Tumor Location in the Head/Uncinate Process and Presence of Fibrosis Impair the Adequacy of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Solid Pancreatic Tumors
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. EUS-TA
2.3. Material Preparation and Macroscopic Evaluation
2.4. Pathologist Work-Up
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Sample Adequacy
3.3. Adequacy Score 2 or 3
3.4. Tumor Fibrosis
3.5. Diagnostic Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gkolfakis, P.; Crinò, S.F.; Tziatzios, G.; Ramai, D.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Triantafyllou, K.; Arvanitakis, M.; Lisotti, A.; Fusaroli, P.; et al. Comparative diagnostic performance of end-cutting fine-needle biopsy needles for EUS tissue sampling of solid pancreatic masses: A network meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitano, M.; Minaga, K.; Hatamaru, K.; Ashida, R. Clinical dilemma of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for resectable pancreatic body and tail cancer. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisotti, A.; Frazzoni, L.; Fuccio, L.; Serrani, M.; Cominardi, A.; Bazzoli, F.; Fusaroli, P. Repeat EUS-FNA of pancreatic masses after nondiagnostic or inconclusive results: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, T.; Kadah, A.; Farraj, M.; Barhoum, M.; Livoff, A.; Mari, A.; Mahamid, M.; Sbeit, W. The role of rapid on-site evaluation on diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound fine needle aspiration for pancreatic, submucosal upper gastrointestinal tract and adjacent lesions. Cytopathology 2019, 30, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Dominguez-Munoz, J.E.; Abdulkader, I.; Larino-Noia, J.; Eugenyeva, E.; Lozano-Leon, A.; Forteza-Vila, J. Influence of on-site cytopathology evaluation on the diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) of solid pancreatic masses. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehmood, S.; Jahan, A.; Loya, A.; Yusuf, M.A. Onsite cytopathology evaluation and ancillary studies beneficial in EUS-FNA of pancreatic, mediastinal, intra-abdominal, and submucosal lesions. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2015, 43, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcidiacono, P.; Petrone, M.C. Basic technique in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for solid lesions: How many passes? Endosc. Ultrasound 2014, 3, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bang, J.Y.; Magee, S.H.; Ramesh, J.; Trevino, J.M.; Varadarajulu, S. Randomized trial comparing fanning with standard technique for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of solid pancreatic mass lesions. Endoscopy 2013, 45, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, S.W.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.; Kae, S.H.; Jang, H.J.; Koh, D.H.; Choi, M.H. Meta-Analysis for Cyto-Pathological Outcomes in Endoscopic Ultrasonography-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration with and without the Stylet. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 2175–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, A.; Hadizadeh, M.; Molaee, M.; Padashi, M.; Shahbaazi, S.; Shariatpanahi, Z.V. Comparison of two techniques for endoscopic ultrasonography fine-needle aspiration in solid pancreatic mass. Endosc. Ultrasound 2014, 3, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Mitri, R.; Mocciaro, F.; Antonini, F.; Scimeca, D.; Conte, E.; Bonaccorso, A.; Scibetta, N.; Unti, E.; Fornelli, A.; Giorgini, S.; et al. Stylet slow-pull vs. standard suction technique for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy in pancreatic solid lesions using 20 Gauge Procore™ needle: A multicenter randomized trial. Dig. Liver Dis. 2020, 52, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, T.; Li, J.; Kwek, A.E.; Thurairajah, P.; Wang, L. The difference in histological yield between 19G EUS-FNA and EUS-fine-needle biopsy needles. Endosc. Ultrasound 2019, 8, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affolter, K.E.; Schmidt, R.L.; Matynia, A.P.; Adler, D.; Factor, R.E. Needle Size Has Only a Limited Effect on Outcomes in EUS-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.Y.; Kirtane, S.; Krall, K.; Navaneethan, U.; Hasan, M.; Hawes, R.; Varadarajulu, S. In memoriam: Fine-needle aspiration, birth: Fine-needle biopsy: The changing trend in endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsenti, D.; Palazzo, L.; Perrot, B.; Zago, J.; Lemaistre, A.-I.; Cros, J.; Napoléon, B. 22G Acquire vs. 20G Procore needle for endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy of pancreatic masses: A randomized study comparing histologic sample quantity and diagnostic accuracy. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokkumar, R.; Ka, C.Y.; Loh, T.; Ling, L.K.; San, T.G.; Ying, H.; Tan, D.; Khor, C.; Lim, T.; Soetikno, R. Comparison of tissue and molecular yield between fine-needle biopsy (FNB) and fine-needle aspiration (FNA): A randomized study. Endosc. Int. Open 2019, 7, E955–E963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jung, Y.S.; Park, J.H.; Park, D.I.; Cho, Y.K.; Sohn, C.I.; Jeon, W.K.; Kim, B.I.; Choi, K.Y.; Ryu, S. Endosonographer’s macroscopic evaluation of EUS-FNAB specimens after interactive cytopathologic training: A single-center prospective validation cohort study. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 4184–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwatari, H.; Sato, J.; Fujie, S.; Sasaki, K.; Kaneko, J.; Satoh, T.; Matsubayashi, H.; Kishida, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Ito, S.; et al. Gross visual inspection by endosonographers during endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.C.N.; Lakhtakia, S.; Nguyen, N.; Hara, K.; Chan, W.K.; Puri, R.; Almadi, M.A.; Ang, T.L.; Kwek, A.; Yasuda, I.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition with or without macroscopic on-site evaluation: Randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Peng, C.Y.; Shen, S.S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xu, G.F.; Kong, B.; Friess, H.; Zou, X.P.; Lv, Y. Factors affecting the accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for the diagnosis of small (≤20 mm) pancreatic lesions. J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 21, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, A.; Thompson, C.; Hall, B.R.; Jain, M.; Kumar, S.; Batra, S.K. Desmoplasia in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Insight into pathological function and therapeutic potential. Genes Cancer 2018, 9, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navina, S.; McGrath, K.; Chennat, J.; Singh, V.; Pal, T.; Zeh, H.; Krasinskas, A.M. Adequacy Assessment of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided, Fine-Needle Aspirations of Pancreatic Masses for Theranostic Studies: Optimization of Current Practices Is Warranted. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 923–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hijioka, S.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Imaoka, H.; Bhatia, V.; Mekky, M.A.; Yoshimura, K.; Yoshida, T.; Okuno, N.; Hieda, N.; et al. Diagnostic performance and factors influencing the accuracy of EUS-FNA of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haba, S.; Yamao, K.; Bhatia, V.; Mizuno, N.; Hara, K.; Hijioka, S.; Imaoka, H.; Niwa, Y.; Tajika, M.; Kondo, S.; et al. Diagnostic ability and factors affecting accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for pancreatic solid lesions: Japanese large single center experience. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, Y.; Isayama, H.; Chang, K.J.; Yamamoto, N.; Hamada, T.; Uchino, R.; Mizuno, S.; Miyabayashi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Kawakubo, K.; et al. Slow Pull Versus Suction in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration of Pancreatic Solid Masses. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 1578–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangiavillano, B.; Frazzoni, L.; Togliani, T.; Fabbri, C.; Tarantino, I.; De Luca, L.; Staiano, T.; Binda, C.; Signoretti, M.; Eusebi, L.H.; et al. Macroscopic on-site evaluation (MOSE) of specimens from solid lesions acquired during EUS-FNB: Multicenter study and comparison between needle gauges. Endosc. Int. Open 2021, 9, E901–E906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitman, M.B.; Centeno, B.A.; Ali, S.Z.; Genevay, M.; Stelow, E.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Max Schmidt, C.; Brugge, W.; Layfield, L.; et al. Standardized terminology and nomenclature for pancreatobiliary cytology: The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology guidelines. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2014, 42, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, T.W.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Guinee, J.D.G.; Holden, J.A.; Cha, I.; Bauermeister, D.E.; Hashimoto, B.; Wolverton, D.; Hartzog, G. Fibroepithelial Lesions with Cellular Stroma on Breast Core Needle Biopsy: Are There Predictors of Outcome on Surgical Excision? Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 124, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopelman, Y.; Marmor, S.; Ashkenazi, I.; Fireman, Z. Value of EUS-FNA cytological preparations compared with cell block sections in the diagnosis of pancreatic solid tumours. Cytopathology 2011, 22, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Mohan, B.P.; Crinò, S.F.; Ofosu, A.; Ramai, D.; Lisotti, A.; Chandan, S.; Fusaroli, P. Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration versus standard fine-needle aspiration in pancreatic masses: A meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
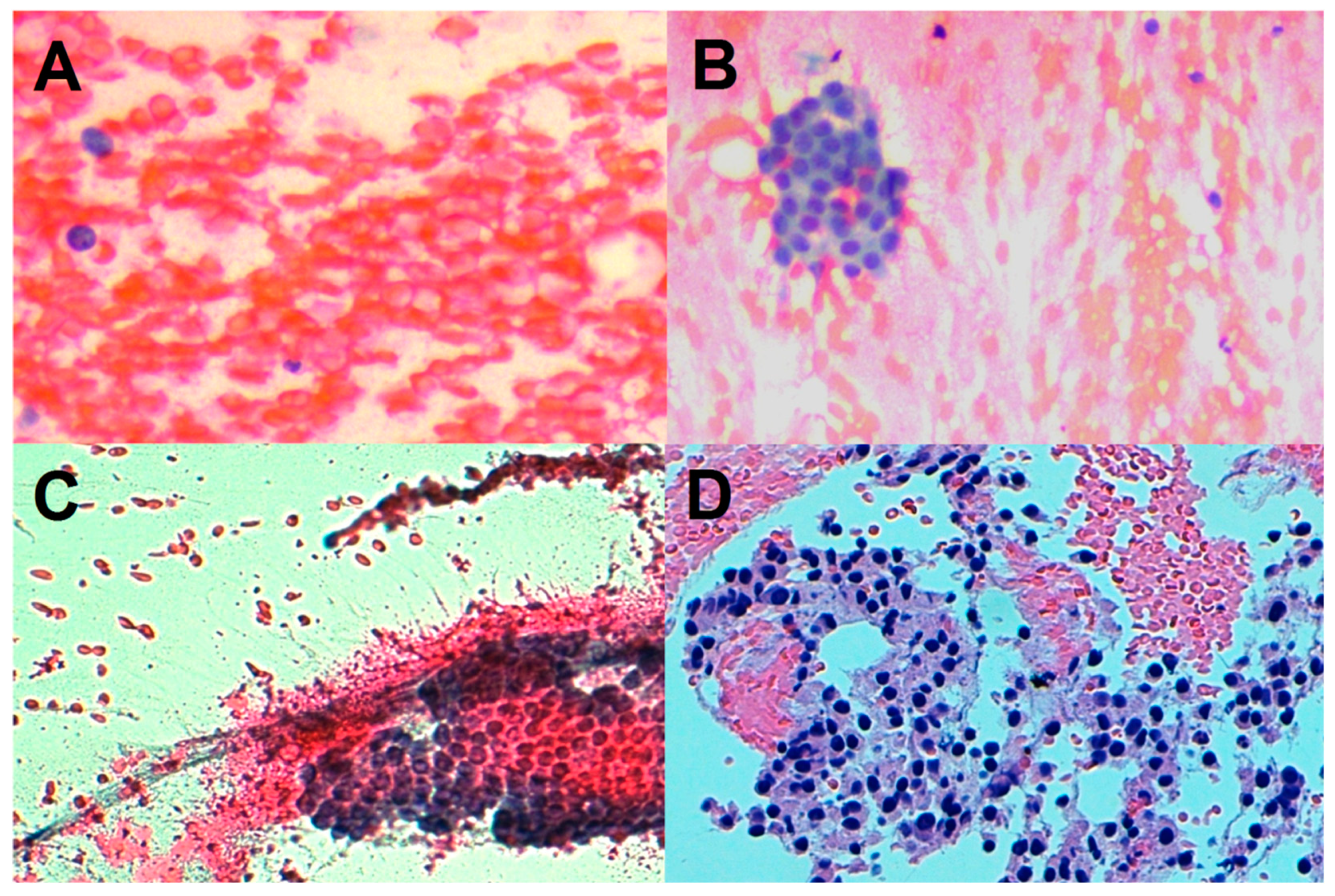
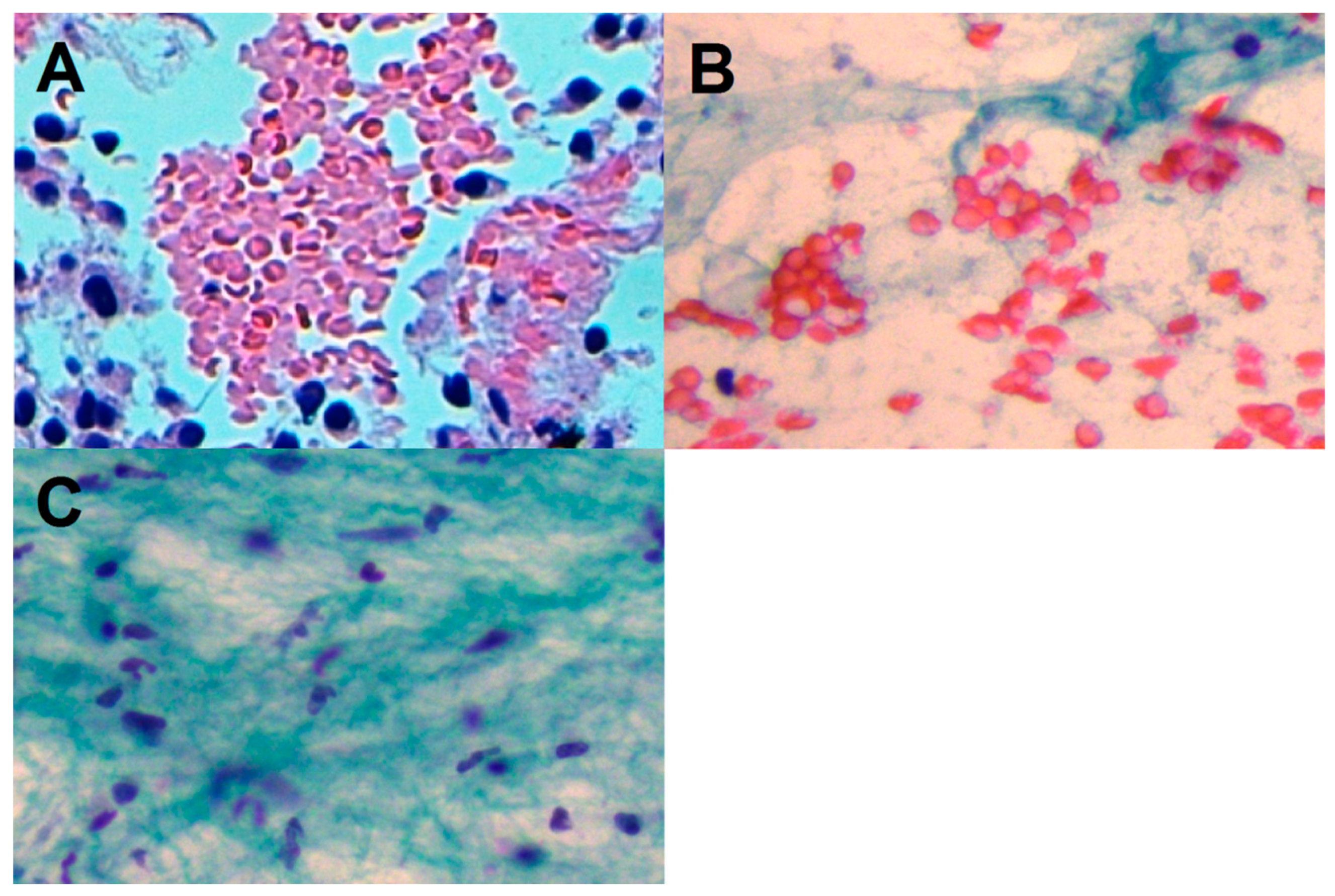
| Characteristic | Total (No. 407) |
|---|---|
| Demographic | |
| Gender (male), no. (%) | 240 (59.0%) |
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 70 [63–77] |
| Study period 2007–2014 | 181 (44.5%) |
| Study period 2015–2020 | 226 (55.5%) |
| Pancreatic tumor | |
| Size (mm), median [IQR] | 31 [24–40] |
| Head, no. (%) | 255 (62.7%) |
| Uncinate process, no. (%) | 32 (7.9%) |
| Neck, no. (%) | 32 (7.9%) |
| Body, no. (%) | 52 (12.8%) |
| Tail, no. (%) | 36 (8.8%) |
| Needle design | |
| FNA-needle, no. (%) | 316 (77.6%) |
| FNB-needle, no. (%) | 91 (22.4%) |
| 1st generation FNB-needle, no. | 23 |
| 2nd generation FNB-needle, no. | 68 |
| Needle size | |
| 19-gauge needle, no. (%) | 5 (1.2%) |
| 20-gauge needle, no. (%) | 63 (15.5%) |
| 22-gauge needle, no. (%) | 191 (46.9%) |
| 25-gauge needle, no. (%) | 148 (36.4%) |
| Needle passes | |
| Number of needle passes, median [IQR] | |
| No. 1, no. (%) | 50 (12.3%) |
| No. 2, no. (%) | 96 (23.6%) |
| No. 3, no. (%) | 132 (32.4%) |
| No. 4, no. (%) | 68 (16.7%) |
| No. 5, no. (%) | 61 (15.0%) |
| EUS-TA specimen | |
| Slides, no. (%) | 316 (77.6%) |
| Formalin vials, no. (%) | 91 (22.4%) |
| Cell-block, no. (%) | 182 (44.7%) |
| Pathology–adequacy | |
| Overall adequacy, no. (%) | 367 (90.2%) |
| Adequacy–Score 0, no. (%) | 40 (9.8%) |
| Adequacy–Score 1, no. (%) | 48 (11.8%) |
| Adequacy–Score 2, no. (%) | 139 (34.2%) |
| Adequacy–Score 3, no. (%) | 180 (44.2%) |
| Pathology–fibrosis | |
| Fibrosis–not evaluable, no. (%) | 45 (11.1%) |
| Fibrosis–Score 0, no. (%) | 217 (53.3%) |
| Fibrosis–Score 1, no. (%) | 127 (31.2%) |
| Fibrosis–Score 2, no. (%) | 18 (4.4%) |
| Accuracy, no. (%) | 339 (94.7%) * |
| EUS-TA Pathological Diagnosis | Total (No. 407) |
|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma, no. (%) | 268 (65.9%) |
| Ductal, no. | 254 |
| Mucinous, no. | 6 |
| Mixed adeno-squamous, no. | 3 |
| Acinar, no. | 2 |
| Hepatoid, no. | 1 |
| Micro-glandular, no. | 1 |
| Pleomorphic, no. | 1 |
| Cholangiocarcinoma, no. (%) | 1 (0.2%) |
| Well-differentiated neuroendocrine neoplasm, no. (%) | 15 (3.7%) |
| Neuroendocrine carcinoma, no. (%) | 3 (0.7%) |
| Chronic pancreatitis, no. (%) | 10 (2.5%) |
| Autoimmune pancreatitis, no. (%) | 2 (0.5%) |
| Metastasis, no. (%) | 10 (2.5%) |
| Renal cancer, no. | 7 |
| Lung cancer, no. | 2 |
| Lung neuroendocrine carcinoma, no. | 1 |
| Benign lymphoid tissue, no. (%) | 10 (2.5%) |
| Benign pancreatic cells with no atypia, no. (%) | 48 (11.8%) |
| Non-diagnostic, no. (%) | 40 (9.8%) |
| Adequacy of EUS-TA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | Multivariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | |
| Gender (male) | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Age | 1.02 [1.00–1.05] | 0.05 | ns | ns |
| Study period 2015–2020 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Size | 1.03 [1.01–1.06] | 0.04 | ns | ns |
| Location (head/uncinate process) | 0.31 [0.12–0.82] | 0.02 | 0.37 [0.14–0.99] | 0.05 |
| FNA needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| FNB needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Second-gen. FNB needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 19-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 20-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 25-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22G or 25G needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Needle passes ≥ 3 | 3.01 [1.54–5.88] | 0.001 | 4.53 [2.22–9.28] | <0.001 |
| Slides | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Cell block | 6.52 [2.50–17.0] | 0.001 | 8.82 [3.26–23.8] | <0.001 |
| Score fibrosis 1 or 2 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Adequacy of EUS-TA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | Multivariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | |
| Gender (male) | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Age | 1.02 [1.00–1.06] | 0.05 | 1.07 [1.03–1.11] | 0.002 |
| Study period 2015–2020 | 2.05 [1.01–4.25] | 0.01 | ns | ns |
| Size | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| FNA needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| FNB needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Second-gen. FNB needle | 4.26 [1.10–7.04] | 0.03 | 2.25 [1.05–3.22] | 0.03 |
| 19-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 20-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 25-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22G or 25G needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Needle passes ≥ 3 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Slides | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Cell block | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Score fibrosis 1 or 2 | 0.25 [0.12–0.62] | 0.04 | 0.30 [0.15–0.38] | 0.01 |
| Adequacy of EUS-TA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | Multivariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | |
| Gender (male) | 0.12 [0.02–0.97] | 0.05 | 0.11 [0.01–0.93] | 0.04 |
| Age | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Study period 2015–2020 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Size | 1.10 [1.03–1.18] | 0.005 | 1.10 [1.03–1.18] | 0.006 |
| FNA needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| FNB needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Second-gen. FNB needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 19-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 20-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 25-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22G or 25G needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Needle passes ≥ 3 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Slides | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Cell block | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Score fibrosis 1 or 2 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Adequacy of EUS-TA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | Multivariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | |
| Gender (male) | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Age | 1.02 [1.00–1.04] | 0.03 | ns | ns |
| Study period 2015–2020 | 2.00 [1.24–3.23] | 0.004 | 2.07 [1.12–3.82] | 0.02 |
| Size | 1.03 [1.01–1.05] | 0.003 | 1.04 [1.01–1.06] | 0.009 |
| Location (head/uncinate process) | 0.42 [0.23–0.77] | 0.005 | ns | ns |
| FNA needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| FNB needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Second-gen. FNB needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 19-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 20-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 25-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22G or 25G needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Needle passes ≥ 3 | 2.26 [1.40–3.65] | 0.001 | ns | ns |
| Slides | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Cell block | 1.76 [1.08–2.88] | 0.02 | ns | ns |
| Score fibrosis 1 or 2 | 0.28 [0.17–0.47] | <0.001 | ns | ns |
| Score fibrosis 2 | 0.03 [0.01–0.06] | <0.001 | 0.03 [0.01–0.06] | <0.001 |
| Score Fibrosis = 0 (No. 217) | Score Fibrosis = 1 (No. 127) | Score Fibrosis = 2 (No. 145) | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Head/uncinate process (no. 248) | 136 (54.8%) | 99 (39.9%) | 13 (5.2%) | |
| Neck, body, and tail (no. 114) | 81 (71.1%) | 28 (24.6%) | 5 (4.4%) | 0.001 |
| Score adequacy = 1 (no. 45) | 26 (57.8%) | 11 (24.4%) | 8 (17.8%) | |
| Score adequacy = 2 (no. 137) | 81 (59.1%) | 50 (36.5%) | 6 (4.4%) | |
| Score adequacy = 3 (no. 180) | 110 (61.1%) | 66 (36.7%) | 4 (2.2%) | 0.001 |
| Adequacy of EUS-TA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | Multivariate Analysis (OR [95% C.I.) | p | |
| Gender (male) | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Age | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Study period 2015–2020 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Size | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| FNA needle | 2.93 [1.11–7.72] | 0.03 | ns | ns |
| FNB needle | 0.34 [0.13–0.90] | 0.03 | ns | ns |
| Second-gen. FNB needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 19-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 20-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 25-gauge needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| 22G or 25G needle | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Needle passes ≥ 3 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Slides | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Cell block | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Score fibrosis 1 or 2 | ns | ns | --- | --- |
| Score fibrosis 2 | 8.37 [2.33–30.0] | 0.001 | 8.37 [2.33–30.0] | 0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Togliani, T.; Lisotti, A.; Rinaldi, R.; Fornelli, A.; Pilati, S.; Passigato, N.; Fusaroli, P. Tumor Location in the Head/Uncinate Process and Presence of Fibrosis Impair the Adequacy of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Solid Pancreatic Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143544
Togliani T, Lisotti A, Rinaldi R, Fornelli A, Pilati S, Passigato N, Fusaroli P. Tumor Location in the Head/Uncinate Process and Presence of Fibrosis Impair the Adequacy of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Solid Pancreatic Tumors. Cancers. 2022; 14(14):3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143544
Chicago/Turabian StyleTogliani, Thomas, Andrea Lisotti, Rosa Rinaldi, Adele Fornelli, Stefano Pilati, Nicola Passigato, and Pietro Fusaroli. 2022. "Tumor Location in the Head/Uncinate Process and Presence of Fibrosis Impair the Adequacy of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Solid Pancreatic Tumors" Cancers 14, no. 14: 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143544
APA StyleTogliani, T., Lisotti, A., Rinaldi, R., Fornelli, A., Pilati, S., Passigato, N., & Fusaroli, P. (2022). Tumor Location in the Head/Uncinate Process and Presence of Fibrosis Impair the Adequacy of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Tissue Acquisition of Solid Pancreatic Tumors. Cancers, 14(14), 3544. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14143544






