EPA Modulates KLK Genes via miR-378: A Potential Therapy in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Sample Collection
2.2. PCa Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.3. Elevating the Level of miR-378 in Cells through Incubation in EPA Medium
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quantification of miR-378
2.5. Detection of KLK Expression Levels before and after miR-378 Elevation
2.6. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Analysis
2.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
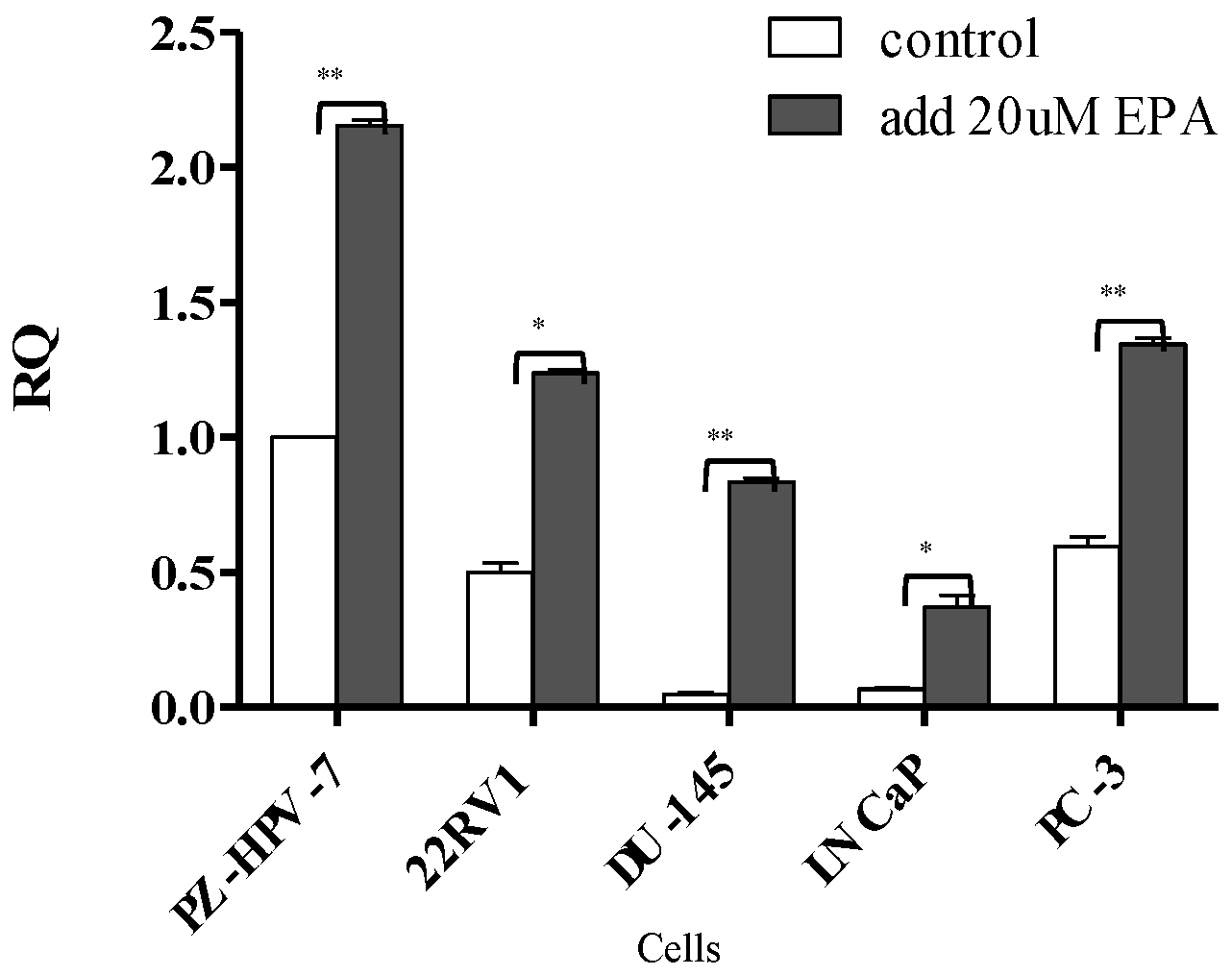
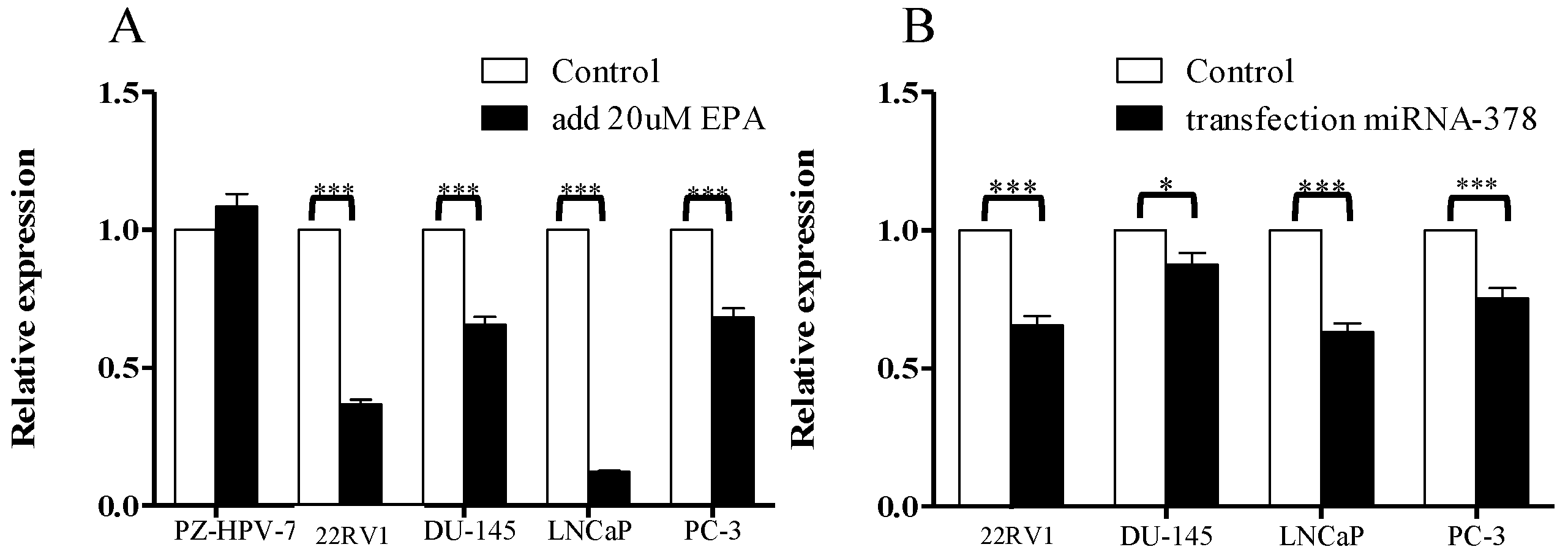
3.1. Comparison of miR-378 Expression between PCa Cells and Normal Prostate Cells before and after EPA Treatment
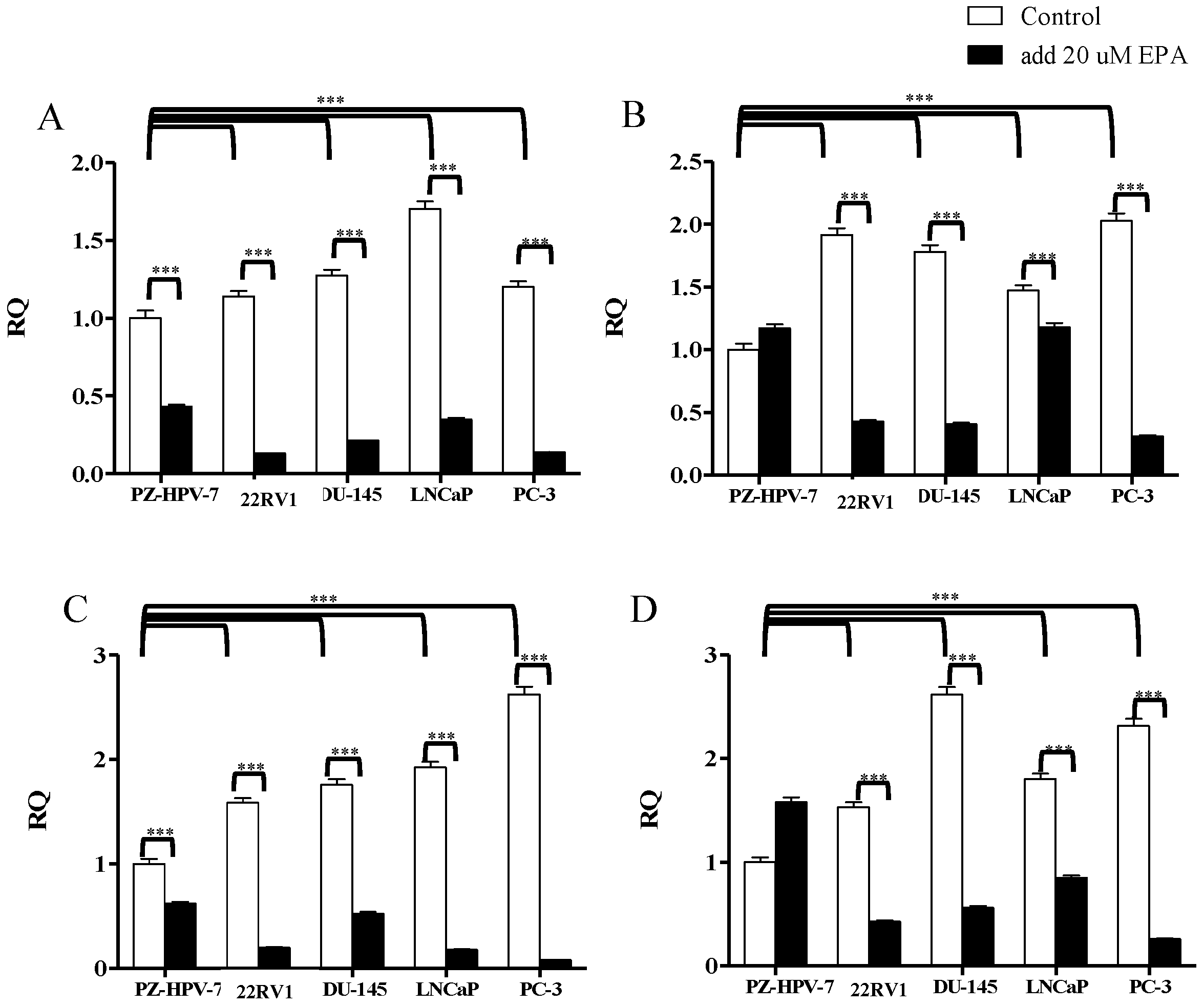
3.2. Gene Expression of KLK2, KLK4, KLK6, and KLK14 in PCa Cells after EPA Treatment
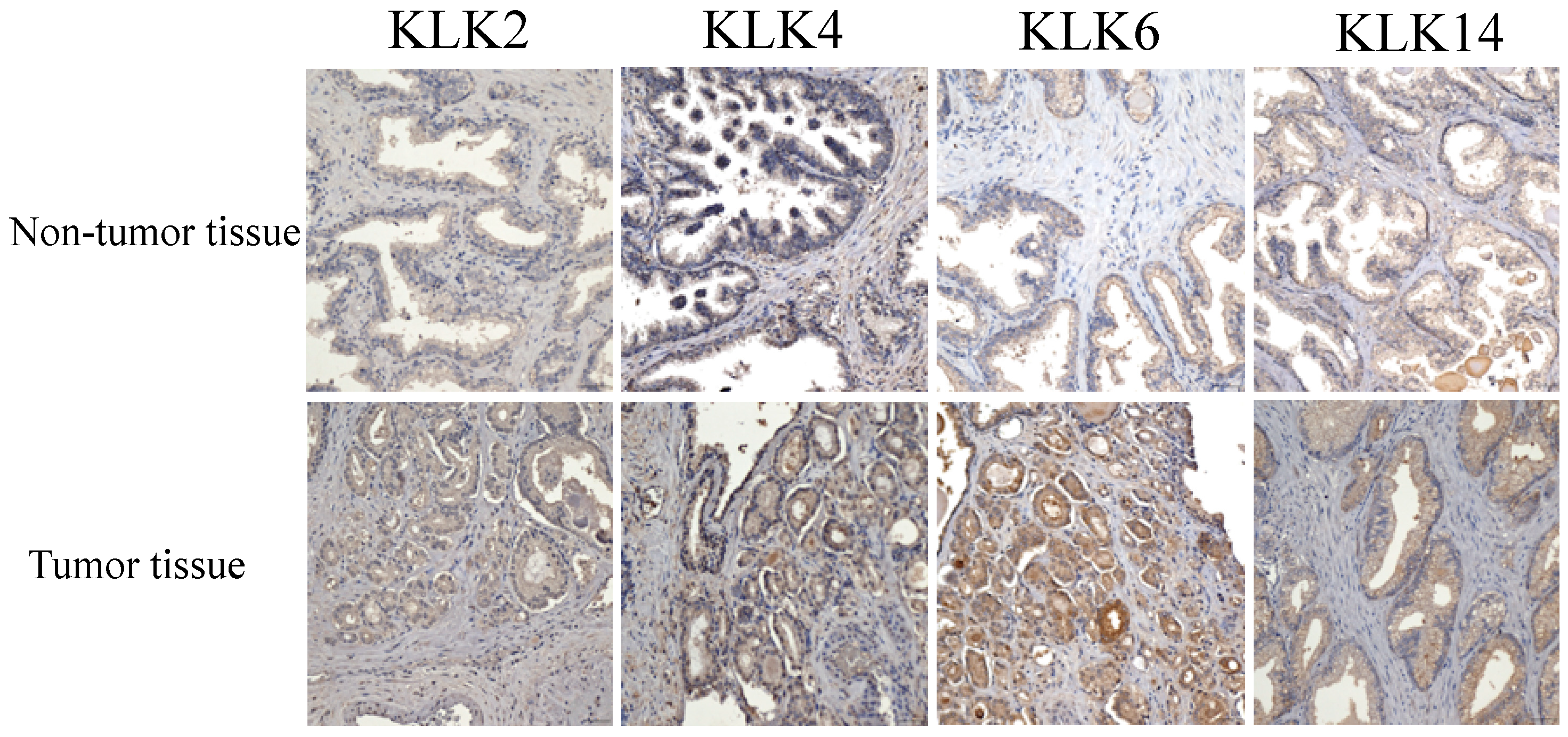
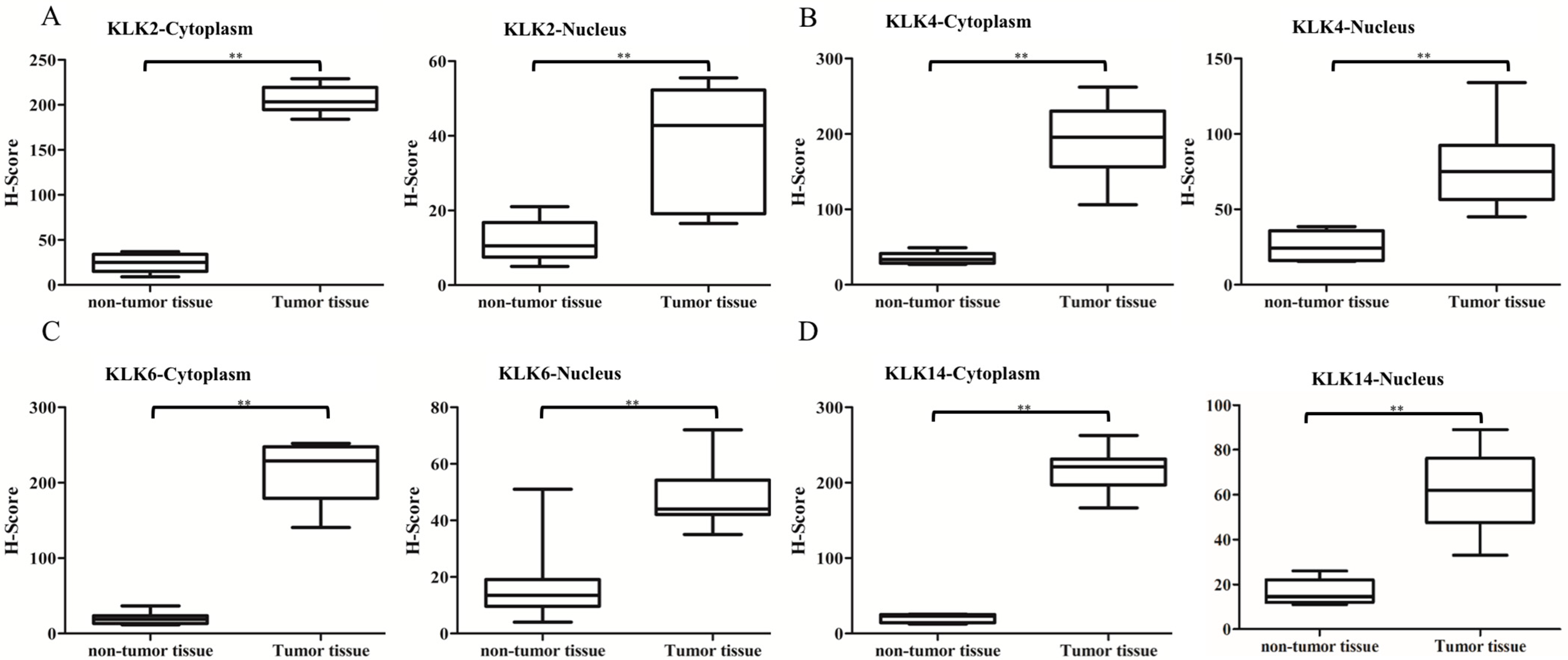
3.3. Immunostaining Analysis of KLK Proteins of Clinical Tissues
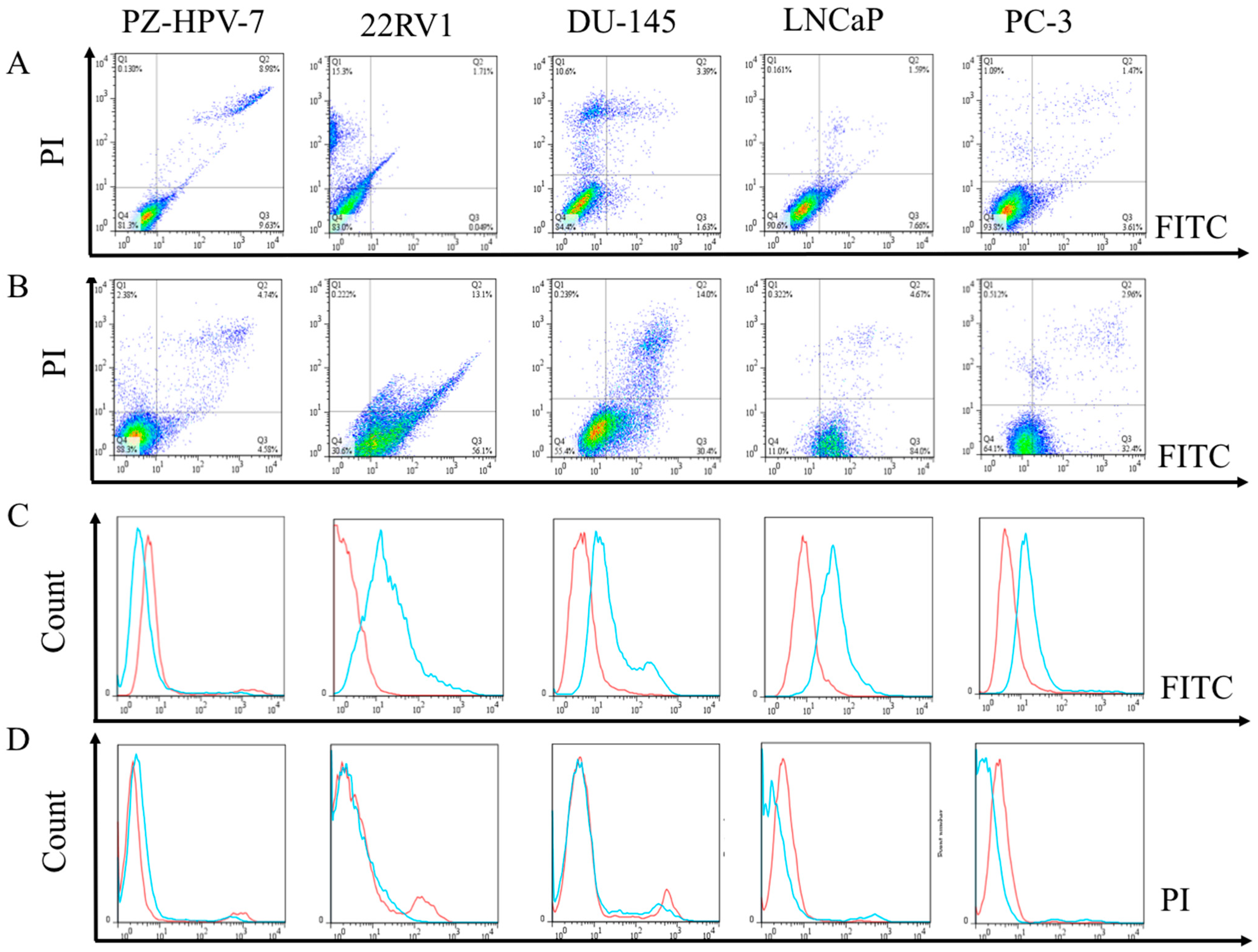
3.4. Flow Cytometric Evaluation of the Apoptosis and Necrosis of PCa Cells after Treated with EPA
3.5. Cell Viability Analysis of PCa Cells after Treatment with EPA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freitas, R.D.S.; Campos, M.M. Protective Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Cancer-Related Complications. Nutrients 2019, 11, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weng, W.; Leung, W.; Pang, Y.J.; Kuo, L.; Hsu, H. EPA significantly improves anti-EGFR targeted therapy by regulating miR-378 expression in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6188–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiede, I.; Fritz, G.; Strand, S.; Poppe, D.; Dvorsky, R.; Strand, D.; Lehr, H.A.; Wirtz, S.; Becker, C.; Atreya, R.; et al. CD28-dependent Rac1 activation is the molecular target of azathioprine in primary human CD4+ T lymphocytes. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crunkhorn, S.; Dearie, F.; Mantzoros, C.; Gami, H.; da Silva, W.S.; Espinoza, D.; Faucette, R.; Barry, K.; Bianco, A.; Patti, M.E. Peroxisome Proliferator Activator Receptor γ Coactivator-1 Expression Is Reduced in Obesity: Potential pathogenic role of saturated fatty acids and p38 mitogen-activated protein ki-nase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15439–15450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerin, I.; Bommer, G.T.; McCoin, C.S.; Sousa, K.M.; Krishnan, V.; MacDougald, O.A. Roles for miRNA-378/378* in adipocyte gene expression and lipogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2010, 299, E198–E206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrer, M.; Liu, N.; Grueter, C.E.; Williams, A.H.; Frisard, M.I.; Hulver, M.W.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. Control of mitochondrial metabolism and systemic energy homeostasis by microRNAs 378 and 378*. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15330–15335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Handschin, C.; Spiegelman, B.M. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borgoño, C.A.; Michael, I.P.; Shaw, J.L.; Luo, L.-Y.; Ghosh, M.C.; Soosaipillai, A.; Grass, L.; Katsaros, D.; Diamandis, E.P. Expression and Functional Characterization of the Cancer-related Serine Protease, Human Tissue Kallikrein 14. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 2405–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samaan, S.; Lichner, Z.; Ding, Q.; Saleh, C.; Samuel, J.; Streutker, C.; Yousef, G.M. Kallikreins are involved in an miRNA network that contributes to prostate cancer progression. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, J.; Bennett, N.C.; Stephens, C.R.; Carroll, M.L.; Magdolen, V.; Clements, J.; Hooper, J.D. In vitro evidence that KLK14 regulates the components of the HGF/Met axis, pro-HGF and HGF-activator inhibitor 1A and 1B. Biol. Chem. 2016, 397, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kryza, T.; Silva, M.L.; Loessner, D.; Heuzé-Vourc’H, N.; Clements, J.A. The kallikrein-related peptidase family: Dysregulation and functions during cancer progression. Biochimie 2016, 122, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgoño, C.A.; Diamandis, E.P. The emerging roles of human tissue kallikreins in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgeris, M.; Scorilas, A. Kallikrein-related peptidases (KLKs) as emerging therapeutic targets: Focus on prostate cancer and skin pathologies. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Niu, Y.; Cai, Q.; Chen, J.; Tian, J.; Yeh, S.; Lai, K.-P.; Chang, C. Human kallikrein 2 (KLK2) promotes prostate cancer cell growth via function as a modulator to promote the ARA70-enhanced androgen receptor transactivation. Tumor Biol. 2013, 35, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Qu, S.; Tesikova, M.; Wang, L.; Kristian, A.; Maelandsmo, G.M.; Kong, H.; Zhang, T.; Jeronimo, C.; Teixeira, M.; et al. Molecular circuit involving KLK4 integrates androgen and mTOR signaling in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2572–E2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lose, F.; Lawrence, M.G.; Srinivasan, S.; O’Mara, T.; Marquart, L.; Chambers, S.K.; Gardiner, R.A.; Aitken, J.; Spurdle, A.; Batra, J.; et al. The kallikrein 14 gene is down-regulated by androgen receptor signalling and harbours genetic variation that is associated with prostate tumour aggressiveness. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mize, G.J.; Wang, W.; Takayama, T.K. Prostate-Specific Kallikreins-2 and -4 Enhance the Proliferation of DU-145 Prostate Cancer Cells through Protease-Activated Receptors-1 and -2. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riegman, P.H.; Vlietstra, R.J.; van der Korput, H.A.; Romijn, J.C.; Trapman, J. Identification and androgen-regulated expression of two major human glandular kallikrein-1 (hGK-1) mRNA species. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1991, 76, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.Y.; Andrews, P.E.; Tindall, D.J. Expression and androgenic regulation of human pros-tate-specific kallikreins. J. Androl. 1995, 16, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, P.S.; Gan, L.; Ferguson, C.; Moss, P.; Gelinas, R.; Hood, L.; Wang, K. Molecular cloning and characterization of prostase, an androgen-regulated serine protease with prostate-restricted expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3114–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darson, M.F.; Pacelli, A.; Roche, P.; Rittenhouse, H.G.; Wolfert, R.L.; Young, C.Y.; Klee, G.G.; Tindall, D.J.; Bostwick, D.G. Human glandular kallikrein 2 (hK2) expression in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and adenocarcinoma: A novel prostate cancer marker. Urology 1997, 49, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrala, A.M.; Porvari, K.S.; Kyllönen, A.P.; Vihko, P.T. Comparison of human prostate specific glandu-lar kallikrein 2 and prostate specific antigen gene expression in prostate with gene amplification and over-expression of prostate specific glandular kallikrein 2 in tumor tissue. Cancer 2001, 92, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klokk, T.I.; Kilander, A.; Xi, Z.; Waehre, H.; Risberg, B.; Danielsen, H.E.; Saatcioglu, F. Kallikrein 4 Is a Proliferative Factor that Is Overexpressed in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avgeris, M.; Stravodimos, K.; Scorilas, A. Kallikrein-related peptidase 4 gene (KLK4) in prostate tumors: Quantitative expression analysis and evaluation of its clinical significance. Prostate 2011, 71, 1780–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgeris, M.; Mavridis, K.; Scorilas, A. Kallikrein-related peptidase genes as promising biomarkers for prognosis and monitoring of human malignancies. Biol. Chem. 2010, 391, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avgeris, M.; Mavridis, K.; Scorilas, A. Kallikrein-related peptidases in prostate, breast, and ovarian cancers: From pathobiology to clinical relevance. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klucky, B.; Mueller, R.; Vogt, I.; Teurich, S.; Hartenstein, B.; Breuhahn, K.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Angel, P.; Hess, J. Kallikrein 6 Induces E-Cadherin Shedding and Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8198–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borgoño, C.A.; Michael, I.P.; Diamandis, E.P. Human tissue kallikreins: Physiologic roles and applications in cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2004, 2, 257–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Kim, J.; Yu, J. Androgen receptor genomic regulation. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2013, 2, 158–177. [Google Scholar]
- Avgeris, M.; Stravodimos, K.; Scorilas, A. Loss of miR-378 in prostate cancer, a common regulator of KLK2 and KLK4, correlates with aggressive disease phenotype and predicts the short-term relapse of the patients. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsopoulos, V.; Wilsher, N.; Arroo, R.; Potter, G.A. Bioactivation of the phytoestrogen diosmetin by CYP1 cytochromes P450. Cancer Lett. 2009, 274, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Ouk, S.; Clegg, N.J.; Chen, Y.; Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.; Wongvipat, J.; Smith-Jones, P.M.; Yoo, D.; Kwon, A.; et al. Development of a Second-Generation Antiandrogen for Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Science 2009, 324, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cornford, P.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part II—2020 Update: Treatment of Relapsing and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 263–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, B.; Ji, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Sun, H.; Wu, H.; Chen, X.; et al. MicroRNA-378-5p suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by targeting BRAF. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weng, W.-H.; Ho, I.-L.; Pang, C.-C.; Pang, S.-N.; Pan, T.-M.; Leung, W.-H. Real-time circulating tumor cells detection via highly sensitive needle-like cytosensor-demonstrated by a blood flow simulation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 116, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, K.-J.; Ji, D.-Y.; Hsieh, M.-L.; Chuang, C.-K.; Pang, S.-T.; Weng, W.-H. EPA Modulates KLK Genes via miR-378: A Potential Therapy in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112813
Yu K-J, Ji D-Y, Hsieh M-L, Chuang C-K, Pang S-T, Weng W-H. EPA Modulates KLK Genes via miR-378: A Potential Therapy in Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(11):2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112813
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Kai-Jie, De-Yi Ji, Ming-Li Hsieh, Cheng-Keng Chuang, See-Tong Pang, and Wen-Hui Weng. 2022. "EPA Modulates KLK Genes via miR-378: A Potential Therapy in Prostate Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 11: 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112813
APA StyleYu, K.-J., Ji, D.-Y., Hsieh, M.-L., Chuang, C.-K., Pang, S.-T., & Weng, W.-H. (2022). EPA Modulates KLK Genes via miR-378: A Potential Therapy in Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 14(11), 2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14112813





