Interaction of HPV16 and Cutaneous HPV in Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Oral HPV Testing
2.4. Outcome Variable
2.5. Exposure Variables
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Interaction of HPV16 and Any Beta or Gamma | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Any Beta or Gamma Absent | Any Beta or Gamma Present | Effect of Any Beta or Gamma within the Strata of HPV16 | |
| OR [95% CI] | OR [95% CI] | OR [95% CI] | |
| HPV16 absent | 1 [Reference] | 0.82 [0.59, 1.14] | 0.82 [0.59, 1.14] |
| HPV16 present | 18.15 [6.19, 53.24] | 20.42 [8.32, 50.11] | 1.12 [0.29, 4.32] |
| Effect of HPV16 within the strata of Any Beta or Gamma | 18.15 [6.19, 53.24] | 24.78 [10.14, 60.58] | |
| Multiplicative scale | 1.37 [0.34, 5.46] | ||
| RERI | 2.44 [−23.27, 28.15] | ||
| AP | 0.12 [−1.07, 1.31] | ||
| SI | 1.14 [0.27, 4.78] | ||
Appendix B
| Interaction of HPV16 and Any Cutaneous HPV (Oropharyngeal Cancers Only) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Any Cutaneous HPV Absent | Any Cutaneous HPV Present | Effect of Any Cutaneous HPV within the Strata of HPV16 | |
| OR [95% CI] | OR [95% CI] | OR [95% CI] | |
| HPV16 absent | 1 [Reference] | 0.71 [0.45, 1.13] | 0.71 [0.45, 1.13] |
| HPV16 present | 40.13 [13.31, 120.99] | 53.9 [19.56, 148.51] | 1.34 [0.33, 5.44] |
| Effect of HPV16 within the strata of Any Cutaneous HPV | 40.13 [13.31, 120.99] | 75.96 [27.68, 208.43] | |
| Multiplicative scale | 1.89 [0.43, 8.27] | ||
| RERI | 14.07 [−51.65, 79.78] | ||
| AP | 0.26 [−0.78, 1.3] | ||
| SI | 1.36 [0.32, 5.73] | ||
References
- Vaccarella, S.; Franceschi, S.; Herrero, R.; Muñoz, N.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Clifford, G.M.; Smith, J.S.; Lazcano-Ponce, E.; Sukvirach, S.; Shin, H.-R.; et al. Sexual Behavior, Condom Use, and Human Papillomavirus: Pooled Analysis of the IARC Human Papillomavirus Prevalence Surveys. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2006, 15, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westra, W.H.; Lewis, J.S. Update from the 4th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumours: Oropharynx. Head Neck Pathol. 2017, 11, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agalliu, I.; Gapstur, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Anderson, R.L.; Teras, L.; Kreimer, A.R.; Hayes, R.B.; Freedman, N.D.; Burk, R.D. Associations of Oral α-, β-, and γ-Human Papillomavirus Types With Risk of Incident Head and Neck Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampa, M.; Mitran, C.I.; Mitran, M.I.; Nicolae, I.; Dumitru, A.; Matei, C.; Manolescu, L.; Popa, G.L.; Caruntu, C.; Georgescu, S.R. The Role of Beta HPV Types and HPV-Associated Inflammatory Processes in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, e5701639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasino, M. HPV and Skin Carcinogenesis. Papillomavirus Res. 2019, 7, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sichero, L.; Rollison, D.E.; Amorrortu, R.P.; Tommasino, M. Beta Human Papillomavirus and Associated Diseases. Acta Cytol. 2019, 63, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Soneidar, W.A.; Harper, S.; Madathil, S.A.; Schlecht, N.F.; Nicolau, B. Do Cutaneous Human Papillomavirus Genotypes Affect Head and Neck Cancer? Evidence and Bias-Correction from a Case-Control Study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2022, 79, 102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.T.; Saveria Campo, M. “Hit and Run” Transformation of Mouse C127 Cells by Bovine Papillomavirus Type 4: The Viral DNA Is Required for the Initiation but Not for Maintenance of the Transformed Phenotype. Virology 1988, 164, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viarisio, D.; Müller-Decker, K.; Accardi, R.; Robitaille, A.; Dürst, M.; Beer, K.; Jansen, L.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Bozza, M.; Harbottle, R.; et al. Beta HPV38 Oncoproteins Act with a Hit-and-Run Mechanism in Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Skin Carcinogenesis in Mice. PLOS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenborn, S.J.; Nindl, I.; Purdie, K.; Harwood, C.; Proby, C.; Breuer, J.; Majewski, S.; Pfister, H.; Wieland, U. Human Papillomavirus-DNA Loads in Actinic Keratoses Exceed Those in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprise, C.; Madathil, S.A.; Schlecht, N.F.; Castonguay, G.; Soulières, D.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Allison, P.; Coutlée, F.; Hier, M.; Rousseau, M.-C.; et al. Human Papillomavirus Genotypes and Risk of Head and Neck Cancers: Results from the HeNCe Life Case-Control Study. Oral Oncol. 2017, 69, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farsi, N.J.; Rousseau, M.-C.; Schlecht, N.; Castonguay, G.; Allison, P.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Souliéres, D.; Coutlée, F.; Hier, M.; Madathil, S.; et al. Aetiological Heterogeneity of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas: The Role of Human Papillomavirus Infections, Smoking and Alcohol. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durán, D.; Al-Soneidar, W.A.; Madathil, S.A.; Kaufman, J.S.; Nicolau, B. Quantitative Bias Analysis of Misclassification in Case-Control Studies: An Example with Human Papillomavirus and Oropharyngeal Cancer. Community Dent. Health 2020, 37, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berney, L.R.; Blane, D.B. Collecting Retrospective Data: Accuracy of Recall after 50 Years Judged against Historical Records. Soc. Sci. Med. 1997, 45, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.; Berney, L.; Blane, D.; Davey-Smith, G. The Lifegrid Method in Health Inequalities Research. Health Var. 1999, 3, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Soneidar, W.A.; (McGill University, Montreal, QC H3A 1G1, Canada); Harper, S.; Coutlée, F.; Gheit, T.; Tommasino, M.; Nicolau, B. Distribution of Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Human Papillomaviruses (HPV) in Oral Cell Samples and Relation to Sexual Behavior and Oral Health. 2022; unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Gheit, T.; Billoud, G.; de Koning, M.N.C.; Gemignani, F.; Forslund, O.; Sylla, B.S.; Vaccarella, S.; Franceschi, S.; Landi, S.; Quint, W.G.V.; et al. Development of a Sensitive and Specific Multiplex PCR Method Combined with DNA Microarray Primer Extension To Detect Betapapillomavirus Types. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2537–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lash, T.L.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Haneuse, S.; Rothman, K.J. Modern Epidemiology, 4th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-4511-9328-2. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, K.J. Epidemiology: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-19-975455-7. [Google Scholar]
- Knol, M.J.; VanderWeele, T.J. Recommendations for Presenting Analyses of Effect Modification and Interaction. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VanderWeele, T.J. Explanation in Causal Inference: Methods for Mediation and Interaction; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-19-932587-0. [Google Scholar]
- VanderWeele, T.J.; Knol, M.J. A Tutorial on Interaction. Epidemiol. Methods 2014, 3, 33–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W.; Lemeshow, S. Confidence Interval Estimation of Interaction. Epidemiology 1992, 3, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alli, B.Y. InteractionR: An R Package for Full Reporting of Effect Modification and Interaction. Softw. Impacts 2021, 10, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklo, M.; Nieto, F.J. Epidemiology: Beyond the Basics, 4th ed.; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-284-11659-5. [Google Scholar]
- VanderWeele, T.J.; Robins, J.M. The Identification of Synergism in the Sufficient-Component-Cause Framework. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWeele, T.J. Epistatic Interactions. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2010, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, M.C.S.; Vlantis, A.C.; Liang, M.; Wong, P.Y.; Ho, W.C.S.; Boon, S.S.; Sze, R.K.H.; Leung, C.; Chan, P.K.S.; Chen, Z. Prevalence and Epidemiologic Profile of Oral Infection with Alpha, Beta, and Gamma Papillomaviruses in an Asian Chinese Population. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winer, R.L.; Gheit, T.; Feng, Q.; Stern, J.E.; Lin, J.; Cherne, S.; Tommasino, M. Prevalence and Correlates of β– and γ–Human Papillomavirus Detection in Oral Samples From Mid-Adult Women. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWeele, T.J. Sample Size and Power Calculations for Additive Interactions. Epidemiol. Methods 2012, 1, 159–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
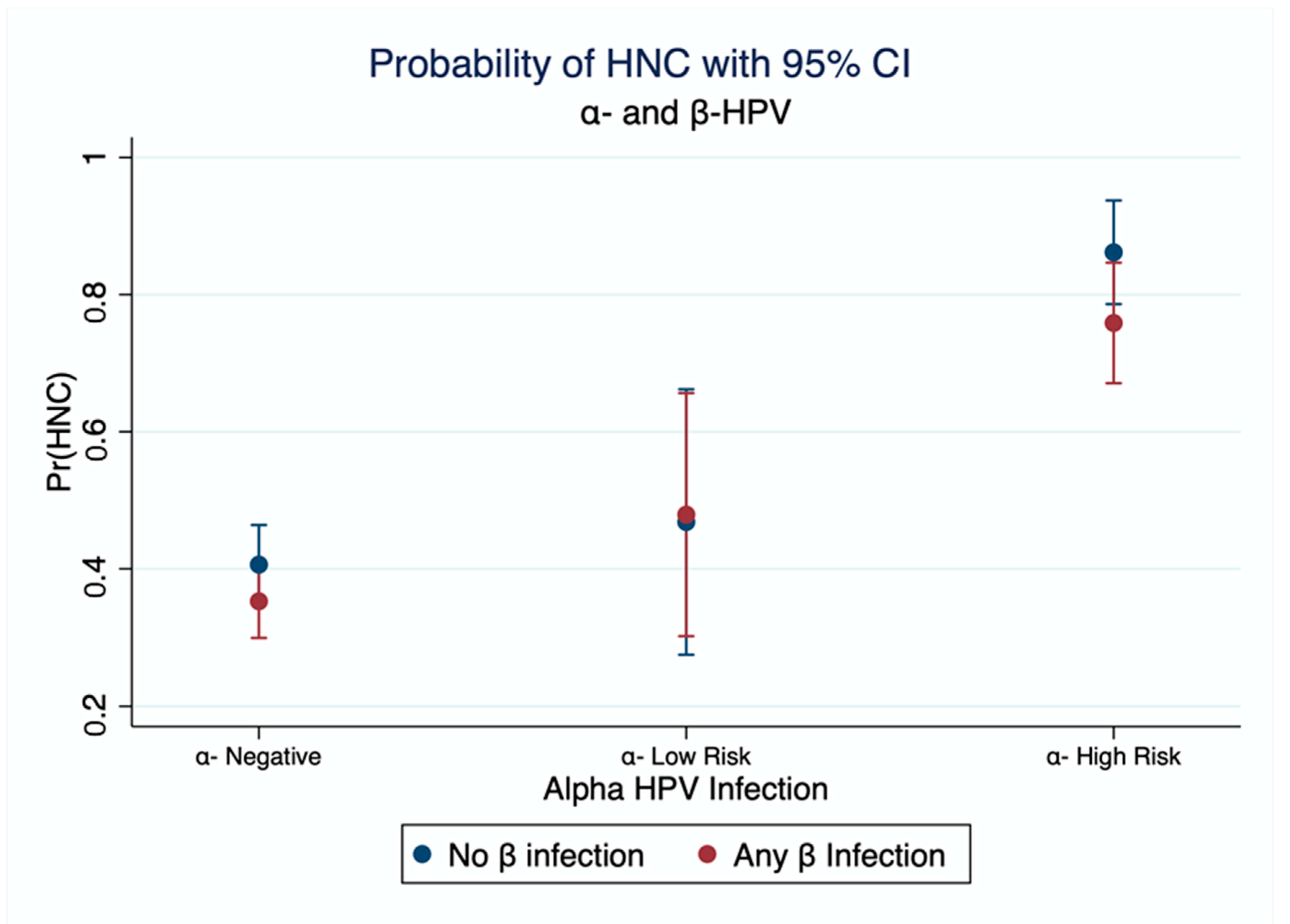

| Controls | Cases | |
|---|---|---|
| n = 294 | n = 241 | |
| Age (mean (SD)) | 60.73 (11.06) | 60.91 (10.34) |
| 20–39 years | 9 (3.1) | 5 (2.1) |
| 40–49 years | 34 (11.6) | 24 (10.0) |
| 50–59 years | 94 (32.0) | 89 (36.9) |
| 60–69 years | 93 (31.6) | 72 (29.9) |
| 70–79 years | 51 (17.3) | 44 (18.3) |
| 80 years and above | 13 (4.4) | 7 (2.9) |
| Sex (%) | ||
| Female | 93 (31.6) | 60 (24.9) |
| Male | 201 (68.4) | 181 (75.1) |
| Years of education (mean (SD)) | 13.95 (4.24) | 12.37 (3.85) |
| Ever smoker (%) | ||
| Ever | 214 (72.8) | 207 (85.9) |
| Never | 80 (27.2) | 34 (14.1) |
| Smoking pack-years (mean (SD)) | 32.32 (44.79) | 46.50 (41.64) |
| Ever drinker | ||
| Ever | 248 (84.4) | 206 (85.5) |
| Never | 46 (15.6) | 35 (14.5) |
| Ethanol liter-years (mean (SD)) | 450.32 (972.15) | 855.93 (1688.93) |
| HPV16 (%) | ||
| Negative | 287 (97.6) | 177 (73.4) |
| Positive | 7 (2.4) | 64 (26.6) |
| Any beta HPV (%) | ||
| Negative | 118 (40.1) | 98 (40.7) |
| Positive | 176 (59.9) | 143 (59.3) |
| Any gamma HPV (%) | ||
| Negative | 222 (75.5) | 159 (66.0) |
| Positive | 72 (24.5) | 82 (34.0) |
| Interaction of HPV16 and Beta HPV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta HPV Absent | Beta HPV Present | Effect of Beta HPV within the Strata of HPV16 | |||
| N cases/controls | OR [95% CI] | N cases/controls | OR [95% CI] | OR [95% CI] | |
| HPV16 absent | 140/183 | 1 [Reference] | 137/230 | 0.73 [0.53, 1.01] | 0.73 [0.53, 1.01] |
| HPV16 present | 51/4 | 20.86 [7.19, 60.56] | 54/6 | 16.87 [6.85, 41.54] | 0.81 [0.21, 3.1] |
| Effect of HPV16 within the strata of Beta HPV | 20.86 [7.19, 60.56] | 23.05 [9.35, 56.82] | |||
| Multiplicative scale | 1.1 [0.28, 4.4] | ||||
| RERI | −3.72 [−29.7, 22.26] | ||||
| AP | −0.22 [−1.87, 1.43] | ||||
| SI | 0.81 [0.19, 3.38] | ||||
| Interaction of HPV16 and Gamma HPV | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma HPV absent | Gamma HPV present | Effect of Gamma HPV within the strata of HPV16 | |||
| N cases/controls | OR [95% CI] | N cases/controls | OR [95% CI] | OR [95% CI] | |
| HPV16 absent | 122/217 | 1 [Reference] | 55/70 | 1.05 [0.67, 1.66] | 1.05 [0.67, 1.66] |
| HPV16 present | 37/5 | 18.5 [6.77, 50.57] | 27/2 | 35.98 [8.05, 160.82] | 1.95 [0.34, 11.15] |
| Effect of HPV16 within the strata of Gamma HPV | 18.5 [6.77, 50.57] | 34.25 [7.38, 158.85] | |||
| Multiplicative scale | 1.85 [0.3, 11.24] | ||||
| RERI | 17.44 [−38.34, 73.21] | ||||
| AP | 0.48 [−0.41, 1.38] | ||||
| SI | 1.99 [0.33, 12.17] | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Soneidar, W.A.; Harper, S.; Alli, B.Y.; Nicolau, B. Interaction of HPV16 and Cutaneous HPV in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215197
Al-Soneidar WA, Harper S, Alli BY, Nicolau B. Interaction of HPV16 and Cutaneous HPV in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215197
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Soneidar, Walid A., Sam Harper, Babatunde Y. Alli, and Belinda Nicolau. 2022. "Interaction of HPV16 and Cutaneous HPV in Head and Neck Cancer" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215197
APA StyleAl-Soneidar, W. A., Harper, S., Alli, B. Y., & Nicolau, B. (2022). Interaction of HPV16 and Cutaneous HPV in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers, 14(21), 5197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215197







