Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Cancer Invasion, Evasion and Metastasis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Neutrophils and NETs
2. NETs—Friend or Foe?
2.1. Heterogeneity of Neutrophils
2.2. Tumor-Infiltrating Neutrophils
3. NETs Are Present in Tumor Microenvironment
4. Circulating NET Markers in Cancer Patients
5. NETs Fuel Cancer Progression and Indicate Poor Prognosis
5.1. How Do NETs Awaken Dormant Cancer Cells?
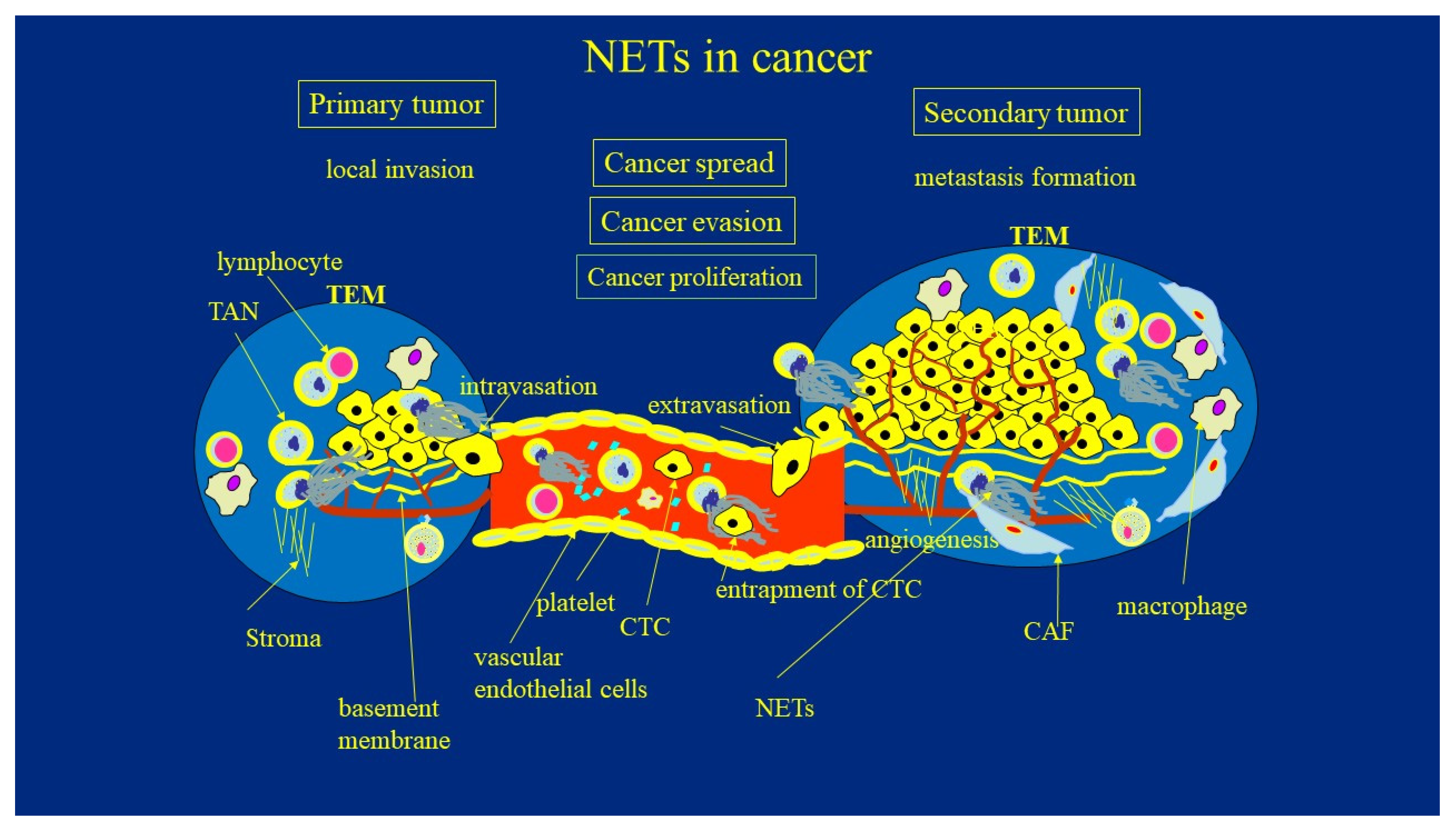
5.2. How NETs Promote Cancer Invasion, Evasion, Its Spread, and Metastasis Formation
5.3. NETs Supports the Cancer Evasion Strategies
5.4. NETs Enhance Invasion Capacity of Cancer Cells
5.5. NETs Enhance Systemic Spread and Tumor-Associated Angiogenesis
5.6. How NETs and Tumor Communicate
5.7. NETs in the Formation of Metastatic Niche
5.8. NETs Is Physically Blocking T-Cell Infiltration to the TME
6. Potential Anti-NETs Therapy of Cancer
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, T.S.; Ji, A.L.; Ji, X.Y.; Li, Y.Z. Neutrophils and Immunity: From Bactericidal Action to Being Conquered. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 9671604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruchniak, M.P.; Demkow, U. Potent NETosis inducers do not show synergistic effects in vitro. Cent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 44, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manda-Handzlik, A.; Bystrzycka, W.; Cieloch, A.; Glodkowska-Mrowka, E.; Jankowska-Steifer, E.; Heropolitanska-Pliszka, E.; Skrobot, A.; Muchowicz, A.; Ciepiela, O.; Wachowska, M.; et al. Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite trigger and enhance release of neutrophil extracellular traps. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 3059–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manda-Handzlik, A.; Fiok, K.; Cieloch, A.; Heropolitanska-Pliszka, E.; Demkow, U. Convolutional Neural Networks-Based Image Analysis for the Detection and Quantification of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Cells 2020, 9, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leliefeld, P.H.C.; Koenderman, L.; Pillay, J. How Neutrophils Shape Adaptive Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pruchniak, M.P.; Ostafin, M.; Wachowska, M.; Jakubaszek, M.; Kwiatkowska, B.; Olesinska, M.; Zycinska, K.; Demkow, U. Neutrophil extracellular traps generation and degradation in patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity 2019, 52, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, R.C. COVID-19-associated vasculitis and vasculopathy. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 50, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Moreno, D.; Adrover, J.M.; Hidalgo, A. Neutrophils as effectors of vascular inflammation. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Velten, L.; Haas, S.F.; Raffel, S.; Blaszkiewicz, S.; Islam, S.; Hennig, B.P.; Hirche, C.; Lutz, C.; Buss, E.C.; Nowak, D.; et al. Human haematopoietic stem cell lineage commitment is a continuous process. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bremnes, R.M.; Dønnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Al-Shibli, K.; Andersen, S.; Sirera, R.; Camps, C.; Marinez, I.; Busund, L.T. The Role of Tumor Stroma in Cancer Progression and Prognosis: Emphasis on Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts and Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishalian, I.; Granot, Z.; Fridlender, Z.G. The diversity of circulating neutrophils in cancer. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masucci, M.T.; Minopoli, M.; Carriero, M.V. Tumor Associated Neutrophils. Their Role in Tumorigenesis, Metastasis, Prognosis and Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y. Different Faces for Different Places: Heterogeneity of Neutrophil Phenotype and Function. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 8016254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Lawler, S.; Kim, Y. Role of neutrophil extracellular traps in regulation of lung cancer invasion and metastasis: Structural insights from a computational model. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaul, M.E.; Fridlender, Z.G. Cancer related circulating and tumor-associated neutrophils—Subtypes, sources and function. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 4316–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczerba, B.M.; Castro-Giner, F.; Vetter, M.; Krol, I.; Gkountela, S.; Landin, J.; Scheidmann, M.C.; Donato, C.; Scherrer, R.; Singer, J.; et al. Neutrophils escort circulating tumour cells to enable cell cycle progression. Nature 2019, 566, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wculek, S.K.; Malanchi, I. Neutrophils support lung colonization of metastasis-initiating breast cancer cells. Nature 2015, 528, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berger-Achituv, S.; Brinkmann, V.; Abed, U.A.; Kühn, L.I.; Ben-Ezra, J.; Elhasid, R.; Zychlinsky, A. A proposed role for neutrophil extracellular traps in cancer immunoediting. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demers, M.; Krause, D.S.; Schatzberg, D.; Martinod, K.; Voorhees, J.R.; Fuchs, T.A.; Scadden, D.T.; Wagner, D.D. Cancers predispose neutrophils to release extracellular DNA traps that contribute to cancer-associated thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13076–13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demers, M.; Wagner, D.D. Neutrophil extracellular traps: A new link to cancer-associated thrombosis and potential implications for tumor progression. Oncoimmunology 2013, 2, e22946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, M.; Yang, L.; Bi, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Yang, H.; Liu, P.; Li, Z.; Xia, Y.; Jiang, W. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induced by IL8 Promote Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolle, F.; Umansky, V.; Utikal, J.; Kreis, S.; Bréchard, S. Neutrophils in Tumorigenesis: Missing Targets for Successful Next Generation Cancer Therapies? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Femel, J.; Dimberg, A.; Olsson, A.K. Neutrophil extracellular traps accumulate in peripheral blood vessels and compromise organ function in tumor-bearing animals. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2653–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gan, T.; Zhou, J.; Hu, F.; Hao, N.; Yuan, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M. Extracellular RNAs from lung cancer cells activate epithelial cells and induce neutrophil extracellular traps. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitroulis, I.; Kambas, K.; Chrysanthopoulou, A.; Skendros, P.; Apostolidou, E.; Kourtzelis, I.; Drosos, G.I.; Boumpas, D.T.; Ritis, K. Neutrophil extracellular trap formation is associated with IL-1beta and autophagy-related signaling in gout. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Joshi, M.B.; Philippova, M.; Erne, P.; Hasler, P.; Hahn, S.; Resink, T.J. Activated endothelial cells induce neutrophil extracellular traps and are susceptible to NETosis-mediated cell death. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3193–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tadie, J.M.; Bae, H.B.; Jiang, S.; Park, D.W.; Bell, C.P.; Yang, H.; Pittet, J.F.; Tracey, K.; Thannickal, V.J.; Abraham, E.; et al. HMGB1 promotes neutrophil extracellular trap formation through interactions with Toll-like receptor 4. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2013, 304, L342–L349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, H.; Havervall, S.; Rosell, A.; Aguilera, K.; Parv, K.; von Meijenfeldt, F.A.; Lisman, T.; Mackman, N.; Thålin, C.; Phillipson, M. Circulating Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are of Prognostic Value in Patients with COVID-19. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oklu, R.; Sheth, R.A.; Wong, K.H.K.; Jahromi, A.H.; Albadawi, H. Neutrophil extracellular traps are increased in cancer patients but does not associate with venous thrombosis. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 7, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.D.; Gu, J.-Y.; Jung, H.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.K. Contact system activation and neutrophil extracellular trap markers: Risk factors for portal vein thrombosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 25, 1076029618825310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosell, A.; Aguilera, K.; Hisada, Y.; Schmedes, C.; Mackman, N.; Wallén, H.; Lundström, S.; Thålin, C. Prognostic value of circulating markers of neutrophil activation, neutrophil extracellular traps, coagulation and fibrinolysis in patients with terminal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saffarzadeh, M.; Juenemann, C.; Queisser, M.A.; Lochnit, G.; Barreto, G.; Galuska, S.P.; Lohmeyer, J.; Preissner, K.T. Neutrophil extracellular traps directly induce epithelial and endothelial cell death: A predominant role of histones. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e0032366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, J.; Hamidi, A.; Olsson, A.-K. Platelets, NETs and cancer. Thromb. Res. 2018, 164, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schedel, F.; Mayer-Hain, S.; Pappelbaum, K.I.; Metze, D.; Stock, M.; Goerge, T.; Loser, K.; Sunderkötter, C.; Luger, T.A.; Weishaupt, C. Evidence and impact of neutrophil extracellular traps in malignant melanoma. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2020, 33, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, J.J.R.; Hendrickse, C.; Gao-Smith, F.; Thickett, D.R. Neutrophil extracellular trap production in patients with colorectal cancer in vitro. Int. J. Inflam. 2017, 2017, 4915062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohme, S.; Yazdani, H.O.; Al-Khafaji, A.B.; Chidi, A.P.; Loughran, P.; Mowen, K.; Wang, Y.; Simmons, R.L.; Huang, H.; Tsung, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote the development and progression of liver metastases after surgical stress. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1367–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yazdani, H.O.; Roy, E.; Comerci, A.J.; van der Windt, D.J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Loughran, P.; Shiva, S.; Geller, D.A.; Bartlett, D.L.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps drive mitochondrial homeostasis in tumors to augment growth. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5626–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanamaru, R.; Ohzawa, H.; Miyato, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Haruta, H.; Kurashina, K.; Saito, S.; Hosoya, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yamashita, H.; et al. Low density neutrophils (LDN) in postoperative abdominal cavity assist the peritoneal recurrence through the production of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thålin, C.; Lundström, S.; Seignez, C.; Daleskog, M.; Lundström, A.; Henriksson, P.; Helleday, T.; Phillipson, M.; Wallén, H.; Demers, M. Citrullinated histone H3 as a novel prognostic blood marker in patients with advanced cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.G.; Monteiro, R.Q. Activation of blood coagulation in cancer: Implications for tumour progression. Biosci. Rep. 2013, 33, e00064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Gu, J.; Kim, J.-E.; Nam, Y.; Song, J.W.; Kim, H.K. Cancer cell-induced neutrophil extracellular traps promote both hypercoagulability and cancer progression. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gervaso, L.; Dave, H.; Khorana, A.A. Venous and Arterial Thromboembolism in Patients with Cancer. JACC CardioOncol. 2021, 3, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, B.A.; Murthy, P.; Miller-Ocuin, J.; Doerfler, W.R.; Ellis, J.T.; Liang, X.; Ross, M.A.; Wallace, C.T.; Sperry, J.L.; Lotze, M.T.; et al. Chloroquine reduces hypercoagulability in pancreatic cancer through inhibition of neutrophil extracellular traps. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phan, T.G.; Croucher, P.I. The dormant cancer cell life cycle. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrengues, J.; Shields, M.A.; Ng, D.; Park, C.G.; Ambrico, A.; Poindexter, M.E.; Upadhyay, P.; Uyeminami, D.L.; Pommier, A.; Kuttner, V.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps produced during inflammation awaken dormant cancer cells in mice. Science 2018, 361, eaao4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orgaz, J.; Pandya, P.; Dalmeida, R.; Karagiannis, P.; Sanchez-Laorden, B.; Viros, A.; Albrengues, J.; Nestle, F.O.; Ridley, A.J.; Gaggioli, C.; et al. Diverse matrix metalloproteinase functions regulate cancer amoeboid migration. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sargiannidou, I.; Qiu, C.; Tuszynski, G.P. Mechanisms of thrombospondin-1-mediated metastasis and angiogenesis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2004, 30, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Moreno, V.; Balkwill, F.R. Mets and NETs: The Awakening Force. Immunity 2018, 49, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoenicke, L.; Zender, L. Immune surveillance of senescent cells–biological significance in cancer- and non-cancer pathologies. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1123–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shankaran, V.; Ikeda, H.; Bruce, A.T.; White, J.M.; Swanson, P.E.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. IFNgamma and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature 2001, 410, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitadze, G.; Lettau, M.; Bhat, J.; Wesch, D.; Steinle, A.; Furst, D.; Mytilineos, J.; Kalthoff, H.; Janssen, O.; Oberg, H.H.; et al. Shedding of endogenous MHC class I-related chain molecules A and B from different human tumor entities: Heterogeneous involvement of the a disintegrin and metalloproteases 10 and 17. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotova, K.; Khodayari, N.; Oshins, R.; Aslanidi, G.; Brantly, M.L. Neutrophil elastase promotes macrophage cell adhesion and cytokine production through the integrin-Src kinases pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Fujita, Y.; Kuroda, A.; Menju, T.; Sonobe, M.; Kondo, N.; Torii, I.; Nakano, T.; Lara, P.N.; et al. Trametinib plus 4-methylumbelliferone exhibits antitumor effects by ERK blockade and CD44 downregulation and affects PD-1 and PD-L1 in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Onuma, A.; He, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Genkin, D.; Tetz, G.; Huang, H. and Tsung, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps blockade in combination with PD-1 inhibition in treatment of colorectal cancer metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. 15), e16002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, J.; Morton, J.P.; Sansom, O.J. Neutrophils: Homing in on the myeloid mechanisms of metastasis. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 110, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Abisoye-Ogunniyan, A.; Metcalf, K.J.; Werb, Z. Concepts of extracellular matrix remodelling in tumour progression and metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brostjan, C.; Oehler, R. The role of neutrophil death in chronic inflammation and cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, A.; Monteiro, M.; Barai, A.; Kumar, S.; Sen, S. MMP Proteolytic Activity Regulates Cancer Invasiveness by Modulating Integrins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Wysocki, R.W.; Amoozgar, Z.; Maiorino, L.; Fein, M.R.; Jorns, J.; Schott, A.F.; Kinugasa-Katayama, Y.; Lee, Y.; Won, N.H.; et al. Cancer cells induce metastasis-supporting neutrophil extracellular DNA traps. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 361ra138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, J.; Huang, D.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Chen, F.; et al. DNA of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Promotes Cancer Metastasis via CCDC25. Nature 2020, 583, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Jenne, C.N.; Surewaard, B.G.; Thanabalasuriar, A.; Lee, W.Y.; Sanz, M.J.; Mowen, K.; Opdenakker, G.; Kubes, P. Molecular mechanisms of NET formation and degradation revealed by intravital imaging in the liver vasculature. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Spicer, J.; McDonald, B.; Gowing, S.; Chow, S.; Giannias, B.; Bourdeau, F.; Kubes, P.; Ferri, L. Neutrophil extracellular traps sequester circulating tumor cells and promote metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najmeh, S.; Cools-Lartigue, J.; Rayes, R.F.; Gowing, S.; Vourtzoumis, P.; Bourdeau, F.; Giannias, B.; Berube, J.; Rousseau, S.; Ferri, L.E.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps sequester circulating tumor cells via β1-integrin mediated interactions. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2321–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, S.; Agthe, M.; Eickhoff, S.; Möller, S.; Karsten, C.M.; Borregaard, N.; Solbach, W.; Laskay, T. Secondary necrotic neutrophils release interleukin-16C and macrophage migration inhibitory factor from stores in the cytosol. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, M.; De Rosa, V.; Iommelli, F.; Carriero, M.V.; Terlizzi, C.; Camerlingo, R.; Belli, S.; Fonti, R.; Di Minno, G.; Del Vecchio, S. Neutrophil extracellular traps as an adhesion substrate for different tumor cells expressing RGD-binding integrins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reymond, N.; d’Agua, B.B.; Ridley, A.J. Crossing the endothelial barrier during metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Stolarska, M.; Othmer, H.G. A hybrid model for tumor spheroid growth in vitro I: Theoretical development and early results. Appl. Sci. 2007, 17, 1773–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Kang, H.; Powathil, G.; Kim, H.; Trucu, D.; Lee, W.; Lawler, S.; Chaplain, M. Role of extracellular matrix and microenvironment in regulation of tumor growth and LAR-mediated invasion in glioblastoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Powathil, G.; Kang, H.; Trucu, D.; Kim, H.; Lawler, S.; Chaplain, M. Strategies of eradicating glioma cells: A multi-scale mathematical model with miR-451-AMPK-mTOR control. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Othmer, H.G. A hybrid model of tumor-stromal interactions in breast cancer. Bull. Math. Biol. 2013, 75, 1304–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Lim, S.; Kim, Y. The role of myosin II in glioma invasion: A mathematical model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, A.C.; Mizurini, D.M.; Gomes, T.; Rochael, N.C.; Saraiva, E.M.; Dias, M.S.; Werneck, C.C.; Sielski, M.S.; Vicente, C.P.; Monteiro, R.Q. Tumor-Derived Exosomes Induce the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps: Implications for the Establishment of Cancer-Associated Thrombosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInturff, A.M.; Cody, M.J.; Elliott, E.A.; Glenn, J.W.; Rowley, J.W.; Rondina, M.T.; Yost, C.C. Mammalian target of rapamycin regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation via induction of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Blood 2012, 120, 3118–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yousefi, S.; Simon, D.; Stojkov, D.; Karsonova, A.; Karaulov, A.; Simon, H.U. In vivo evidence for extracellular DNA trap formation. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, C.; Teijeira, A.; Oñate, C.; Pérez, G.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Andueza, M.P.; Alignani, D.; Labiano, S.; Azpilikueta, A.; Rodriguez-Paulete, A.; et al. Tumor-produced interleukin-8 attracts human myeloid-derived suppressor cells and elicits extrusion of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Clin. Cancer 2016, 22, 3924–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paolillo, M.; Schinelli, S. Extracellular Matrix Alterations in Metastatic Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masucci, M.T.; Minopoli, M.; Del Vecchio, S.; Carriero, M.V. The Emerging Role of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Cardoso, K.; Almeida, V.H.; Bagri, K.M.; Rossi, M.I.D.; Mermelstein, C.S.; König, S.; Monteiro, R.Q. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) Promote Pro-Metastatic Phenotype in Human Breast Cancer Cells through Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers 2020, 12, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnov, G.S.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Lakunina, V.A.; Beniaminov, A.D.; Melnikova, N.V.; Dmitriev, A.A. Pan-Cancer Analysis of TCGA Data Revealed Promising Reference Genes for qPCR Normalization. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zha, C.; Meng, X.; Li, L.; Mi, S.; Qian, D.; Li, Z.; Wu, P.; Hu, S.; Zhao, S.; Cai, J.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate the crosstalk between glioma progression and the tumor microenvironment via the HMGB1/RAGE/IL-8 axis. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescangeli, F.; Laura De Angelis, M.; Zeuner, A. COVID-19: A potential driver of immune-mediated breast cancer recurrence? Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolaczkowska, E.; Kubes, P. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillack, K.; Breiden, P.; Martin, R.; Sospedra, M. T Lymphocyte Priming by Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Links Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3150–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilyy, R.; Fedorov, V.; Vovk, V.; Leppkes, M.; Dumych, T.; Chopyak, V.; Schett, G.; Herrmann, M. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Form a Barrier between Necrotic and Viable Areas in Acute Abdominal Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinde-Jadhav, S.; Mansure, J.J.; Rayes, R.F.; Marcq, G.; Ayoub, M.; Skowronski, R.; Kool, R.; Bourdeau, F.; Brimo, F.; Spicer, J.; et al. Role of neutrophil extracellular traps in radiation resistance of invasive bladder cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Melero, I. CXCR1 and CXCR2 Chemokine Receptor Agonists Produced by Tumors Induce Neutrophil Extracellular Traps that Interfere with Immune Cytotoxicity. Immunity 2020, 52, 856–871.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, B.; Kress, H.G. Indirect CB2 receptor and mediator-dependent stimulation of human whole-blood neutrophils by exogenous and endogenous cannabinoids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mabou Tagn, A.; Marino, F.; Legnaro, M.; Luini, A.; Pacchetti, B.; Cosentino, M. A novel Standardized Cannabis sativa L. extract and its constituent cannabidiol inhibit human polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munir, H.; Jones, J.O.; Janowitz, T.; Hoffmann, M.; Euler, M.; Martins, C.P.; Welsh, S.J.; Shields, J.D. Stromal-driven and Amyloid β-dependent induction of neutrophil extracellular traps modulates tumor growth. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzhalin, A.E.; Gordon-Weeks, A.N.; Tognoli, M.L.; Jones, K.; Markelc, B.; Konietzny, R.; Fischer, R.; Muth, A.; O’Neill, E.; Thompson, P.R.; et al. Colorectal cancer liver metastatic growth depends on PAD4-driven citrullination of the extracellular matrix. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lin, C.; Deng, H.; Strnad, J.; Bernabei, L.; Vogl, D.T.; Burke, J.J.; Nefedova, Y. A Novel Peptidylarginine Deiminase 4 (PAD4) Inhibitor BMS-P5 Blocks Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Delays Progression of Multiple Myeloma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Aloe, C.; Wilson, N.; Bozinovski, S. G-CSFR antagonism reduces neutrophilic inflammation during pneumococcal and influenza respiratory infections without compromising clearance. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schenten, V.; Plançon, S.; Jung, N.; Hann, J.; Bueb, J.-L.; Bréchard, S.; Tschirhart, E.J.; Tolle, F. Secretion of the phosphorylated form of S100A9 from neutrophils is essential for the proinflammatory functions of extracellular S100A8/A9. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passey, R.J.; Xu, K.; Hume, D.A.; Geczy, C. S100A8: Emerging functions and regulation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 66, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiratsuka, S.; Watanabe, A.; Sakurai, Y.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Ishibashi, S.; Miyake, K.; Shibuya, M.; Akira, S.; Aburatani, H.; Maru, Y. The S100A8-serum amyloid A3-TLR4 paracrine cascade establishes a pre-metastatic phase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, S.; Chitayat, S.; Hashemi, M.; Eshraghi, M.; Chazin, W.J.; Halayko, A.J.; Kerkhoff, C. S100A8/A9: A Janus-faced molecule in cancer therapy and tumorgenesis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 625, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayes, R.F.; Mouhanna, J.G.; Nicolau, I.; Bourdeau, F.; Giannias, B.; Rousseau, S.; Quail, D.; Walsh, L.; Sangwan, V.; Bertos, N.; et al. Primary tumors induce neutrophil extracellular traps with targetable metastasis promoting effects. JCI Insight 2019, 5, e128008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Cong, M.; Li, J.; He, D.; Wu, Q.; Tian, P.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Liang, C.; Liang, Y.; et al. Cathepsin C promotes breast cancer lung metastasis by modulating neutrophil infiltration and neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Cancer Cell 2020, 39, 423–437.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.; Maenpaa, J.; Jauhiainen, A.; Larsson, B.; Mo, J.; Russell, M.; Root, J.; Prothon, S.; Chialda, L.; Forte, P.; et al. Dipeptidyl Peptidase 1 Inhibitor AZD7986 Induces a Sustained, Exposure-Dependent Reduction in Neutrophil Elastase Activity in Healthy Subjects. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 104, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menegazzo, L.; Scattolini, V.; Cappellari, R.; Bonora, B.M.; Albiero, M.; Bortolozzi, M.; Romanato, F.; Ceolotto, G.; de Kreutzeberg, S.V.; Avogaro, A.; et al. The antidiabetic drug metformin blunts NETosis in vitro and reduces circulating NETosis biomarkers in vivo. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, B.A.; Orlichenko, L.; Schapiro, N.E.; Loughran, P.; Gianfrate, G.C.; Ellis, J.T.; Singhi, A.D.; Kang, R.; Tang, D.; Lotze, M.T.; et al. The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) enhances autophagy and neutrophil extracellular traps in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demkow, U. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Cancer Invasion, Evasion and Metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174495
Demkow U. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Cancer Invasion, Evasion and Metastasis. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174495
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemkow, Urszula. 2021. "Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Cancer Invasion, Evasion and Metastasis" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174495
APA StyleDemkow, U. (2021). Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in Cancer Invasion, Evasion and Metastasis. Cancers, 13(17), 4495. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174495




