Dual Hyaluronic Acid and Folic Acid Targeting pH-Sensitive Multifunctional 2DG@DCA@MgO-Nano-Core–Shell-Radiosensitizer for Breast Cancer Therapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of DDM
2.1.1. Preparation of MgO Nanoparticles
2.1.2. Preparation of MgO@DCA@2DG
2.1.3. Preparation of MgO@DCA@2DG Conjugated with HA and FA
2.2. Characterization of DDM
2.3. Stability of DDM
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Cytotoxicity/Morphology Assay
2.6. DDM Release
2.7. Cell Selectivity and DDM Uptake
2.8. γ-ray Irradiation
2.9. Multi-MTT Assay
2.10. Protocol of the Study
2.11. Cell Cycle, Apoptosis, and CD44 Analysis Using Flow Cytometry
2.12. Determination of Glucose, Lactate, and Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Metabolism
2.13. Analysis of Hexokinase (HK) and Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH) Activities
2.14. RNA Isolation and Real Time PCR Analysis
2.15. Measurement of Intracellular PKM2, HIF-1α, PDK1, NF-κB, VEGF, and ROS Levels by ELISA Assay
2.16. Western Blotting Analysis
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of DDM
3.2. DDM Stability
3.3. The Anti-Proliferative Effects of DDM on BC Cell Growth
3.4. DDM Release
3.5. Selective Delivery and Cellular Uptake of DDM in BC Cells
3.6. DDM Inhibited Tumorigenesis and Enhanced Radiosensitivity of Human Breast Cancer Cells
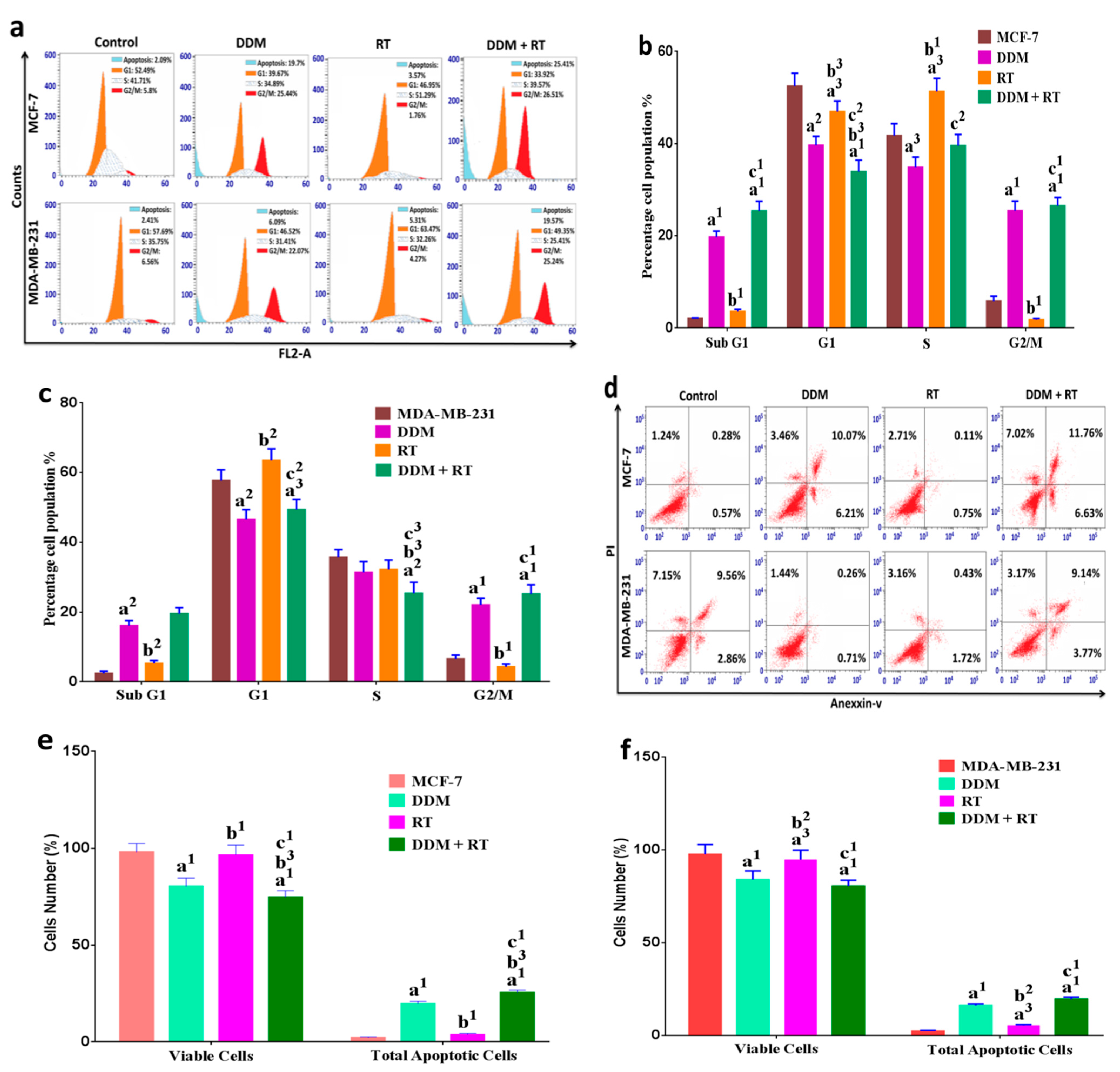
3.7. DDM and/or RT Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cells
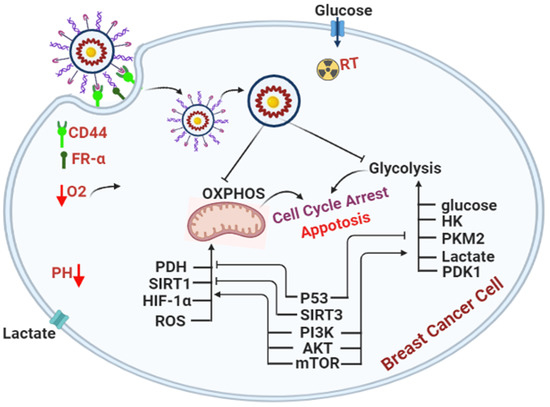
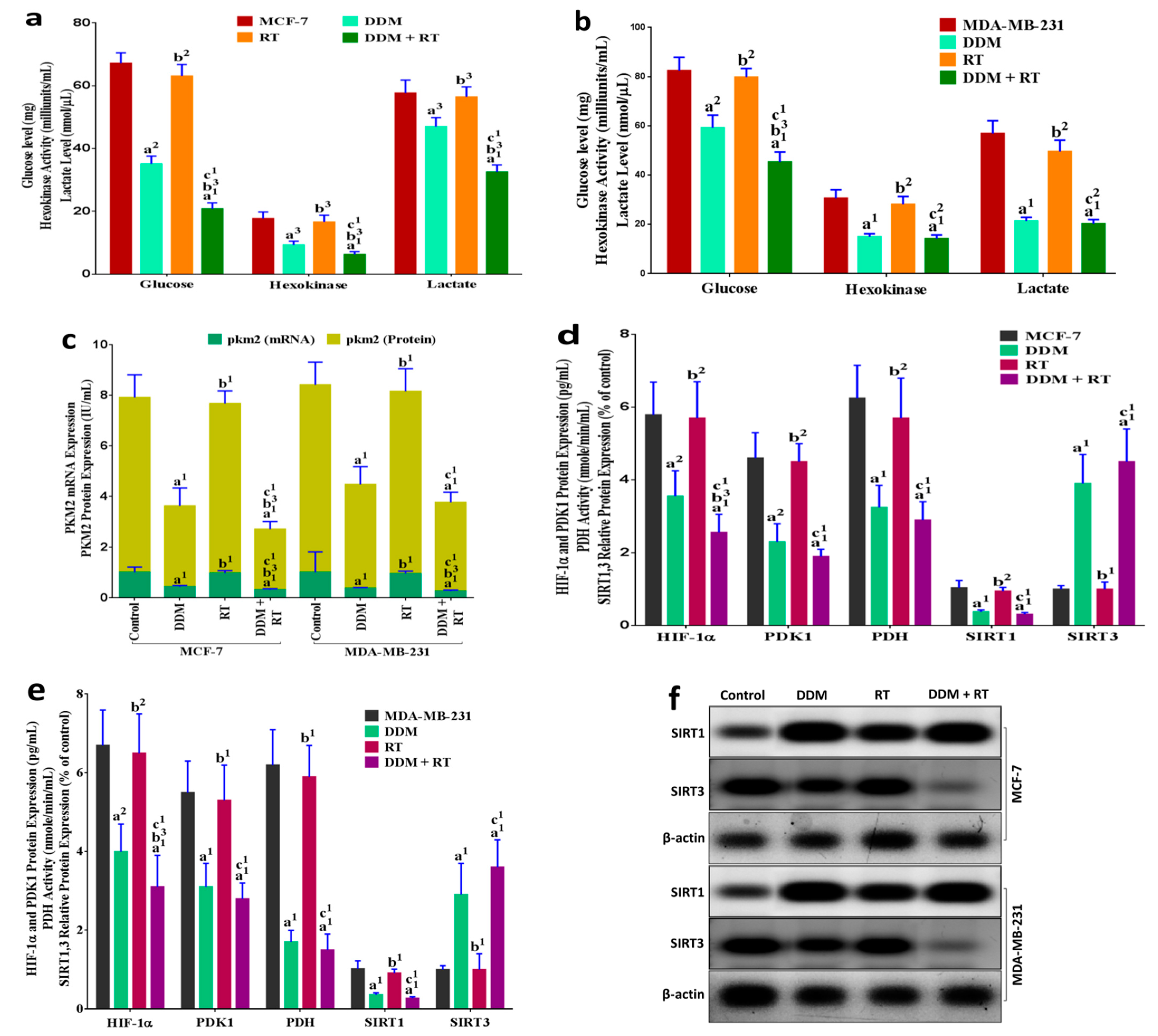
3.8. DDM Was a Dual-Targeting for Glycolysis and OXPHOS Pathways and Improved Radio-Sensitivity of Breast Cancer Cells
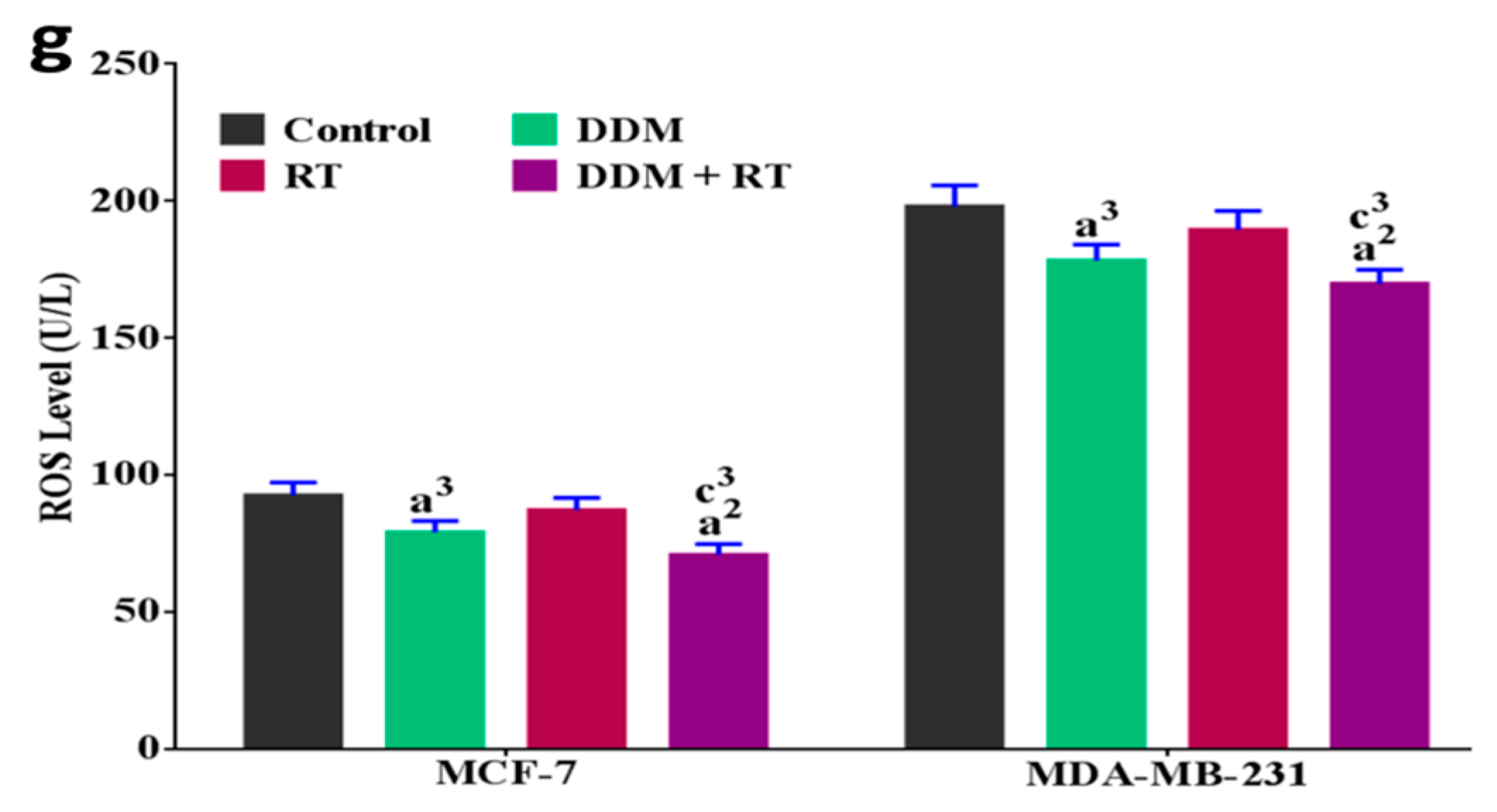
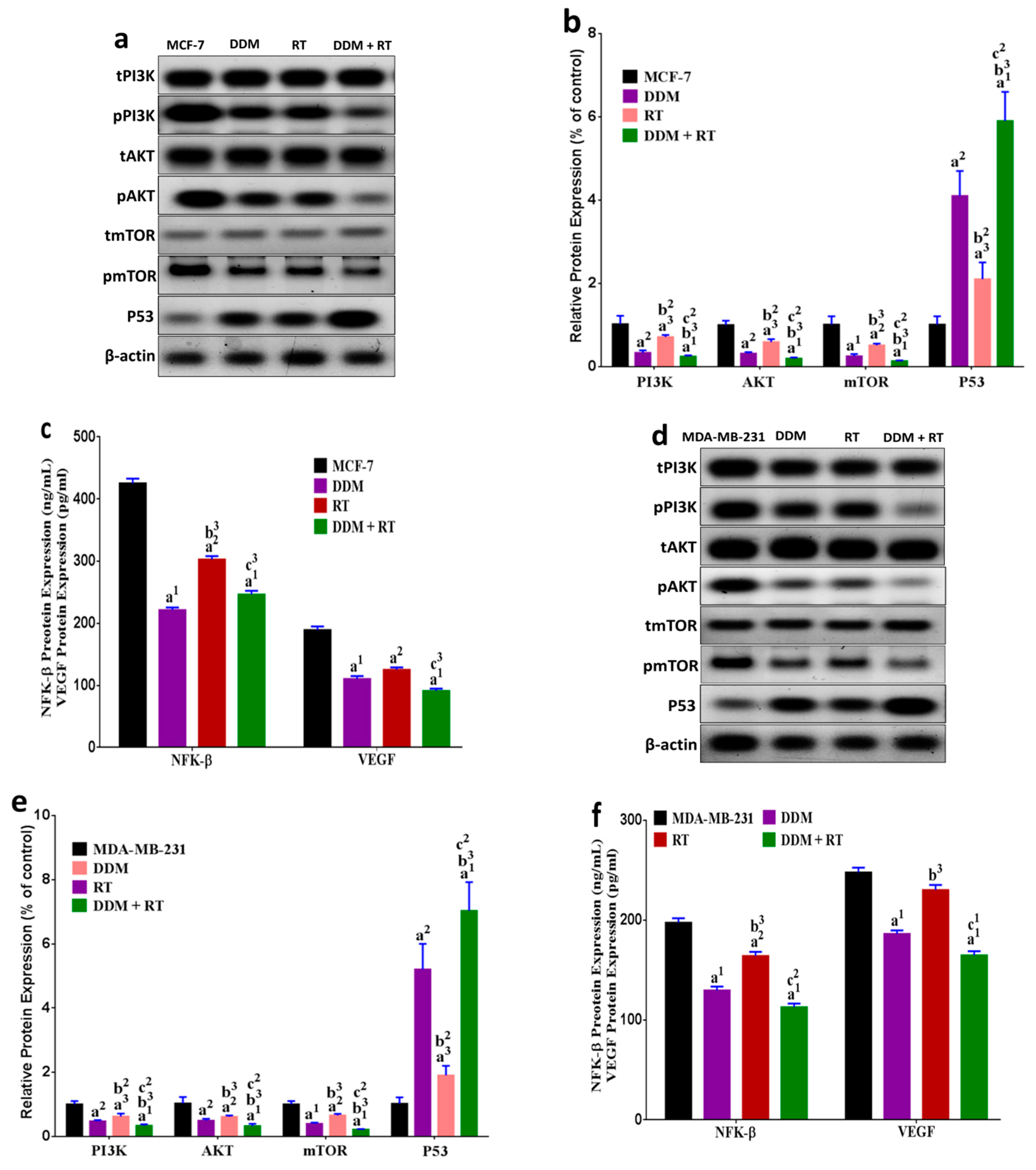
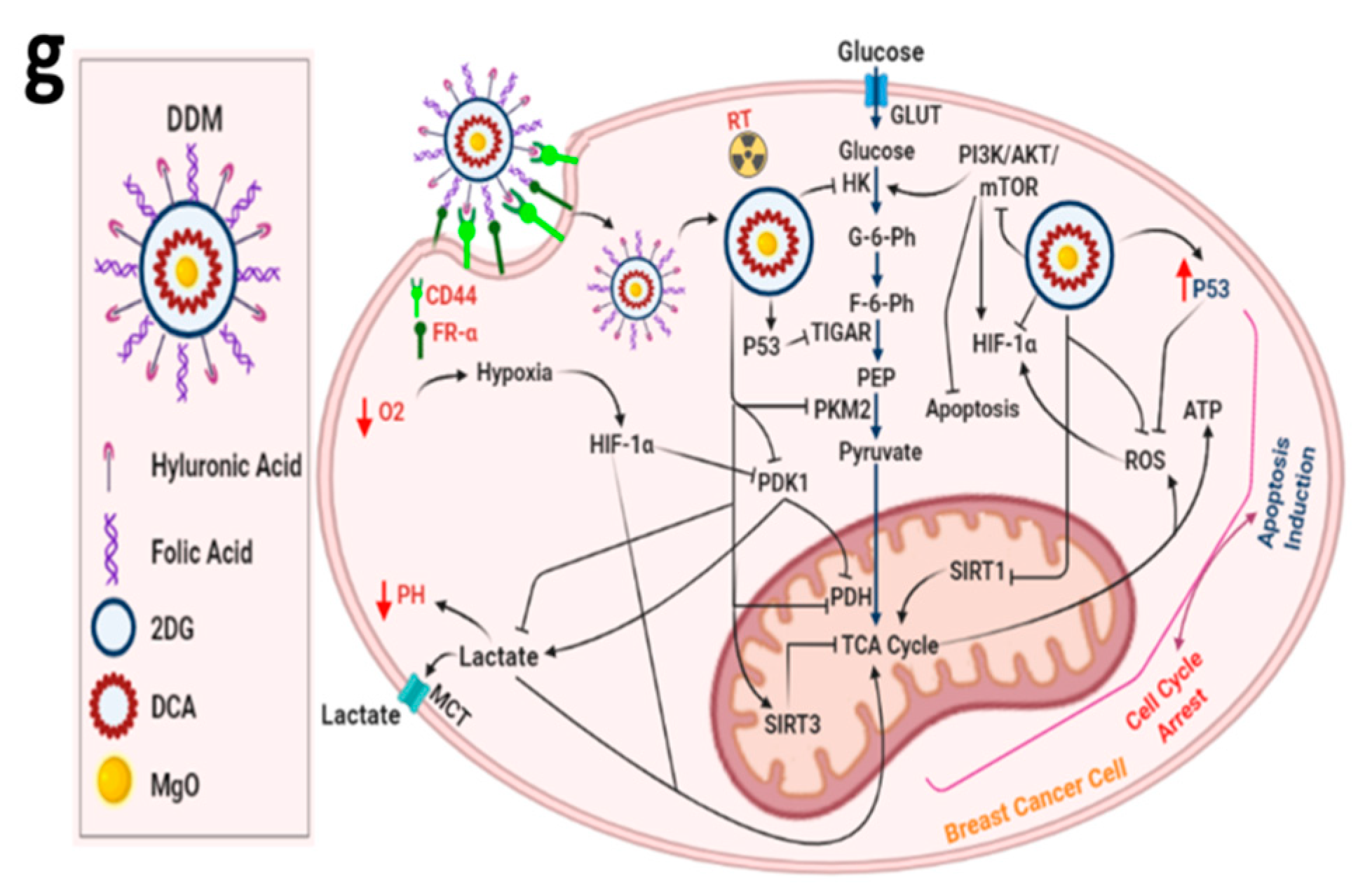
3.9. DDM and/or Radiotherapy Regulated Metabolic Glycolysis and OXPHOS through a Novel PI3K/AKT/mTOR/P53/NF-κB/VEGF Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pengying, W.; Yue, S.; Wei, D.; Huige, Z.; Shifang, G.; Lei, Z.; Xiaobing, W.; Mingxi, W.; Yujin, Z. Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of hyaluronic acid modified nanocomposites combined with sonochemotherapy against subcutaneous and metastatic breast tumors. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 11470–11483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, B. Targeted therapeutic options and future perspectives for HER2-positive breast cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucantoni, F.; Dussmann, H.; Prehn, J.H.M. Metabolic targeting of breast cancer cells with the 2-Deoxy-D-glucose and the mitochondrial bioenergetics inhibitor MDIVI-1. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lan, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, L. Reduction-sensitive cD44 receptor-targeted hyaluronic acid derivative micelles for doxorubicin delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4361–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, A.; Kolokithas-Ntoukas, A.; Fytas, C.; Avgoustakis, K. Folic acid-functionalized, condensed magnetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of doxorubicin to tumor cancer cells overexpressing the folate receptor. ASC Omega J. 2019, 4, 22214–22227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, M.A.; Fraile-Martínez, O.; Asúnsolo, Á.; Buján, J.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Coca, S. Signal transduction pathways in breast cancer: The important role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR. J. Oncol. 2020, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Nanoparticle-mediated combination therapy: Two-in-one approach for cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyaskovskaya, O.N.; Kolesnik, D.L.; Fedorchuk, A.G.; Prokhorova, I.V.; Solyanik, G.I. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose enhances dichloroacetate antitumor action against Lewis lung carcinoma. Exp. Oncol. 2016, 38, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwarakanath, B.S.; Singh, D.; Banerji, A.K.; Sarin, R.; Venkataramana, N.K.; Jalali, R.; Vishwanath, P.N.; Mohanti, B.K.; Tripathi, R.P.; Kalia, V.K.; et al. Clinical studies for improving radiotherapy with 2-Deoxy-D-glucose: Present status and future prospects. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2009, 5, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tataranni, T.; Piccoli, C. Dichloroacetate (DCA) and cancer: An overview towards clinical applications. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8201079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzadi, E.; Sarsharzadeh, R.; Nouri, M.; Attar, F.; Akhtari, K.; Shahpasand, K.; Falahati, M. Albumin binding and anticancer effect of magnesium oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maksoud, M.A.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Ashour, A.H.; El-Batal, A.I.; Abd-Elmonem, M.S.; Hendawy, H.A.M.; Abdel-Khalek, E.K.; Labib, S.; Abdeltwab, E.; El-Okr, M.M. Synthesis and characterization of metals-substituted cobalt ferrite [Co (1− x)] MxFe2O4;(M = Zn, Cu, Mn; x = 0, 05)] nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents and sensors for Anagrelide determination in biological samples. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 1, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, F.u.; Aman, W.; Ullah, I.; Qureshi, O.S.; Mustapha, O.; Shafique, S.; Zeb, A. Effective use of nanocarriers as drug delivery systems for the treatment of selected tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7291–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biau, J.; Chautard, E.; Verrelle, P.; Dutreix, M. Altering DNA repair to improve radiation therapy: Specific and multiple pathway targeting. Front. Oncol. 2019, 10, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.Y.; Cheng, R.; Yang, Z.; Tian, Z.M. Nanotechnology for cancer therapy based on chemotherapy. Molecules 2018, 23, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golombek, S.K.; May, J.N.; Theek, B.; Appold, L.; Drude, N.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Tumor targeting via EPR: Strategies to enhance patient responses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 130, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Guo, C.; Hou, X.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, D. Novel multifunctional triple folic acid, biotin and CD44 targeting pH-sensitive nano-actiniaes for breast cancer combinational therapy. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, P.; Saravanakumar, S.; Prasad, K.H.; Sivaganesh, D.; Chidhambaram, N.; Isaac, R.S.R.; Alshahrani, T.; Shkir, M.; AIFaify, S.; Ali, K.S.S. Enhanced photocatalytic decomposition efficacy of novel MgO NPs: Impact of annealing temperatures. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 3027–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belavi, P.; Chavana, G.N.; Naika, L.R.; Somashekar, R.; Kotnalac, R.K. Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of cadmium substituted nickel–copper ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Reheem, A.M.; Atta, A.; Abdel Maksoud, M.I.A. Low energy ion beam induced changes in structural and thermal properties of polycarbonate. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2016, 127, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.C.; Tseng, C.N.; Yang, J.I.; Huang, H.W.; Fang, Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Chang, F.R.; Chang, H.W. Antiproliferation and induction of apoptosis in Ca9-22 oral cancer cells by ethanolic extract of Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Molecules 2012, 17, 10916–10927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planeta, K.; Kubala-Kukus, A.; Drozdz, A.; Matusiak, K.; Setkowicz, Z.; Chwiej, J. The assessment of the usability of selected instrumental techniques for the elemental analysis of biomedical samples. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janic, B.; Liu, F.; Bobbitt, K.R.; Brown, S.L.; Chetty, I.J.; Mao, G.; Movsas, B.; Wen, N. Cellular uptake and radio-sensitization effect of small gold nanoparticles in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1000499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/ASTM E 51026. Practice for Using the Fricke Dosimeter System. 2015. Available online: https://www.sis.se/std-919097 (accessed on 7 May 2015).
- Minafra, L.; Minafra, L.; Porcino, N.; Bravatà, V.; Gaglio, D.; Bonanomi, M.; Amore, E.; Cammarata, F.P.; Russo, G.; Militello, C.; et al. Radiosensitizing effect of curcumin-loaded lipid nanoparticles in breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, K.; Peters, T.; Nawroth, T.; Sänger, M.; Schmidberger, H.; Langguth, P. Determination of cell survival after irradiation via clonogenic assay versus multiple MTT Assay -A comparative study. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, K.; Kojima, K.; Takahashi, S.; Saito, S.; Endo, Y.; Nittami, T.; Nozaki, T.; Sobti, R.C.; Watanabe, M. Combined effects of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and chemotherapeutic agents on prostate cancer cells in vitro. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korga, A.; Ostrowska, M.; Iwan, M.; Herbet, M.; Dudka, J. Inhibition of glycolysis disrupts cellular antioxidant defense and sensitizes HepG2 cells to doxorubicin treatment. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, S.; Honoki, K.; Tsukamoto, S.; Fujii, H.; Kondo, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Kuniyasu, H. Dual inhibition of distinct metabolic features targets osteosarcoma stem cells. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, nr801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajengi, A.L.; Sasaki, T.; Bhanage, B.M. Mechanistic aspects of formation of MgO nanoparticles under microwave irradiation and its catalytic application. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.H.; El-Batal, A.I.; AbdelMaksoud, M.I.A.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Labib, S.H.; Abdeltwab, E.; El-Okr, M.M. Antimicrobial activity of metal-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel technique. Particuology 2018, 40, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipare, K.; Bandgar, S.; Shahane, G. Effect of Dy-substitution on structural and magnetic properties of MnZn ferrite nanoparticles. J. Rare Earths 2018, 36, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Qin, C.; Wu, Y.C.; Xu, W.; Zhang, S.; Lu, A. Structure and properties of Fe2O3-doped 50Li2O-10B2O3-40P2O5 glass and glass-ceramic electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 2020, 345, 115177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebanova, O.N.; Lazor, P. Raman spectroscopic study of magnetite (FeFe2O4): A new assignment for the vibrational spectrum. J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 174, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayyad, G.S.; Mosallam, F.M.; El-Batal, A.I. One-pot green synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using Penicillium chrysogenum melanin pigment and gamma rays with antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant microbes. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Y.; Wang, C.X.; Jin, P.K.; Zhao, B.; Fan, X. Complexation of anthracene with folic acid studied by FTIR and UV spectroscopies. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 72, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, S.A.; da Silva, B.C.; Riegel-Vidotti, I.C.; Urbano, A.; de Sousa, F.P.C.; Tischer, C.A. Production and characterization of bacterial cellulose membranes with hyaluronic acid from chicken comb. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikiori, H.; Tagahara, M.; Mukoyama, L.; Fujii, T. Photocatalytic degradation of dichloroacetyl chloride adsorbed on TiO2. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2010, 36, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akan, Z.; Demiroglu, H.; Avcibasi, U.; Oto, G.; Ozdemir, H.; Deniz, S.; Basak, A.S. Complexion of boric acid with 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (DG) as a novel boron carrier for BNCT. Med. Sci. Discov. 2014, 1, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mohammed, E. Qualitative and quantitative determination of folic acid in tablets by FTIR spectroscopy. IJAPBC 2014, 3, 773–780. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.J.; Karunakaran, K. Purification and characterization of hyaluronic acid produced by Streptococcus zooepidemicus strain 3523-7. J. BioSci. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Wu, T.; Qin, Y.; Qi, Y.; Sun, Y.; Kong, M.; Jiang, X.; Qin, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Z. A facile doxorubicin-dichloroacetate conjugate nanomedicine with high drug loading for safe drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Du, Z.; Wang, P.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Lei, X.; Ren, F. 2-deoxyglucose-modified folate derivative: Self-assembling nanoparticle able to load cisplatin. Molecules 2019, 24, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Velavan, R.; Batoob, K.M.; Raslan, E.H. Microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties of MgO nanoparticles. Res. Phys. 2020, 16, 10301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Zhong, W.; Zhang, H. Construction of hierarchically one-dimensional core-shell CNT@Microporous carbon by covalent bond-induced surface-confined cross-linking for high-performance supercapacitor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 15557–15565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, I.K.; Robert, G.N.; Dmitry, M.; Wendelin, S.J. Synthesis and covalent surface functionalization of nonoxidic iron core–shell nanomagnets. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3275–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, T.; Li, P. Ultra-broadband and covalently linked core-shell CoFe2O4@PPy nanoparticles with reduced graphene oxide for microwave absorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 595, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonn, M.; Hunger, J. Between a hydrogen and a covalent bond. Science 2021, 8, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppuluri, S.; Swanson, D.; Piehler, L.; Li, J.; Hagnauer, G.; Tomalia, D. Core–shell tecto (dendrimers): I. Synthesis and characterization of saturated shell models. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivask, A.; Titma, T.; Visnapuu, M.; Vija, H.; Kakinen, A.; Sihtmae, M.; Pokhrel, S.; Madler, L.; Heinlaan, M.; Kisand, V.; et al. Toxicity of 11 metal oxide nanoparticles to three mammalian cell types in vitro. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1914–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, S.; Yang, D.; Fang, Y.; Lin, X.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, K.; Shi, K. Influencing factors and strategies of enhancing nanoparticles into tumors in vivo. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 03, 2211–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ruan, B.J.; Wang, L.; Xiang, A.; Wu, D.; Lu, Z. Co-delivery nanocarriers targeting folate receptor and encapsulating 2-Deoxyglucose and α-tocopheryl succinate enhance anti-tumor effect. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5701–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skeberdytė, A.; Sarapinienė, I.; Aleksander-Krasko, J.; Stankevičius, V.; Sužiedėlis, K.; Jarmalaitė, S. Dichloroacetate and salinomycin exert a synergistic cytotoxic effect in colorectal cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodossis, A.T.; Ali, M.; Grigalavicius, M.; Grallert, B.; Dillard, P.; Schink, K.O.; Olsen, C.E.; Wälchli, S.; Inderberg, E.M.; Kubin, A.; et al. Simultaneous defeat of MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 resistances by a hypericin PDT–tamoxifen hybrid therapy. NPJ Breast Cancer 2019, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanga, Z.; Sau, S.; Alsaab, H.O.; Iyer, A.K. CD44 directed nanomicellar payload delivery platform for selective anticancer effect and tumor specific imaging of triple negative breast cancer. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 1441–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennie, L.; Bennie, L.; Belhout, S.A.; Quinn, S.J.; Coulter, J.A. Polymer-supported gold nanoparticle radiosensitizers with enhanced cellular uptake efficiency and increased cell death in human prostate cancer cells. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3157–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Yan, X.; Huang, Z.; Xu, P. Hyaluronic acid and Arg-Gly-Asp peptide modified graphene oxide with dual receptor-targeting function for cancer therapy. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 32, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, S.; Zhang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Liu, X. pH-sensitive biomaterials for drug delivery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.R.; Mangesius, J.; Skvortsova, I.I.; Ganswindt, U. The role of cancer stem cells in radiation resistance. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velesiotis, C.; Vasileiou, S.; Vynios, D.H. A guide to hyaluronan and related enzymes in breast cancer: Biological significance and diagnostic value. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3057–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezar, S.K.; Prevc, A.; Zakelj, M.N.; Brozic, A.; Cemazar, M.; Strojan, P.; Sersa, G. Synergistic effect of cisplatin chemotherapy combined with fractionated radiotherapy regimen in HPV-positive and HPV-negative experimental pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islamian, J.P.; Aghaee, F.; Farajollahi, A.; Baradaran, B.; Fazel, M. Combined treatment with 2-Deoxy-D-glucose and doxorubicin enhances the in vitro efficiency of breast cancer radiotherapy. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi Fard, A.; Tavakoli, M.B.; Salehi, H.; Hamid, E. Synergetic effects of docetaxel and ionizing radiation reduced cell viability on MCF-7 breast cancer cell. Appl. Cancer Res. 2017, 37, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangmano, S.; Sae-Lim, P.; Suksamrarn, A.; Patmasiriwat, P.; Domann, F.E. Cucurbitacin B causes increased radiation sensitivity of human breast cancer cells via G2/M cell cycle arrest. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 601682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Ni, Y.H.; Liao, K.F.; Chiu, S.C. Anti-tumor and radiosensitization effects of N-butylidenephthalide on human breast cancer cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etti, I.C.; Abdullah, R.; Kadir, A.; Hashim, N.M.; Yeap, S.K.; Imam, M.U.; Ramli, F.; Malami, I.; Lam, K.L.; Etti, U.; et al. The molecular mechanism of the anticancer effect of artonin E in MDA-MB 231 triple negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wei, F.; Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Shi, L.; Xiong, F.; Gong, Z.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Deng, H.; et al. Role of metabolism in cancer cell radioresistance and radiosensitization methods. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Chen, M.; Gao, S.; Yuan, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zou, X. LY294002 inhibits the Warburg effect in gastric cancer cells by downregulating pyruvate kinase M2. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4358–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.A.; Schumacher, B. p53 in the DNA-damage-repair process. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiang, M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Khat Promotes human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell apoptosis via mitochondria and MAPK-associated pathways. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3947–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Park, K.C.; Yun, M. The bifunctional autophagic flux by 2-Deoxyglucose to control survival or growth of prostate cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 7, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Kong, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Geng, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Feng, S.; et al. Preliminary study on radiosensitivity to carbon ions in human breast cancer. J. Radiat. Res. 2020, 61, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Zhong, L.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, K.; Pang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Mi, P.; Cao, H.; et al. Matrine reverses the warburg effect and suppresses colon cancer cell growth via negatively regulating HIF-1α. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurbubu, T.M.; Mokhosoev, I.M.; Terentiev, A.A. Metabolic heterogeneity of cancer cells: An interplay between HIF-1, GLUTs, and AMPK. Cancers 2020, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Nam, J.S. Targeting cancer stem cells in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, A.M.; Antolin, I.; Puente-Moncada, N.; Suarez, S.; Gomez-Lobo, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Martin, V. Melatonin cytotoxicity is associated to Warburg effect inhibition in ewing sarcoma cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 7, e0135420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.Y.; Park, E.Y.; Woo, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, E.K.; De, U.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.H.; et al. Anticancer effects of a new SIRT inhibitor, MHY2256, against human breast cancer MCF-7 cells via regulation of MDM2-p53 binding. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Shen, S.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P.; Gu, L. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the proliferation of leukemia cells K562 by suppressing PKM2 and GLUT1 mediated aerobic glycolysis. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2020, 14, 2091–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugrud, A.B.; Zhuang, Y.; Coppock, J.D.; Miskimins, W.K. Dichloroacetate enhances apoptotic cell death via oxidative damage and attenuates lactate production in metformin-treated breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orang, A.V.; Petersen, J.; McKinnon, R.A.; Michael, M.Z. Micromanaging aerobic respiration and glycolysis in cancer cells. Mol. Metab. 2019, 23, 98–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Yang, Z.; Huang, R.; Min, Z.; Ye, M. SIRT6 promotes the Warburg effect of papillary thyroid cancer cell BCPAP through reactive oxygen species. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Dorfman, R.G.; Liu, L.; Cai, R.; Jiang, C.; Tang, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. SIRT3 elicited an anti-Warburg effect through HIF1α/PDK1/PDHA1 to inhibit cholangiocarcinoma tumorigenesis. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2380–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Huang, G. Dichloroacetic acid (DCA) synergizes with the SIRT2 inhibitor sirtinol and AGK2 to enhance anti-tumor efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Wilkinson, F.L.; Sandhu, M.A.; Santos, J.M.D.; Alexander, M.Y. Modulating oxidative stress in drug-induced injury and metabolic disorders: The role of natural and synthetic antioxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3206401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajak, B.; Siwiak, E.; Sołtyka, M.; Priebe, A.; Zieliński, R.; Fokt, I.; Ziemniak, M.; Jaśkiewicz, A.; Borowski, R.; Domoradzki, T.; et al. 2-Deoxy-d-glucose and its analogs: From diagnostic to therapeutic agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antognelli, C.; Palumbo, I.; Aristei, C.; Talesa, V.N. Glyoxalase I inhibition induces apoptosis in irradiated MCF-7 cells via a novel mechanism involving Hsp27, p53 and NF-κB. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Genes | Forward Primers | Reverse Primers |
|---|---|---|
| FR-α | 5′-CTGGCTGGTGTTGGTAGAACAG-3′ | 5′-AGGCCCCGAGGACAAGTT-3′ |
| PKM2 | 5′-GAGGCCTCCTTCAAGTGCTG-3′ | 5′-CATGGCAAAGTTCACCCGGA-3′ |
| GAPDH | 5′-GTCAAGGCTGAGAACGGGAA-3′ | 5′-AAATGAGCCCCAGCCTTCTC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Askar, M.A.; Thabet, N.M.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; El-Batal, A.I.; Abd Elkodous, M.; El Shawi, O.E.; Helal, H.; Abdel-Rafei, M.K. Dual Hyaluronic Acid and Folic Acid Targeting pH-Sensitive Multifunctional 2DG@DCA@MgO-Nano-Core–Shell-Radiosensitizer for Breast Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 5571. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215571
Askar MA, Thabet NM, El-Sayyad GS, El-Batal AI, Abd Elkodous M, El Shawi OE, Helal H, Abdel-Rafei MK. Dual Hyaluronic Acid and Folic Acid Targeting pH-Sensitive Multifunctional 2DG@DCA@MgO-Nano-Core–Shell-Radiosensitizer for Breast Cancer Therapy. Cancers. 2021; 13(21):5571. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215571
Chicago/Turabian StyleAskar, Mostafa A., Noura M. Thabet, Gharieb S. El-Sayyad, Ahmed I. El-Batal, Mohamed Abd Elkodous, Omama E. El Shawi, Hamed Helal, and Mohamed K. Abdel-Rafei. 2021. "Dual Hyaluronic Acid and Folic Acid Targeting pH-Sensitive Multifunctional 2DG@DCA@MgO-Nano-Core–Shell-Radiosensitizer for Breast Cancer Therapy" Cancers 13, no. 21: 5571. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215571
APA StyleAskar, M. A., Thabet, N. M., El-Sayyad, G. S., El-Batal, A. I., Abd Elkodous, M., El Shawi, O. E., Helal, H., & Abdel-Rafei, M. K. (2021). Dual Hyaluronic Acid and Folic Acid Targeting pH-Sensitive Multifunctional 2DG@DCA@MgO-Nano-Core–Shell-Radiosensitizer for Breast Cancer Therapy. Cancers, 13(21), 5571. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13215571