Simple Summary
Regorafenib has proven its efficacy for later-line treatment of mCRC. However, treatment often brings substantial toxicities that lead clinicians to assess the risk-to-benefit ratio in heavily pretreated patients. Thus, it is crucial to develop a prognostic factor and model for guiding patient selection. In this study, we represent a new serum biomarker to serve as an independent prognostic factor for patients receiving regorafenib. All 4 factors of the prognostic model were employed with an excellent discriminatory ability. This result should be validated in further confirmatory studies.
Abstract
(1) Background: To investigate the prognostic value of cancer-inflammation prognostic index (CIPI) in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) on regorafenib treatment; (2) Methods: Patients with mCRC who were given regorafenib as later-line treatment at Kaohsiung and Linkou Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital between November 2014 and January 2021 were consecutively enrolled. All relevant clinicopathologic, laboratory data and survival status were recorded. Independent prognostic factors were determined by the multivariate Cox regression method; (3) Results: In total, 106 patients in the training cohort and 250 in the validation cohort were enrolled. The median OS for patients with CIPI ≥ 300 and < 300 in the training cohort was 3.8 and 9.0 months, respectively (hazard ratio (HR) 2.78, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.82–4.23; p < 0.0001). Time to regorafenib, liver metastasis and CIPI were independent factors by multivariate Cox regression analyses. A new scoring model demonstrated a good discriminatory ability to risk stratification of a patient’s survival; (4) Conclusions: We identified CIPI as a novel serum marker highly associated with overall survival in patients with mCRC receiving regorafenib treatment. Further confirmatory studies are warranted.
1. Introduction
Metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) is a lethal disease and was the third leading cause of cancer deaths in 2018 [1,2]. With major advances in chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and aggressive surgical resection over the past two decades, the median overall survival (OS) of patients with mCRC has been significantly prolonged from 12 to 36 months [3,4,5]. Some patients have the chance to achieve a durable survival by integrating radical surgery, chemotherapy, and targeting therapy including anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (anti-EGFR) or anti-vascular epidermal growth factor (VEGF) antibody [6]. However, most patients with mCRC eventually experience progressive disease and unendurable symptoms. Later-line therapy, such as regorafenib and trifluridine/tipiracil (TAS-102), demonstrated a modest anti-tumor efficacy and overall survival benefits compared to a placebo for chemorefractory mCRC [7,8,9,10].
Regorafenib is a potent, oral-form tyrosine kinase inhibitor that effectively blocks the angiogenic (VEGFR1/3, PDGF-b), stromal (FGFR1), and some driver oncogenic kinases (KIT, RET and BRAF) [11]. The pivotal CORRECT study demonstrated that patients on regorafenib treatment had a significant survival benefit compared with those on placebo treatment (6.4 months vs. 5.0 months; hazard ratio 0.77; 95% CI 0.64–0.94) [8]. The efficacy of regorafenib for mCRC in third-line treatment was confirmed by several real-world studies [12,13]. The CORRELATE study designed as a prospective, observational study that aimed to evaluate the real-world safety and efficacy of regorafenib disclosed a similar toxic profile and disease control rate to that in the CORRECT study [12,13]. Nevertheless, only a small fraction of patients benefit from regorafenib treatment (objective response rate 1%; disease control rate 41% in CORRECT study) and that limits physicians’ willingness to use it unless a reliable predictive or prognostic biomarker is discovered.
Previous studies have identified and developed some potential predictive factors to estimate the OS on regorafenib. Novakova-Jiresova et al. reported a large retrospective series of 555 patients with mCRC on regorafenib and found 3 independent good prognostic factors by multivariate analysis: high body-mass index (BMI), longer interval from metastatic disease to regorafenib and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) of 0 [14]. On top of that, Del Prete et al. found that serum inflammation markers, such as high neutrophil, platelet counts and high neutrophil to lymphocyte ration (NLR), negatively influenced OS in patients receiving regorafenib [15]. A recent study constructed a prognostic model for patients who underwent regorafenib and identified that low carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), slow rate of tumor progression, and fewer organ metastatic sites were highly correlated with good overall survival [16]. Collectively, this imperative research emphasized that a good predictive model should consider both patient (ECOG PS), tumor (CEA, numbers of metastatic site) and immune (NLR) related factors simultaneously.
Here, we introduced a novel prognostic index, defined as the cancer-inflammation prognostic index (CIPI) by calculating the values of CEA multiply NLR, that was developed and validated externally. By incorporation of this novel marker with previous established predictors, we aimed to develop a new prognostic model that makes it easy for physicians to choose patients for regorafenib wisely.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, Data Process and Treatment
This retrospective cohort study analyzed patient data from two independent medical centers in Taiwan: Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (the training cohort) and Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (the validation cohort). Patients with histologically proven mCRC and refractory to standard chemotherapy (fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, irinotecan) plus anti-VEGF or anti-EGFR therapy were enrolled for analysis. All clinicopathologic and laboratory data were retrieved from electrical medical recording (EMR) systems. Database variables included age, sex, ECOG PS, primary tumor site, RAS status, visceral organ metastasis, interval from metastasis to regorafenib administration, and serological factors (white blood cell count, hemoglobin, platelet count, neutrophil count, lymphocyte count and CEA). We collected laboratory data within 1 week prior to patients undergoing regorafenib treatment. The starting dosage of regorafenib treatment depended on a physician’s discretion considering the patient’s performance status, comorbidities, and potential adverse effects. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Medical Foundation (201801598B0C502).
2.2. Response Evaluation and Endpoints
All patients on regorafenib therapy had been regularly scheduled for a clinic visit and evaluated for treatment response by CT scans of the chest or abdomen or serologic tumor markers. As application of regorafenib reimbursement required the latest CT images to prove therapeutic efficacy, patients had to receive a CT scan every 8 weeks, and that ensured the window of radiographic evaluation was similar to that in the CORRELATE study. The assessment of treatment response was using the criteria of Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (version 1.1). The primary endpoint of this study was OS, which was defined as the interval between the date of initiating regorafenib treatment and the date of death.
2.3. Cancer-Inflammation Prognostic Index (CIPI)
We defined CIPI by calculating the following equation: CIPI = CEA × NLR, where NLR represents the ratio of neutrophil and lymphocyte count. To obtain the optimal cutoff value of CIPI, we used X-tile 3.6.1 software (Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA) for analysis of data from the training cohort [17]. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was employed to evaluate the distinguish ability of CIPI and the prognostic model.
2.4. Statistics
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 25.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and R software 4.1.1. Data visualization and depiction of survival curves was plotted using GraphPad Prism version 8.21 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). Descriptive analysis of all clinicopathological variables of the training and validation cohorts were examined by using chi-squared (χ2) and t tests for categorical and continuous variables, respectively. Estimates of overall survival were determined by the Kaplan–Meier method and examined for group differences statistically with the log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses of independent factors were performed using the Cox proportional hazards regression analysis. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
In total, 356 eligible patients were incorporated into the final analysis, including 106 patients in the training cohort and 250 patients in the validation cohort. The median age of all patients was 61 years (interquartile range (IQR), 53–68 years), and the median follow-up time was 20.7 months. Among all, 210 (59%) patients were men, and 74.7% of patients had a left-sided tumor. The differences of demographic and clinical features between the training and validation cohorts are shown in Table 1. Except for ECOG performance status (p = 0.01) and the initial dose of regorafenib (p < 0.001), all other characteristics were compared without significant difference.

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the training and validation cohorts.
3.2. Determine the Cutoff Level of CIPI
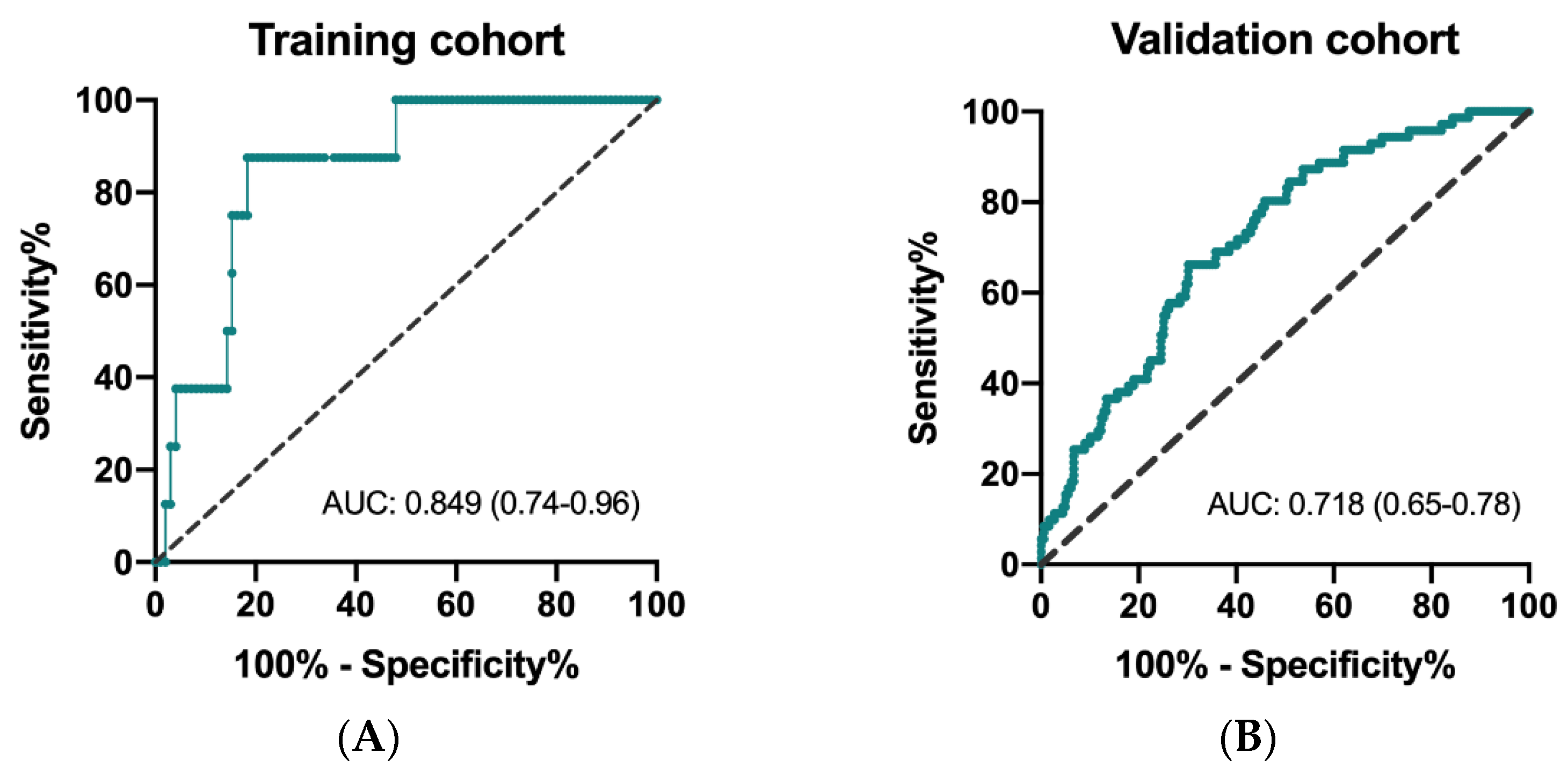
The ROC curves to determine predictivity of CIPI and overall survival are depicted for the training and validation cohorts. As shown in Figure 1A,B, the area under curve (AUC) was 0.849 (95% CI: 0.74–0.96; p = 0.001) in the training cohort and 0.718 (95% CI: 0.65–0.78; p < 0.0001) in the validation cohort, respectively. The results of X-tile analysis disclosed that the optimal cutoff level of CIPI in the training cohort was 302.0 (maximum high/low chi-square = 24.3955, Miller–Seigmund p < 0.0001). We defined the recommended cut-off value of CIPI as 300 for further validation analysis.
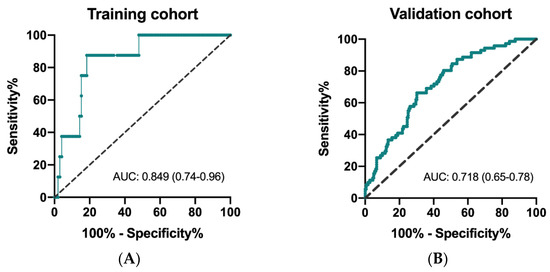
Figure 1.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for CIPI and mortality in the training cohort (A) and in the validation cohort (B).
3.3. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of OS and PFS in the Training Cohort
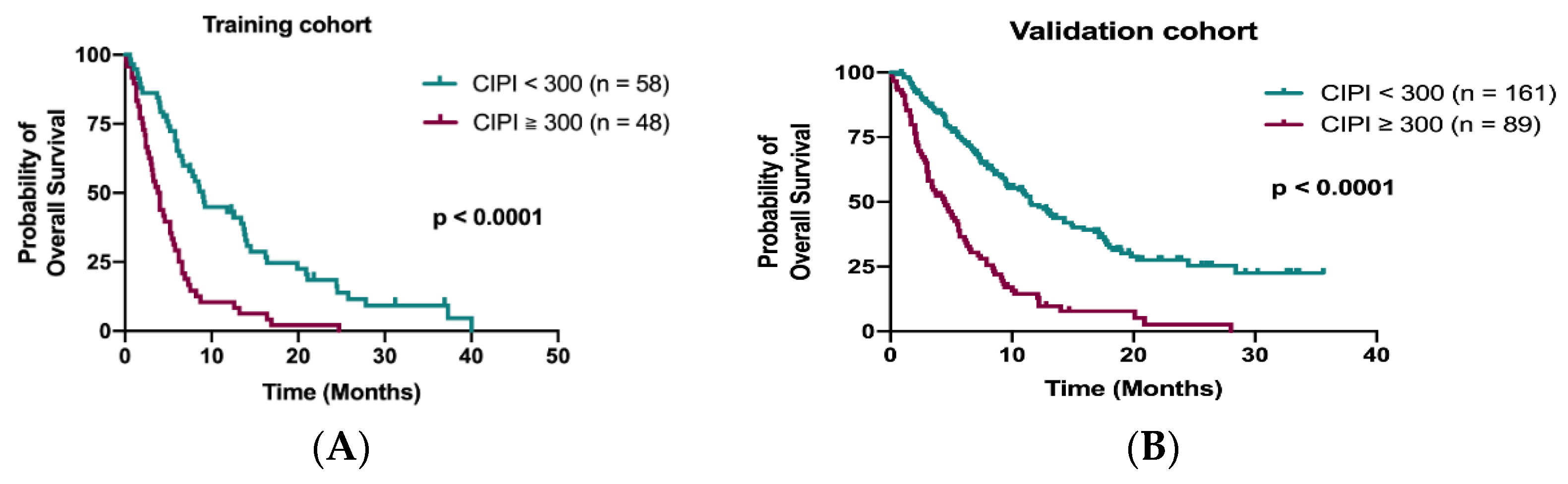
Data from the training cohort were used to identify prognostic factors and to build up a predictive model. A total of 98 out of 106 patients (92.5%) died during the follow-up period. The median OS in the training cohort was 6.0 months (95% confidence interval (CI), 4.7–7.3 months). The Kaplan–Meier analysis demonstrated that patients with CIPI ≥ 300 had a significantly worse OS than those with CIPI < 300 (3.8 months vs. 9.0 months; p < 0.0001; Figure 2A). The other significant prognostic factors in the training cohort from the univariate analysis were ECOG PS, time to regorafenib treatment, primary tumor resection, hemoglobin, visceral metastasis (liver, bone and peritoneum) and initial dose of regorafenib (Table 2). Multivariable Cox regression analyses of these factors and OS from the training cohort disclosed that time to regorafenib treatment < 24 months (HR 2.27; 95% CI, 1.44–3.60; p < 0.0001), liver metastasis (HR 1.61; 95% CI, 1.00–2.64; p = 0.05) and CIPI ≥ 300 (HR 2.14; 95% CI, 1.23–3.74; p = 0.007) determined OS significantly (Table 2).
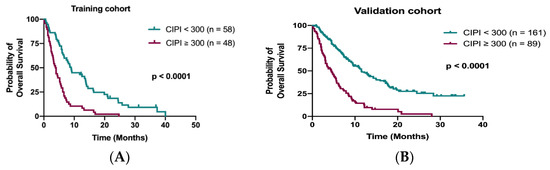
Figure 2.
Kaplan–Meier curve for OS stratified by CIPI at 300 in the training cohort (A) and in the validation cohort (B).

Table 2.
Univariate and multivariate analyses for OS in the training cohort.
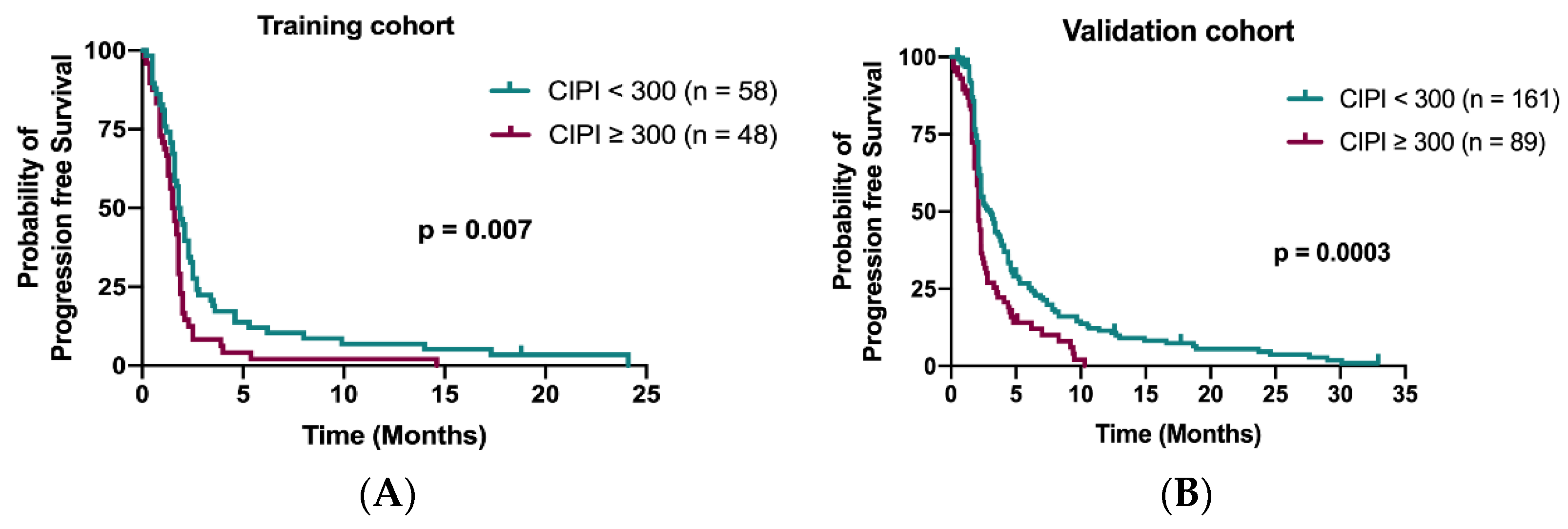
The median PFS in the training cohort was 1.7 months (95% confidence interval (CI), 1.58–1.91 months). Patients with CIPI < 300 demonstrated a better PFS than those with CIPI ≥ 300 in the training cohort (1.8 months vs. 1.5 months; p = 0.007; Figure 3A) and in the validation cohort (3.0 months vs. 2.1 months; p = 0.0003; Figure 3B). Multivariable Cox regression analyses demonstrated that time to regorafenib treatment < 24 months (HR 1.76; 95% CI, 1.15–2.68; p = 0.009) and peritoneum metastasis (HR 2.18; 95% CI, 1.34–3.56; p = 0.002) were significant independent factors for PFS (Table 3).
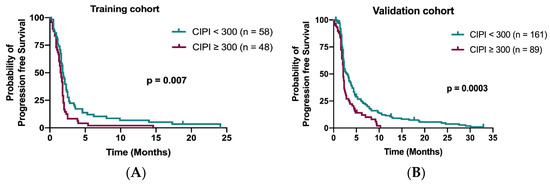
Figure 3.
Kaplan–Meier curve for PFS stratified by CIPI at 300 in the training cohort (A) and in the validation cohort (B).

Table 3.
Univariate and multivariate analyses for PFS in the training cohort.
3.4. Build Up and Validation of the Prognostic Model
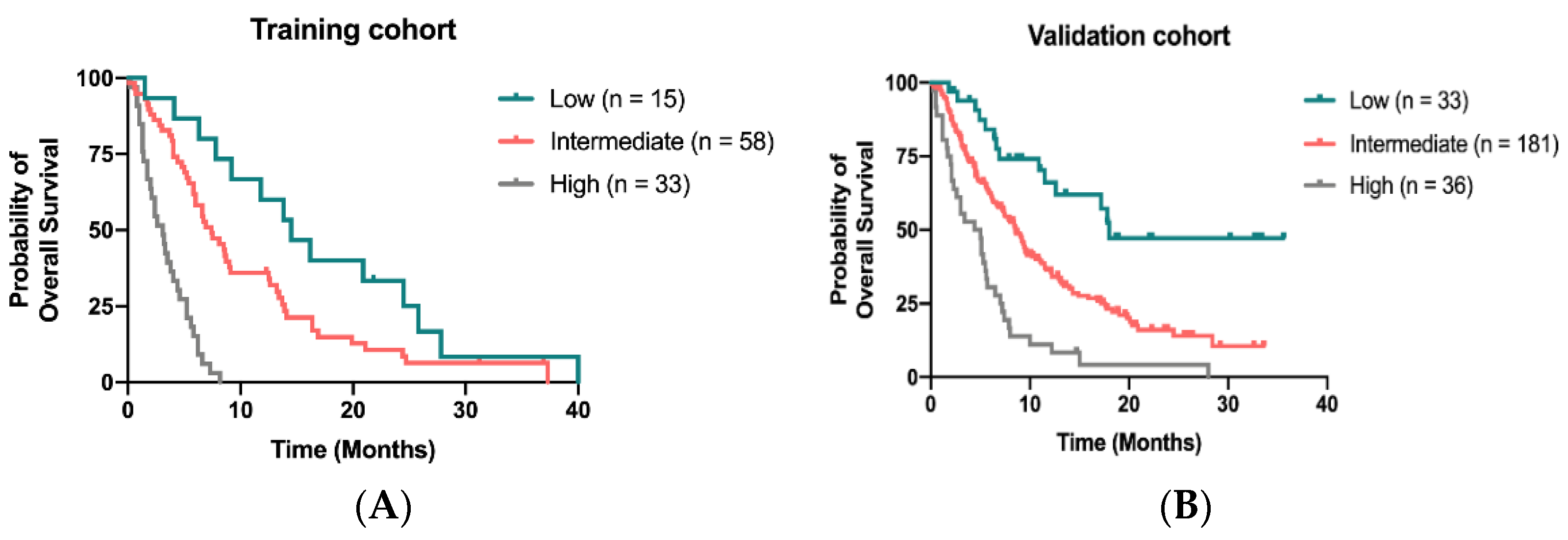
We developed a novel prognostic model to predict OS for patients receiving regorafenib by calculating 4 independent factors: time to regorafenib treatment < 24 months, liver metastasis, peritoneal metastasis and CIPI ≥ 300. By attributing one point for each risk factor and summed up for a total score, patients with scores of 0, 1–2 and 3–4 were classified as low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups, respectively. The median OS was 14.5 months (95% CI, 8.9–20.1 months) 7.4 months (95% CI, 5.5–9.3 months) and 3.1 months (95% CI, 2.1–4.1 months) for patients in low-, intermediate- and high-risk groups, respectively (Figure 4A). In the validation cohort, the median OS for patients assigned to low, intermediate and high-risk groups was 18.0 months, 8.6 months and 4.4 months, respectively (Figure 4B).
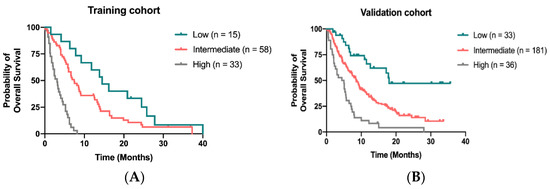
Figure 4.
Kaplan–Meier curve for OS stratified by the scoring model in the training cohort (A) and in the validation (B).
4. Discussion
Regorafenib is approved globally as a recommended drug in the third-line treatment for mCRC [18,19]. Although the survival benefit for patients on regorafenib reached significance statistically, only a small fraction of patients responded to regorafenib. Given the substantial toxicity from regorafenib and frailty of chemorefractory patients, it is crucial for physicians to balance treatment efficacy and consequent adverse effects. Identification of a predictive biomarker to guide decision making is becoming a fundamental aspect of clinical practice. Our results confirmed that CIPI has a good discriminatory power in predicting mortality for patients who underwent regorafenib. In combination with the other poor prognostic factors, we developed a new scoring model that can separate curves of OS nicely according to different risk groups. We believe this model can help physicians to make clinical decisions wisely.
Several exploratory studies that aimed to identify the reliable molecular marker of regorafenib failed to reach consensus because they lacked validation and reproducibility. In the CORRECT study, Tabernero et al. demonstrated that KRAS and PIK3CA mutation status determined by BEAMing analysis of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) were not correlated with regorafenib efficacy [20]. In addition to tumor genomic alteration, the study also analyzed many serum proteins aimed at finding therapeutic correlation. High serum concentrations of TIE1 were associated with longer overall survival than low serum TIE1 in univariate analyses, but did not show significance in the multivariate analyses [20]. The exploratory analysis of 16 plasma proteins concentration and OS in the CONCUR study also failed to identify any potential candidate, suggesting that plasma protein level was not suitable for predicting regorafenib efficacy [21].
CEA has been routinely employed as a surrogate marker to detect early recurrence for patients with localized CRC who underwent surgical resection [22]. For advanced mCRC, the level of CEA has shown an inverse correlation with poor survival despite patients receiving therapy aggressively [23,24,25]. Soluble CEA can elicit proangiogenic endothelial cell adhesion and migration, and it enhances tumor neovascularization independent of the VEGF signaling pathway [26]. In the subgroup analysis of the RAISE study, a low level of baseline CEA (cutoff 10 ng/mL) was a decisive factor to differentiate patients who gained benefits from ramucirumab and chemotherapy combination [25]. Prager et al. also reported the predictive role of baseline CEA only for bevacizumab-based therapy, not for cetuximab and chemotherapy combination [27]. However, data of the CEA level were not recorded and analyzed in the prospective large trials (CORRECT, CONCUR and REBECCA), leading to no convincing evidence to understand the predictive role of baseline CEA for regorafenib therapy [8,9,28]. A recent study enrolled a total of 613 patients to explore the predictive clinicopathologic factors for mCRC on regorafenib treatment [16]. Hsu et al. disclosed that serum CEA level was inversely correlated with the OS of patients receiving regorafenib. Our findings demonstrated consistent results, suggesting that the level of circulating CEA has a critical role in determining the OS for patients on regorafenib therapy.
Cancer is well-recognized as a chronic inflammation disease. Cancer-associated inflammation is a complex phenomenon that involves numerous circulating blood cells, chemokines, stromal cells and metabolic factors [29]. It is known that leukocytes, particularly neutrophils, play a crucial role in tumor microenvironment promoting cancer cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis and resistance to chemotherapy [30,31,32,33]. Elevated absolute neutrophil count (ANC) was proven as a strong predictor for treatment outcome in patients receiving curative surgery or systemic chemotherapy [34,35]. The predictive and prognostic role of NLR has been extensively discussed in CRC and other solid cancers [36,37,38]. Several studies investigated the prognostic role of NLR in patients treated with regorafenib. Del Prete et al. found that several serum markers such as high LDH levels, neutrophil, platelet counts and high NLR were negatively correlated to OS [15]. Our data demonstrated similar results: high NLR (cutoff at 4) determining OS powerfully in the univariate Cox regression analysis (HR 2.01; 95% CI 1.30–3.10). Although NLR is undoubtedly a robust surrogate marker of overall survival, the hurdle of clinical utilization is lacking a definitive cutoff level of NLR. Further studies and more data are needed to come up with the ideal level of NLR.
One of the impressive findings in this study is that the combination of CEA with NLR as a new predictor (CIPI) contributed highly to the risk stratification of patients’ survival. Our predictive model, by counting only 4 factors (CIPI, time to regorafenib, liver and peritoneum metastasis), has a good discrimination effect to risk stratification of survival. Several prognostic models have been developed and implemented in clinical practice. The “Colon Life” nomogram raised by Pietrantonio et al. consisted of simple 4 clinical factors: ECOG PS, primary tumor resection, LDH and peritoneal metastasis [39]. The nomogram discriminative ability in both the developing and validating set were excellent (Harrell C index 0.778). However, despite the fact that ECOG PS < 2 and primary tumor resection are associated with a favorable survival in the univariate analysis of our patients, the prognostic significances were not shown in the multivariate Cox regression model. We believe a comprehensive model covering all aspects including patient, tumor and therapy has the best predictive value for patients with mCRC who are treated with regorafenib.
There are several limitations in this study. First, the nature of retrospective design has a hidden selective bias. Because the study lacks a control group, it is better to claim CIPI is a prognostic rather than a predictive marker. Second, toxicity from regorafenib was not reported in the retrospective study because many constitutional symptoms and non-hematologic abnormal data were not recorded in medical charts. Third, the initial dosage of regorafenib was not uniform. Heavily pretreated patients with mCRC may not be suitable for a standard dosage of regorafenib. Dose escalation strategy, such as the ReDDoS study protocol, is commonly used in real-world practice [40]. Lastly, our real-world data are based on a small sample size included in only two medical centers. Further research with a larger sample size may provide better homogeneity and validity.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the results of the present study identified CIPI as a robust and easy to use clinical factor for patients with mCRC who are receiving regorafenib. The new scoring model by integrating CIPI, time to regorafenib, liver and peritoneal metastasis demonstrated an excellent discriminant validity of OS. Further big sample-size studies are needed to confirm our findings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.-L.S.; methodology, Y.-L.S. and K.-L.T.; software, T.-J.C. and C.-C.W.; validation, Y.-M.L. and K.-C.L.; resources, C.-C.L. and H.-H.C.; data curation, H.-C.H., K.-C.L., K.-L.T. and C.-C.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.-L.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.-L.S.; visualization, Y.-L.S.; supervision, H.-C.H.; funding acquisition, Y.-L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported partly by a grant from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Kaohsiung, Taiwan (CFRPG8H0461).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chang Gung Medical Foundation (201801598B0C502, date of approval: 22 July 2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective design of this study.
Data Availability Statement
The data present in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
We thank all experts in the Biostatistics Center of Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital for gracious help in statistical analysis of raw data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Ahnen, D.J.; Meester, R.G.S.; Barzi, A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kopetz, S.; Chang, G.J.; Overman, M.J.; Eng, C.; Sargent, D.; Larson, D.W.; Grothey, A.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Nagorney, D.M.; McWilliams, R.R. Improved survival in metastatic colorectal cancer is associated with adoption of hepatic resection and improved chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3677–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meulenbeld, H.J.; van Steenbergen, L.N.; Janssen-Heijnen, M.L.G.; Lemmens, V.E.P.P.; Creemers, G.J. Significant improvement in survival of patients presenting with metastatic colon cancer in the south of The Netherlands from 1990 to 2004. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremolini, C.; Loupakis, F.; Antoniotti, C.; Lupi, C.; Sensi, E.; Lonardi, S.; Mezi, S.; Tomasello, G.; Ronzoni, M.; Zaniboni, A.; et al. FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: Updated overall survival and molecular subgroup analyses of the open-label, phase 3 TRIBE study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgewater, J.A.; Pugh, S.A.; Maishman, T.; Eminton, Z.; Mellor, J.; Whitehead, A.; Stanton, L.; Radford, M.; Corkhill, A.; Griffiths, G.O.; et al. Systemic chemotherapy with or without cetuximab in patients with resectable colorectal liver metastasis (New EPOC): Long-term results of a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, V.; Napolitano, S.; Roselló, S.; Huerta, M.; Cervantes, A.; Ciardiello, F.; Troiani, T. How we treat metastatic colorectal cancer. ESMO Open 2020, 4, e000813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothey, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Sobrero, A.; Siena, S.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouché, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C.; et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qin, S.; Xu, R.; Yau, T.C.C.; Ma, B.; Pan, H.; Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; Chi, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Regorafenib plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care in Asian patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CONCUR): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Falcone, A.; Yoshino, T.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Mizunuma, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Shimada, Y.; Tabernero, J.; Komatsu, Y.; et al. Randomized trial of TAS-102 for refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Dumas, J.; Adnane, L.; Lynch, M.; Carter, C.A.; Schütz, G.; Thierauch, K.-H.; Zopf, D. Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): A new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 129, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducreux, M.; Petersen, L.N.; Öhler, L.; Bergamo, F.; Metges, J.-P.; de Groot, J.W.; Wang, J.-Y.; Paredes, B.G.; Dochy, E.; Fiala-Buskies, S.; et al. Safety and effectiveness of regorafenib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer in routine clinical practice in the prospective, observational CORRELATE study. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 123, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeh, K.-H.; Yang, T.-S.; Hsu, T.-C.; Chen, W.T.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Teng, H.-W.; Lin, B.-W.; Kuan, F.-C.; Chiang, F.-F.; Duann, C.-W.; et al. Real-world evidence of the safety and effectiveness of regorafenib in Taiwanese patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: CORRELATE Taiwan. J. Formos. Med Assoc. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakova-Jiresova, A.; Kopeckova, K.; Boublikova, L.; Chloupkova, R.; Melichar, B.; Petruzelka, L.; Finek, J.; Fiala, O.; Grell, P.; Batko, S.; et al. Regorafenib for metastatic colorectal cancer: An analysis of a registry-based cohort of 555 patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5365–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prete, M.; Giampieri, R.; Loupakis, F.; Prochilo, T.; Salvatore, L.; Faloppi, L.; Bianconi, M.; Bittoni, A.; Aprile, G.; Zaniboni, A.; et al. Prognostic clinical factors in pretreated colorectal cancer patients receiving regorafenib: Implications for clinical management. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33982–33992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Huang, K.-C.; Chen, W.-S.; Jiang, J.-K.; Yang, S.-H.; Wang, H.-S.; Chang, S.-C.; Lan, Y.-T.; Lin, C.-C.; Lin, H.-H.; et al. Preference criteria for regorafenib in treating refractory metastatic colorectal cancer are the small tumor burden, slow growth and poor/scanty spread. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, R.L.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Rimm, D.L. X-Tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Nordlinger, B.; Arnold, D.; Group, E.G.W. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iii1–iii9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Arnold, D.; Taniguchi, H.; Pentheroudakis, G.; Yamazaki, K.; Xu, R.-H.; Kim, T.; Ismail, F.; Tan, I.; Yeh, K.-H.; et al. Pan-Asian adapted ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A JSMO–ESMO initiative endorsed by CSCO, KACO, MOS, SSO and TOS. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 44–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, I.; Patel, M.; Dennison, A.R.; Thomas, M.W.; Garcea, G. Utility of postoperative CEA for surveillance of recurrence after resection of primary colorectal cancer. Int. J. Surg. 2015, 16, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, J.; Lenz, H.-J.; Siena, S.; Sobrero, A.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouché, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C.; et al. Analysis of circulating DNA and protein biomarkers to predict the clinical activity of regorafenib and assess prognosis in patients with metastatic colo-rectal cancer: A retrospective, exploratory analysis of the CORRECT trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, M.; Kalmus, J.; Rutstein, M.D.; Koechert, K.; Seidel, H.; Reischl, J.; Skubala, A.; Vonk, R.; Wilhelm, S.; Kobina, S.; et al. Analysis of plasma protein biomarkers from the phase 3 CONCUR study of regorafenib in Asian patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, M.R.; Haukoos, J.S.; Udani, S.M.; Naghi, J.J.; Arnell, T.D.; Kumar, R.R.; Stamos, M.J. Carcinoembryonic antigen and albumin predict survival in patients with advanced colon and rectal cancer. Arch. Surg. 2003, 138, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moretto, R.; Rossini, D.; Conca, V.; Lonardi, S.; Rasola, C.; Antoniotti, C.; Santini, D.; Marmorino, F.; Tomasello, G.; Borelli, B.; et al. CEA increase as a marker of disease progression after first-line induction therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. A pooled analysis of TRIBE and TRIBE2 studies. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Obermannová, R.; Bodoky, G.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Ciuleanu, T.; Portnoy, D.C.; Kim, T.W.; Hsu, Y.; Ferry, D.; Nasroulah, F.; et al. Baseline carcinoembryonic antigen as a predictive factor of ramucirumab efficacy in RAISE, a second-line metastatic colorectal carcinoma phase III trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 78, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bramswig, K.H.; Pöttler, M.; Unseld, M.; Wrba, F.; Uhrin, P.; Zimmermann, W.; Zielinski, C.C.; Prager, M.G. Soluble carcinoembryonic antigen activates endothelial cells and tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6584–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prager, G.W.; Braemswig, K.H.; Martel, A.; Unseld, M.; Heinze, G.; Brodowicz, T.; Scheithauer, W.; Kornek, G.; Zielinski, C.C. Baseline carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) serum levels predict bevacizumab-based treatment response in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenis, A.; De La Fouchardiere, C.; Paule, B.; Burtin, P.; Tougeron, D.; Wallet, J.; Dourthe, L.-M.; Etienne, P.-L.; Mineur, L.; Clisant, S.; et al. Survival, safety, and prognostic factors for outcome with Regorafenib in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to standard therapies: Results from a multicenter study (REBECCA) nested within a compassionate use program. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and cancer: Triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, R.; Kawada, K.; Itatani, Y.; Ogawa, R.; Kiyasu, Y.; Sakai, Y. The role of tumor-associated neutrophils in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galdiero, M.R.; Bianchi, P.; Grizzi, F.; Di Caro, G.; Basso, G.; Ponzetta, A.; Bonavita, E.; Barbagallo, M.; Tartari, S.; Polentarutti, N.; et al. Occurrence and significance of tumor-associated neutrophils in patients with colorectal cancer: Significance of tumor-associated neutrophils in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiffmann, L.M.; Fritsch, M.; Gebauer, F.; Günther, S.D.; Stair, N.R.; Seeger, J.M.; Thangarajah, F.; Dieplinger, G.; Bludau, M.; Alakus, H.; et al. Tumour-infiltrating neutrophils counteract anti-VEGF therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, U.; Chowdhury, S.; Billah, M.; Islam, K.; Thorlacius, H.; Rahman, M. Neutrophil extracellular traps in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watt, D.G.; Martin, J.C.; Park, J.H.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C. Neutrophil count is the most important prognostic component of the differential white cell count in patients undergoing elective surgery for colorectal cancer. Am. J. Surg. 2015, 210, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothey, A.; Yoshino, T.; Bodoky, G.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; García-Alfonso, P.; Van Cutsem, E.; Muro, K.; Mytelka, D.S.; Li, L.; et al. Association of baseline absolute neutrophil counts and survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with second-line antiangiogenic therapies: Exploratory analyses of the RAISE trial and validation in an electronic medical record data set. ESMO Open 2018, 3, e000347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feliciano, E.M.C.; Kroenke, C.H.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Prado, C.M.; Bradshaw, P.T.; Kwan, M.L.; Xiao, J.; Alexeeff, S.; Corley, D.; Weltzien, E.; et al. Association of systemic inflammation and sarcopenia with survival in nonmetastatic colorectal cancer: Results from the C SCANS Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, e172319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowska, K.; Koda, M.; Kisielewski, W.; Kańczuga-Koda, L.; Grudzińska, M.; Famulski, W. Pre- and postoperative neutrophil and lymphocyte count and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with colorectal cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, S.; Sheth, R.A.; Niekamp, A.S.; Aloia, T.A.; Chun, Y.S.; Lee, J.E.; Vauthey, J.-N.; Conrad, C. Comprehensive complication index predicts cancer-specific survival after resection of colorectal metastases independent of RAS mutational status. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Miceli, R.; Rimassa, L.; Lonardi, S.; Aprile, G.; Mennitto, A.; Marmorino, F.; Bozzarelli, S.; Antonuzzo, L.; Tamburini, E.; et al. Estimating 12-week death probability in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: The Colon Life nomogram. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 28, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaii-Saab, T.S.; Ou, F.-S.; Ahn, D.H.; Boland, P.M.; Ciombor, K.K.; Heying, E.N.; Dockter, T.J.; Jacobs, N.L.; Pasche, B.C.; Cleary, J.M.; et al. Regorafenib dose-optimisation in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer (ReDOS): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).