Setting the Research Agenda for Clinical Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Imaging
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
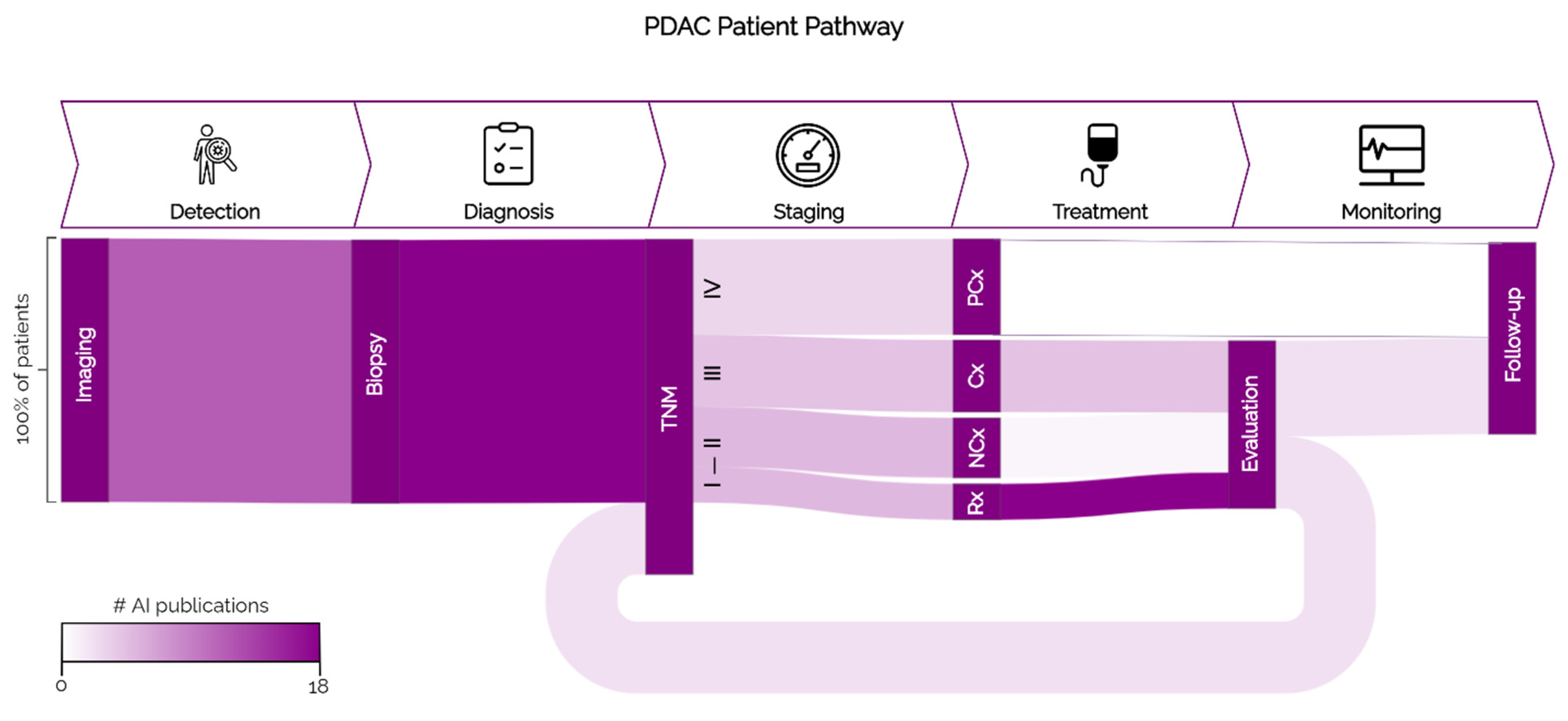
2. PDAC Patient Pathway
2.1. Detection
2.2. Diagnosis
2.3. Staging
2.4. Treatment
2.5. Treatment Monitoring
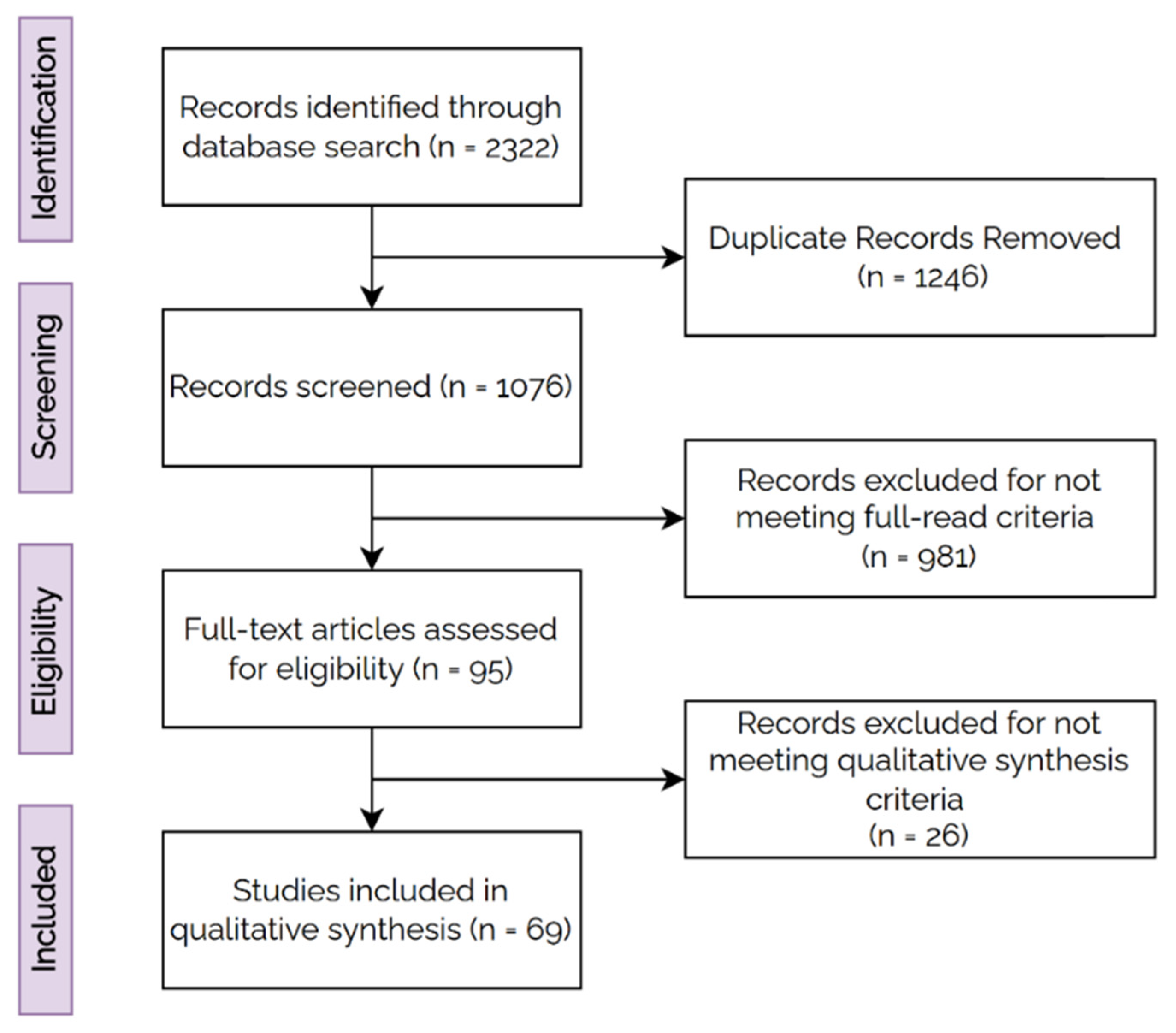
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
4.1. Detection
4.2. Diagnosis
4.3. Staging
4.4. Treatment
4.5. Treatment Monitoring
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| PubMed | (“Pancreatic Neoplasms”(Mesh:NoExp) OR “Carcinoma, Pancreatic Ductal”(Mesh) OR “Pancreatic Intraductal Neoplasms”(Mesh) OR (Pancrea*(tiab) AND (Neoplasm*[tiab] OR cancer*[tiab] OR Carcinoma*[tiab] OR Adenocarcinoma*[tiab])) OR PDAC(tiab)) AND (“Artificial Intelligence”(Mesh) OR AI(tiab) OR Artificial Intelligence(tiab) OR CNN(tiab) OR Convnet(tiab) OR Deep Learning(tiab) OR Machine learning (tiab) OR Neural network*(tiab) OR pathomic*(tiab) OR radiomic*(tiab) OR supervised Learning(tiab) OR Transfer Learning(tiab) OR Unet(tiab) OR unsupervised Learning(tiab)) |
| Embase | (“Pancreatic Neoplasms” or “Carcinoma, Pancreatic Ductal” or “Pancreatic Intraductal Neoplasms” or (Pancrea* and (Neoplasm* or cancer* or Carcinoma* or Adenocarcinoma*)) or PDAC).mp. and (“Artificial IntelligenceOR AI” or CNN or Convnet or “Deep Learning” or “Machine learning” or “Neural network*” or pathomic* or radiomic* or “supervised Learning” or “Transfer Learning” or Unet or “unsupervised Learning”). |
| Web of Science | (TS = ((“Pancreatic Neoplasms” OR “Carcinoma, Pancreatic Ductal” OR “Pancreatic Intraductal Neoplasms” OR (Pancrea* AND (Neoplasm* OR cancer* OR Carcinoma* OR Adenocarcinoma*)) OR PDAC))) AND TS = ((“Artificial Intelligence”OR AI OR CNN OR Convnet OR “Deep Learning” OR “Machine learning” OR “Neural network*” OR pathomic* OR radiomic* OR “supervised Learning” OR “Transfer Learning” OR Unet OR “unsupervised Learning”)) |
| Cochrane | (“Pancreatic Neoplasms”(Mesh:NoExp) OR “Carcinoma, Pancreatic Ductal”(Mesh) OR (Pancrea*[tiab] AND (Neoplasm*[tiab] OR cancer*[tiab] OR Carcinoma*[tiab] OR Adenocarcinoma*[tiab])) OR PDA*(tiab)) AND (“Artificial Intelligence”(Mesh) OR AI(tiab) OR Artificial Intelligence(tiab) OR CNN(tiab) OR Convnet(tiab) OR Deep Learning(tiab) OR Machine learning (tiab) OR Neural network*(tiab) OR pathomic*(tiab) OR radiomic*(tiab) OR supervised Learning(tiab) OR Transfer Learning(tiab) OR Unet(tiab) OR unsupervised Learning(tiab)) |
- (1)
- Study was published in a peer-reviewed journal and was not an abstract, review paper, conference paper, commentary, editorial, or not available. (n = 293)
- (2)
- Study considered patients clinically diagnosed with pancreatic cancer (pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma or non-specified type of pancreatic cancer). (n = 343)
- (3)
- Study used AI to predict an outcome related to one of the following tasks (n = 289):
- ○
- Detection: determine the presence or absence of PDAC in an input image with or without localization of the tumours.
- ○
- Diagnosis: differentiate between PDAC and other benign and/or malignant pancreatic lesions.
- ○
- Staging: stratify PDAC patients into different subgroups based on clinical/histopathological outcomes or survival.
- ○
- Treatment indication: predict treatment response based on pre-treatment data.
- ○
- Treatment response prediction: monitor treatment response based on follow-up data.
- (4)
- Study used medical images as input. Included modalities were computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR), ultrasound (EUS), 18fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18FDG PET/CT), and whole-slide images (WSI). (n = 56)
- (5)
- Study included a population larger than 20 patients. (n = 3)
- (6)
- Clinical information regarding patients in the used cohorts was available. Minimum required fields were: number of patients, age distribution, and sex distribution. (n = 14)
- (7)
- Study reports results in at least one patient cohort not used to train the model. (n = 3)
- (8)
- Study reports how the results were obtained. (n = 6)
- Modality (CT, MR, EUS, 8FDG PET/CT, WSI)
- Task (detection, diagnosis, staging, treatment, monitoring)
- Tissue of interest (PDAC, pancreatic cancer)
- Tumour location (head, neck, body, tail)
- Disease stage (I, II, III, IV)
- Therapy
- Type of AI (Radiomics, Deep Learning, other)
- Model
- Ground truth
- Performance metric
- Type of internal validation (single split, cross-validation)
- Performance on training set
- Performance on internal validation set
- Performance on internal test set
- Performance on external test set
- Cohort size for development set (train/validation)
- Patient distribution for development set with regard to considered ground truth
- Cohort size for internal test set
- Patient distribution for internal test set with regard to considered ground truth
- Cohort size for external test set
- Patient distribution for external test set with regard to considered ground truth
References
- Bengtsson, A.; Andersson, R.; Ansari, D. The Actual 5-Year Survivors of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Based on Real-World Data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michl, P.; Löhr, M.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Capurso, G.; Rebours, V.; Malats, N.; Ollivier, M.; Ricciardiello, L. UEG Position Paper on Pancreatic Cancer. Bringing Pancreatic Cancer to the 21st Century: Prevent, Detect, and Treat the Disease Earlier and Better. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2021, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löhr, J.M. Pancreatic Cancer Should Be Treated as a Medical Emergency. BMJ 2014, 349, g5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latenstein, A.E.J.; van der Geest, L.G.M.; Bonsing, B.A.; Groot Koerkamp, B.; Haj Mohammad, N.; de Hingh, I.H.J.T.; de Meijer, V.E.; Molenaar, I.Q.; van Santvoort, H.C.; van Tienhoven, G.; et al. Nationwide Trends in Incidence, Treatment and Survival of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 125, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elbanna, K.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Kim, T.K. Imaging Diagnosis and Staging of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baxi, V.; Edwards, R.; Montalto, M.; Saha, S. Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence in Translational Medicine and Clinical Practice. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 35, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sántha, P.; Lenggenhager, D.; Finstadsveen, A.; Dorg, L.; Tøndel, K.; Amrutkar, M.; Gladhaug, I.P.; Verbeke, C. Morphological Heterogeneity in Pancreatic Cancer Reflects Structural and Functional Divergence. Cancers 2021, 13, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Mi, W.; Pan, B.; Guo, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Zheng, J.; Zou, C.; Zhang, T.; Liang, Z.; et al. Automatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Detection in Whole Slide Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 665929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, B.V.; Tutucu, F.; van Roessel, S.; Adsay, V.; Basturk, O.; Campbell, F.; Doglioni, C.; Esposito, I.; Feakins, R.; Fukushima, N.; et al. Amsterdam International Consensus Meeting: Tumor Response Scoring in the Pathology Assessment of Resected Pancreatic Cancer after Neoadjuvant Therapy. Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kann, B.H.; Hosny, A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Oncology. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 916–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, K.G.; Schalekamp, S.; Rutten, M.J.C.M.; van Ginneken, B.; de Rooij, M. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: 100 Commercially Available Products and Their Scientific Evidence. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3797–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Commun ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A Survey on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Survival Rates for Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/pancreatic-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Egawa, S.; Toma, H.; Ohigashi, H.; Okusaka, T.; Nakao, A.; Hatori, T.; Maguchi, H.; Yanagisawa, A.; Tanaka, M. Japan Pancreatic Cancer Registry; 30th Year Anniversary: Japan Pancreas Society. Pancreas 2012, 41, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho Yoon, S.; Min Lee, J.; Yoon Cho Kyung Bun Lee, J.; Eun Kim, J.; Kyoung Moon, S.; Jin Kim, S.; Hyun Baek, J.; Ho Kim, S.; Hyung Kim, S.; Young Lee, J.; et al. Small (≤20 mm) Pancreatic Adenocarcinomas: Analysis of Enhancement Patterns and Secondary Signs with Multiphasic Multidetector CT. Radiology 2011, 259, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Yu, E.S.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, J.; Byun, J.H.; Lee, S.S.; Hwang, H.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Visually Isoattenuating Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma at Dynamic-Enhanced CT: Frequency, Clinical and Pathologic Characteristics, and Diagnosis at Imaging Examinations. Radiology 2010, 257, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.P.; Sheedy, S.; Goenka, A.H.; Wells, M.; Lee, N.J.; Barlow, J.; Sharma, A.; Kandlakunta, H.; Chandra, S.; Garg, S.K.; et al. Computerized Tomography Scan in Pre-Diagnostic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Stages of Progression and Potential Benefits of Early Intervention: A Retrospective Study. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual and the Future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo-Marin, J.; Vila, J.J.; Perez-Miranda, M. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 6, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Miao, D.L.; Chen, L. Nomogram for Predicting Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Roessel, S.; Kasumova, G.G.; Verheij, J.; Najarian, R.M.; Maggino, L.; de Pastena, M.; Malleo, G.; Marchegiani, G.; Salvia, R.; Ng, S.C.; et al. International Validation of the Eighth Edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM Staging System in Patients with Resected Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, e183617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittel, U.A.; Lubgan, D.; Ghadimi, M.; Belyaev, O.; Uhl, W.; Bechstein, W.O.; Grützmann, R.; Hohenberger, W.M.; Schmid, A.; Jacobasch, L.; et al. Consensus in Determining the Resectability of Locally Progressed Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma—Results of the Conko-007 Multicenter Trial. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.B.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Byun, J.H.; Hong, S.M.; Song, K.B.; Kim, S.C. Pancreatic Cancer CT: Prediction of Resectability According to NCCN Criteria. Radiology 2018, 289, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, A.; Schwarz, L.; Borbath, I.; Henry, A.; van Laethem, J.L.; Malka, D.; Ducreux, M.; Conroy, T. An Update on Treatment Options for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2019, 11, 1758835919875568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pearce, A.; Haas, M.; Viney, R.; Pearson, S.A.; Haywood, P.; Brown, C.; Ward, R. Incidence and Severity of Self-Reported Chemotherapy Side Effects in Routine Care: A Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harder, F.N.; Jungmann, F.; Kaissis, G.A.; Lohöfer, F.K.; Ziegelmayer, S.; Havel, D.; Quante, M.; Reichert, M.; Schmid, R.M.; Demir, I.E.; et al. [18F]FDG PET/MRI Enables Early Chemotherapy Response Prediction in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. EJNMMI Res. 2021, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I.E.; Jäger, C.; Schlitter, M.M.; Konukiewitz, B.; Stecher, L.; Schorn, S.; Tieftrunk, E.; Scheufele, F.; Calavrezos, L.; Schirren, R.; et al. R0 Versus R1 Resection Matters after Pancreaticoduodenectomy, and Less after Distal or Total Pancreatectomy for Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2017, 268, 1058–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjol, U.; Chandranath, A.; Jonnada, P.; Cherukuru, S.; Annavarjula, V.; Morla, S.A. Lymph Node Ratio as a Prognostic Marker in Pancreatic Cancer Survival: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2020, 12, e9597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummers, W.S.; Groen, J.V.; Sibinga Mulder, B.G.; Farina-Sarasqueta, A.; Morreau, J.; Putter, H.; van de Velde, C.J.; Vahrmeijer, A.L.; Bonsing, B.A.; Mieog, J.S.; et al. Impact of Resection Margin Status on Recurrence and Survival in Pancreatic Cancer Surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2019, 106, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perri, G.; Prakash, L.R.; Katz, M.H.G. Response to Preoperative Therapy in Localized Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baliyan, V.; Kordbacheh, H.; Parakh, A.; Kambadakone, A. Response Assessment in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Role of Imaging. Abdom. Radiol. 2018, 43, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Roessel, S.; Janssen, B.V.; Soer, E.C.; Fariña Sarasqueta, A.; Verbeke, C.S.; Luchini, C.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Verheij, J.; Besselink, M.G. Scoring of Tumour Response after Neoadjuvant Therapy in Resected Pancreatic Cancer: Systematic Review. Br. J. Surg. 2021, 108, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeke, C.; Häberle, L.; Lenggenhager, D.; Esposito, I. Pathology Assessment of Pancreatic Cancer Following Neoadjuvant Treatment: Time to Move On. Pancreatology 2018, 18, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, N.; Schuurmans, M.; Litjens, G.; Bosma, J.S.; Hermans, J.; Huisman, H. Fully Automatic Deep Learning Framework for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Detection on Computed Tomography. Cancers 2022, 14, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Lin, X.; Qian, X. Model-Driven Deep Learning Method for Pancreatic Cancer Segmentation Based on Spiral-Transformation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 41, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Wu, T.; Chen, P.T.; Tsai, Y.M.; Roth, H.; Wu, M.S.; Liao, W.C.; Wang, W. Deep Learning to Distinguish Pancreatic Cancer Tissue from Non-Cancerous Pancreatic Tissue: A Retrospective Study with Cross-Racial External Validation. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e303–e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, W.; Fishman, E.K.; Yuille, A.L. Learning Inductive Attention Guidance for Partially Supervised Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Prediction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 2723–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Liu, Z.X.; Zhang, J.J.; Wu, F.T.; Xu, C.F.; Shen, Z.; Yu, C.H.; Li, Y.M. Construction of a Convolutional Neural Network Classifier Developed by Computed Tomography Images for Pancreatic Cancer Diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 5156–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.C.; Solmaz, B.; Park, S.; Kawamoto, S.; Yuille, A.L.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K. Diagnostic Performance of Commercially Available vs. in-House Radiomics Software in Classification of CT Images from Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma vs. Healthy Controls. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 2469–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Yao, Y. An Effective Computer Aided Diagnosis Model for Pancreas Cancer on PET/CT Images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 165, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonozuka, R.; Itoi, T.; Nagata, N.; Kojima, H.; Sofuni, A.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tanaka, R.; Nagakawa, Y.; Mukai, S. Deep Learning Analysis for the Detection of Pancreatic Cancer on Endosonographic Images: A Pilot Study. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2021, 28, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.J.; Yin, J.; Qian, W.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, Z.X.; Yu, H.P.; Ji, L.; Zeng, X.X. A Novel Multiresolution-Statistical Texture Analysis Architecture: Radiomics-Aided Diagnosis of PDAC Based on Plain CT Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.C.; Park, S.; Kawamoto, S.; Fouladi, D.F.; Shayesteh, S.; Zinreich, E.S.; Graves, J.S.; Horton, K.M.; Hruban, R.H.; Yuille, A.L.; et al. Utility of CT Radiomics Features in Differentiation of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma From Normal Pancreatic Tissue. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozkan, M.; Cakiroglu, M.; Kocaman, O.; Kurt, M.; Yilmaz, B.; Can, G.; Korkmaz, U.; Dandil, E.; Eksi, Z. Age-Based Computer-Aided Diagnosis Approach for Pancreatic Cancer on Endoscopic Ultrasound Images. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Si, K.; Xue, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q.; Gong, W.; Liang, T.; Duan, S. Fully End-to-End Deep-Learning-Based Diagnosis of Pancreatic Tumors. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.; Tsuneki, M.; Fukushima, N.; Koga, Y.; Higashi, M.; Notohara, K.; Aishima, S.; Ohike, N.; Tajiri, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. A Deep Learning Model to Detect Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma on Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegsmann, M.; Kriegsmann, K.; Steinbuss, G.; Zgorzelski, C.; Kraft, A.; Gaida, M.M. Deep Learning in Pancreatic Tissue: Identification of Anatomical Structures, Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia, and Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ming, B.; Zhou, T.; Wu, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Chen, T.W.; Zhang, X.M. Radiomics Model Based on MR Images to Discriminate Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Mass-Forming Chronic Pancreatitis Lesions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegelmayer, S.; Kaissis, G.; Harder, F.; Jungmann, F.; Müller, T.; Makowski, M.; Braren, R. Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Assisted Feature Extraction for Diagnostic Discrimination and Feature Visualization in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) versus Autoimmune Pancreatitis (AIP). J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Li, S.; Guo, Y.T.; Zhou, Y.P.; Zhang, Z.D.; Li, S.; Lu, Y. Establishment and Application of an Artificial Intelligence Diagnosis System for Pancreatic Cancer with a Faster Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 2795–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Səftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Dietrich, C.F.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Hocke, M.; Seicean, A.; Ignee, A.; Hassan, H.; Streba, C.T.; Ioncicə, A.M.; et al. Quantitative Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic EUS in Differential Diagnosis of Focal Pancreatic Masses (with Videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimian, S.; Singh, R.; Netaji, A.; Madhusudhan, K.S.; Homayounieh, F.; Primak, A.; Lades, F.; Saini, S.; Kalra, M.K.; Sharma, S. Characterization of Benign and Malignant Pancreatic Lesions with DECT Quantitative Metrics and Radiomics. Acad. Radiol. 2021, 29, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wang, Y.-R.; Zhuo, L.-Y.; Yin, X.-P.; Ren, J.-L.; Li, C.-Y.; Xing, L.-H.; Zheng, T.-T. Retrospective Analysis of the Value of Enhanced CT Radiomics Analysis in the Differential Diagnosis between Pancreatic Cancer and Chronic Pancreatitis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Zuo, C.; Yang, Z.; Yang, X.; Ren, S.; Peng, Y.; Sun, G.; Shen, J.; Cheng, C.; et al. Radiomics Model of Dual-Time 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT Imaging to Distinguish between Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6983–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Zhao, R.; Cui, W.; Qiu, W.; Guo, K.; Cao, Y.; Duan, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R. Computed Tomography-Based Radiomics Signature for the Preoperative Differentiation of Pancreatic Adenosquamous Carcinoma From Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, S.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, J.; Guo, K.; Gu, X.; Duan, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R. Diagnostic Accuracy of Unenhanced CT Texture Analysis to Differentiate Mass-Forming Pancreatitis from Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Chu, L.C.; Hruban, R.H.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W.; Yuille, A.L.; Fouladi, D.F.; Shayesteh, S.; Ghandili, S.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. Differentiating Autoimmune Pancreatitis from Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with CT Radiomics Features. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wan, J.; Li, J.; Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Tian, J.; Xue, H. Differentiation of Atypical Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using CT Based Radiomics. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 117, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Cui, W.; Zhao, R.; Qiu, W.; Duan, S.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of Texture Analysis for the Differential Diagnosis of Mass-Forming Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma on Contrast-Enhanced CT Images. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Pan, G.; Sun, G.; Chang, Y.; Zuo, C.; Yang, X. Radiomics Analysis for the Differentiation of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma in 18 F-FDG PET/CT. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 4520–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sǎftoiu, A.; Vilmann, P.; Gorunescu, F.; Janssen, J.; Hocke, M.; Larsen, M.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Arcidiacono, P.; Will, U.; Giovannini, M.; et al. Efficacy of an Artificial Neural Network-Based Approach to Endoscopic Ultrasound Elastography in Diagnosis of Focal Pancreatic Masses. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, C.; Li, D.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Tong, T.; Liu, L.; Jiang, D.; Jiang, L.; Ruan, G.; Hai, N.; et al. Deep Learning Radiomics of Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Predicting Lymph Node Metastases of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 49, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaddad, A.; Sargos, P.; Desrosiers, C. Modeling Texture in Deep 3D CNN for Survival Analysis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021, 25, 2454–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Ma, C.; Huang, X.; Cao, D. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Radiomics-Based Nomogram From Primary Tumor for Pretreatment Prediction of Peripancreatic Lymph Node Metastasis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Multicenter Study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 55, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N.; Cui, L.; Luo, Y.; Chang, Z.; Yu, B.; Liu, Z. Development and Multicenter Validation of a CT-Based Radiomics Signature for Discriminating Histological Grades of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.W.; Lee, J.H. New Morphological Features for Grading Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 175271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, Y.; Guo, S.; Jiang, H.; Gao, S.; Shao, C.; Cao, K.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; et al. Radiomics Nomogram for the Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Imaging 2022, 22, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Jiang, H.; Meng, Y.; Liu, F.; Cao, K.; Zhang, H.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; et al. Machine Learning for MRI Radiomics: A Study Predicting Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 4800–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, C.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Wu, A.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Han, P.; Wang, S. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma at CT: A Combined Nomogram Model to Preoperatively Predict Cancer Stage and Survival Outcome. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dong, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Hang, J.; Wu, L. Development and Validation of a Radiomics Nomogram to Discriminate Advanced Pancreatic Cancer with Liver Metastases or Other Metastatic Patterns. Cancer Biomark 2021, 32, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, W.; Sun, D.; Ding, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Huo, L. Preoperative Prediction of Pathological Grade in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Based on 18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics. EJNMMI Res. 2021, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaissis, G.A.; Ziegelmayer, S.; Lohöfer, F.K.; Harder, F.N.; Jungmann, F.; Sasse, D.; Muckenhuber, A.; Yen, H.Y.; Steiger, K.; Siveke, J.; et al. Image-Based Molecular Phenotyping of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhang, R.; Gao, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, L. Radiomics-Assisted Presurgical Prediction for Surgical Portal Vein-Superior Mesenteric Vein Invasion in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Gu, Q.; Hu, X.; Tan, X.; Liu, J.; Xie, A.; Huang, F. Applying a Radiomics-Based Strategy to Preoperatively Predict Lymph Node Metastasis in the Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. X Ray Sci. Technol. 2020, 28, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Li, M.; Yang, J.; Hou, W.; Du, M.; Chen, K.; Qu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Contrast-Enhanced CT Radiomics for Predicting Lymph Node Metastasis in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Pilot Study. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longlong, Z.; Xinxiang, L.; Yaqiong, G.; Wei, W. Predictive Value of the Texture Analysis of Enhanced Computed Tomographic Images for Preoperative Pancreatic Carcinoma Differentiation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Duan, N.; Chen, X.; Ren, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Machine Learning-Based Quantitative Computed Tomography Texture Analysis For Prediction Of Histopathological Grade. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 9253–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Healy, G.M.; Salinas-Miranda, E.; Jain, R.; Dong, X.; Deniffel, D.; Borgida, A.; Hosni, A.; Ryan, D.T.; Njeze, N.; McGuire, A.; et al. Pre-Operative Radiomics Model for Prognostication in Resectable Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma with External Validation. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 32, 2492–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lobo-Mueller, E.M.; Karanicolas, P.; Gallinger, S.; Haider, M.A.; Khalvati, F. CNN-Based Survival Model for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma in Medical Imaging. BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Shi, Y.; Cao, K.; Lu, L.; Lu, J.; Song, Q.; Jin, G.; Xiao, J.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, L. DeepPrognosis: Preoperative Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer Survival and Surgical Margin via Comprehensive Understanding of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced CT Imaging and Tumor-Vascular Contact Parsing. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 73, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.D.; Baimas-George, M.R.; Murphy, K.J.; Pickens, R.C.; Iannitti, D.A.; Martinie, J.B.; Baker, E.H.; Vrochides, D.; Ocuin, L.M. Pure and Hybrid Deep Learning Models Can Predict Pathologic Tumor Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: A Pilot Study. Am. Surg. 2021, 87, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lobo-Mueller, E.M.; Karanicolas, P.; Gallinger, S.; Haider, M.A.; Khalvati, F. Improving Prognostic Performance in Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using Radiomics and Deep Learning Features Fusion in CT Images. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wan, Y.; Lou, J.; Xu, L.; Shi, A.; Yang, L.; Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; et al. Preoperative Recurrence Prediction in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma after Radical Resection Using Radiomics of Diagnostic Computed Tomography. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 43, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Wei, Y.; Cheng, S.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, K.; Xu, Q. Survival Prediction after Upfront Surgery in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Radiomic, Clinic-Pathologic and Body Composition Analysis. Pancreatology 2021, 21, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Gu, B.; Song, S.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. A Novel Validated Recurrence Stratification System Based on 18 F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics to Guide Surveillance After Resection of Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 650266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Tong, T.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Z. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Radiomics Nomogram Outperforms Clinical Model and TNM Staging for Survival Estimation after Curative Resection. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Sham, J.G.; Kawamoto, S.; Blair, A.B.; Rozich, N.; Fouladi, D.F.; Shayesteh, S.; Hruban, R.H.; He, J.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. CT Radiomics-Based Preoperative Survival Prediction in Patients With Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, E.; Du, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lin, C.; Kamal, A.; McAlister, J.; Liang, X.; Bavitz, K.; Rux, G.; Hollingsworth, M.; et al. Radiomics-Based Outcome Prediction for Pancreatic Cancer Following Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaissis, G.A.; Jungmann, F.; Ziegelmayer, S.; Lohöfer, F.K.; Harder, F.N.; Schlitter, A.M.; Muckenhuber, A.; Steiger, K.; Schirren, R.; Friess, H.; et al. Multiparametric Modelling of Survival in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using Clinical, Histomorphological, Genetic and Image-Derived Parameters. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, B.; Qiu, J.J.; Liu, J.H.; Ke, N.W. Identification of Pancreaticoduodenectomy Resection for Pancreatic Head Adenocarcinoma: A Preliminary Study of Radiomics. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2020, 2020, 2761627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ma, C.; Cao, K.; Fang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; Lu, J. Performance of CT-Based Radiomics in Diagnosis of Superior Mesenteric Vein Resection Margin in Patients with Pancreatic Head Cancer. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Liang, T.-B.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Lao, M.; Shen, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ying, S.; Sun, K.; et al. Development of a Novel Multiparametric MRI Radiomic Nomogram for Preoperative Evaluation of Early Recurrence in Resectable Pancreatic Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.F.; Han, Y.Q.; Lu, J.; Wei, J.W.; Guo, J.H.; Zhu, H.D.; Huang, M.; Ji, J.S.; Lv, W.F.; Chen, L.; et al. Radiomics Facilitates Candidate Selection for Irradiation Stents Among Patients With Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cozzi, L.; Comito, T.; Fogliata, A.; Franzese, C.; Franceschini, D.; Bonifacio, C.; Tozzi, A.; Brina, L.D.; Clerici, E.; Tomatis, S.; et al. Computed Tomography Based Radiomic Signature as Predictive of Survival and Local Control after Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Pancreatic Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaissis, G.; Ziegelmayer, S.; Lohöfer, F.; Steiger, K.; Algül, H.; Muckenhuber, A.; Yen, H.Y.; Rummeny, E.; Friess, H.; Schmid, R.; et al. A Machine Learning Algorithm Predicts Molecular Subtypes in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with Differential Response to Gemcitabine-Based versus FOLFIRINOX Chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaissis, G.; Ziegelmayer, S.; Lohöfer, F.; Algül, H.; Eiber, M.; Weichert, W.; Schmid, R.; Friess, H.; Rummeny, E.; Ankerst, D.; et al. A Machine Learning Model for the Prediction of Survival and Tumor Subtype in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma from Preoperative Diffusion-Weighted Imaging. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, J.; Langdon-Embry, L.; Cunanan, K.M.; Escalon, J.G.; Allen, P.J.; Lowery, M.A.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Gönen, M.; Do, R.G.; Simpson, A.L. Preliminary Study of Tumor Heterogeneity in Imaging Predicts Two Year Survival in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Song, J.; Pollom, E.; Alagappan, M.; Shirato, H.; Chang, D.T.; Koong, A.C.; Li, R. Quantitative Analysis of (18)F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Identifies Novel Prognostic Imaging Biomarkers in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Patients Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol Phys. 2016, 96, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, B.V.; Theijse, R.; van Roessel, S.; de Ruiter, R.; Berkel, A.; Huiskens, J.; Busch, O.R.; Wilmink, J.W.; Kazemier, G.; Valkema, P.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Based Segmentation of Residual Tumor in Histopathology of Pancreatic Cancer after Neoadjuvant Treatment. Cancers 2021, 13, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasief, H.; Zheng, C.; Schott, D.; Hall, W.; Tsai, S.; Erickson, B.; Allen Li, X. A Machine Learning Based Delta-Radiomics Process for Early Prediction of Treatment Response of Pancreatic Cancer. Npj Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenner, B.; Chari, S.T.; Kelsen, D.; Klimstra, D.S.; Pandol, S.J.; Rosenthal, M.; Rustgi, A.K.; Taylor, J.A.; Yala, A.; Abul-Husn, N.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: 2020 Summative Review. Pancreas 2021, 50, 251–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.P.; Hong, T.S.; Bardeesy, N. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Authors (Year) | Data | Approach | Model | Metric | Validation Performance | Test Performance | Dev. Cohort | Test Cohort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alves et al. (2022) [35] | CT | DL | 3D nnU-Net | AUC | 0.991 (0.970–1.0) | ** 0.889 (0.833–0.946) | 242 | ** 361 |
| Wang et al. (2021) [38] | CT | DL | 2D U-Net | SEN, SPE | 0.998, 0.965 | .. | 800 | .. |
| Liu et al. (2020) [37] | CT | DL | 2D VGG | AUC | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | * 0.997 (0.992–1.000) * 0.999 (0.998–1.000) ** 0.920 (0.891–0.948) | 412 | * 139 * 189 ** 363 |
| Ma et al. (2020) [39] | CT | DL | 2D 4-layer CNN | AUC | 0.9652 | .. | 412 | .. |
| Tonozuka et al. (2020) [42] | EUS | DL | 2D 7-layer CNN | AUC | 0.924 | * 0.940 | 93 | * 47 |
| Qiu et al. (2021) [43] | CT | Radiomics | SVM | AUC | 0.88 (0.84–0.92) | * 0.79 (0.71–0.87) | 312 | * 93 |
| Chen et al. (2021) [36] | CT | Radiomics | XGBoost | AUC | .. | * 0.98 (0.96–0.99) ** 0.76 (0.71–0.82) | 944 | * 383 ** 212 |
| Chu et al. (2020) [40] | CT | Radiomics | RF | SEN, SPE, ACC | 0.950, 0.923, 0.936 | .. | 380 | .. |
| Chu et al. (2019) [44] | CT | Radiomics | RF | AUC | .. | * 0.999 | 255 | * 125 |
| Li et al. (2018) [41] | 18FDG PET-CT | Radiomics | SVM-RF | SEN, SPE, ACC | 0.952 ± 0.009, 0.975 ± 0.004, 0.965 ± 0.007 | .. | 80 | .. |
| Ozkan et al. (2015) [45] | EUS | Radiomics | ANN | SEN, SPE, ACC | .. | * 0.833 ± 0.112, 0.933 ± 0.075, 0.875 ± 0.047 | 172 | * 72 images |
| Authors (Year) | Tissues of Interest | Data | Approach | Model | Metric | Validation Results | Test Results | Dev. Cohort | Test Cohort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si et al. (2021) [46] | PDAC, IPMN, SCN, other | CT | DL | ResNet + U-Net | ACC | .. | ** 0.827 | 319 | ** 347 |
| Naito et al. (2021) [47] | PDAC | WSI | DL | EfficientNet-B1 | AUC | .. | * 0.984 (0.960–0.998) | 413 | * 120 |
| Fu et al. (2021) [8] | PDAC | WSI | DL | Inception + U-Net | ACC | .. | * 1.0 ** 0.904 | 90 | * 47 ** 52 |
| Kriegsmann et al. (2021) [48] | PDAC | WSI | DL | EfficientNet | BACC | .. | * 0.921 | 201 | .. |
| Ziegelmayer et al. (2020) [50] | PDAC, AIP | CT | DL | RF | AUC | 0.90 ± 0.02 | .. | 86 | .. |
| Liu et al. (2019) [51] | PDAC | CT | DL | Faster R-CNN | AUC | .. | * 0.9632 | 238 | * 100 |
| Saftoiu et al. (2015) [52] | PDAC, MFP | EUS | ML | 2-layer ANN | SEN, SPE | .. | * 0.946 (0.882–0.978), 0.944 (0.839–0.986) | 142 | * 25 |
| Ebrahimian et al. (2021) [53] | Benign vs Malignant | CT | Radiomics | RF | AUC | .. | * 0.76 | 59 | * 44 |
| Deng et al. (2021) [49] | PDAC, MFP | MR | Radiomics | SVM | AUC | 0.997 (0.990–1.0) | ** 0.962 (0.907–1.0) | 64 | ** 55 |
| Ma et al. (2021) [54] | PDAC, CP | CT + clinical | Radiomics | LASSO | AUC | 0.980 (0.961–1.000) | .. | 175 | .. |
| Liu et al. (2021) [55] | PDAC, AIP | 18FDG PET-CT | Radiomics | SVM | AUC | 0.966 ± 0.008 | .. | 112 | .. |
| Ren et al. (2020) [56] | PDAC, PAC | CT | Radiomics | RF | AUC | 0.82 | .. | 112 | .. |
| Ren et al. (2020) [57] | PDAC, MFP | CT | Radiomics | RF | AUC | 0.98 (0.97–1.0) | .. | 109 | .. |
| Park et al. (2020) [58] | PDAC, AIP | CT | Radiomics | RF | AUC | .. | * 0.975 (0.936–1.0) | 120 | * 62 |
| He et al. (2019) [59] | PDAC, PNEN | CT | Radiomics | LASSO | AUC | 0.960 (0.942–0.979) | * 0.884 (0.831–0.927) | 100 | * 47 |
| Ren et al. (2019) [60] | PDAC, MFP | CT | Radiomics | LR | AUC | .. | * 0.9 | 109 | * 40 |
| Zhang et al. (2019) [61] | PDAC, AIP | 18FDG PET-CT | Radiomics | SVM- RF | AUC | 0.93 | .. | 111 | .. |
| Saftoiu et al. (2012) [62] | PDAC, CP | EUS | Radiomics | 2-layer ANN | AUC | 0.94 (0.91–0.97) | .. | 258 | .. |
| Authors (Year) | Ground Truth | Data | Approach | Model | Metric | Validation Performance | Test Performance | Dev. Cohort | Test Cohort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An et al. (2021) [63] | LNM | CT + clinical | DL | Resnet-18 | AUC | 0.90 (0.88–0.92) | * 0.92 (0.91–0.92) | 113 | * 35 |
| Chaddad et al. (2020) [64] | Short term vs. long-term survival | CT | DL + ML | CNN + RF | AUC | 0.72 | .. | 159 | .. |
| Song et al. (2013) [67] | Grading 1 vs. 2 | WSI | ML | SVM | AUC | 0.79 | .. | 240 | .. |
| Bianet al. (2022) [68] | LNM | MR | Radiomics | LR | AUC | 0.75 (0.68–0.82) | * 0.81 (0.69–0.94) | 180 | * 45 |
| Shi et al. (2022) [65] | LNM | MR + clinical | Radiomics | LR | AUC | 0.909 (0.854–0.964) | * 0.835 (0.751–0.919) ** 0.805 (0.720–0.890) | 199 | ** 52 |
| Bian et al. (2021) [69] | TIL | MR | Radiomics | XGBoost | AUC | 0.86 (0.79–0.93) | * 0.79 (0.64–0.93) | 116 | * 40 |
| Cen et al. (2021) [70] | Stage I–II vs. Stage III–IV | CT | Radiomics | LR | AUC | 0.940 (0.871–0.979) | * 0.912 (0.781–0.978) | 94 | * 41 |
| Zhang et al. (2021) [71] | Liver metastasis vs. other metastasis | CT | Radiomics | RF | AUC | 0.81 | .. | 77 | .. |
| Xing et al. (2021) [72] | Grading 1 vs. 2/3 | 18FDG PET-CT | Radiomics | XGBoost | AUC | .. | * 0.921 (0.846–0.996) | 99 | * 50 |
| Kaissis et al. (2020) [73] | QMS | CT | Radiomics | RF | AUC | 0.93 ± 0.01 | .. | 181 | .. |
| Chen et al. (2020) [74] | PV-SMV invasion | CT | Radiomics | ElasticNet | AUC | 0.871 (0.795–0.946) | * 0.848 (0.724–0.971) | 88 | 58 |
| Liu et al. (2020) [75] | LNM | CT | Radiomics | LR | AUC | 0.841 (0.768–0.925) | .. | 85 | .. |
| Li et al. (2020) [76] | LNM | CT + clinical | Radiomics | LR | AUC | .. | * 0.912 (0.778–1) | 118 | *41 |
| Chang et al. (2020) [66] | Grading 1/2 vs. 3 | CT | Radiomics | LASSO | AUC | 0.961 (0.935–0.987) | * 0.91 (0.864–0.956) ** 0.77 (0.661–0.878) | 151 | * 150 ** 100 |
| Longlong et al. (2020) [77] | Grading 1 vs. 2 vs. 3 | CT | Radiomics | RF | AUC | 0.77 (0.64–0.87) | * 0.70 (0.47–0.86) | 58 | * 25 |
| Qiu et al. (2019) [78] | Grading 1/2 vs. 3 | CT | Radiomics | SVM | SEN, SPE, ACC | 78 95 86 | .. | 56 | .. |
| Authors (Year) | Treatment | Predict | Data | Approach | Model | Metric | Validation Results | Test Results | Dev. Cohort | Test Cohort |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yao et al. (2021) [81] | Resection | OS | CT | DL | Conv- LSTM | CI | 0.667 | .. | 296 | .. |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [80] | Resection | OS | CT | DL | CNN | CI | .. | ** 0.651 | 68 | ** 30 |
| Watson et al. (2020) [82] | Chemotherapy | PR vs. NR | CT + clinical | DL | LeNet | AUC | .. | * 0.785 | .. | * 65 |
| Zhang et al. (2021) [83] | Resection | 2-year survival | CT | DL + ML | RF | AUC | .. | * 0.84 (0.70–0.98) | 68 | * 30 |
| Li et al. (2021) [84] | Resection | 1-year and 2-year recurrence risk | CT + clinical | DL + ML | ANN | AUC | 0.916 (0.860–0.955) 0.872 (0.809–0.921) | ** 0.764 (0.644–0.859) ** 0.773 (0.654–0.866) | 153 | ** 47 |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [83] | Resection | Death risk | CT | DL + ML | RF | AUC | 0.72 (0.58–0.86) | ** 0.81 (0.64–0.98) | 68 | ** 30 |
| Healy et al. (2021) [79] | Resection | OS | CT | Radiomics | CPH | CI | 0.626 (0.625–0.627) | ** 0.545 (0.543–0.546) | 352 | ** 215 |
| Shi et al. (2021) [85] | Resection | OS | CT | Radiomics | CPH | CI | 0.74 (0.70–0.78) | * 0.73 (0.66–0.79) | 210 | * 89 |
| Wei et al. (2021) [86] | Resection | 1-year RFS | 18FDG PET-CT | Radiomics | CPH | CI | 0.890 (0.835–0.945) | * 0.865 (0.778–0.952) | 109 | * 47 |
| Xie et al. (2020) [87] | Resection | OS | CT | Radiomics | CPH | CI | .. | * 0.726 (0.646–0.806) | 147 | * 73 |
| Park et al. (2020) [88] | Resection | OS | CT | Radiomics | RF | CI | 0.74 | .. | 153 | .. |
| Parr et al. (2020) [89] | Radiotherapy | OS | CT | Radiomics | CPH | CI | 0.68 | .. | 74 | .. |
| Kaissis et al. (2020) [90] | Resection | OS | CT + clinical + genomics | Radiomics | LPCA | CI | 0.65 (0.60–0.69) | .. | 103 | |
| Hui et al. (2020) [91] | Resection margin | R0 vs. R1 | CT | Radiomics | SVM | AUC | 0.8641 | .. | 86 | .. |
| Bian et al. (2020) [92] | Resection margin | R0 vs. R1 | CT | Radiomics | LR | AUC | 0.750 (0.672–0.824) | .. | 181 | .. |
| Tang et al. (2019) [93] | Resection | NER (>12 months) vs. ER (<12 months) | MR | Radiomics | LR | AUC | 0.802 (0.721–0.868) | * 0.807 (0.677–0.902) ** 0.781 (0.699–0.850) | 177 | * 74 ** 126 |
| Zhou et al. (2019) [94] | Irradiation stent | RSFS | CT | Radiomics | CPH | CI | 0.791 (0.614–0.967) | * 0.779 (0.504–1.000) | 74 | * 32 |
| Cozzi et al. (2019) [95] | Radiotherapy | OS | CT | Radiomics | CPH | CI | .. | * 0.75 ± 0.03 | 60 | * 40 |
| Kaissis et al. (2019) [96] | Chemotherapy | OS | MR | Radiomics | GBDT | CI | 0.71 (0.60–0.80) | .. | 55 | .. |
| Kaissis et al. (2019) [97] | Resection | Above vs. below average OS | MR | Radiomics | RF | AUC | 0.93 ± 0.07 | * 0.9 | 102 | * 30 |
| Chakraborty et al. (2017) [98] | Resection | Survival < 2 years vs. survival > 2 years | CT | Radiomics | Bayes | AUC | 0.9 | .. | 35 | .. |
| Cui et al. (2016) [99] | Radiotherapy | OS | 18FDG PET-CT | Radiomics | CPH | CI | 0.623 | * 0.661 (0.418–0.841) | 90 | * 49 |
| Research Agenda for Clinical AI in PDAC Imaging |
|---|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schuurmans, M.; Alves, N.; Vendittelli, P.; Huisman, H.; Hermans, J. Setting the Research Agenda for Clinical Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Imaging. Cancers 2022, 14, 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143498
Schuurmans M, Alves N, Vendittelli P, Huisman H, Hermans J. Setting the Research Agenda for Clinical Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Imaging. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143498
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchuurmans, Megan, Natália Alves, Pierpaolo Vendittelli, Henkjan Huisman, and John Hermans. 2022. "Setting the Research Agenda for Clinical Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Imaging" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143498
APA StyleSchuurmans, M., Alves, N., Vendittelli, P., Huisman, H., & Hermans, J. (2022). Setting the Research Agenda for Clinical Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Imaging. Cancers, 14(14), 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143498






