | 27 | 45 | 0.0107 | up | |
| hsa-miR-376a-000565 | 28 | 45 | 0.0126 | down | |
| hsa-miR-331-000545 | 28 | 46 | 0.0133 | down | |
| hsa-miR-324-5p-000539 | 27 | 46 | 0.0140 | down | |
| hsa-miR-330-000544 | 24 | 42 | 0.0142 | down | |
| hsa-miR-502-001109 | 15 | 27 | 0.0216 | up |
| Model | TRS Data AUC (95% CI) | TES Data AUC (95% CI) | n. miRNAs Included | miRNAs Included |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 0.726 (0.556; 0.897) | 0.708 (0.580; 0.837) | 4 | hsa-miR-423-5p-002340; hsa-miR-181c-000482; hsa-miR-625-002431; hsa-miR-301b-002392 |
| M2 | 0.769 (0.562; 0.976) | 0.683 (0.546; 0.820) | 4 | hsa-miR-423-5p-002340; hsa-miR-181c-000482; hsa-miR-301b-002392; hsa-miR-370-002275 |
| M3 | 0.712 (0.527; 0.897) | 0.696 (0.564; 0.828) | 3 | hsa-miR-181c-000482; hsa-miR-625-002431; hsa-miR-301b-002392 |
| M4 | 0.753 (0.559; 0.946) | 0.675 (0.539; 0.812) | 3 | hsa-miR-423-5p-002340; hsa-miR-625-002431; hsa-miR-370-002275 |
| M5 | 0.688 (0.515; 0.861) | 0.657 (0.522; 0.791) | 3 | hsa-miR-423-5p-002340; hsa-miR-625-002431; hsa-miR-301b-002392 |
| M6 | 0.763 (0.557; 0.970) | 0.660 (0.522; 0.799) | 3 | hsa-miR-181c-000482; hsa-miR-301b-002392; hsa-miR-370-002275 |
| M7 | 0.680 (0.511; 0.849) | 0.632 (0.507; 0.758) | 2 | hsa-miR-181c-000482; hsa-miR-301b-002392 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giussani, M.; Ciniselli, C.M.; De Cecco, L.; Lecchi, M.; Dugo, M.; Gargiuli, C.; Mariancini, A.; Mancinelli, E.; Cosentino, G.; Veneroni, S.; et al. Circulating miRNAs as Novel Non-Invasive Biomarkers to Aid the Early Diagnosis of Suspicious Breast Lesions for Which Biopsy Is Recommended. Cancers 2021, 13, 4028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164028
Giussani M, Ciniselli CM, De Cecco L, Lecchi M, Dugo M, Gargiuli C, Mariancini A, Mancinelli E, Cosentino G, Veneroni S, et al. Circulating miRNAs as Novel Non-Invasive Biomarkers to Aid the Early Diagnosis of Suspicious Breast Lesions for Which Biopsy Is Recommended. Cancers. 2021; 13(16):4028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164028
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiussani, Marta, Chiara Maura Ciniselli, Loris De Cecco, Mara Lecchi, Matteo Dugo, Chiara Gargiuli, Andrea Mariancini, Elisa Mancinelli, Giulia Cosentino, Silvia Veneroni, and et al. 2021. "Circulating miRNAs as Novel Non-Invasive Biomarkers to Aid the Early Diagnosis of Suspicious Breast Lesions for Which Biopsy Is Recommended" Cancers 13, no. 16: 4028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164028
APA StyleGiussani, M., Ciniselli, C. M., De Cecco, L., Lecchi, M., Dugo, M., Gargiuli, C., Mariancini, A., Mancinelli, E., Cosentino, G., Veneroni, S., Paolini, B., Orlandi, R., Gennaro, M., Iorio, M. V., Depretto, C., Ferranti, C., Sozzi, G., Sensi, M., Colombo, M. P., ... Verderio, P. (2021). Circulating miRNAs as Novel Non-Invasive Biomarkers to Aid the Early Diagnosis of Suspicious Breast Lesions for Which Biopsy Is Recommended. Cancers, 13(16), 4028. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164028








