Elucidating the Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Pancreatic Cancer
1.2. Extracellular Vesicle Overview
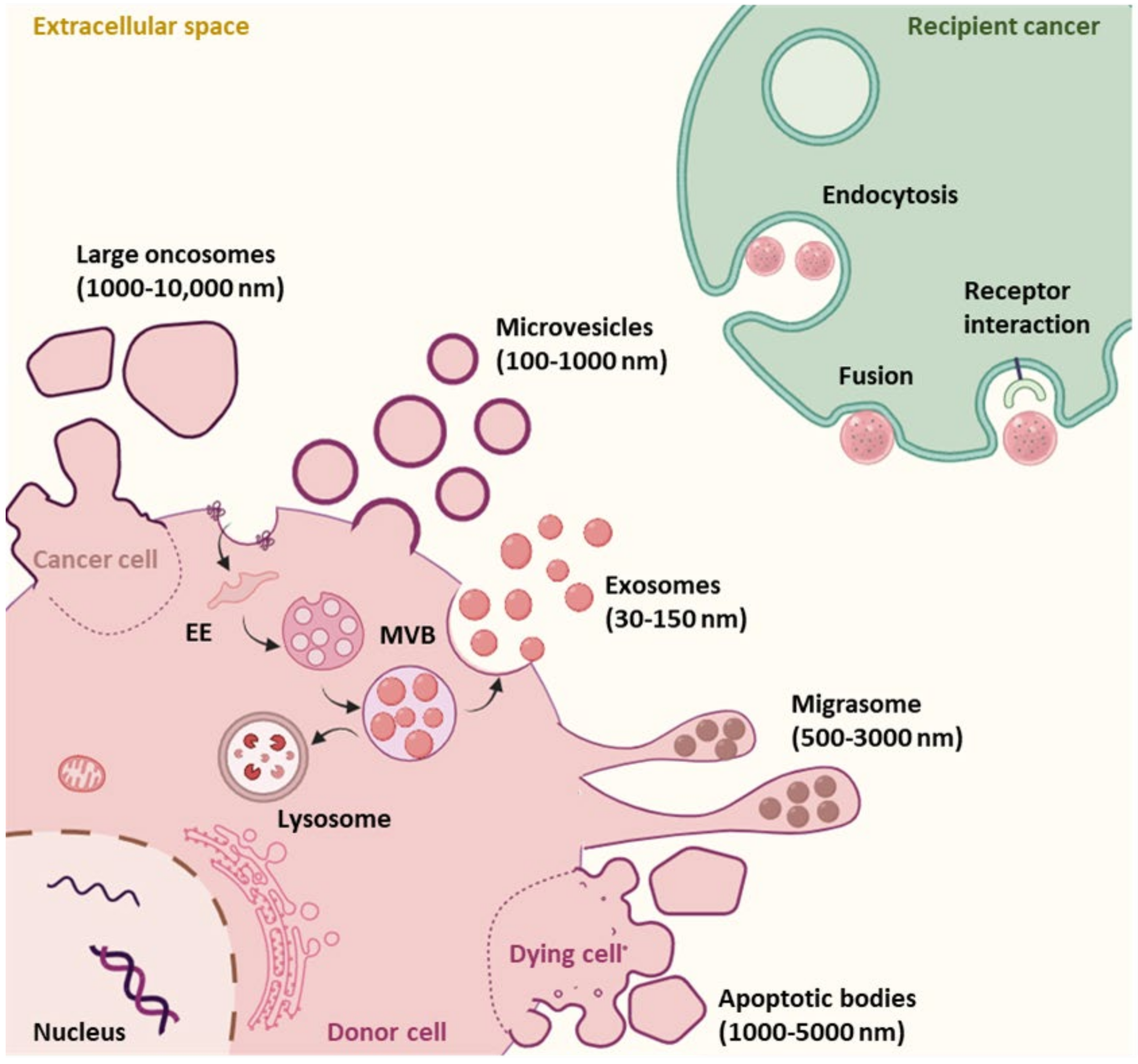
1.2.1. EV Subtypes and Biogenesis
1.2.2. Key Methodologies to Isolate and Characterize EVs
1.2.3. EV Cell-to-Cell Signalling and Cargo Delivery
2. The Role of EVs in Pancreatic Cancer
2.1. EVs Aid PC Cell Proliferation and Angiogenesis
2.2. PC EVs Modulate Invasion and Metastasis
2.3. PC EVs Promote Chemoresistance in PC
2.4. EVs Regulate Tumour-Associated Immunity
2.5. EVs Participate in PC Metabolic Disfunction
3. Potential Applications of EVs in Diagnosis and Treatment of PC
3.1. EVs as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers
3.2. EVs as Drug Delivery Tools
3.3. EVs as Potential Therapeutic Targets
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleeff, J.; Korc, M.; Apte, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Johnson, C.D.; Biankin, A.V.; Neale, R.E.; Tempero, M.; Tuveson, D.A.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deplanque, G.; Demartines, N. Pancreatic cancer: Are more chemotherapy and surgery needed? Lancet 2017, 389, 985–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, D.P.; Hong, T.S.; Bardeesy, N. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Yang, Y.M.; Pandol, S.J.; Seki, E. Exosome Migration Inhibitory Factor as a Marker and Therapeutic Target for Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1033–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathivanan, S.; Ji, H.; Simpson, R.J. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.-K.; Giebel, B. Exosomes: Small vesicles participating in intercellular communication. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzás, E.I.; Di Vizio, D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossetti, C.; Iraci, N.; Mercer, T.; Leonardi, T.; Alpi, E.; Drago, D.; Alfaro-Cervello, C.; Saini, H.K.; Davis, M.; Schaeffer, J.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Neural Stem Cells Transfer IFN-γ via Ifngr1 to Activate Stat1 Signaling in Target Cells. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalra, H.; Drummen, G.P.C.; Mathivanan, S. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Introducing the Next Small Big Thing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samuel, M.; Chisanga, D.; Liem, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Anand, S.; Ang, C.-S.; Adda, C.; Versteegen, E.; Jois, M.; Mathivanan, S. Bovine milk-derived exosomes from colostrum are enriched with proteins implicated in immune response and growth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palviainen, M.; Saari, H.; Kärkkäinen, O.; Pekkinen, J.; Auriola, S.; Yliperttula, M.; Puhka, M.; Hanhineva, K.; Siljander, P.R.-M. Metabolic signature of extracellular vesicles depends on the cell culture conditions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1596669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzan, A.L.; Nedeva, C.; Mathivanan, S. Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolism and Metabolic Diseases. Subcell Biochem. 2021, 97, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangoda, L.; Liem, M.; Ang, C.-S.; Keerthikumar, S.; Adda, C.G.; Parker, B.; Mathivanan, S. Proteomic Profiling of Exosomes Secreted by Breast Cancer Cells with Varying Metastatic Potential. Proteomics 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Moita, C.F.; van Niel, G.; Kowal, J.; Vigneron, J.; Benaroch, P.; Manel, N.; Moita, L.F.; Théry, C.; Raposo, G. Analysis of ESCRT functions in exosome biogenesis, composition and secretion highlights the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 5553–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wollert, T.; Hurley, J.H. Molecular mechanism of multivesicular body biogenesis by ESCRT complexes. Nature 2010, 464, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simons, M.; Raposo, G. Exosomes – vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, M.; Carmo, N.B.; Krumeich, S.; Fanget, I.; Raposo, G.; Savina, A.; Moita, C.F.; Schauer, K.; Hume, A.N.; Freitas, R.P.; et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cocucci, E.; Racchetti, G.; Meldolesi, J. Shedding microvesicles: Artefacts no more. Trends Cell Biol. 2009, 19, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthikumar, S.; Gangoda, L.; Liem, M.; Fonseka, P.; Atukorala, I.; Ozcitti, C.; Mechler, A.; Adda, C.G.; Ang, C.-S.; Mathivanan, S. Proteogenomic analysis reveals exosomes are more oncogenic than ectosomes. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15375–15396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pollet, H.; Conrard, L.; Cloos, A.-S.; Tyteca, D. Plasma Membrane Lipid Domains as Platforms for Vesicle Biogenesis and Shedding? Biomolecules 2018, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tricarico, C.; Clancy, J.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Biology and biogenesis of shed microvesicles. Small GTPases 2016, 8, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vietri, M.; Radulovic, M.; Stenmark, H. The many functions of ESCRTs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baietti, M.F.; Zhang, Z.; Mortier, E.; Melchior, A.; DeGeest, G.; Geeraerts, A.; Ivarsson, Y.; Depoortere, F.; Coomans, C.; Vermeiren, E.; et al. Syndecan–syntenin–ALIX regulates the biogenesis of exosomes. Nature 2012, 14, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.E.; Scruggs, B.S.; Schaffer, J.E.; Hanson, P.I. Effects of Inhibiting VPS4 Support a General Role for ESCRTs in Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis. Biophys. J. 2017, 113, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathieu, M.; Névo, N.; Jouve, M.; Valenzuela, J.I.; Maurin, M.; Verweij, F.J.; Palmulli, R.; Lankar, D.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; et al. Specificities of exosome versus small ectosome secretion revealed by live intracellular tracking of CD63 and CD9. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, G.L.; Reményi, G.; Friese, P. Tetraspanin CD9 is required for microparticle release from coated-platelets. Platelets 2009, 20, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabhan, J.F.; Hu, R.; Oh, R.S.; Cohen, S.N.; Lu, Q. Formation and release of arrestin domain-containing protein 1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) at plasma membrane by recruitment of TSG101 protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4146–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anand, S.; Samuel, M.; Kumar, S.; Mathivanan, S. Ticket to a bubble ride: Cargo sorting into exosomes and extracellular vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019, 1867, 140203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, S.; Poon, I.K.H.; Caruso, S.; Poon, I.K.H. Apoptotic Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: More Than Just Debris. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Liang, M.; Peng, J.; Wu, D.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, X.; Du, Y.; Yu, L. Discovery of the migrasome, an organelle mediating release of cytoplasmic contents during cell migration. Cell Res. 2014, 25, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Rocha-Azevedo, B.; Schmid, S.L. Migrasomes: A new organelle of migrating cells. Cell Res. 2014, 25, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Vizio, D.; Morello, M.; Dudley, A.C.; Schow, P.W.; Adam, R.M.; Morley, S.; Mulholland, D.; Rotinen, M.; Hager, M.H.; Insabato, L.; et al. Large Oncosomes in Human Prostate Cancer Tissues and in the Circulation of Mice with Metastatic Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and Characterization of Exosomes from Cell Culture Supernatants and Biological Fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, C.; Di Vizio, D.; Sahoo, S.; Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Wauben, M.; Hill, A.F. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Results of a worldwide survey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 32945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, B.J.; Greening, D.; Mathias, R.; Ji, H.; Mathivanan, S.; Scott, A.; Simpson, R.J. Comparison of ultracentrifugation, density gradient separation, and immunoaffinity capture methods for isolating human colon cancer cell line LIM1863-derived exosomes. Methods 2012, 56, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvjetkovic, A.; Lötvall, J.; Lässer, C. The influence of rotor type and centrifugation time on the yield and purity of extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.D.; Shah, S. Methods of isolating extracellular vesicles impact down-stream analyses of their cargoes. Methods 2015, 87, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böing, A.N.; van der Pol, E.; Grootemaat, A.E.; Coumans, F.A.W.; Sturk, A.; Nieuwland, R. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gámez-Valero, A.; Monguió-Tortajada, M.; Carreras-Planella, L.; Franquesa, M.; Beyer, K.; Borràs, F.E. Size-Exclusion Chromatography-based isolation minimally alters Extracellular Vesicles’ characteristics compared to precipitating agents. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep33641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konoshenko, M.Y.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles: General Methodologies and Latest Trends. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8545347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momen-Heravi, F. Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles by Ultracentrifugation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1660, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araùjo, M.E.; Huber, L.A.; Stasyk, T. Isolation of endocitic organelles by density gradient centrifugation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 424, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, M.L.; Powell, D.W.; Wilkey, D.W.; Cummins, T.D.; Deegens, J.K.; Rood, I.M.; McAfee, K.J.; Fleischer, C.; Klein, E.; Klein, J.B. Microfiltration isolation of human urinary exosomes for characterization by MS. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2010, 4, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchetti, D.; Fattorossi, A.; Sgambato, A. Extracellular Vesicles in Oncology: Progress and Pitfalls in the Methods of Isolation and Analysis. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 14, e1700716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakai, W.; Yoshida, T.; Diez, D.; Miyatake, Y.; Nishibu, T.; Imawaka, N.; Naruse, K.; Sadamura, Y.; Hanayama, R. A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, srep33935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liangsupree, T.; Multia, E.; Riekkola, M.-L. Modern isolation and separation techniques for extracellular vesicles. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1636, 461773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linares, R.; Tan, S.; Gounou, C.; Brisson, A.R. Imaging and Quantification of Extracellular Vesicles by Transmission Electron Microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1545, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enderle, D.; Spiel, A.; Coticchia, C.M.; Berghoff, E.; Mueller, R.; Schlumpberger, M.; Sprenger-Haussels, M.; Shaffer, J.M.; Lader, E.; Skog, J.; et al. Characterization of RNA from Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles Isolated by a Novel Spin Column-Based Method. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano-Pertierra, E.; Oliveira-Rodríguez, M.; Rivas, M.; Oliva, P.; Villafani, J.; Navarro, A.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Cernuda-Morollón, E. Characterization of Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Isolated by Different Methods: A Comparison Study. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Kastresana, A.; Telford, B.; Musich, T.A.; McKinnon, K.; Clayborne, C.; Braig, Z.; Rosner, A.; Demberg, T.; Watson, D.C.; Karpova, T.; et al. Labeling Extracellular Vesicles for Nanoscale Flow Cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Silva, C.; Suárez, H.; Acevedo, R.J.; Linares-Espinós, E.; Martinez-Piñeiro, L.; Yáñez-Mó, M.; Valés-Gómez, M. High sensitivity detection of extracellular vesicles immune-captured from urine by conventional flow cytometry. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Théry, C.; Duban, L.; Segura, E.; Véron, P.; Lantz, O.; Amigorena, S. Indirect activation of naïve CD4+ T cells by dendritic cell–derived exosomes. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, E.; Amigorena, S.; Théry, C. Mature dendritic cells secrete exosomes with strong ability to induce antigen-specific effector immune responses. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2005, 35, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernomordik, L.V.; Kozlov, M.M. Mechanics of membrane fusion. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahn, R.; Südhof, T.C. Membrane Fusion and Exocytosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 863–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadli, A.S.; Ballasy, N.; Edalat, P.; Patel, V.B. Inside(sight) of tiny communicator: Exosome biogenesis, secretion, and uptake. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 467, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Rong, Y.; Kuang, T.; Xu, X.; Wu, W.; Wang, D.; Lou, W. Exosomal miRNA-106b from cancer-associated fibroblast promotes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 383, 111543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Zhou, Y.-Y.; Liang, G.-F.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Hu, F.-H.; Xiao, Z.-D. Exosome Uptake through Clathrin-mediated Endocytosis and Macropinocytosis and Mediating miR-21 Delivery. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 22258–22267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, K.M.; Gullberg, L.; Nelson, K.K.; Stefan, C.J.; Blumer, K.; Lemmon, S.K. Novel functions of clathrin light chains: Clathrin heavy chain trimerization is defective in light chain-deficient yeast. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabi, I.R.; Le, P.U. Caveolae/raft-dependent endocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Zhao, W.-L.; Ye, Y.-Y.; Bai, X.-C.; Liu, R.-Q.; Chang, L.-F.; Zhou, Q.; Sui, S.-F. Cellular Internalization of Exosomes Occurs Through Phagocytosis. Traffic 2010, 11, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdera, H.C.; Gitz-Francois, J.J.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Vader, P. Cellular uptake of extracellular vesicles is mediated by clathrin-independent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. J. Control. Release 2017, 266, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: From biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, S.J.; Stewart, S.E. Socially Distanced Intercellular Communication: Mechanisms for Extracellular Vesicle Cargo Delivery. Subcell Biochem. 2021, 97, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhange, K.; Makler, A.; Wen, Y.; Ramnauth, N.; Mao, W.; Asghar, W.; Wan, Y. Small extracellular vesicles in cancer. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3705–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, M.; Iinuma, H.; Yagi, T.; Matsuda, K.; Hashiguchi, Y. Circulating Exosomal MicroRNA-21 as a Biomarker in Each Tumor Stage of Colorectal Cancer. Oncology 2017, 92, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademaker, G.; Hennequière, V.; Brohee, L.; Nokin, M.-J.; Lovinfosse, P.; Durieux, F.; Gofflot, S.; Bellier, J.; Costanza, B.; Herfs, M.; et al. Myoferlin controls mitochondrial structure and activity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, and affects tumor aggressiveness. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4398–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blomme, A.; Fahmy, K.; Peulen, O.; Costanza, B.; Fontaine, M.; Struman, I.; Baiwir, D.; De Pauw, E.; Thiry, M.; Bellahcène, A.; et al. Myoferlin is a novel exosomal protein and functional regulator of cancer-derived exosomes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tao, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Li, J.; Peng, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, K.; Liu, H.; Zhen, P.; et al. Tumor-Secreted Exosomal miR-222 Promotes Tumor Progression via Regulating P27 Expression and Re-Localization in Pancreatic Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 51, 610–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.E.; Zeleniak, A.E.; Fishel, M.L.; Wu, J.; Littlepage, L.E.; Hill, R. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leca, J.; Martinez, S.; Lac, S.; Nigri, J.; Secq, V.; Rubis, M.; Bressy, C.; Sergé, A.; Lavaut, M.-N.; Dusetti, N.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived annexin A6+ extracellular vesicles support pancreatic cancer aggressiveness. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4140–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, D.; Xie, C.; Hu, J.; Tan, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z. Pancreatic cancer cell–derived exosomal microRNA-27a promotes angiogenesis of human microvascular endothelial cells in pancreatic cancer via BTG2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 24, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novizio, N.; Belvedere, R.; Pessolano, E.; Tosco, A.; Porta, A.; Perretti, M.; Campiglia, P.; Filippelli, A.; Petrella, A. Annexin A1 Released in Extracellular Vesicles by Pancreatic Cancer Cells Activates Components of the Tumor Microenvironment, through Interaction with the Formyl-Peptide Receptors. Cells 2020, 9, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oettle, H.; Post, S.; Neuhaus, P.; Gellert, K.; Langrehr, J.; Ridwelski, K.; Schramm, H.; Fahlke, J.; Zuelke, C.; Burkart, C.; et al. Adjuvant Chemotherapy with Gemcitabine vs Observation in Patients Undergoing Curative-Intent Resection of Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA 2007, 297, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreger, B.T.; Johansen, E.R.; Cerione, R.A.; Antonyak, M.A. The Enrichment of Survivin in Exosomes from Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Paclitaxel Promotes Cell Survival and Chemoresistance. Cancers 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagathihalli, N.S.; Castellanos, J.A.; Shi, C.; Beesetty, Y.; Reyzer, M.L.; Caprioli, R.; Chen, X.; Walsh, A.; Skala, M.C.; Moses, H.L.; et al. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3, Mediated Remodeling of the Tumor Microenvironment Results in Enhanced Tumor Drug Delivery in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1932–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.-F.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Zhao, Q.-N.; Yang, D.-T.; Dong, Y.-P.; Jiang, L.; Xing, W.-X.; Li, X.-Y.; Xing, H.; Shi, M.; et al. Microvesicles mediate transfer of P-glycoprotein to paclitaxel-sensitive A2780 human ovarian cancer cells, conferring paclitaxel-resistance. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Hua, Y.; Sun, L.; Cheng, K.; Jia, Z.; Han, Y.; Dong, J.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Z. Exosomes play an important role in the process of psoralen reverse multidrug resistance of breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikamori, M.; Yamada, D.; Eguchi, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Kishimoto, T.; Tomimaru, Y.; Asaoka, T.; Noda, T.; Wada, H.; Kawamoto, K.; et al. MicroRNA-155 Controls Exosome Synthesis and Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, G.K.; Khan, M.A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Zubair, H.; Patton, M.C.; Singh, S.; Khushman, M.; Singh, A.P. Exosomes confer chemoresistance to pancreatic cancer cells by promoting ROS detoxification and miR-155-mediated suppression of key gemcitabine-metabolising enzyme, DCK. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Cui, J.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Peng, T. Exosomes derived from cancer stem cells of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells enhance drug resistance by delivering miR-210. Cell. Oncol. 2019, 43, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeung, C.L.A.; Co, N.-N.; Tsuruga, T.; Yeung, T.-L.; Kwan, S.Y.; Leung, C.S.; Li, Y.; Lu, E.S.; Kwan, K.; Wong, K.-K.; et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goto, T.; Fujiya, M.; Konishi, H.; Sasajima, J.; Fujibayashi, S.; Hayashi, A.; Utsumi, T.; Sato, H.; Iwama, T.; Ijiri, M.; et al. An elevated expression of serum exosomal microRNA-191, − 21, −451a of pancreatic neoplasm is considered to be efficient diagnostic marker. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriyama, T.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Yu, J.; Sato, N.; Nabae, T.; Takahata, S.; Toma, H.; Nagai, E.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Namba, T.; Kodama, R.; Moritomo, S.; Hoshino, T.; Mizushima, T. Zidovudine, an anti-viral drug, resensitizes gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine by inhibition of the Akt-GSK3β-Snail pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.L. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5904–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Ding, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Anderson, G.J.; Nie, G. Cancer Cell-derived Exosomes Induce Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase-dependent Monocyte Survival by Transport of Functional Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8453–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, G.; Zhou, L.; Qian, Y.; Fu, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Xiang, J.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, G.; Cao, L. Pancreatic cancer-derived exosomes transfer miRNAs to dendritic cells and inhibit RFXAP expression via miR-212-3p. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29877–29888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Ding, G.; Cao, L. Pancreatic cancer derived exosomes regulate the expression of TLR4 in dendritic cells via miR-203. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 292, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiougiannis, S.; Chia, D.; Kim, Y.; Singh, R.P.; Wong, D.T.W. Saliva exosomes from pancreatic tumor–bearing mice modulate NK cell phenotype and antitumor cytotoxicity. FASEB J. 2016, 31, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javeed, N.; Gustafson, M.; Dutta, S.K.; Lin, Y.; Bamlet, W.; Oberg, A.L.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T.; Dietz, A.; Mukhopadhyay, D. Immunosuppressive CD14+HLA-DRlo/neg monocytes are elevated in pancreatic cancer and “primed” by tumor-derived exosomes. OncoImmunology 2016, 6, e1252013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basso, D.; Gnatta, E.; Padoan, A.; Fogar, P.; Furlanello, S.; Aita, A.; Bozzato, D.; Zambon, C.-F.; Arrigoni, G.; Frasson, C.; et al. PDAC-derived exosomes enrich the microenvironment in MDSCs in a SMAD4-dependent manner through a new calcium related axis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 84928–84944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gastpar, R.; Gehrmann, M.; Bausero, M.A.; Asea, A.; Gross, C.; Schroeder, J.A.; Multhoff, G. Heat Shock Protein 70 Surface-Positive Tumor Exosomes Stimulate Migratory and Cytolytic Activity of Natural Killer Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5238–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.-B.; Sun, H.-Y.; Luo, Z.-L.; Cheng, L.; Duan, X.-M.; Ren, J.-D. Plasma-derived exosomes contribute to pancreatitis-associated lung injury by triggering NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis in alveolar macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javeed, N.; Sagar, G.; Dutta, S.K.; Smyrk, T.C.; Lau, J.S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Truty, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Kaufman, R.J.; Chari, S.T.; et al. Pancreatic Cancer–Derived Exosomes Cause Paraneoplastic β-cell Dysfunction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 21, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagar, G.; Sah, R.P.; Javeed, N.; Dutta, S.K.; Smyrk, T.C.; Lau, J.S.; Giorgadze, N.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L.; Chari, S.T.; et al. Pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer exosome-induced lipolysis in adipose tissue. Gut 2015, 65, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, X.; Zhang, G.; Cui, X.; Liu, M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; et al. ZIP4 Promotes Muscle Wasting and Cachexia in Mice With Orthotopic Pancreatic Tumors by Stimulating RAB27B-Regulated Release of Extracellular Vesicles From Cancer Cells. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, H.-X.; Xu, J.-W.; Wu, D.; Zhang, T.-P.; Hu, S.-Y. Pancreatic cancer stem cells: New insight into a stubborn disease. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, C.; Cavallini, L.; Spinelli, C.; Yang, J.; Reis-Sobreiro, M.; De Candia, P.; Minciacchi, V.R.; Di Vizio, D. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: New Frontiers of Cell-to-Cell Communication in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Que, R.; Ding, G.; Chen, J.; Cao, L. Analysis of serum exosomal microRNAs and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taller, D.; Richards, K.; Slouka, Z.; Senapati, S.; Hill, R.; Go, D.B.; Chang, H.-C. On-chip surface acoustic wave lysis and ion-exchange nanomembrane detection of exosomal RNA for pancreatic cancer study and diagnosis. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Deitz-McElyea, S.; Liyanage, T.U.L.H.; Lawrence, K.N.; Mali, S.; Sardar, R.; Korc, M. Label-Free Nanoplasmonic-Based Short Noncoding RNA Sensing at Attomolar Concentrations Allows for Quantitative and Highly Specific Assay of MicroRNA-10b in Biological Fluids and Circulating Exosomes. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11075–11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.-F.; Hannafon, B.N.; Zhao, Y.D.; Postier, R.G.; Ding, W.-Q. Plasma exosome miR-196a and miR-1246 are potential indicators of localized pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77028–77040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, B.; Yue, S.; Galli, U.; Rana, S.; Gross, W.; Müller, M.; Giese, N.A.; Kalthoff, H.; Becker, T.; Büchler, M.W.; et al. Combined evaluation of a panel of protein and miRNA serum-exosome biomarkers for pancreatic cancer diagnosis increases sensitivity and specificity. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, 2616–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa-Silva, B.; Aiello, N.M.; Ocean, A.J.; Singh, S.; Zhang, H.; Thakur, B.K.; Becker, A.; Hoshino, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer exosomes initiate pre-metastatic niche formation in the liver. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, K.B.; Gudbergsson, J.M.; Skov, M.N.; Pilgaard, L.; Moos, T.; Duroux, M. A comprehensive overview of exosomes as drug delivery vehicles—Endogenous nanocarriers for targeted cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2014, 1846, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vader, P.; Mol, E.A.; Pasterkamp, G.; Schiffelers, R.M. Extracellular vesicles for drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamerkar, S.; LeBleu, V.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Ruivo, C.; Melo, S.; Lee, J.J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascucci, L.; Coccè, V.; Bonomi, A.; Ami, D.; Ceccarelli, P.; Ciusani, E.; Viganò, L.; Locatelli, A.; Sisto, F.; Doglia, S.M.; et al. Paclitaxel is incorporated by mesenchymal stromal cells and released in exosomes that inhibit in vitro tumor growth: A new approach for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 192, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Mahajan, V.; Deygen, I.; Klyachko, N.L.; Inskoe, E.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Okolie, O.; et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osterman, C.J.D.; Lynch, J.C.; Leaf, P.; Gonda, A.; Bennit, H.R.F.; Griffiths, D.; Wall, N.R. Curcumin Modulates Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell-Derived Exosomal Function. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aspe, J.R.; Osterman, C.D.; Jutzy, J.; Deshields, S.; Whang, S.; Wall, N.R. Enhancement of Gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by novel exosome-mediated delivery of the Survivin-T34A mutant. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Role in PC | EV Content | In Vivo/In Vitro | Diagnostic/ Prognostic Marker | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proteins | ||||
| Reflective of tumour burden | Glypican-1 | In vivo | Yes | [54] |
| Promotes diabetes and lipolysis | Adrenomedullin | In vivo | - | [60,62,63] |
| Muscle wasting | Zinc transporter ZIP4 | In vivo | Yes | [60] |
| Adrenomedullin | In vivo | - | [60,62,63] | |
| PC progression and metastasis | Annexin A1 | In vitro | Yes | [57] |
| Liver metastasis | Integrin αvβ5 | In vivo | Yes | [61] |
| Lung metastasis | Integrin α6β4 and α6β1 | In vivo | Yes | [61] |
| Promotes pre-metastatic formation | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) | In vivo | Yes | [55] |
| Induces proliferation, migration and invasion | Myoferlin | In vitro | - | [58,59] |
| Annexin A6 | In vivo | Yes | [56] | |
| Zinc transporter ZIP4 | In vivo | Yes | [60] | |
| Chemoresistance | Zinc transporter ZIP4 | In vivo | Yes | [60] |
| miRNA | ||||
| Induces immunosuppression | miR-1260a | In vitro | - | [68] |
| miR-494-3p | In vitro | - | [68] | |
| Induces chemoresistance | miR-155 | In vivo | - | [69,70] |
| miR-210 | In vivo | - | [71] | |
| miR-21 | In vivo | Yes | [72] | |
| miR-106b | - | [43] | ||
| Upregulated in PC patients | miR-17-5p | In vivo | Yes | [10] |
| miR-550 | In vivo | Yes | [73] | |
| miR-10b | In vivo | Yes | [74] | |
| miR-196a | In vivo | Yes | [75] | |
| Detected in the serum of PC patients | miR-1246 | In vivo | Yes | [76] |
| miR-4644 | In vivo | Yes | [76] | |
| miR-4306 | In vivo | Yes | [76] | |
| miR-3976 | In vivo | Yes | [76] | |
| Promotes proliferation, invasion and angiogenesis | miR-222 | In vivo | - | [64] |
| miR-27a | In vivo | - | [65] | |
| Induces immunosurveillance escape | miR-203 | In vitro | - | [66] |
| Induces immune tolerance | miR-212-3p | In vitro | - | [67] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marzan, A.L.; Stewart, S.E. Elucidating the Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5669. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225669
Marzan AL, Stewart SE. Elucidating the Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(22):5669. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225669
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarzan, Akbar Lulu, and Sarah Elizabeth Stewart. 2021. "Elucidating the Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 22: 5669. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225669
APA StyleMarzan, A. L., & Stewart, S. E. (2021). Elucidating the Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 13(22), 5669. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13225669






