Multi-Platform Classification of IDH-Wild-Type Glioblastoma Based on ERK/MAPK Pathway: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
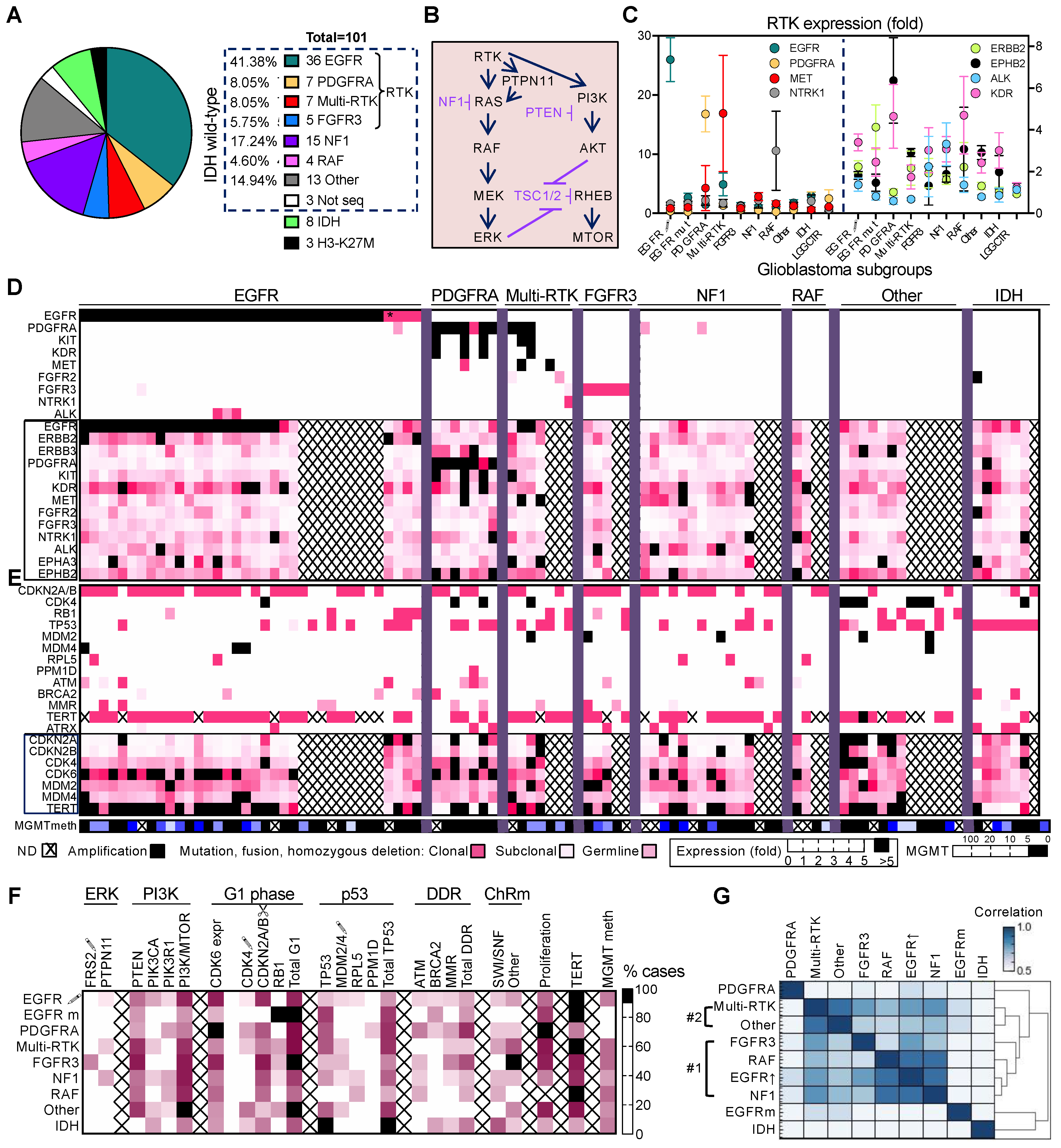
3.1. Non-Redundant Molecular Classification of Glioblastoma Based on ERK/MAPK Pathway
3.2. Glioblastoma Subgroup Clustering Based on Pathway Analysis
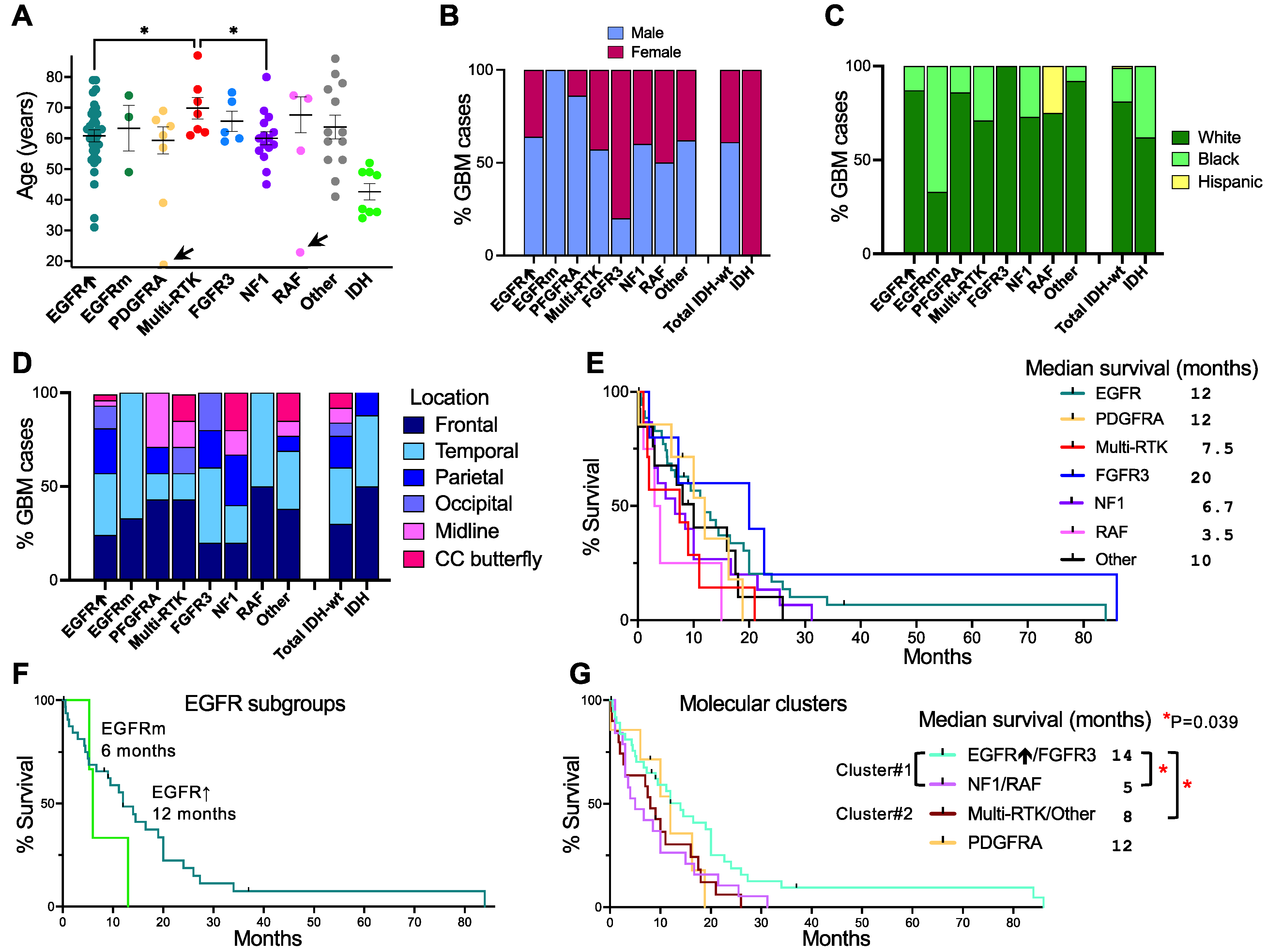
3.3. Glioblastoma Subgroup Demographic Characterization
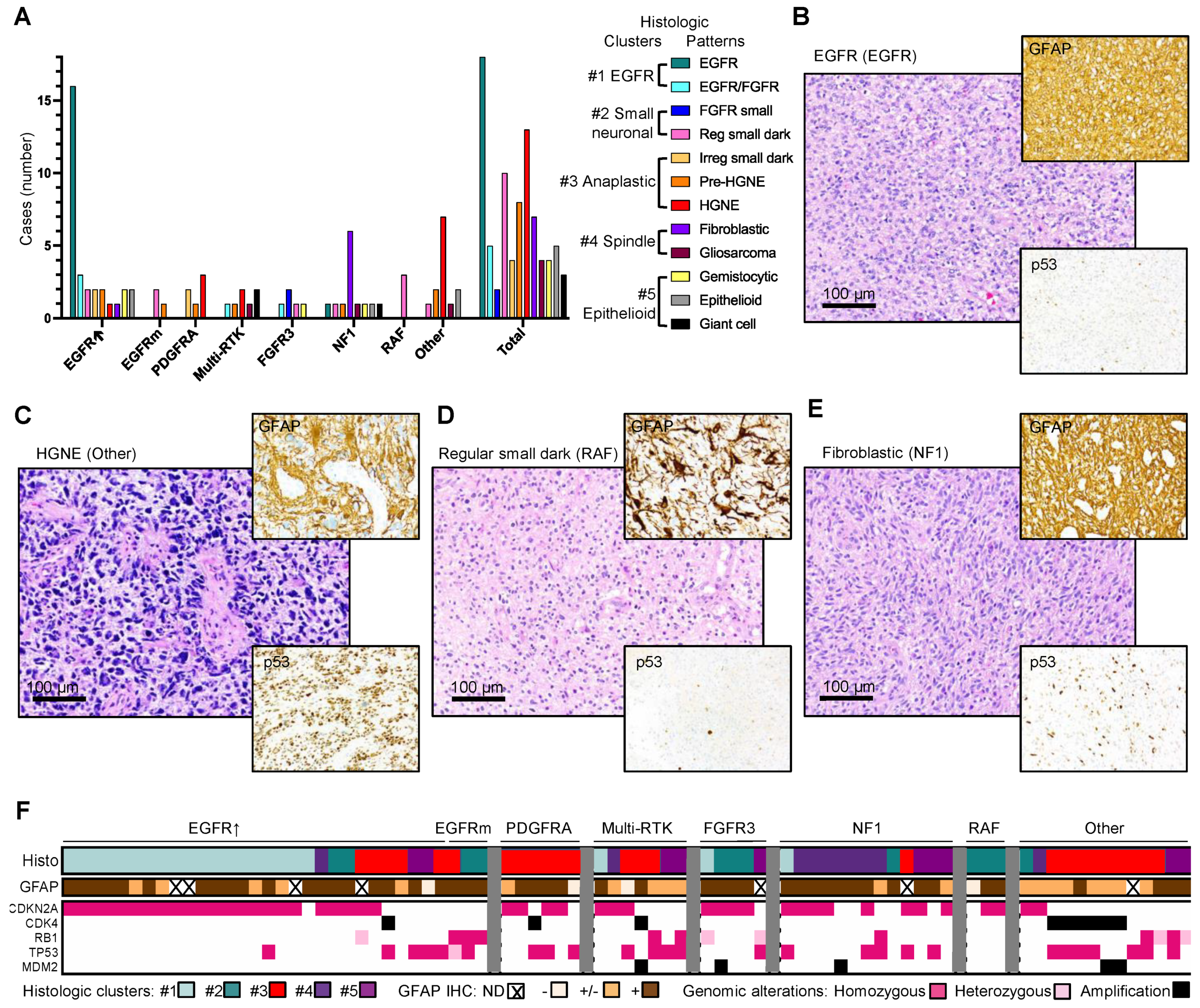
3.4. Enrichment of Histologic Patterns in Molecular Glioblastoma Subgroups
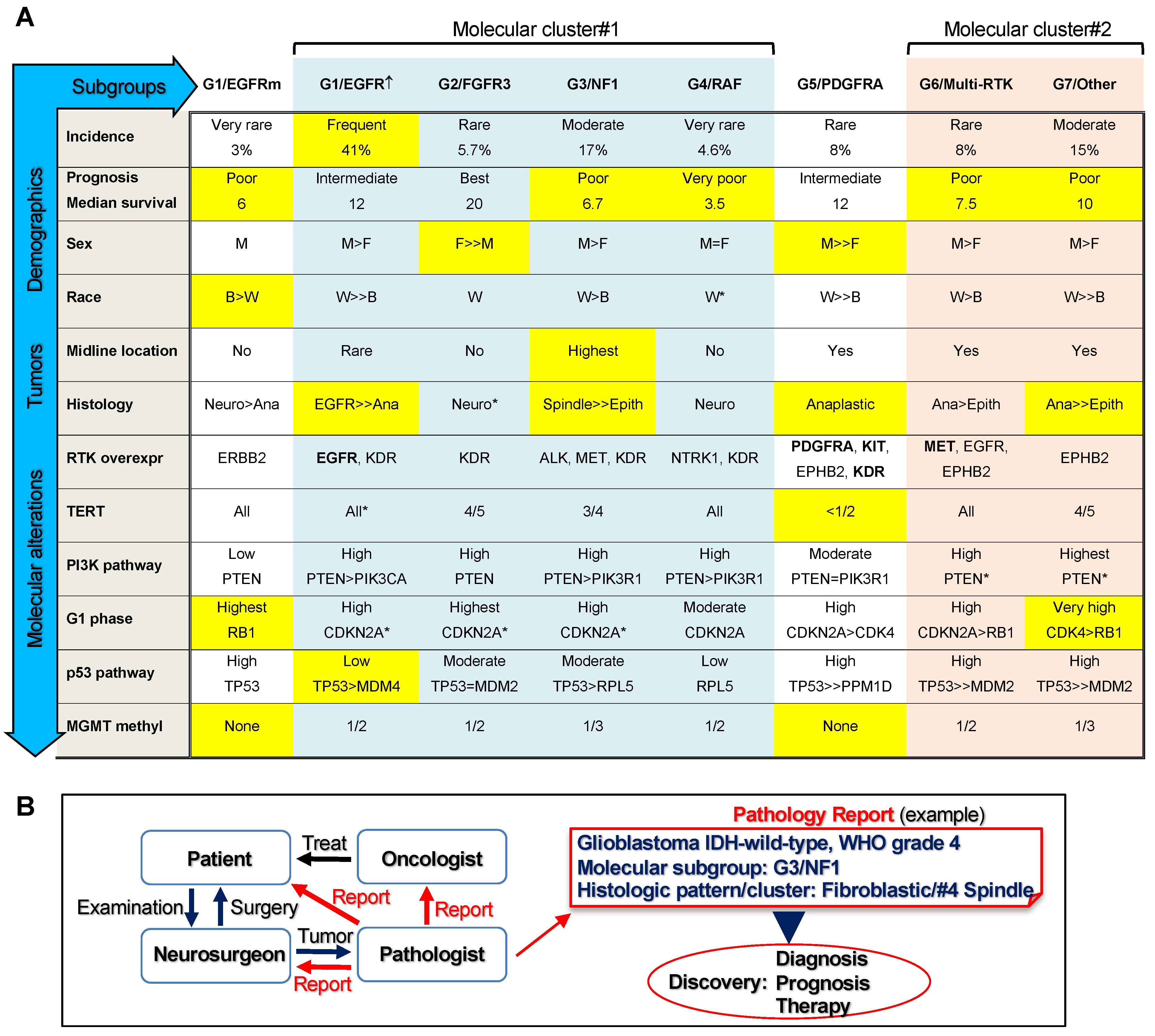
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C- | carboxyl |
| CN | copy number |
| DDR | DNA damage response |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor; EGFR↑, EGFR with gene amplification with or without other genetic alterations; EGFRm, EGFR with gene mutation only |
| ERK/MAPK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| FFPE | formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| FGFR | fibroblast growth factor receptor |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| H&E | hematoxylin eosin |
| IDH | isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| LOH | loss of heterozygosity |
| NF1 | neurofibromatosis type 1 |
| NGS | next generation sequencing |
| PDGFR | platelet-derived growth factor receptor |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-OH kinase |
| RTK | receptor tyrosine kinase |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Truitt, G.; Gittleman, H.; Brat, D.J.; Kruchko, C.; Wilson, R.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Relative survival after diagnosis with a primary brain or other central nervous system tumor in the National Program of Cancer Registries, 2004 to 2014. Neuro-Oncol. Pr. 2020, 7, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Caveneee, W.K. WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System; IARC: Lyon, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu, M.-M. PTEN Tumor Suppressor Network in PI3K-Akt Pathway Control. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ségaliny, A.I.; Tellez-Gabriel, M.; Heymann, M.-F.; Heymann, D. Receptor tyrosine kinases: Characterisation, mechanism of action and therapeutic interests for bone cancers. J. Bone Oncol. 2015, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M.-M.; Islam, M.Z.; Li, Y.; Traylor, J.; Nanda, A. Novel targetable FGFR2 and FGFR3 alterations in glioblastoma associate with aggressive phenotype and distinct gene expression programs. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawazoe, T.; Taniguchi, K. The Sprouty/Spred family as tumor suppressors: Coming of age. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidger, A.M.; Keyse, S.M. The regulation of oncogenic Ras/ERK signalling by dual-specificity mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatases (MKPs). Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 50, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, N.; Miller, S.J. A RASopathy gene commonly mutated in cancer: The neurofibromatosis type 1 tumour suppressor. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M.-M.; Li, Y.; Islam, M.; Notarianni, C.; Sun, H.; Olar, A.; Fuller, G.N. Mutations of the MAPK/TSC/mTOR pathway characterize periventricular glioblastoma with epithelioid SEGA-like morphology-morphological and therapeutic implications. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4038–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M.M.; Olar, A. Genetic and histologic spatiotemporal evolution of recurrent, multifocal, multicentric and metastatic glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M.-M.; Olar, A.; Mobley, B.C.; Faust, P.L.; Raisanen, J.M. Epithelial differentiation with microlumen formation in meningioma: Diagnostic utility of NHERF1/EBP50 immunohistochemistry. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 28652–28665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Georgescu, M.-M.; Islam, M.Z.; Li, Y.; Circu, M.L.; Traylor, J.; Notarianni, C.M.; Kline, C.N.; Burns, D.K. Global activation of oncogenic pathways underlies therapy resistance in diffuse midline glioma. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.K.; Zhu, X.; Gagea, M.; White, C.L., 3rd; Cote, G.; Georgescu, M.M. PHLPP2 suppresses the NF-kappaB pathway by inactivating IKKbeta kinase. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Georgescu, M.M.; Gagea, M.; Cote, G. NHERF1/EBP50 Suppresses Wnt-beta-Catenin Pathway-Driven Intestinal Neoplasia. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, M.-M.; Nanda, A.; Li, Y.; Mobley, B.C.; Faust, P.L.; Raisanen, J.M.; Olar, A. Mutation Status and Epithelial Differentiation Stratify Recurrence Risk in Chordoid Meningioma—A Multicenter Study with High Prognostic Relevance. Cancers 2020, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolte, H.; MacVicar, T.D.; Tellkamp, F.; Krüger, M. Instant Clue: A Software Suite for Interactive Data Visualization and Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M. Canonical and non-canonical WNT signaling in cancer stem cells and their niches: Cellular heterogeneity, omics reprogramming, targeted therapy and tumor plasticity (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbelstein, M.; Levine, A.J. Mdm2: Open questions. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohgaki, H.; Kleihues, P. The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Aisner, D.L.; Birks, D.K.; Foreman, N. Epithelioid GBMs Show a High Percentage of BRAF V600E Mutation. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielle, F.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Meyronet, D.; Picca, A.; Villa, C.; Bernier, M.; Schmitt, Y.; Giry, M.; Rousseau, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; et al. Diffuse gliomas with FGFR3-TACC3 fusion have characteristic histopathological and molecular features. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilani, A.; Davies, K.D.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K. Can adult IDH-wildtype glioblastomas with FGFR3:TACC3 fusions be reliably predicted by histological features? Clin. Neuropathol. 2021, 40, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilak, M.; Holborn, J.; New, L.; Lalonde, J.; Jones, N. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling and Targeting in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies Clinically Relevant Subtypes of Glioblastoma Characterized by Abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, N.; Akahane, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Yonezawa, H.; Uchida, H.; Takajo, T.; Kirishima, M.; Hamada, T.; Matsuo, K.; Fujio, S.; et al. A tailored next-generation sequencing panel identified distinct subtypes of wildtype IDH and TERT promoter glioblastomas. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3902–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, A.L.; Picca, A.; Saragoussi, E.; Bielle, F.; Ducray, F.; Villa, C.; Eoli, M.; Paterra, R.; Bellu, L.; Mathon, B.; et al. Clinical, molecular, and radiomic profile of gliomas with FGFR3-TACC3 fusions. Neuro. Oncol. 2020, 22, 1614–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaíno, M.A.; Shah, S.; Eberhart, C.G.; Rodriguez, F.J. Clinicopathologic implications of NF1 gene alterations in diffuse gliomas. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, G.; De Salvo, G.L.; Brandes, A.A.; Eoli, M.; Rudà, R.; Faedi, M.; Lolli, I.; Pace, A.; Daniele, B.; Pasqualetti, F.; et al. Regorafenib compared with lomustine in patients with relapsed glioblastoma (REGOMA): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Da Silva, E.; Mercier, M.C.; Etienne-Selloum, N.; Dontenwill, M.; Choulier, L. A Systematic Review of Glioblastoma-Targeted Therapies in Phases II, III, IV Clinical Trials. Cancers 2021, 13, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, O.G.; Brzozowski, J.S.; Skelding, K.A. Glioblastoma Multiforme: An Overview of Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleczko, E.K.; Heasley, L.E. Mechanisms of rapid cancer cell reprogramming initiated by targeted receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors and inherent therapeutic vulnerabilities. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Total IDH wt n = 87 | EGFR ↑ n = 33 | EGFR m n = 3 | PDGFRA n = 7 | Multi-RTK n = 7 | FGFR3 n = 5 | NF1 n = 15 | RAF n = 4 | Other n = 13 | IDH m n = 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TERT 1 | 85 (81.2) | 96.4 | 100 | 42.9 | 100 | 80 | 73.3 | 100 | 81.8 | 28.6 |
| PTEN | 53 | 48.5 | 33.3 | 28. 6 | 71.4 | 80 | 46. 7 | 50 | 69.2 | 0 |
| PIK3CA | 18.4 | 27.3 | 0 | 0 | 14.3 | 0 | 13.3 | 0 | 15.4 | 28.6 |
| PIK3R1 | 12.6 | 9.1 | 0 | 28.6 | 0 | 0 | 26.7 | 25 | 7.7 | 0 |
| PI3K/mTOR 2 | 75.9 | 75.8 | 33.3 | 42.9 | 71.4 | 80 | 80 | 75 | 100 | 42.9 |
| CDKN2A ↓ | 55.2 | 72.7 | 0 | 57.1 | 42.9 | 80 | 60 | 50 | 15.4 | 42.9 |
| CDK4 ↑ | 11.5 | 3 | 0 | 28.6 | 14.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 46.2 | 14.3 |
| RB1 | 12.6 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 28.6 | 20 | 6.7 | 0 | 30.8 | 0 |
| G1 phase 3 | 79.3 | 75.8 | 100 | 85.7 | 85.7 | 100 | 66.7 | 50 | 92.3 | 57.1 |
| TP53 | 33.3 | 18.2 | 66.7 | 57.1 | 57.1 | 20 | 33.3 | 0 | 53.8 | 100 |
| MDM2 ↑ | 5.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.3 | 20 | 6.7 | 0 | 15.4 | 0 |
| MDM4 ↑ | 4.6 | 9.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.7 | 0 |
| RPL5 | 5.7 | 6.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13.3 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| PPM1D | 1.1 | 0 | 0 | 14.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TP53 path 4 | 49.4 | 33.3 | 66.7 | 71.4 | 71.4 | 40 | 53.3 | 25 | 69.2 | 100 |
| ATM | 12.6 | 12.1 | 0 | 42.9 | 0 | 20 | 13.3 | 25 | 0 | 0 |
| BRCA2 | 5.7 | 9.1 | 33.3 | 14.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.6 |
| MMR 5 | 11.5 | 12.1 | 0 | 28.6 | 14.3 | 40 | 6.7 | 0 | 0 | 14.3 |
| DDR path 6 | 26.4 | 27.3 | 33.3 | 71.4 | 14.3 | 60 | 20 | 25 | 0 | 42.9 |
| STAG2 | 12.6 | 15.2 | 0 | 14.3 | 14.3 | 20 | 13.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SWI/SNF 7 | 13.8 | 15.2 | 0 | 14.3 | 28.6 | 0 | 20 | 25 | 0 | 57.1 |
| Other ChRm 8 | 32.2 | 30.3 | 0 | 14.3 | 57.1 | 100 | 20 | 0 | 38.5 | 14.3 |
| MGMT methyl | 36.1 | 43.3 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 50 | 27.3 | 50 | 36.4 | 42.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgescu, M.-M. Multi-Platform Classification of IDH-Wild-Type Glioblastoma Based on ERK/MAPK Pathway: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2021, 13, 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184532
Georgescu M-M. Multi-Platform Classification of IDH-Wild-Type Glioblastoma Based on ERK/MAPK Pathway: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers. 2021; 13(18):4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184532
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgescu, Maria-Magdalena. 2021. "Multi-Platform Classification of IDH-Wild-Type Glioblastoma Based on ERK/MAPK Pathway: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications" Cancers 13, no. 18: 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184532
APA StyleGeorgescu, M.-M. (2021). Multi-Platform Classification of IDH-Wild-Type Glioblastoma Based on ERK/MAPK Pathway: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers, 13(18), 4532. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13184532





