Non-Oncological Neuroradiological Manifestations in NF1 and Their Clinical Implications
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Brain
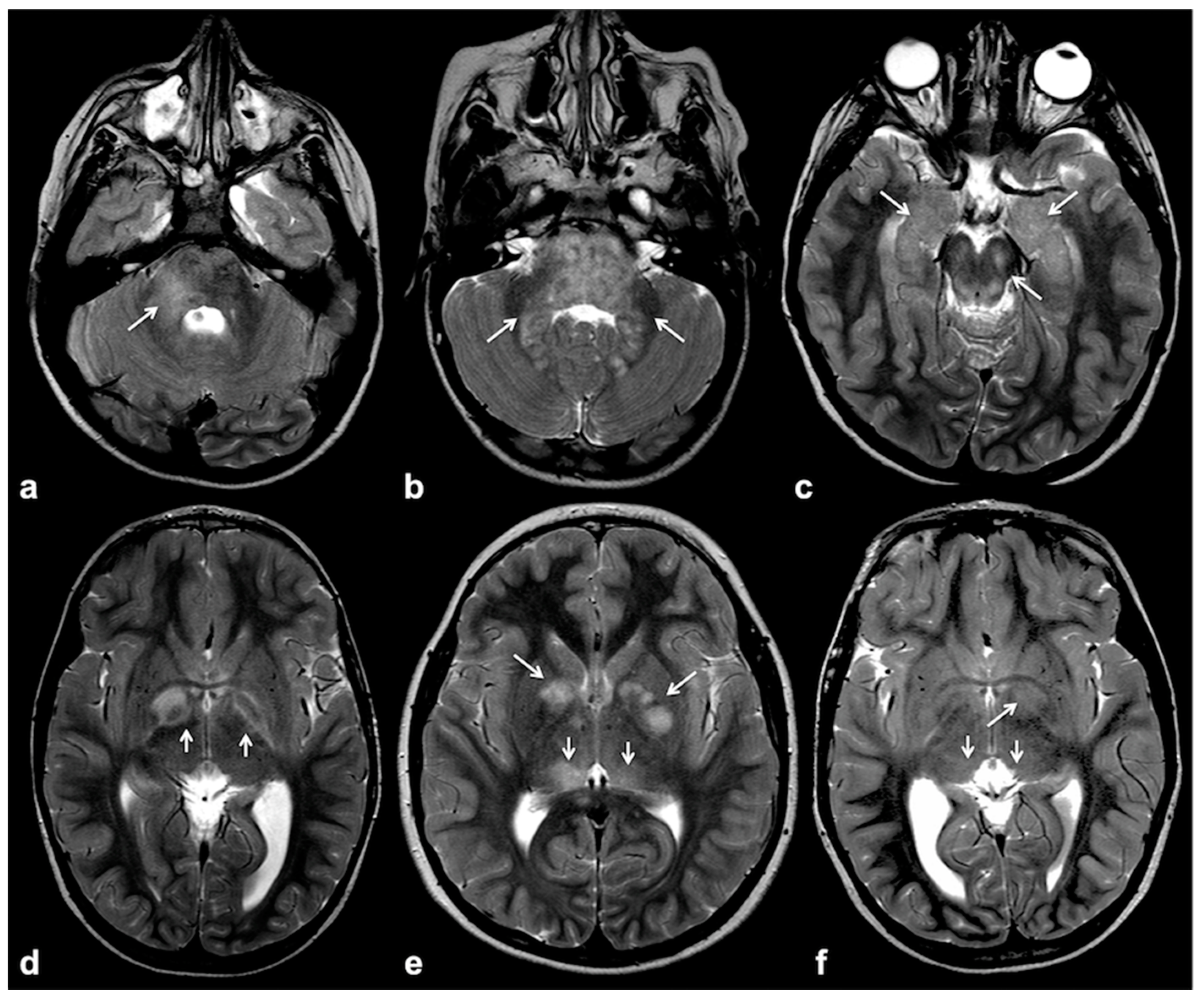
2.1. Focal Abnormal Signal Intensities: Neuroradiological Tips and Tricks
2.2. Volume, Structural and Functional Connectivity Changes: More Than Meet the Eye
2.3. Epileptogenic Lesions in NF1
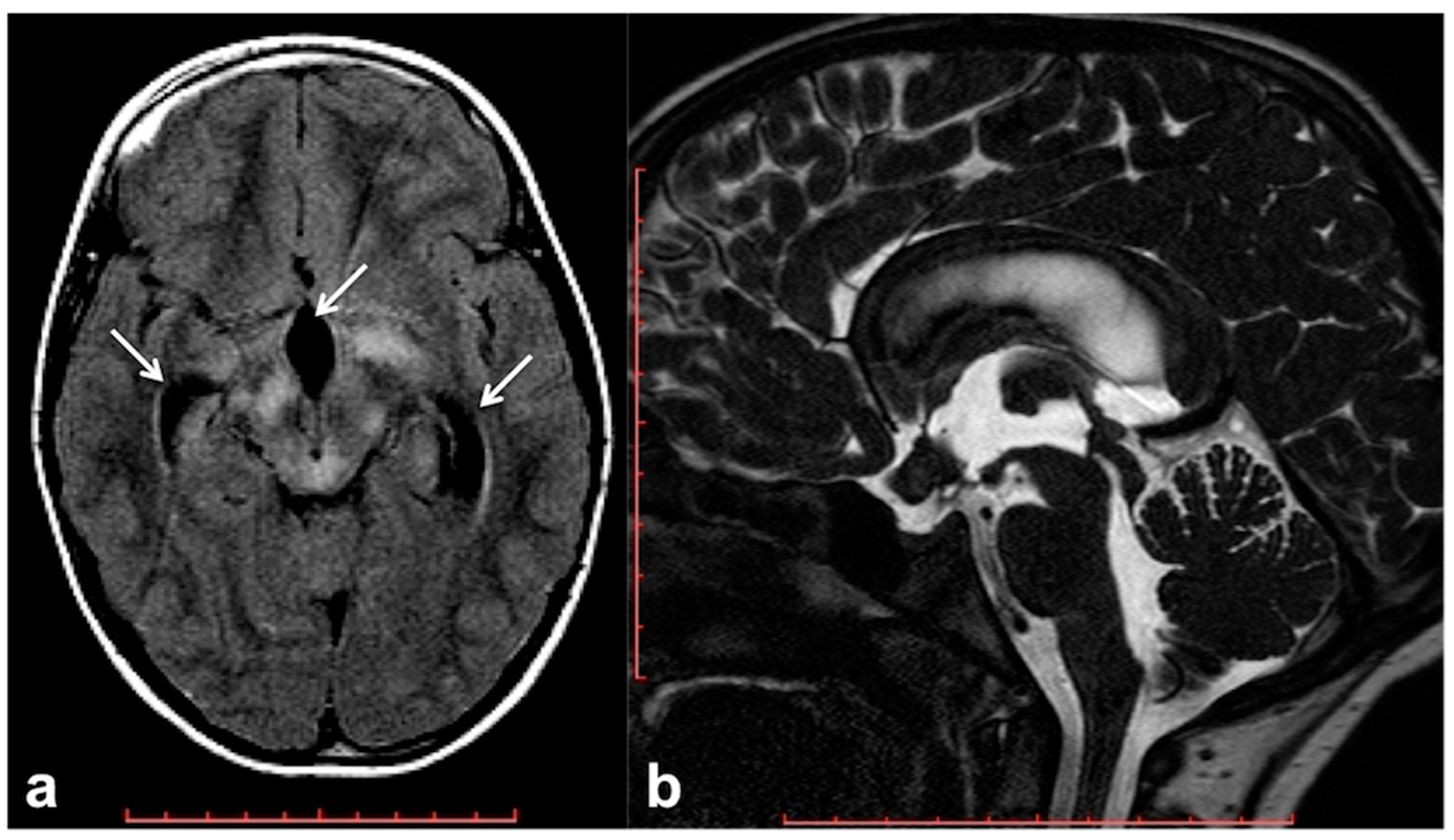
2.4. Altered Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics: Obstructive Hydrocephalus Other Than Tumor-Related
2.5. CNS Vascular Manifestations of NF1
3. Skull and Orbit
3.1. Sutural Defects
3.2. Skull Bone Defects and Associated Dural Dysplasia
3.2.1. Sphenoid Wing Dysplasia
3.2.2. Imaging Manifestation of Orbital Involvement
3.2.3. Imaging Manifestation of Oral Involvement
3.3. Macrocephaly
4. Spine
4.1. Medullary UBOs: A Stumbling Block to Neuroimaging
4.2. Dural Ectasia, Meningocele and Spinal Deformity: An Etiopathological Continuum
4.3. Chiari Malformation and Syrinx
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Hirbe, A.C.; Gutmann, D.H. Neurofi bromatosis type 1: A multidisciplinary approach to care. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jett, K.; Friedman, J.M. Clinical and genetic aspects of neurofibromatosis 1. Genet. Med. 2009, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cichowski, K.; Jacks, T. NF1 Tumor Suppressor Gene Function: Narrowing the GAP. Cell 2001, 104, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiuru, M.; Busam, K.J. The NF1 gene in tumor syndromes and melanoma. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legius, E.; Brems, H. Genetic basis of neurofibromatosis type 1 and related conditions, including mosaicism. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2285–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczkowska, M.; Callens, T.; Chen, Y.; Gomes, A.; Hicks, A.D.; Sharp, A.; Johns, E.; Uhas, K.A.; Armstrong, L.; Bosanko, K.A.; et al. Clinical spectrum of individuals with pathogenic NF1 missense variants affecting p.Met1149, p.Arg1276, and p.Lys1423: Genotype–phenotype study in neurofibromatosis type 1. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 41, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Gianino, S.M.; Gutmann, D.H. Neurofibromatosis-1 regulation of neural stem cell proliferation and multilineage differentiation operates through distinct RAS effector pathways. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassina, M.; Frizziero, L.; Opocher, E.; Parrozzani, R.; Sorrentino, U.; Viscardi, E.; Miglionico, G.; Midena, E.; Clementi, M.; Trevisson, E. Optic Pathway Glioma in Type 1 Neurofibromatosis: Review of Its Pathogenesis, Diagnostic Assessment, and Treatment Recommendations. Cancers 2019, 11, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santoro, C.; Picariello, S.; Palladino, F.; Spennato, P.; Melis, D.; Roth, J.; Cirillo, M.; Quaglietta, L.; D’Amico, A.; Gaudino, G.; et al. Retrospective Multicentric Study on Non-Optic CNS Tumors in Children and Adolescents with Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Cancers 2020, 12, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.D.A.; Gutmann, D.H. Brain tumors in neurofibromatosis type 1. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, C.; Perrotta, S.; Picariello, S.; Scilipoti, M.; Cirillo, M.; Quaglietta, L.; Cinalli, G.; Cioffi, D.; Di Iorgi, N.; Maghnie, M.; et al. Pretreatment Endocrine Disorders Due to Optic Pathway Gliomas in Pediatric Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e2214–e2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggs-Andrews, K.A.; Gutmann, D.H. Modeling cognitive dysfunction in neurofibromatosis-1. Trends Neurosci. 2013, 36, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyman, S.L.; Shores, A.; North, K.N. The nature and frequency of cognitive deficits in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Neurology 2005, 65, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, D.S.; Hyman, S.L.; Steinberg, A.; North, K.N. Age-related findings on MRI in neurofibromatosis type 1. Pediatr. Radiol. 2006, 36, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes Ferraz-Filho, J.R.; Munis, M.P.; Souza, A.S.; Sanches, R.A.; Goloni-Bertollo, E.M.; Pavarino-Bertelli, E.C. Unidentified bright objects on brain MRI in children as a diagnostic criterion for neurofibromatosis type 1. Pediatr. Radiol. 2008, 38, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes Ferraz-Filho, R.J.; da Rocha, A.J.; Pontes Muniz, M.; Soares Souza, A.; Goloni-Bertollo, E.M.; Pavarino-Bertelli, E.C. Unidentified bright objects in neurofibromatosis type 1: Conventional MRI in the follow-up and correlation of microstructural lesions on diffusion tensor images. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2012, 16, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvez, S.; Levy, R.; Calvez, R.; Roux, C.-J.; Grévent, D.; Purcell, Y.; Beccaria, K.; Blauwblomme, T.; Grill, J.; Dufour, C.; et al. Focal Areas of High Signal Intensity in Children with Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Expected Evolution on MRI. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudou, E.; Nemmi, F.; Biotteau, M.; Maziero, S.; Peran, P.; Chaix, Y. Can the Cognitive Phenotype in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) Be Explained by Neuroimaging? A Review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 10, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salman, M.S.; Hossain, S.; Alqublan, L.; Bunge, M.; Rozovsky, K. Cerebellar radiological abnormalities in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Part 1—Clinical and neuroimaging findings. Cerebellum Ataxias 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.S.; Hossain, S.; Gorun, S.; Alqublan, L.; Bunge, M.; Rozovsky, K. Cerebellar radiological abnormalities in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Part 2—A neuroimaging natural history study with clinical correlations. Cerebellum Ataxias 2018, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeBella, K.; Poskitt, K.; Szudek, J.; Friedman, J.M. Use of “unidentified bright objects” on MRI for diagnosis of neurofibromatosis 1 in children. Neurology 2000, 54, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Paolo, D.P.; Zimmerman, R.A.; Rorke, L.B.; Zackai, E.H.; Bilaniuk, L.T.; Yachnis, A.T. Neurofibromatosis type 1: Pathologic substrate of high-signal-intensity foci in the brain. Radiology 1995, 195, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkovich, M.J.; Tan, C.H.; Kline, C.; Dale, A.M.; Jernigan, T.L.; Sugrue, L.P.; Barkovich, A.J.; Desikan, R.S.; Nillo, R.M.; Li, Y.; et al. Abnormal Morphology of Select Cortical and Subcortical Regions in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Radiology 2018, 289, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, H.; Barkovich, A.J.; Edwards, M.S.; Ciricillo, S.M. Evolution of high-intensity basal ganglia lesions on T1-weighted MR in neurofibromatosis type 1. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1996, 17, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alkan, A.; Sigirci, A.; Kutlu, R.; Ozcan, H.; Erdem, G.; Aslan, M.; Ates, O.; Yakinci, C.; Egri, M. Neurofibromatosis type 1: Diffusion weighted imaging findings of brain. Eur. J. Radiol. 2005, 56, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tritt, S.; Hillenbrand, N.; Liesirova, K.; Moein, G.; Kieslich, M.; Porto, L. Comparison of the detectability of UBOs in Neurofibromatosis Type I patients with proton density-weighted and FLAIR sequences in 3T MRI. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.Y.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Koth, C.W.; Denckla, M.B.; Barker, P.B. Thalamic involvement in neurofibromatosis type 1: Evaluation with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 47, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, C.; Chabernaud, C.; Barantin, L.; Bertrand, P.; Sembely, C.; Sirinelli, D.; Castelnau, P.; Cottier, J.-P. Proton MR spectroscopic imaging of basal ganglia and thalamus in neurofibromatosis type 1: Correlation with T2 hyperintensities. Neuroradiology 2010, 53, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billiet, T.; Mädler, B.; D’Arco, F.; Peeters, R.; Deprez, S.; Plasschaert, E.; Leemans, A.; Zhang, H.; Bergh, B.V.D.; Vandenbulcke, M.; et al. Characterizing the microstructural basis of “unidentified bright objects” in neurofibromatosis type 1: A combined in vivo multicomponent T2 relaxation and multi-shell diffusion MRI analysis. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 4, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenbaum, T.; Engelbrecht, V.; Krölls, W.; Van Dorsten, F.A.; Hoehn-Berlage, M.; Lenard, H.-G. MRI abnormalities in neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1): A study of men and mice. Brain Dev. 1999, 21, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eby, N.S.; Griffith, J.L.; Gutmann, D.H.; Morris, S.M. Adaptive functioning in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Relationship to cognition, behavior, and magnetic resonance imaging. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2019, 61, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Barbarot, S.; Charbonnier, V.; Gayet-Delacroix, M.; Stalder, J.-F.; Roulin, J.-L.; Le Gall, D. Examining the frontal subcortical brain vulnerability hypothesis in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Are T2-weighted hyperintensities related to executive dysfunction? Neuropsychology 2015, 29, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koini, M.; Rombouts, S.A.R.B.; Veer, I.M.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Huijbregts, S.C.J. White matter microstructure of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 and its relation to inhibitory control. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017, 11, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goh, W.H.S.; Khong, P.-L.; Leung, C.S.Y.; Wong, V.C.N. T 2-Weighted Hyperintensities (Unidentified Bright Objects) in Children With Neurofibromatosis 1: Their Impact on Cognitive Function. J. Child Neurol. 2004, 19, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabernaud, C.; Sirinelli, D.; Barbier, C.; Cottier, J.-P.; Sembely, C.; Giraudeau, B.; Deseille-Turlotte, G.; Lorette, G.; Barthez, M.-A.; Castelnau, P. Thalamo-Striatal T2-Weighted Hyperintensities (Unidentified Bright Objects) Correlate With Cognitive Impairments in Neurofibromatosis Type 1 During Childhood. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2009, 34, 736–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMario, F.J. Brain Abnormalities in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex. J. Child Neurol. 2004, 19, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, B.D., III; Slopis, J.M.; Jackson, E.F.; De Winter, A.E.; Leeds, N.E. Brain volume in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Relation to neuropsychological status. Neurology 2000, 54, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giedd, J.N.; Castellanos, F.; Casey, B.J.; Kozuch, P.; King, A.C.; Hamburger, S.D.; Rapoport, J.L. Quantitative morphology of the corpus callosum in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 1994, 151, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cutting, L.; Cooper, K.; Koth, C.; Mostofsky, S.; Kates, W.; Denckla, M.; Kaufmann, W. Megalencephaly in NF1: Predominantly white matter contribution and mitigation by ADHD. Neurology 2002, 59, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Kurtcan, S.; Alkan, A.; Guler, S.; Filiz, M.; Yilmaz, T.F.; Sahin, T.U.; Aralasmak, A. Relationship between the corpus callosum and neurocognitive disabilities in children with NF-1: Diffusion tensor imaging features. Clin. Imaging 2016, 40, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violante, I.R.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Silva, E.D.; Castelo-Branco, M. Gyrification, cortical and subcortical morphometry in neurofibromatosis type 1: An uneven profile of developmental abnormalities. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2013, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huijbregts, S.C.; Loitfelder, M.; Rombouts, S.A.; Swaab, H.; Verbist, B.M.; Arkink, E.B.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Veer, I.M. Cerebral volumetric abnormalities in Neurofibromatosis type 1: Associations with parent ratings of social and attention problems, executive dysfunction, and autistic mannerisms. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2015, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santoro, C.; Giugliano, T.; Bernardo, P.; Palladino, F.; Torella, A.; Blanco, F.D.V.; Onore, M.E.; Carotenuto, M.; Nigro, V.; Piluso, G. A novel RAB39B mutation and concurrent de novo NF1 mutation in a boy with neurofibromatosis type 1, intellectual disability, and autism: A case report. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudou, E.; Nemmi, F.; Biotteau, M.; Maziero, S.; Assaiante, C.; Cignetti, F.; Vaugoyeau, M.; Audic, F.; Peran, P.; Chaix, Y. Are morphological and structural MRI characteristics related to specific cognitive impairments in neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) children? Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2020, 28, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billingsley, R.L.; Schrimsher, G.W.; Jackson, E.F.; Slopis, J.M.; Moore, B.D., III. Significance of Planum Temporale and Planum Parietale Morphologic Features in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Billingsley, R.L.; Jackson, E.F.; Slopis, J.M.; Swank, P.R.; Mahankali, S.; Moore, B.D., III. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Phonologic Processing in Neurofibromatosis 1. J. Child. Neurol. 2003, 18, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engelen, S.; Krab, L.C.; Moll, H.A.; de Goede-Bolder, A.; Pluijm, S.; Catsman-Berrevoets, C.; Elgersma, Y.; Lequin, M.H. Quantitative Differentiation Between Healthy and Disordered Brain Matter in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type I Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemmi, F.; Cignetti, F.; Assaiante, C.; Maziero, S.; Audic, F.; Péran, P.; Chaix, Y. Discriminating between neurofibromatosis-1 and typically developing children by means of multimodal MRI and multivariate analyses. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2019, 40, 3508–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsgodt, K.H.; Rosser, T.; Lutkenhoff, E.S.; Cannon, T.D.; Silva, A.; Bearden, C.E. Alterations in White Matter Microstructure in Neurofibromatosis-1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.F.; Montojo, C.A.; Haut, K.M.; Karlsgodt, K.H.; Hansen, L.; Congdon, E.; Rosser, T.; Bilder, R.M.; Silva, A.J.; Bearden, C.E. Spatial working memory in neurofibromatosis 1: Altered neural activity and functional connectivity. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 15, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loitfelder, M.; Huijbregts, S.C.; Veer, I.M.; Swaab, H.S.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Schmidt, R.; Rombouts, S.A. Functional Connectivity Changes and Executive and Social Problems in Neurofibromatosis Type I. Brain Connect. 2015, 5, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomson, S.N.; Schreiner, M.J.; Narayan, M.; Rosser, T.; Enrique, N.; Silva, A.J.; Allen, G.I.; Bookheimer, S.Y.; Bearden, C.E. Resting state functional MRI reveals abnormal network connectivity in neurofibromatosis 1. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2015, 36, 4566–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Violante, I.R.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Cunha, G.; Bernardino, I.; Duarte, J.V.; Ramos, F.; Saraiva, J.; Silva, E.; Castelo-Branco, M. Abnormal Brain Activation in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: A Link between Visual Processing and the Default Mode Network. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, M.; Violante, R.; Bernardino, I.; Edden, R.; Castelo-Branco, M. ScienceDirect Abnormal relationship between GABA, neurophysiology and impulsive behavior in neurofibromatosis type 1. Cortex 2014, 4, 194–208. [Google Scholar]
- Violante, I.R.; Ribeiro, M.J.; Edden, R.A.E.; Guimarães, P.; Bernardino, I.; Rebola, J.; Cunha, G.; Silva, E.; Castelo-Branco, M. GABA deficit in the visual cortex of patients with neurofibromatosis type 1: Genotype–phenotype correlations and functional impact. Brain 2013, 136, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachon, C.; Iannuzzi, S.; Chaix, Y. Behavioural and cognitive phenotypes in children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1): The link with the neurobiological level. Brain Dev. 2011, 33, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, P.; Santoro, C.; Rubino, A.; Mirone, G.; Cinalli, G. Epilepsy surgery in neurofibromatosis type 1: An overlooked therapeutic approach. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2909–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoraro, A.; Arehart, E.; Gallentine, W.; Radtke, R.; Smith, E.; Pizoli, C.; Kansagra, S.; Abdelnour, E.; McLendon, R.; Mikati, M.A. Epilepsy & Behavior Epilepsy in neurofibromatosis type 1. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 73, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Ostendorf, A.P.; Gutmann, D.H.; Weisenberg, J.L.Z. Epilepsy in individuals with neurofibromatosis type 1. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1810–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, P.; Cinalli, G.; Santoro, C. Epilepsy in NF1: A systematic review of the literature. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2333–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, H.-Y.; Fung, H.-C.; Wang, C.-J.; Chin, S.-C.; Wu, T. Epileptic seizures in neurofibromatosis type 1 are related to intracranial tumors but not to neurofibromatosis bright objects. Seizure 2011, 20, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moutal, A.; Dustrude, E.T.; Khanna, R. Sensitization of Ion Channels Contributes to Central and Peripheral Dysfunction in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 3342–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafstrom, C.E.; Staedtke, V.; Comi, A.M. Epilepsy Mechanisms in Neurocutaneous Disorders: Tuberous Sclerosis Complex, Neurofibromatosis Type 1, and Sturge–Weber Syndrome. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serdaroglu, E.; Konuskan, B.; Oguz, K.K.; Gurler, G.; Yalnizoglu, D.; Anlar, B. Epilepsy in neurofibromatosis type 1: Diffuse cerebral dysfunction? Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 98, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, C.; Jacques, T.; Kahane, P.; Polster, T.; Isnard, J.; Leijten, F.S.; Özkara, Ç.; Tassi, L.; Giordano, F.; Castagna, M.; et al. Epilepsy surgery in Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 105, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, J.; Constantini, S.; Cinalli, G. Neurofibromatosis type 1–related hydrocephalus: Causes and treatment considerations. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2385–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill Kang, Y.; Park, E.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Thomale, U.W.; Shim, K.W. Altered cerebrospinal fluid dynamics in neurofibromatosis type l: Severe arachnoid thickening in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 may cause abnormal CSF dynamic. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanrikulu, B.; Özek, M.M. Neurofibromatosis and Hydrocephalus. In Pediatric Hydrocephalus; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1107–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Glombova, M.; Petrak, B.; Lisy, J.; Zamecnik, J.; Sumerauer, D.; Liby, P. Brain gliomas, hydrocephalus and idiopathic aqueduct stenosis in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Brain Dev. 2019, 41, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.; Ber, R.; Wisoff, J.H.; Hidalgo, E.T.; Limbrick, D.D.; Berger, D.S.; Thomale, U.W.; Schulz, M.; Cinalli, G.; Santoro, C.; et al. Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 1: A Multicenter International Experience. World Neurosurg. 2017, 107, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, B.; Huisman, T.A.G.M.; Tekes, A.; Bergner, A.; Blakeley, J.O.; Jordan, L.C. Spectrum and Prevalence of Vasculopathy in Pediatric Neurofibromatosis Type 1. J. Child. Neurol. 2012, 28, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rerat, K.; Parker, F.; Nasser, G.; Vidaud, D.; Riant, F.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Denier, C. Occurrence of multiple Cerebral Cavernous Malformations in a patient with Neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 350, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I.; Riedinger, M.; Maya, M.M. Frequency of incidental intracranial aneurysms in neurofibromatosis type 1. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2005, 134A, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morvan, T.; De Broucker, F.; De Broucker, T. Subarachnoid hemorrhage in neurofibromatosis type 1: Case report of extracranial cerebral aneurysm rupture into a meningocele. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 38, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, A.G.; North, K.N. Cerebrovascular dysplasia in neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto-Duarte, B.; Andrade-Gomes, F.H.; Arriaga, M.B.; Araujo-Pereira, M.; Cubillos-Angulo, J.M.; Bruno Andrade, B. Association between neurofibromatosis type 1 and cerebrovascular diseases in children: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0241096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, C.; Giugliano, T.; Kraemer, M.; Torella, A.; Schwitalla, J.C.; Cirillo, M.; Melis, D.; Berlit, P.; Nigro, V.; Perrotta, S.; et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies MRVI1 as a susceptibility gene for moyamoya syndrome in neurofibromatosis type 1. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandicourt, P.; Bonnet, L.; Béjot, Y.; Drouet, C.; Moulin, T.; Thines, L. Moya-Moya syndrome after cranial radiation for optic glioma with NF1. Case report and literature review of syndromic cases. Neurochirurgie 2018, 64, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, D.; Brandsema, J.F.; Armstrong, D.; Parkin, P.C.; DeVeber, G.; MacGregor, D.; Logan, W.J.; Askalan, R. Cerebral Arteriopathy in Children With Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Pediatrics 2009, 124, e476–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoal, J.K.S.F.; Paschoal, F., Jr.; de Lima, F.; Pinho, R.; Pereira Vilanova, L.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Masruha, M.R. Detection of Cerebral Vasculopathy by Transcranial Doppler in Children With Neurofibromatosis Type 1. J. Child. Neurol. 2016, 31, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, A.; Ugga, L.; Cocozza, S.; Giorgio, S.M.D.A.; Cicala, D.; Santoro, C.; Melis, D.; Cinalli, G.; Brunetti, A.; Pappatà, S. Multimodal evaluation of the cerebrovascular reserve in Neurofibromatosis type 1 patients with Moyamoya syndrome. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Doty, S.B.; Hicks, J.; Phan, K.; Mendoza-Londono, R.; Blazo, M.; Tran, A.; Carter, S.; Lewis, R.A.; Plon, S.E.; et al. Generalized metabolic bone disease in Neurofibromatosis type I. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 94, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Nyman, J.S.; Ono, K.; Stevenson, D.A.; Yang, X.; Elefteriou, F. Mice lacking Nf1 in osteochondroprogenitor cells display skeletal dysplasia similar to patients with neurofibromatosis type I. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3910–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solanki, C.; Ramachandran, S.; Devi, B.I.; Sharma, R. Calvarial defects in the region of the lambdoid suture in neurofibromatosis type-1 patients. J. Pediatric Neurosci. 2015, 10, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Knight, R.D.; Schilling, T.F. Cranial Neural Crest and Development of the Head Skeleton. In Neural Crest Induction and Differentiation. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Saint-Jeannet, J.P., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 589, pp. 120–133. [Google Scholar]
- Chauvel-Picard, J.; Lion-Francois, L.; Beuriat, P.-A.; Paulus, C.; Szathmari, A.; Mottolese, C.; Gleizal, A.; Di Rocco, F. Craniofacial bone alterations in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heervä, E.; Peltonen, S.; Pirttiniemi, P.; Happonen, R.-P.; Visnapuu, V.; Peltonen, J. Short mandible, maxilla and cranial base are common in patients with neurofibromatosis 1. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 119, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajeski, B.L.; Kettner, N.W.; Awwad, E.E.; Boesch, R.J. Neurofibromatosis type I: Clinical and imaging features of Von Recklinghausen’s disease. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2003, 26, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskochil, D.H.; Stevenson, D.A. Skeletal Manifestations in NF1. In Multidisciplinary Approach to Neurofibromatosis Type 1; Tadini, G., Legius, E., Brems, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, V.; Mahore, A.; Patil, M.; Sathe, P.; Kaswa, A.; Gore, S.; Dharurkar, P.; Kawale, J. Brain Herniation in Neurofibromatosis with Dysplasia of Occipital Bone and Posterior Skull Base. Case Rep. Neurol. Med. 2015, 2015, 816079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malhotra, A.; Tu, L.; Kalra, V.B.; Wu, X.; Mian, A.; Mangla, R.; Michaelides, E.; Sanelli, P.; Gandhi, D. Neuroimaging of Meckel’s cave in normal and disease conditions. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serindere, M.; Taşar, M.; Hamcan, S.; Bozlar, U. Imaging Findings of Jugular Foramen Meningocele in a Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Patient. Case Rep. Radiol. 2017, 2017, 7047696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milburn, J.M.; Gimenez, C.R.; Dutweiler, E. Imaging Manifestations of Orbital Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Ochsner J. 2016, 16, 431–434. [Google Scholar]
- Oystreck, D.T.; Morales, J.; Chaudhry, I.; Alorainy, I.A.; Elkhamary, S.M.; Pasha, T.M.; Bosley, T.M. Visual Loss in Orbitofacial Neurofibromatosis Type 1. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 2168–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkatan, H.M.; Bakry, S.S. Ocular Findings in Neurofibromatosis. Neurofibromatosis Curr. Trends. Future Dir. 2015, 14 (Suppl. 1), 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Visnapuu, V.; Peltonen, S.; Alivuotila, L.; Happonen, R.-P.; Peltonen, J. Craniofacial and oral alterations in patients with Neurofibromatosis 1. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2018, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, M.; Spurlock, G.; Kluwe, L.; Chuzhanova, N.; Bennett, E.; Thomas, N.; Guha, A.; Mautner, V. The spectrum of somatic and germline NF1 mutations in NF1 patients with spinal neurofibromas. Neurogenetics 2009, 10, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, A.; Mazio, F.; Ugga, L.; Cuocolo, R.; Cirillo, M.; Santoro, C.; Perrotta, S.; Melis, D.; Brunetti, A. Medullary unidentified bright objects in Neurofibromatosis type 1: A case series. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katz, B.H.; Quencer, R.M. Hamartomatous spinal cord lesion in neurofibromatosis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1989, 10 (Suppl. 5), S101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rüegger, A.D.; Coleman, L.; Hansford, J.R.; McLean, N.; Dabscheck, G. Spinal Cord Hyperintensities in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Are They the Cord Equivalent of Unidentified Bright Objects in the Brain? Pediatr. Neurol. 2018, 86, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; George, K.J. The association of spinal deformity with dural ectasia in neurofibromatosis type 1. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 33, 620–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdabi, I.; El Jouadi, H.; Edderai, M. Dural ectasia: A manifestation of type 1 neurofibromatosis. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2018, 31, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirikos, A.I.; Saifuddin, A.; Noordeen, M.H. Spinal deformity in neurofibromatosis type-1: Diagnosis and treatment. Eur. Spine J. 2005, 14, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, R.; Dombi, E.; Akshintala, S.; Baldwin, A.; Widemann, B.C. Characterization of spinal findings in children and adults with neurofibromatosis type 1 enrolled in a natural history study using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2015, 121, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Goyal, T.; Hunt, M.A. Intrathoracic meningocele associated with neurofibromatosis Type 1 and a novel technique for surgical repair: Case report. J. Neurosurg. Spine 2017, 27, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenov, K.V.; Spiro, A.S.; Krajewski, K.L.; Stücker, R.; Kunkel, P. Management of spinal deformities and tibial pseudarthrosis in children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1). Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2409–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainov, N.G.; Heidecke, V.; Burkert, W. Thoracic and lumbar meningocele in neurofibromatosis type 1. Report of two cases and review of the literature. Neurosurg. Rev. 1995, 18, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.G.; Chang, Y.J.; Cho, K.D.; Hong, J.T. Collaborative treatment of huge intrathoracic meningoceles associated with neurofibromatosis type 1: A case report. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2015, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Copp, A.J.; Stanier, P.; Greene, N.D.E. Genetic Basis of Neural Tube Defects. In Textbook of Pediatric Neurosurgery; Di Rocco, C., Pang, D., Rutka, J., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.-M.; Zhang, W.-J.; Huang, A.-B.; Chen, Q.; He, Y.-L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.-L. Coexistence of multiple rare spinal abnormalities in type 1 neurofibromatosis: A case report and literature review. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 17289–17294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belsuzarri, T.A.B.; Pozetti, M.; Belsuzarri, N.C.B.; Seixas, N.B.; Araujo, J.F.M. Neurofibromatosis type 1 and Chiari type 1 malformation: A case report and literature review of a rare association. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2016, 7, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felício, A.C.; Godeiro-Junior, C.D.O.; Borges, V.; Silva, S.M.D.A.; Ferraz, H.B. Hemifacial spasm in a patient with neurofibromatosis and Arnold-Chiari malformation: A unique case association. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2007, 65, 855–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frič, R.; Eide, P.K. Chiari type 1—A malformation or a syndrome? A critical review. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbizu, A.; Khan, T.N.; Ashley-Koch, A.E. Genetic dissection of Chiari malformation type 1 using endophenotypes and stratification. J. Rare Dis. Res. Treat. 2017, 2, 35–42. [Google Scholar]







| Location | Neural Crest-Derived Cells |
|---|---|
| Cranial NC | Chondrocytes, Osteocytes, Odontoblasts (Cranio-facial skeleton) Cranial ganglia, Thyroid cells |
| Vagal NC | Smooth muscle cells, Cardiac septa, Pericytes (Cardiac development) Enteric ganglia |
| Trunk NC | Schwann cells Pigmented cells (Melanocytes) Dorsal root ganglia, Sympathetic ganglia Adrenal medulla |
| Sacral NC | Sympathetic ganglia, Enteric ganglia |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, C.; Russo, C.; Cascone, D.; Mazio, F.; Santoro, C.; Covelli, E.M.; Cinalli, G. Non-Oncological Neuroradiological Manifestations in NF1 and Their Clinical Implications. Cancers 2021, 13, 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081831
Russo C, Russo C, Cascone D, Mazio F, Santoro C, Covelli EM, Cinalli G. Non-Oncological Neuroradiological Manifestations in NF1 and Their Clinical Implications. Cancers. 2021; 13(8):1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081831
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Camilla, Carmela Russo, Daniele Cascone, Federica Mazio, Claudia Santoro, Eugenio Maria Covelli, and Giuseppe Cinalli. 2021. "Non-Oncological Neuroradiological Manifestations in NF1 and Their Clinical Implications" Cancers 13, no. 8: 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081831
APA StyleRusso, C., Russo, C., Cascone, D., Mazio, F., Santoro, C., Covelli, E. M., & Cinalli, G. (2021). Non-Oncological Neuroradiological Manifestations in NF1 and Their Clinical Implications. Cancers, 13(8), 1831. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081831






