Resistin Induces LIN28A-Mediated Let-7a Repression in Breast Cancer Cells Leading to IL-6 and STAT3 Upregulation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Antibodies, microRNAs, and siRNAs
2.3. Treatment and Transfection
2.4. Total RNA Isolation and Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.5. Cell Growth Assay
2.6. Plating Efficiency Assay
2.7. Sphere Formation Assay
2.8. Protein Extraction and Immunoblot Analyses
2.9. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis
2.10. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.11. Dual-Luciferase 3′ UTR-Reporter Assay
2.12. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
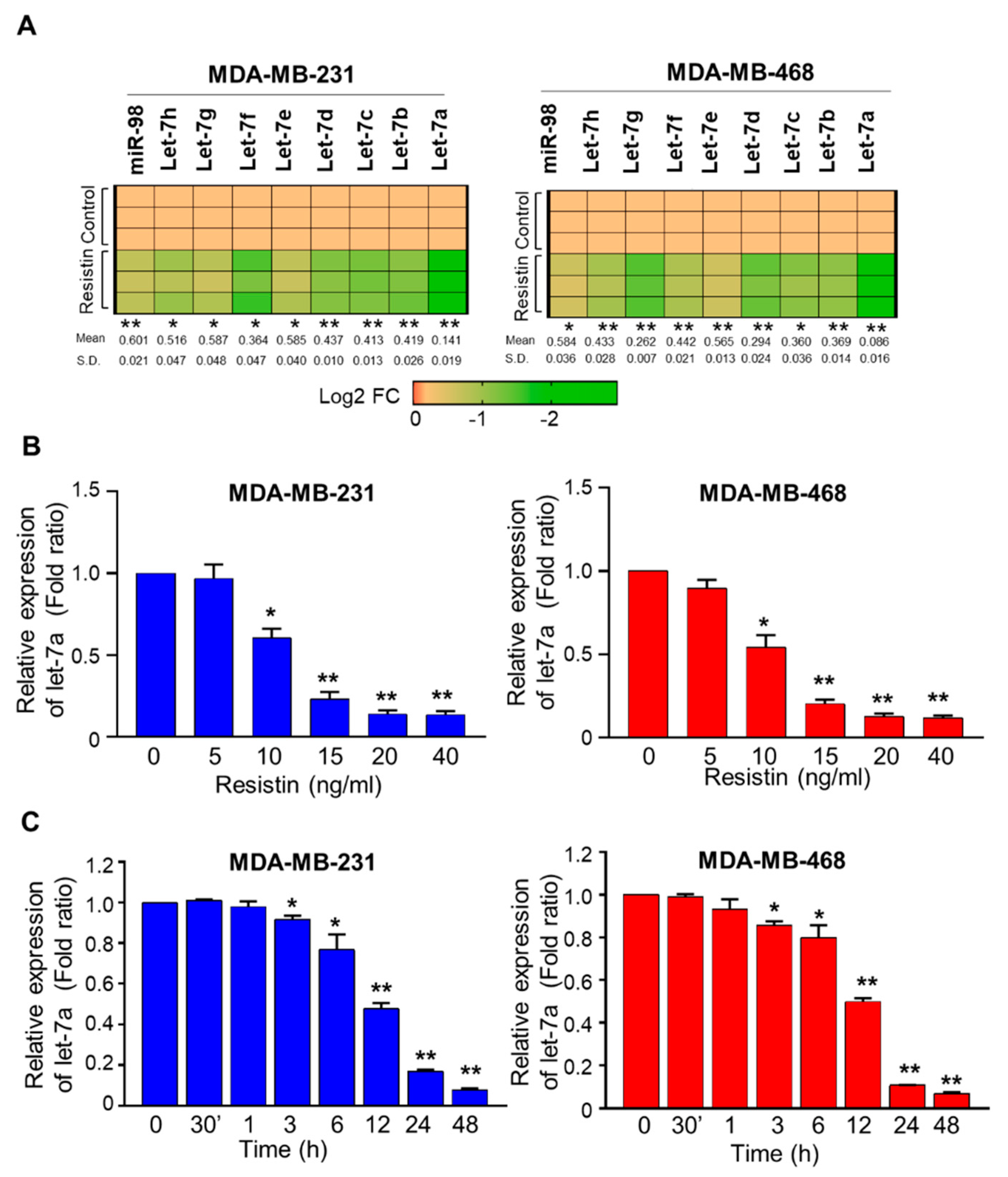
3.1. Resistin Downregulates the Expression of Let-7a in Breast Cancer Cells
3.2. Suppression of Let-7a by Resistin in Breast Cancer Cells Is Mediated through LIN28A
3.3. Let-7a Restoration or Silencing of LIN28A Abrogates Resistin-Induced Growth, Clonogenic Survival, and Sphere-Forming Ability of Breast Cancer
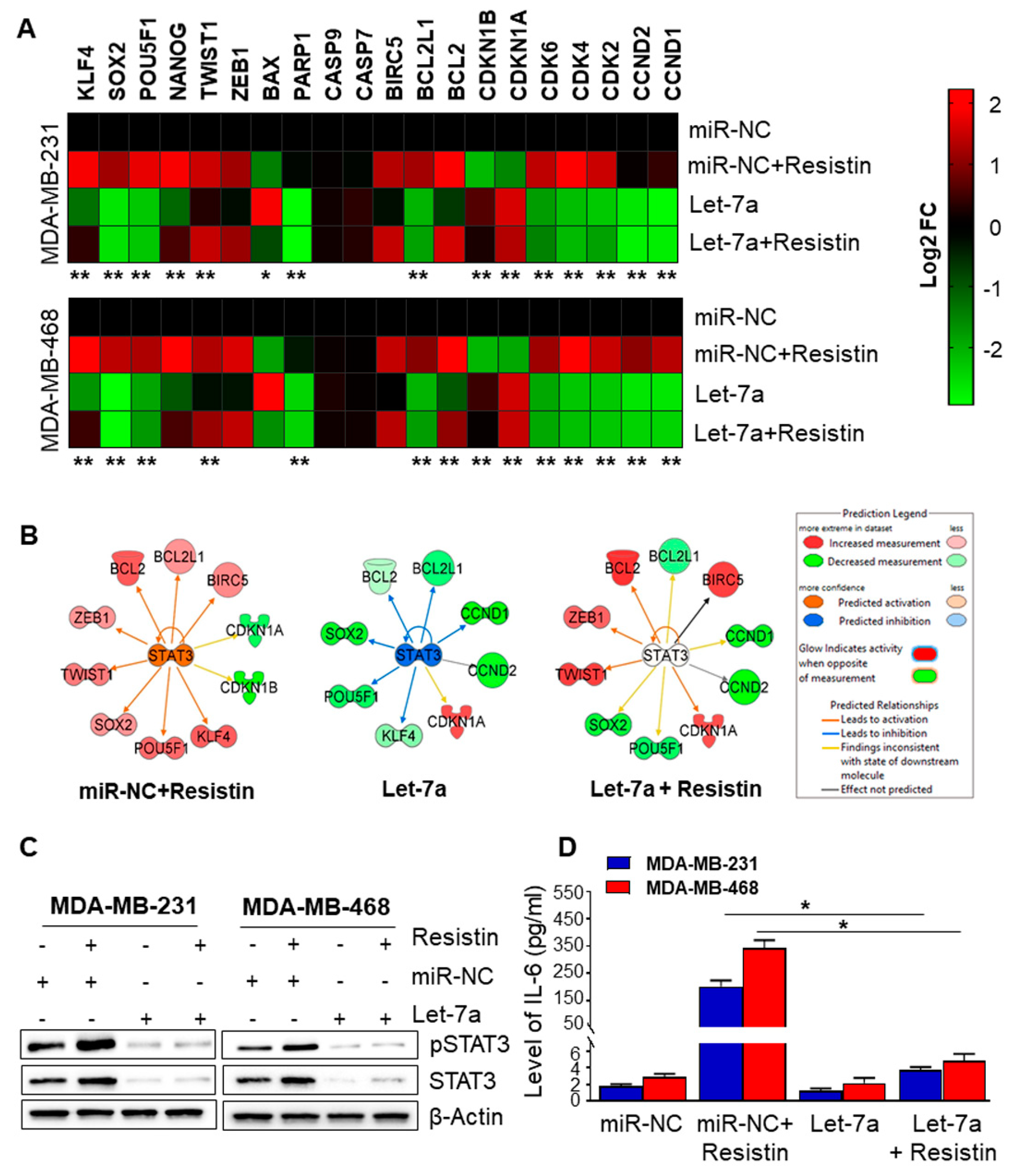
3.4. Let-7a Downregulation Caused by Resistin Treatment Is Associated with Upregulation of STAT3 and IL-6 in Breast Cancer Cells
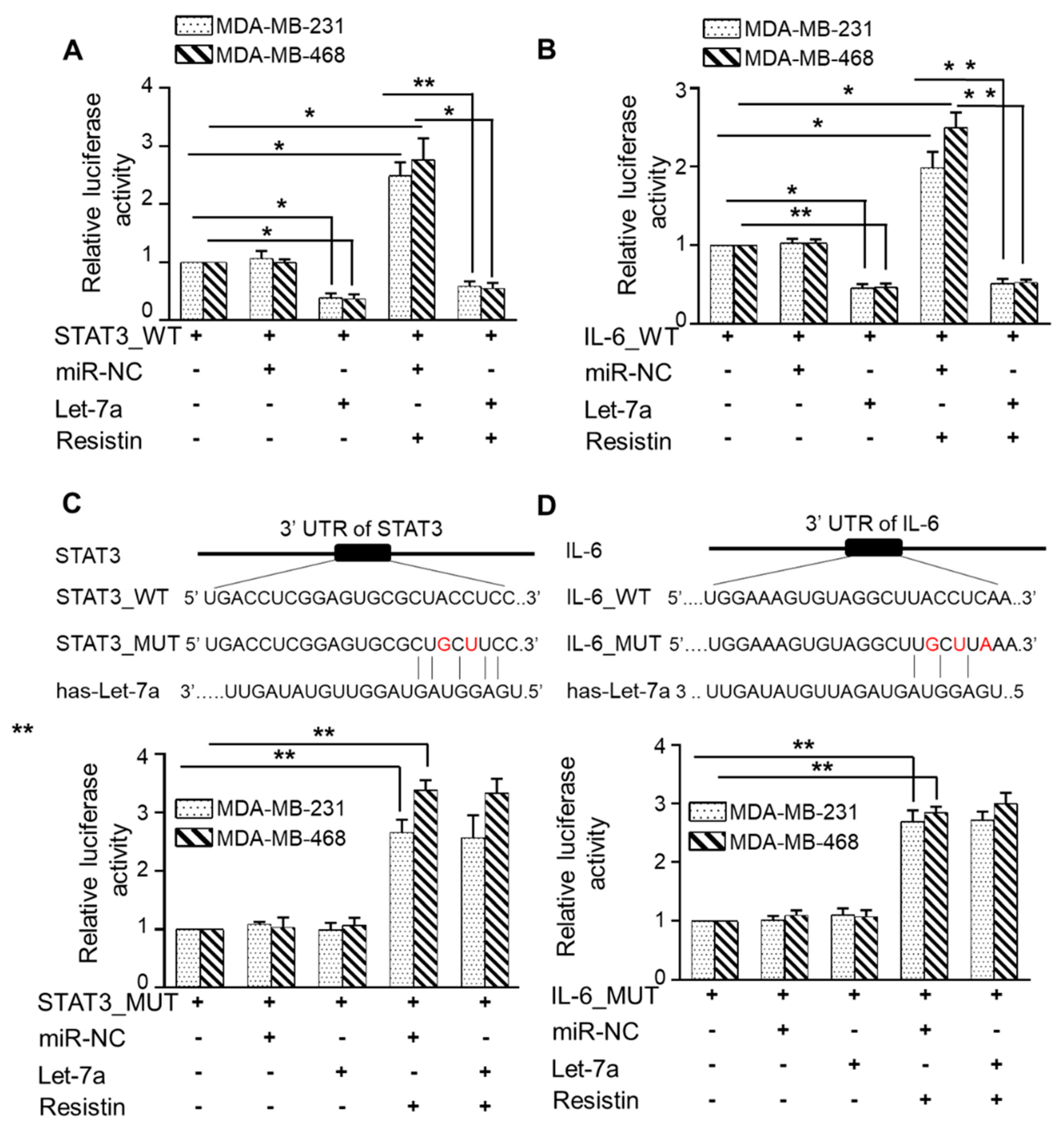
3.5. Let-7a Suppresses Resistin-Induced STAT3 and IL-6 Expression by Directly Targeting Its 3′UTR
4. Discussion
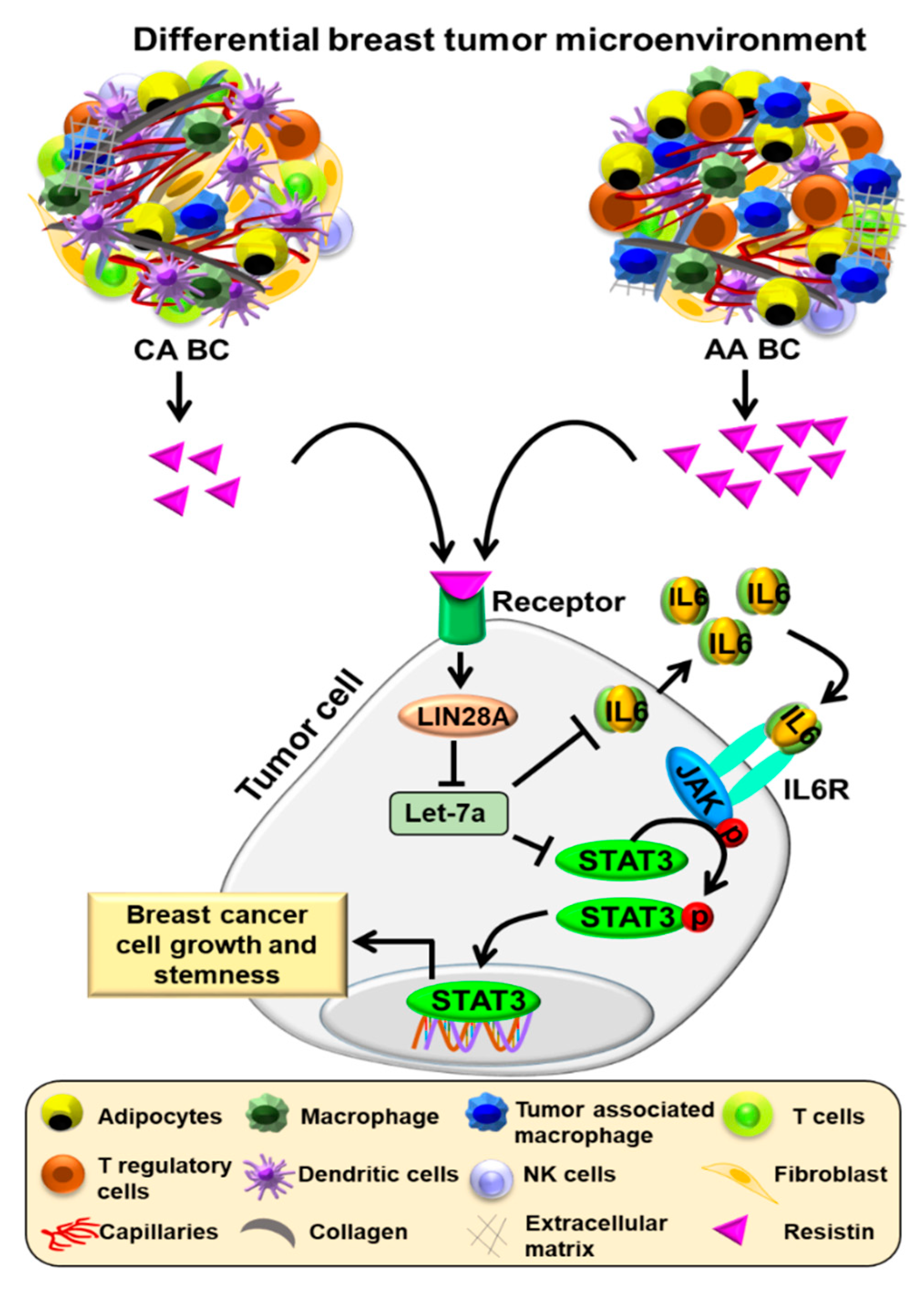
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, S.K.; Azim, S.; Ahmad, A.; Zubair, H.; Tyagi, N.; Srivastava, S.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, S.; Rocconi, R.P.; Singh, A.P. Biological basis of cancer health disparities: Resources and challenges for research. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, F.; Thompson, E. Disparities in breast cancer stage at diagnosis: Importance of race, poverty, and age. J. Health Dispar. Res. Pract. 2017, 10, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lytle, J.R.; Yario, T.A.; Steitz, J.A. Target mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the 5’ UTR as in the 3’ UTR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9667–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.; Mo, Y.Y. Role of microRNAs in breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, J.; Bartschat, S.; Wintsche, A.; Otto, C.; Students of the Bioinformatics Computer Lab; Stadler, P.F. Evolution of the let-7 microRNA family. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Han, S.; Kwon, C.S.; Lee, D. Biogenesis and regulation of the let-7 miRNAs and their functional implications. Protein Cell 2016, 7, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasquinelli, A.E.; Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.; Martindale, M.Q.; Kuroda, M.I.; Maller, B.; Hayward, D.C.; Ball, E.E.; Degnan, B.; Muller, P.; et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 2000, 408, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, I.; Joo, C.; Cho, J.; Ha, M.; Han, J.; Kim, V.N. Lin28 mediates the terminal uridylation of let-7 precursor MicroRNA. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, H.; Han, K.; Kim, S.C.; Choi, Y.; Park, S.W.; Bak, G.; Lee, Y.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, T.K.; et al. SET7/9 methylation of the pluripotency factor LIN28A is a nucleolar localization mechanism that blocks let-7 biogenesis in human ESCs. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newman, M.A.; Thomson, J.M.; Hammond, S.M. Lin-28 interaction with the Let-7 precursor loop mediates regulated microRNA processing. RNA 2008, 14, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piskounova, E.; Polytarchou, C.; Thornton, J.E.; LaPierre, R.J.; Pothoulakis, C.; Hagan, J.P.; Iliopoulos, D.; Gregory, R.I. Lin28A and Lin28B inhibit let-7 microRNA biogenesis by distinct mechanisms. Cell 2011, 147, 1066–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iorio, M.V.; Casalini, P.; Piovan, C.; Braccioli, L.; Tagliabue, E. Breast cancer and microRNAs: Therapeutic impact. Breast 2011, 20 (Suppl. S3), S63–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimono, Y.; Mukohyama, J.; Nakamura, S.; Minami, H. MicroRNA regulation of human breast cancer stem cells. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y. Tumor microenvironment and cancer therapy resistance. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charan, M.; Verma, A.K.; Hussain, S.; Misri, S.; Mishra, S.; Majumder, S.; Ramaswamy, B.; Ahirwar, D.; Ganju, R.K. Molecular and cellular factors associated with racial disparity in breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, A.P.; Tyagi, N.; Marimuthu, S.; Dyess, D.L.; Dal Zotto, V.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. Resistin and interleukin-6 exhibit racially-disparate expression in breast cancer patients, display molecular association and promote growth and aggressiveness of tumor cells through STAT3 activation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11231–11241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Tyagi, N.; Ahmad, A.; Singh, A.P.; Ghadhban, A.A.L.; Dyess, D.L.; Carter, J.E.; Dugger, K.; Singh, S. Emerging evidence for the role of differential tumor microenvironment in breast cancer racial disparity: A closer look at the surroundings. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudan, S.K.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Poosarla, T.; Holliday, N.P.; Dyess, D.L.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, S. Resistin: An inflammatory cytokine with multi-faceted roles in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1874, 188419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, D.; Kant, S.; Pandey, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z. Resistin in metabolism, inflammation, and disease. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Zubair, H.; Bhardwaj, A.; Tyagi, N.; Al-Ghadhban, A.; Singh, A.P.; Dyess, D.L.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. Resistin potentiates chemoresistance and stemness of breast cancer cells: Implications for racially disparate therapeutic outcomes. Cancer Lett. 2017, 396, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.K.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, S.; Arora, S.; Wang, B.; Grizzle, W.E.; Singh, A.P. MicroRNA-150 directly targets MUC4 and suppresses growth and malignant behavior of pancreatic cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, N.; Marimuthu, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, A.P.; McClellan, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. p-21 activated kinase 4 (PAK4) maintains stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells through activation of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zubair, H.; Azim, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; Ahmad, A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Khan, M.A.; Patel, G.K.; Arora, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S.; et al. Glucose metabolism reprogrammed by overexpression of IKKepsilon promotes pancreatic tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7254–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danforth, D.N., Jr. Disparities in breast cancer outcomes between Caucasian and African American women: A model for describing the relationship of biological and nonbiological factors. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturtz, L.A.; Melley, J.; Mamula, K.; Shriver, C.D.; Ellsworth, R.E. Outcome disparities in African American women with triple negative breast cancer: A comparison of epidemiological and molecular factors between African American and Caucasian women with triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elghoroury, E.A.; ElDine, H.G.; Kamel, S.A.; Abdelrahman, A.H.; Mohammed, A.; Kamel, M.M.; Ibrahim, M.H. Evaluation of miRNA-21 and miRNA Let-7 as prognostic markers in patients with breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e721–e726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Ding, Y.; Tu, T.; Zhou, F.; Qi, W.; Chen, H.; Sun, X. Let-7a inhibits growth and migration of breast cancer cells by targeting HMGA1. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wielgos, M.E.; Rajbhandari, R.; Cooper, T.S.; Wei, S.; Nozell, S.; Yang, E.S. Let-7 Status is crucial for PARP1 expression in HER2-overexpressing breast tumors. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enriquez, V.A.; Cleys, E.R.; Da Silveira, J.C.; Spillman, M.A.; Winger, Q.A.; Bouma, G.J. High LIN28A expressing ovarian cancer cells secrete exosomes that induce invasion and migration in HEK293 cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 701390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, M.; Yang, X.; Shen, R.; Ni, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, P.; Chen, M.; Lu, X.; et al. High LIN28A and PLK4 coexpression is associated with poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 5327–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamano, R.; Miyata, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Sugimura, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kurokawa, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Takiguchi, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Mori, M.; et al. High expression of Lin28 is associated with tumour aggressiveness and poor prognosis of patients in oesophagus cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, J.; Niu, Y. Lin28A and androgen receptor expression in ER-/Her2+ breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 156, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzeau, J.; Menezes, M.R.; Cao, S.; Hagan, J.P. The LIN28/let-7 pathway in cancer. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viswanathan, S.R.; Daley, G.Q.; Gregory, R.I. Selective blockade of microRNA processing by Lin28. Science 2008, 320, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, T.C.; Zeitels, L.R.; Hwang, H.W.; Chivukula, R.R.; Wentzel, E.A.; Dews, M.; Jung, J.; Gao, P.; Dang, C.V.; Beer, M.A.; et al. Lin-28B transactivation is necessary for Myc-mediated let-7 repression and proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3384–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cimadamore, F.; Amador-Arjona, A.; Chen, C.; Huang, C.T.; Terskikh, A.V. SOX2-LIN28/let-7 pathway regulates proliferation and neurogenesis in neural precursors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3017–E3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Hirsch, H.A.; Struhl, K. An epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell 2009, 139, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silswal, N.; Singh, A.K.; Aruna, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, S.; Ehtesham, N.Z. Human resistin stimulates the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-12 in macrophages by NF-kappaB-dependent pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitzsch, C.; Tyutyunnykova, A.; Pantel, K.; Dubrovska, A. Cancer stem cells: The root of tumor recurrence and metastases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 44, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudas, J.; Skvortsov, S.; Ganswindt, U.; Riechelmann, H.; Skvortsova, I. Therapy resistance mediated by cancer stem cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.M.; Zhang, J.G.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q. Targeting cancer stem cells for reversing therapy resistance: Mechanism, signaling, and prospective agents. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhao, W.; Wang, J.; Seifer, B.J.; Ye, C.; Chen, Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Oncogenic mechanisms of Lin28 in breast cancer: New functions and therapeutic opportunities. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25721–25735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Wang, W.; Meng, X.X.; Du, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.Z.; Zhou, B.H.; Fu, Z.H. Let-7 inhibits self-renewal of hepatocellular cancer stem-like cells through regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the Wnt signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Li, S.; Jia, W.; Deng, H.; Chen, K.; Zhu, L.; Yu, F.; Su, F. Reduced Let-7a Is associated with chemoresistance in primary breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.H.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Role of STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell. Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.D. STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer: A systematic review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Zubair, H.; Khan, M.A.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, S. Resistin Induces LIN28A-Mediated Let-7a Repression in Breast Cancer Cells Leading to IL-6 and STAT3 Upregulation. Cancers 2021, 13, 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184498
Deshmukh SK, Srivastava SK, Zubair H, Khan MA, Singh AP, Singh S. Resistin Induces LIN28A-Mediated Let-7a Repression in Breast Cancer Cells Leading to IL-6 and STAT3 Upregulation. Cancers. 2021; 13(18):4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184498
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeshmukh, Sachin Kumar, Sanjeev Kumar Srivastava, Haseeb Zubair, Mohammad Aslam Khan, Ajay Pratap Singh, and Seema Singh. 2021. "Resistin Induces LIN28A-Mediated Let-7a Repression in Breast Cancer Cells Leading to IL-6 and STAT3 Upregulation" Cancers 13, no. 18: 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184498
APA StyleDeshmukh, S. K., Srivastava, S. K., Zubair, H., Khan, M. A., Singh, A. P., & Singh, S. (2021). Resistin Induces LIN28A-Mediated Let-7a Repression in Breast Cancer Cells Leading to IL-6 and STAT3 Upregulation. Cancers, 13(18), 4498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184498






