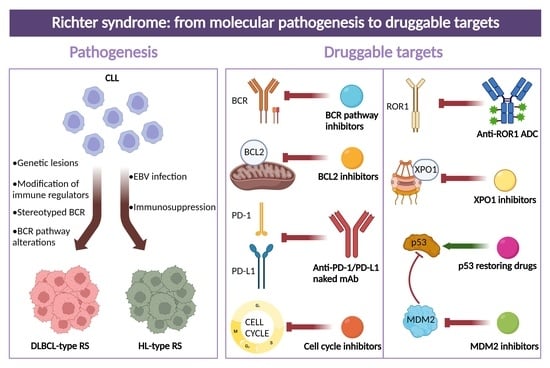
Richter Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Druggable Targets
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Definition of Richter Syndrome
2. Epidemiology
3. Molecular Pathways in RS
4. Molecular History of Clonally Related DLBCL-Type RS
5. Molecular Differences between Clonally Related and Clonally Unrelated DLBCL-Type RS
6. Druggable Targets for the Treatment of DLBCL-Type RS
7. Druggable Targets for the Treatment of HL-Type RS
8. Perspectives of New Potential Molecular Targets for RS
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richter, M.N. Generalized Reticular Cell Sarcoma of Lymph Nodes Associated with Lymphatic Leukemia. Am. J. Pathol. 1928, 4, 285–292.287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised, Revised 4th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Z.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Raffeld, M.; Richter, M.; Krugmann, J.; Burek, C.; Hartmann, E.; Rudiger, T.; Jaffe, E.S.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; et al. IgVH mutational status and clonality analysis of Richter’s transformation: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma in association with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) represent 2 different pathways of disease evolution. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.; Ding, W.; Viswanatha, D.S.; Chen, D.; Shi, M.; Van Dyke, D.; Tian, S.; Dao, L.N.; Parikh, S.A.; Shanafelt, T.D.; et al. PD-1 Expression in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (CLL/SLL) and Large B-cell Richter Transformation (DLBCL-RT): A Characteristic Feature of DLBCL-RT and Potential Surrogate Marker for Clonal Relatedness. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbri, G.; Khiabanian, H.; Holmes, A.B.; Wang, J.; Messina, M.; Mullighan, C.G.; Pasqualucci, L.; Rabadan, R.; Dalla-Favera, R. Genetic lesions associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2273–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Deambrogi, C.; Rasi, S.; Laurenti, L.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Arcaini, L.; Lucioni, M.; Rocque, G.B.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; et al. The genetics of Richter syndrome reveals disease heterogeneity and predicts survival after transformation. Blood 2011, 117, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condoluci, A.; Rossi, D. Biology and Treatment of Richter Transformation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 829983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Mittal, A.; Duggal, R.; Dadu, T.; Agarwal, A.; Handoo, A. Hodgkin Variant of Richter’s Transformation in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): An Illustrative Case Report and Literature Review. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2021, 15, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, W.W.; Sorbara, L.; Davies-Hill, T.; Pittaluga, S.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Hodgkin lymphoma variant of Richter transformation: Morphology, Epstein-Barr virus status, clonality, and survival analysis-with comparison to Hodgkin-like lesion. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 55, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia-Cancer Stat Facts. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. 2022. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/clyl.html (accessed on 7 September 2022).
- Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G. Richter syndrome. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 792, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solh, M.; Rai, K.R.; Peterson, B.L.; Kolitz, J.E.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Tallman, M.S.; Belch, A.; Larson, R.A.; Morrison, V.A. The impact of initial fludarabine therapy on transformation to Richter syndrome or prolymphocytic leukemia in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Analysis of an intergroup trial (CALGB 9011). Leuk Lymphoma 2013, 54, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Goede, V.; Herling, C.D.; Cramer, P.; Langerbeins, P.; von Tresckow, J.; Engelke, A.; Maurer, C.; et al. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: Updated results of the CLL8 trial. Blood 2016, 127, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oscier, D.; Else, M.; Matutes, E.; Morilla, R.; Strefford, J.C.; Catovsky, D. The morphology of CLL revisited: The clinical significance of prolymphocytes and correlations with prognostic/molecular markers in the LRF CLL4 trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 174, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Robrecht, S.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Cramer, P.; Tresckow, V.T.; Lange, E.; Kiehl, M.; Dreyling, M.; Ritgen, M.; et al. Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)-a pooled analysis of German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) front line treatment trials. Leukemia 2021, 35, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnair, R.; Ellithi, M.; Kallam, A.; Shostrom, V.; Bociek, R.G. Outcomes of Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL): An analysis of the SEER database. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 2513–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Greil, R.; Demirkan, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Anz, B.; Larratt, L.; Simkovic, M.; Samoilova, O.; Novak, J.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; et al. Ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in first-line treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (iLLUMINATE): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzmab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE TN): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Hillmen, P.; D’Rozario, J.; Assouline, S.; Owen, C.; Gerecitano, J.; Robak, T.; De la Serna, J.; et al. Venetoclax-Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munir, T.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Barr, P.M.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Final analysis from RESONATE: Up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, I.E.; Underbayev, C.; Albitar, A.; Herman, S.E.; Tian, X.; Maric, I.; Arthur, D.C.; Wake, L.; Pittaluga, S.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Clonal evolution leading to ibrutinib resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Hillmen, P.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.E.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; Barr, P.M.; et al. Extended follow-up and impact of high-risk prognostic factors from the phase 3 RESONATE study in patients with previously treated CLL/SLL. Leukemia 2018, 32, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byrd, J.C.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Kay, N.E.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, S.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Sharman, J.P.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Richards, D.A.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma: An open-label, multicentre, phase 1b/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Keating, M.; Wierda, W.; Estrov, Z.; Ferrajoli, A.; Jain, N.; George, B.; James, D.; Kantarjian, H.; Burger, J.; et al. Outcomes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia after discontinuing ibrutinib. Blood 2015, 125, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqui, M.Z.H.; Valdez, J.; Martyr, S.; Aue, G.; Saba, N.; Niemann, C.U.; Herman, S.E.M.; Tian, X.; Marti, G.; Soto, S.; et al. Ibrutinib for previously untreated and relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with TP53 aberrations: A phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Nabhan, C.; Barr, P.M.; Ujjani, C.S.; Hill, B.T.; Lamanna, N.; Skarbnik, A.P.; Howlett, C.; Pu, J.J.; Sehgal, A.R.; et al. Outcomes of CLL patients treated with sequential kinase inhibitor therapy: A real world experience. Blood 2016, 128, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Sharman, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W.; Davids, M.S.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Puvvada, S.D.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Brown, J.R.; Gressick, L.; et al. Targeting BCL2 with Venetoclax in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.A.; Tam, C.; Lew, T.E.; Juneja, S.; Juneja, M.; Westerman, D.; Wall, M.; Lade, S.; Gorelik, A.; Huang, D.C.S.; et al. Clinicopathological features and outcomes of progression of CLL on the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax. Blood 2017, 129, 3362–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, M.; Kroll-Balcerzak, R.; Balcerzak, A.; Czechowska, E.; Gil, L.; Sawiński, K.; Szczepaniak, A.; Komarnicki, M. Hodgkin lymphoma transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Cases report and discussion. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Keating, M.J. Richter syndrome: Biology, incidence, and therapeutic strategies. Cancer 2005, 103, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigrinova, E.; Rinaldi, A.; Kwee, I.; Rossi, D.; Rancoita, P.M.; Strefford, J.C.; Oscier, D.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Papadaki, T.; Berger, F.; et al. Two main genetic pathways lead to the transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to Richter syndrome. Blood 2013, 122, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Gaidano, G. Biology and treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2018, 131, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; Synnott, N.C.; Crown, J. Mutant p53 as a target for cancer treatment. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 83, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherr, C.J. Ink4-Arf locus in cancer and aging. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Martines, C.; Porro, F.; Fortunati, I.; Bonato, A.; Dimishkovska, M.; Piazza, S.; Yadav, B.S.; Innocenti, I.; Fazio, R.; et al. B-cell receptor signaling and genetic lesions in TP53 and CDKN2A/CDKN2B cooperate in Richter transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosati, E.; Baldoni, S.; De Falco, F.; Del Papa, B.; Dorillo, E.; Rompietti, C.; Albi, E.; Falzetti, F.; Di Ianni, M.; Sportoletti, P. NOTCH1 Aberrations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, G.; Rasi, S.; Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Khiabanian, H.; Ma, J.; Grunn, A.; Fangazio, M.; Capello, D.; Monti, S.; et al. Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: Role of NOTCH1 mutational activation. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Fangazio, M.; Monti, S.; Greco, M.; Ciardullo, C.; Famà, R.; Cresta, S.; Bruscaggin, A.; et al. Different impact of NOTCH1 and SF3B1 mutations on the risk of chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanasekaran, R.; Deutzmann, A.; Mahauad-Fernandez, W.D.; Hansen, A.S.; Gouw, A.M.; Felsher, D.W. The MYC oncogene—The grand orchestrator of cancer growth and immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paoli, L.; Cerri, M.; Monti, S.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Greco, M.; Ciardullo, C.; Famà, R.; Cresta, S.; et al. MGA, a suppressor of MYC, is recurrently inactivated in high risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2013, 54, 1087–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintman, J.; Appleby, N.; Stamatopoulos, B.; Ridout, K.; Eyre, T.A.; Robbe, P.; Pascua, L.L.; Knight, S.J.L.; Dreau, H.; Cabes, M.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic correlates of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 137, 2800–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whillock, A.L.; Mambetsariev, N.; Lin, W.W.; Stunz, L.L.; Bishop, G.A. TRAF3 regulates the oncogenic proteins Pim2 and c-Myc to restrain survival in normal and malignant B cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Abad, C.; Pisonero, H.; Blanco-Aparicio, C.; Roncador, G.; González-Menchén, A.; Martinez-Climent, J.A.; Mata, E.; Rodríguez, M.E.; Muñoz-González, G.; Sánchez-Beato, M.; et al. PIM2 inhibition as a rational therapeutic approach in B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2011, 118, 5517–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondello, P.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Mian, M. Pim kinases in hematological malignancies: Where are we now and where are we going? J. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dance, M.; Montagner, A.; Salles, J.P.; Yart, A.; Raynal, P. The molecular functions of Shp2 in the Ras/Mitogen-activated protein kinase (ERK1/2) pathway. Cell Signal. 2008, 20, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.J.; Carpenter, P.B. Understanding the language of Lys36 methylation at histone H3. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeriah, S.; Brennan, C.; Meng, S.; Singh, B.; Fagin, J.A.; Solit, D.B.; Paty, P.B.; Rohle, D.; Vivanco, I.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. The tyrosine phosphatase PTPRD is a tumor suppressor that is frequently inactivated and mutated in glioblastoma and other human cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9435–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spina, V.; Khiabanian, H.; Messina, M.; Monti, S.; Cascione, L.; Bruscaggin, A.; Spaccarotella, E.; Holmes, A.B.; Arcaini, L.; Lucioni, M.; et al. The genetics of nodal marginal zone lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 1362–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sinha, S.; Wellik, L.E.; Secreto, C.R.; Rech, K.L.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Kenderian, S.S.; Muchtar, E.; Hayman, S.R.; et al. Distinct immune signatures in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter syndrome. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmaninejad, A.; Valilou, S.F.; Shabgah, A.G.; Aslani, S.; Alimardani, M.; Pasdar, A.; Sahebkar, A. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Basic biology and role in cancer immunotherapy. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 16824–16837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffo, E.; Wu, R.C.; Bruno, T.C.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG3): The next immune checkpoint receptor. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 42, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, C.; Lickiss, J.; Kankanige, Y.; Yerneni, S.; Lade, S.; Gandhi, M.K.; Chin, C.; Yannakou, C.K.; Villa, D.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Characterisation of immune checkpoints in Richter syndrome identifies LAG3 as a potential therapeutic target. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 195, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harjunpää, H.; Guillerey, C. TIGIT as an emerging immune checkpoint. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2020, 200, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treanor, B. B-cell receptor: From resting state to activate. Immunology 2012, 136, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerousi, M.; Laidou, S.; Gemenetzi, K.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Chatzidimitriou, A. Distinctive Signaling Profiles With Distinct Biological and Clinical Implications in Aggressive CLL Subsets With Stereotyped B-Cell Receptor Immunoglobulin. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 771454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatopoulos, K.; Belessi, C.; Moreno, C.; Boudjograh, M.; Guida, G.; Smilevska, T.; Belhoul, L.; Stella, S.; Stavroyianni, N.; Crespo, M.; et al. Over 20% of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia carry stereotyped receptors: Pathogenetic implications and clinical correlations. Blood 2007, 109, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Cerri, M.; Rasi, S.; Deambrogi, C.; De Paoli, L.; Laurenti, L.; Maffei, R.; Forconi, F.; Bertoni, F.; et al. Stereotyped B-cell receptor is an independent risk factor of chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Bomben, R.; Rasi, S.; Dal-Bo, M.; Bruscaggin, A.; Rossi, F.M.; Monti, S.; Degan, M.; Ciardullo, C.; et al. Association between molecular lesions and specific B-cell receptor subsets in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4902–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounari, M.; Ntoufa, S.; Apollonio, B.; Papakonstantinou, N.; Ponzoni, M.; Chu, C.C.; Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G.; Chiorazzi, N.; Stamatopoulos, K.; et al. Excessive antigen reactivity may underlie the clinical aggressiveness of chronic lymphocytic leukemia stereotyped subset #8. Blood 2015, 125, 3580–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, J.A.; Wiestner, A. Targeting B cell receptor signalling in cancer: Preclinical and clinical advances. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Ma, J.; Guo, A.; Lu, P.; Leonard, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Liu, M.; Buggy, J.J.; Furman, R.R.; Wang, Y.L. BTK inhibition targets in vivo CLL proliferation through its effects on B-cell receptor signaling activity. Leukemia 2014, 28, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringshausen, I.; Schneller, F.; Bogner, C.; Hipp, S.; Duyster, J.; Peschel, C.; Decker, T. Constitutively activated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K) is involved in the defect of apoptosis in B-CLL: Association with protein kinase Cdelta. Blood 2002, 100, 3741–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlhaas, V.; Blakemore, S.J.; Al-Maarri, M.; Nickel, N.; Pal, M.; Roth, A.; Hövelmeyer, N.; Schäfer, S.C.; Knittel, G.; Lohneis, P.; et al. Active Akt signaling triggers CLL toward Richter transformation via overactivation of Notch1. Blood 2021, 137, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeu, F.; Royo, R.; Massoni-Badosa, R.; Playa-Albinyana, H.; Garcia-Torre, B.; Duran-Ferrer, M.; Dawson, K.J.; Kulis, M.; Diaz-Navarro, A.; Villamor, N.; et al. Detection of early seeding of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, S.; Savage, K.J.; Kutok, J.L.; Feuerhake, F.; Kurtin, P.; Mihm, M.; Wu, B.; Pasqualucci, L.; Neuberg, D.; Aguiar, R.C.; et al. Molecular profiling of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies robust subtypes including one characterized by host inflammatory response. Blood 2005, 105, 1851–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, P.; Kishan, A.U.; Norberg, E.; Stanley, I.A.; Chapuy, B.; Ficarro, S.B.; Polak, K.; Tondera, D.; Gounarides, J.; Yin, H.; et al. Metabolic signatures uncover distinct targets in molecular subsets of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norberg, E.; Lako, A.; Chen, P.H.; Stanley, I.A.; Zhou, F.; Ficarro, S.B.; Chapuy, B.; Chen, L.; Rodig, S.; Shin, D.; et al. Differential contribution of the mitochondrial translation pathway to the survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subsets. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Ailawadhi, S.; Bojanini, L.; Mehta, A.; Biswas, S.; Sher, T.; Roy, V.; Vishnu, P.; Marin-Acevedo, J.; Alegria, V.R.; et al. Trends in the risk of second primary malignancies among survivors of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2019, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Rabe, K.G.; Call, T.G.; Zent, C.S.; Habermann, T.M.; Ding, W.; Leis, J.F.; Schwager, S.M.; Hanson, C.A.; Macon, W.R.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (Richter syndrome) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL): A cohort study of newly diagnosed patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favini, C.; Talotta, D.; Almasri, M.; Andorno, A.; Rasi, S.; Adhinaveni, R.; Kogila, S.; Awikeh, B.; Schipani, M.; Boggione, P.; et al. Clonally unrelated Richter syndrome are truly de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with a mutational profile reminiscent of clonally related Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 198, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappella, A.; Diop, F.; Agostinelli, C.; Novo, M.; Nassi, L.; Evangelista, A.; Ciccone, G.; Di Rocco, A.; Martelli, M.; Melle, F.; et al. Prognostic impact of TP53 mutation in newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated in the FIL-DLCL04 trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, M.; Del Giudice, I.; Khiabanian, H.; Rossi, D.; Chiaretti, S.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Holmes, A.B.; Marinelli, M.; Fabbri, G.; et al. Genetic lesions associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia chemo-refractoriness. Blood 2014, 123, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, S.A.; Kay, N.E.; Shanafelt, T.D. How we treat Richter syndrome. Blood 2014, 123, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Gaidano, G. Richter syndrome: Molecular insights and clinical perspectives. Hematol. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langerbeins, P.; Busch, R.; Anheier, N.; Dürig, J.; Bergmann, M.; Goebeler, M.-E.; Hurtz, H.-J.; Stauch, M.B.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Döhner, H.; et al. Poor efficacy and tolerability of R-CHOP in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E239–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.A.; Huang, Y.; Ruppert, A.S.; Salem, G.; Stephens, D.M.; Heerema, N.A.; Andritsos, L.A.; Awan, F.T.; Byrd, J.C.; Flynn, J.M.; et al. A single-institution retrospective cohort study of first-line R-EPOCH chemoimmunotherapy for Richter syndrome demonstrating complex chronic lymphocytic leukaemia karyotype as an adverse prognostic factor. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabaja, B.S.; O’Brien, S.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E.; Thomas, D.A.; Albitar, M.; Schlette, E.S.; Faderl, S.; Sarris, A.; Keating, M.J.; et al. Fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, liposomal daunorubicin (daunoXome), and dexamethasone (hyperCVXD) regimen in Richter’s syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma 2001, 42, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wierda, W.G.; Wen, S.; Plunkett, W.; O’Brien, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Jones, J.A.; Badoux, X.; Kantarjian, H.; Keating, M.J. Phase I-II clinical trial of oxaliplatin, fludarabine, cytarabine, and rituximab therapy in aggressive relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or Richter syndrome. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2013, 13, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Clifford, R.; Bloor, A.; Boyle, L.; Roberts, C.; Cabes, M.; Collins, G.P.; Devereux, S.; Follows, G.; Fox, C.P.; et al. NCRI phase II study of CHOP in combination with ofatumumab in induction and maintenance in newly diagnosed Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballa, S.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J. BTK Inhibitors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2021, 16, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Call, T.G.; Ding, W.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Leis, J.F.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Bowen, D.; Conte, M.; Schwager, S.M.; et al. The efficacy of ibrutinib in the treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2015, 125, 1676–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Hahn, A.; Yaghmour, G.; Martin, M.G. Ibrutinib has some activity in Richter’s syndrome. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Master, S.; Leary, C.; Takalkar, A.; Coltelingam, J.; Mansour, R.; Mills, G.M.; Koshy, N. Successful Treatment of Richter Transformation with Ibrutinib in a Patient with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Case Rep. Oncol. 2017, 10, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Bastian, S.; Cogliatti, S.; Mey, U.; Saub, J.; Schanz, U.; Padberg, B.; Hohloch, K. Ibrutinib-induced rapid response in chemotherapy-refractory Richter’s syndrome. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Schuh, A.; Wierda, W.G.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Pagel, J.M.; Furman, R.R.; Cheung, J.; Hamdy, A.; Izumi, R.; et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ACE-CL-001): Analysis of the Richter transformation cohort of an open-label, single-arm, phase 1-2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e912–e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, K.; Bhat, S.A.; Grever, M.R.; Lozanski, A.; Doong, T.-J.; Blachly, J.S.; Lozanski, G.; Jones, D.; et al. Resistance to Acalabrutinib in CLL Is Mediated Primarily By BTK Mutations. Blood 2019, 134, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczak, W.; Shah, N.N.; Lamanna, N.; Eyre, T.A.; Woyach, J.; Lech-Maranda, E.; Wierda, W.G.; Lewis, D.; Thompson, M.C.; Wang, D.; et al. Pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305), a next generation highly selective non-covalent BTK inhibitor in previously treated Richter transformation: Results from the phase 1/2 BRUIN study. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, C.C.; Pagel, J.M.; Shah, N.N.; Lamanna, N.; Lech-Maranda, E.; Eyre, T.A.; Woyach, J.A.; Wierda, W.G.; Cheah, C.Y.; Roeker, L.; et al. CLL-039: Pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305), a Next-Generation, Highly Selective, Non-Covalent BTK Inhibitor in Previously Treated CLL/SLL: Results from the Phase 1/2 BRUIN Study. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, S315–S316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiff, S.D.; Mantel, R.; Smith, L.L.; Greene, J.T.; Muhowski, E.M.; Fabian, C.A.; Goettl, V.M.; Tran, M.; Harrington, B.K.; Rogers, K.A.; et al. The BTK Inhibitor ARQ 531 Targets Ibrutinib-Resistant CLL and Richter Transformation. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1300–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalniz, F.F.; Wierda, W.G. Targeting BCL2 in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Other Hematologic Malignancies. Drugs 2019, 79, 1287–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moia, R.; Diop, F.; Favini, C.; Kodipad, A.A.; Gaidano, G. Potential of BCL2 as a target for chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2018, 11, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stilgenbauer, S.; Eichhorst, B.; Schetelig, J.; Hillmen, P.; Seymour, J.F.; Coutre, S.; Jurczak, W.; Mulligan, S.P.; Schuh, A.; Assouline, S.; et al. Venetoclax for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with 17p Deletion: Results from the Full Population of a Phase II Pivotal Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1973–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Puvvada, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Study of Venetoclax in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Tyekucheva, S.; Wang, Z.; Pazienza, S.; Renner, S.K.; Montegaard, J.; Ihuoma, U.; Lehmberg, T.Z.; Parry, E.M.; et al. Venetoclax plus dose-adjusted R-EPOCH for Richter syndrome. Blood 2022, 139, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; LaPlant, B.R.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; He, R.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Sinha, S.; Le-Rademacher, J.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood 2017, 129, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Murawski, N.; Molin, D.; Zain, J.; Eichhorst, B.; Gulbas, Z.; Hawkes, E.A.; Pagel, J.M.; Phillips, T.; Ribrag, V.; et al. Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, e117–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, A.; Brody, J.; Carpio, C.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; Ferhanoglu, B.; Nagler, A.; Ozcan, M.; Avivi, I.; Bosch, F.; et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A phase 1/2a study. Lancet Haematol 2019, 6, e67–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Ferrajoli, A.; Thompson, P.A.; Konopleva, M.; Green, M.R.; Sampath, D.; Neelapu, S.S.; Takahashi, K.; Strati, P.; Burger, J.A.; et al. Venetoclax, Obinutuzumab and Atezolizumab (PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibitor) for Treatment for Patients with Richter Transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; O’Brien, S.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Koller, C.; Hagemeister, F.B.; Fayad, L.; Lerner, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.E.; Keating, M.J. Hodgkin transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: The M. D. Anderson Cancer Center experience. Cancer 2006, 107, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadmor, T.; Shvidel, L.; Goldschmidt, N.; Ruchlemer, R.; Fineman, R.; Bairey, O.; Rahimi-Levene, N.; Herishanu, Y.; Yuklea, M.; Arad, A.; et al. Hodgkin’s variant of Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia; a retrospective study from the Israeli CLL study group. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 785–790. [Google Scholar]
- Bockorny, B.; Codreanu, I.; Dasanu, C.A. Hodgkin lymphoma as Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A retrospective analysis of world literature. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 156, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.G.; Ristow, K.M.; Habermann, T.M.; Colgan, J.P.; Witzig, T.E.; Ansell, S.M. Bleomycin pulmonary toxicity has a negative impact on the outcome of patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7614–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualberto, A. Brentuximab Vedotin (SGN-35), an antibody-drug conjugate for the treatment of CD30-positive malignancies. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xing, Z.; Mi, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wei, T.; Wu, W. Novel Agents For Relapsed and Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 929012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvetti, C.; Vitale, C.; Griggio, V.; Drandi, D.; Jones, R.; Bonello, L.; Bomben, R.; Bragoni, A.; Bagnara, D.; Fais, F.; et al. Case Report: Sequential Development of Three Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms in a Single Patient: Clonal Relationship and Molecular Insights. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 917115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisitti, T.; Braggio, E.; Allan, J.N.; Arruga, F.; Serra, S.; Zamò, A.; Tam, W.; Chadburn, A.; Furman, R.R.; Deaglio, S. Novel Richter Syndrome Xenograft Models to Study Genetic Architecture, Biology, and Therapy Responses. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3413–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhao, Z.J.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y. Tyrosine Kinase ROR1 as a Target for Anti-Cancer Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 680834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipps, T.J. ROR1—An Orphan Becomes Apparent. Blood 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, U.; Tu, Y.; Stolovitzky, G.A.; Mattioli, M.; Cattoretti, G.; Husson, H.; Freedman, A.; Inghirami, G.; Cro, L.; Baldini, L.; et al. Gene expression profiling of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia reveals a homogeneous phenotype related to memory B cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, S.; Kwong, K.Y.; Hofer, T.; Levy, J.M.; Kennedy, M.G.; Lee, E.; Staudt, L.M.; Wilson, W.H.; Wiestner, A.; Rader, C. Unique cell surface expression of receptor tyrosine kinase ROR1 in human B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Daneshmanesh, A.H.; Moshfegh, A.; Kokhaei, P.; Vågberg, J.; Schultz, J.; Olin, T.; Harrysson, S.; Smedby, K.E.; Drakos, E.; et al. ROR1 Is Expressed in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and a Small Molecule Inhibitor of ROR1 (KAN0441571C) Induced Apoptosis of Lymphoma Cells. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisitti, T.; Arruga, F.; Vitale, N.; Lee, T.T.; Ko, M.; Chadburn, A.; Braggio, E.; Di Napoli, A.; Iannello, A.; Allan, J.N.; et al. ROR1 targeting with the antibody-drug conjugate VLS-101 is effective in Richter syndrome patient-derived xenograft mouse models. Blood 2021, 137, 3365–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisitti, T.; Vitale, N.; Iannello, A.; Brandimarte, L.; Micillo, M.; Papotti, M.G.; Di Napoli, A.; Orlik, C.; Kulke, M.; Pahl, A.; et al. Anti-CD37 Alpha-Amanitin Conjugated Antibodies As Therapeutic Weapons for Richter’s Syndrome. Blood 2021, 138, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, A.; Imbergamo, S.; Scomazzon, E.; Pravato, S.; Frezzato, F.; Bonaldi, L.; Pizzi, M.; Vio, S.; Gregianin, M.; Burei, M.; et al. BCR kinase inhibitors, idelalisib and ibrutinib, are active and effective in Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffold, A.; Stilgenbauer, S. Revolution of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Therapy: The Chemo-Free Treatment Paradigm. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerdt, I.; Koopmans, S.M.; Kater, A.P.; van Gelder, M. Incidence and management of toxicity associated with ibrutinib and idelalisib: A practical approach. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannello, A.; Vitale, N.; Coma, S.; Arruga, F.; Chadburn, A.; Di Napoli, A.; Laudanna, C.; Allan, J.N.; Furman, R.R.; Pachter, J.A.; et al. Synergistic efficacy of the dual PI3K-δ/γ inhibitor duvelisib with the Bcl-2 inhibitor venetoclax in Richter syndrome PDX models. Blood 2021, 137, 3378–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojarczuk, K.; Wienand, K.; Ryan, J.A.; Chen, L.; Villalobos-Ortiz, M.; Mandato, E.; Stachura, J.; Letai, A.; Lawton, L.N.; Chapuy, B.; et al. Targeted inhibition of PI3Kα/δ is synergistic with BCL-2 blockade in genetically defined subtypes of DLBCL. Blood 2019, 133, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.T.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Leis, J.F.; LaPlant, B.; Call, T.; Pettinger, A.; Hanson, C.; Erlichman, C.; Habermann, T.M.; Reeder, C.; et al. Akt inhibitor MK-2206 in combination with bendamustine and rituximab in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results from the N1087 alliance study. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stade, K.; Ford, C.S.; Guthrie, C.; Weis, K. Exportin 1 (Crm1p) is an essential nuclear export factor. Cell 1997, 90, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.S.; Hing, Z.A.; Harrington, B.; Baumhardt, J.; Ozer, H.G.; Lehman, A.; Giacopelli, B.; Beaver, L.; Williams, K.; Skinner, J.N.; et al. Recurrent XPO1 mutations alter pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosson, A.; Chapiro, E.; Bougacha, N.; Lambert, J.; Herbi, L.; Cung, H.A.; Algrin, C.; Keren, B.; Damm, F.; Gabillaud, C.; et al. Gain in the short arm of chromosome 2 (2p+) induces gene overexpression and drug resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Analysis of the central role of XPO1. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuruvilla, J.; Byrd, J.C.; Flynn, J.M.; Garzon, R.; Porcu, P.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Savoie, M.L.; Stone, R.M.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Mau-Sorensen, M.; et al. The Oral Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export (SINE) Selinexor (KPT-330) Demonstrates Broad and Durable Clinical Activity in Relapsed/Refractory Non Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL). Blood 2014, 124, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moia, R.; Boggione, P.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Kodipad, A.A.; Adhinaveni, R.; Sagiraju, S.; Patriarca, A.; Gaidano, G. Targeting p53 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2020, 24, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahi, H.; Lehmann, S.; Mollgard, L.; Bengtzen, S.; Selivanova, G.; Wiman, K.G.; Paul, C.; Merup, M. Effects of PRIMA-1 on chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells with and without hemizygous p53 deletion. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 127, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardullo, C.; Aptullahoglu, E.; Woodhouse, L.; Lin, W.Y.; Wallis, J.P.; Marr, H.; Marshall, S.; Bown, N.; Willmore, E.; Lunec, J. Non-genotoxic MDM2 inhibition selectively induces a pro-apoptotic p53 gene signature in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Martines, C.; Porro, F.; Fortunati, I.; Bonato, A.; Dimishkovska, M.; Yadav, B.; Innocenti, I.; Fazio, R.; Vaisitti, T.; et al. Combined Genetic Lesions in TP53 and CDKN2A/CDKN2B Drive B Cell Receptor-Dependent/Costimulatory Signal-Independent Proliferation in Richter Syndrome. Blood 2020, 136, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number of CLL Patients | Study Population | Treatment | RS Prevalence (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 391 | Relapsed | Ibrutinib, ofatumumab | 1 | Byrd, 2014 [23] |
| 29 | Progressive untreated | Ibrutinib | 3 | O’Brien, 2014 [24] |
| 194 | R/R | Venetoclax-rituximab | 3 | Seymour, 2018 [19] |
| 127 | R/R | Ibrutinib | 5 | Jain, 2015 [25] |
| 84 | 17p deleted or ≥65 years | Ibrutinib | 6 | Ahn, 2017 [21] |
| 358 | Treatment-naïve | Acalabrutinib, Obinutuzumab | 2 | Sharman, 2020 [18] |
| 51 | 17p deleted | Ibrutinib | 6 | Farooqui, 2015 [26] |
| 178 | BCRi treated | Ibrutinib, idelalisib | 7 | Mato, 2016 [27] |
| 113 | Treatment-naïve | Ibrutinib-obinutuzumab | 0 | Moreno, 2019 [17] |
| 85 | R/R | Ibrutinib | 8 | Byrd, 2013 [28] |
| 116 | R/R | Venetoclax | 16 | Roberts, 2016 [29] |
| 67 | R/R, 17p deleted | Venetoclax | 25 | Anderson, 2017 [30] |
| 2975 | R/R | B, F, C, Clb, rituximab, obinutuzumab, ibrutinib, venetoclax | 3 | Al-Sawaf, 2021 [15] |
| 195 | R/R | Ibrutinib | 10 | Munir, 2019 [20] |
| Intervention | Phase | Main Target | NCT Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| VR-EPOCH/VR-CHOP | II | BCL2 | NCT03054896 |
| Obinutuzumab + rituximab + venetoclax | II | BCL2 | NCT04939363 |
| R-CHOP + blinatumomab | II | CD19 | NCT03931642 |
| Epcoritamab | I/II | CD20 | NCT04623541 |
| Polatuzumab vedotin + R-EPCH | II | CD79b | NCT04679012 |
| Duvelisib + venetoclax | I/II | PI3K, BCL2 | NCT03534323 |
| Zanubrutinib + tislelizumab | II | BTK, PD-1 | NCT04271956 |
| Acalabrutinib + durvalumab + venetoclax | II | BTK, PD-L1, BCL2 | NCT05388006 |
| Duvelisib + nivolumab | I | PI3K, PD-1 | NCT03892044 |
| VIP152 | I | CDK9 | NCT04978779 |
| Atezolizumab + Obinutuzumab + venetoclax | II | PD-L1, BCL2 | NCT02846623 |
| Acalabrutinib | I/II | BTK | NCT02029443 |
| Copanlisib + nivolumab | I | PI3K, PD-1 | NCT03884998 |
| Obinutuzumab + atezolizumab + venetoclax | II | PD-L1, BCL2 | NCT04082897 |
| Cosibelimab ± ublituximab and bendamustine | I | PD-L1 | NCT03778073 |
| MOR00208 ± lenalidomide or ibrutinib | II | CD19, BTK | NCT02005289 |
| Polatuzumab vedotin | I/II | CD79b | NCT04491370 |
| Pembrolizumab + acalabrutinib | I/II | PD-1, BTK | NCT02362035 |
| Pevonedistat | I | NAE, BTK | NCT03479268 |
| Pembrolizumab ± idelalisib or ibrutinib | II | PD-1, PI3K, BTK | NCT02332980 |
| LP-118 | I | BCL2 | NCT04771572 |
| TG-1801 ± ublituximab | I | CD47, CD19 | NCT04806035 |
| NX-1607 | I | CBL-B | NCT05107674 |
| Nemtabrutinib | I/II | BTK | NCT03162536 |
| VLS-101 | I | BTK | NCT03833180 |
| DTRMWXHS-12+everolimus ± pomalidomide | II | BTK, mTOR | NCT04305444 |
| HMPL-760 | I | BTK | NCT05176691 |
| ALX148 + rituximab + lenalidomide | I/II | CD47 | NCT05025800 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mouhssine, S.; Gaidano, G. Richter Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Druggable Targets. Cancers 2022, 14, 4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194644
Mouhssine S, Gaidano G. Richter Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Druggable Targets. Cancers. 2022; 14(19):4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194644
Chicago/Turabian StyleMouhssine, Samir, and Gianluca Gaidano. 2022. "Richter Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Druggable Targets" Cancers 14, no. 19: 4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194644
APA StyleMouhssine, S., & Gaidano, G. (2022). Richter Syndrome: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Druggable Targets. Cancers, 14(19), 4644. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14194644