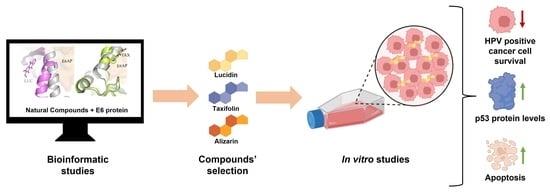
Taxifolin and Lucidin as Potential E6 Protein Inhibitors: p53 Function Re-Establishment and Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. In Silico Studies
E6 Protein Preparation
Ligands Preparation
Grid Map Calculations
Molecular Docking Simulations
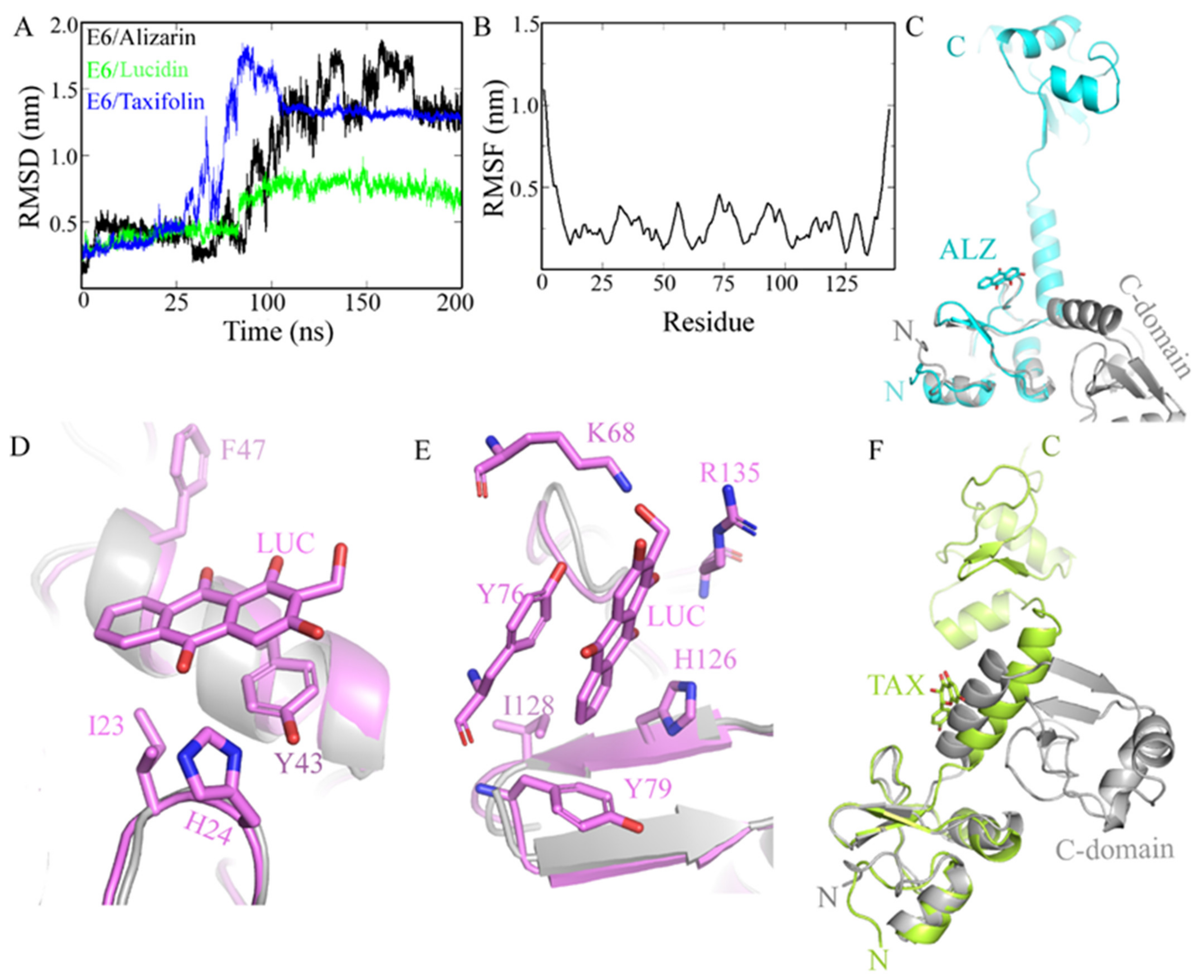
Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.2.2. In Vitro Studies
Cell Culture
Preparation of Compound Solutions
Cell Viability Assays
Western Blot Analysis
RT-PCR Analysis
Caspase-3/7 Assay
Hoechst/Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining
Flow Cytometry
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Screening and Natural Compounds Identification
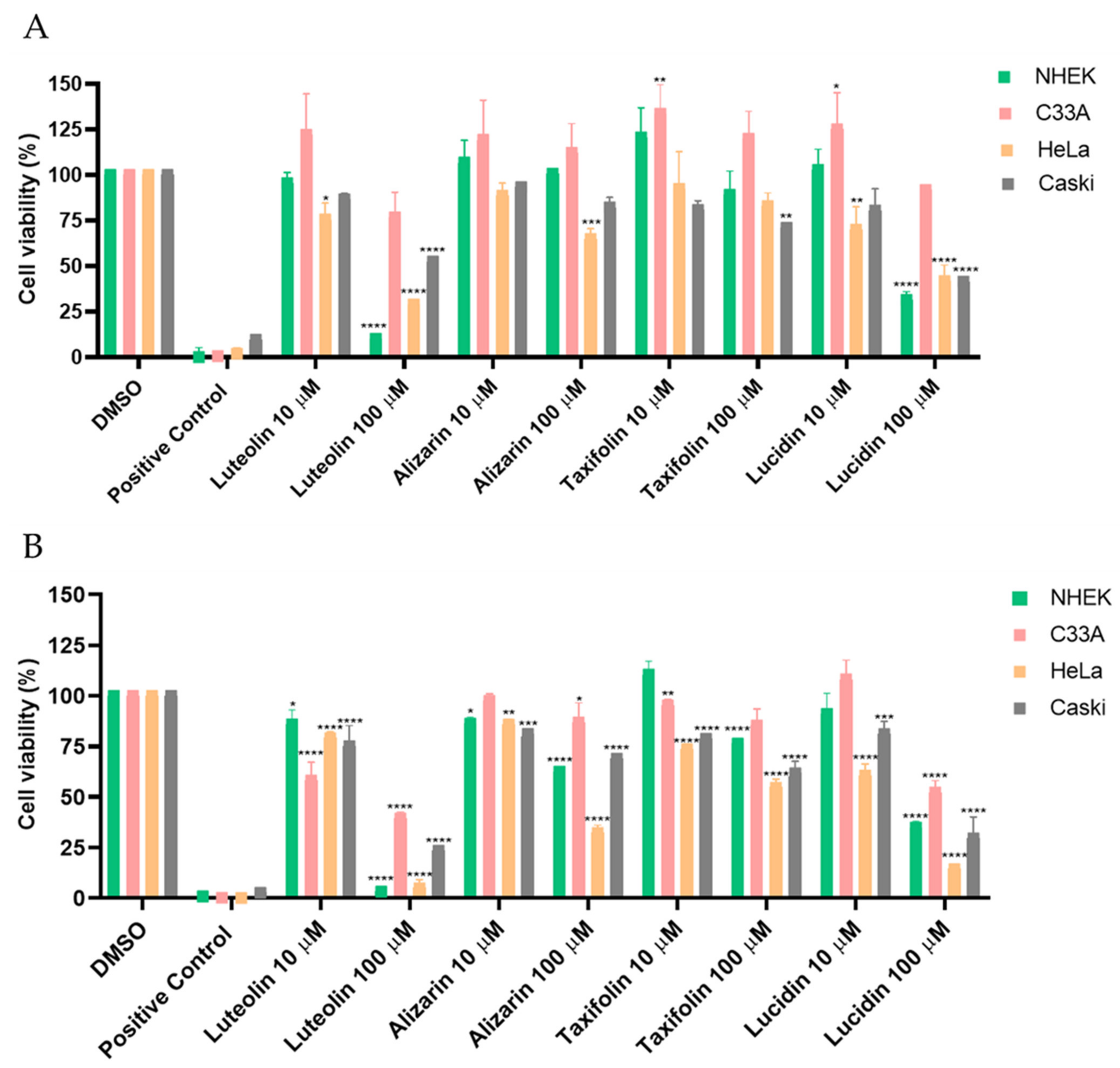
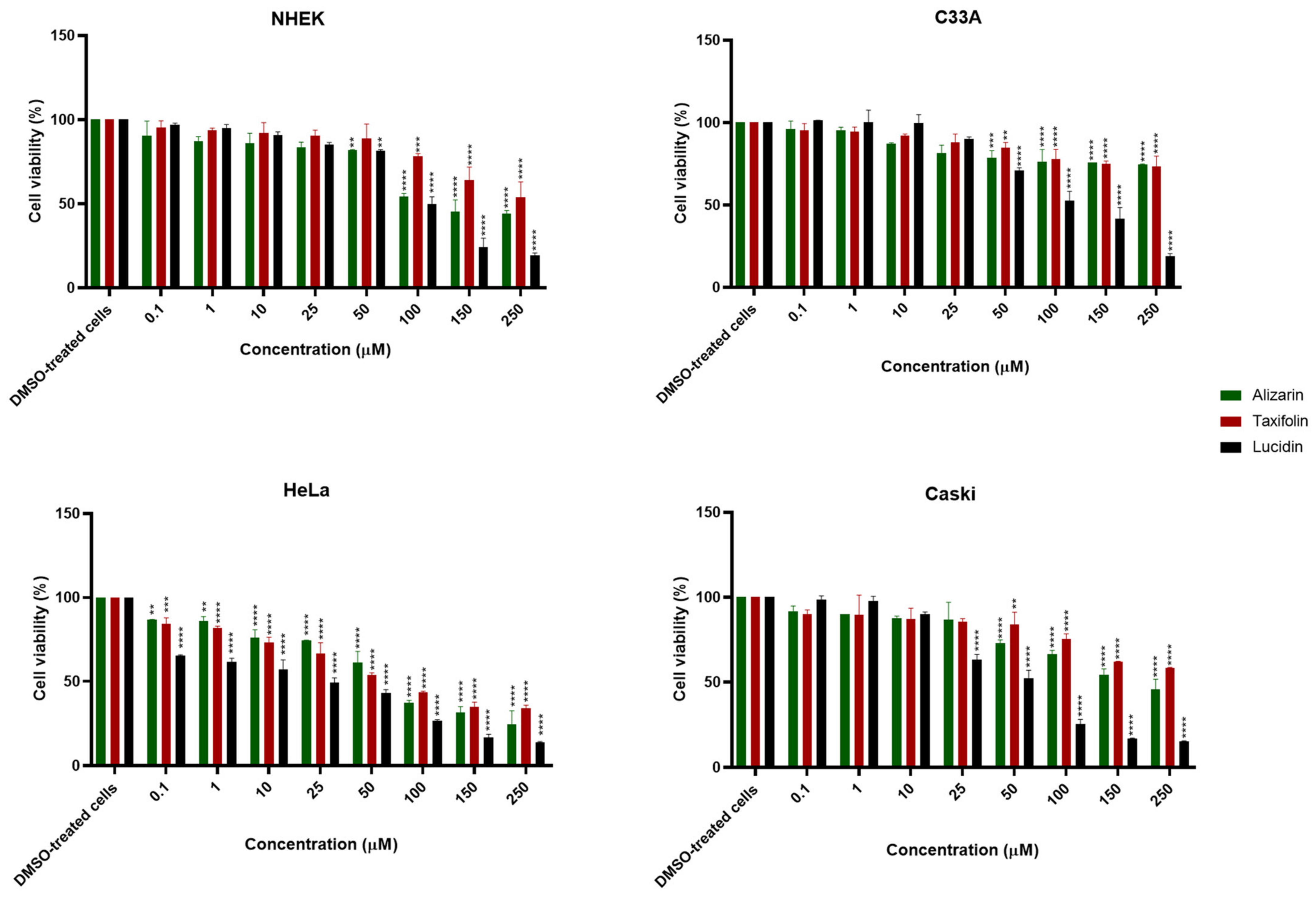
3.2. Alizarin, Taxifolin, and Lucidin Cytotoxicity Studies in Cervical Cancer Cells
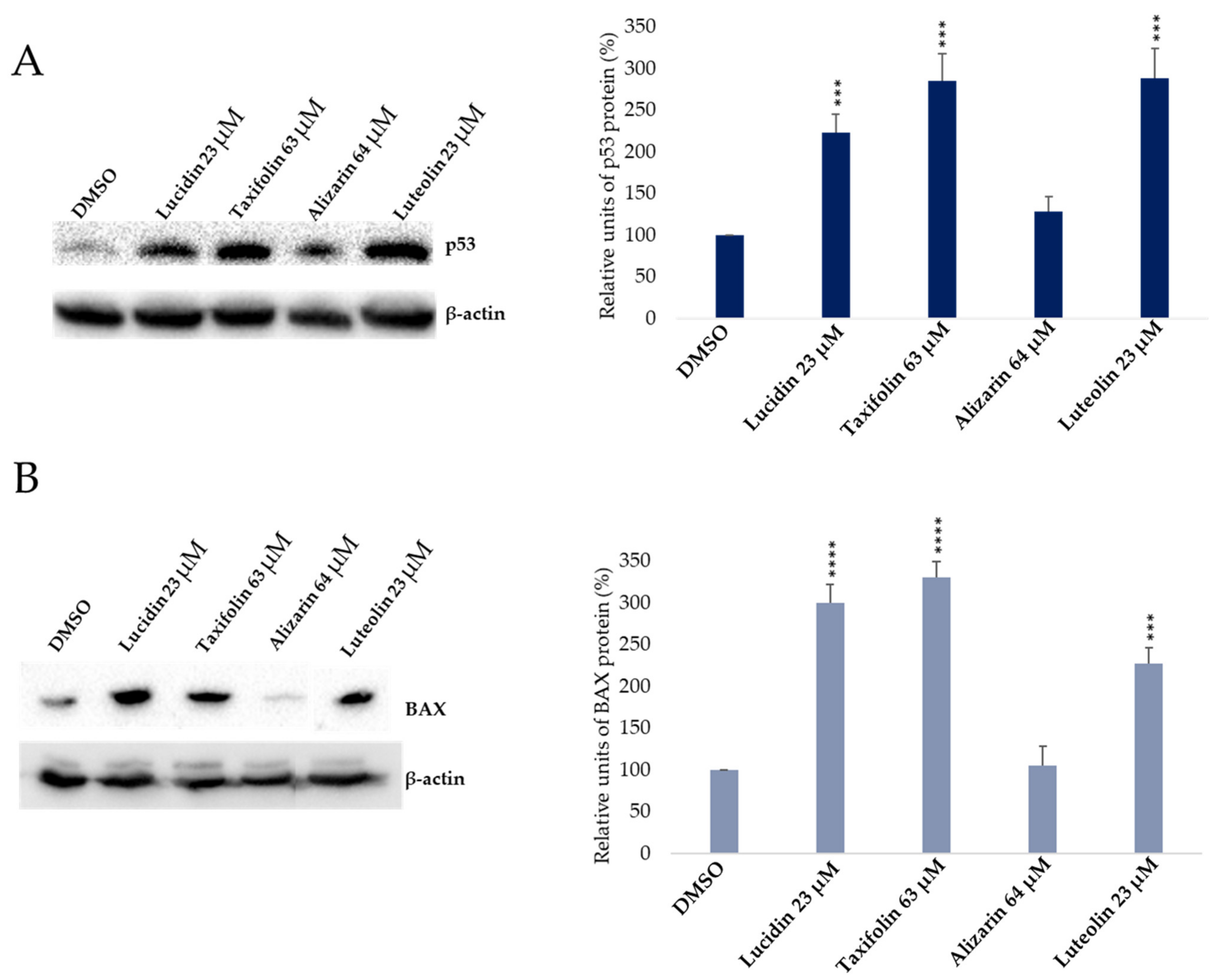
3.3. Evaluation of p53 and BAX Protein Levels in Anthraquinone and Flavonoid Treated Cells
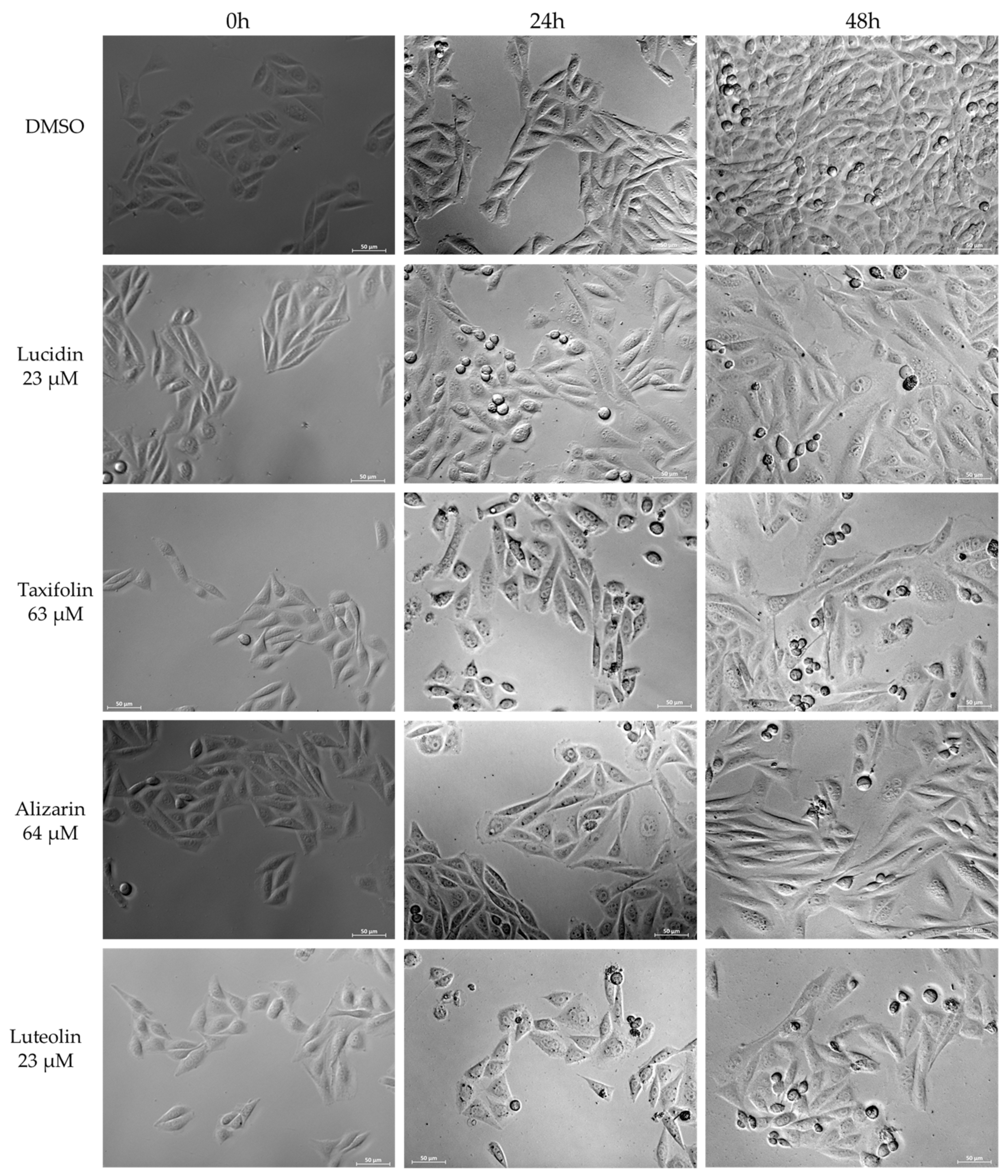
3.4. Lucidin and Taxifolin Induce Apoptosis in HPV18-Positive Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Kundu, R. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7: The Cervical Cancer Hallmarks and Targets for Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prigge, E.S.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M.; Reuschenbach, M. Clinical relevance and implications of HPV-induced neoplasia in different anatomical locations. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 772, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorbar, J.; Egawa, N.; Griffin, H.; Kranjec, C.; Murakami, I. Human papillomavirus molecular biology and disease association. Rev. Med. Virol. 2016, 25, 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farthing, A.J.; Vousden, K.H. Functions of human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins. Trends Microbiol. 1994, 2, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, M.N.; De Lima, R.D.C.P.; Paolini, F.; Melo, A.R.D.S.; Campos, A.P.F.; Venuti, A.; De Freitas, A.C. Current research into novel therapeutic vaccines against cervical cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 18, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra, F.; Lorusso, D.; Leone Roberti Maggiore, U.; Ditto, A.; Bogani, G.; Raspagliesi, F.; Ferrero, S. Investigational drugs for the treatment of cervical cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, S.; Banks, L. Molecular mechanisms underlying human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoprotein-induced cell transformation. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2017, 772, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanier, K.; Charbonnier, S.; Sidi, A.O.M.H.O.; McEwen, A.G.; Ferrario, M.G.; Poussin-Courmontagne, P.; Cura, V.; Brimer, N.; Babah, K.O.; Ansari, T.; et al. Structural Basis for Hijacking of Cellular LxxLL Motifs by Papillomavirus E6 Oncoproteins. Science 2013, 339, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherry, J.J.; Rietz, A.; Malinkevich, A.; Liu, Y.; Xie, M.; Bartolowits, M.; Davisson, V.J.; Baleja, J.D.; Androphy, E.J. Structure based identification and characterization of flavonoids that disrupt human papillomavirus-16 E6 function. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanier, K.; Stutz, C.; Kintscher, S.; Reinz, E.; Sehr, P.; Bulkescher, J.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Trave, G.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. The E6AP binding pocket of the HPV16 E6 oncoprotein provides a docking site for a small inhibitory peptide unrelated to E6AP, indicating druggability of E6. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Celegato, M.; Messa, L.; Goracci, L.; Mercorelli, B.; Bertagnin, C.; Spyrakis, F.; Suarez, I.; Cousido-Siah, A.; Trave, G.; Banks, L.; et al. A novel small-molecule inhibitor of the human papillomavirus E6-p53 interaction that reactivates p53 function and blocks cancer cells growth. Cancer Lett. 2020, 470, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sima, N.; Wang, W.; Kong, D.; Deng, D.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xu, G.; Meng, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. RNA interference against HPV16 E7 oncogene leads to viral E6 and E7 suppression in cervical cancer cells and apoptosis via upregulation of Rb and p53. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2008, 13, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Zapien, D.; Ruiz, F.X.; Poirson, J.; Mitschler, A.; Ramirez, J.; Forster, A.; Cousido-Siah, A.; Masson, M.; Pol, S.V.; Podjarny, A.; et al. Structure of the E6/E6AP/p53 complex required for HPV-mediated degradation of p53. Nature 2016, 529, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Macalino, S.J.; Gosu, V.; Hong, S.; Choi, S. Role of computer-aided drug design in modern drug discovery. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 1686–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yella, J.K.; Yaddanapudi, S.; Wang, Y.; Jegga, A.G. Changing Trends in Computational Drug Repositioning. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, D.; Silvestre, S.; Duarte, A.P.; Passarinha, L.; Sousa, Â. In Silico Approaches: A Way to Unveil Novel Therapeutic Drugs for Cervical Cancer Management. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abotaleb, M.; Samuel, S.M.; Varghese, E.; Varghese, S.; Kubatka, P.; Liskova, A.; Büsselberg, D. Flavonoids in Cancer and Apoptosis. Cancers 2019, 11, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mark, P.; Nilsson, L. Structure and Dynamics of the TIP3P, SPC, and SPC/E Water Models at 298 K. J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 9954–9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, V.; Santos, A.O.; Almeida, P.; Silvestre, S. Novel 4-azaandrostenes as prostate cancer cell growth inhibitors: Synthesis, antiproliferative effects, and molecular docking studies. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2019, 22, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, I.M.; Rocha, S.M.; Gaspar, C.; Alvelos, M.I.; Santos, C.R.; Socorro, S.; Maia, C.J. Knockdown of STEAP1 inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in LNCaP prostate cancer cells counteracting the effect of androgens. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed Abdul Rahman, S.N.; Abdul Wahab, N.; Abd Malek, S.N. In Vitro Morphological Assessment of Apoptosis Induced by Antiproliferative Constituents from the Rhizomes of Curcuma zedoaria. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2013, 2013, 257108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batra, P.; Sharma, A.K. Anti-cancer potential of flavonoids: Recent trends and future perspectives. 3 Biotech 2013, 3, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raina, R.; Pramodh, S.; Rais, N.; Haque, S.; Shafarin, J.; Bajbouj, K.; Hamad, M.; Hussain, A. Luteolin inhibits proliferation, triggers apoptosis and modulates Akt/mTOR and MAP kinase pathways in HeLa cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaduvanshi, S.; Ero, R.; Kumar, V. The mechanism of complex formation between calmodulin and voltage gated calcium channels revealed by molecular dynamics. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci-Lopez, J.; Vidal-Limon, A.; Zunniga, M.; Jimenez, V.A.; Alderete, J.B.; Brizuela, C.A.; Aguila, S. Molecular modeling simulation studies reveal new potential inhibitors against HPV E6 protein. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Soto, A.F.; Salas-Vidal, E.; Milan-Pacheco, C.; Sanchez-Carranza, J.N.; Peralta-Zaragoza, O.; Gonzalez-Maya, L. Quercetin induces G2 phase arrest and apoptosis with the activation of p53 in an E6 expression independent manner in HPVpositive human cervical cancer derived cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 2097–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, J.S.M.; Sethi, G.; Lee, G.S.; Malek, S.N.A. Chalepin: Isolated from Ruta angustifolia L. Pers induces mitochondrial mediated apoptosis in lung carcinoma cells. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyd, L.S.; Gozuacik, D.; Joubert, A.M. The in vitro effects of a novel estradiol analog on cell proliferation and morphology in human epithelial cervical carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2018, 23, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ham, S.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, T.H.; Bak, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Song, Y.S.; Park, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, M.S.; Kang, J.W.; et al. Luteolin induces intrinsic apoptosis via inhibition of E6/E7 oncogenes and activation of extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways in HPV-18-associated cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2683–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matlashewski, G.; Banks, L.; Pim, D.; Crawford, L. Analysis of human p53 proteins and mRNA levels in normal and transformed cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1986, 154, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yang, D.; Zhou, C.; Cheng, K.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Fang, L.; Xie, P. β-Actin as a loading control for plasma-based Western blot analysis of major depressive disorder patients. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 427, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, A.N.; Bhargava, P.; Dhanjal, J.K.; Putri, J.F.; Radhakrishnan, N.; Shefrin, S.; Ishida, Y.; Terao, K.; Sundar, D.; Kaul, S.C.; et al. Combination of Withaferin-A and CAPE Provides Superior Anticancer Potency: Bioinformatics and Experimental Evidence to Their Molecular Targets and Mechanism of Action. Cancers 2021, 12, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.R. (Ed.) Chapter 9: The Cell Cycle and Cancer. In Medical Cell Biology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, R.; Chaudhry, G.-E.S. Understanding Apoptosis and Apoptotic Pathways Targeted Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, D.A.; Yang, N.; Ray, S.D. Apoptosis. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oancea, M.; Mazumder, S.; Crosby, M.E.; Almasan, A. Apoptosis assays. Methods Mol. Med. 2006, 129, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wu, S.; Teraishi, F.; Davis, J.J.; Jacob, D.; Fang, B. Induction of S-phase arrest and p21 overexpression by a small molecule 2[[3-(2,3-dichlorophenoxy)propyl] amino]ethanol in correlation with activation of ERK. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4984–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiffman, M.; Doorbar, J.; Wentzensen, N.; Sanjosé, S.D.; Fakhry, C.; Monk, B.J.; Stanley, M.A.; Franceschi, S. Carcinogenic human papillomavirus infection. Nat. Rev. 2016, 2, 16086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagala, R.; Kausar, H.; Munjal, C.; Gupta, R.C. Withaferin A induces p53-dependent apoptosis by repression of HPV oncogenes and upregulation of tumor suppressor proteins in human cervical cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Lozano, G. p53: Multiple Facets of a Rubik’s Cube. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2017, 1, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grilo, A.L.; Mantalaris, A. Apoptosis: A mammalian cell bioprocessing perspective. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.W.; Pattanayak, S.P. Taxifolin Inhibits 7,12-Dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced Breast Carcinogenesis by Regulating AhR/CYP1A1 Signaling Pathway. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2018, 13, S749–S755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manigandan, K.; Manimaran, D.; Jayaraj, R.L.; Elangovan, N.; Dhivya, V.; Kaphle, A. Taxifolin curbs NF-κB-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling via up-regulating Nrf2 pathway in experimental colon carcinogenesis. Biochimie 2015, 119, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, E.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, Q.; Cao, H. The anti-tumor effect of taxifolin on lung cancer via suppressing stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and oncogenesis in nude mice. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gu, N.; Xue, C.; Li, B.R. Plant flavonoid taxifolin inhibits the growth, migration and invasion of human osteosarcoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3239–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.R.; Al Zaharna, M.; Wong, M.M.-K.; Chiu, S.-K.; Cheung, H.-Y. Taxifolin Enhances Andrographolide-Induced Mitotic Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Prostate Cancer Cells via Spindle Assembly Checkpoint Activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selivanova, G. Wild type p53 reactivation: From lab bench to clinic. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2628–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zawacka-Pankau, J.; Selivanova, G. Pharmacological reactivation of p53 as a strategy to treat cancer. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 277, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
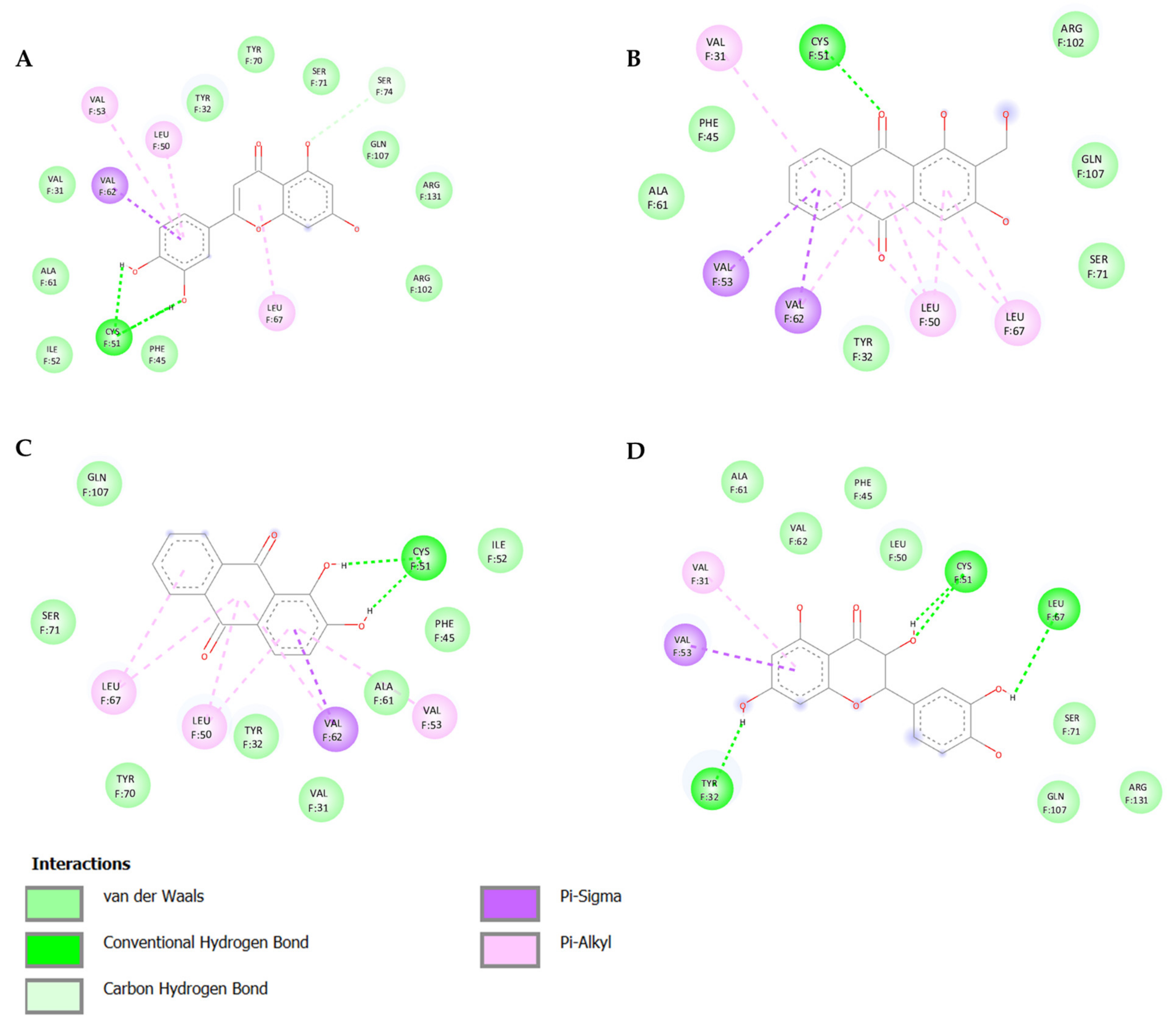

| Natural Products | Structure | Binding Energy (Kcal/mol) | Main Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alizarin | 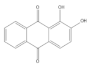 | −6.52 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Caffeic acid | 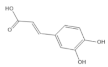 | −5.42 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Cyanidin-3-O-glycoside | 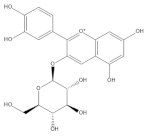 | −5.45 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Arg55 |
| Cineol |  | −4.73 | Leu67, Tyr32, Cys51, Leu50, Val62 |
| Kuromanin |  | −5.22 | Cys51, Leu67, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Ellagic acid | 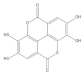 | −5.36 | Tyr70, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62, Arg131 |
| Ferulic acid |  | −5.45 | Cys51, Leu67, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Gallic acid | 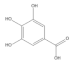 | −4.43 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Leu50, Tyr32, Val62 |
| Genistin | 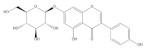 | −5.29 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Linalool |  | −4.56 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Lucidin | 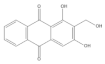 | −5.87 | Cys51, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| p-coumaric acid | 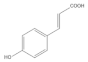 | −5.43 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Quercetin-3-4′-di-O-glycoside |  | −3.66 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Arg55, Val62, Arg131 |
| Rosmarinic acid |  | −5.11 | Cys51, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Sabinene |  | −4.53 | Cys51, Leu67, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Syringic acid |  | −4.69 | Cys51, Leu67, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Taxifolin |  | −5.63 | Cys51, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62, Arg131 |
| Rutin | 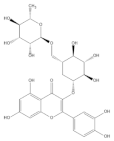 | −4.76 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62, Arg55, Arg131 |
| Vanillic acid | 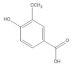 | −4.44 | Cys51, Leu67, Leu50, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Luteolin | 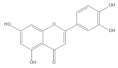 | −6.28 | Cys51, Tyr70, Leu67, Gln107, Leu50, Arg131, Tyr32, Val31, Val62 |
| Compound Concentration that Reduces Cell Viability by 50% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic Compounds | NHEK | C33A | HeLa | Caski |
| Alizarin | >100 µM | >100 µM | 64 µM | >100 µM |
| Lucidin | >100 µM | >100 µM | 23 µM | 45 µM |
| Taxifolin | >100 µM | >100 µM | 63 µM | >100 µM |
| Percentage of Necrotic Cells (%) | Percentage of Apoptotic Cells (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| DMSO | 0.74 ± 0.6 | 1.43 ± 0.44 |
| Lucidin 23 µM | 1.78 ± 0.69 (*) | 5.16 ± 0.69 (****) |
| Taxifolin 63 µM | 2.54 ± 0.51 (**) | 6.43 ± 0.44 (****) |
| Alizarin 64 µM | 8.94 ± 0.35 (****) | 3.24 ± 0.80 (**) |
| Luteolin 23 µM | 2.56 ± 0.62 (*) | 4.46 ± 0.91 (***) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, D.; Yaduvanshi, S.; Silvestre, S.; Duarte, A.P.; Santos, A.O.; Soares, C.P.; Kumar, V.; Passarinha, L.; Sousa, Â. Taxifolin and Lucidin as Potential E6 Protein Inhibitors: p53 Function Re-Establishment and Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122834
Gomes D, Yaduvanshi S, Silvestre S, Duarte AP, Santos AO, Soares CP, Kumar V, Passarinha L, Sousa Â. Taxifolin and Lucidin as Potential E6 Protein Inhibitors: p53 Function Re-Establishment and Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2022; 14(12):2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122834
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, Diana, Shivani Yaduvanshi, Samuel Silvestre, Ana Paula Duarte, Adriana O. Santos, Christiane P. Soares, Veerendra Kumar, Luís Passarinha, and Ângela Sousa. 2022. "Taxifolin and Lucidin as Potential E6 Protein Inhibitors: p53 Function Re-Establishment and Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells" Cancers 14, no. 12: 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122834
APA StyleGomes, D., Yaduvanshi, S., Silvestre, S., Duarte, A. P., Santos, A. O., Soares, C. P., Kumar, V., Passarinha, L., & Sousa, Â. (2022). Taxifolin and Lucidin as Potential E6 Protein Inhibitors: p53 Function Re-Establishment and Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells. Cancers, 14(12), 2834. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14122834