Clearing the Haze: How Does Nicotine Affect Hematopoiesis before and after Birth?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
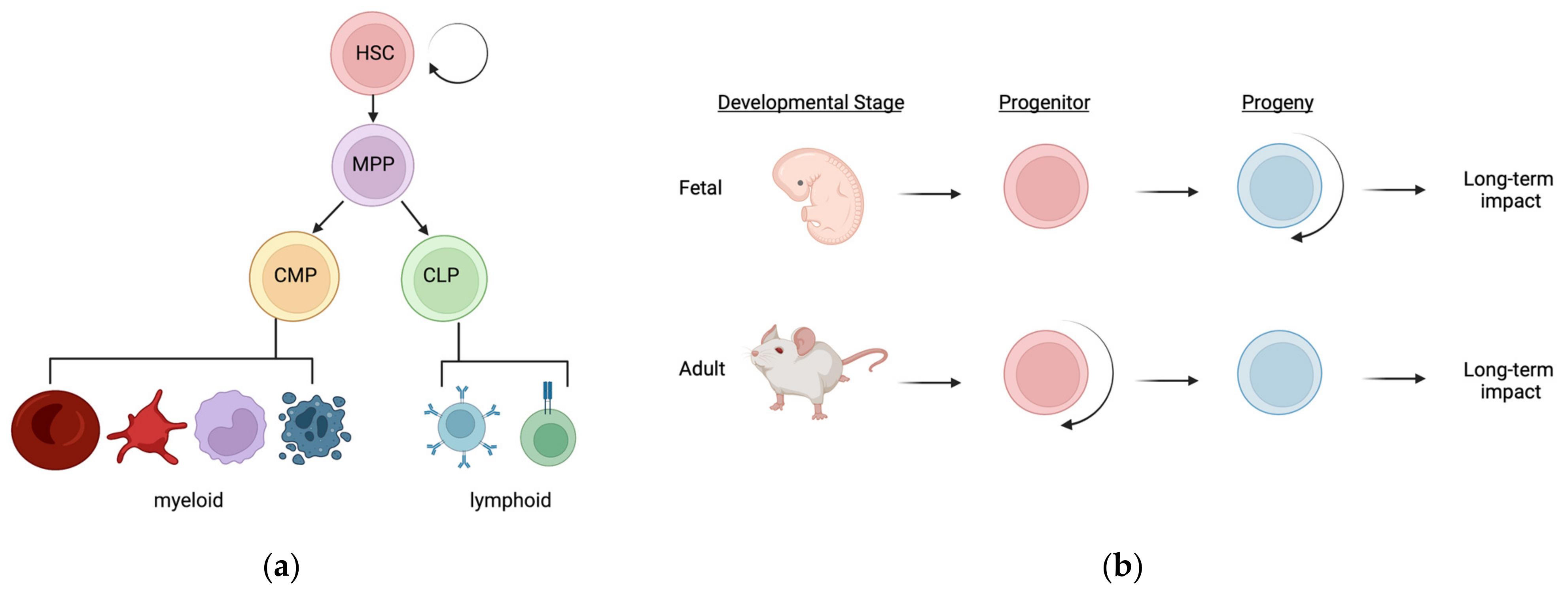
2. The Hematopoietic Hierarchy
3. Regulation of Hematopoietic Homeostasis
4. Does Nicotine Alter Hematopoiesis by Direct Action on HSCs?
4.1. Do HSCs Express Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors (nAChRs)?
4.2. Do Other Hematopoietic Cells Express nAChRs?
5. Does Nicotine Affect Hematopoiesis via an Altered Inflammatory State?
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Institute on Drug Abuse. What is the Scope of Tobacco, Nicotine, and E-Cigarette Use in the United States? Available online: www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/tobacco-nicotine-e-cigarettes/what-scope-tobacco-use-its-cost-to-society (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Ramanathan, G.; Craver-Hoover, B.; Arechavala, R.J.; Herman, D.A.; Chen, J.H.; Lai, H.Y.; Renusch, S.R.; Kleinman, M.T.; Fleischman, A.G. E-Cigarette Exposure Decreases Bone Marrow Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flouris, A.D.; Vardavas, C.I.; Metsios, G.S.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Koutedakis, Y. Biological Evidence for the Acute Health Effects of Secondhand Smoke Exposure. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2010, 298, L3–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, G.; Simoni, M.; Cibella, F.; Ferrara, F.; Liotta, G.; Malizia, V.; Corsello, G.; Viegi, G.; La Grutta, S. Third-Hand Smoke Exposure and Health Hazards in Children. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2015, 79, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmful and Potentially Harmful Constituents in Tobacco Products and Tobacco Smoke: Established List. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/tobacco-products/rules-regulations-and-guidance/harmful-and-potentially-harmful-constituents-tobacco-products-and-tobacco-smoke-established-list (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Mayer, B. How Much Nicotine Kills a Human? Tracing Back the Generally Accepted Lethal Dose to Dubious Self-Experiments in the Nineteenth Century. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, S.L.; Oller, L.; Sawyer, T. Fatal Intravenous Injection of Electronic Nicotine Delivery System Refilling Solution. J. Med. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerfeld, K.; Łukasik-Głębocka, M.; Kulza, M.; Drużdż, A.; Panieński, P.; Florek, E.; Zielińska-Psuja, B. Intravenous and Oral Suicidal E-Liquid Poisonings with Confirmed Nicotine and Cotinine Concentrations. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 262, e15–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkoniene, M.; Socquet, J.; Njemba-Freiburghaus, D.; Pellaton, C. Near Fatal Intoxication by Nicotine and Propylene Glycol Injection: A Case Report of an e-Liquid Poisoning. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 20, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Chaturvedi, P.; Datta, S.; Sinukumar, S.; Joshi, P.; Garg, A. Harmful Effects of Nicotine. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2015, 36, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Forsberg, E.C.; Wu, J.; Bingyin Wang, B.; Prohaska, S.S.; Allsopp, R.; Weissman, I.L.; Cooke, J.P. Cholinergic Activation of Hematopoietic Stem Cells: Role in Tobacco-Related Disease? Vasc. Med. 2010, 15, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalokar, J.B.; Richard, J.L.; Claude, J.R. Leukocyte Count, Smoking, and Myocardial Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 1981, 304, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Kinmonth, A.-L.; Luben, R.N.; Bingham, S.; Day, N.E.; Wareham, N.J.; Welch, A.; Khaw, K.-T. Smoking Status and Differential White Cell Count in Men and Women in the EPIC-Norfolk Population. Atherosclerosis 2003, 169, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, G.D.; Siegelaub, A.B.; Seltzer, C.C.; Feldman, R.; Collen, M.F. Smoking Habits and the Leukocyte Count. Arch. Environ. Health Int. J. 1973, 26, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roethig, H.J.; Koval, T.; Muhammad-Kah, R.; Jin, Y.; Mendes, P.; Unverdorben, M. Short Term Effects of Reduced Exposure to Cigarette Smoke on White Blood Cells, Platelets and Red Blood Cells in Adult Cigarette Smokers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.A.; Prats, J.; Artero, J.V.; Mora, A.; Fariñas, A.; Espinal, A.; Méndez, J.A. Systemic Inflammation in 222.841 Healthy Employed Smokers and Nonsmokers: White Blood Cell Count and Relationship to Spirometry. Tob. Induc. Dis. 2012, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez y Baena, A.; Manso, B.A.; Forsberg, E.C. CFU-S Assay: A Single-Cell Historical Assay Offers Modern Insight to Clonal Hematopoiesis. Exp. Hematol. 2021, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Till, J.E.; Mcculloch, E.A. A Direct Measurement of the Radiation Sensitivity of Normal Mouse Bone Marrow Cells. Radiat. Res. 1961, 14, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzierzak, E.; Bigas, A. Blood Development: Hematopoietic Stem Cell Dependence and Independence. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cool, T.; Forsberg, E.C. Chasing Mavericks: The Quest for Defining Developmental Waves of Hematopoiesis. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 132, pp. 1–2. ISBN 978-0-12-810489-7. [Google Scholar]
- Klaus, A.; Robin, C. Embryonic Hematopoiesis under Microscopic Observation. Dev. Biol. 2017, 428, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittamer, V.; Bertrand, J.Y. Yolk Sac Hematopoiesis: Does It Contribute to the Adult Hematopoietic System? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 4081–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudin, A.E.; Boyer, S.W.; Perez-Cunningham, J.; Hernandez, G.E.; Derderian, S.C.; Jujjavarapu, C.; Aaserude, E.; MacKenzie, T.; Forsberg, E.C. A Transient Developmental Hematopoietic Stem Cell Gives Rise to Innate-like B and T Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 768–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudin, A.E.; Forsberg, E.C. To B1a or Not to B1a: Do Hematopoietic Stem Cells Contribute to Tissue-Resident Immune Cells? Blood 2016, 128, 2765–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laval, B.; Maurizio, J.; Kandalla, P.K.; Brisou, G.; Simonnet, L.; Huber, C.; Gimenez, G.; Matcovitch-Natan, O.; Reinhardt, S.; David, E.; et al. C/EBPβ-Dependent Epigenetic Memory Induces Trained Immunity in Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 657–674.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.P.; Shvedunova, M.; Akhtar, A. Epigenetic Regulators as the Gatekeepers of Hematopoiesis. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Peng, H.; Zhu, Y.; Mohandas, N.; Liu, J. Interplay between Cofactors and Transcription Factors in Hematopoiesis and Hematological Malignancies. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Chen, C.; Howell, E.D.; Li, Y.; Tober, J.; Uzun, Y.; He, B.; Gao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Siekmann, A.F.; et al. Transcriptional Regulatory Network Controlling the Ontogeny of Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 950–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietras, E.M. Inflammation: A Key Regulator of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Fate in Health and Disease. Blood 2017, 130, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuettpelz, L.G.; Link, D.C. Regulation of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Activity by Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldridge, M.T.; King, K.Y.; Goodell, M.A. Inflammatory Signals Regulate Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, A.; Mitchell, C.A.; Passague, E. Inflammatory Signaling Regulates Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Development and Homeostasis. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20201545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flouris, A.D.; Poulianiti, K.P.; Chorti, M.S.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Kouretas, D.; Owolabi, E.O.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Tsatsakis, A.M.; Koutedakis, Y. Acute Effects of Electronic and Tobacco Cigarette Smoking on Complete Blood Count. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 3600–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, K.M.; Çolak, Y.; Ellervik, C.; Hasselbalch, H.C.; Bojesen, S.E.; Nordestgaard, B.G. Smoking and Increased White and Red Blood Cells: A Mendelian Randomization Approach in the Copenhagen General Population Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewski, P.P.; Strzelec, B. Elevated Leukocyte Count as a Harbinger. Folia Morphol. 2018, 77, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dani, J.A. Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Structure and Function and Response to Nicotine. In International Review of Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 124, pp. 3–19. ISBN 978-0-12-801583-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Lukas, R.J. Naturally-Expressed Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Subtypes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Pierre, S.; Jiang, W.; Roy, P.; Champigny, C.; LeBlanc, É.; Morley, B.J.; Hao, J.; Simard, A.R. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate Bone Marrow-Derived pro-Inflammatory Monocyte Production and Survival. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osgoei, L.T.; Parivar, K.; Ebrahimi, M.; Mortaz, E. Nicotine Modulates the Release of Inflammatory Cytokines and Expression of TLR2, TLR4 of Cord Blood Mononuclear Cells. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 17, 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsenzadeh, Y.; Rahmani, A.; Cheraghi, J.; Pyrani, M.; Asadollahi, K. Prenatal Exposure to Nicotine in Pregnant Rat Increased Inflammatory Marker in Newborn Rat. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 274048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Chamier, M.; Reyes, L.; Hayward, L.F.; Brown, M.B. Impact of Gestational Nicotine Exposure on Intrauterine and Fetal Infection in a Rodent Model. Biol. Reprod. 2017, 96, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, G.; Chan, Y.L.; Chapman, D.G.; Sukjamnong, S.; Nguyen, T.; Annissa, T.; McGrath, K.C.; Sharma, P.; Oliver, B.G. Maternal E-Cigarette Exposure in Mice Alters DNA Methylation and Lung Cytokine Expression in Offspring. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 58, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, A.; Thompson, P.R.; Segal, B.H.; Urban, C.F. Nicotine Induces Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelak, A.; Ratajczak, A.; Adamiec, A.; Feleszko, W. Tobacco Smoke Induces and Alters Immune Responses in the Lung Triggering Inflammation, Allergy, Asthma and Other Lung Diseases: A Mechanistic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajiasgharzadeh, K.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Mansoori, B.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shanehbandi, D.; Doustvandi, M.A.; Asadzadeh, Z.; Baradaran, B. Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Lung Inflammation and Carcinogenesis: Friends or Foes? J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14666–14679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breit, S.; Kupferberg, A.; Rogler, G.; Hasler, G. Vagus Nerve as Modulator of the Brain-Gut Axis in Psychiatric and Inflammatory Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, G.R.; Webster, N.R. Cytokines and the Immunomodulatory Function of the Vagus Nerve. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 102, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.K.; Barra, N.G.; Alfaidy, N.; Hardy, D.B.; Holloway, A.C. Adverse Effects of Perinatal Nicotine Exposure on Reproductive Outcomes. Reproduction 2015, 150, R185–R193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, M.C. Exposure to Nicotine Is Probably a Major Cause of Inflammatory Diseases among Non-Smokers. Med. Hypotheses 2005, 65, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azagba, S.; Manzione, L.; Shan, L.; King, J. Trends in Smoking during Pregnancy by Socioeconomic Characteristics in the United States, 2010–2017. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2020, 20, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, J.A.; Busso, D.; Ramà rez, G.; Campos, M.; Rigotti, A.; Eugenà n, J.; von Bernhardi, R. Prenatal Nicotine Exposure Enhances Cx43 and Panx1 Unopposed Channel Activity in Brain Cells of Adult Offspring Mice Fed a High-Fat/Cholesterol Diet. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Yon, J.-M.; Hong, J.T.; Lee, J.K.; Jeong, J.; Baek, I.-J.; Lee, B.J.; Yun, Y.W.; Nam, S.-Y. 4-O-Methylhonokiol Inhibits Serious Embryo Anomalies Caused by Nicotine via Modulations of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Inflammation: 4-O-METHYLHONOKIOL PREVENTS NICOTINE-INDUCED EMBRYOTOXICITY. Birth Defects Res. B 2014, 101, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostol, A.C.; Jensen, K.D.C.; Beaudin, A.E. Training the Fetal Immune System through Maternal Inflammation—A Layered Hygiene Hypothesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Sezaki, M.; Takizawa, H. Development of the Hematopoietic System: Role of Inflammatory Factors. WIREs Dev. Biol. 2019, 8, e341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, W.; Liu, H.; Yan, H.; Hou, L.; Ping, J.; Zhao, W.; Wen, X. Prenatal Nicotine Exposure Induces Thymic Hypoplasia in Mice Offspring from Neonatal to Adulthood. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 304, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N. Effects of in Utero Nicotine Exposure on Immune Cell Disposition after P. Aeruginosa Lung Infection. Master’s Thesis, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Luck, W.; Nau, H. Nicotine and Cotinine Concentrations in Serum and Milk of Nursing Smokers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1984, 18, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlström, A.; Lundell, B.; Curvall, M.; Thapper, L. Nicotine and Cotinine Concentrations in the Nursing Mother and Her Infant. Acta Paediatr. 1990, 79, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruin, J.E.; Gerstein, H.C.; Holloway, A.C. Long-Term Consequences of Fetal and Neonatal Nicotine Exposure: A Critical Review. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 116, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofhuis, W.; de Jongste, J.C.; Merkus, P.J.F.M. Adverse Health Effects of Prenatal and Postnatal Tobacco Smoke Exposure on Children. Arch. Dis. Child. 2003, 88, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Shenassa, E.D.; Paradis, A.D. Maternal Smoking, Breastfeeding, and Risk of Childhood Overweight: Findings from a National Cohort. Matern. Child Health J. 2013, 17, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Romero, E.; Martínez-Valiente, C.; García-Ruiz, C.; Vázquez-Manrique, R.P.; Cervera, J.; Sanjuan-Pla, A. CRISPR to Fix Bad Blood: A New Tool in Basic and Clinical Hematology. Haematologica 2019, 104, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidhi, S.; Anand, U.; Oleksak, P.; Tripathi, P.; Lal, J.A.; Thomas, G.; Kuca, K.; Tripathi, V. Novel CRISPR–Cas Systems: An Updated Review of the Current Achievements, Applications, and Future Research Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Wu, B.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. ATAC-seq: A Method for Assaying Chromatin Accessibility Genome-Wide. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2015, 109, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Giresi, P.G.; Zaba, L.C.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. Transposition of Native Chromatin for Fast and Sensitive Epigenomic Profiling of Open Chromatin, DNA-Binding Proteins and Nucleosome Position. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merad, M.; Manz, M.G.; Karsunky, H.; Wagers, A.; Peters, W.; Charo, I.; Weissman, I.L.; Cyster, J.G.; Engleman, E.G. Langerhans Cells Renew in the Skin throughout Life under Steady-State Conditions. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, G.A.; Cool, T.; Valencia, C.H.; Worthington, A.; Beaudin, A.E.; Forsberg, E.C. The Lymphoid-Associated Interleukin 7 Receptor (IL7R) Regulates Tissue-Resident Macrophage Development. Development 2019, 146, dev176180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cool, T.; Worthington, A.; Poscablo, D.; Hussaini, A.; Forsberg, E.C. Interleukin 7 Receptor Is Required for Myeloid Cell Homeostasis and Reconstitution by Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Exp. Hematol. 2020, 90, 39–45.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthington, A.; Cool, T.; Poscablo, D.; Hussaini, A.; Beaudin, A.E.; Forsberg, E.C. IL7R⍺, but not Flk2/Flt3, is required for hematopoietic stem cell reconstitution of tissue-resident lymphoid cells. Development 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cool, T.; Baena, A.R.y.; Forsberg, E.C. Clearing the Haze: How Does Nicotine Affect Hematopoiesis before and after Birth? Cancers 2022, 14, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010184
Cool T, Baena ARy, Forsberg EC. Clearing the Haze: How Does Nicotine Affect Hematopoiesis before and after Birth? Cancers. 2022; 14(1):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010184
Chicago/Turabian StyleCool, Taylor, Alessandra Rodriguez y Baena, and E. Camilla Forsberg. 2022. "Clearing the Haze: How Does Nicotine Affect Hematopoiesis before and after Birth?" Cancers 14, no. 1: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010184
APA StyleCool, T., Baena, A. R. y., & Forsberg, E. C. (2022). Clearing the Haze: How Does Nicotine Affect Hematopoiesis before and after Birth? Cancers, 14(1), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14010184





