Simple Summary
Poorly immunogenic head and neck squamous carcinomas (HNSCC) remain difficult to treat due to poor response rates to immunotherapy. Inhibition of the PI3K catalytic subunit p110γ, which is expressed in leukocytes and some HNSCCs, has shown promise in treating HNSCC; with clinical trials underway to gauge its effectiveness. However, the effect of PI3K p110γ inhibition on the host immune system in poorly immunogenic HNSCC has not been fully described. In this study, our group characterized the immune response to poorly immunogenic HNSCC in the absence of PI3K p110γ using an orthotopic mouse model with the MOC2 cell line. We found that mice lacking p110γ did not demonstrate significantly different tumor growth or metastasis, though we observed substantial elevation in both anti-tumor and immunosuppressive activity at the primary tumor site. Our results indicate that PI3K p110γ inhibition may potentially enhance anti-tumor immunity against poorly immunogenic HNSCC if administered with checkpoint inhibitors.
Abstract
HNSCC is the sixth most common cancer, with around 650,000 new cases yearly. Gain of function mutations in the PI3K pathway are common in HNSCC, and inhibition of the PI3K p110γ subunit has shown promise in HNSCC treatment. However, given that PI3K p110γ plays an important role in myeloid and lymphoid immune cell function, it is essential to understand how PI3K p110γ inhibition affects the anti-tumor immune response independent of tumor cells. To elucidate PI3K p110γ function in HNSCC, we employed an orthotopic mouse model using poorly immunogenic and aggressive cell line MOC2 on Pik3cg−/− mice. We observed that wild-type and Pik3cg−/− mice displayed similar rates of HNSCC tumor growth and metastasis after 20 days following tumor injection. T-cell infiltration and intrinsic T-cell responses to MOC2 oral tumors were comparable between wild-type and Pik3cg−/− mice. Interestingly, the immune response of tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice was marked by increased anti-tumor cytotoxic molecules (IFN-γ, IL-17)) by T-cells and immune checkpoint marker (PD-L1, PD-1) expression by myeloid cells and T-cells compared to tumor-bearing wild-type mice. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that inhibition of PI3K p110γ modulates tumor-associated immune cells, which likely potentiates HNSCC treatment when used in combination with selective checkpoint inhibitors.
1. Introduction
HNSCC is the sixth most common form of cancer and the ninth deadliest, with around 650,000 new cases a year and 330,000 deaths attributed to the disease worldwide [1]. Current estimates demonstrate that HNSCC accounts for almost 4% of cancer cases in the United States [2]. Because the genetics of HNSCC are considerably varied across patients, therapies must be tailored to each individual in order to ensure the best medical outcomes [3].
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) has emerged as a potential target for treating patients with HNSCC. There are four classes of PI3K that are categorized based on their protein structure and roles in cell biology, of which Class I PI3Ks are most well defined [4]. Class I PI3Ks are heterodimeric proteins consisting of a regulatory subunit and a catalytic subunit, of which there are four isoforms—p110α, p110β, p110γ, and p110δ [4]. Class I PI3Ks catalyze the phosphorylation of inactive phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to the signal transducer phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) after activation from extracellular signaling compounds such as epithelial growth factor (EGF) in epithelial cells and CD28 in T-cells [5]. Downstream, Akt activation induces cellular changes that ultimately lead to cell growth, activity, and survival [5,6]. PI3K signaling has been shown to be important in a number of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. For example, PI3K p110γ inhibition has been shown to confer a therapeutic anti-inflammatory effect in preclinical and clinical studies of asthma and COPD [7]. In vitro cultures of human HNSCC cells as well as mouse xenograft models indicate that PI3K signaling is linked to cancer radiation resistance, and PI3K inhibition has shown promise in potentiating the cytotoxic and anti-mitotic effects of radiotherapy [8,9]. This is an area that is undergoing active preclinical and clinical investigation [10]. The role of PI3K in resistance to irradiation involves several mechanisms, including elevated DNA damage repair through activation of DNA-protein kinases (DNAPK), and induction of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) dependent gene transcription [11,12].
The mitogenic and anti-apoptotic properties of PI3K activity results in HNSCC cancer cells tumorigenicity [13]. A meta-analytical study showed that 66% of examined clinical HNSCC cases demonstrate an increase in pathway activity due to aberrant expression of key mediators of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway, including downregulation of the repressor PTEN and upregulation in the activity of PI3K catalytic subunits [14]. Notably, whole-exome sequencing in a cohort of HNSCC patients showed that 30.5% of HNSCC tumors contained mutations in the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway, mostly in Pik3ca, Pik3cg, and Pten [15]. These studies associated increased PI3K-Akt-mTOR activity with poor prognosis. Due to the frequency of genetic aberrations that increase activity in the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway, there is a rationale for directly targeting frequently mutated mediators of this pathway to control the progression of HNSCC, including Class I PI3K catalytic subunits [15]. Currently, there are many clinical trials employing PI3K inhibitors as monotherapies against solid tumors, including a phase II clinical trial utilizing the p110γ inhibitor IPI-549 on locally advanced HNSCC [5,16]. However, suboptimal patient response rates have been observed in studies employing PI3K inhibitors as monotherapies on tumors exhibiting gain-of-function in this pathway, necessitating further exploration of their activity and usage [17].
On the other hand, selective PI3K inhibitors, such as IPI-549, have seen success in clinical trials when combined with other therapeutic strategies [18]. Such studies indicate that inhibition of PI3K p110γ in combination with other therapies could enhance anti-tumor immune function. For example, a recent study in a murine melanoma model showed that adoptively transferred CD8+ T-cells treated with IPI-549 exhibit increased cytotoxicity [19]. Further, IPI-549, in conjunction with anti-PD1 therapy, led to a stronger anti-tumor effect than either therapy alone in mouse models of HNSCC, lung, and breast carcinoma [20]. These findings are particularly intriguing because they indicate that PI3K p110γ may serve as a target of host-directed therapies that improve the anti-tumor immune response independent of PI3K p110γ expression by tumor cells.
Despite these encouraging findings, the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway in T cells, mediated through p110γ, has been shown to be critical for their development and functional responses [21,22,23,24]. Because PI3K inhibitors do not discriminate between cancer cells and healthy cells, it stands to reason that the suboptimal response to PI3K inhibition may be due to a deleterious global effect on normal cell functioning. Therefore, targeting PI3K p110γ could lead to undesirable changes in a host’s immune phenotype. For example, it has been shown that in some metastatic breast cancer patients, the use of PI3K inhibitors correlates with depletion of anti-tumor CD8+ T cells and expansion of suppressor cells [25]. Further, dual inhibition of p110γ and p110δ has been shown to abrogate murine CD8+ activity ex-vivo [19], while in-vivo demonstrated limited effect on poorly immunogenic HNSCC in a mouse model, even in conjunction with PD-L1 blockade [26].
At this point, significant gaps remain in the understanding of PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling within the host’s immune cells in the context of HNSCC. While PI3K p110γ inhibitors have shown promise as a host-directed approach to improving the immune response against HNSCC, the global effect of PI3K p110γ inhibition in host immune cells is not well understood. Additionally, a primary factor of resistance to therapeutics targeting the PD-1-PD-L1 axis is low tumor immunogenicity [27]. Previous experiments have not demonstrated whether host-directed PI3K p110γ inhibition confers improved cytotoxic function against poorly immunogenic HNSCC tumors. Filling such gaps is necessary to fine-tune the administration of PI3K p110γ inhibitors against HNSCC, and elucidate the mechanisms that lead to low response rates.
In view of these findings, our group sought to investigate the effect of PI3K p110γ deficiency on host immune responses to poorly immunogenic HNSCC tumors using an orthotopic murine model with Pik3cg+/+ wild-type (WT) mice and Pik3cg−/− mice. To establish HNSCC, we utilized the syngeneic C57BL/6J murine oral cancer cell line (MOC2), which is known to establish tumors with low immunogenicity, high metastatic incidence, and poor responsiveness to checkpoint inhibition [28,29]. MOC2 cells were derived from a tumor in the floor of the mouth of a mouse experimentally induced with an oral carcinogen 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA); and next-generation sequencing of MOC2 cells used in this study demonstrates striking similarities to the aberrant genetic signature of human HNSCC [30]. Further, our orthotopic model used mouse HNSCC cell lines in immunocompetent mice, which possesses distinct advantages for the elucidation of immunological responses to HNSCC both systemically and in the tumor microenvironment. Our results showed that mice deficient in Pik3cg−/− did not display a significant reduction in tumor growth or survival compared to WT mice. However, we discovered remarkable differences in the expression of cytotoxic molecules and immunosuppressive markers that could potentially be exploited in combatting poorly immunogenic HNSCC.
2. Results
2.1. Host PI3K p110γ Inhibition Does Not Significantly Affect Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Mice Injected with MOC2 Oral Cells
To determine the involvement of host Pik3cg in the response against HNSCC, we injected an aggressive murine oral cancer cell line MOC2 into the right buccal mucosa of both WT and Pik3cg−/− C57BL/6 mice. As expected, based on previous studies utilizing this cell line, tumor growth occurred rapidly until mice reached early-removal criteria at 20 days. The rates of tumor growth in WT and Pi3kcg−/− mice assumed a similar trajectory. No difference was observed in tumor size based on caliper volume measurements (Figure 1A,B). This was not entirely surprising, given the rapid and aggressive growth pattern of this orthotopic HNSCC model. Our analysis of tumor weights demonstrated no statistically significant difference between groups, although the weights of tumors of Pi3kcg−/− mice appeared slightly lower than in WT mice (Figure 1C,D). In addition to their high growth rates, MOC2 cells are known to display high rates of lymph node metastasis, which is characteristic of aggressive human HNSCC. We, therefore, performed histological analysis of lymph nodes and tumors of tumor-bearing WT and Pi3kcg−/− mice to visualize tumor cell infiltration and metastatic tumor establishment. We observed similar tumor morphology and rates of lymph node metastasis in tumor-bearing WT and Pi3kcg−/− mice. (Figure 1E). PI3Kγ immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining showed mild positivity in tumors of WT and Pi3kcg−/− mice, while draining lymph nodes of tumor-bearing WT and Pi3kcg−/− mice showed moderate and very light positivity, respectively (Figure 1E). Taken together, our phenotypic and histological analyses of HNSCC tumors in WT and Pi3kcg−/− mice demonstrate that host PI3K p110γ inhibition did not have a significant effect on tumor growth and metastasis in the orthotopic MOC2 mouse model of poorly immunogenic HNSCC.
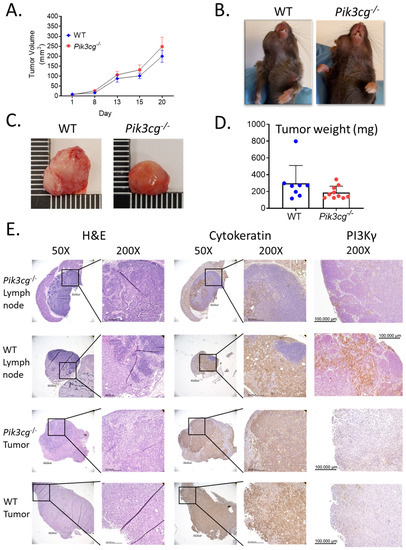
Figure 1.
Host PI3K p110γ inhibition does not have a significant effect on tumor growth or metastasis in mice injected with MOC2 oral cells. (A) Tumor volume in WT and Pik3cg−/− mice over the duration of the experiment. (B) Images of WT and Pik3cg- mice. Tumors were located on the right buccal side of the mice. (C) Images of whole tumors excised from experimental mice at terminal sacrifice. (D) Tumor weights were taken from whole tumors removed at terminal sacrifice. (E) Representative hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistological images of lymph node and tumor sections from tumor-bearing WT and Pik3cg−/− mice stained with AE1/3 pan-cytokeratin or PI3K p110γ antibodies and counterstained with hematoxylin at 50× and 200×. Lymph node sections demonstrate regions stained positive for pan-cytokeratin, indicative of regional metastasis.
2.2. Tumor-Bearing Pik3cg−/− Mice Do Not Possess Inherent Deficiencies in T Cell Activity
Because PI3K p110γ-mediated signaling has been described to be involved in T cell maturation and survival [23], we determined whether there were deficiencies in the anti-tumor immune function of T-cells of tumor bearing Pik3cg−/− mice. First, we analyzed CD4+ and CD8+ T cell populations in the lymph nodes, spleens, and tumors of tumor bearing and non-tumor bearing WT and Pik3cg−/− mice. As expected, in non-tumor bearing mice, proportions of CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells were significantly lower in lymph nodes and spleens of Pik3cg−/− mice compared to WT mice. This trend was also observed among T-cells in lymph nodes and spleens tumor bearing Pik3cg−/− mice compared to WT mice (Figure 2A,B). However, among CD8+ T-cells, we observed a marked increase in the infiltration of CD8+ T cells in Pik3cg−/− mice compared to WT mice. (Figure 2B).
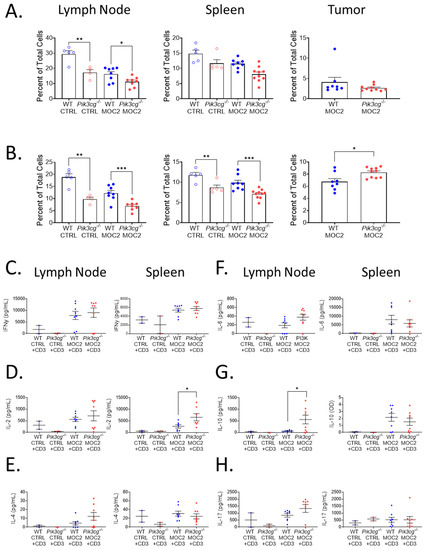
Figure 2.
Tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice do not possess inherent deficiencies in T-cell activity. (A,B) Population frequency of (A) CD4+ T-cells and (B) CD8+ T-cells among total live cells within the lymph node, spleen, and tumor of WT and Pik3cg−/− mice as determined by flow cytometry. (C–H) Production of (C) IFN-γ, (D) IL-2, (E) IL-4, (F) IL-6, (G) IL-10, (H) IL-17 by CD3-stimulated T-cells isolated from the lymph node and spleens of experimental mice as determined by cytokine ELISA. * p-value < 0.05; ** p-value < 0.01; *** p-value < 0.005 between groups, as determined by Student’s t-test.
To determine whether there were inherent deficiencies in T-cell ability to respond to oral tumor insult, we isolated T-cells from the lymph nodes and spleens of both tumor-bearing and non-tumor bearing mice and examined their ability to produce T-cells associated cytokines — IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17, and IFN-γ —following CD3 stimulation. We found that IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-17 production by lymph nodal and splenic T-cells were comparable between both Pik3cg−/− and WT mice. However, we also observed an elevation of IL-2 by splenic T-cells and IL-10 by T-cells from the cervical lymph nodes of Pik3cg−/− mice, compared to T-cells from WT mice (Figure 2C–H). Taken together, we show that intrinsic T cell activity in the absence of host PI3K p110γ remains sufficient to engage in anti-tumor immunity. Further CD8+ T-cell infiltration into the HNSCC tumor microenvironment is enhanced in the absence of host PI3K p110γ.
2.3. Host PI3Kγ Inhibition Augments the Anti-Tumor CD8+ T-Cell Response to Poorly Immunogenic Experimental HNSCC
CD8+ T-cell tumor infiltration is associated with heightened anti-tumor immunity, and cytotoxic responses in HNSCC [31], and anti-tumor activity elicited by PI3K inhibition has been shown to be dependent on interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and IL-17 [32]. Therefore, we investigated the effect of host PI3Kγ inhibition on intracellular production of IFN-γ and IL-17 by T-cells of experimental mice via flow cytometry. We observed a significant increase in intracellular IFN-γ expression by CD8+ T-cells in the tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice. No significant differences were observed in IFN-γ production by CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in the spleens and lymph nodes of tumor-bearing mice (Figure 3A,B). We further found significantly enhanced Ifng gene expression in the tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice, though the expression was not different in the spleen or lymph nodes (Figure 3E). Because of the increased presence of IFN-γ+CD8+ T-cells and Ifng expression in the tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice, we more closely examined factors that could potentially underlie and contribute to the cytotoxic activity of this T-cell subpopulation. Stat1, which is involved in anti-tumor responses following IFN-γ stimulation, was much more highly expressed in the tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice compared to WT mice (Figure 3J). Additionally, Gzmb, an effector molecule involved in CD8+ killing of cancer cells, and Cxcl9, a chemokine important to CD8+ recruitment, were both highly elevated in the tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice compared to WT mice (Figure 3G, H). We also examined Il12b, which is known to promote IFN-γ production and cytotoxic activity by CD8+ T-cells [33]. Expression of this cytokine was not elevated significantly in any analyzed tissues, indicating that enhanced the IFN-γ production in Pik3cg−/− CD8+ T-cells was unlikely to be dependent on IL-12 signaling (Figure 3I). We also investigated intracellular IL-17 production by T-cells, which has been implicated in the recruitment and engagement of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes [34]. We observed significant increases in IL-17 expression by both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells in the spleens and lymph nodes of tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/−, though not in the tumor (Figure 3C,D). Il17 expression was significantly elevated in the tumor, while its expression was low or undetectable for all mice in the lymph nodes and spleens (Figure 3F). Together, these findings indicate that host PI3K p110γ inhibition augments the anti-tumor CD8+ T-cell response to poorly immunogenic HNSCC.
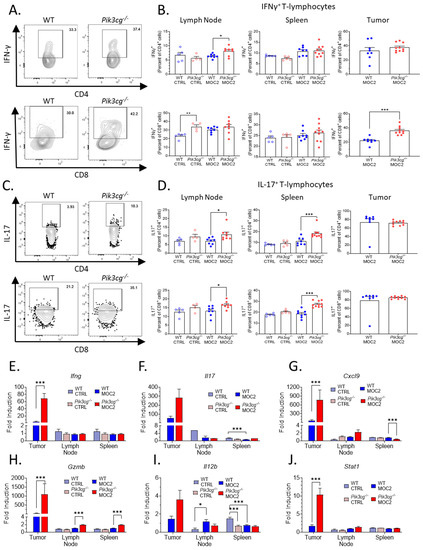
Figure 3.
Host PI3Kγ inhibition augments the anti-tumor CD8+ T-cell response to poorly immunogenic experimental HNSCC. (A) Flow cytometry gating for CD4+ IFN-γ+ T-cells and CD8+ IFN-γ+ T-cells. (B) Population frequencies of CD4+ IFN-γ+ T-cells and CD8+ IFN-γ+ T-cells among parent T-cell populations in the lymph node, spleen, and tumor. (C) Flow cytometry gating for CD4+ IL-17+ T-cells and CD8+ IL-17+ T-cells. (D) Population frequencies of CD4+ IL-17+ T-cells and CD8+ IL-17+ T-cells among parent T-cell populations in the lymph node, spleen and tumor. (E–J) Expression of (E) Ifng, (F) Il17, (G) Cxcl9, (H) Gzmb, (I) Il12b, (J) Stat1 within the sentinel lymph nodes, spleens, and tumors of experimental mice determined by RT-qPCR. * p-value < 0.05; ** p-value < 0.01; *** p-value < 0.005 between groups, as determined by Student’s t-test.
2.4. PD-1 Expression by T-Cells Is Upregulated in Pik3cg−/− Mice
Previous studies show that small molecule inhibition of PI3K p110γ enhances the efficacy of PD-1 blockade in HNSCC [20]. This led us to explore PD-1 expression by T-cells in tumor-bearing mice using our highly aggressive HNSCC model. We first examined the surface expression of PD-1 by CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell populations with flow cytometry (Figure 4A). We found that in tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice, PD-1 expression was significantly higher in both CD4+ and CD8+ cells of the lymph nodes and spleens, though we did not observe this difference in the tumor microenvironment (Figure 4B). Our observations on PD-1 expression in Pik3cg−/− mice led us to further examine the potential for immune suppression in tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice. Using RT-qPCR, we investigated the expression of lymphocytic immune checkpoint surface markers PD-1 and CTLA-4, as well as the immunosuppressive cytokine IL-10, via RT-qPCR in the lymph nodes, spleens, and tumors of experimental mice. While we saw no significant differences in the spleens and lymph nodes, Ctla4, Il10, and Pd1 were significantly elevated in the tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice (Figure 4C-E). Taken together, these data demonstrate that T-cells of tumor-bearing mice display markers of tumor immune suppression in the absence of PI3K p110γ signaling.
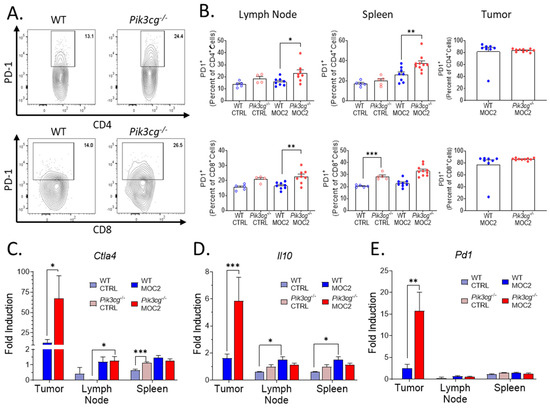
Figure 4.
PD-1 expression by T-cells is upregulated in Pik3cg−/− mice (A) Flow cytometry gating strategy for CD4+ PD-1+ T-cells and CD8+ PD-1+ T-cells. (B) Population frequencies of CD4+ PD-1+ T-cells and CD8+ PD-1+ T-cells among parent T-cell populations in the lymph node, spleen and tumor. (C–E) Expression of (C) Ctla4, (D) Il10, (E) Pd1, and within the sentinel lymph nodes, spleens, and tumors of experimental mice determined by RT-qPCR. * p-value < 0.05; ** p-value < 0.01; *** p-value < 0.005 between groups, as determined by Student’s t-test.
2.5. PI3Kγ Inhibition Promotes Tumor Associated Myeloid Populations Which Express the Immunosuppressive Marker PD-L1 in the HNSCC Tumor Microenvironment
Immunosuppressive myeloid populations, including myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and alternatively activated macrophages (M2s), are known to be highly involved in aggressive and poorly immunogenic HNSCC, in part due to PD-L1 mediated suppression of anti-tumor lymphocytes [26,35]. Therefore, we analyzed Ly6C+ Ly6G+ granulocytic MDSCs (G-MDSCs), Ly6Chi Ly6G- monocytic MDSCs (M-MDSCs), and F4/80+ CD206+ Ly6G- M2 macrophages, as well as their expression of PD-L1 (Figure 5A). Within the spleens and primary tumor sites of tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice, there was increased infiltrate of G-MDSCs (Figure 5B), though no differences were observed in M-MDSC and M2 populations in any of the analyzed tissues (data not shown). We further found Pdl1 gene expression to be significantly elevated in the tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice (Figure 5C). Notably, at the tumor site, all of the aforementioned populations showed significantly higher expression of PD-L1 in tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice, suggestive of enhanced immunosuppression compared to WT mice (Figure 5D–F). In Pik3cg−/− mice, we also observed that M2 populations showed enhanced expression of PD-L1 in the spleens but not the lymph nodes, while G-MDSCs and M-MDSCs showed no difference in the spleens or lymph nodes (data not shown). Taken together, our data suggest a mixed tumor-associated immune response characterized by PD-L1 driven immune suppression by myeloid cells combined with pro- and anti-tumor CD8+ T-cell responses in the tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice.
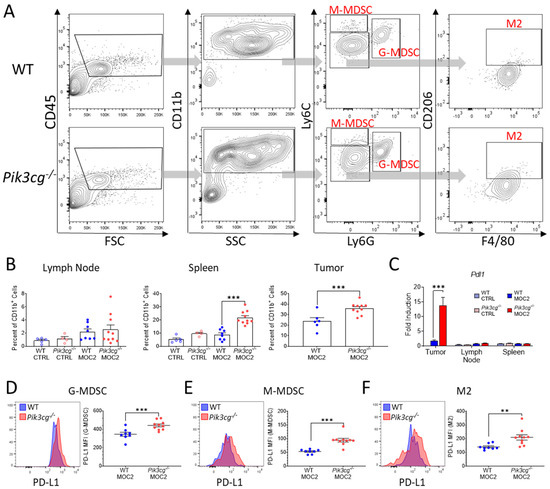
Figure 5.
PI3Kγ inhibition promotes tumor-associated myeloid populations, which express the immunosuppressive marker PD-L1 in the HNSCC tumor microenvironment. (A) Flow cytometry gating strategy for Ly6C+ Ly6G+ granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (G-MDSCs), Ly6Chi Ly6G- monocytic MDSCs (M-MDSCs), and F4/80+ CD206+ Ly6G- alternatively-activated macrophages (M2s) of experimental mice. (B) Population frequencies of G-MDSCs among CD11b+ populations in the lymph nodes, spleens, and tumors of experimental mice. (C) Expression of Pdl1 within the sentinel lymph nodes, spleens, and tumors of experimental mice determined by RT-qPCR; (D–F) Mean fluorescent intensity of PD-L1 expression by (D) G-MDSC, (E) M-MDSC, (F) M2 populations in experimental mice accompanied by representative histograms demonstrating disparities in PD-L1 expression between WT and Pik3cg−/− mice.; ** p-value < 0.01; *** p-value < 0.005 between groups, as determined by Student’s t-test.
3. Discussion
Poorly immunogenic HNSCC is associated with poor diagnosis and is extremely difficult to treat because of resistance to immunotherapies, including checkpoint inhibitors [36,37]. Therefore, novel approaches are required to overcome the challenges associated with the treatment of such frequent cases of HNSCC [38]. PI3K p110γ inhibition has presented itself as a novel means of combating HNSCC, although it has mostly been studied using pharmaceutical compounds that do not differentiate between healthy and tumor cell populations. Because we designed our experimental mouse study to only measure the effects of PI3K p110γ mediated signaling in host cells, we were able to focus on how PI3K p110γ inhibition affects the host immune response to HNSCC.
In this study, we have highlighted the effects of PI3K p110γ-mediated signal transduction on the immune response to aggressive HNSCC with low immunogenicity. By utilizing an orthotopic cancer model with the MOC2 cell line injected into WT and Pik3cg−/− mice, we have demonstrated that PI3K p110γ modulates host immune activity in a manner that likely potentiates the efficacy of anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy against HNSCC. While PI3K p110γ inhibition in host immune cells did not significantly lower tumor burden or influence lymph node metastasis, the immune response in the tumor microenvironment was substantially modulated in Pik3cg−/− mice. Remarkably, we observed increased expression of both anti-tumor cytotoxic and immunosuppressive markers in the tumor site of Pik3cg−/− mice, which may have resulted in counteracting effects on HNSCC development. Such findings may explain the suboptimal response rates of PI3K p110γ inhibition when employed alone against tumors in early phase clinical trials [17]. Although our study used a murine HNSCC model, we believe these results provide essential information that can potentially be applied to HNSCC patients in future studies.
Despite a lack of difference in tumor growth and metastasis, it was surprising to observe increased CD8+ T-cell tumor infiltration in tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice, a phenotype generally associated with improved prognosis in human HNSCC [39]. These cells demonstrated enhanced anti-tumor activity, characterized by increased IFN-γ and IL-17 expression and related responses. The role of IFN-γ is well-established in the induction of a protective effect against clinical and experimental HNSCC [40,41], and CD8+ T-cells are known to produce and become activated by this cytokine [42]. Further, we observed an elevation in the IFN-γ associated transcription factor Stat1 in tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice. Previously, our group showed that STAT1 is essential to priming T-lymphocytes for anti-tumor immunity against aggressive HNSCC [43]. Our observation of higher expression of IFN-γ and STAT1 in Pik3cg−/− mice at the tumor site indicates a potential anti-tumor cytotoxic response. We also observed increases in IL-17 expression by T-cells in the lymph nodes and spleen of tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice. Previous studies have reported similar increases in IL-17 production by Pik3cg−/− mice in response to various stimuli [44]. While the role of IL-17 in HNSCC remains controversial, our group has previously shown that increased IL-17 is associated with lower metastatic burden and enhanced anti-tumor immunity in experimental murine HNSCC [34,45]. Further substantiating this observation was the elevated expression of Cxcl9 and Gzmb in the primary tumors of Pik3cg−/− mice, which are respectively associated with chemotactic recruitment of lymphocytes and lymphocytic induction of tumor cytotoxicity [46,47]. Our findings are consistent with previous studies showing that p110γ blockade induces cytotoxic T-cell infiltration into and activity within the tumor microenvironment of solid tumors, including HNSCC and urothelial cancer [20,48]. Moreover, in the context of findings that IFN-γ and IL-17 are necessary for eliciting a therapeutic effect from PI3K inhibition in melanoma [32], our results suggest that host inhibition of PI3K p110γ enhances the anti-tumor activity of CD8+ T-cells via IFN-γ and/or IL-17 associated pathways. In summary, because the enhancement of CD8+ T-cell activity persisted even against non-immunogenic HNSCC, PI3K p110γ inhibition may serve as a host-directed approach to bolster the anti-tumor immune response.
It should be noted that our data indicate that PI3K p110γ inhibition was not sufficient to cause a substantial reduction in tumors in this highly aggressive murine HNSCC model. Therefore, PI3K p110γ inhibitors alone are unlikely to elicit a strongly therapeutic effect against highly aggressive clinical HNSCC. We further observed increased expression of PD-1 by T-cells in the tumor microenvironment of tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice, which is associated with susceptibility to PD-L1-induced immune suppression [49]. We also observed a significant upregulation of PD-L1 among Pik3cg−/− G-MDSCs, M-MDSCs, and M2s at the primary tumor site and metastasized lymph nodes. These findings were surprising given our observation of increased cytotoxic markers at the tumor site. However, it is likely that this elevation in cytotoxicity counteracts the enhanced pro-tumor activity also present in Pik3cg−/− mice. A previous study showed that PI3Kγ inhibition using the small molecule inhibitor IPI-549 diminishes the accumulation of F4/80+CD206+ M2 populations in murine melanoma and breast cancer [50]. We did not observe an increase in M2 populations of Pik3cg−/− mice. However, we observed an increase in G-MDSC populations, which are known to significantly inhibit the anti-tumor activity of T-cells [51,52]. This finding supports previous observations on the role of the PI3K pathway in inhibiting MDSC immunosuppressive activity [53]. Taken together, our data show increases in PD-L1 expression and MDSC populations likely preclude the enhanced cytotoxic activity in Pik3cg−/− mice from making a significant impact on tumor growth. Given these findings, our results provide a rationale for targeting MDSC function or PD-L1 in conjunction with PI3K p110γ inhibition to promote cytotoxicity and enhanced efficacy of other therapeutics such as immune checkpoint inhibitors against poorly immunogenic HNSCC [54]. Future research will explore the efficacy of such combination therapies.
Recent studies investigating PI3K p110γ in the context of experimental murine HNSCC indicate that selective inhibitors show promise when administered in combination with PD-1 blockade. However, such studies were only performed in conjunction with HNSCC that had already been responsive to PD-1 inhibition alone [20]. About 60% of HNSCC patients are unresponsive to immune checkpoint therapy employing monoclonal antibodies against PD-1 or PD-L1 [37]. One reason for this low response rate is low tumor immunogenicity, marked by diminished infiltration of CD8+ T-cells and cytotoxic markers, such as IFN-γ and granzyme b, at the primary tumor site [55]. Our study shows that host inhibition of PI3K p110γ can potentially address this limitation, as tumor-bearing Pik3cg−/− mice demonstrated an increase in CD8+ T-cell infiltration into the tumor microenvironment of this poorly immunogenic HNSCC. Taken together, these data demonstrate that PI3K p110γ inhibition has the potential to enhance the anti-tumor response against HNSCC with low immunogenicity, especially in combination with checkpoint inhibitors.
The synergistic therapeutic effect of PD-1 and PI3K p110γ inhibition on HNSCC is currently being explored clinically [18]. However, the efficacy of PI3K p110γ inhibition with other immune checkpoint inhibitors has not been explored to a comparable extent. It has previously been shown that in vivo treatment of MOC2 tumors in a murine HNSCC model with PD-1 and CTLA-4 blockade does not confer increased anti-tumor immunity or increased presence of CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes [28]. Interestingly, this poorly immunogenic murine HNSCC line has shown response to therapeutic inhibitors of mTOR but not PD-L1, though neither treatment increased infiltration of CD8+ TILs [56]. Our observation of increases in CD8+ T-cell presence and PD-L1 expression by immunosuppressive myeloid populations in the tumor microenvironment highlight counteracting forces that together fail to influence tumor development. Theoretically, disrupting this balance of cytotoxicity and immunosuppression could skew tumor development. Previously, dual p110δ/γ inhibition with the pharmaceutical IPI-145 has been shown to be ineffective in combination with anti-PD-L1 therapy in murine MOC2 HNSCC [26]. However, it has also been shown that dual inhibition of p110δ/γ abrogates CD8+ T-cell function while selective inhibition of p110δ or p110γ does not [19]. Therefore, because our findings indicate PI3K p110γ inhibition alone enhances CD8+ T-cell recruitment and preserves CD8+ T-cell function, this provides a rationale to combine PI3K p110γ inhibition with PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors against poorly immunogenic HNSCC. Currently, combination therapy of anti-PD-L1 and IPI-549 is being explored as a treatment for patients with triple-negative breast cancer and renal cell carcinoma [57] and might prove effective in patients with poorly immunogenic HNSCC in the future.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mouse Handling
Female Pik3cg−/− (n = 15) and Pik3cg+/+ wild-type (WT; n = 15) C57BL/6 mice, age-matched at 7–8 weeks, were used for these studies. From each genotype group, mice were selected to receive cancer injections (n = 10) or act as healthy controls (n = 5). WT mice were acquired from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME, USA), and Pik3cg−/− mice were descendants of inbred mice acquired as described previously [58,59]. Animals were housed in Ohio State University animal facilities in accordance with state and federal guidelines provided by University Laboratory Animal Resources (ULAR). Animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol #2018A00000054) and Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) of the Ohio State University.
4.2. Cancer Cell Line
MOC2 cell line, a highly aggressive mouse oral cancer cell line derived from the primary tumor in the floor-of-mouth of a Cxcr3−/− mouse treated with the carcinogen DMBA, was obtained from Kerafast (Boston, MA, USA) and cultured according to recommended protocol at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Cells were grown to 75% confluence and passed after dissociation in TrypLE (Thermo Fisher Scientific; Waltham, MA, USA).
4.3. Antibodies
All antibodies used for flow cytometry and ELISA were purchased from BioLegend (San Diego, CA, USA). Primary monoclonal rat anti-mouse pan Cytokeratin (AE-1/AE-3) primary antibodies for IHC were acquired from BD Biosciences (San Jose, CA, USA), while horseradish peroxidase(HRP)-conjugated polyclonal goat anti-rat IgG secondary antibody was acquired from Southern Biotech (Birmingham, AL, USA). PIK3CG primary monoclonal antibody (OTI6H5) was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific.
4.4. Orthotopic HNSCC Model
We orthotopically injected 3 × 104 MOC2 cells in 30 µL PBS into the right buccal mucosa of designated experimental C57BL/6 mice. Mice were weighed and tumor measurements were taken biweekly via calipers. Tumors were allowed to grow until meeting the threshold for termination. At terminal sacrifice, the lymph nodes, tumors, lungs, and spleens were harvested from experimental mice and processed for downstream analysis.
4.5. Flow Cytometry
Single cell suspensions were prepared from cervical lymph nodes, spleens, and tumors. Splenic cells were treated for 2 min with ACK Lysis Buffer to lyse erythrocytes. Tumor cells were digested with collagenase (Thermo Fisher Scientific; Waltham, MA) for 60 min at 37 °C before passing through nylon mesh filters. From each tissue, 106 cells were processed with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies for CD45, CD11b, Ly6G, Ly6C, F4/80, PD-L1, and CD206. Additionally, 2 × 106 cells from each organ were treated with a cell activation cocktail containing PMA and ionomycin (Biolegend) for 6 h, after which they were stained with fluorophore-conjugated antibodies against CD3, CD4, CD8, and PD-1. Samples were subsequently intracellularly stained with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies against IFN-γ and IL-17. Samples were run using a BD FACS Aria flow cytometer (BD Biosciences), and subsequent analysis was performed using FlowJo software (Tree Star, Inc., Ashland, OR, USA).
4.6. T-Cell Stimulation and ELISA
Splenic and lymph node cells from single cell suspensions were cultured on 96-well plates bound to αCD3 (1 µg/mL) and αCD28 (1 µg/mL) (BioLegend) for 72 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. Following this incubation, supernatants were examined for IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-17 concentrations using cytokine ELISA. Capture and detection antibodies for these cytokines were purchased from Biolegend Streptavidin-alkaline phosphatase (BD Biosciences) and para-nitrophenyl phosphate (Thermo-Fisher Scientific) in glycine buffer were used for signal detection. Plates were read using a SpectraMax 190 plate reader (Molecular Devices; San Jose, CA, USA) at 405 nm. Concentrations of cytokines in supernatants were determined by extrapolation on the standard curve established by cytokine standard absorbance readings.
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Portions of the lymph nodes, spleens, and tumors of experimental mice were placed in RNA-Later (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and stored at −80 C. Tissues were homogenized in 1 mL of TRIzol using a Bead Mill (VWR; Radnor, PA, USA). RNA was isolated using the Direct-zol RNA Miniprep kit (Zymo Research; Irvine, CA, USA). cDNA was prepared using 1μg RNA with High Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). PCR amplification was performed in a CFX-384 Real-Time System (BioRad; Hercules, CA, USA). Samples were prepared in duplicate using PowerUp SYBR Green Master Mix (BioRad). Gene expression was normalized using β-actin (Actb) and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) as reference genes. Fold inductions of Ctla4, Cxcl9, Gzmb, Mhcii, Ifng, Il2, Il10, Il12, Il17, Pd1, and Pdl1 were calculated using the 2-ΔΔct method. Primers were designed based on sequences previously verified by PrimerBank (https://pga.mgh.harvard.edu/primerbank/; accessed January 2020).
4.8. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
Primary tumors, draining cervical lymph nodes, and spleens were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin followed by paraffin embedding. Paraffin-embedded tissue sections were cut into 5 μm-thick cross-sections for histopathology and immunohistochemistry (IHC). Histopathological samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. For IHC, tissue sections were rehydrated in xylenes and graded ethanol before heat treatment to induce epitope retrieval. After antigen retrieval, IHC samples were blocked for 30 min in a 0.3% hydrogen peroxide/methanol to inhibit endogenous peroxidase activity. Tissue sections were blocked for 30 min in 10% normal goat serum prior to overnight incubation with monoclonal rat anti-mouse pan Cytokeratin (AE-1/AE-3) primary antibody. Samples were incubated for 1 h with HRP conjugated polyclonal goat anti-rat IgG secondary antibody. DAB peroxidase kit (Vector Laboratories Inc., Burlingame CA, USA) was used to detect the presence of HRP.
4.9. Statistics
Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism v8.0.2 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). Student’s t-test was used to determine statistically significant differences between groups with a p-value cut off of <0.05.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we demonstrate that host PI3K p110γ inhibition does not affect the growth or metastasis of aggressive murine HNSCC with poor immunogenicity, though it has potent immunomodulatory effects that lead to elevations in both cytotoxic and immunosuppressive responses. These altered responses are marked by enhanced infiltration and activity of both anti-tumor CD8+ T-lymphocytes and immunosuppressive MDSCs in the tumor microenvironment. These results might explain why PI3K inhibition response rates are suboptimal when used as a monotherapy against patients with solid tumors. Nevertheless, our findings show that PI3K p110γ inhibition may serve as a strategy for potentially enhancing the cytotoxic response against poorly immunogenic HNSCC and likely potentiates HNSCC treatment when used in combination with selective checkpoint inhibitors. Future research will explore the clinical potential of PI3K p110γ inhibition in combination with therapies that inhibit host immunosuppressive pathways.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.O.; methodology, S.O.; validation, K.A., N.R., A.A., A.S. and S.O.; formal analysis, K.A., A.A.; investigation, K.A., N.R., A.S. and S.O.; resources, S.O.; data curation, K.A. and A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, K.A., A.A. and S.O.; writing—review and editing, S.O.; visualization, K.A., A.A. and S.O.; supervision, S.O.; project administration, K.A., N.R. and S.O.; funding acquisition, S.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI/NIH), grant number K01CA207599 and the American Cancer Society (ACS), grant number RSG-19-079-01-TBG awarded to S.O. The Article Processing Charge was funded by ACS.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Animals were housed in Ohio State University animal facilities in accordance with state and federal guidelines provided by University Laboratory Animal Resources (ULAR). Animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol #2018A00000054) and Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) of the Ohio State University.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article. The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Velculescu, V.E.; Zhou, S.; Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Kinzler, K.W. Cancer genome landscapes. Science 2013, 339, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean, S.; Kiger, A.A. Classes of phosphoinositide 3-kinases at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, M.C.; Gulluni, F.; Campa, C.C.; Martini, M.; Hirsch, E. Targeting PI3K signaling in cancer: Challenges and advances. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2019, 1871, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitulescu, G.M.; Van De Venter, M.; Nitulescu, G.; Ungurianu, A.; Juzenas, P.; Peng, Q.; Olaru, O.T.; Gradinaru, D.; Tsatsakis, A.; Tsoukalas, D.; et al. The Akt pathway in oncology therapy and beyond (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.K.; Sriskantharajah, S.; Hessel, E.M.; Okkenhaug, K. PI3K inhibitors in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 23, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blas, K.; Wilson, T.G.; Tonlaar, N.; Galoforo, S.; Hana, A.; Marples, B.; Wilson, G.D. Dual blockade of PI3K and MEK in combination with radiation in head and neck cancer. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiker, A.J.; DeGraff, W.; Choudhuri, R.; Sowers, A.L.; Thetford, A.; Cook, J.A.; Van Waes, C.; Mitchell, J.B. Radiation Enhancement of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by the Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor PF-05212384. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2792–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, D.; Hess, J.; Freier, K.; Hoffmann, J.; Freudlsperger, C. Targeting EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling enhances radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorieux, M.; Dok, R.; Nuyts, S. The influence of PI3K inhibition on the radiotherapy response of head and neck cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussink, J.; van der Kogel, A.J.; Kaanders, J.H. Activation of the PI3-K/AKT pathway and implications for radioresistance mechanisms in head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.L.; Cantley, L.C. PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: Variations on a theme. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5497–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Broek, R.; Mohan, S.; Eytan, D.F.; Chen, Z.; Van Waes, C. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in head and neck cancer: Functions, aberrations, cross-talk, and therapies. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lui, V.W.; Hedberg, M.L.; Li, H.; Vangara, B.S.; Pendleton, K.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Du, Y.; Gilbert, B.R.; et al. Frequent mutation of the PI3K pathway in head and neck cancer defines predictive biomarkers. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Window of Opportunity Study of IPI-549 in Patients With Locally Advanced HPV+ and HPV- Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma; US National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2020.
- Janku, F.; Hong, D.S.; Fu, S.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Naing, A.; Falchook, G.S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Stepanek, V.M.; Moulder, S.L.; Lee, J.J.; et al. Assessing PIK3CA and PTEN in early-phase trials with PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.J.; Hong, D.S.; Tolcher, A.W.; Patnaik, A.; Shapiro, G.; Chmielowski, B.; Ribas, A.; Brail, L.H.; Roberts, J.; Lee, L.; et al. Initial results from first-in-human study of IPI-549, a tumor macrophage-targeting agent, combined with nivolumab in advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, C.J.; Arhontoulis, D.C.; Rangel Rivera, G.O.; Knochelmann, H.M.; Smith, A.S.; Wyatt, M.M.; Rubinstein, M.P.; Atkinson, C.; Thaxton, J.E.; Neskey, D.M.; et al. Ex vivo blockade of PI3K gamma or delta signaling enhances the antitumor potency of adoptively transferred CD8(+) T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, M.M.; Messer, K.S.; Ralainirina, N.; Li, H.; Leem, C.J.; Gorjestani, S.; Woo, G.; Nguyen, A.V.; Figueiredo, C.C.; Foubert, P.; et al. PI3Kgamma is a molecular switch that controls immune suppression. Nature 2016, 539, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazar, I.; Marques, M.; Kumar, A.; Hirsch, E.; Wymann, M.; Carrera, A.C.; Barber, D.F. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma participates in T cell receptor-induced T cell activation. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 2977–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, L.; Fruman, D.A. PI3K signalling in B- and T-lymphocytes: New developments and therapeutic advances. Biochem. J. 2012, 442, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Irie-Sasaki, J.; Jones, R.G.; Oliveira-dos-Santos, A.J.; Stanford, W.L.; Bolon, B.; Wakeham, A.; Itie, A.; Bouchard, D.; Kozieradzki, I.; et al. Function of PI3Kgamma in thymocyte development, T cell activation, and neutrophil migration. Science 2000, 287, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Guillermet-Guibert, J.; Graupera, M.; Bilanges, B. The emerging mechanisms of isoform-specific PI3K signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.B.; Nebhan, C.A.; Yang, J.; Starnes, L.S.; Yan, C.; Vilgelm, A.E.; Chen, S.C.; Dan Ayers, G.; Abramson, V.; Mayer, I.A.; et al. Correlative studies investigating effects of PI3K inhibition on peripheral leukocytes in metastatic breast cancer: Potential implications for immunotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 184, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.J.; Moore, E.C.; Clavijo, P.E.; Friedman, J.; Cash, H.; Chen, Z.; Silvin, C.; Van Waes, C.; Allen, C. Anti-PD-L1 Efficacy Can Be Enhanced by Inhibition of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells with a Selective Inhibitor of PI3Kdelta/gamma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, T.S.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Ribas, A. Mechanisms of Resistance to PD-1 and PD-L1 Blockade. Cancer J. 2018, 24, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolkind, P.; Przybylski, D.; Marjanovic, N.; Nguyen, L.; Lin, T.; Johanns, T.; Alexandrov, A.; Zhou, L.; Allen, C.T.; Miceli, A.P.; et al. Cancer immunogenomic approach to neoantigen discovery in a checkpoint blockade responsive murine model of oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 4109–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onken, M.D.; Winkler, A.E.; Kanchi, K.L.; Chalivendra, V.; Law, J.H.; Rickert, C.G.; Kallogjeri, D.; Judd, N.P.; Dunn, G.P.; Piccirillo, J.F.; et al. A surprising cross-species conservation in the genomic landscape of mouse and human oral cancer identifies a transcriptional signature predicting metastatic disease. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2873–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, N.P.; Winkler, A.E.; Murillo-Sauca, O.; Brotman, J.J.; Law, J.H.; Lewis, J.S., Jr.; Dunn, G.P.; Bui, J.D.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Uppaluri, R. ERK1/2 regulation of CD44 modulates oral cancer aggressiveness. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, D.J.; Ahmad, F.; Ferris, R.L.; Rimm, D.L.; Pantanowitz, L. Utility of CD8 score by automated quantitative image analysis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2018, 86, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, N.A.; Galvin, K.C.; Corcoran, A.M.; Boon, L.; Higgs, R.; Mills, K.H. Immunotherapy with PI3K inhibitor and Toll-like receptor agonist induces IFN-gamma+IL-17+ polyfunctional T cells that mediate rejection of murine tumors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komita, H.; Homma, S.; Saotome, H.; Zeniya, M.; Ohno, T.; Toda, G. Interferon-gamma produced by interleukin-12-activated tumor infiltrating CD8+T cells directly induces apoptosis of mouse hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, X.; Hu, L.; Huang, Q.; Jin, Y. Interleukin-17 acts as double-edged sword in anti-tumor immunity and tumorigenesis. Cytokine 2017, 89, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobin, R.P.; Davis, D.; Jordan, K.R.; McCarter, M.D. The clinical evidence for targeting human myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer patients. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.T.; Clavijo, P.E.; Van Waes, C.; Chen, Z. Anti-Tumor Immunity in Head and Neck Cancer: Understanding the Evidence, How Tumors Escape and Immunotherapeutic Approaches. Cancers 2015, 7, 2397–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, V.C. Current Understanding of the Mechanisms Underlying Immune Evasion From PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Head and Neck Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oghumu, S.; Casto, B.C.; Ahn-Jarvis, J.; Weghorst, L.C.; Maloney, J.; Geuy, P.; Horvath, K.Z.; Bollinger, C.E.; Warner, B.M.; Summersgill, K.F.; et al. Inhibition of Pro-inflammatory and Anti-apoptotic Biomarkers during Experimental Oral Cancer Chemoprevention by Dietary Black Raspberries. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Li, X.; Ma, D.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Xia, J.; Cheng, B.; Wang, Z. Prognostic significance of tumor infiltrating immune cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussu, F.; Graziani, C.; Gallus, R.; Cittadini, A.; Galli, J.; De Corso, E.; Di Cintio, G.; Corbi, M.; Almadori, G.; Boninsegna, A.; et al. IFN-gamma and other serum cytokines in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. ACTA Otorhinolaryngologica Italica 2018, 38, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Jamal, S.M.; Taylor, E.B.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; Alamodi, A.A.; Selimovic, D.; Alkhateeb, A.; Hannig, M.; Hassan, S.Y.; Santourlidis, S.; Friedlander, P.L.; et al. Interferon gamma-induced apoptosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is connected to indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase via mitochondrial and ER stress-associated pathways. Cell Div. 2016, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, P.; Leggatt, G.; Waterhouse, N.; Frazer, I.H. Interferon-gamma derived from cytotoxic lymphocytes directly enhances their motility and cytotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, N.; Anderson, K.; Volpedo, G.; Hamza, O.; Varikuti, S.; Satoskar, A.R.; Oghumu, S. STAT1 inhibits T-cell exhaustion and myeloid derived suppressor cell accumulation to promote antitumor immune responses in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1717–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.J.; Ciuclan, L.; Finan, P.M.; Wymann, M.P.; Walker, C.; Westwick, J.; Ward, S.G.; Thomas, M.J. Genetic ablation of PI3Kgamma results in defective IL-17RA signalling in T lymphocytes and increased IL-17 levels. Eur. J. Immunol. 2012, 42, 3394–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Ryan, N.; Volpedo, G.; Varikuti, S.; Satoskar, A.R.; Oghumu, S. Immune Suppression Mediated by STAT4 Deficiency Promotes Lymphatic Metastasis in HNSCC. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, I.G.; Savas, P.; Lai, J.; Chen, A.X.Y.; Oliver, A.J.; Teo, Z.L.; Todd, K.L.; Henderson, M.A.; Giuffrida, L.; Petley, E.V.; et al. Macrophage-Derived CXCL9 and CXCL10 Are Required for Antitumor Immune Responses Following Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretscher, D.; Distel, L.V.; Grabenbauer, G.G.; Wittlinger, M.; Buettner, M.; Niedobitek, G. Distribution of immune cells in head and neck cancer: CD8+ T-cells and CD20+ B-cells in metastatic lymph nodes are associated with favourable outcome in patients with oro- and hypopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcoman, E.; De La Rochere, P.; Richer, W.; Vacher, S.; Chemlali, W.; Krucker, C.; Sirab, N.; Radvanyi, F.; Allory, Y.; Pignot, G.; et al. Inhibition of PI3K pathway increases immune infiltrate in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1581556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Kadletz, L.; Wiebringhaus, R.; Kenner, L.; Selzer, E.; Fureder, T.; Rajky, O.; Berghoff, A.S.; Preusser, M.; Heiduschka, G. PD-1 and PD-L1 expression in HNSCC primary cancer and related lymph node metastasis—Impact on clinical outcome. Histopathology 2018, 73, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Henau, O.; Rausch, M.; Winkler, D.; Campesato, L.F.; Liu, C.; Cymerman, D.H.; Budhu, S.; Ghosh, A.; Pink, M.; Tchaicha, J.; et al. Overcoming resistance to checkpoint blockade therapy by targeting PI3Kgamma in myeloid cells. Nature 2016, 539, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wondergem, N.E.; Nauta, I.H.; Muijlwijk, T.; Leemans, C.R.; van de Ven, R. The Immune Microenvironment in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: On Subsets and Subsites. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oghumu, S.; Knobloch, T.J.; Terrazas, C.; Varikuti, S.; Ahn-Jarvis, J.; Bollinger, C.E.; Iwenofu, H.; Weghorst, C.M.; Satoskar, A.R. Deletion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibits murine oral carcinogenesis: Potential role for chronic pro-inflammatory immune mediators. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikha, P.; Carson, W.E. 3rd. Signaling pathways involved in MDSC regulation. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 2014, 1846, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Skora, A.D.; Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Tam, A.J.; Blosser, R.L.; Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Papadopoulos, N.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; et al. Eradication of metastatic mouse cancers resistant to immune checkpoint blockade by suppression of myeloid-derived cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11774–11779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubin, M.M.; Zhang, X.; Schuster, H.; Caron, E.; Ward, J.P.; Noguchi, T.; Ivanova, Y.; Hundal, J.; Arthur, C.D.; Krebber, W.J.; et al. Checkpoint blockade cancer immunotherapy targets tumour-specific mutant antigens. Nature 2014, 515, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.C.; Cash, H.A.; Caruso, A.M.; Uppaluri, R.; Hodge, J.W.; Van Waes, C.; Allen, C.T. Enhanced Tumor Control with Combination mTOR and PD-L1 Inhibition in Syngeneic Oral Cavity Cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaluation of IPI-549 Combined With Front-Line Treatments in Pts. With Triple-Negative Breast Cancer or Renal Cell Carcinoma (MARIO-3) (MARIO-3); US National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2020.
- Barbi, J.; Cummings, H.E.; Lu, B.; Oghumu, S.; Ruckle, T.; Rommel, C.; Lafuse, W.; Whitacre, C.C.; Satoskar, A.R. PI3Kgamma (PI3Kgamma) is essential for efficient induction of CXCR3 on activated T cells. Blood 2008, 112, 3048–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, H.E.; Barbi, J.; Reville, P.; Oghumu, S.; Zorko, N.; Sarkar, A.; Keiser, T.L.; Lu, B.; Ruckle, T.; Varikuti, S.; et al. Critical role for phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma in parasite invasion and disease progression of cutaneous leishmaniasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





