The Presence of EGFR T790M in TKI-Naïve Lung Cancer Samples of Patients Who Developed a T790M-Positive Relapse on First or Second Generation TKI Is Rare
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
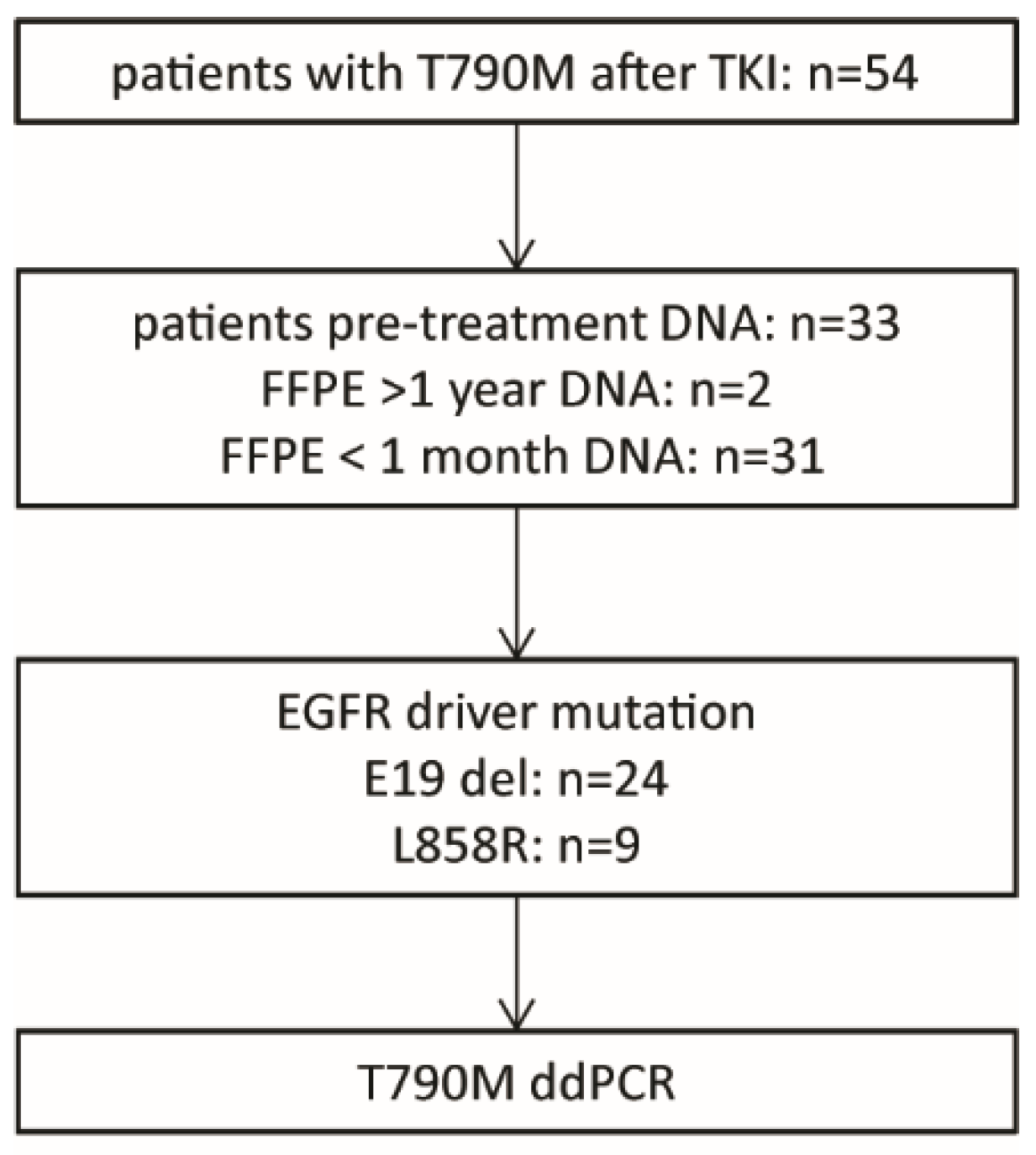
2.1. Patient Selection and Control Samples
2.2. Droplet Digital (dd)PCR
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. T790M Background Levels in FFPE Tissue Samples
3.2. Patient Characteristics and Detection of T790M in Pre-Treatment Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D. Pathology of lung cancer. Clin. Chest Med. 2011, 32, 669–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerner, G.S.; Schuuring, E.; Sietsma, J.; Hiltermann, T.J.; Pieterman, R.M.; de Leede, G.P.; van Putten, J.W.; Liesker, J.; Renkema, T.E.; van Hengel, P.; et al. Common and rare EGFR and KRAS mutations in a Dutch non-small-cell lung cancer population and their clinical outcome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Remon, J.; Hendriks, L.E.L. Osimertinib Should be the Standard of Care for the Adjuvant Therapy of Stage IB to IIIA EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.H.; Chu, D.T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.G.; Shih, J.Y. Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, B.; Cajiao Garcia, B.N.; Kuijpers, C.; Damhuis, R.A.M.; van der Wekken, A.J.; Groen, H.J.M.; Schuuring, E.; Willems, S.M.; van Kempen, L.C. A Nationwide Study on the Impact of Routine Testing for EGFR Mutations in Advanced NSCLC Reveals Distinct Survival Patterns Based on EGFR Mutation Subclasses. Cancers 2021, 13, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Yamaguchi, M.; Dong, R.P. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor “gefitinib (Iressa)” for cancer therapy. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi 2003, 122, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moyer, J.D.; Barbacci, E.G.; Iwata, K.K.; Arnold, L.; Boman, B.; Cunningham, A.; DiOrio, C.; Doty, J.; Morin, M.J.; Moyer, M.P.; et al. Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by CP-358,774, an inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4838–4848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wecker, H.; Waller, C.F. Afatinib. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018, 211, 199–215. [Google Scholar]
- da Cunha Santos, G.; Shepherd, F.A.; Tsao, M.S. EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Annu Rev. Pathol. 2011, 6, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hata, A.N.; Niederst, M.J.; Archibald, H.L.; Gomez-Caraballo, M.; Siddiqui, F.M.; Mulvey, H.E.; Maruvka, Y.E.; Ji, F.; Bhang, H.E.; Krishnamurthy Radhakrishna, V.; et al. Tumor cells can follow distinct evolutionary paths to become resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrell, J.A.; Mazieres, J.; Senal, R.; Rouquette, I.; Quantin, X.; Pujol, J.L.; Roch, B.; Bouidioua, A.; Godreuil, S.; Coyaud, E.; et al. Ultra-sensitive EGFR (T790M) Detection as an Independent Prognostic Marker for Lung Cancer Patients Harboring EGFR (del19) Mutations and Treated with First-generation TKIs. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4280–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lettig, L.; Sahnane, N.; Pepe, F.; Cerutti, R.; Albeni, C.; Franzi, F.; Veronesi, G.; Ogliari, F.; Pastore, A.; Tuzi, A.; et al. EGFR T790M detection rate in lung adenocarcinomas at baseline using droplet digital PCR and validation by ultra-deep next generation sequencing. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.; Che, N. Origin of the T790M mutation and its impact on the clinical outcomes of patients with lung adenocarcinoma receiving EGFR-TKIs. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Chen, M.; Peng, D.; Zong, D.; Shang, Q.; Tao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, Y.; et al. Dynamics of Plasma EGFR T790M Mutation in Advanced NSCLC: A Multicenter Study. Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, T.; Perera, S.; Weiss, J.; Grenier, S.; Ranich, L.; Shepherd, F.; Stockley, T.L. Clinical implementation of circulating tumour DNA testing for EGFR T790M for detection of treatment resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Pathol 2021, 74, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Guo, H.; Zhu, L.; Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Guo, Y. Highly Sensitive Droplet Digital PCR Method for Detection of de novo EGFR T790M Mutation in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 10621–10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beau-Faller, M.; Pencreach, E.; Leduc, C.; Blons, H.; Merlio, J.P.; Bringuier, P.P.; de Fraipont, F.; Escande, F.; Lemoine, A.; Ouafik, L.; et al. Independent prognostic value of ultra-sensitive quantification of tumor pre-treatment T790M subclones in EGFR mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated by first/second generation TKI.; depends on variant allele frequency (VAF): Results of the French cooperative thoracic intergroup (IFCT) biomarkers France project. Lung Cancer 2020, 140, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Sawa, K.; Fukui, M.; Oyanagi, J.; Yoshimoto, N.; Suzumura, T.; Watanabe, T.; Kaneda, H.; Mitsuoka, S.; Asai, K.; et al. Predictive impact of low-frequency pretreatment T790M mutation in patients with EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer treated with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Lung Cancer 2020, 139, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu Koyyala, V.P.; Batra, U.; Jain, P.; Sharma, M.; Goyal, P.; Medisetty, P.; Jajodia, A.; Maheshwari, U.D. Frequency of T790M mutations after progression on epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer in Indian patients: Real-time data from tertiary cancer hospital. Lung India 2018, 35, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Q.; Li, J.; Tan, A.Y.; Vedururu, R.; Pang, J.M.; Do, H.; Ellul, J.; Doig, K.; Bell, A.; MacArthur, G.A.; et al. Sequence artefacts in a prospective series of formalin-fixed tumours tested for mutations in hotspot regions by massively parallel sequencing. BMC Med. Genom. 2014, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathieson, W.; Thomas, G.A. Why Formalin-fixed, Paraffin-embedded Biospecimens Must Be Used in Genomic Medicine: An Evidence-based Review and Conclusion. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2020, 68, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwama, E.; Takayama, K.; Harada, T.; Okamoto, I.; Ookubo, F.; Kishimoto, J.; Baba, E.; Oda, Y.; Nakanishi, Y. Highly sensitive and quantitative evaluation of the EGFR T790M mutation by nanofluidic digital PCR. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20466–20473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.Y.; Molina-Vila, M.A.; Ruan, S.Y.; Su, K.Y.; Liao, W.Y.; Yu, K.L.; Ho, C.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Coexistence of EGFR T790M mutation and common activating mutations in pretreatment non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2016, 94, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Isa, S.; Ando, M.; Tamiya, A.; Kubo, A.; Saka, H.; Takeo, S.; Adachi, H.; Tagawa, T.; et al. Ultra-Sensitive Detection of the Pretreatment EGFR T790M Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with an EGFR-Activating Mutation Using Droplet Digital PCR. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Xiong, Z.C.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.L.; Ma, J.T.; Han, C.B. Meta-analysis of the impact of de novo and acquired EGFR T790M mutations on the prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving EGFR-TKIs. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 2267–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, K.Y.; Tseng, J.S.; Liao, K.M.; Yang, T.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Hsu, K.H.; Yang, P.C.; Yu, S.L.; Chang, G.C. Mutational monitoring of EGFR T790M in cfDNA for clinical outcome prediction in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Yuan, J.Q.; Yang, Z.Y.; Fu, X.H.; Wu, X.Y.; Tang, J.L. Blood as a Substitute for Tumor Tissue in Detecting EGFR Mutations for Guiding EGFR TKIs Treatment of Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.H.; Mengwasser, K.E.; Toms, A.V.; Woo, M.S.; Greulich, H.; Wong, K.K.; Meyerson, M.; Eck, M.J. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 75ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Meng, P.; Terpstra, M.M.; van Rijk, A.; Tamminga, M.; Scherpen, F.; Ter Elst, A.; Alimohamed, M.Z.; Johansson, L.F.; Stigt, J.; et al. Clinical Value of EGFR Copy Number Gain Determined by Amplicon-Based Targeted Next Generation Sequencing in Patients with EGFR-Mutated NSCLC. Target. Oncol. 2021, 16, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavic, M.; Kovacevic, T.; Zaric, B.; Stojiljkovic, D.; Korda, N.J.; Rancic, M.; Jankovic, R.; Radosavljevic, D.; Stojanovic, G.; Spasic, J. Lung Cancer in Serbia. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.T.; Nguyen, S.; Nguyen, K.K.; Pham, D.X.; Nguyen, U.H.; Le, A.T.; Nguyen, G.H.; Tran, D.V.; Phung, S.D.H.; Do, H.M.; et al. Lung Cancer in Vietnam. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1443–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennell, N.A.; Neal, J.W.; Chaft, J.E.; Azzoli, C.G.; Janne, P.A.; Govindan, R.; Evans, T.L.; Costa, D.B.; Wakelee, H.A.; Heist, R.S.; et al. SELECT: A Phase II Trial of Adjuvant Erlotinib in Patients With Resected Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, D.; Moore, A.C.; Roy, U.B. The 2021 Global Lung Cancer Therapy Landscape. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, G.K.; Hwang, J.A.; Yun, T.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, J.S. Clinical likelihood of sporadic primary EGFR T790M mutation in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2015, 16, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, K.; Hata, Y.; Tochigi, N.; Kaburaki, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Makino, T.; Otsuka, H.; Ishida, F.; Hirota, N.; Sano, G.; et al. Usefulness of nanofluidic digital PCR arrays to quantify T790M mutation in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2015, 12, 31–37. [Google Scholar]

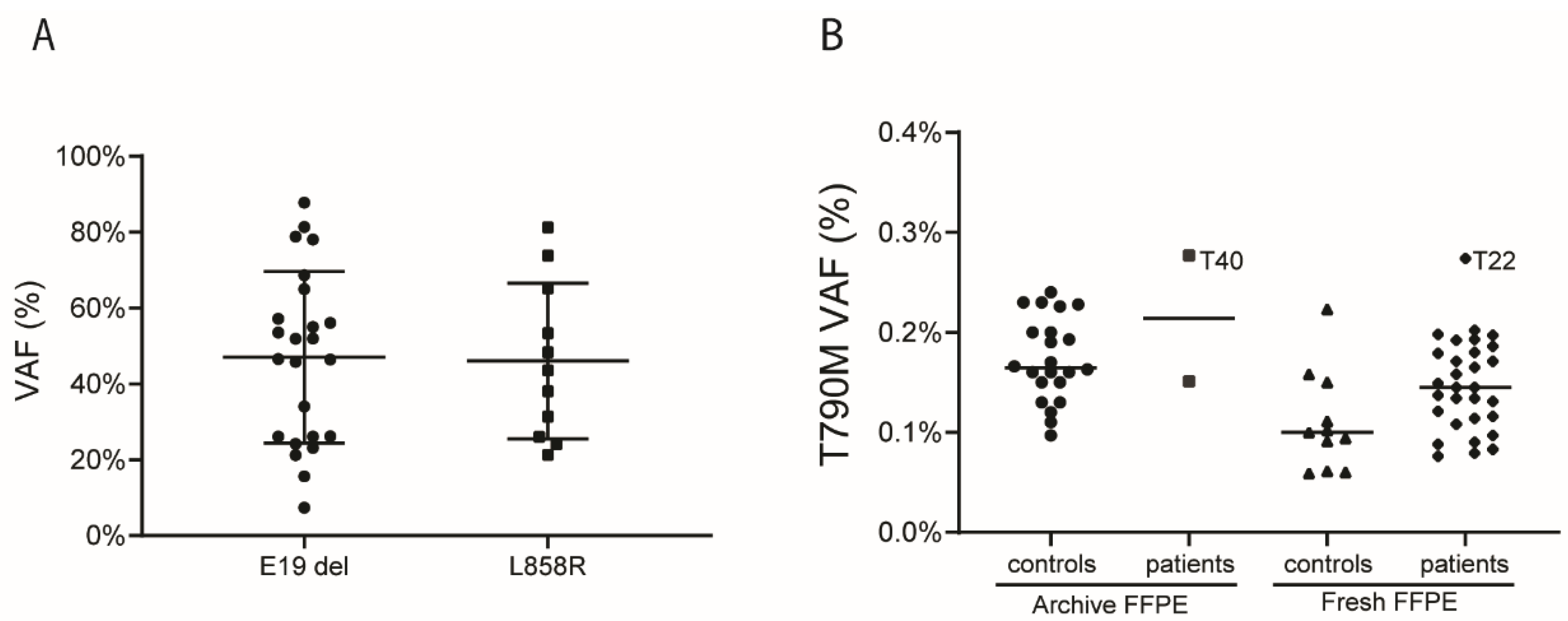
| ddPCR Assay | Sample Group | Median VAF (%) | IQR | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR T790M C>T | archive FFPE | 0.160 | 0.145–0.207 | Poverall < 0.001 (archive vs. blood < 0.001; archive vs. fresh 0.003) |
| fresh FFPE | 0.100 | 0.061–0.150 | ||
| Blood | 0.035 | 0.028–0.045 | ||
| KRAS G12D C>T | archive FFPE | 0.158 | 0.071–0.220 | Poverall < 0.001 (archive vs. blood < 0.001) |
| fresh FFPE | 0.047 | 0.010–0.090 | ||
| Blood | 0.020 | 0.016–0.025 | ||
| KRAS G12V nonC>T | archive FFPE | 0.000 | 0.000–0.074 | NS |
| fresh FFPE | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | ||
| Blood | 0.000 | 0.000–0.008 | ||
| EGFR L858R nonC>T | archive FFPE | 0.000 | 0.000–0.006 | NS |
| fresh FFPE | 0.000 | 0.000–0.002 | ||
| Blood | 0.000 | 0.000–0.011 |
| Patient Characteristics | Number/Frequency |
|---|---|
| Gender (male/female) | 16/17 |
| Age (median (range) | 61 (38–81) |
| TKI (n=) Gefitinib Erlotinib Afatinib | 17 10 6 |
| PFS median (range) in months | 10 (2–27) |
| Driver mutation (n=) E19del L858R | 24 9 |
| Median variant allele frequency (range) (%) | 47 (7–88) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Kok, K.; Tan, G.W.; Meng, P.; Mastik, M.; Rifaela, N.; Scherpen, F.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Groen, H.J.M.; Wekken, A.J.v.d.; et al. The Presence of EGFR T790M in TKI-Naïve Lung Cancer Samples of Patients Who Developed a T790M-Positive Relapse on First or Second Generation TKI Is Rare. Cancers 2022, 14, 3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143511
Li W, Kok K, Tan GW, Meng P, Mastik M, Rifaela N, Scherpen F, Hiltermann TJN, Groen HJM, Wekken AJvd, et al. The Presence of EGFR T790M in TKI-Naïve Lung Cancer Samples of Patients Who Developed a T790M-Positive Relapse on First or Second Generation TKI Is Rare. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143511
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Weiting, Klaas Kok, Geok Wee Tan, Pei Meng, Mirjam Mastik, Naomi Rifaela, Frank Scherpen, T. Jeroen N. Hiltermann, Harry J. M. Groen, Anthonie J. van der Wekken, and et al. 2022. "The Presence of EGFR T790M in TKI-Naïve Lung Cancer Samples of Patients Who Developed a T790M-Positive Relapse on First or Second Generation TKI Is Rare" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143511
APA StyleLi, W., Kok, K., Tan, G. W., Meng, P., Mastik, M., Rifaela, N., Scherpen, F., Hiltermann, T. J. N., Groen, H. J. M., Wekken, A. J. v. d., & van den Berg, A. (2022). The Presence of EGFR T790M in TKI-Naïve Lung Cancer Samples of Patients Who Developed a T790M-Positive Relapse on First or Second Generation TKI Is Rare. Cancers, 14(14), 3511. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143511








