Functional Interaction among lncRNA HOTAIR and MicroRNAs in Cancer and Other Human Diseases
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HOTAIR and Its Role in Cancer
3. HOTAIR and MiRNAs Interaction in Embryonic Development and Human Diseases
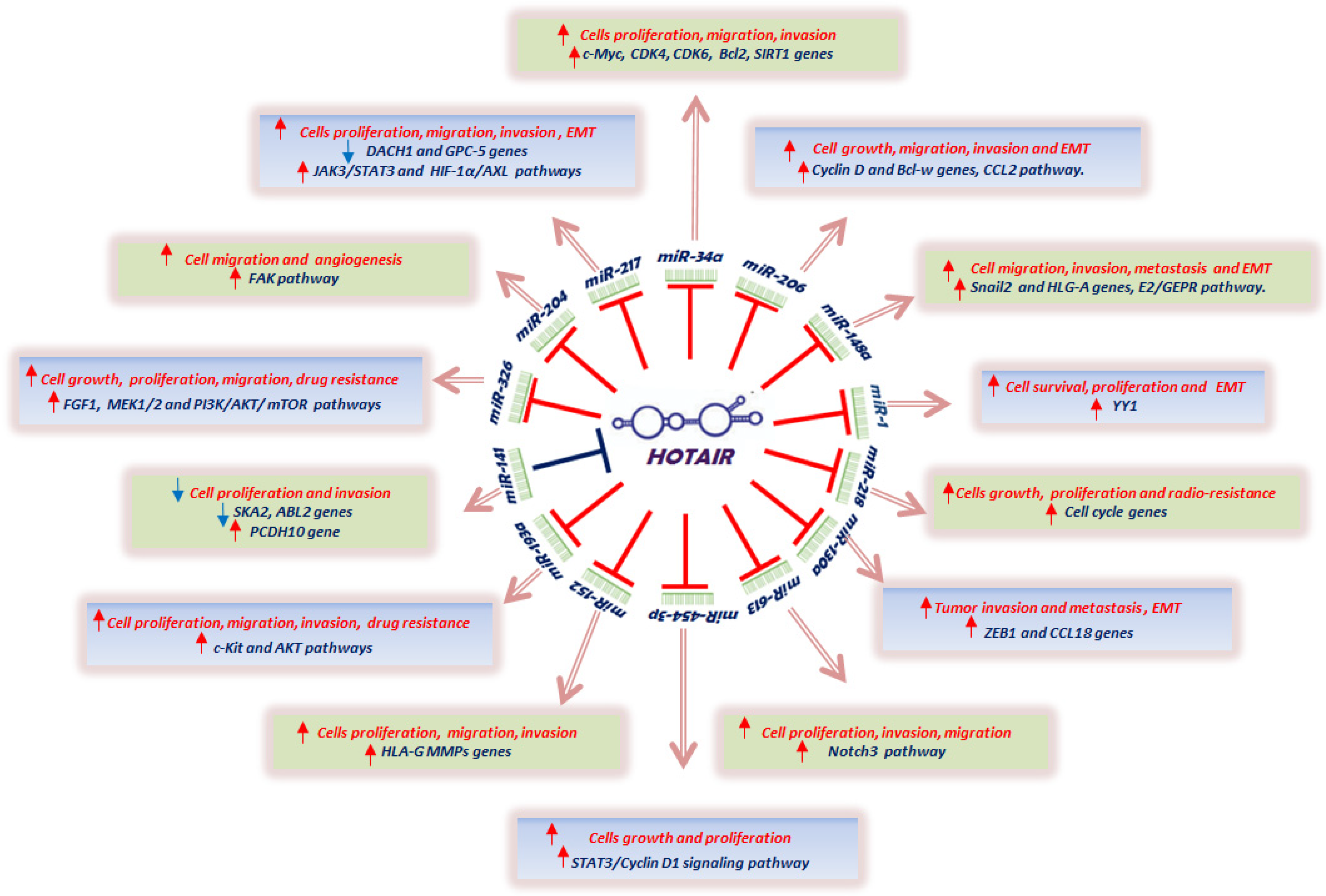
4. HOTAIR and MicroRNAs Interaction in Cancer
4.1. Breast Cancer
4.2. Glioma
4.3. Lung Cancer
4.4. Urinary Tract Tumors
4.5. Gynecological Cancers
4.6. Gastric Cancer
4.7. Colon Cancer
4.8. Liver Cancer
4.9. Pancreatic Cancer
4.10. Esophageal Cancer
4.11. Other Cancers
5. Prediction of lncRNA–miRNA Interactions
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, N.K.; Huang, C.L.; Islam, R.; Yip, S.P. Long non-coding RNAs in hematological malignancies: Translating basic techniques into diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ransohoff, J.D.; Wei, Y.; Khavari, P.A. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, P.J.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, Q.; Pu, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, B.; Li, F.; Liu, B. Regulatory Roles of Related Long Non-coding RNAs in the Process of Atherosclerosis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 564604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Shi, X.; Sun, X. Long noncoding RNAs: Potential therapeutic targets in cardiocerebrovascular diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 10, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Liu, W.; Cao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zou, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, H.; Mo, Y.; Peng, S.; Shuai, C. CircRNAs and LncRNAs in Osteoporosis. Differentiation 2020, 116, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lu, X.; Yuan, L. LncRNA: A link between RNA and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1839, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, W.X.; Koirala, P.; Mo, Y.Y. LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez Calle, A.; Kawamura, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2093–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, M.K.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Malik, R.; Singhal, U.; Sahu, A.; Hosono, Y.; Barrette, T.R.; Prensner, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Zhao, S. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xiong, M.; Xu, C.; Xiang, P.; Zhong, X. Long Noncoding RNAs: An Overview. Adv. Struct. Saf. Stud. 2016, 1402, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Davidovich, C.; Cech, T.R. The recruitment of chromatin modifiers by long noncoding RNAs: Lessons from PRC. RNA 2015, 21, 2007–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tu, S.; Yuan, G.C.; Shao, Z. The PRC2-binding long non-coding RNAs in human and mouse genomes are associated with predictive sequence features. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hung, T.; Wang, Y.; Lin, M.F.; Koegel, A.K.; Kotake, Y.; Grant, G.D.; Horlings, H.M.; Shah, N.; Umbricht, C.; Wang, P.; et al. Extensive and coordinated transcription of noncoding RNAs within cell-cycle promoters. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kretz, M.; Siprashvili, Z.; Chu, C.; Webster, D.E.; Zehnder, A.; Qu, K.; Lee, C.S.; Flockhart, R.J.; Groff, A.F.; Chow, J.; et al. Control of somatic tissue differentiation by the long non-coding RNA TINCR. Nature 2013, 493, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Vlachos, I.S.; Karagkouni, D.; Georgakilas, G.; Kanellos, I.; Vergoulis, T.; Zagganas, K.; Tsanakas, P.; Floros, E.; Dalamagas, T.; et al. DIANA-LncBase v2: Indexing microRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D231–D238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhu, W.; Dong, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Shen, F. Mechanisms and Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs at Multiple Regulatory Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazimierczyk, M.; Kasprowicz, M.K.; Kasprzyk, M.E.; Wrzesinski, J. Human Long Noncoding RNA Interactome: Detection, Characterization and Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shengnan, J.; Dafei, X.; Hua, J.; Sunfu, F.; Xiaowei, W.; Liang, X. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR as a competitive endogenous RNA to sponge miR-206 to promote colorectal cancer progression by activating CCL. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 4431–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Ren, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, D. Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Modulates MiR-206-mediated Bcl-w Signaling to Facilitate Cell Proliferation in Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Du, P.; Yuan, W.; Du, Z.; Yu, M.; Yu, X.; Hu, T. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR regulates cyclin J via inhibition of microRNA-205 expression in bladder cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR: A master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1856, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majello, B.; Gorini, F.; Saccà, C.D.; Amente, S. Expanding the role of the histone lysine-specific demethylase LSD1 in cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.; Qu, K.; Zhong, F.L.; Artandi, S.E.; Chang, H.Y. Genomic maps of long noncoding RNA occupancy reveal principles of RNA-chromatin interactions. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 667–678. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Hann, S.S. HOTAIR: An Oncogenic Long Non-Coding RNA in Human Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Hussain, I.; Ansari, K.I.; Kasiri, S.; Bashyal, A.; Mandal, S.S. Antisense Transcript Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) HOTAIR is Transcriptionally Induced by Estradiol. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 3707–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botti, G.; Scognamiglio, G.; Aquino, G.; Liguori, G.; Cantile, M. LncRNA HOTAIR in Tumor Microenvironment: What Role? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, Y.; Jia, H.H.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, X.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Kang, C.S.; Mei, M. Paracrine and epigenetic control of CAF-induced metastasis: The role of HOTAIR stimulated by TGF-ß1 secretion. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.Z.; Li, C.X.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, M.Z.; Zhang, M.D.; Qin, Y.Y. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR, a c-Myc activated driver of malignancy, negatively regulates miRNA-130a in gallbladder cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, H.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ding, L.; Zeng, L. Overexpression of MiR-146a-5p Upregulates lncRNA HOTAIR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells and Predicts Poor Prognosis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819882949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiyomaru, T.; Fukuhara, S.; Saini, S.; Majid, S.; Deng, G.; Shahryari, V.; Chang, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is targeted and regulated by miR-141 in human cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12550–12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dasgupta, P.; Kulkarni, P.; Majid, S.; Shahryari, V.; Hashimoto, Y.; Bhat, N.S.; Shiina, M.; Deng, G.; Saini, S.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; et al. MicroRNA-203 Inhibits Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR and Regulates Tumorigenesis through Epithelial-to-mesenchymal Transition Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, G.; Zhai, J.; Liu, F.; Li, G. miR-101-3p Suppresses HOX Transcript Antisense RNA (HOTAIR)-Induced Proliferation and Invasion Through Directly Targeting SRF in Gastric Carcinoma Cells. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ren, D.; Liu, H.; Kang, C.; Chen, J. HOTAIR, a long noncoding RNA, is a marker of abnormal cell cycle regulation in lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2717–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.; Kong, D.; Chen, Q.; Ping, Y.; Pang, D. Oncogenic long noncoding RNA landscape in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botti, G.; Collina, F.; Scognamiglio, G.; Aquino, G.; Cerrone, M.; Liguori, G.; Gigantino, V.; Malzone, M.G.; Cantile, M. LncRNA HOTAIR Polymorphisms Association with Cancer Susceptibility in Different Tumor Types. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2018, 19, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Alsager, S.; Zhuo, Y.; Shan, B. HOX transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 454, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantile, M.; Di Bonito, M.; Cerrone, M.; Collina, F.; De Laurentiis, M.; Botti, G. Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR in Breast Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhan, A.; Hussain, I.; Ansari, K.I.; Bobzean, S.A.; Perrotti, L.I.; Mandal, S.S. Bisphenol-A and diethylstilbestrol exposure induces the expression of breast cancer associated long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in vitro and in vivo. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 141, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökmen-Polar, Y.; Vladislav, I.T.; Neelamraju, Y.; Janga, S.C.; Badve, S. Prognostic impact of HOTAIR expression is restricted to ER-negative breast cancers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Collina, F.; Aquino, G.; Brogna, M.; Cipolletta, S.; Buonfanti, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Di Bonito, M.; Cantile, M.; Botti, G. LncRNA HOTAIR upregulation is strongly related with lymph nodes metastasis and LAR subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawłowska, E.; Szczepanska, J.; Blasiak, J. The Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR in Breast Cancer: Does Autophagy Play a Role? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Gao, T.H.; Cui, Y.; Ma, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.J. Elevated HOTAIR expression associated with cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer patients. J. Thorac. Dis. 2016, 8, 3314–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, A.; Zhao, J.C.; Kim, J.; Fong, K.W.; Yang, Y.A.; Chakravarti, D.; Mo, Y.Y.; Yu, J. LncRNA HOTAIR Enhances the Androgen-Receptor-Mediated Transcriptional Program and Drives Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, T.H.; Lu, S.W.; Huang, Y.Q.; Que, G.B.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, H.B.; Liang, X.L.; Jiang, J.H. Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA HOTAIR predicts recurrence in stage Ta/T1 bladder cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 10249–10257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Y.X. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is a prognostic biomarker and inhibits chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Ye, L.C.; Ding, J.X.; Feng, W.W.; Jin, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Hua, K.Q. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR predicts poor patient prognosis and promotes tumor metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 134, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Liao, L.M.; Liu, A.W.; Wu, J.B.; Cheng, X.L.; Lin, J.X.; Zheng, M. Overexpression of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR predicts a poor prognosis in patients with cervical cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2014, 290, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Bao, W.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Che, Q.; Wang, H.; Wan, X.P. The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is upregulated in endometrial carcinoma and correlates with poor prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, M.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.N.; Rahman, K.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, H. Autophagy regulated by lncRNA HOTAIR contributes to the cisplatin-induced resistance in endometrial cancer cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.F.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.Q.; Cui, Y.X.; Ma, N.; Lu, C.X.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhou, Y. Clinical significance of HOTAIR expression in colon cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 5254–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Dong, S.; Duan, B.; Chen, P.; Shi, L.; Gao, H.; Qi, H. HOTAIR is a predictive and prognostic biomarker for patients with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma receiving fluorouracil and platinum combination chemotherapy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Xiao, X.; Wu, C.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, L. The role of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in the progression and development of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma interacting with EZH. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Luo, P.; Jing, W.; Zhu, M.; Tu, J. Identification of Circulating Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR as a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Dong, R.; Qiu, H. A high level of circulating HOTAIR is associated with progression and poor prognosis of cervical cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Kogo, R.; Shibata, K.; Sawada, G.; Takahashi, Y.; Kurashige, J.; Akiyoshi, S.; Sasaki, S.; Iwaya, T.; Sudo, T. Clinical significance of the expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Yang, M.; Jiang, R.; An, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, B. Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Regulates the Proliferation, Self-Renewal Capacity, Tumor Formation and Migration of the Cancer Stem-Like Cell (CSC) Subpopulation Enriched from Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Tian, N. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR enhances angiogenesis by induction of VEGFA expression in glioma cells and transmission to endothelial cells via glioma cell derived-extracellular vesicles. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 5012–5021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujisaka, Y.; Iwata, T.; Tamai, K.; Nakamura, M.; Mochizuki, M.; Shibuya, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shimosegawa, T.; Satoh, K. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR up-regulates chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 and promotes proliferation of macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cantile, M.; Scognamiglio, G.; Marra, L.; Aquino, G.; Botti, C.; Falcone, M.R.; Malzone, M.G.; Liguori, G.; Di Bonito, M.; Franco, R.; et al. HOTAIR role in melanoma progression and its identification in the blood of patients with advanced disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3422–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Sunkin, S.M. Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goff, L.A.; Groff, A.F.; Sauvageau, M. Spatiotemporal expression and transcriptional perturbations by long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6855–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rotini, A.; Martínez-Sarrà, E.; Pozzo, E.; Sampaolesi, M. Interactions between microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in cardiac development and repair. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 127, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, J.; Xu, Z.; Zuo, B. Functions and Regulatory Mechanisms of lncRNAs in Skeletal Myogenesis, Muscle Disease and Meat Production. Cells 2019, 8, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amândio, A.R.; Necsulea, A.; Joye, E.; Mascrez, B.; Duboule, D. Hotair Is Dispensible for Mouse Development. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, B.; Wapinski, O.L.; Tsai, M.C.; Qu, K.; Zhang, J. Targeted disruption of Hotair leads to homeotic transformation and gene derepression. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hammer, T.; Lohbauer, S. The master of genomic programs: HOTAIR in cellular development and cancer metastasis. Aquil. Stud. Res. J. 2010, 461, 10711076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallstrom, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. MCP 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Botti, G.; Cillo, C.; De Cecio, R.; Malzone, M.G.; Cantile, M. Paralogous HOX13 Genes in Human Cancers. Cancers 2019, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrion, K.; Dyo, J.; Patel, V.; Sasik, R.; Mohamed, S.A.; Hardiman, G.; Nigam, V. The long non-coding HOTAIR is modulated by cyclic stretch and WNT/β-CATENIN in human aortic valve cells and is a novel repressor of calcification genes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, B.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Lei, C.; Huang, B.; Chen, H. Characterization of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network to Reveal Potential Functional ceRNAs in Bovine Skeletal Muscle. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, J.; Liu, N.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, F.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; He, J. Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Involvement of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Networks in Hair Follicle Induction in Aohan Fine Wool Sheep Skin. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Cheng, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Z. The comprehensivedetection of miRNA, lncRNA, and circRNA in regulation of mouse melanocyte and skin development. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballantyne, M.D.; McDonald, R.A.; Baker, A.H. lncRNA/MicroRNA interactions in the vasculature. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 99, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, H.; Wang, B.; Xue, Y.S. LncRNA HOTAIR regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells through targeting miRNA-130b-3p/PPARα axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 10989–10995. [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima, N.; Levine, B. Autophagy in mammalian development and differentiation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, J. The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR activates autophagy by upregulating ATG3 and ATG7 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 2605–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, A.F.; Costa, M.C.; Enguita, F.J. Interactions Among Regulatory Non-coding RNAs Involved in Cardiovascular Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1229, 79–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarro, E.; Mallén, A.; Cruzado, J.M.; Torras, J.; Hueso, M. Unveiling ncRNA regulatory axes in atherosclerosis progression. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, B.; Wei, W.; Zhao, B.; Guo, X.; Liu, S. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits miR-17-5p to regulate osteogenic differentiation and proliferation in non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Shan, Y.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Jia, L. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes osteoarthritis progression via miR-17-5p/FUT2/β-catenin axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Qi, J.; Bi, Q.; Zhang, S. Expression profile of long noncoding RNA (HOTAIR) and its predicted target miR-17-3p in LPS-induced inflammatory injury in human articular chondrocyte C28/I2 cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 9146–9157. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, Z.Y.; Song, F.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhang, W.L.; Samartzis, D.; Ma, C.J.; Che, L.; Liu, X.; Ali, M.A.; et al. Aberrantly expressed long noncoding RNAs in human intervertebral disc degeneration: A microarray related study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, T.; Hu, Y.; Tang, W.; Shen, H.; Yu, Z.; Gu, J. The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR serves as a microRNA-34a-5p sponge to reduce nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis via a NOTCH1-mediated mechanism. Gene 2019, 715, 144029. [Google Scholar]
- Wasson, C.W.; Abignano, G.; Hermes, H.; Malaab, M.; Ross, R.L.; Jimenez, S.A.; Chang, H.Y.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Del Galdo, F. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR drives EZH2-dependent myofibroblast activation in systemic sclerosis through miRNA 34a-dependent activation of NOTCH. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Chen, B.; Dong, P.; Zheng, J. HOTAIR Epigenetically Modulates PTEN Expression via MicroRNA-29b: A Novel Mechanism in Regulation of Liver Fibrosis. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Cui, B.; Dai, Z.X.; Shi, P.K.; Wang, Z.H.; Guo, Y.Y. Long Non-coding RNA HOTAIR Promotes Parkinson's Disease Induced by MPTP Through up-regulating the Expression of LRRK. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2016, 13, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Hou, S.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, N.; Lin, Y. LncRNA HOTAIR targets miR-126-5p to promote the progression of Parkinson's disease through RAB3IP. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Monte, D.A. Mitochondrial DNA and Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 1991, 41, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Chang, N. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes MPP+-induced neuronal injury in Parkinson's disease by regulating the miR-874-5p/ATG10 axis. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.M.; Liao, J.X.; Dong, Y.K.; Zhu, J.L.; He, C.C.; Huang, J.; Tang, Y.W.; Wu, D.; Tian, J.Y. LncRNA HOTAIR Promotes Neuronal Damage Through Facilitating NLRP3 Mediated-Pyroptosis Activation in Parkinson's Disease via Regulation of miR-326/ELAVL1 Axis. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Fei, K.L.; Li, P. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates theprogression of preeclampsia through inhibiting miR-106 in an EZH2-dependent manner. Life Sci. 2020, 253, 117668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.M.; Zheng, Z.H.; Wang, S.; Wen, X.; Han, X.R.; Wang, Y.J.; Shen, M.; Fan, S.H.; Zhang, Z.F.; Shan, Q.; et al. The role of HOTAIR-induced downregulation of microRNA-126 and interleukin-13 in the development of bronchial hyperresponsiveness in neonates. J. Cell Physiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, Z.Q. LncRNA HOTAIR aggravates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by sponging microRNA-126 to upregulate SRSF. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 9046–9054. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Mo, H.; Luo, J.; Zhao, S.; Liang, S.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, J. HOTAIR Is a Potential Novel Biomarker in Patients with Congenital Heart Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 2850657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Yao, R.; Wu, L.; Xiao, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Circulating Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR is an Essential Mediator of Acute Myocardial Infarction. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1497–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Chang, Q.; Pei, H.; Sun, X.; Qian, X.; Tian, C.; Lin, H. Long Non-coding RNA-mRNA Correlation Analysis Reveals the Potential Role of HOTAIR in Pathogenesis of Sporadic Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 54, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W. LncRNA-HOTAIR inhibition aggravates oxidative stress-induced H9c2 cells injury through suppression of MMP2 by miR-125. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, B.; Ma, M.; Yu, K.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X. lncRNA HOTAIR Protects Myocardial Infarction Rat by Sponging miR-519d-3p. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2019, 12, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, S.; Xiao, L.; Liang, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yao, R.; Liu, Y.; et al. LncRNA HOTAIR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to upregulate SIRT1 by sponging miR-34a in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 4944–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Fan, Z.W.; Sun, W.L.; Tang, Y. Influence of lncRNA HOTAIR on acute kidney injury in sepsis rats through regulating miR-34a/Bcl-2 pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.J.; Wei, Q.F.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Geng, Q.; Cui, Y.H.; Wang, X.H. LncRNA HOTAIR alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by targeting miR-138 and inactivating NF-κB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 50, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.N.; Wu, S.P.; Chen, H.T.; He, J.H. HOTAIR, a long non-coding RNA driver of malignancy whose expression is activated by FOXC1, negatively regulates miRNA-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4061–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Fu, J.; Zhou, W. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes medulloblastoma growth, migration and invasion by sponging miR-1/miR-206 and targeting YY1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 124, 109887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, K.; Wang, J. MiR-7, inhibited indirectly by lincRNA HOTAIR, directly inhibits SETDB1 and reverses the EMT of breast cancer stem cells by downregulating the STAT3 pathway. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 2858–2868. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, F.; Wuerkenbieke, D.; He, Y.; Ding, Y.; Du, R. Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR: An Oncogene in Human Cervical Cancer Interacting With MicroRNA-17-5p. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiyomaru, T.; Yamamura, S.; Fukuhara, S.; Yoshino, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Majid, S.; Saini, S.; Chang, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Enokida, H.; et al. Genistein inhibits prostate cancer cell growth by targeting miR-34a and oncogenic HOTAIR. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhi, Q.; Wang, J.; Qin, C. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits cisplatin resistance of gastric cancer cells through inhibiting the PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways by up-regulating miR-34a. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, M.S.; Brenner, A.J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y.K.; Stoudemire, J. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Xu, W.; Shi, Y.; Dai, W. lncRNA HOTAIR upregulates COX-2 expression to promote invasion and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by interacting with miR-101. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Deng, J.; Zhang, B.; He, X.; Meng, Z.; Li, G.; Ye, H.; Zheng, S.; Wei, L.; Deng, X.; et al. LncRNA HOTAIR epigenetically suppresses miR-122 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma via DNA methylation. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Wu, D.; He, X.; Hu, X.; Hu, C.; Shen, Z.; Lin, J.; Pan, Z.; He, Z.; Lin, H.; et al. CCL18-induced HOTAIR upregulation promotes malignant progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the miR-130a-5p-ZEB1 axis. Cancer Lett. 2019, 460, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ai, H.; Fan, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reverses cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells through inhibiting miR-138-5p-regulated EZH2 and SIRT. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, E.B.; Ma, C.C.; He, X.J.; Wang, C.; Zong, G.; Wang, H.L.; Zhao, B. Epigenetic modification of miR-141 regulates SKA2 by an endogenous ‘sponge’ HOTAIR in glioma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 30610–30625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, J.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W. TGF-β1 elevates P-gp and BCRP in hepatocellular carcinoma through HOTAIR/miR-145 axis. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2019, 40, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; He, H.; Chen, Q. Estradiol induces HOTAIR levels via GPER-mediated miR-148a inhibition in breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Chu, H.; Ji, J.; Huo, G.; Song, Q.; Zhang, X. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates HLA-G expression by absorbing miR-148a in human cervical cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, J. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR functions as miRNA sponge to promote the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in esophageal cancer. Biomed. Pharm. 2017, 90, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, Z.; Tian, N.; Han, L.; Fu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Tian, Y. miR-148b-3p inhibits malignant biological behaviors of human glioma cells induced by high HOTAIR expression. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.B.; Hou, J.Q.; Chang, J.K.; Li, S.; Liu, G.C.; Cao, S.Q. The mechanism of HOTAIR regulating the proliferation and apoptosis of prostate cancer cells by targeting down-regulation of miR-152 to improve the expression of FOXR. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2019, 99, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Guan, Z.; Liu, F.; Sun, D.; Wang, K.; Qu, H. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes HLA-G expression via inhibiting miR-152 in gastric cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.; Wang, X.; Tao, T.; Zhang, L.; Guan, H.; You, Z.; Lu, K.; Zhang, G.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Involvement of aberrantly activated HOTAIR/EZH2/miR-193a feedback loop in progression of prostate cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, C.Y.; Hu, X.Q.; Xie, F.Y. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR modulates c-KIT expression through sponging miR-193a in acute myeloid leukemia. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Chu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zuo, J. miR-200c overexpression inhibits the invasion and tumorigenicity of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by suppressing lncRNA HOTAIR in mice. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Romero, A.; Astudillo-de la Vega, H.; Terrones-Gurrola, M.C.D.R.; Marchat, L.A.; Hernández-Sotelo, D.; Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Ramos-Payan, R.; Silva-Cázares, M.B.; Nuñez- Olvera, S.I.; Hernández-de la Cruz, O.N.; et al. HOX Transcript Antisense RNA HOTAIR Abrogates Vasculogenic Mimicry by Targeting the AngiomiR-204/FAK Axis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Noncoding RNA 2020, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yeh, C.R.; Sun, Y.; Lin, C.; Chou, J.; Ou, Z.; Chang, C.; Qi, J.; Yeh, S. Estrogen receptor β promotes renalcell carcinoma progression via regulating LncRNA HOTAIR-miR-138/200c/204/217 associated CeRNA network. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5037–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Guo, R.; Yuan, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhang, D. LncRNA HOTAIR Regulates CCND1 and CCND2 Expression by Sponging miR-206 in Ovarian Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1289–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Q.; Pan, S.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, S.; Xiao, Y.; Jia, L. The HOTAIR/miR-214/ST6GAL1 crosstalk modulates colorectal cancer procession through mediating sialylated c-Met via JAK2/STAT3 cascade. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.S.; Peng, M.; Zhou, G.Z.; Pu, Y.C.; Yi, M.C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, B. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR regulates the development of non-small cell lung cancer through miR-217/DACH1 signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.; Li, O.; Zheng, W.; Xiao, W.Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Cai, G.Y.; He, J.C.; Chen, X.M. LncRNA HOTAIR regulates HIF-1α/AXL signaling through inhibition of miR-217 in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Qu, X.L.; Liu, J.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Z.Y. HOTAIR promotes osteosarcoma development by sponging miR-217 and targeting ZEB1. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 6173–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; He, X.; Guan, A.; Huang, W.; Jia, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, J.; Wang, H. Long non-coding RNA Hotair promotes gastric cancer progression via miR-217-GPC5 axis. Life Sci. 2019, 217, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Zhu, Z. Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Contributes to Progression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Sponging miR-217-5p. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ding, D.; Zhang, J.; Cui, J. Knockdown of lncRNA HOTAIR sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation through activating miR-218. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, W.M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, W.M.; Lu, Y.F.; Hu, B.G.; Wang, H.; Liang, W.C.; Wang, S.S.; Ko, C.H.; Waye, M.M.; et al. Hotair mediates hepatocarcinogenesis through suppressing miRNA-218 expression and activating P14 and P16 signaling. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Yao, Y.L.; Zheng, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.H.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.B.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.H.; et al. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits malignant biological behaviors of human glioma cells via modulation of miR-326. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21934–21949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Xu, T.; Xia, R.; Han, L.; Chen, W.; De, W.; Shu, Y. MiR-326 regulates cell proliferation and migration in lung cancer by targeting phox2a and is regulated by HOTAIR. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jin, M.; Yu, W. miR-326 reverses chemoresistance in human lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting specificity protein. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 13287–13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, B.; Ren, X.; Qi, X.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, C.; Jia, L. HOTAIR/miR-326/FUT6 axis facilitates colorectal cancer progression through regulating fucosylation of CD44 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Sun, M.; Nie, F.Q.; Ge, Y.B.; Zhang, E.B.; Yin, D.D.; Kong, R.; Xia, R.; Lu, K.H.; Li, J.H.; et al. Lnc RNA HOTAIR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Sun, Y.; Tong, X. LncRNA HOTAIR controls the expression of Rab22a by sponging miR-373 in ovarian cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Xiao, H.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Jin, Y.; Li, H.; Cui, M.; Fan, S. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances breast cancer radioresistance through facilitating HSPA1A expression via sequestering miR-449b-5p. Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 1801–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, H.; Xiang, H.; Gao, M.; Yin, C.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Xiong, M. Long Chain Non- Coding RNA (lncRNA) HOTAIR Knockdown Increases miR-454-3p to Suppress Gastric Cancer Growth by Targeting STAT3/Cyclin D. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Ren, T.; Huang, Y.; Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Zheng, B.; Guo, W. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR increases miR-454-3p by targeting Stat3 and Atg12 to inhibit chondrosarcoma growth. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, T.; Tang, X.; Li, S.; Liang, R.; Wang, Y. Medulloblastoma malignant biological behaviors are associated with HOTAIR/miR-483-3p/CDK4 axis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lu, S. MicroR-545 mediates colorectal cancer cells proliferation through up-regulating epidermal growth factor receptor expression in HOTAIR long non-coding RNA dependent. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 431, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Yao, J.; An, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Wu, D.; Luo, B.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, D.; et al. LncRNA HOTAIR acts a competing endogenous RNA to control the expression of notch3 via sponging miR-613 in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32905–32917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.; Fu, Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Dong, H.; Li, Q. LncRNA HOTAIR/miR-613/c-met axis modulated epithelial-mesenchymal transition of retinoblastoma cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5083–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, H.; An, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Chen, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, F.; Jiang, Y.; He, X. Epigenetic inhibition of miR-663b by long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation via up-regulation of insulin-like growth factor. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86857–86870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, Y.; Nguyen, H.T.; Burow, M.E.; Zhuo, Y.; El-Dahr, S.S.; Yao, X.; Cao, S.; Flemington, E.K.; Nephew, K.P.; Fang, F. Elevated expression of long intergenic non-coding RNA HOTAIR in a basal-like variant of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 1656–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, B.; Peng, X.; Cheng, D.; Zhu, Y.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Yu, X. Delphinidin suppresses breast carcinogenesis through the HOTAIR/microRNA-34a axis. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3089–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.X.; Han, L.; Bao, Z.S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Yan, W.; Yu, S.Z.; Pu, P.Y.; Liu, N.; You, Y.P.; et al. Chinese Glioma Cooperative, G. HOTAIR, a cell cycle-associated long noncoding RNA and a strong predictor of survival, is preferentially expressed in classical and mesenchymal glioma. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Han, L.; Chen, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, A.; Ye, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes glioblastoma cell cycle progression in an EZH2 dependent manner. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bao, J.; Du, C.; Wang, J.; Tong, Q.; Liu, C. Schisandrin B inhibits the proliferation and invasion of glioma cells by regulating the HOTAIR- micoRNA-125a-mTOR pathway. Neuroreport 2017, 28, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, P.; Ortiz, R.; Diaz, J.; Quest, A.; Leyton, L.; Stupack, D.; Torres, V.A. Rab5 activation promotes focal adhesion disassembly, migration and invasiveness in tumor cells. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 3835–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Cai, X.; Yung, M.M.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. miR-137 mediates the functional link between c-Myc and EZH2 that regulates cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 564–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, H.; Shiroki, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Yokoyama, M.; Tamai, K.; Yamanami, H.; Fujiya, T.; Sato, I. Enhanced expression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with the development of gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.W.; Sun, M.; Xia, R.; Zhang, E.B.; Liu, X.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, T.P.; De, W.; Liu, B.R.; Wang, Z.X. LincHOTAIR epigenetically silences miR34a by binding to PRC2 to promote the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.L.; Zhao, X.J.; Wei, C.C.; Wu, J.W. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes colon cancer development by down-regulating miRNA-34a. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 5752–5761. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Luo, S.; Jin, C.; Ma, H.; Zhou, H.; Jia, L. FUT family mediates the multidrug resistance of human hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flum, M.; Kleemann, M.; Schneider, H. miR-217-5p induces apoptosis by directly targeting PRKCI, BAG3, ITGAV and MAPK1 in colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Xiao, Z.; Tong, J.H.; To, K.F.; Fang, X.; Cheng, A.S.; Chen, Y. EZH2 coupled with HOTAIR to silence MicroRNA-34a by the induction of heterochromatin formation in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, M.K.; Sharma, R.; Panda, N.K.; Khullar, M. Role of non-coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A narrative review. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qin, Y.; Zhen, Z.; Shen, H.; Cong, T.; Schiferle, E.; Xiao, S. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR/microRNA-206 sponge regulates STC2 and further influences cell biological functions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, B.; Su, Y.; Yang, Q.; Lv, D.; Zhang, W.; Tang, K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y. Overexpression of Long Non-Coding RNA HOTAIR Promotes Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Human Osteosarcoma. Mol. Cells. 2015, 38, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.N.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.H.; Gao, L.; Wang, X.R.; Wang, W.; Kang, H.Y.; Yan, G.T.; Wang, L.L.; Yu, L. MicroRNA-193a represses c-kit expression and functions as a methylation-silenced tumor suppressor in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3416–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.J.; Tay, Y. Noncoding RNA:RNA Regulatory Networks in Cancer. Int. J. Molsci. 2018, 19, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silverman, E.K.; Schmidt, H.H.H.W.; Anastasiadou, E.; Altucci, L.; Angelini, M.; Badimon, L.; Balligand, J.L.; Benincasa, G.; Capasso, G.; Glass, K.; et al. Molecular networks in Network Medicine: Development and applications. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2020, 12, e1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Duan, H.; He, Z. Competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulation network of lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs in Wilms tumour. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Li, W.; Huang, F.; Sun, J.; Li, K.P.; Shi, J.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Hu, N.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of the Expression Profiles of Long Non-Coding RNAs with Associated ceRNA Network Involved in the Colon Cancer Staging and Progression. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; He, K.; Yu, Z. Characterization of ceRNA network to reveal potential prognostic biomarkers in triple-negative breast cancer. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yin, H.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Ling, X.; Xin, Y.; Liang, H.; et al. The construction and analysis of the aberrant lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 1772–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneziano, D.; Marceca, G.P.; Di Bella, S.; Nigita, G.; Distefano, R.; Croce, C.M. Investigating miRNA-lncRNA Interactions: Computational Tools and Resources. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1970, 251–277. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C.N.; Ma, L.; Liu, N. Systematic analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network identifies four-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.S.; Zhang, E.X.; Sun, Q.F.; Ye, Z.J.; Liu, J.W.; Zhou, D.H.; Tang, Y. Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.A.; Chan, K.C.C.; You, Z.H. Constructing prediction models from expression profiles for large scale lncRNA-miRNA interaction profiling. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.A.; Huang, Z.A.; You, Z.H.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, W.Z.; Guo, J.X.; Yu, C.Q. Predicting lncRNA-miRNA Interaction via Graph Convolution Auto-Encoder. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, L.; Huang, Y.A.; You, Z.H.; Chen, Z.H.; Cao, M.Y. LNRLMI: Linear neighbor representation for predicting lncRNA-miRNA interactions. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhou, X.H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.G.; Qian, B.Z.; He, A.N.; Shen, Z.; Hu, H.Y.; Yao, Y. Bufalin suppresses the migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells through HOTAIR, the sponge of miR-520b. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; Feng, T.; Chen, F.; Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Lin, Q.; He, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. HOTAIR regulates HK2 expression by binding endogenous miR-125 and miR-143 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86410–86422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; He, X.; Chen, A.; Tan, K.; Du, X. LncRNA HOTAIR contributes to the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma by enhancing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via sponging miR-23b-3p from ZEB1. Gene 2018, 670, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.X.; Han, L.; Mei, M.; Kang, C.S. Targeted design and identification of AC1NOD4Q to block activity of HOTAIR by abrogating the scaffold interaction with EZH2. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cai, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, K.; Yi, K.; et al. A Compound AC1Q3QWB Selectively Disrupts HOTAIR-Mediated Recruitment of PRC2 and Enhances Cancer Therapy of DZNep. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4608–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Luo, G.; Liang, S.; Lü, M. Research progress on the interactions between long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs in human cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, F.; Fiscon, G.; Conte, F.; Rizzo, M.; Paci, P.; Pellegrini, M. Interplay Between Long Noncoding RNAs and MicroRNAs in Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1819, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Cui, S.; Wan, T.; Li, X.; Tian, W.; Zhang, R.; Luo, L.; Shi, Y. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR acts as a competing endogenous RNA to promote glioma progression by sponging miR-126-5p. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 6822–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, H.L.; Reesink, H.W.; Lawitz, E.J.; Zeuzem, S.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Patel, K. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Zandwijk, N.; Pavlakis, N.; Kao, S.C.; Linton, A.; Boyer, M.J.; Clarke, S. Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: A first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| miRNA ID | HOTAIR Role on Expression | Tumor Types | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1 | suppression | Liver cancer, medulloblastoma | [108,109] |
| miR-7 | suppression | Breast cancer | [110] |
| miR-17-5p | suppression | Cervical cancer | [111] |
| miR-34a | suppression | Breast, pancreatic, gastric, prostate, colon cancers | [105,106,112,113,114] |
| miR-101 | suppression | Head and neck cancer | [115] |
| miR-101-3p | inverse suppression | Gastric cancer | [37] |
| miR-122 | suppression | Liver cancer | [116] |
| miR-124 | suppression | Gastric cancer | [113] |
| miR-130a-5p | suppression | esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, gall bladder | [117] |
| miR-138-5p | suppression | Ovarian cancer | [118] |
| miR-141 | inverse suppression | Kidney cancer, glioma | [35,119] |
| miR-145 | suppression | Liver cancer | [120] |
| miR-146a-5p | inverse suppression | Breast cancer | [34] |
| miR-148a | suppression | Breast, cervical, esophageal squamous cell cancers | [121,122,123] |
| miR-148b-3p | suppression | Glioma | [124] |
| miR-152 | suppression | Prostate, gastric cancers | [125,126] |
| miR-193a | suppression | Prostate cancer, myeloid leukemia | [127,128] |
| miR-200c | suppression | Ovarian cancer | [129] |
| miR-204 | suppression | Breast, kidney cancers | [130,131] |
| miR-205 | suppression | Bladder cancer | [24] |
| miR-206 | suppression | Breast, colon cancer, ovarian cancer, medulloblastoma | [22,23,109,132] |
| miR-214 | suppression | Colon cancer | [133] |
| miR-217 | suppression | Lung, kidney, gastric cancers, osteosarcoma | [134,135,136,137] |
| miR-217-5p | suppression | Liver cancer | [138] |
| miR-218 | suppression | Breast, liver cancers | [139,140] |
| miR-326 | suppression | Lung cancer, colon cancer, glioma | [141,142,143,144] |
| miR-331-3p | suppression | Gastric cancer | [145] |
| miR-373 | suppression | Ovarian cancer | [146] |
| miR-449b | suppression | Breast cancer | [147] |
| miR-454-3p | suppression | Gastric cancer, chondrosarcoma | [148,149] |
| miR-483-3p | suppression | Medulloblastoma | [150] |
| miR-545 | suppression | Colon cancer | [151] |
| miR-613 | suppression | Pancreatic cancer, retinoblastoma | [152,153] |
| miR-663b | suppression | Pancreatic cancer | [154] |
| Name | URL | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Diana Tools | http://diana.imis.athena-innovation.gr/DianaTools/index.php | A package that provides algorithms, databases, and software for interpreting and archiving data in a systematic framework starting from deep sequencing data, the annotation of miRNA regulatory elements, and targets to define the role of ncRNAs in different diseases. |
| GDCRNATools | http://bioconductor.org/packages/devel/bioc/html/GDCRNATools.html | An R package that provides a standard tool to downloading, organizing, and integrative analyzing of RNA expression data in the Genomic Data Commons (GDC) portal, deciphering mainly the lncRNA-mRNA-related ceRNAs regulatory network in cancer. |
| Microcosm Targets | http://www.ebi.ac.uk/enright-srv/microcosm/htdocs/targets/v5/ | A web resource containing computationally predicted targets for miRNAs across many species, including humans. MicroCosm Targets database uses dynamic programming alignment to identify highly complementary miRNA–mRNA pairs. |
| miRanda | http://www.mirbase.org/ | The miRBase website provides a wide range of information on published miRNAs, including their sequences, their biogenesis precursors, genome coordinates and context, literature references, deep sequencing expression data, and community-driven annotation. |
| miRcode | http://www.mircode.org/ | The miRcode web interface provides basic search functionality for finding putative miRNA–target sites in lncRNAs of interest or predicted targets of specific miRNAs. |
| MiRDB | http://www.mirdb.org/ | An online database able to predict miRNAs target by a bioinformatics tool, MirTarget, which was developed by analyzing thousands of miRNA–target interactions from high-throughput sequencing experiments. |
| miRge | http://atlas.pathology.jhu.edu/baras/miRge.html | MiRge employs a Bayesian alignment approach, whereby reads are sequentially aligned against customized mature miRNA, hairpin miRNA, noncoding RNA, and mRNA sequence libraries. Reads for all other RNA species are provided, which is useful for identifying potential contaminants and optimizing small RNA purification strategies. |
| miRLAB | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/miRLAB.html | An R package for automating the procedure of inferring and validating miRNA–mRNA regulatory relationships. It includes a pipeline to obtain matched miRNA and mRNA expression datasets directly from TCGA, the functions for validating the predictions using experimentally validated miRNA target data and miRNA perturbation data. |
| miRNApath | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/miRNApath.html | A package for provision pathway enrichment techniques for miRNA expression data. miRNApath online database uses miRNA target genes to link miRNAs to metabolic pathways. |
| miRTarBase | http://mirtarbase.mbc.nctu.edu.tw/ | A database containing miRNA–target interactions (MTIs). The collected MTIs are validated experimentally by reporter assays, Western blot, or microarray experiments with overexpression or knockdown of miRNAs. |
| PicTar | http://www.pictar.org/ | A computational method for identifying common targets of miRNAs. Through statistical tests using genome-wide alignments of eight vertebrate genomes, PicTar is able to specifically recover published miRNA targets. |
| RegRNA | http://regrna.mbc.nctu.edu.tw/html/prediction.html | An integrated web server to identify homologs of the regulatory RNA motifs and elements against an input mRNA sequence. RegRNA displays prediction results in a graphical interface generated by various integrated analytical tools, and allows users to annotate their own experimental sequences or to discover homologs of their desired motifs. |
| RNA22 | https://cm.jefferson.edu/rna22/ | A pattern-based method for the identification of miRNA binding sites and their corresponding heteroduplexes. |
| starBase v2.0 | http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/ | A database able to provide: the miRNA-pseudogene interaction networks, interaction maps between miRNAs and circRNAs, ceRNA functional networks based on miRNA–target interactions overlapping with high-throughput CLIP-Seq data, miRNA–lncRNA interactions, and a variety of interfaces and graphic visualizations to facilitate analysis of CLIP-Seq data, RBP binding sites, miRNA targets, and ceRNA regulatory networks in normal and cancer cells. |
| TargetScan | http://www.targetscan.org/ | A web server that predicts miRNA target genes by searching for the presence of 6- to 8-mer sites that match the seed region of a given miRNA and make use of species alignment to locate conserved sites. |
| TargetScore | https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/TargetScore.html | A Bayesian probabilistic scoring method taking into account the fold-change due to miRNA overexpression and sequence-based information. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cantile, M.; Di Bonito, M.; Tracey De Bellis, M.; Botti, G. Functional Interaction among lncRNA HOTAIR and MicroRNAs in Cancer and Other Human Diseases. Cancers 2021, 13, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030570
Cantile M, Di Bonito M, Tracey De Bellis M, Botti G. Functional Interaction among lncRNA HOTAIR and MicroRNAs in Cancer and Other Human Diseases. Cancers. 2021; 13(3):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030570
Chicago/Turabian StyleCantile, Monica, Maurizio Di Bonito, Maura Tracey De Bellis, and Gerardo Botti. 2021. "Functional Interaction among lncRNA HOTAIR and MicroRNAs in Cancer and Other Human Diseases" Cancers 13, no. 3: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030570
APA StyleCantile, M., Di Bonito, M., Tracey De Bellis, M., & Botti, G. (2021). Functional Interaction among lncRNA HOTAIR and MicroRNAs in Cancer and Other Human Diseases. Cancers, 13(3), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13030570







