Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Status and Breast Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
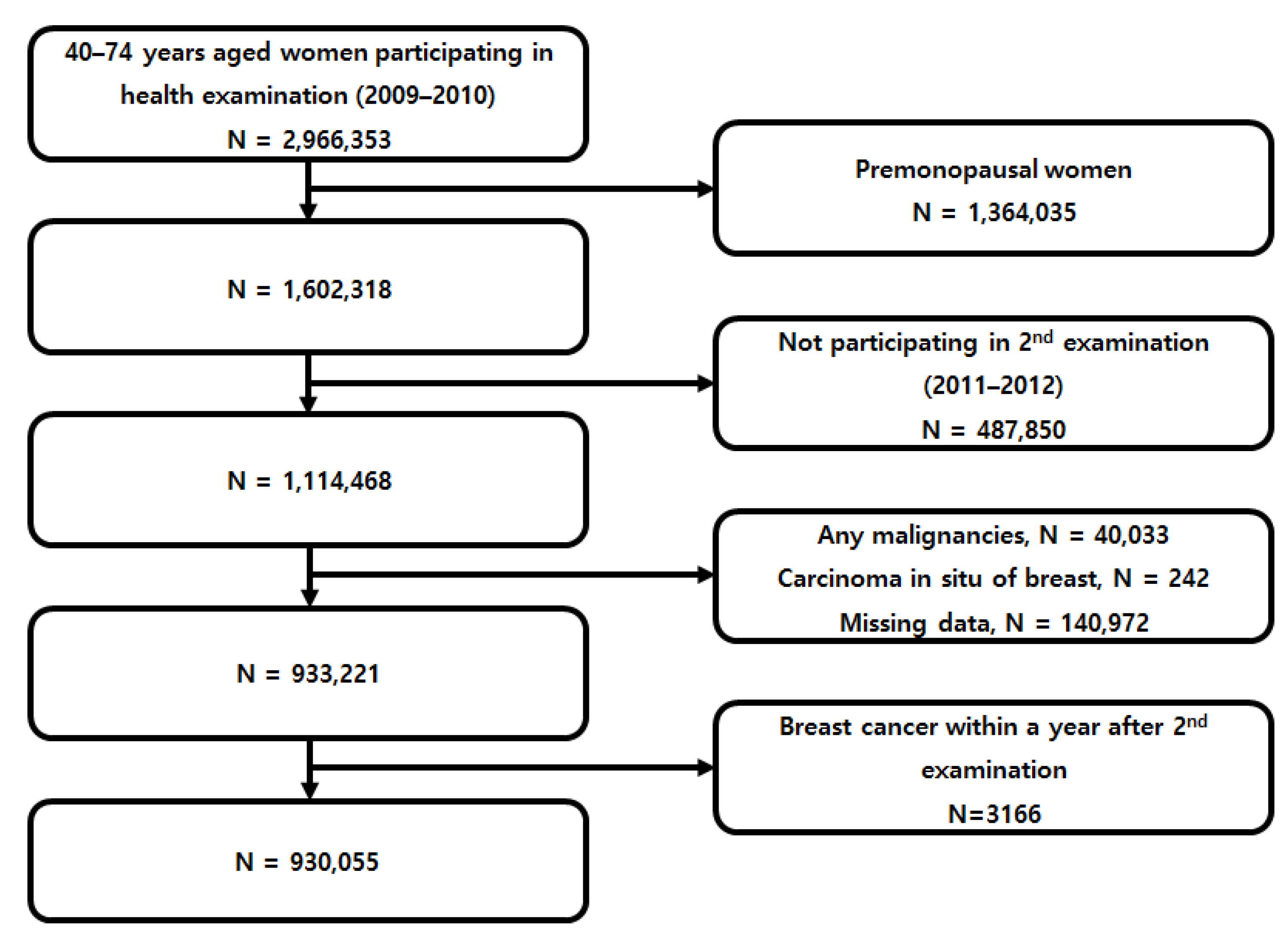
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Independent Variables
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Outcome Variable and Follow-Up
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. The Risk of BC and Basal MetS
3.3. The Risk of BC based on Changes of MetS Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Lippi, G. Current cancer epidemiology. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A. Breast cancer statistics: Recent trends. In Breast Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bettio, M.; Gavin, A.; Visser, O.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 103, 356–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Won, Y.-J.; Park, Y.R.; Jung, K.-W.; Kong, H.-J.; Lee, E.S. Cancer Statistics in Korea: Incidence, Mortality, Survival, and Prevalence in 2017. Cancer Res. Treat. Off. J. Korean Cancer Assoc. 2020, 52, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.A.; Kim, T.H.; Park, S.; Choy, Y.S.; Ju, Y.J.; Park, E.-C. Projection of Breast Cancer Burden due to Reproductive/Lifestyle Changes in Korean Women (2013–2030) Using an Age-Period-Cohort Model. Cancer Res. Treat. Off. J. Korean Cancer Assoc. 2018, 50, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauner, D.; Hauner, H. Metabolic Syndrome and Breast Cancer: Is There a Link? Breast Care 2014, 9, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabat, G.C.; Kim, M.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Khandekar, J.; Ko, M.G.; McTiernan, A.; Neuhouser, M.L.; Parker, D.R.; Shikany, J.M.; Stefanick, M.L. A longitudinal study of the metabolic syndrome and risk of postmenopausal breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2009, 18, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnoli, C.; Berrino, F.; Abagnato, C.A.; Muti, P.; Panico, S.; Crosignani, P.; Krogh, V. Metabolic syndrome and postmenopausal breast cancer in the ORDET cohort: A nested case–control study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 20, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Autelitano, M.; Bisanti, L. Metabolic syndrome and cancer risk. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaki, Y.; Taniguchi, S.-i.; Tahara, A.; Okamoto, M.; Kishimoto, T. Metabolic syndrome and incidence of liver and breast cancers in Japan. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012, 36, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, K.; Chiodini, P.; Capuano, A.; Bellastella, G.; Maiorino, M.I.; Rafaniello, C.; Giugliano, D. Metabolic syndrome and postmenopausal breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Menopause 2013, 20, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, R.; Kelley, G.A.; Hartley, T.A.; Rockett, I.R.H. Metabolic Syndrome Is Associated with Increased Breast Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2014, 2014, 189384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, T.; Li, P.; Wang, T.; Zeng, C.; Yang, M.; Li, G.; Han, J.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R. Association Between Metabolic Syndrome and Breast Cancer Risk: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Follow-Up Studies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, C.; Jones, P.; Nelson, K.; O’Brian Smith, E.; Ballantyne, C. Impact of weight loss on the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2002, 4, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakka, T.A.; Laaksonen, D.E. Physical activity in prevention and treatment of the metabolic syndrome. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2007, 32, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard-Barbash, R.; Hunsberger, S.; Alciati, M.H.; Blair, S.N.; Goodwin, P.J.; McTiernan, A.; Wing, R.; Schatzkin, A. Physical activity, weight control, and breast cancer risk and survival: Clinical trial rationale and design considerations. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 630–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cho, J.; Shin, D.W.; Lee, S.P.; Hwang, S.S.; Oh, J.; Yang, H.K.; Hwang, S.H.; Son, K.Y.; Chun, S.H.; et al. Association of cardiovascular health screening with mortality, clinical outcomes, and health care cost: A nationwide cohort study. Prev. Med. 2015, 70, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Yoon, M.; Song, S.H.; Suh, M.; Park, B.; Jung, K.W.; Jun, J.K. Effect of mammography screening on stage at breast cancer diagnosis: Results from the Korea National Cancer Screening Program. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Cho, B.; Guallar, E. Korean national health insurance database. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheol Seong, S.; Kim, Y.Y.; Khang, Y.H.; Heon Park, J.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, H.; Do, C.H.; Song, J.S.; Hyon Bang, J.; Ha, S.; et al. Data Resource Profile: The National Health Information Database of the National Health Insurance Service in South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 799–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Shin, D.W.; Han, K.; Kim, D.; Yoo, J.E.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Son, K.Y.; Cho, B.; Kim, M.J. Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Status and Risk of Dementia. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Han, K.; Shin, D.W.; Yeo, Y.; Chang, J.W.; Yoo, J.E.; Jeong, S.-M.; Lee, S.-K.; Ryu, J.M.; Park, Y.-M. Obesity and breast cancer risk for pre- and postmenopausal women among over 6 million Korean women. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avgerinos, K.I.; Spyrou, N.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Dalamaga, M. Obesity and cancer risk: Emerging biological mechanisms and perspectives. Metabolism 2019, 92, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.-C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; national heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; world heart federation; international atherosclerosis society; and international association for the study of obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Lee, W.-Y.; Kang, J.-H.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, B.T.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, E.M.; Suh, S.-H.; Shin, H.J.; Lee, K.R. 2014 clinical practice guidelines for overweight and obesity in Korea. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 29, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W.; Chang, J.W.; Han, K.-D.; Jeon, K.H.; Yoo, J.E.; Cho, I.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Hong, J.Y. Obesity Has a Stronger Relationship with Colorectal Cancer in Postmenopausal Women Than Premenopausal Women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K.H.; Shin, D.W.; Han, K.; Kim, D.; Yoo, J.E.; Jeong, S.-M.; Ho Cho, J. Female reproductive factors and the risk of lung cancer in postmenopausal women: A nationwide cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandekar, M.J.; Cohen, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Molecular mechanisms of cancer development in obesity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.-T.; Han, K.-D.; Oh, S.; Koo, B.K.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.; Seo, H.J.; Jung, J.; Kim, B.H.; Hur, H. Influence of Metabolic Syndrome on Risk of Breast Cancer: A Study Analyzing Nationwide Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2020, 29, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-H.; Li, R.-H.; Huang, S.-L.; Sia, H.-K.; Chen, Y.-L.; Tang, F.-C. Lifestyle factors and metabolic syndrome among workers: The role of interactions between smoking and alcohol to nutrition and exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 15967–15978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-W.; Park, B.-J.; Kang, H.-T.; Lee, Y.-J. Alcohol-drinking patterns and metabolic syndrome risk: The 2007 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Alcohol 2011, 45, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Yoon, Y.S.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, W.K.; Park, C.; Lee, S.; Jeong, E.-K.; Yoo, T. Association between cigarette smoking and metabolic syndrome: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2064–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlebowski, R.T. Nutrition and physical activity influence on breast cancer incidence and outcome. Breast 2013, 22, S30–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petracci, E.; Decarli, A.; Schairer, C.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Pee, D.; Masala, G.; Palli, D.; Gail, M.H. Risk factor modification and projections of absolute breast cancer risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudet, M.M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Sun, J.; Diver, W.R.; Hannan, L.M.; Thun, M.J. Active smoking and breast cancer risk: Original cohort data and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, G.K.; Pirie, K.; Green, J.; Bull, D.; Beral, V.; Collaborators, M.W.S. Comparison of the effects of genetic and environmental risk factors on in situ and invasive ductal breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peila, R.; Arthur, R.; Rohan, T.E. Risk factors for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast in the UK Biobank cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2020, 64, 101648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Breast Cancer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | p-Value | |
| Number of participants | 6844 | 923,211 | |
| Age | 59.0 ± 6.5 | 60.3 ± 7.0 | <0.0001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 3.1 | 24.2 ± 3.1 | <0.0001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 80.2 ± 8.1 | 79.9 ± 8.5 | 0.0199 |
| Smoking history | 0.0292 | ||
| Never | 6606 (96.52) | 893,906 (96.83) | |
| Former | 87 (1.27) | 8834 (0.96) | |
| Current | 151 (2.21) | 20,471 (2.22) | |
| Alcohol consumption | 0.0852 | ||
| None | 5910 (86.35) | 805,477 (87.25) | |
| Mild-to-moderate | 900 (13.15) | 113,300 (12.27) | |
| Heavy | 34 (0.50) | 4434 (0.48) | |
| Physical activity | 1419 (20.73) | 179,330 (19.42) | 0.0064 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Hypertension | 3053 (44.61) | 408,484 (44.25) | 0.5476 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 852 (12.45) | 112,937 (12.23) | 0.5873 |
| Dyslipidemia | 2463 (35.99) | 320,072 (34.67) | 0.0224 |
| Age at menarche | 16.1 ± 1.8 | 16.4 ± 1.8 | <0.0001 |
| Age at menopause | 50.6 ± 3.8 | 50.1 ± 3.9 | <0.0001 |
| HRT | <0.0001 | ||
| Never | 5076 (74.17) | 730,674 (79.14) | |
| Less than 2 years | 758 (11.08) | 92,850 (10.06) | |
| 2–5 years | 392 (5.73) | 38,692 (4.19) | |
| More than 5 years | 383 (5.60) | 29,688 (3.22) | |
| Do not know | 235 (3.43) | 31,307 (3.39) | |
| Bottom 3% income | 1605 (23.45) | 215,670 (23.36) | 0.8603 |
| Blood pressure (mmHg) | |||
| Systolic | 124.9 ± 15.9 | 125.0 ± 15.9 | 0.4753 |
| Diastolic | 76.6 ± 10.1 | 76.7 ± 10.1 | 0.4183 |
| Laboratory findings (mg/dL) | |||
| Glucose | 99.1 ± 22.8 | 99.1 ± 23.0 | 0.8546 |
| Total cholesterol | 208.2 ± 44.8 | 208.4 ± 43.3 | 0.737 |
| HDL cholesterol | 58.2 ± 37.4 | 57.9 ± 35.3 | 0.5449 |
| Triglycerides * | 113.3 (111.9, 114.7) | 114.4 (114.3, 114.6) | 0.0115 |
| Number of Participants | Number of Breast Cancer Cases | Person-Years (P-Y) | Rate (Per 1000 P-Y) | Model 1 * | Model 2 † | Model 3 ‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic syndrome § | |||||||
| No | 596,264 | 4759 | 3,815,960.9 | 1.25 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| Yes | 333,791 | 2636 | 2,130,328.8 | 1.24 | 1.10 (1.04, 1.15) | 1.10 (1.05, 1.15) | 1.11 (1.06, 1.17) |
| Individual components § | |||||||
| Waist circumference | |||||||
| No | 677,776 | 5348 | 4,334,934.3 | 1.23 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| Yes | 252,279 | 2047 | 1,611,355.4 | 1.27 | 1.12 (1.06, 1.18) | 1.12 (1.07, 1.18) | 1.15 (1.09, 1.21) |
| Fasting glucose | |||||||
| No | 596,665 | 4730 | 3,821,633.4 | 1.24 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| Yes | 333,390 | 2665 | 2,124,656.3 | 1.25 | 1.06 (1.01, 1.12) | 1.06 (1.02, 1.12) | 1.07 (1.02, 1.13) |
| Blood pressure | |||||||
| No | 393,351 | 3131 | 2,520,229.0 | 1.24 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| Yes | 536,704 | 4264 | 3,426,060.7 | 1.24 | 1.13 (1.08, 1.18) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.18) | 1.13 (1.08, 1.19) |
| Triglycerides | |||||||
| No | 582,539 | 4612 | 3,724,540.1 | 1.24 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| Yes | 347,516 | 2783 | 2,221,749.6 | 1.25 | 1.07 (1.02, 1.12) | 1.07 (1.02, 1.12) | 1.08 (1.03, 1.13) |
| HDL cholesterol | |||||||
| No | 530,770 | 4206 | 3,393,404.4 | 1.24 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| Yes | 399,285 | 3189 | 2,552,885.2 | 1.25 | 1.06 (1.01, 1.11) | 1.06 (1.01, 1.11) | 1.06 (1.01, 1.11) |
| Number of components | |||||||
| 0 | 144,848 | 1160 | 927,582.2 | 1.25 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| 1 | 226,443 | 1776 | 1,449,657.9 | 1.23 | 1.05 (0.98, 1.13) | 1.05 (0.98, 1.13) | 1.05 (0.97, 1.13) |
| 2 | 224,973 | 1823 | 1,438,720.7 | 1.27 | 1.14 (1.06, 1.23) | 1.14 (1.06, 1.23) | 1.15 (1.07, 1.24) |
| 3 | 182,378 | 1373 | 1,165,700.3 | 1.18 | 1.10 (1.02, 1.20) | 1.11 (1.02, 1.20) | 1.12 (1.03, 1.21) |
| 4 | 111,414 | 908 | 710,635.6 | 1.28 | 1.23 (1.13, 1.35) | 1.23 (1.13, 1.35) | 1.25 (1.15, 1.37) |
| 5 | 39,999 | 355 | 253,992.9 | 1.40 | 1.39 (1.23, 1.56) | 1.39 (1.23, 1.57) | 1.43 (1.26, 1.61) |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| Number of Participants | Number of Breast Cancer Cases | Duration | Rate | Model 1 * | Model 2 † | Model 3 ‡ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Syndrome Status § | ||||||||
| No MetS–No MetS | 431,790 | 3429 | 2,762,581.6 | 1.24 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | |
| No MetS–MetS | 164,474 | 1330 | 1,053,379.3 | 1.26 | 1.11 (1.04, 1.18) | 1.11 (1.04, 1.18) | 1.11 (1.04, 1.19) | |
| MetS–No MetS | 79,687 | 595 | 509,303.6 | 1.17 | 1.03 (0.94,1.12) | 1.03 (0.94,1.12) | 1.05 (0.96, 1.14) | |
| MetS–MetS | 254,104 | 2041 | 1,621,025.2 | 1.26 | 1.17 (1.10, 1.23) ** | 1.17 (1.10, 1.24) ** | 1.18 (1.12, 1.25) ** | |
| Metabolic Syndrome Components § | ||||||||
| Waist Circumference (≥85 cm) | No–No | 588,701 | 4620 | 3,764,454.1 | 1.23 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| No–Yes | 89,075 | 728 | 570,480.1 | 1.28 | 1.11 (1.03, 1.20) | 1.11 (1.03, 1.20) | 1.13 (1.04, 1.22) | |
| Yes–No | 86,298 | 645 | 551,433.3 | 1.17 | 1.03 (0.95, 1.12) | 1.04 (0.95, 1.13) | 1.06 (0.97, 1.15) | |
| Yes–Yes | 165,981 | 1402 | 1,059,922.1 | 1.32 | 1.19 (1.12, 1.27) ** | 1.20 (1.13, 1.27) ** | 1.23 (1.16, 1.31) ** | |
| Fasting Glucose (≥100 mg/dL) | No–No | 474,211 | 3782 | 3,038,048.5 | 1.24 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| No–Yes | 122,454 | 948 | 783,584.9 | 1.21 | 1.00 (0.94, 1.08) | 1.01 (0.94, 1.08) | 1.02 (0.95, 1.09) | |
| Yes–No | 110,767 | 813 | 708,623.8 | 1.15 | 0.94 (0.88, 1.02) | 0.95 (0.88,1.02) | 0.95 (0.89, 1.03) | |
| Yes–Yes | 222,623 | 1852 | 1,416,032.5 | 1.31 | 1.13 (1.07, 1.20) ** | 1.13 (1.07, 1.20) ** | 1.14 (1.08, 1.21) ** | |
| Blood Pressure (Systolic ≥130 or diastolic ≥85 mmHg) | No–No | 260,587 | 2179 | 1,669,554.1 | 1.31 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| No–Yes | 132,764 | 952 | 850,674.9 | 1.12 | 0.93 (0.86, 1.00) | 0.93 (0.86, 1.00) | 0.94 (0.87, 1.02) | |
| Yes–No | 73,625 | 571 | 471718.6 | 1.21 | 0.99 (0.90, 1.09) | 0.99 (0.91, 1.09) | 1.00 (0.92, 1.10) | |
| Yes–Yes | 463,079 | 3693 | 2,954,342.1 | 1.25 | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) ** | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) ** | 1.13 (1.07, 1.20) ** | |
| Triglycerides (≥150 mg/dL) | No–No | 398,941 | 3146 | 2,548,932.5 | 1.23 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| No–Yes | 183,598 | 1466 | 1,175,607.6 | 1.25 | 1.07 (1.00, 1.14) | 1.07 (1.00, 1.14) | 1.07 (1.00, 1.14) | |
| Yes–No | 91,795 | 700 | 586,557.3 | 1.19 | 1.01 (0.93, 1.10) | 1.01 (0.93, 1.10) | 1.03 (0.95, 1.12) | |
| Yes–Yes | 255,721 | 2083 | 1,635,192.3 | 1.27 | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) ** | 1.12 (1.06, 1.19) ** | 1.13 (1.07, 1.20) ** | |
| HDL cholesterol (<50 mg/dL) | No–No | 328,992 | 2619 | 2,101,628.0 | 1.25 | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) | 1 (Ref.) |
| No–Yes | 201,778 | 1,587 | 1,291,776.4 | 1.23 | 1.05 (0.98, 1.12) | 1.05 (0.98, 1.12) | 1.04 (0.98, 1.11) | |
| Yes–No | 108,086 | 828 | 691,023.8 | 1.20 | 1.01 (0.93, 1.09) | 1.01 (0.93, 1.09) | 1.01 (0.94, 1.10) | |
| Yes–Yes | 291,199 | 2361 | 1,861,861.5 | 1.27 | 1.11 (1.05, 1.17) ** | 1.11 (1.05, 1.17) ** | 1.10 (1.04, 1.16) ** | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, I.Y.; Chun, S.; Shin, D.W.; Han, K.; Jeon, K.H.; Yu, J.; Chae, B.J.; Suh, M.; Park, Y.-M. Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Status and Breast Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051177
Choi IY, Chun S, Shin DW, Han K, Jeon KH, Yu J, Chae BJ, Suh M, Park Y-M. Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Status and Breast Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Cancers. 2021; 13(5):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051177
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, In Young, Sohyun Chun, Dong Wook Shin, Kyungdo Han, Keun Hye Jeon, Jonghan Yu, Byung Joo Chae, Mina Suh, and Yong-Moon Park. 2021. "Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Status and Breast Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study" Cancers 13, no. 5: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051177
APA StyleChoi, I. Y., Chun, S., Shin, D. W., Han, K., Jeon, K. H., Yu, J., Chae, B. J., Suh, M., & Park, Y.-M. (2021). Changes in Metabolic Syndrome Status and Breast Cancer Risk: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Cancers, 13(5), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051177





