Heterodimeric IL-15 in Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
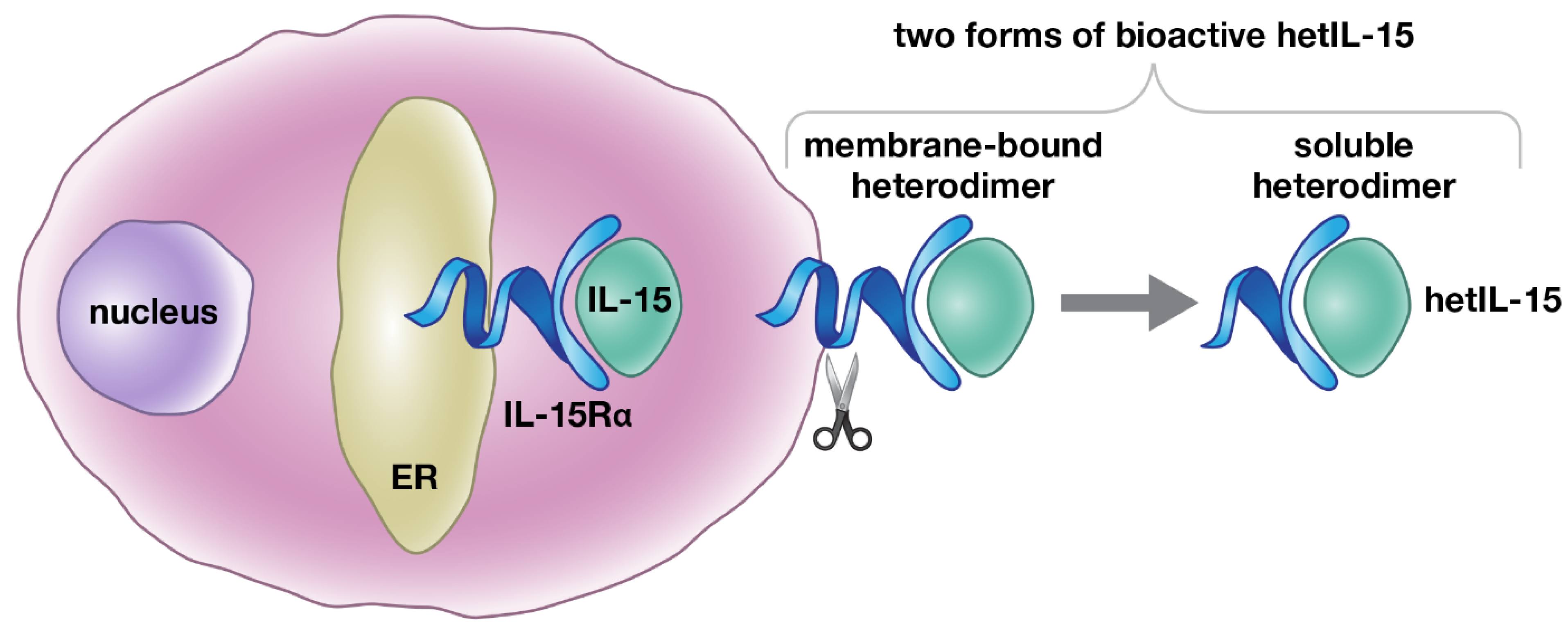
2. Regulation of Heterodimeric IL-15 Production: Trans-Presentation and Soluble hetIL-15
3. Source and Physiological Function of hetIL-15
4. IL-15:IL-15Rα Complexes as Cytokine Agonists in Animal Models and Their Efficacy in Preclinical Cancer Studies
4.1. sch rhIL-15
4.2. hetIL-15 (NIZ985)
4.3. hetIL-15Fc
4.4. N-803 (Anktiva, Formerly ALT-803)
4.5. RLI (Receptor-Linker-IL-15) Superagonist
4.6. Optimized DNAs Expressing hetIL-15
5. IL-15 in Combination Therapy for Cancer
5.1. Combination of IL-15 with Checkpoint Inhibitors and Monoclonal Antibodies
5.2. Combination of IL-15 with Chemotherapy and Radiation
5.3. Combination of IL-15 with Adoptive Cell Therapy
5.4. γ-Chain Family of Cytokines
6. IL-15 in Clinical Trials for Cancer Immunotherapy
6.1. sch rhIL-15
6.2. hetIL-15 (NIZ985)
6.3. N-803 (Anktiva, Formerly ALT-803)
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, A.; Koka, R.; Burkett, P. Diverse functions of IL-2, IL-15, and IL-7 in lymphoid homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 657–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A. The biology of interleukin-2 and interleukin-15: Implications for cancer therapy and vaccine design. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprent, J.; Cho, J.H.; Boyman, O.; Surh, C.D. T cell homeostasis. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2008, 86, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyman, O.; Purton, J.F.; Surh, C.D.; Sprent, J. Cytokines and T-cell homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surh, C.D.; Boyman, O.; Purton, J.F.; Sprent, J. Homeostasis of memory T cells. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 211, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berard, M.; Brandt, K.; Bulfone-Paus, S.; Tough, D.F. IL-15 promotes the survival of naive and memory phenotype CD8+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5018–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carson, W.E.; Giri, J.G.; Lindemann, M.J.; Linett, M.L.; Ahdieh, M.; Paxton, R.; Anderson, D.; Eisenmann, J.; Grabstein, K.; Caligiuri, M.A. Interleukin (IL) 15 is a novel cytokine that activates human natural killer cells via components of the IL-2 receptor. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, S.; Hwang, I.; Tough, D.F.; Sprent, J. Potent and selective stimulation of memory-phenotype CD8+ T cells in vivo by IL-15. Immunity 1998, 8, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lotze, M.T.; Chang, A.E.; Seipp, C.A.; Simpson, C.; Vetto, J.T.; Rosenberg, S.A. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 in the treatment of patients with disseminated cancer. Responses, treatment-related morbidity, and histologic findings. JAMA 1986, 256, 3117–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Muul, L.M.; Leitman, S.; Chang, A.E.; Ettinghausen, S.E.; Matory, Y.L.; Skibber, J.M.; Shiloni, E.; Vetto, J.T.; et al. Observations on the systemic administration of autologous lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2 to patients with metastatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 1485–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, J.G.; Ahdieh, M.; Eisenman, J.; Shanebeck, K.; Grabstein, K.; Kumaki, S.; Namen, A.; Park, L.S.; Cosman, D.; Anderson, D. Utilization of the beta and gamma chains of the IL-2 receptor by the novel cytokine IL-15. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlack, B.; Merz, H.; Schorle, H.; Schimpl, A.; Feller, A.C.; Horak, I. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell 1993, 75, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, T.R.; Porter, B.O.; Codias, E.K.; Scibelli, P.; Yu, A. Normal lymphoid homeostasis and lack of lethal autoimmunity in mice containing mature T cells with severely impaired IL-2 receptors. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, T.R.; Yu, A.; Vincek, V.; Scibelli, P.; Kong, L. CD4 regulatory T cells prevent lethal autoimmunity in IL-2Rbeta-deficient mice. Implications for the nonredundant function of IL-2. Immunity 2002, 17, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spolski, R.; Li, P.; Leonard, W.J. Biology and regulation of IL-2: From molecular mechanisms to human therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 648–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.K.; Glaccum, M.; Brown, S.N.; Butz, E.A.; Viney, J.L.; Embers, M.; Matsuki, N.; Charrier, K.; Sedger, L.; Willis, C.R.; et al. Reversible defects in natural killer and memory CD8 T cell lineages in interleukin 15-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colpitts, S.L.; Stonier, S.W.; Stoklasek, T.A.; Root, S.H.; Aguila, H.L.; Schluns, K.S.; Lefrancois, L. Transcriptional regulation of IL-15 expression during hematopoiesis. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3017–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Hara, T.; Simmons, S.; Wagatsuma, K.; Abe, A.; Miyachi, H.; Kitano, S.; Ishii, M.; Tani-ichi, S.; Ikuta, K. Characterization of the IL-15 niche in primary and secondary lymphoid organs in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giri, J.G.; Kumaki, S.; Ahdieh, M.; Friend, D.J.; Loomis, A.; Shanebeck, K.; DuBose, R.; Cosman, D.; Park, L.S.; Anderson, D.M. Identification and cloning of a novel IL-15 binding protein that is structurally related to the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 3654–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, C.; Bear, J.; Rosati, M.; Beach, R.K.; Alicea, C.; Sowder, R.; Chertova, E.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Circulating IL-15 exists as heterodimeric complex with soluble IL-15Ralpha in human and mouse serum. Blood 2012, 120, e1–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grabstein, K.H.; Eisenman, J.; Shanebeck, K.; Rauch, C.; Srinivasan, S.; Fung, V.; Beers, C.; Richardson, J.; Schoenborn, M.A.; Ahdieh, M.; et al. Cloning of a T cell growth factor that interacts with the beta chain of the interleukin-2 receptor. Science 1994, 264, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, J.D.; Bamford, R.N.; Peters, C.; Grant, A.J.; Kurys, G.; Goldman, C.K.; Brennan, J.; Roessler, E.; Waldmann, T.A. A lymphokine, provisionally designated interleukin T and produced by a human adult T-cell leukemia line, stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4935–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chirifu, M.; Hayashi, C.; Nakamura, T.; Toma, S.; Shuto, T.; Kai, H.; Yamagata, Y.; Davis, S.J.; Ikemizu, S. Crystal structure of the IL-15-IL-15Ralpha complex, a cytokine-receptor unit presented in trans. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villinger, F.; Brar, S.S.; Mayne, A.; Chikkala, N.; Ansari, A.A. Comparative sequence analysis of cytokine genes from human and nonhuman primates. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 3946–3954. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.M.; Johnson, L.; Glaccum, M.B.; Copeland, N.G.; Gilbert, D.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; Valentine, V.; Kirstein, M.N.; Shapiro, D.N.; Morris, S.W.; et al. Chromosomal assignment and genomic structure of Il15. Genomics 1995, 25, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagaya, Y.; Bamford, R.N.; DeFilippis, A.P.; Waldmann, T.A. IL-15: A pleiotropic cytokine with diverse receptor/signaling pathways whose expression is controlled at multiple levels. Immunity 1996, 4, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldmann, T.A.; Tagaya, Y. The multifaceted regulation of interleukin-15 expression and the role of this cytokine in NK cell differentiation and host response to intracellular pathogens. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 19–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubois, S.; Mariner, J.; Waldmann, T.A.; Tagaya, Y. IL-15Ralpha recycles and presents IL-15 In trans to neighboring cells. Immunity 2002, 17, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burkett, P.R.; Koka, R.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Boone, D.L.; Ma, A. Coordinate expression and trans presentation of interleukin (IL)-15Ralpha and IL-15 supports natural killer cell and memory CD8+ T cell homeostasis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 200, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koka, R.; Burkett, P.R.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Chan, F.; Lodolce, J.P.; Boone, D.L.; Ma, A. Interleukin (IL)-15R[alpha]-deficient natural killer cells survive in normal but not IL-15R[alpha]-deficient mice. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandau, M.M.; Schluns, K.S.; Lefrancois, L.; Jameson, S.C. Cutting edge: Transpresentation of IL-15 by bone marrow-derived cells necessitates expression of IL-15 and IL-15R alpha by the same cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6537–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruckert, R.; Brandt, K.; Bulanova, E.; Mirghomizadeh, F.; Paus, R.; Bulfone-Paus, S. Dendritic cell-derived IL-15 controls the induction of CD8 T cell immune responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, N.; Nagai, M.; Jacobson, S.; Waldmann, T.A. IL-15 plays a major role in the persistence of Tax-specific CD8 cells in HAM/TSP patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 14559–14564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mariner, J.M.; Mamane, Y.; Hiscott, J.; Waldmann, T.A.; Azimi, N. IFN regulatory factor 4 participates in the human T cell lymphotropic virus type I-mediated activation of the IL-15 receptor alpha promoter. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5667–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, C.; Rosati, M.; Jalah, R.; Valentin, A.; Kulkarni, V.; Alicea, C.; Zhang, G.M.; Patel, V.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Intracellular interaction of Interleukin-15 with its Receptor {alpha} during production leads to mutual stabilization and increased bioactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 4189–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mortier, E.; Woo, T.; Advincula, R.; Gozalo, S.; Ma, A. IL-15Ralpha chaperones IL-15 to stable dendritic cell membrane complexes that activate NK cells via trans presentation. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1213–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergamaschi, C.; Jalah, R.; Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Zhang, G.M.; Alicea, C.; Zolotukhin, A.S.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Secretion and biological activity of short signal peptide IL-15 is chaperoned by IL-15 receptor alpha in vivo. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3064–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, M.P.; Kovar, M.; Purton, J.F.; Cho, J.H.; Boyman, O.; Surh, C.D.; Sprent, J. Converting IL-15 to a superagonist by binding to soluble IL-15R{alpha}. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9166–9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoklasek, T.A.; Schluns, K.S.; Lefrancois, L. Combined IL-15/IL-15Ralpha immunotherapy maximizes IL-15 activity in vivo. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6072–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burkett, P.R.; Koka, R.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Chan, F.; Ma, A.; Boone, D.L. IL-15R alpha expression on CD8+ T cells is dispensable for T cell memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4724–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koka, R.; Burkett, P.; Chien, M.; Chai, S.; Boone, D.L.; Ma, A. Cutting edge: Murine dendritic cells require IL-15R alpha to prime NK cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3594–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schluns, K.S.; Klonowski, K.D.; Lefrancois, L. Transregulation of memory CD8 T-cell proliferation by IL-15Ralpha+ bone marrow-derived cells. Blood 2004, 103, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huntington, N.D.; Legrand, N.; Alves, N.L.; Jaron, B.; Weijer, K.; Plet, A.; Corcuff, E.; Mortier, E.; Jacques, Y.; Spits, H.; et al. IL-15 trans-presentation promotes human NK cell development and differentiation in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.; Schachterle, W.; Oberle, K.; Aichele, P.; Diefenbach, A. Dendritic cells prime natural killer cells by trans-presenting interleukin 15. Immunity 2007, 26, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stonier, S.W.; Ma, L.J.; Castillo, E.F.; Schluns, K.S. Dendritic cells drive memory CD8 T-cell homeostasis via IL-15 transpresentation. Blood 2008, 112, 4546–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonuleit, H.; Wiedemann, K.; Muller, G.; Degwert, J.; Hoppe, U.; Knop, J.; Enk, A.H. Induction of IL-15 messenger RNA and protein in human blood-derived dendritic cells: A role for IL-15 in attraction of T cells. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 2610–2615. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carson, W.E.; Ross, M.E.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Marien, M.J.; Boiani, N.; Grabstein, K.; Caligiuri, M.A. Endogenous production of interleukin 15 by activated human monocytes is critical for optimal production of interferon-gamma by natural killer cells in vitro. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 2578–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.M.; Seder, R.A.; Sher, A. Induction and regulation of IL-15 expression in murine macrophages. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mortier, E.; Advincula, R.; Kim, L.; Chmura, S.; Barrera, J.; Reizis, B.; Malynn, B.A.; Ma, A. Macrophage- and dendritic-cell-derived interleukin-15 receptor alpha supports homeostasis of distinct CD8+ T cell subsets. Immunity 2009, 31, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spranger, S.; Koblish, H.K.; Horton, B.; Scherle, P.A.; Newton, R.; Gajewski, T.F. Mechanism of tumor rejection with doublets of CTLA-4, PD-1/PD-L1, or IDO blockade involves restored IL-2 production and proliferation of CD8(+) T cells directly within the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spranger, S.; Sivan, A.; Corrales, L.; Gajewski, T.F. Tumor and host factors controlling antitumor immunity and efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Immunol. 2016, 130, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tumeh, P.C.; Harview, C.L.; Yearley, J.H.; Shintaku, I.P.; Taylor, E.J.; Robert, L.; Chmielowski, B.; Spasic, M.; Henry, G.; Ciobanu, V.; et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature 2014, 515, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, V.V.; Esposito, D.; Sumpter, T.L.; Broadt, T.L.; Hartley, J.; Knapp, G.C.t.; Cheng, W.; Jiang, M.S.; Roach, J.M.; Yang, X.; et al. Clinical manufacturing of recombinant human interleukin 15. I. Production cell line development and protein expression in E. coli with stop codon optimization. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 28, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertova, E.; Bergamaschi, C.; Chertov, O.; Sowder, R.; Bear, J.; Roser, J.D.; Beach, R.K.; Lifson, J.D.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Characterization and favorable in vivo properties of heterodimeric soluble IL-15.IL-15Ralpha cytokine compared to IL-15 monomer. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18093–18103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, K.P.; Zhu, X.; Liu, B.; Jeng, E.; Kong, L.; Yovandich, J.L.; Vyas, V.V.; Marcus, W.D.; Chavaillaz, P.A.; Romero, C.A.; et al. IL-15:IL-15 receptor alpha superagonist complex: High-level co-expression in recombinant mammalian cells, purification and characterization. Cytokine 2011, 56, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mortier, E.; Quemener, A.; Vusio, P.; Lorenzen, I.; Boublik, Y.; Grotzinger, J.; Plet, A.; Jacques, Y. Soluble interleukin-15 receptor alpha (IL-15R alpha)-sushi as a selective and potent agonist of IL-15 action through IL-15R beta/gamma. Hyperagonist IL-15 x IL-15R alpha fusion proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lugli, E.; Goldman, C.K.; Perera, L.P.; Smedley, J.; Pung, R.; Yovandich, J.L.; Creekmore, S.P.; Waldmann, T.A.; Roederer, M. Transient and persistent effects of IL-15 on lymphocyte homeostasis in nonhuman primates. Blood 2010, 116, 3238–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneller, M.C.; Kopp, W.C.; Engelke, K.J.; Yovandich, J.L.; Creekmore, S.P.; Waldmann, T.A.; Lane, H.C. IL-15 administered by continuous infusion to rhesus macaques induces massive expansion of CD8+ T effector memory population in peripheral blood. Blood 2012, 118, 6845–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picker, L.J.; Reed-Inderbitzin, E.F.; Hagen, S.I.; Edgar, J.B.; Hansen, S.G.; Legasse, A.; Planer, S.; Piatak, M., Jr.; Lifson, J.D.; Maino, V.C.; et al. IL-15 induces CD4 effector memory T cell production and tissue emigration in nonhuman primates. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A.; Lugli, E.; Roederer, M.; Perera, L.P.; Smedley, J.V.; Macallister, R.P.; Goldman, C.K.; Bryant, B.R.; Decker, J.M.; Fleisher, T.A.; et al. Safety (toxicity), pharmacokinetics, immunogenicity, and impact on elements of the normal immune system of recombinant human IL-15 in rhesus macaques. Blood 2011, 117, 4787–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klebanoff, C.A.; Finkelstein, S.E.; Surman, D.R.; Lichtman, M.K.; Gattinoni, L.; Theoret, M.R.; Grewal, N.; Spiess, P.J.; Antony, P.A.; Palmer, D.C.; et al. IL-15 enhances the in vivo antitumor activity of tumor-reactive CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1969–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, H.; Dubois, S.; Sato, N.; Sabzevari, H.; Sakai, Y.; Waldmann, T.A.; Tagaya, Y. Role of trans-cellular IL-15 presentation in the activation of NK cell-mediated killing, which leads to enhanced tumor immunosurveillance. Blood 2005, 105, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munger, W.; DeJoy, S.Q.; Jeyaseelan, R., Sr.; Torley, L.W.; Grabstein, K.H.; Eisenmann, J.; Paxton, R.; Cox, T.; Wick, M.M.; Kerwar, S.S. Studies evaluating the antitumor activity and toxicity of interleukin-15, a new T cell growth factor: Comparison with interleukin-2. Cell. Immunol. 1995, 165, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Zhao, L.T.; Jiang, Y.; Ba de, N.; Cui, L.X.; He, W. Activity of recombinant human interleukin-15 against tumor recurrence and metastasis in mice. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 5, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.; Steel, J.C.; Zhang, M.; Morris, J.C.; Waitz, R.; Fasso, M.; Allison, J.P.; Waldmann, T.A. Simultaneous inhibition of two regulatory T-cell subsets enhanced Interleukin-15 efficacy in a prostate tumor model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6187–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.; Steel, J.C.; Zhang, M.; Morris, J.C.; Waldmann, T.A. Simultaneous blockade of multiple immune system inhibitory checkpoints enhances antitumor activity mediated by interleukin-15 in a murine metastatic colon carcinoma model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6019–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Ju, W.; Yao, Z.; Yu, P.; Wei, B.R.; Simpson, R.M.; Waitz, R.; Fasso, M.; Allison, J.P.; Waldmann, T.A. Augmented IL-15Ralpha expression by CD40 activation is critical in synergistic CD8 T cell-mediated antitumor activity of anti-CD40 antibody with IL-15 in TRAMP-C2 tumors in mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 6156–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thaysen-Andersen, M.; Chertova, E.; Bergamaschi, C.; Moh, E.S.; Chertov, O.; Roser, J.; Sowder, R.; Bear, J.; Lifson, J.; Packer, N.H.; et al. Recombinant human heterodimeric IL-15 complex displays extensive and reproducible N- and O-linked glycosylation. Glycoconj. J. 2016, 33, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, C.; Watson, D.C.; Valentin, A.; Bear, J.; Peer, C.J.; Figg, W.D., Sr.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Optimized administration of hetIL-15 expands lymphocytes and minimizes toxicity in rhesus macaques. Cytokine 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.C.; Moysi, E.; Valentin, A.; Bergamaschi, C.; Devasundaram, S.; Fortis, S.P.; Bear, J.; Chertova, E.; Bess, J., Jr.; Sowder, R.; et al. Treatment with native heterodimeric IL-15 increases cytotoxic lymphocytes and reduces SHIV RNA in lymph nodes. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
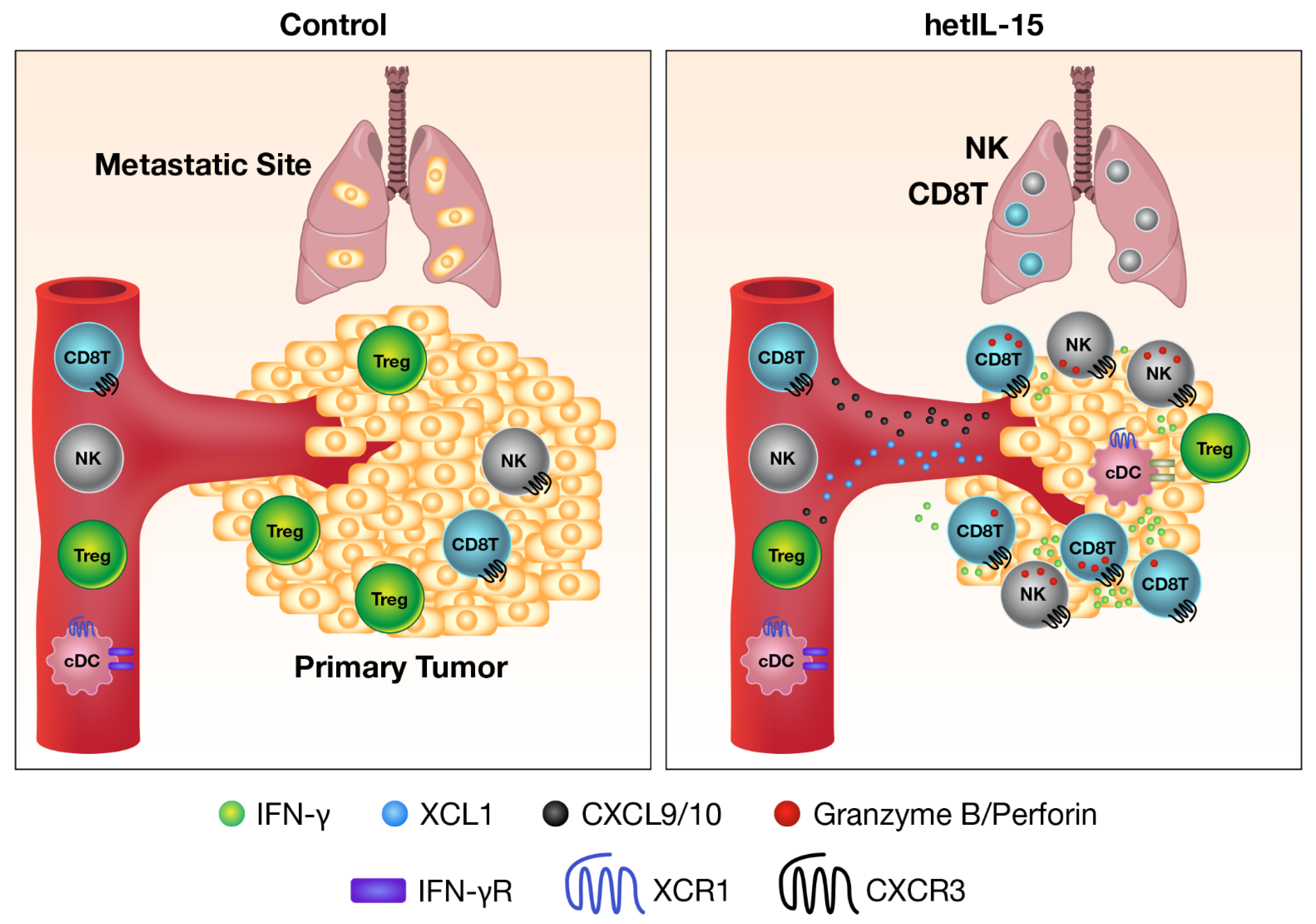
- Bergamaschi, C.; Pandit, H.; Nagy, B.A.; Stellas, D.; Jensen, S.M.; Bear, J.; Cam, M.; Valentin, A.; Fox, B.A.; Felber, B.K.; et al. Heterodimeric IL-15 delays tumor growth and promotes intratumoral CTL and dendritic cell accumulation by a cytokine network involving XCL1, IFN-gamma, CXCL9 and CXCL10. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.S.; Nagy, B.A.; Jensen, S.M.; Hu, X.; Alicea, C.; Fox, B.A.; Felber, B.K.; Bergamaschi, C.; Pavlakis, G.N. Heterodimeric IL-15 treatment enhances tumor infiltration, persistence and effector functions of adoptively transferred tumor-specific T cells in the absence of lymphodepletion. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2817–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlecnik, B.; Bindea, G.; Angell, H.K.; Sasso, M.S.; Obenauf, A.C.; Fredriksen, T.; Lafontaine, L.; Bilocq, A.M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Tosolini, M.; et al. Functional network pipeline reveals genetic determinants associated with in situ lymphocyte proliferation and survival of cancer patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 228ra237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, S.; Patel, H.J.; Zhang, M.; Waldmann, T.A.; Muller, J.R. Preassociation of IL-15 with IL-15R alpha-IgG1-Fc enhances its activity on proliferation of NK and CD8+/CD44high T cells and its antitumor action. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2099–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elpek, K.G.; Rubinstein, M.P.; Bellemare-Pelletier, A.; Goldrath, A.W.; Turley, S.J. Mature natural killer cells with phenotypic and functional alterations accumulate upon sustained stimulation with IL-15/IL-15Ralpha complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21647–21652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Epardaud, M.; Elpek, K.G.; Rubinstein, M.P.; Yonekura, A.R.; Bellemare-Pelletier, A.; Bronson, R.; Hamerman, J.A.; Goldrath, A.W.; Turley, S.J. Interleukin-15/interleukin-15R alpha complexes promote destruction of established tumors by reviving tumor-resident CD8+ T cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2972–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, E.; Usiskin, I.M.; Bergamaschi, C.; Hanlon, D.J.; Edelson, R.L.; Justesen, S.; Pavlakis, G.N.; Flavell, R.A.; Fahmy, T.M. Configuration-dependent presentation of multivalent IL-15:IL-15Ralpha enhances the antigen-specific T cell response and anti-tumor immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Marcus, W.D.; Xu, W.; Lee, H.I.; Han, K.; Egan, J.O.; Yovandich, J.L.; Rhode, P.R.; Wong, H.C. Novel human interleukin-15 agonists. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3598–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, P.S.; Kwilas, A.R.; Xu, W.; Alter, S.; Jeng, E.K.; Wong, H.C.; Schlom, J.; Hodge, J.W. IL-15 superagonist/IL-15RalphaSushi-Fc fusion complex (IL-15SA/IL-15RalphaSu-Fc; ALT-803) markedly enhances specific subpopulations of NK and memory CD8+ T cells, and mediates potent anti-tumor activity against murine breast and colon carcinomas. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16130–16145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jones, M.; Kong, L.; Noel, T.; Jeng, E.K.; Shi, S.; England, C.G.; Alter, S.; Miller, J.S.; Cai, W.; et al. Evaluation of the biological activities of the IL-15 superagonist complex, ALT-803, following intravenous versus subcutaneous administration in murine models. Cytokine 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhode, P.R.; Egan, J.O.; Xu, W.; Hong, H.; Webb, G.M.; Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Wen, J.; You, L.; et al. Comparison of the superagonist complex, ALT-803, to IL15 as cancer immunotherapeutics in animal models. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Jones, M.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Johnson, C.B.; Edwards, A.C.; Kong, L.; Jeng, E.K.; Han, K.; Marcus, W.D.; et al. Efficacy and mechanism-of-action of a novel superagonist interleukin-15: Interleukin-15 receptor alphaSu/Fc fusion complex in syngeneic murine models of multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3075–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathios, D.; Park, C.K.; Marcus, W.D.; Alter, S.; Rhode, P.R.; Jeng, E.K.; Wong, H.C.; Pardoll, D.M.; Lim, M. Therapeutic administration of IL-15 superagonist complex ALT-803 leads to long-term survival and durable antitumor immune response in a murine glioblastoma model. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felices, M.; Chu, S.; Kodal, B.; Bendzick, L.; Ryan, C.; Lenvik, A.J.; Boylan, K.L.M.; Wong, H.C.; Skubitz, A.P.N.; Miller, J.S.; et al. IL-15 super-agonist (ALT-803) enhances natural killer (NK) cell function against ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 145, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, M.; Liu, B.; Kong, L.; Collins, L.I.; Schneider, S.E.; Chen, X.; Han, K.; Jeng, E.K.; Rhode, P.R.; Leong, J.W.; et al. The IL-15-Based ALT-803 complex enhances FcgammaRIIIa-triggered NK cell responses and in vivo clearance of B cell lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 596–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bessard, A.; Sole, V.; Bouchaud, G.; Quemener, A.; Jacques, Y. High antitumor activity of RLI, an interleukin-15 (IL-15)-IL-15 receptor alpha fusion protein, in metastatic melanoma and colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2736–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desbois, M.; Beal, C.; Charrier, M.; Besse, B.; Meurice, G.; Cagnard, N.; Jacques, Y.; Bechard, D.; Cassard, L.; Chaput, N. IL-15 superagonist RLI has potent immunostimulatory properties on NK cells: Implications for antimetastatic treatment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, C.; Kulkarni, V.; Rosati, M.; Alicea, C.; Jalah, R.; Chen, S.; Bear, J.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Valentin, A.; Felber, B.K.; et al. Intramuscular delivery of heterodimeric IL-15 DNA in macaques produces systemic levels of bioactive cytokine inducing proliferation of NK and T cells. Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, L.S.; Anderson, B.G.; Strait-Bodey, L.; Wolden-Hanson, T. Serum and muscle interleukin-15 levels decrease in aging mice: Correlation with declines in soluble interleukin-15 receptor alpha expression. Exp. Gerontol. 2010, 45, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, L.S. Interleukin-15: A muscle-derived cytokine regulating fat-to-lean body composition. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, E75–E83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, L.S.; Haugk, K.L.; Grabstein, K.H. Interleukin-15: A novel anabolic cytokine for skeletal muscle. Endocrinology 1995, 136, 3669–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Stolina, M.; Lin, Y.; Gardner, B.; Miller, P.W.; Kronenberg, M.; Dubinett, S.M. T cell-derived IL-10 promotes lung cancer growth by suppressing both T cell and APC function. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 5020–5028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Jin, W.; Wahl, S.M. Engagement of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) induces transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) production by murine CD4(+) T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Sakaguchi, N.; Shimizu, J.; Yamazaki, S.; Sakihama, T.; Itoh, M.; Kuniyasu, Y.; Nomura, T.; Toda, M.; Takahashi, T. Immunologic tolerance maintained by CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells: Their common role in controlling autoimmunity, tumor immunity, and transplantation tolerance. Immunol. Rev. 2001, 182, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Clements, V.K.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S. Reduction of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and induction of M1 macrophages facilitate the rejection of established metastatic disease. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visconti, R.; Morra, F.; Guggino, G.; Celetti, A. The between now and then of lung cancer chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desbois, M.; Le Vu, P.; Coutzac, C.; Marcheteau, E.; Beal, C.; Terme, M.; Gey, A.; Morisseau, S.; Teppaz, G.; Boselli, L.; et al. IL-15 trans-Signaling with the superagonist RLI promotes effector/memory CD8+ T cell responses and enhances antitumor activity of PD-1 antagonists. J. Immunol. 2016, 197, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Judge, S.J.; Darrow, M.A.; Thorpe, S.W.; Gingrich, A.A.; O’Donnell, E.F.; Bellini, A.R.; Sturgill, I.R.; Vick, L.V.; Dunai, C.; Stoffel, K.M.; et al. Analysis of tumor-infiltrating NK and T cells highlights IL-15 stimulation and TIGIT blockade as a combination immunotherapy strategy for soft tissue sarcomas. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yao, Z.; Dubois, S.; Ju, W.; Muller, J.R.; Waldmann, T.A. Interleukin-15 combined with an anti-CD40 antibody provides enhanced therapeutic efficacy for murine models of colon cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7513–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, S.R.; Carbone, F.R.; Karamalis, F.; Flavell, R.A.; Miller, J.F.; Heath, W.R. Help for cytotoxic-T-cell responses is mediated by CD40 signalling. Nature 1998, 393, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, M.C.; Minute, L.; Lopez, A.; Perez-Ruiz, E.; Gomar, C.; Vasquez, M.; Inoges, S.; Etxeberria, I.; Rodriguez, I.; Garasa, S.; et al. Enhancement of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of cetuximab by a chimeric protein encompassing interleukin-15. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1393597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberti, M.P.; Rocca, Y.S.; Amat, M.; Pampena, M.B.; Loza, J.; Colo, F.; Fabiano, V.; Loza, C.M.; Arriaga, J.M.; Bianchini, M.; et al. IL-2- or IL-15-activated NK cells enhance Cetuximab-mediated activity against triple-negative breast cancer in xenografts and in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moga, E.; Canto, E.; Vidal, S.; Juarez, C.; Sierra, J.; Briones, J. Interleukin-15 enhances rituximab-dependent cytotoxicity against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and overcomes transforming growth factor beta-mediated immunosuppression. Exp. Hematol. 2011, 39, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wen, B.; Anton, O.M.; Yao, Z.; Dubois, S.; Ju, W.; Sato, N.; DiLillo, D.J.; Bamford, R.N.; Ravetch, J.V.; et al. IL-15 enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by NK cells and macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10915–E10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Kong, L.; Han, K.; Hong, H.; Marcus, W.D.; Chen, X.; Jeng, E.K.; Alter, S.; Zhu, X.; Rubinstein, M.P.; et al. A novel fusion of ALT-803 (Interleukin (IL)-15 superagonist) with an antibody demonstrates antigen-specific antitumor responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 23869–23881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felices, M.; Kodal, B.; Hinderlie, P.; Kaminski, M.F.; Cooley, S.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Vallera, D.A.; Miller, J.S.; Bachanova, V. Novel CD19-targeted TriKE restores NK cell function and proliferative capacity in CLL. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmohl, J.U.; Felices, M.; Taras, E.; Miller, J.S.; Vallera, D.A. Enhanced ADCC and NK cell activation of an anticarcinoma bispecific antibody by genetic insertion of a modified IL-15 cross-linker. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vallera, D.A.; Felices, M.; McElmurry, R.; McCullar, V.; Zhou, X.; Schmohl, J.U.; Zhang, B.; Lenvik, A.J.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Verneris, M.R.; et al. IL15 Trispecific Killer Engagers (TriKE) make Natural Killer cells specific to CD33+ targets while also inducing persistence, in vivo expansion, and enhanced function. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vincent, M.; Bessard, A.; Cochonneau, D.; Teppaz, G.; Sole, V.; Maillasson, M.; Birkle, S.; Garrigue-Antar, L.; Quemener, A.; Jacques, Y. Tumor targeting of the IL-15 superagonist RLI by an anti-GD2 antibody strongly enhances its antitumor potency. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beha, N.; Harder, M.; Ring, S.; Kontermann, R.E.; Muller, D. IL15-based trifunctional antibody-fusion proteins with costimulatory TNF-superfamily ligands in the single-chain format for cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermer, V.; Baum, V.; Hornig, N.; Kontermann, R.E.; Muller, D. An antibody fusion protein for cancer immunotherapy mimicking IL-15 trans-presentation at the tumor site. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapoval, A.I.; Fuller, J.A.; Kremlev, S.G.; Kamdar, S.J.; Evans, R. Combination chemotherapy and IL-15 administration induce permanent tumor regression in a mouse lung tumor model: NK and T cell-mediated effects antagonized by B cells. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 6977–6984. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, R.; Fuller, J.A.; Christianson, G.; Krupke, D.M.; Troutt, A.B. IL-15 mediates anti-tumor effects after cyclophosphamide injection of tumor-bearing mice and enhances adoptive immunotherapy: The potential role of NK cell subpopulations. Cell. Immunol. 1997, 179, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Ye, H.; Yu, S.; He, C.; Chen, X. Interleukin-15 and cisplatin co-encapsulated thermosensitive polypeptide hydrogels for combined immuno-chemotherapy. J. Control Release 2017, 255, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, D. IL-15/sIL-15Ralpha gene transfer suppresses Lewis lung cancer growth in the lungs, liver and kidneys. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilones, K.A.; Charpentier, M.; Garcia-Martinez, E.; Demaria, S. IL15 synergizes with radiotherapy to reprogram the tumor immune contexture through a dendritic cell connection. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1790716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, C.H.; O’Connor, R.S.; Kawalekar, O.U.; Ghassemi, S.; Milone, M.C. CAR T cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Science 2018, 359, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, C.; Jensen, M.C.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Gough, M.; Elliott, C.; Riddell, S.R. Adoptive transfer of effector CD8+ T cells derived from central memory cells establishes persistent T cell memory in primates. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Perazzelli, J.; Grupp, S.A.; Barrett, D.M. Early memory phenotypes drive T cell proliferation in patients with pediatric malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 320ra323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattinoni, L.; Lugli, E.; Ji, Y.; Pos, Z.; Paulos, C.M.; Quigley, M.F.; Almeida, J.R.; Gostick, E.; Yu, Z.; Carpenito, C.; et al. A human memory T cell subset with stem cell-like properties. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, D.; Wong, R.A.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Pecoraro, J.R.; Kuo, C.F.; Aguilar, B.; Qi, Y.; Ann, D.K.; Starr, R.; et al. IL15 enhances CAR-T cell antitumor activity by reducing mTORC1 activity and preserving their stem cell memory phenotype. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochenderfer, J.N.; Somerville, R.P.T.; Lu, T.; Shi, V.; Bot, A.; Rossi, J.; Xue, A.; Goff, S.L.; Yang, J.C.; Sherry, R.M.; et al. Lymphoma remissions caused by anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells are associated with high serum Interleukin-15 levels. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurton, L.V.; Singh, H.; Najjar, A.M.; Switzer, K.C.; Mi, T.; Maiti, S.; Olivares, S.; Rabinovich, B.; Huls, H.; Forget, M.A.; et al. Tethered IL-15 augments antitumor activity and promotes a stem-cell memory subset in tumor-specific T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E7788–E7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krenciute, G.; Prinzing, B.L.; Yi, Z.; Wu, M.F.; Liu, H.; Dotti, G.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Gottschalk, S. Transgenic expression of IL15 improves antiglioma activity of IL13Ralpha2-CAR T cells but results in antigen loss variants. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanitis, E.; Rota, G.; Kosti, P.; Ronet, C.; Spill, A.; Seijo, B.; Romero, P.; Dangaj, D.; Coukos, G.; Irving, M. Optimized gene engineering of murine CAR-T cells reveals the beneficial effects of IL-15 coexpression. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, V.; Savoldo, B.; Quintarelli, C.; Mahendravada, A.; Zhang, M.; Vera, J.; Heslop, H.E.; Rooney, C.M.; Brenner, M.K.; Dotti, G. Engineering CD19-specific T lymphocytes with interleukin-15 and a suicide gene to enhance their anti-lymphoma/leukemia effects and safety. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, E.; Marin, D.; Banerjee, P.; Macapinlac, H.A.; Thompson, P.; Basar, R.; Nassif Kerbauy, L.; Overman, B.; Thall, P.; Kaplan, M.; et al. Use of CAR-transduced Natural Killer cells in CD19-Positive lymphoid tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Tong, Y.; Dotti, G.; Shaim, H.; Savoldo, B.; Mukherjee, M.; Orange, J.; Wan, X.; Lu, X.; Reynolds, A.; et al. Cord blood NK cells engineered to express IL-15 and a CD19-targeted CAR show long-term persistence and potent antitumor activity. Leukemia 2018, 32, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franks, S.E.; Wolfson, B.; Hodge, J.W. Natural Born Killers: NK Cells in cancer therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, W.; Chen, P.; Xu, X.; Han, W. Programming CAR T cells to enhance anti-tumor efficacy through remodeling of the immune system. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 726–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Bai, X.; Handley, M.; Shan, F. Biological effects of IL-15 on immune cells and its potential for the treatment of cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 91, 107318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weninger, W.; Crowley, M.A.; Manjunath, N.; von Andrian, U.H. Migratory properties of naive, effector, and memory CD8(+) T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenardo, M.J. Interleukin-2 programs mouse alpha beta T lymphocytes for apoptosis. Nature 1991, 353, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebanoff, C.A.; Gattinoni, L.; Palmer, D.C.; Muranski, P.; Ji, Y.; Hinrichs, C.S.; Borman, Z.A.; Kerkar, S.P.; Scott, C.D.; Finkelstein, S.E.; et al. Determinants of successful CD8+ T-cell adoptive immunotherapy for large established tumors in mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5343–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadzadeh, M.; Rosenberg, S.A. IL-2 administration increases CD4+ CD25(hi) Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in cancer patients. Blood 2006, 107, 2409–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldmann, T. The contrasting roles of IL-2 and IL-15 in the life and death of lymphocytes: Implications for the immunotherapy of rheumatological diseases. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4 (Suppl. 3), S161–S167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachella, L.A.; Madsen, L.T.; Dains, J.E. The toxicity and benefit of various dosing strategies for Interleukin-2 in metastatic melanoma and renal cell carcinoma. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2015, 6, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyman, O.; Kovar, M.; Rubinstein, M.P.; Surh, C.D.; Sprent, J. Selective stimulation of T cell subsets with antibody-cytokine immune complexes. Science 2006, 311, 1924–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitra, S.; Ring, A.M.; Amarnath, S.; Spangler, J.B.; Li, P.; Ju, W.; Fischer, S.; Oh, J.; Spolski, R.; Weiskopf, K.; et al. Interleukin-2 activity can be fine tuned with engineered receptor signaling clamps. Immunity 2015, 42, 826–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, D.A.; Yu, S.; Ulge, U.Y.; Spangler, J.B.; Jude, K.M.; Labao-Almeida, C.; Ali, L.R.; Quijano-Rubio, A.; Ruterbusch, M.; Leung, I.; et al. De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15. Nature 2019, 565, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sockolosky, J.T.; Trotta, E.; Parisi, G.; Picton, L.; Su, L.L.; Le, A.C.; Chhabra, A.; Silveria, S.L.; George, B.M.; King, I.C.; et al. Selective targeting of engineered T cells using orthogonal IL-2 cytokine-receptor complexes. Science 2018, 359, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, E.W.; Moore, C.J.; Suriano, S.; Johnson, C.B.; Songalia, N.; Patterson, A.; Neitzke, D.J.; Andrijauskaite, K.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Mehrotra, S.; et al. IL-2Ralpha mediates temporal regulation of IL-2 signaling and enhances immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 311ra170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conlon, K.C.; Lugli, E.; Welles, H.C.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Fojo, A.T.; Morris, J.C.; Fleisher, T.A.; Dubois, S.P.; Perera, L.P.; Stewart, D.M.; et al. Redistribution, hyperproliferation, activation of natural killer cells and CD8 T cells, and cytokine production during first-in-human clinical trial of recombinant human interleukin-15 in patients with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.S.; Morishima, C.; McNeel, D.G.; Patel, M.R.; Kohrt, H.E.K.; Thompson, J.A.; Sondel, P.M.; Wakelee, H.A.; Disis, M.L.; Kaiser, J.C.; et al. A first-in-human Phase I study of subcutaneous outpatient recombinant human IL15 (rhIL15) in adults with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conlon, K.C.; Potter, E.L.; Pittaluga, S.; Lee, C.R.; Miljkovic, M.D.; Fleisher, T.A.; Dubois, S.; Bryant, B.R.; Petrus, M.; Perera, L.P.; et al. IL15 by continuous intravenous infusion to adult patients with solid tumors in a Phase I trial induced dramatic NK-cell subset expansion. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4945–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, S.; He, F.; Bachanova, V.; Vercellotti, G.M.; DeFor, T.E.; Curtsinger, J.M.; Robertson, P.; Grzywacz, B.; Conlon, K.C.; Waldmann, T.A.; et al. First-in-human trial of rhIL-15 and haploidentical natural killer cell therapy for advanced acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1970–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romee, R.; Cooley, S.; Berrien-Elliott, M.M.; Westervelt, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Wagner, J.E.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Blazar, B.R.; Ustun, C.; DeFor, T.E.; et al. First-in-human Phase 1 clinical study of the IL-15 superagonist complex ALT-803 to treat relapse after transplantation. Blood 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolin, K.; Morishima, C.; Velcheti, V.; Miller, J.S.; Lee, S.M.; Silk, A.W.; Holtan, S.G.; Lacroix, A.M.; Fling, S.P.; Kaiser, J.C.; et al. Phase I Trial of ALT-803, A novel recombinant IL15 complex, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5552–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrangle, J.M.; Velcheti, V.; Patel, M.R.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Hill, E.G.; Ravenel, J.G.; Miller, J.S.; Farhad, M.; Anderton, K.; Lindsey, K.; et al. ALT-803, an IL-15 superagonist, in combination with nivolumab in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A non-randomised, open-label, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| IL-15 Agents | Combination Immunotherapy | Route of IL-15 Delivery | Dose Tested or MTD 1 | Application | Best Clinical Response | NCT/ Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sch rhIL-15 | - | IV | 0.3 µg/kg/dose daily for 12 days | Malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma | SD | [144] |
| sch rhIL-15 | - | SC | 2 µg/kg/dose 5 days/week for 2 weeks | Advanced solid tumors | SD | [145] |
| sch rhIL-15 | - | CIV | 2 µg/kg/dose for 10 days | Metastatic tumors | SD | [146] |
| sch rhIL-15 | Lympho-depleting regimen and haploidentical NK cell infusion | IV/SC | 0.3 µg/kg/dose daily for 12 days IV; 2 µg/kg/dose for 10 days SC | Acute myeloid leukemia | 35% remission | [147] |
| sch rhIL-15 | Nivolumab and Ipilimumab | SC | Daily on day 1–8 and 22–29 | Refractory cancers | Active/ recruiting | NCT03388632 |
| sch rhIL-15 | Avelumab | CIV | 1, 2, 3 and 4 µg/kg/day for 5 days (max 6 cycles) | Refractory T cell malignancies | Active/ recruiting | NCT03905135 |
| sch rhIL-15 | Obinutuzumab | CIV | 0.5, 1 and 2 µg/kg/day for 5 days (max 6 cycles) | CLL | Active/ recruiting | NCT03759184 |
| sch rhIL-15 | Alemtuzumab | SC | 0.5–2 µg/kg/dose 5 days/week for 2 weeks | ATL | Active/ recruiting | NCT02689453 |
| hetIL-15 (NIZ985) | - | SC | 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2 or 4 μg/kg 3 times/week for 2 weeks | Metastatic solid tumors | Active | NCT02452268 |
| hetIL-15 (NIZ985) | PDR001 /Spartalizumab | SC | 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2 or 4 μg/kg 3 times/week for 2 weeks | Metastatic solid tumors | Active | NCT02452268 |
| hetIL-15 (NIZ985) | Spartalizumab | SC | 2 or 4 μg/kg weekly | Advanced solid tumors and lymphoma (checkpoint inhibitors relapsed) | Active | NCT04261439 |
| N-803 | - | IV/SC | 10 µg/kg/dose IV for 10 days or SC weekly for 4 weeks | Hematological malignancies | 1 CR, 1 PR, 3 SD | [148] |
| N-803 | - | IV/SC | 20 µg/kg/dose weekly for 4 weeks, every 6 weeks | Solid tumors | No response | [149] |
| N-803 | Nivolumab | SC | 20 µg/kg/dose + 240 mg nivolumab iv every 2 weeks | Non-small cell lung carcinoma | 6 PR, 10 SD | [150] |
| N-803 | Rituximab | IV/SC | Weekly for 4 weeks | B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma | Active | NCT02384954 |
| N-803 | Pembrolizumab/ Nivolumab/ Atezolizumab | SC | 15 µg/kg/dose every 3 weeks | Advanced cancers | Active/ recruiting | NCT03228667 |
| N-803 | Standard-of-care chemotherapy/ aldoxorubicin HCl/ PD-L1 t-haNK | SC | 15 µg/kg/dose every 3 weeks | Pancreatic cancer | Active/ recruiting | NCT04390399 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bergamaschi, C.; Stravokefalou, V.; Stellas, D.; Karaliota, S.; Felber, B.K.; Pavlakis, G.N. Heterodimeric IL-15 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040837
Bergamaschi C, Stravokefalou V, Stellas D, Karaliota S, Felber BK, Pavlakis GN. Heterodimeric IL-15 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers. 2021; 13(4):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040837
Chicago/Turabian StyleBergamaschi, Cristina, Vasiliki Stravokefalou, Dimitris Stellas, Sevasti Karaliota, Barbara K. Felber, and George N. Pavlakis. 2021. "Heterodimeric IL-15 in Cancer Immunotherapy" Cancers 13, no. 4: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040837
APA StyleBergamaschi, C., Stravokefalou, V., Stellas, D., Karaliota, S., Felber, B. K., & Pavlakis, G. N. (2021). Heterodimeric IL-15 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers, 13(4), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040837







