Hypoxic Jumbo Spheroids On-A-Chip (HOnAChip): Insights into Treatment Efficacy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
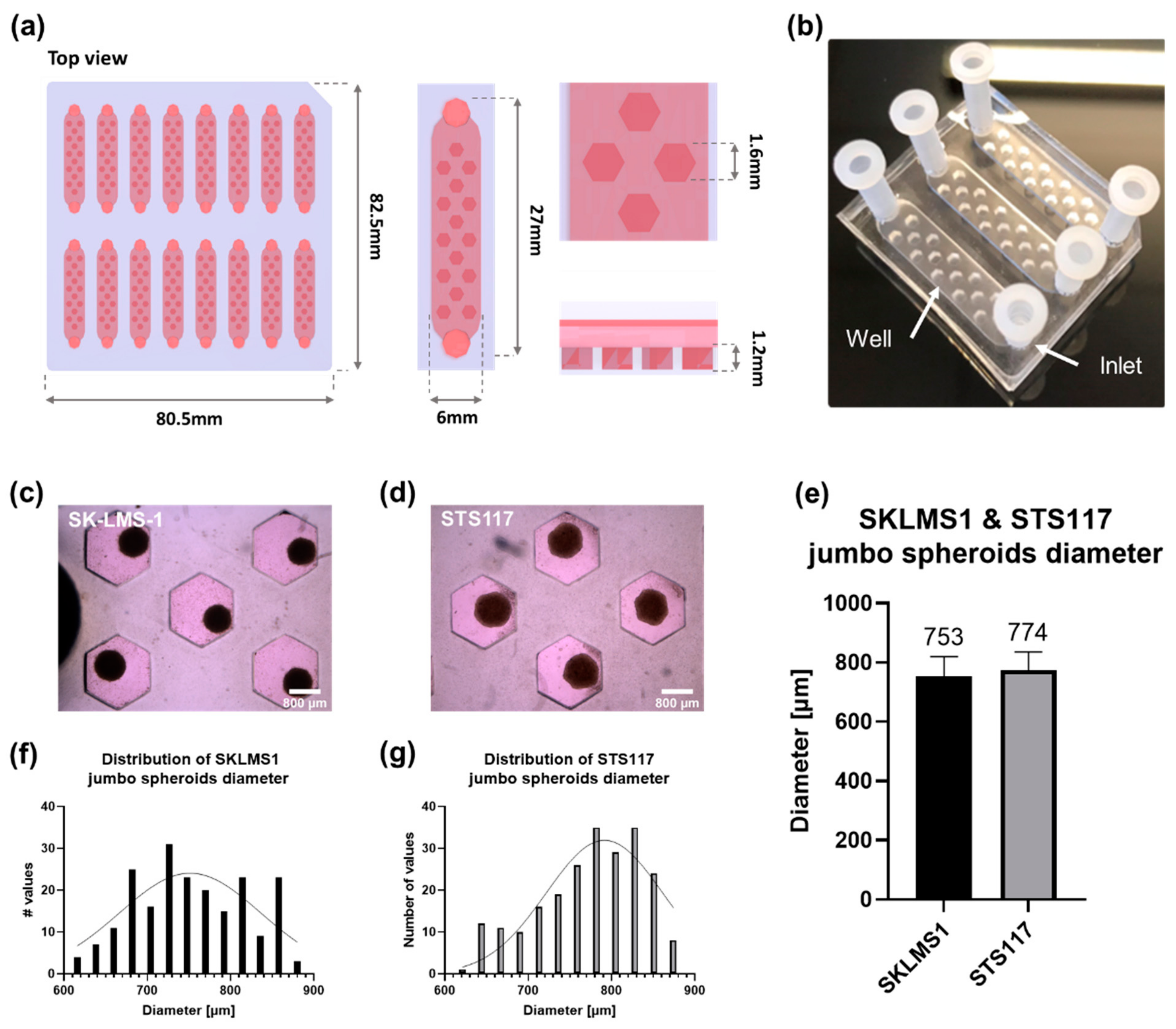
2.1. Microfluidic Chip
2.1.1. Microfluidic Device Fabrication
2.1.2. Microfluidic Device Preparation for Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Culture
2.2.1. Cell Culture
2.2.2. Spheroid Formation
2.3. Hypoxic Protein Analysis
2.3.1. Western Blot
2.3.2. Immunofluorescence
2.3.3. In Silico Modeling of Oxygen Consumption
2.4. Treatment Modalities
2.4.1. Tirapazamine (TPZ)
2.4.2. Conventional Radiotherapy
2.4.3. Combination Therapy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Microfluidic Chip Allows Formation of Size-Controlled Jumbo Spheroids
3.2. Presence of Hypoxia in Small vs. Jumbo Spheroids
3.3. Evaluation of Treatment Response in Jumbo Spheroids
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Mold Fabrication
Appendix A.2. Control Spheroids Formation and Hypoxia Induction
Appendix A.3. Image Analysis
Appendix A.3.1. Spheroid Diameter
Appendix A.3.2. CAIX Localization and Quantification
Appendix A.3.3. γH2AX Foci Quantification


References
- Brown, J.M.; Wilson, W.R. Exploiting Tumour Hypoxia in Cancer Treatment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.C.; Lebedev, A.; Aten, E.; Madsen, K.; Marciano, L.; Kolb, H.C. The Clinical Importance of Assessing Tumor Hypoxia: Relationship of Tumor Hypoxia to Prognosis and Therapeutic Opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1516–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomlinson, R.H.; Gray, L.H. The Histological Structure of Some Human Lung Cancers and the Possible Implications for Radiotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 1955, 9, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rankin, E.B.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxic Control of Metastasis. Science 2016, 352, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilkes, D.M.; Semenza, G.L.; Wirtz, D. Hypoxia and the Extracellular Matrix: Drivers of Tumour Metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Mehren, M.; Randall, R.L.; Benjamin, R.S.; Boles, S.; Bui, M.M.; Ganjoo, K.N.; George, S.; Gonzalez, R.J.; Heslin, M.J.; Kane, J.M.; et al. Soft Tissue Sarcoma, Version 2.2018, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 536–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.P.; Cranmer, L.D.; Van Tine, B.A.; Reed, D.R.; Okuno, S.H.; Butrynski, J.E.; Adkins, D.R.; Hendifar, A.E.; Kroll, S.; Ganjoo, K.N. Phase II Study of the Safety and Antitumor Activity of the Hypoxia-Activated Prodrug TH-302 in Combination with Doxorubicin in Patients with Advanced Soft Tissue Sarcoma. JCO 2014, 32, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, C.; Man, Y.K.S.; Chisholm, J.C.; Lepicard, E.Y.; Robinson, S.P.; Shipley, J.M. Hypoxia and Its Therapeutic Possibilities in Paediatric Cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. 2019. Available online: https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2019/advanced-information/ (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Leek, R.; Grimes, D.R.; Harris, A.L.; McIntyre, A. Methods: Using Three-Dimensional Culture (Spheroids) as an In Vitro Model of Tumour Hypoxia. In Tumor Microenvironment; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Koumenis, C., Coussens, L.M., Giaccia, A., Hammond, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 899, pp. 167–196. ISBN 978-3-319-26664-0. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L. Oxygen Sensing, Hypoxia-Inducible Factors, and Disease Pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2014, 9, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia—A Key Regulatory Factor in Tumour Growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ian, F.T.; Richard, P.H.; Robert, G.B. Lea Harrington. In The Basic Science of Oncology, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 0-07-138774-9. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Azab, A.K. The Role of Hypoxia in Cancer Progression, Angiogenesis, Metastasis, and Resistance to Therapy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Måseide, K.; Kandel, R.A.; Bell, R.S.; Catton, C.N.; O’Sullivan, B.; Wunder, J.S.; Pintilie, M.; Hedley, D.; Hill, R.P. Carbonic Anhydrase IX as a Marker for Poor Prognosis in Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4464–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Kuijk, S.J.A.; Yaromina, A.; Houben, R.; Niemans, R.; Lambin, P.; Dubois, L.J. Prognostic Significance of Carbonic Anhydrase IX Expression in Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkateswaran, G.; Dedhar, S. Interplay of Carbonic Anhydrase IX With Amino Acid and Acid/Base Transporters in the Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 602668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Forker, L.; Irlam, J.J.; Pillay, N.; Choudhury, A.; West, C.M.L. Validation of a Hypoxia Related Gene Signature in Multiple Soft Tissue Sarcoma Cohorts. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 3946–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewhirst, M.W.; Cao, Y.; Moeller, B. Cycling Hypoxia and Free Radicals Regulate Angiogenesis and Radiotherapy Response. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bristow, R.G.; Hill, R.P. Hypoxia, DNA Repair and Genetic Instability. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, S.K.; Sullivan, K.M.; Labadie, K.P.; Pillarisetty, V.G. Hypoxia as a Barrier to Immunotherapy in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequeux, A.; Noman, M.Z.; Xiao, M.; Sauvage, D.; Van Moer, K.; Viry, E.; Bocci, I.; Hasmim, M.; Bosseler, M.; Berchem, G.; et al. Impact of Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment and Tumor Cell Plasticity on the Expression of Immune Checkpoints. Cancer Lett. 2019, 458, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.Z.; Hasmim, M.; Lequeux, A.; Xiao, M.; Duhem, C.; Chouaib, S.; Berchem, G.; Janji, B. Improving Cancer Immunotherapy by Targeting the Hypoxic Tumor Microenvironment: New Opportunities and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, S.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. Targeting Hypoxia in the Tumor Microenvironment: A Potential Strategy to Improve Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J. SR 4233 (Tirapazamine): A New Anticancer Drug Exploiting Hypoxia in Solid Tumours. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 67, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, K.B.; Brown, J.M. Tirapazamine: A Hypoxia-Activated Topoisomerase II Poison. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 1916–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Marcu, L.; Olver, I. Tirapazamine: From Bench to Clinical Trials. CCP 2006, 1, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.R.; Hay, M.P. Targeting Hypoxia in Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; George, T.J.; Ben-Josef, E.; Bradley, J.; Choe, K.S.; Edelman, M.J.; Guha, C.; Krishnan, S.; Lawrence, T.S.; Le, Q.-T.; et al. Opportunities and Challenges in the Era of Molecularly Targeted Agents and Radiation Therapy. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirschhaeuser, F.; Menne, H.; Dittfeld, C.; West, J.; Mueller-Klieser, W.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A. Multicellular Tumor Spheroids: An Underestimated Tool Is Catching up Again. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 148, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, R.H.; Kurtcuoglu, V.; Scholz, C.C.; Marti, H.H.; Hoogewijs, D. Frequently Asked Questions in Hypoxia Research. Hypoxia 2015, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Yotnda, P. Induction and Testing of Hypoxia in Cell Culture. J. Vis. Exp. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousset, N.; Monet, F.; Gervais, T. Simulation-Assisted Design of Microfluidic Sample Traps for Optimal Trapping and Culture of Non-Adherent Single Cells, Tissues, and Spheroids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, B.; Lafontaine, J.; Bavoux, M.; Zerouali, K.; Glory, A.; Ahanj, M.; Carrier, J.-F.; Gervais, T.; Wong, P. On-Chip Combined Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy Testing on Soft-Tissue Sarcoma Spheroids to Study Cell Death Using Flow Cytometry and Clonogenic Assay. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavoux, M.; Kamio, Y.; Vigneux-Foley, E.; Lafontaine, J.; Najyb, O.; Refet-Mollof, E.; Carrier, J.-F.; Gervais, T.; Wong, P. X-Ray on Chip: Quantifying Therapeutic Synergies between Radiotherapy and Anticancer Drugs Using Soft Tissue Sarcoma Tumor Spheroids. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 157, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, J.A.; Graeser, R.; de Hoogt, R.; Vidic, S.; Brito, C.; Gutekunst, M.; van der Kuip, H. IMI PREDECT consortium Three-Dimensional Models of Cancer for Pharmacology and Cancer Cell Biology: Capturing Tumor Complexity in Vitro/Ex Vivo. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marimuthu, M.; Rousset, N.; St-Georges-Robillard, A.; Lateef, M.A.; Ferland, M.; Mes-Masson, A.-M.; Gervais, T. Multi-Size Spheroid Formation Using Microfluidic Funnels. Lab. Chip. 2018, 18, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafontaine, J.; Cardin, G.B.; Malaquin, N.; Boisvert, J.-S.; Rodier, F.; Wong, P. Senolytic Targeting of Bcl-2 Anti-Apoptotic Family Increases Cell Death in Irradiated Sarcoma Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffle, S.; Hegde, R.S. Modeling Tumor Cell Adaptations to Hypoxia in Multicellular Tumor Spheroids. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenhizer, D.; Dean, T.; D’Arcangelo, E.; McGuigan, A.P. The Current Landscape of 3D In Vitro Tumor Models: What Cancer Hallmarks Are Accessible for Drug Discovery? Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, J.; Seidel, C.; Ebner, R.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A. Spheroid-Based Drug Screen: Considerations and Practical Approach. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, D.R.; Kelly, C.; Bloch, K.; Partridge, M. A Method for Estimating the Oxygen Consumption Rate in Multicellular Tumour Spheroids. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20131124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- T47D Cell Line Spheroid Generation and Characterization for HT Assays. Thermo Fisher Scientific: Carlsbad, CA, USA; Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/ca/en/home/references/protocols/cell-culture/3-d-cell-culture-protocol/t47d-cell-line-spheroid-generation.html (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Brown, J.M. The Hypoxic Cell: A Target for Selective Cancer Therapy—Eighteenth Bruce F. Cain Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5863–5870. [Google Scholar]
- Michl, J.; Park, K.C.; Swietach, P. Evidence-Based Guidelines for Controlling PH in Mammalian Live-Cell Culture Systems. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vordermark, D.; Brown, J.M. Endogenous Markers of TumorHypoxia. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2003, 179, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, T.-M.; Eisinger-Mathason, T.S.K.; Zhang, A.Y.; Schmidt, B.; Karl, D.L.; Nakazawa, M.S.; Park, P.J.; Simon, M.C.; et al. Overcoming Evasive Resistance from Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor a Inhibition in Sarcomas by Genetic or Pharmacologic Targeting of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doe, M.R.; Ascano, J.; Kaur, M.; Cole, M.D. Myc Post-Transcriptionally Induces HIF1 Protein and Target Gene Expression in Normal and Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the CBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The CBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, K.; Pierce, S.E.; Li, A.; Spees, K.; Anderson, G.R.; Seoane, J.A.; Lo, Y.-H.; Dubreuil, M.; Olivas, M.; Kamber, R.A.; et al. CRISPR Screens in Cancer Spheroids Identify 3D Growth-Specific Vulnerabilities. Nature 2020, 580, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluz, S.; Kaluzová, M.; Liao, S.-Y.; Lerman, M.; Stanbridge, E.J. Transcriptional Control of the Tumor- and Hypoxia-Marker Carbonic Anhydrase 9: A One Transcription Factor (HIF-1) Show? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1795, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIntyre, A.; Patiar, S.; Wigfield, S.; Li, J.; Ledaki, I.; Turley, H.; Leek, R.; Snell, C.; Gatter, K.; Sly, W.S.; et al. Carbonic Anhydrase IX Promotes Tumour Growth and Necrosis in Vivo and Inhibition Enhances Anti-VEGF Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olive, P.L.; Aquino-Parsons, C.; MacPhail, S.H.; Liao, S.Y.; Raleigh, J.A.; Lerman, M.I.; Stanbridge, E.J. Carbonic Anhydrase 9 as an Endogenous Marker for Hypoxic Cells in Cervical Cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8924–8929. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, C.; Meehan, J.; Gray, M.; Kunkler, I.H.; Langdon, S.P.; Argyle, D.J. Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CAIX), Cancer, and Radiation Responsiveness. Metabolites 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muriel López, C.; Esteban, E.; Berros, J.P.; Pardo, P.; Astudillo, A.; Izquierdo, M.; Crespo, G.; Sanmamed, M.; Fonseca, P.J.; Martínez-Camblor, P. Prognostic Factors in Patients With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2012, 10, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafreshi, N.K.; Lloyd, M.C.; Proemsey, J.B.; Bui, M.M.; Kim, J.; Gillies, R.J.; Morse, D.L. Evaluation of CAIX and CAXII Expression in Breast Cancer at Varied O2 Levels: CAIX Is the Superior Surrogate Imaging Biomarker of Tumor Hypoxia. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Baia, G.S.; Smith, J.S.; McDermott, M.W.; Bollen, A.W.; VandenBerg, S.R.; Lamborn, K.R.; Lal, A. Expression of the Hypoxia Marker Carbonic Anhydrase 9 Is Associated with Anaplastic Phenotypes in Meningiomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, K.H.; Diaz-Gonzalez, J.A.; Russell, J.; Chen, Q.; Burgman, P.; Li, X.-F.; Ling, C.C. Detecting Changes in Tumor Hypoxia with Carbonic Anhydrase IX and Pimonidazole. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheta, E.A.; Trout, H.; Gildea, J.J.; Harding, M.A.; Theodorescu, D. Cell Density Mediated Pericellular Hypoxia Leads to Induction of HIF-1α via Nitric Oxide and Ras/MAP Kinase Mediated Signaling Pathways. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7624–7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papandreou, I.; Cairns, R.A.; Fontana, L.; Lim, A.L.; Denko, N.C. HIF-1 Mediates Adaptation to Hypoxia by Actively Downregulating Mitochondrial Oxygen Consumption. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, F.; Deng, X.; Wen, B.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Xing, L.; Minami, A.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zanzonico, P.B.; et al. Noninvasive Molecular Imaging of Hypoxia in Human Xenografts: Comparing Hypoxia-Induced Gene Expression with Endogenous and Exogenous Hypoxia Markers. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8597–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sørensen, B.S.; Hao, J.; Overgaard, J.; Vorum, H.; Honoré, B.; Alsner, J.; Horsman, M.R. Influence of Oxygen Concentration and PH on Expression of Hypoxia Induced Genes. Radiother. Oncol. 2005, 76, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Höckel, M.; Mayer, A. Detection and Characterization of Tumor Hypoxia Using PO2 Histography. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2007, 9, 1221–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerk, D.G. Measuring Tissue PO2 with Microelectrodes. In Methods in Enzymology; Oxygen Sensing; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 381, pp. 665–690. [Google Scholar]
- Denny, W.A.; Wilson, W.R. Tirapazamine: A Bioreductive Anticancer Drug That Exploits Tumour Hypoxia. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.B.; Williamson, S.K. Tirapazamine: A Novel Agent Targeting Hypoxic Tumor Cells. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, F.W.; Wouters, B.G.; Wilson, W.R. Hypoxia-Activated Prodrugs: Paths Forward in the Era of Personalised Medicine. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKeown, S.R. Defining Normoxia, Physoxia and Hypoxia in Tumours—Implications for Treatment Response. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luoto, K.R.; Kumareswaran, R.; Bristow, R.G. Tumor Hypoxia as a Driving Force in Genetic Instability. Genome Integr. 2013, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olive, P.L.; Banáth, J.P.; Sinnott, L.T. Phosphorylated Histone H2AX in Spheroids, Tumors, and Tissues of Mice Exposed to Etoposide and 3-Amino-1,2,4-Benzotriazine-1,3-Dioxide. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5363–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumareswaran, R.; Ludkovski, O.; Meng, A.; Sykes, J.; Pintilie, M.; Bristow, R.G. Chronic Hypoxia Compromises Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks to Drive Genetic Instability. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wardman, P. Chemical Radiosensitizers for Use in Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 19, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, I.N.; Thomas, M.; Calder, E.D.D.; Conway, S.J.; Hammond, E.M. Clinical Advances of Hypoxia-Activated Prodrugs in Combination With Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Spheroids | |
|---|---|
| SKLMS1 jumbo | 3.65 × 10−2 |
| STS117 jumbo | 4.07 × 10−2 |
| SKLMS1 small | 2.61 × 10−2 |
| STS117 small | 2.33 × 10−2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Refet-Mollof, E.; Najyb, O.; Chermat, R.; Glory, A.; Lafontaine, J.; Wong, P.; Gervais, T. Hypoxic Jumbo Spheroids On-A-Chip (HOnAChip): Insights into Treatment Efficacy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164046
Refet-Mollof E, Najyb O, Chermat R, Glory A, Lafontaine J, Wong P, Gervais T. Hypoxic Jumbo Spheroids On-A-Chip (HOnAChip): Insights into Treatment Efficacy. Cancers. 2021; 13(16):4046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164046
Chicago/Turabian StyleRefet-Mollof, Elena, Ouafa Najyb, Rodin Chermat, Audrey Glory, Julie Lafontaine, Philip Wong, and Thomas Gervais. 2021. "Hypoxic Jumbo Spheroids On-A-Chip (HOnAChip): Insights into Treatment Efficacy" Cancers 13, no. 16: 4046. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13164046






