The Role of microRNAs in the Cisplatin- and Radio-Resistance of Cervical Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
Cervical Cancer Treatments and Cisplatin Resistance
2. Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Cisplatin Resistance: The Role of microRNAs
2.1. Up-Regulated miRNAs Determine Resistance to Cisplatin in Cervical Cancer
2.2. The Downregulation of Cellular miRNAs Promotes Cisplatin Resistance in Cervical Cancer
2.3. miRNAs Enhancing the Sensitivity to Cisplatin
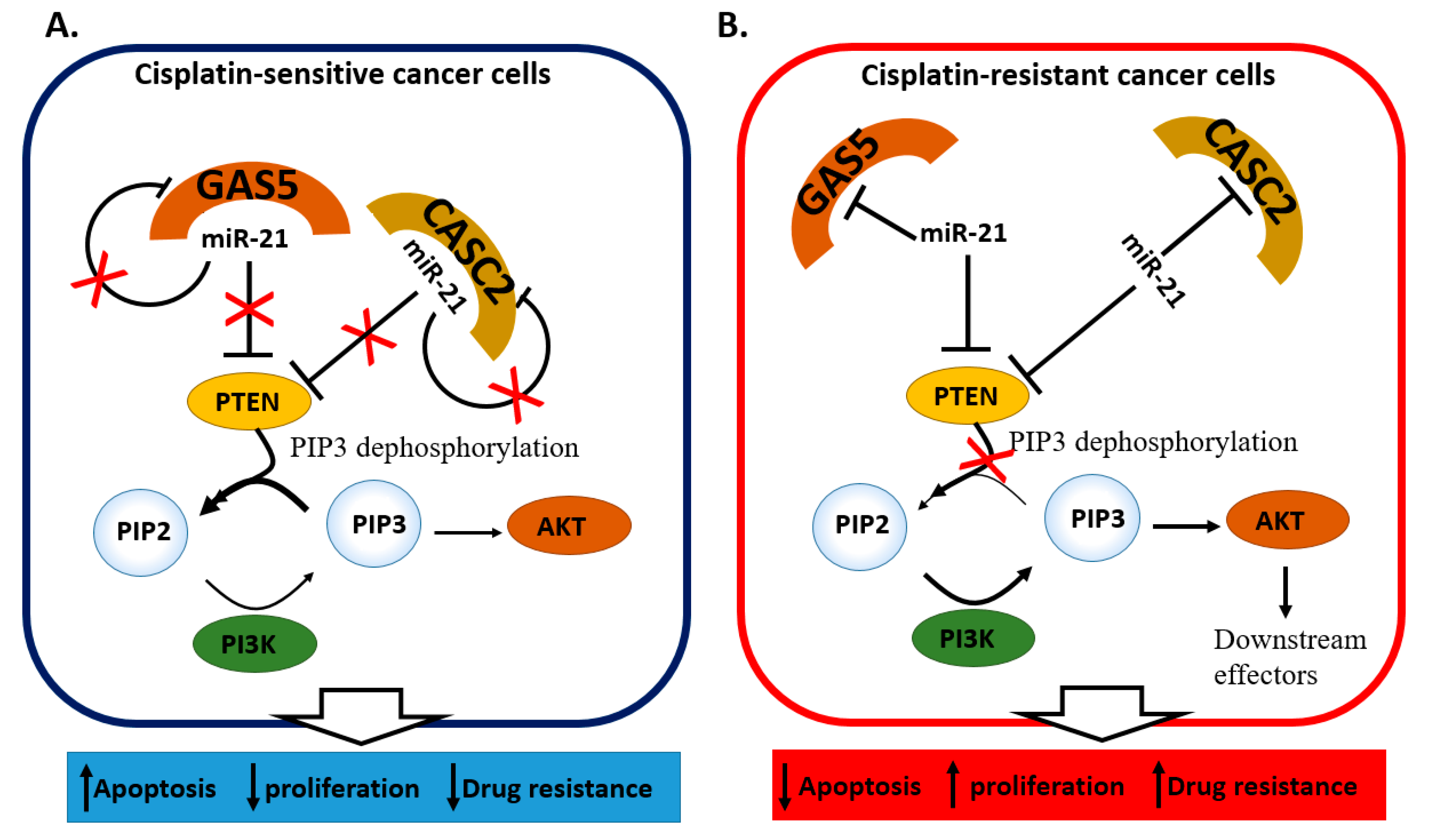
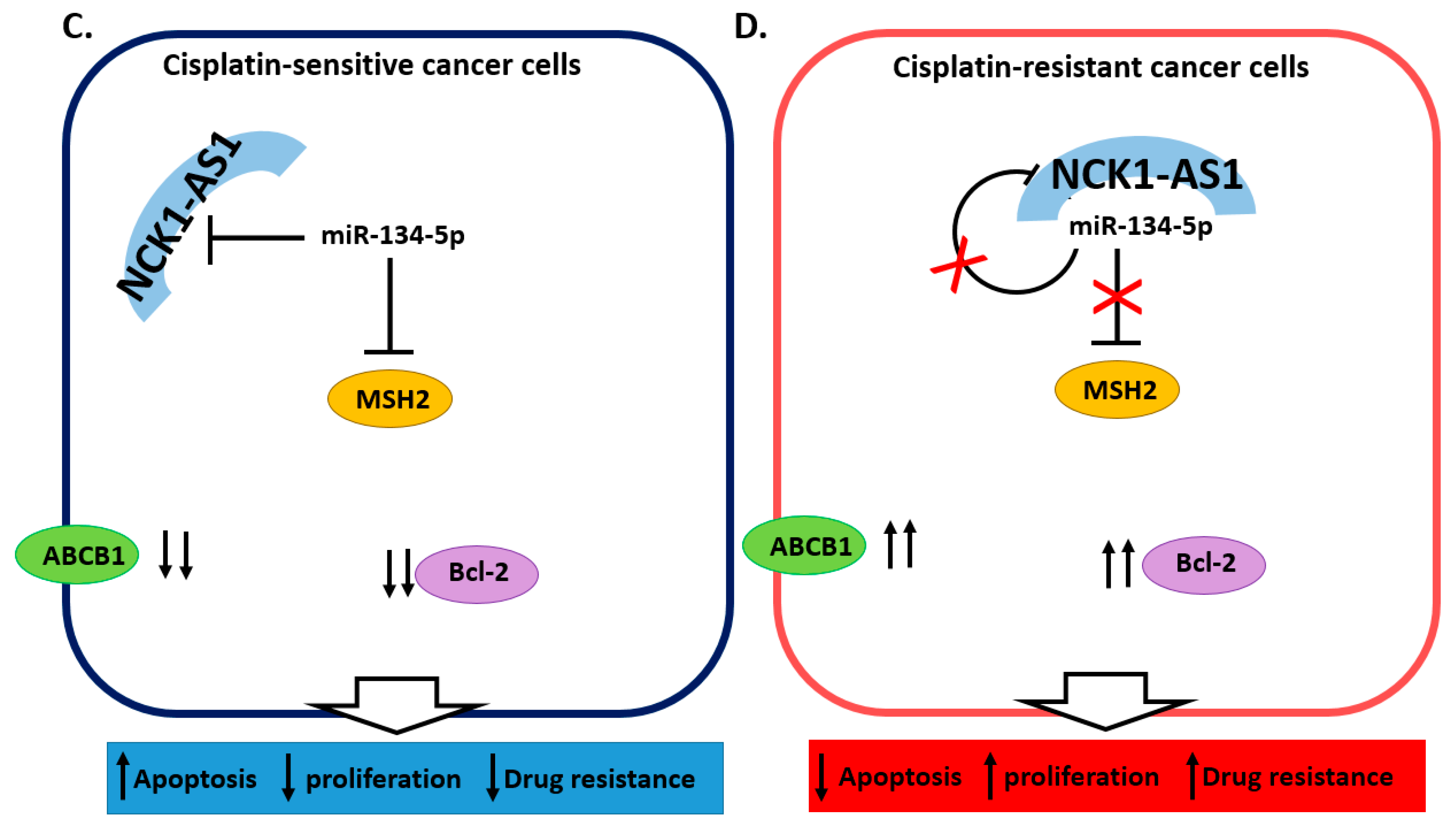
2.4. miRNA and lncRNA Regulatory Loops Determine Cisplatin Resistance in Cervical Cancer Cells
2.5. miRNAs Contributing to Radioresistance in Cervical Cancer
2.6. miRNAs Associated with the Response to Chemoradiotherapy
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods. Int. J. Cancer 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghardt, E.; Ostör, A.G. Site and Origin of Squamous Cervical Cancer: A Histomorphologic Study. Obstet. Gynecol. 1983, 62, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.; Sherman, M.E.; Hildesheim, A.; Lacey, J.V.; Devesa, S. Cervical Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma Incidence Trends among White Women and Black Women in the United States for 1976–2000. Cancer 2004, 100, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostör, A.G. Natural History of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia: A Critical Review. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 1993, 12, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, E.J.; Einstein, M.H.; Franceschi, S.; Kitchener, H.C. Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Cancer. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2013, 382, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walboomers, J.M.; Jacobs, M.V.; Manos, M.M.; Bosch, F.X.; Kummer, J.A.; Shah, K.V.; Snijders, P.J.; Peto, J.; Meijer, C.J.; Muñoz, N. Human Papillomavirus Is a Necessary Cause of Invasive Cervical Cancer Worldwide. J. Pathol. 1999, 189, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Rylander, E.; Larsson, B.; Strand, A.; Silfversvärd, C.; Wilander, E. The Role of Human Papillomavirus in Cervical Adenocarcinoma Carcinogenesis. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 1990 2001, 37, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.-J.; Greer, B.E.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Apte, S.M.; Campos, S.M.; Cho, K.R.; Chu, C.; Cohn, D.; Crispens, M.A.; Dorigo, O.; et al. Cervical Cancer, Version 2.2015. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 2015, 13, 395–404, quiz 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landoni, F.; Maneo, A.; Colombo, A.; Placa, F.; Milani, R.; Perego, P.; Favini, G.; Ferri, L.; Mangioni, C. Randomised Study of Radical Surgery versus Radiotherapy for Stage Ib-IIa Cervical Cancer. Lancet Lond. Engl. 1997, 350, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waggoner, S.E. Cervical Cancer. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2003, 361, 2217–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eifel, P.J.; Winter, K.; Morris, M.; Levenback, C.; Grigsby, P.W.; Cooper, J.; Rotman, M.; Gershenson, D.; Mutch, D.G. Pelvic Irradiation with Concurrent Chemotherapy versus Pelvic and Para-Aortic Irradiation for High-Risk Cervical Cancer: An Update of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Trial (RTOG) 90-01. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffney, D.K.; Du Bois, A.; Narayan, K.; Reed, N.; Toita, T.; Pignata, S.; Blake, P.; Portelance, L.; Sadoyze, A.; Pötter, R.; et al. Practice Patterns of Radiotherapy in Cervical Cancer among Member Groups of the Gynecologic Cancer Intergroup (GCIG). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, H.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhu, X. Drug Design, Development and Therapy Dovepress Molecular Mechanisms of Cisplatin Resistance in Cervical Cancer. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Shen, J.; Li, X.; Huang, K.; Yang, R.; Wu, L.; Chen, Z.; Jia, Y.; et al. Matched-Case Comparison of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with FIGO Stage IB1-IIB Cervical Cancer to Establish Selection Criteria. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 2353–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thigpen, T.; Shingleton, H.; Homesley, H.; Lagasse, L.; Blessing, J. Cis-Platinum in Treatment of Advanced or Recurrent Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix: A Phase II Study of the Gynecologic Oncology Group. Cancer 1981, 48, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.G.; Bundy, B.N.; Watkins, E.B.; Thigpen, J.T.; Deppe, G.; Maiman, M.A.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L.; Insalaco, S. Concurrent Cisplatin-Based Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy for Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomi, P.; Blessing, J.A.; Stehman, F.B.; DiSaia, P.J.; Walton, L.; Major, F.J. Randomized Trial of Three Cisplatin Dose Schedules in Squamous-Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix: A Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 1985, 3, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thigpen, J.T.; Blessing, J.A.; DiSaia, P.J.; Fowler, W.C.; Hatch, K.D. A Randomized Comparison of a Rapid versus Prolonged (24 Hr) Infusion of Cisplatin in Therapy of Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 1989, 32, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Ochiai, K.; Lim, S.; Aoki, D.; Kamiura, S.; Lin, H.; Katsumata, N.; Cha, S.-D.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, B.-G.; et al. Phase III Study of Cisplatin with or without S-1 in Patients with Stage IVB, Recurrent, or Persistent Cervical Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.H.; Tian, C.; Monk, B.J.; Long, H.J.; Omura, G.A.; Bloss, J.D. Prognostic Factors for Response to Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in Advanced Cervical Carcinoma: A Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 116, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, K.W.; Lippard, S.J.; Vassiliades, G.A.; Bauer, W.R. Metallointercalation Reagents. 2-Hydroxyethanethiolato(2,2′,2″-Terpyridine)-Platinum(II) Monocation Binds Strongly to DNA By Intercalation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3839–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makovec, T. Cisplatin and Beyond: Molecular Mechanisms of Action and Drug Resistance Development in Cancer Chemotherapy. Radiol. Oncol. 2019, 53, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The First Metal Based Anticancer Drug. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S. Tumour Stem Cells and Drug Resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Zheng, P.-S. High Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Activity Identifies Cancer Stem Cells in Human Cervical Cancer. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 2462–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Guo, L.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Liu, M. MicroRNA-7-5p Promotes Cisplatin Resistance of Cervical Cancer Cells and Modulation of Cellular Energy Homeostasis by Regulating the Expression of the PARP-1 and BCL2 Genes. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2018, 24, 6506–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Sun, F.; Dong, P.; Watari, H.; Yue, J.; Yu, M.; Lan, C.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z. IASPP Induces EMT and Cisplatin Resistance in Human Cervical Cancer through MiR-20a-FBXL5/BTG3 Signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Li, Y. MiR-25-3p Reverses Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition via Targeting Sema4C in Cisplatin-resistance Cervical Cancer Cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Bo, W.; Yourong, F.; Tian, W.; Shixuan, W.; Mingfu, W. Sema4C Mediates EMT Inducing Chemotherapeutic Resistance of MiR-31-3p in Cervical Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-Y.; Liu, Y.-J.; He, Y.; Chen, P. Suppression of Long Noncoding RNA NCK1-AS1 Increases Chemosensitivity to Cisplatin in Cervical Cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 4302–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, J.; Ding, X.; He, M.; Cheng, S.Y. MicroRNA and Cancer. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laengsri, V.; Kerdpin, U.; Plabplueng, C.; Treeratanapiboon, L.; Nuchnoi, P. Cervical Cancer Markers: Epigenetics and MicroRNAs. Lab. Med. 2018, 49, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.C.; Feinbaum, R.L.; Ambros, V. The C. Elegans Heterochronic Gene Lin-4 Encodes Small RNAs with Antisense Complementarity to Lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent Deletions and Down-Regulation of Micro- RNA Genes MiR15 and MiR16 at 13q14 in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Briskin, D.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA in Cancer: New Hopes for Antineoplastic Chemotherapy. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 117, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.O.; Peixoto da Silva, S.; Costa, N.R.; Gil da Costa, R.M.; Medeiros, R. The Role of MicroRNAs in the Metastatic Process of High-Risk HPV-Induced Cancers. Cancers 2018, 10, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Du, L.; Liu, D.; Qian, L.; Hu, M.; Yu, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Chen, C.; Guo, L.; et al. Glucocorticoid Regulation of a Novel HPV–E6–P53–MiR-145 Pathway Modulates Invasion and Therapy Resistance of Cervical Cancer Cells. J. Pathol. 2012, 228, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, J.T.; Welker, Á.; Győrffy, B. MiRNA Expression Signatures of Therapy Response in Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancers 2020, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Ma, F.; Hu, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Hou, T.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. SOX9/MiR-130a/CTR1 Axis Modulates DDP-Resistance of Cervical Cancer Cell. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Xu, B.; Yang, H.; Xue, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Ying, X.; Dai, Z. MicroRNA-218 Regulates the Chemo-Sensitivity of Cervical Cancer Cells through Targeting Survivin. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 6511–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Su, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, T. MiR-144 Reverses Cisplatin Resistance in Cervical Cancer via Targeting LHX2. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 15018–15026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Shi, M. MiR-181a Promotes Apoptosis and Reduces Cisplatin Resistance by Inhibiting Osteopontin in Cervical Cancer Cells. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2019, 34, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wu, X.-L.; Wu, K.-H.; Zhang, R.; Ju, L.-L.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Xue, S.-L.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Yang, Y.-F.; et al. MicroRNA-497 Regulates Cisplatin Chemosensitivity of Cervical Cancer by Targeting Transketolase. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2690–2699. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Mi, Y.; Jin, H.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Han, L.; Huang, T.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; et al. MicroRNA-499a Promotes the Progression and Chemoresistance of Cervical Cancer Cells by Targeting SOX6. Apoptosis 2020, 25, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, G. MiR-1284 Enhances Sensitivity of Cervical Cancer Cells to Cisplatin via Downregulating HMGB1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. MiR-214 Reduces Cell Survival and Enhances Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity via down-Regulation of Bcl2l2 in Cervical Cancer Cells. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Cui, H.; Yu, H.; Ji, Q.; Kang, L.; Han, B.; Wang, J.; Dong, Q.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z.; et al. MiR-125a Promotes Paclitaxel Sensitivity in Cervical Cancer through Altering STAT3 Expression. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; Gao, Y.; Li, L. MiR-23b Controls ALDH1A1 Expression in Cervical Cancer Stem Cells. BMC Cancer 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Xu, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, N.; Yin, Q.; Li, J.; Sheng, X. Long Noncoding RNA GAS5, Which Acts as a Tumor Suppressor via MicroRNA 21, Regulates Cisplatin Resistance Expression in Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2017, 27, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zou, W.; Hu, C.; Li, G.; Zhou, S.; He, Y.; Ma, F.; Deng, C.; Sun, L. Modulation of CASC2/MiR-21/PTEN Pathway Sensitizes Cervical Cancer to Cisplatin. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 623–624, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, C.A.; Blair, B.G.; Safaei, R.; Howell, S.B. The Role of the Mammalian Copper Transporter 1 in the Cellular Accumulation of Platinum-Based Drugs. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, G.; Hu, C.; Zou, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L. Nuclear Factor-ΚB-Dependent MicroRNA-130a Upregulation Promotes Cervical Cancer Cell Growth by Targeting Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 598, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Dong, M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Shi, Y. MiR-499a-5p Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, Migration, and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition, and Enhances Radiosensitivity of Cervical Cancer Cells via Targeting EIF4E. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 2913–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Tian, Y.; Li, F.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhai, C.; Han, X.; Zhang, L. Tumor-Suppressing Roles of MiR-214 and MiR-218 in Breast Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3178–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, L.; Hu, Q.; Xia, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Xiong, H.; Gurbani, D.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-218 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Lung Cancer by Targeting IL-6/STAT3 and Negatively Correlates with Poor Prognosis. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X. MiR-218 Functions as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Cervical Cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ping, Z.; Ning, H. MiR-218 Impairs Tumor Growth and Increases Chemo-Sensitivity to Cisplatin in Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16053–16064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Gou, S.; Xiong, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, T. Oncogenicity of LHX2 in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 8163–8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmanov, A.; Hopfer, U.; Marti, P.; Meyer-Schaller, N.; Yilmaz, M.; Christofori, G. LIM-Homeobox Gene 2 Promotes Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Inducing Autocrine and Paracrine PDGF-B Signaling. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Y.; Shang, H. Genome-Wide Analysis of Aberrant Gene Expression and Methylation Profiles Reveals Susceptibility Genes and Underlying Mechanism of Cervical Cancer. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 207, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadasz, Z.; Toubi, E. Semaphorin3A: A Potential Therapeutic Tool in Immune-Mediated Diseases. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2018, 5, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabinejad, M.; Asadi, G.; Ranjbar, S.; Afshar Hezarkhani, L.; Salari, F.; Gorgin Karaji, A.; Rezaiemanesh, A. Semaphorin 4A, 4C, and 4D: Function Comparison in the Autoimmunity, Allergy, and Cancer. Gene 2020, 746, 144637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.-C.; Yang, J.; Liu, D.; Wu, M.-F.; Qiao, L.; Wang, J.-N.; Ma, Q.-F.; Zeng, Z.; Ye, S.-M.; Guo, E.-S.; et al. Tumor-Associated Lymphatic Endothelial Cells Promote Lymphatic Metastasis by Highly Expressing and Secreting SEMA4C. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, N.W.; Yeom, B.W.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.W. Osteopontin Expression Correlates with Invasiveness in Cervical Cancer. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2009, 49, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Hong, S.W.; Oh, Y.J.; Kim, M.A.; Kang, E.S.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.T.; et al. Clinical Significance of Osteopontin Expression in Cervical Cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 134, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xiong, D.; Ye, L.; Yang, H.; Mei, S.; Wu, J.; Chen, S.; Mi, R. SPP1 Inhibition Improves the Cisplatin Chemo-Sensitivity of Cervical Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2019, 83, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotte, J.; Fletcher, N.M.; Awonuga, A.O.; Alexis, M.; Abu-Soud, H.M.; Saed, M.G.; Diamond, M.P.; Saed, G.M. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Development of Cisplatin Resistance in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 21, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-M.; Kim, H.-K.; Shim, W.; Anwar, M.A.; Kwon, J.-W.; Kwon, H.-K.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, H.; Kim, H.M.; Hwang, D.; et al. Mechanism of Cisplatin-Induced Cytotoxicity Is Correlated to Impaired Metabolism Due to Mitochondrial ROS Generation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prejanò, M.; Medina, F.E.; Fernandes, P.A.; Russo, N.; Ramos, M.J.; Marino, T. The Catalytic Mechanism of Human Transketolase. ChemPhysChem 2019, 20, 2881–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, K.C.; Hay, N. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohrenhagen, N.; Voelker, H.U.; Schmidt, M.; Kapp, M.; Krockenberger, M.; Frambach, T.; Dietl, J.; Kammerer, U. Expression of Transketolase-like 1 (TKTL1) and p-Akt Correlates with the Progression of Cervical Neoplasia. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2008, 34, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Livesey, K.M.; Zeh, H.J.; Loze, M.T.; Tang, D. HMGB1: A Novel Beclin 1-Binding Protein Active in Autophagy. Autophagy 2010, 6, 1209–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasinska, I.M.; Silva, I.G.; Sakhnevych, S.S.; Ruegg, L.; Hussain, R.; Siligardi, G.; Fiedler, W.; Wellbrock, J.; Bardelli, M.; Varani, L.; et al. High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) Acts as an “Alarmin” to Promote Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Progression. OncoImmunology 2018, 7, e1438109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wei, Y. Association of HMGB1, BRCA1 and P2 Expressionin Ovarian Cancer and Chemotherapy Sensitivity. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9572–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, L. The Function and Mechanism of HMGB1 in Lung Cancer and Its Potential Therapeutic Implications. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6799–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liang, T.-T. CD59 Receptor Targeted Delivery of MiRNA-1284 and Cisplatin-Loaded Liposomes for Effective Therapeutic Efficacy against Cervical Cancer Cells. AMB Express 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Brassinin Inhibits STAT3 Signaling Pathway through Modulation of PIAS-3 and SOCS-3 Expression and Sensitizes Human Lung Cancer Xenograft in Nude Mice to Paclitaxel. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6386–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Almanza, G.; Ortíz-Sánchez, E.; Rocha-Zavaleta, L.; Rivas-Santiago, C.; Esparza-Ibarra, E.; Olmos, J. Cervical Cancer Stem Cells and Other Leading Factors Associated with Cervical Cancer Development. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3423–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, N.; Baker, S.J. PTEN and the PI3-Kinase Pathway in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, A.; Pandolfi, P.P. The PTEN−PI3K Axis in Cancer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Wong, E.W.T.; Chang, F.; Lehmann, B.; Terrian, D.M.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A.; et al. Roles of the Raf/Mek/Erk Pathway in Cell Growth, Malignant Transformation and Drug Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, M.; Bai, T.; Tsang, B.K. Akt Promotes Cisplatin Resistance in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells through Inhibition of P53 Phosphorylation and Nuclear Function. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.-J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Wu, G.S. Role of the Akt/MTOR Survival Pathway in Cisplatin Resistance in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, Z. Transcriptome Profiling of Cervical Cancer Cells Acquired Resistance to Cisplatin by Deep Sequencing. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2820–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, H.; Okuma, K.; Kawana, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Oda, K.; Yano, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Wakui, R.; Ohtomo, K.; Nakagawa, K. Comparison between Conventional Surgery plus Postoperative Adjuvant Radiotherapy and Concurrent Chemoradiation for FIGO Stage IIB Cervical Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 33, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Cai, M.; Tan, C.; Han, X.; Han, L. LncRNA GAS5 Confers the Radio Sensitivity of Cervical Cancer Cells via Regulating MiR-106b/IER3 Axis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Liang, L.; Yang, J.M.; Huang, X.; Han, D.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zha, R.; He, X.; Wu, X. MiR-181a Confers Resistance of Cervical Cancer to Radiation Therapy through Targeting the pro-Apoptotic PRKCD Gene. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3019–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Suh, D.-S.; Kim, T.-H.; Yeom, J.-H.; Lee, K.; Bae, J. IER3 Is a Crucial Mediator of TAp73β-Induced Apoptosis in Cervical Cancer and Confers Etoposide Sensitivity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayda, M.; Isin, M.; Tambas, M.; Guveli, M.; Meral, R.; Altun, M.; Sahin, D.; Ozkan, G.; Sanli, Y.; Isin, H.; et al. Do Circulating Long Non-Coding RNAs (LncRNAs) (LincRNA-P21, GAS 5, HOTAIR) Predict the Treatment Response in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer Treated with Chemoradiotherapy? Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Huang, J.; Xu, H.; Gong, Z. Over-Expression of MiR-15a-3p Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Cervical Cancer by Targeting Tumor Protein D52. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-F.; Zhang, S.-H.; Li, X.-F.; Cao, L.-Y.; Fu, Z.-Z.; Yu, S.-N. Overexpression of MicroRNA-132 Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Cervical Cancer Cells by down-Regulating Bmi-1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80757–80769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Sun, N.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, S.; Sun, S.; Wang, F.; Li, W. MicroRNA-145 Contributes to Enhancing Radiosensitivity of Cervical Cancer Cells. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Li, X.; Jin, Q.; Yuan, J. MicroRNA-145 Sensitizes Cervical Cancer Cells to Low-Dose Irradiation by Downregulating OCT4 Expression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Fan, G.; Deng, C.; Wu, L. MiR-4429 Sensitized Cervical Cancer Cells to Irradiation by Targeting RAD51. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Jiang, J.; Qiao, Z. Elevation of MicroRNA-512-5p Inhibits MUC1 to Reduce Radioresistance in Cervical Cancer. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 652–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-C.; Li, C.-L.; Cui, J.; Jiao, M.; Wu, T.; Jing, L.; Nan, K.-J. BMI-1, a Promising Therapeutic Target for Human Cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Yang, L. MiR-145 Inhibits Cervical Cancer Progression and Metastasis by Targeting WNT2B by Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 3740–3751. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pedroza-Torres, A.; Fernández-Retana, J.; Peralta-Zaragoza, O.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.; Cantú de Leon, D.; Cerna-Cortés, J.F.; Lopez-Camarillo, C.; Pérez-Plasencia, C. A MicroRNA Expression Signature for Clinical Response in Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 142, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| miRNA | Expression in Cisplatin Res-Cells/Tissues | Cell Type | Target | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-7-5p [26] | Up in resistant cells and tissues | Resistant HeLa and SiHa | PARP-1, BCL2 | Inhibition of apoptosis, reduction in the DNA repair activity, increased autophagy |
| miR-130a [39] | Up in DDP-resistant tissue | Resistant HeLa, CaSki | CTR1 | Proliferation, reduction in cisplatin cellular uptake |
| miR-20a [27] | Up in cancer tissue | HeLa | FBXL5, BTG3 | Enhanced EMT phenotype, and resistance to cisplatin |
| miR-218 [40] | Down in resistant cell | Resistant HeLa and SiHa | Survivin | Increased survival in resistant cells, apoptosis escape mechanisms. |
| miR-144 [41] | Down in resistant cell | Resistant HeLa and SiHa | LHX2 | Cisplatin resistance, reduced apoptosis, increased migration, and invasion. |
| miR-25-3p [28] | Down in resistant cells | Resistant HeLa and CaSki cells | SEMA4C | Decreased sensitivity to cisplatin cells, enhanced EMT phenotype |
| miR-31-3p [29] | Down in tumor tissue | Caski | SEMA4C | Decreased sensitivity to cisplatin, enhanced EMT phenotype |
| miR-181a [42] | Down in resistant cells | Resistant HeLa and CaSki cells | OPN | Decreased sensitivity to cisplatin, enhanced proliferation, and resistance to apoptosis |
| miR-497 [43] | Down in resistant cells | Resistant HeLa and SiHa cells | TKT | Increased NADPH and GHS production. Hampering the ROS-dependent drug cytotoxicity |
| miR-499a-5p [44] | Low in HeLa High in SiHa | HeLa, SiHa | SOX6 | Increased migration, invasion, and resistance to cisplatin |
| miR-1284 [45] | Down in tumor tissue | SiHa | HMGB1 | Decreased sensitivity to cisplatin |
| miR-214 [46] | Down in cancer cells | HeLa and SiHa cells | BCL2L2 | Decreased sensitivity to cisplatin, resistance to apoptosis. |
| miR-125 [47] | Down in cancer cells | HeLa | STAT3 | Increased sensitivity to cisplatin |
| miR-23b [48] | Down in cervical cancer stem cells | HeLa, Caski | ALDH1A1 | Decreased sensitivity to cisplatin |
| miR-21 [49] | Up in DDP-resistant cells and tissue | Resistant SiHa cells | PTEN, GAS5 | Cellular growth and drug resistance through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway |
| miR-21 [50] | Up in DDP-resistant cells and tissue | Resistant HeLa and CaSki cells | PTEN, CASC2 | Cellular growth and drug resistance through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway |
| miR-134-5p [30] | Down in tumor tissue and resistant cells | HeLa | MSH2 | Decreased sensitivity to cisplatin |
| miRNA | Expression in Radio-Resistant Cancer Cell/Tissues | Cell Type | Target | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-106b [86] | Up in resistant cells and tissue | Radio-resistant SiHa and ME180 | IER3 | Increased surviving fraction of a radio-resistant cells |
| miR-181a [87] | Up in resistant cells | Radio-resistant SiHa and ME180 | PRKCD | Inhibition of apoptosis |
| miR-15a-3p [90] | Down in resistant cells and tissues | Radio-resistant HeLa and SiHa | TPD52 | Increased proliferation and reduced apoptosis of cells exposed to the radiation |
| miR-132 [91] | Down in resistant cells and tissues | Radio-resistant HeLa, SiHa, and C33A | BMI-1 | Increased proliferation and reduced apoptosis of cells exposed to the radiation |
| miR-145 [92] | n/a | HeLa, SiHa, and Caski | HLTF | Enhanced radiation-induced cell viability, reduction and apoptosis of cancer cells |
| miR-145 [93] | n/a | Tera cells | n/a | Induced radiosensitivity by reducing cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis |
| miR-499a-5p [53] | Down in cancer tissue and cells, overexpression enhance radiosensitivity of cells | HeLa and CaSki | EIF4E | Increased proliferation, invasion, and cell migration. Apoptosis inhibition |
| miR-4429 [94] | Down in resistant cells and tissues | Radio-resistant HeLa and SiHa | RAD51 | Induce proliferation and DNA damage repair of cancer cells |
| miR-512-5p [95] | Down in resistant cells and tissues | Radio-resistant SiHa and radio-sensitive Me180 | MUC1 | Increase survival of cancer cells and decrease apoptosis |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masadah, R.; Rauf, S.; Pratama, M.Y.; Tiribelli, C.; Pascut, D. The Role of microRNAs in the Cisplatin- and Radio-Resistance of Cervical Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051168
Masadah R, Rauf S, Pratama MY, Tiribelli C, Pascut D. The Role of microRNAs in the Cisplatin- and Radio-Resistance of Cervical Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(5):1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051168
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasadah, Rina, Syahrul Rauf, Muhammad Yogi Pratama, Claudio Tiribelli, and Devis Pascut. 2021. "The Role of microRNAs in the Cisplatin- and Radio-Resistance of Cervical Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 5: 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051168
APA StyleMasadah, R., Rauf, S., Pratama, M. Y., Tiribelli, C., & Pascut, D. (2021). The Role of microRNAs in the Cisplatin- and Radio-Resistance of Cervical Cancer. Cancers, 13(5), 1168. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051168






