Targeting the IL-6/STAT3 Signalling Cascade to Reverse Tamoxifen Resistance in Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Stable Cell Lines Establishment
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. ELISA Assay
2.5. Gene Silencing, Plasmids, qPCR, Gene Expression Analysis and Promoter Analysis
2.6. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
2.7. Tissue Microarray
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.10. Preparation of Conditional Medium
2.11. Tamoxifen Response Assay
2.12. Western Blot and Co-Immunoprecipitation
2.13. Xenograft
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
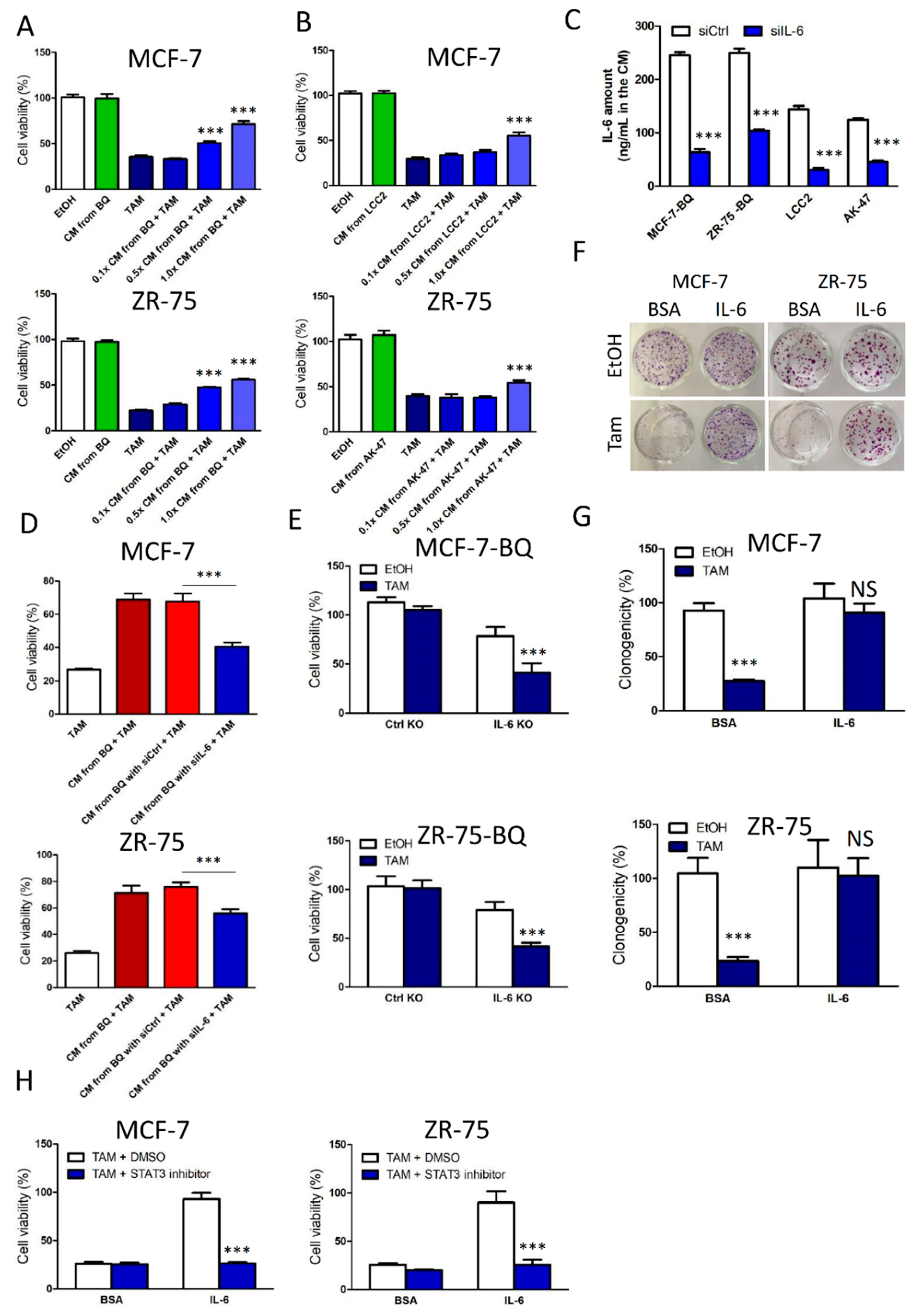
3.1. Overexpression of BQ Enhanced IL-6/STAT3 Signalling Pathway
3.2. Activation of IL-6/STAT3 Pathway Could Induce Tamoxifen Resistance
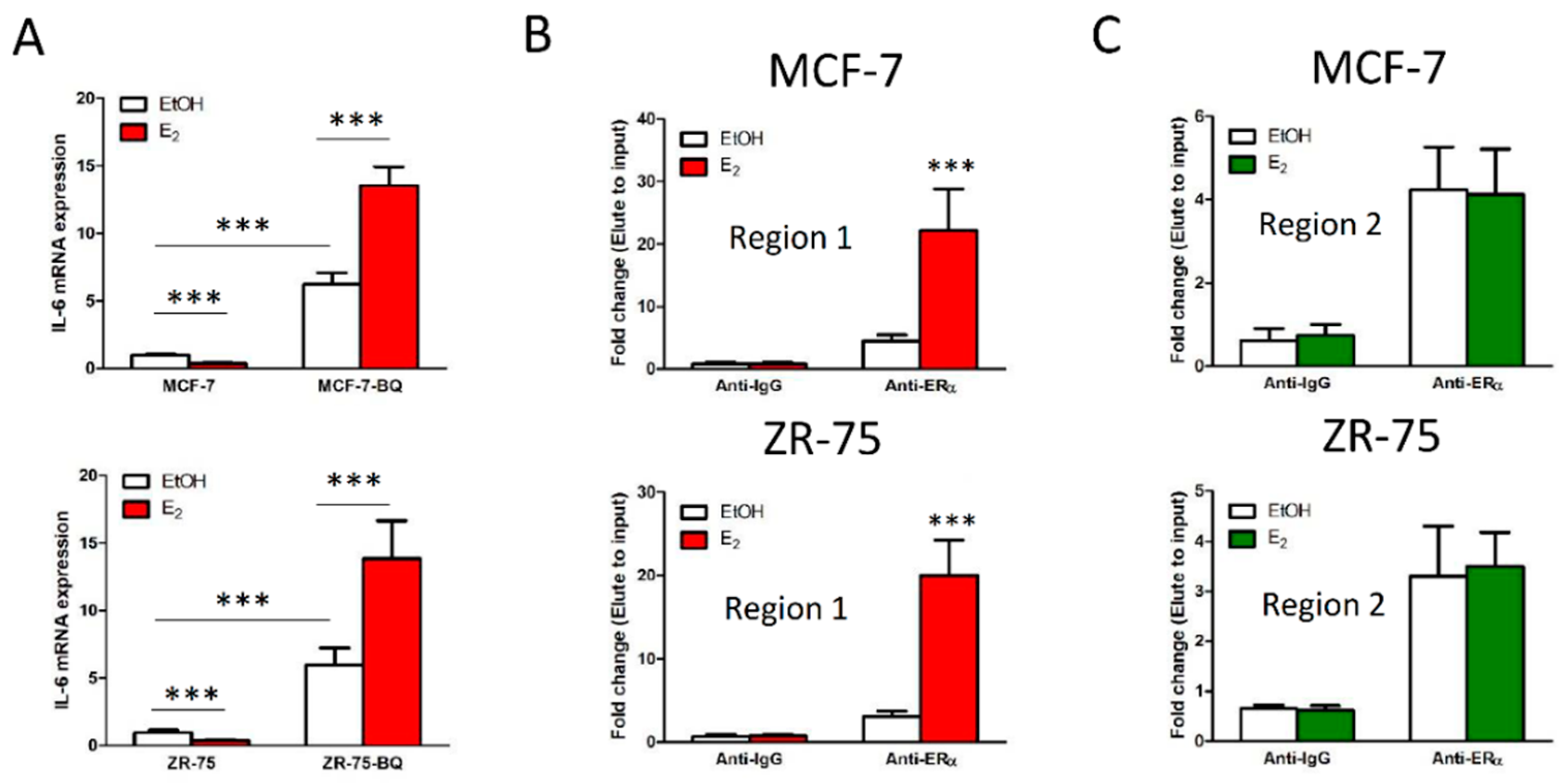
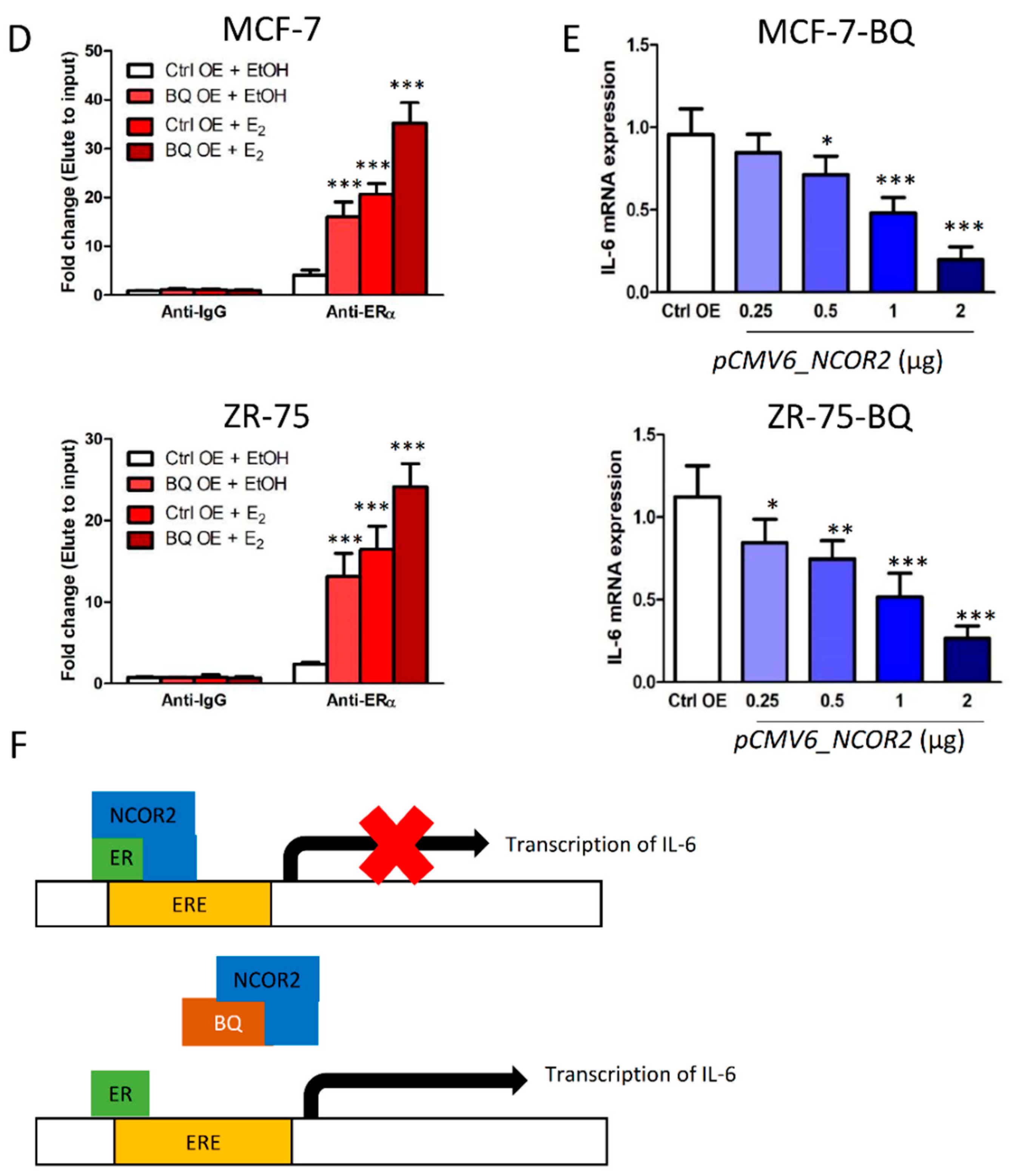
3.3. Overexpression BQ Could Enhance the Transcription of IL-6 Mediated by Estrogen Receptor α (ER)
3.4. Overexpression BQ Could Enhance the Transcription of IL-6R Mediated by NF-kB
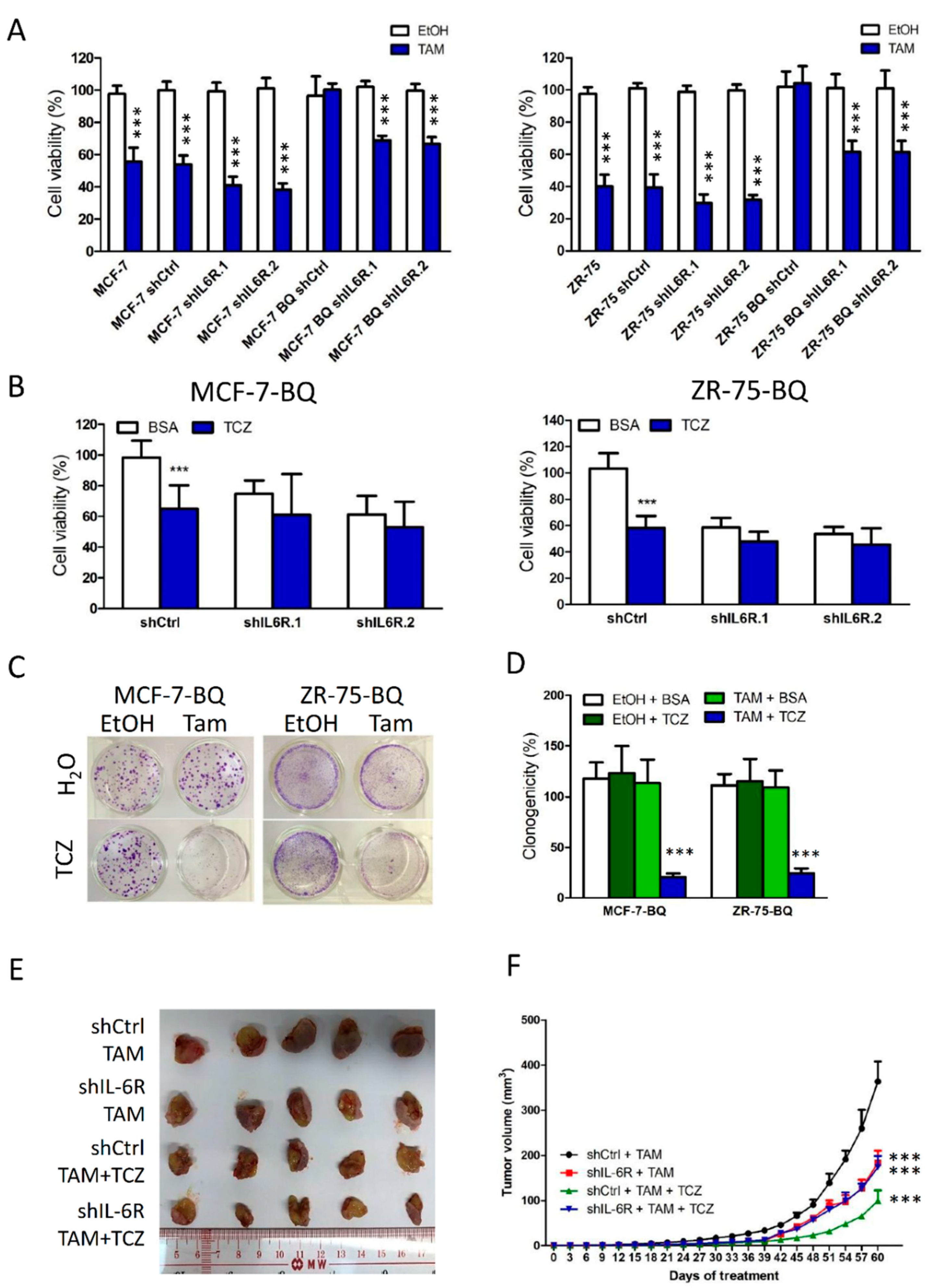
3.5. Targeting IL-6R Could Reduce Tamoxifen Resistance
3.6. Clinical Significance of BQ and IL-6R in Breast Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perou, C.M.; Sorlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siersbaek, R.; Kumar, S.; Carroll, J.S. Signaling pathways and steroid receptors modulating estrogen receptor a function in breast cancer. Gene Dev. 2018, 32, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Hilakivi-Clarke, L.; Clarke, R. Molecular mechanisms of tamoxifen-associated endometrial cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matutino, A.; Joy, A.A.; Brezden-Masley, C.; Chia, S.; Verma, S. Hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: Redrawing the lines. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, S131–S141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, A.; Dowsett, M. Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2004, 11, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, J.; Massarweh, S.; Osborne, C.K.; Wakeling, A.E.; Ali, S.; Weiss, H.; Schiff, R. Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: Increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggins, R.B.; Schrecengost, R.S.; Guerrero, M.S.; Bouton, A.H. Pathways to tamoxifen resistance. Cancer Lett. 2007, 256, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sette, C.; Ladomery, M.; Ghigna, C. Alternative splicing: Role in cancer development and progression. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 2013, 421606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauer, J.; Denson, J.L.; Bruning, J.C. Versatile functions for IL-6 in metabolism and cancer. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siersbaek, R.; Scabia, V.; Nagarajan, S.; Chernukhin, I.; Papachristou, E.K.; Broome, R.; Johnston, S.J.; Joosten, S.E.P.; Green, A.R.; Kumar, S.; et al. IL6/STAT3 Signaling Hijacks Estrogen Receptor alpha Enhancers to Drive Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 412–423.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, R.; Ye, Y.; Liu, P.; Yu, W.; Wei, F.; Ren, X.; Yu, J. Interleukin-6 Trans-Signaling Pathway Promotes Immunosuppressive Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells via Suppression of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 in Breast Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelot, T.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Menetrier-Caux, C.; Rastkha, M.; Duc, A.; Blay, J.Y. Prognostic value of serum levels of interleukin 6 and of serum and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in hormone-refractory metastatic breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, R.; Junius, S.; Benoy, I.; Van Dam, P.; Vermeulen, P.; Van Marck, E.; Huget, P.; Dirix, L.Y. Circulating interleukin-6 predicts survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 103, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, J.; Chand, A.; Gough, D.; Ernst, M. Therapeutically exploiting STAT3 activity in cancer—Using tissue repair as a road map. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashizume, M.; Tan, S.L.; Takano, J.; Ohsawa, K.; Hasada, I.; Hanasaki, A.; Ito, I.; Mihara, M.; Nishida, K. Tocilizumab, a Humanized Anti-IL-6R Antibody, as an Emerging Therapeutic Option for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Molecular and Cellular Mechanistic Insights. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 34, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbo, V.C.D.; Jara, C.P.; Mendes, N.F.; Morari, J.; Velloso, L.A.; Araujo, E.P. Interleukin-6 Expression by Hypothalamic Microglia in Multiple Inflammatory Contexts: A Systematic Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1365210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliani, C.; Bucci, I.; Napolitano, G. The Role of the Transcription Factor Nuclear Factor-kappa B in Thyroid Autoimmunity and Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, S.; Maguire, O.; Campbell, M.J. Transcription factor co-repressors in cancer biology: Roles and targeting. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.J.; Karmakar, S.; Pace, M.C.; Gao, T.; Smith, C.L. The silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor (SMRT) corepressor is required for full estrogen receptor alpha transcriptional activity. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 5933–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, L.; Ingles-Esteve, J.; Robert-Moreno, A.; Bigas, A. IkappaBalpha and p65 regulate the cytoplasmic shuttling of nuclear corepressors: Cross-talk between Notch and NFkappaB pathways. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.D.; Gong, C.; Lau, S.L.Y.; Yang, N.; Wong, O.G.W.; Cheung, A.N.Y.; Tsang, J.W.H.; Chan, K.Y.K.; Khoo, U.S. SpliceArray Profiling of Breast Cancer Reveals a Novel Variant of NCOR2/SMRT That Is Associated with Tamoxifen Resistance and Control of ER alpha Transcriptional Activity. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, C.; Man, E.P.S.; Tsoi, H.; Lee, T.K.W.; Lee, P.; Ma, S.T.; Wong, L.S.; Luk, M.Y.; Rakha, E.A.; Green, A.R.; et al. BQ323636.1, a Novel Splice Variant to NCOR2, as a Predictor for Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3681–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.J.; Dai, P.; Lu, J.F.; Lou, M.A.; Clarke, R.; Nazarov, V. AIB1 gene amplification and the instability of polyQ encoding sequence in breast cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreos, R.; Ambrosini, G.; Perier, R.C.; Bucher, P. The Eukaryotic Promoter Database: Expansion of EPDnew and new promoter analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D92–D96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottis, A.; Mouchiroud, L.; Auwerx, J. Emerging roles of the corepressors NCoR1 and SMRT in homeostasis. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; Yang, X.Y.; Mihalic, K.; Xiao, W.H.; Li, D.P.; Farrar, W.L. Activation of estrogen receptor blocks interleukin-6-inducible cell growth of human multiple myeloma involving molecular cross-talk between estrogen receptor and STAT3 mediated by co-regulator PLAS3. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31839–31844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galien, R.; Garcia, T. Estrogen receptor impairs interleukin-6 expression by preventing protein binding on the NF-kappa B site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 2424–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Csh. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crescenzo, R.; Abate, F.; Lasorsa, E.; Tabbo’, F.; Gaudiano, M.; Chiesa, N.; Di Giacomo, F.; Spaccarotella, E.; Barbarossa, L.; Ercole, E.; et al. Convergent Mutations and Kinase Fusions Lead to Oncogenic STAT3 Activation in Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 516–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.H.; Chen, M.T.; Wang, M.L.; Lee, Y.Y.; Chiou, G.Y.; Chien, C.S.; Huang, P.I.; Chen, Y.W.; Huang, M.C.; Chiou, S.H.; et al. Cisplatin-selected resistance is associated with increased motility and stem-like properties via activation of STAT3/Snail axis in atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1750–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Kalimutho, M.; Dunne, P.D.; Carson, R.; Allen, W.; Jithesh, P.V.; Redmond, K.L.; Sasazuki, T.; Shirasawa, S.; Blayney, J.; et al. ADAM17-Dependent c-MET-STAT3 Signaling Mediates Resistance to MEK Inhibitors in KRAS Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 1940–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, Y.; Waxman, S.; Germain, D. Tamoxifen stimulates the growth of cyclin D1—Overexpressing breast cancer cells by promoting the activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


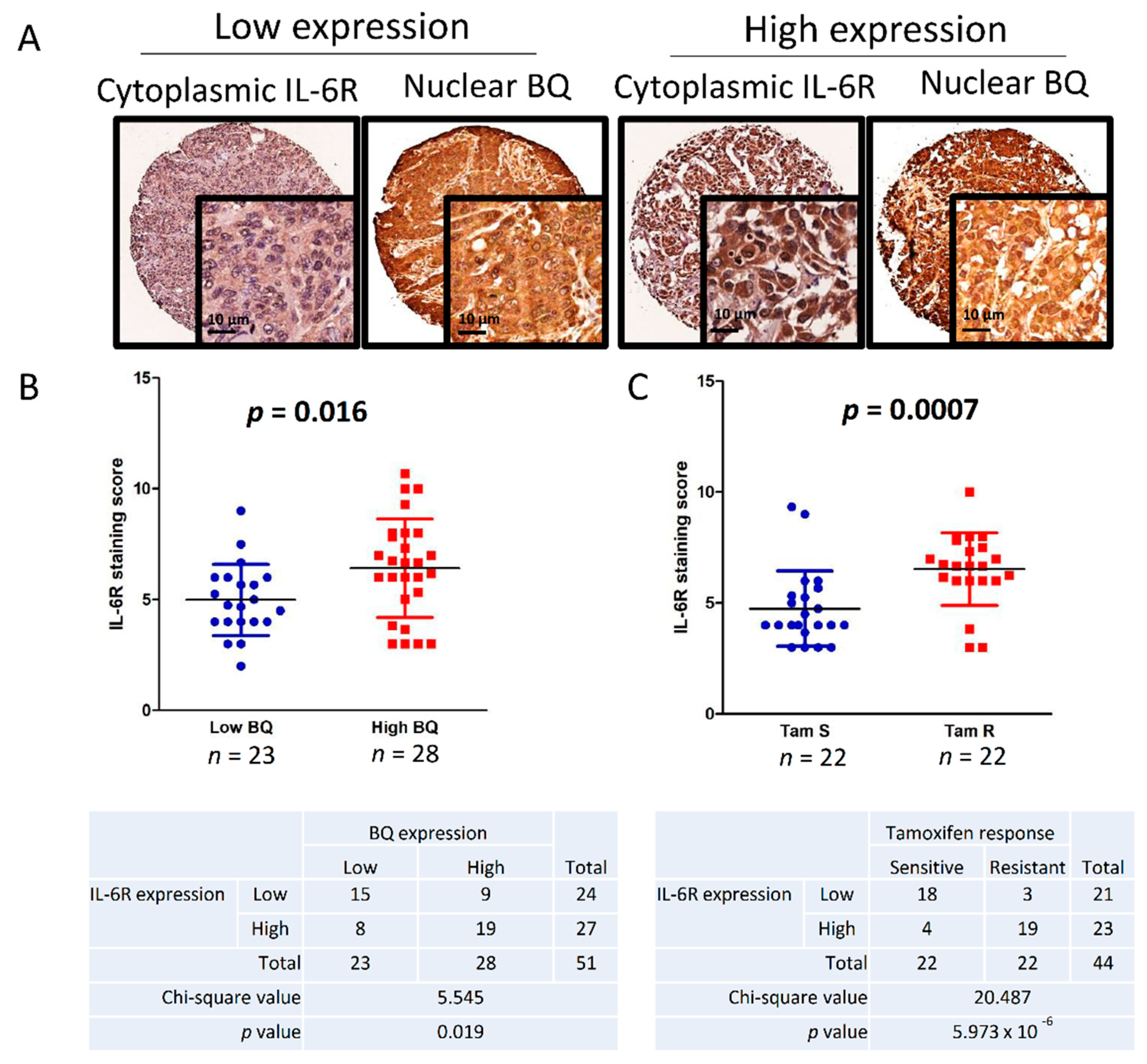
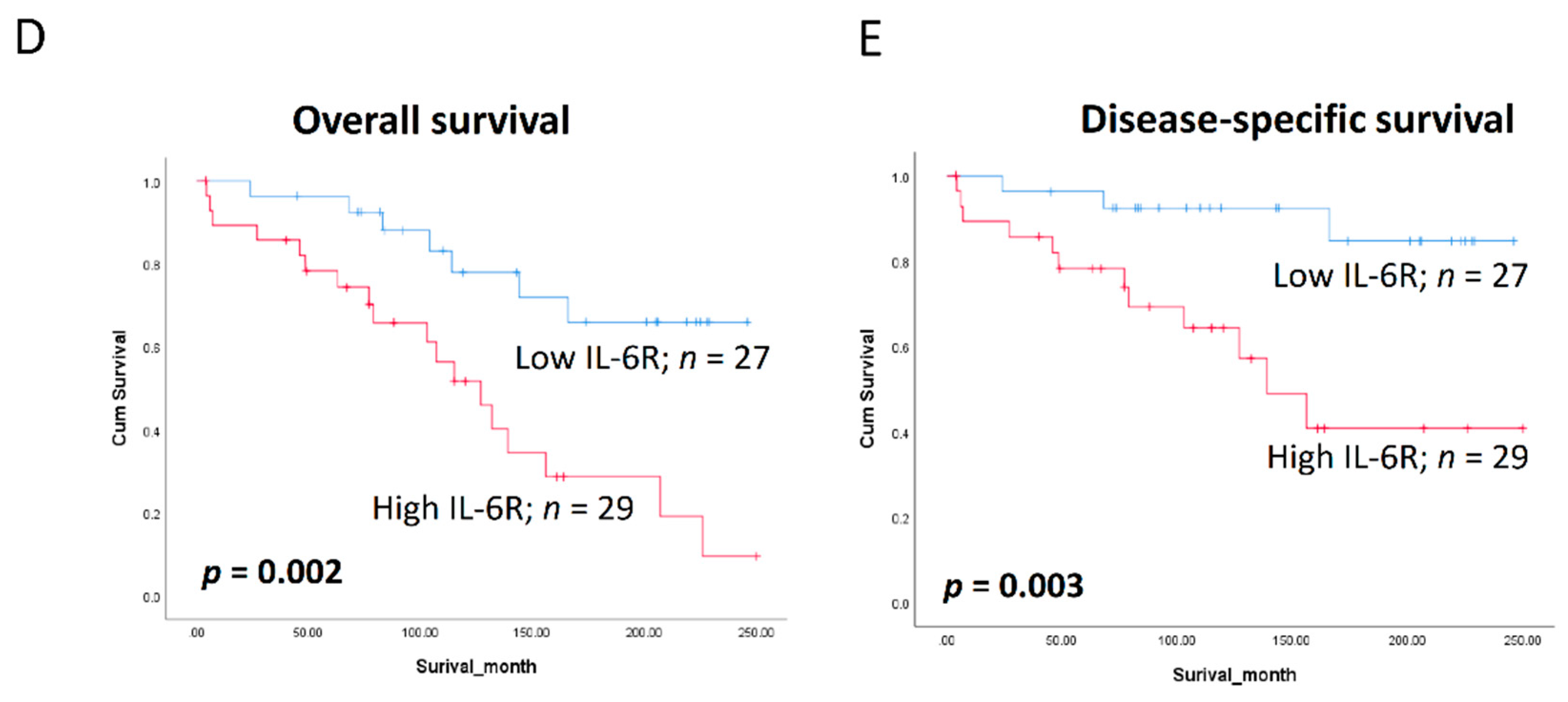
| Clinical Characteristic | Type | Cases | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of breast cancer patients | 132 | ||
| Median Age | 56 | ||
| T stage | |||
| I | 16 | 12.1 | |
| II | 25 | 18.9 | |
| III | 5 | 3.8 | |
| Missing | 86 | 65.2 | |
| Lymph Node status | |||
| Positive | 62 | 47.0 | |
| Negative | 56 | 42.4 | |
| Missing | 14 | 10.6 | |
| Tumor Grade | |||
| 1 | 19 | 14.4 | |
| 2 | 29 | 22.0 | |
| 3 | 71 | 53.8 | |
| Missing | 13 | 9.8 | |
| Tumor Size | |||
| <2 cm | 37 | 28.0 | |
| ≥2 cm | 53 | 40.2 | |
| Missing | 42 | 31.8 | |
| Estrogen Receptor status | |||
| Positive | 71 | 53.8 | |
| Negative | 23 | 17.4 | |
| Missing | 38 | 28.8 | |
| Progesterone receptor status | |||
| Positive | 48 | 36.3 | |
| Negative | 34 | 25.8 | |
| Missing | 50 | 37.9 | |
| HER2 receptor status | |||
| Positive | 33 | 25.0 | |
| Negative | 34 | 27.3 | |
| Missing | 50 | 47.7 | |
| Triple Negative status | |||
| Positive | 12 | 9.10 | |
| Negative | 68 | 51.5 | |
| Missing | 52 | 39.4 | |
| Clinical Characteristic | Type | Cases | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of ER+ breast cancer patients | 71 | ||
| Median Age | 51 | ||
| T stage | |||
| I | 8 | 11.3 | |
| II | 18 | 25.3 | |
| III | 3 | 4.2 | |
| Missing | 42 | 59.2 | |
| Lymph Node status | |||
| Positive | 37 | 52.1 | |
| Negative | 28 | 39.4 | |
| Missing | 6 | 8.5 | |
| Tumor Grade | |||
| 1 | 13 | 18.3 | |
| 2 | 21 | 29.6 | |
| 3 | 36 | 50.7 | |
| Missing | 1 | 1.4 | |
| Tumor Size | |||
| <2 cm | 22 | 31.0 | |
| ≥2 cm | 32 | 45.1 | |
| Missing | 17 | 23.9 | |
| Progesterone receptor status | |||
| Positive | 47 | 66.2 | |
| Negative | 12 | 16.9 | |
| Missing | 12 | 16.9 | |
| HER2 receptor status | |||
| Positive | 27 | 38.0 | |
| Negative | 23 | 32.4 | |
| Missing | 21 | 29.6 | |
| Clinical-Pathological Parameters | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristic | RR (95% CI) | p Value | RR (95% CI) | p Value |
| Age (n = 69) | 1.975 (0.931, 4.188) | 0.076 | ||
| T-stage (n = 28) | 8.097 (1.441, 45.491) | 0.018 | 4.262 (0.561, 32.405) | 0.161 |
| Lymph-node involvement (n = 63) | 0.904 (0.412, 1.986) | 0.802 | ||
| Tumor-Grade (n = 68) | 1.171 (0.550, 2.497) | 0.682 | ||
| Histological type (n = 69) | 1.166 (0.351, 3.873) | 0.802 | ||
| HER2 status (n = 48) | 1.159 (0.445, 3.016) | 0.762 | ||
| Tumor size (n = 52) | 0.941 (0.388, 2.278) | 0.892 | ||
| Cases with high IL-6R cytoplasm score (n = 55) | 3.716 (1.537, 8.984) | 0.004 | 10.967 (1.169, 102.878) | 0.036 |
| Clinical-Pathological Parameters | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical characteristic | RR (95% CI) | p Value | RR (95% CI) | p Value |
| Age (n = 69) | 1.198 (0.472, 3.040) | 0.703 | ||
| T-stage (n = 28) | 8.097 (1.441, 45.491) | 0.018 | ||
| Lymph-node involvement (n = 63) | 1.402 (0.508, 3.864) | 0.514 | ||
| Tumor-Grade (n = 68) | 3.672 (1.208, 11.162) | 0.022 | 4.612 (1.298, 16.386) | 0.018 |
| Histological type (n = 71) | 1.022 (0.235, 4.452) | 0.976 | ||
| HER2 status (n = 48) | 1.777 (0.517, 6.110) | 0.361 | ||
| Tumor size (n = 52) | 1.472 (0.442, 4.898) | 0.529 | ||
| Cases with high IL-6R cytoplasm score (n = 55) | 5.664 (1.569, 20.441) | 0.008 | 5.586 (1.534, 20.349) | 0.009 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsoi, H.; Man, E.P.S.; Chau, K.M.; Khoo, U.-S. Targeting the IL-6/STAT3 Signalling Cascade to Reverse Tamoxifen Resistance in Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071511
Tsoi H, Man EPS, Chau KM, Khoo U-S. Targeting the IL-6/STAT3 Signalling Cascade to Reverse Tamoxifen Resistance in Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2021; 13(7):1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071511
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsoi, Ho, Ellen P. S. Man, Ka Man Chau, and Ui-Soon Khoo. 2021. "Targeting the IL-6/STAT3 Signalling Cascade to Reverse Tamoxifen Resistance in Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer" Cancers 13, no. 7: 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071511
APA StyleTsoi, H., Man, E. P. S., Chau, K. M., & Khoo, U.-S. (2021). Targeting the IL-6/STAT3 Signalling Cascade to Reverse Tamoxifen Resistance in Estrogen Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers, 13(7), 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13071511






