Inhibition of IκB Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Circumvent Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Cell Culture
2.2. PKI Screening
2.3. Clonogenic Survival Assay
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Reporter Gene Assay
2.6. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) Analysis
2.7. Quantitative Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
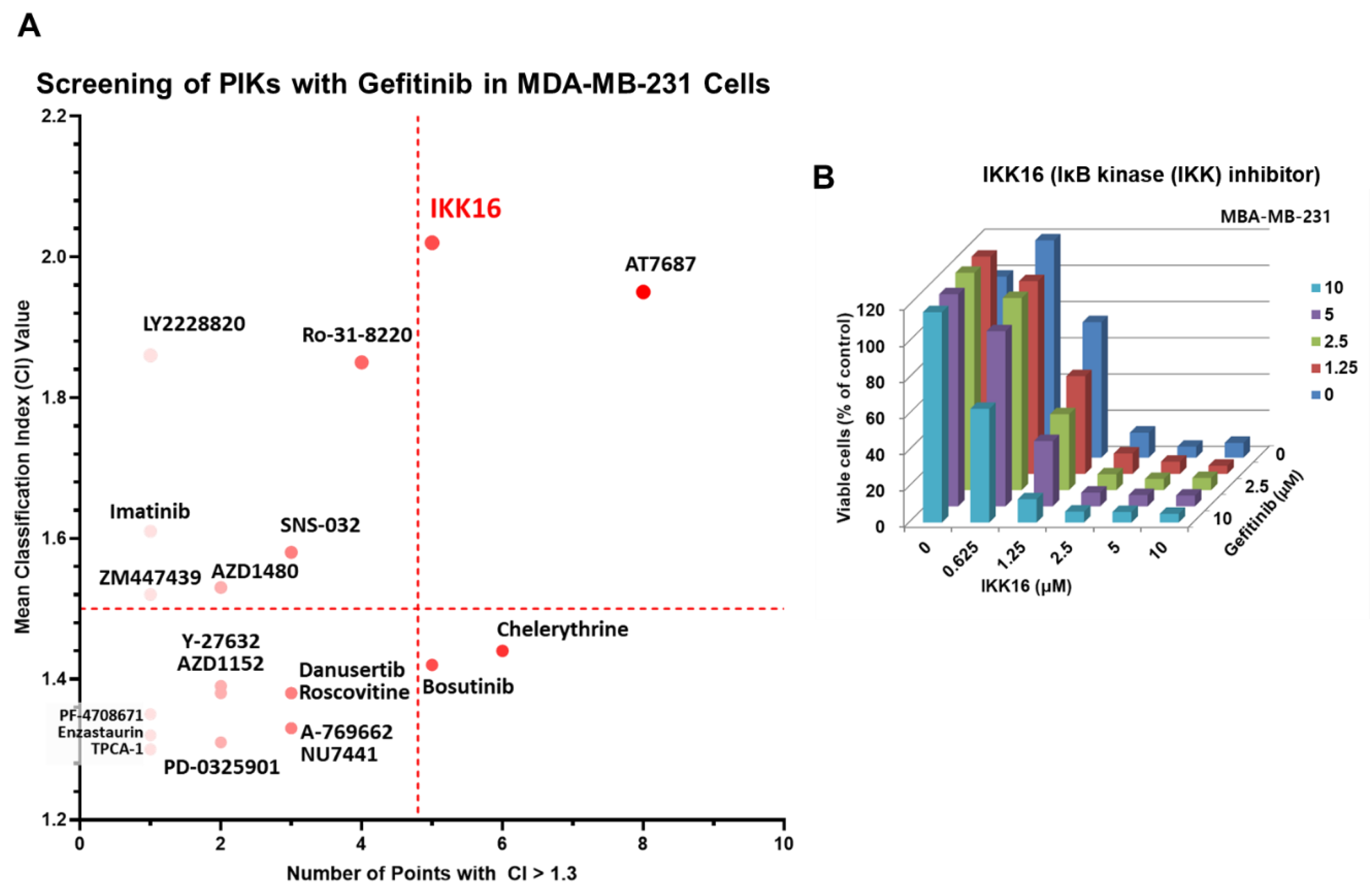
3.1. Identification of IKK16, an IKK Inhibitor, as a Potentiator of Gefitinib
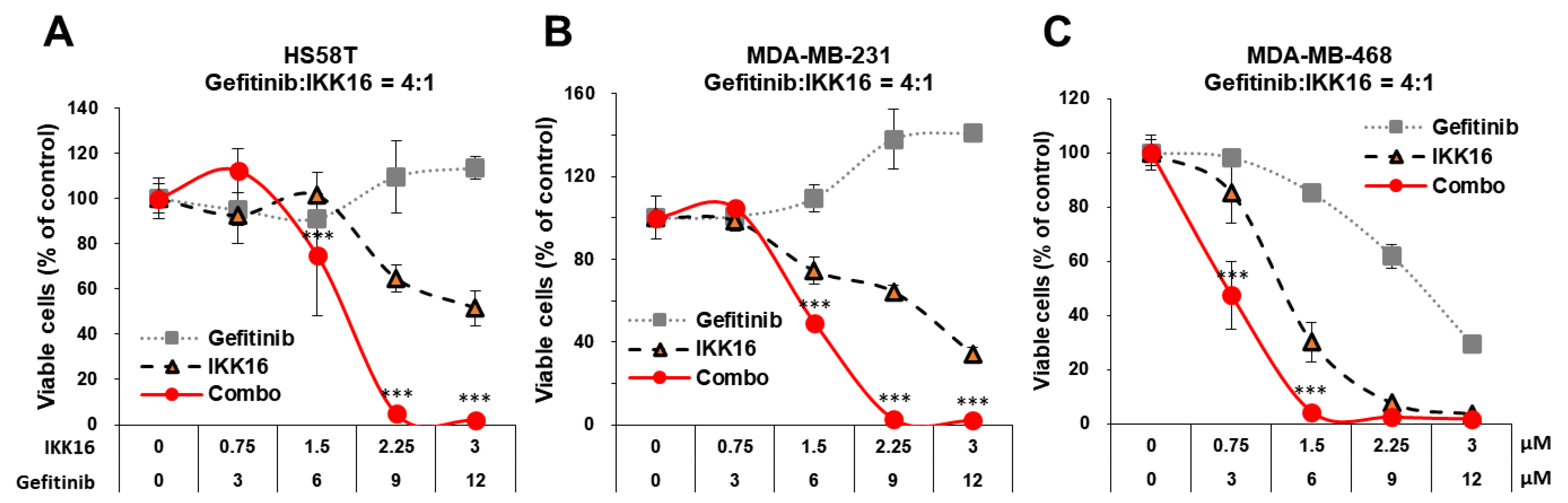
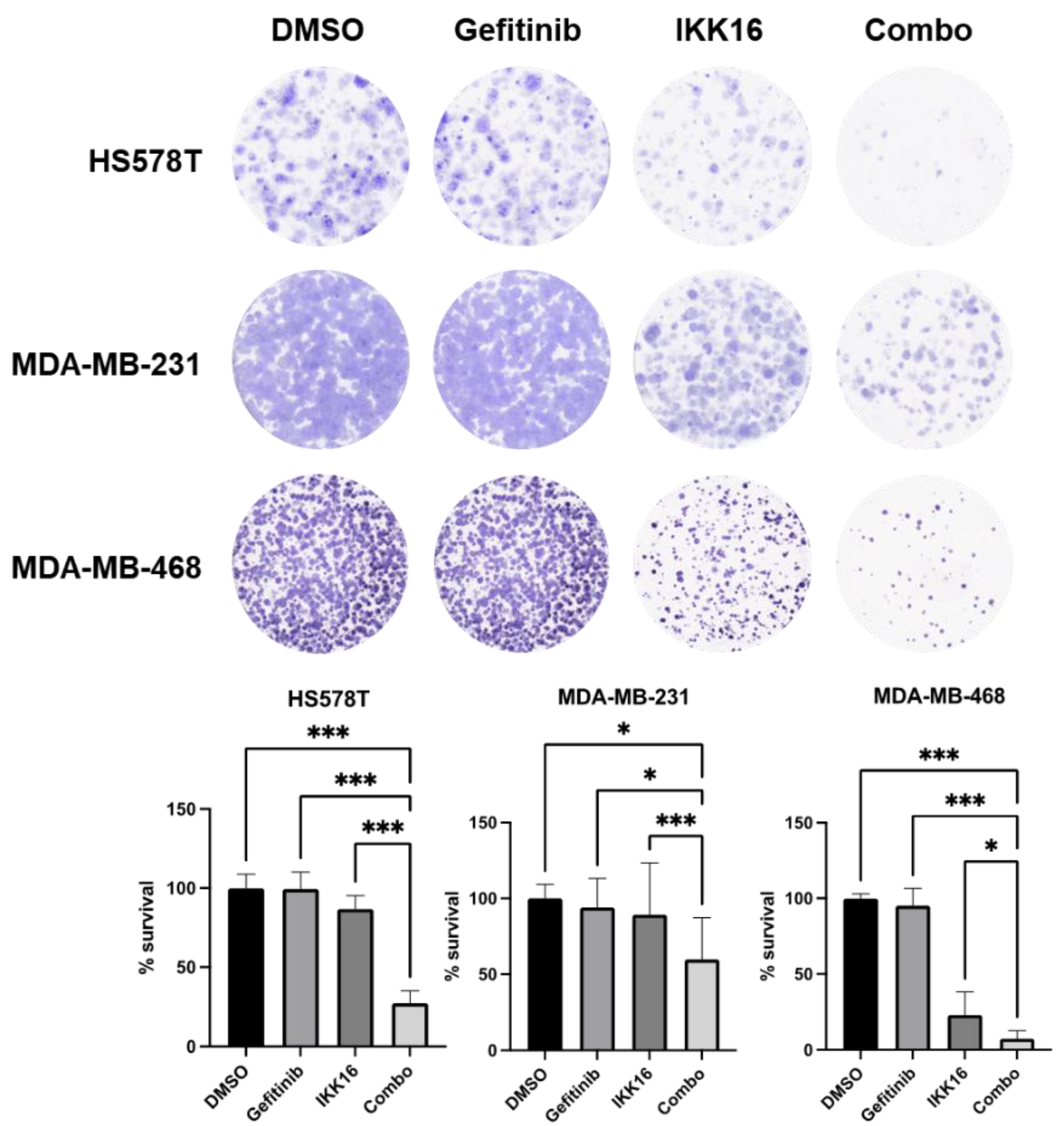
3.2. Inhibition of Long-Term Survival of TNBC Cells by the Gefitinib+IKK16 Treatment
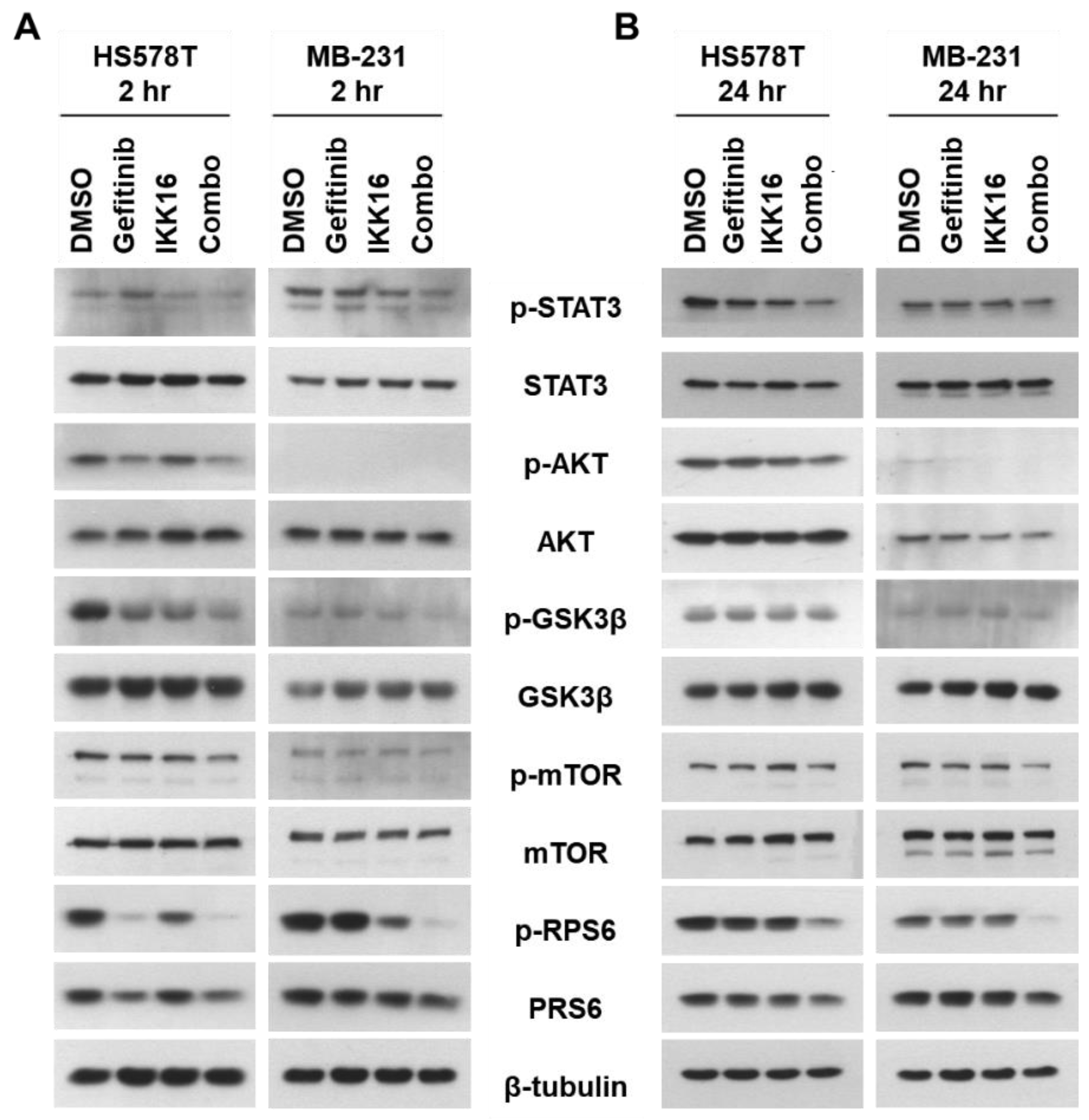
3.3. Downregulation of p-STAT3, p-AKT, p-mTOR, p-GSK3β, p-RPS6 in TNBC Cells by the Gefitinib+IKK16 Treatment
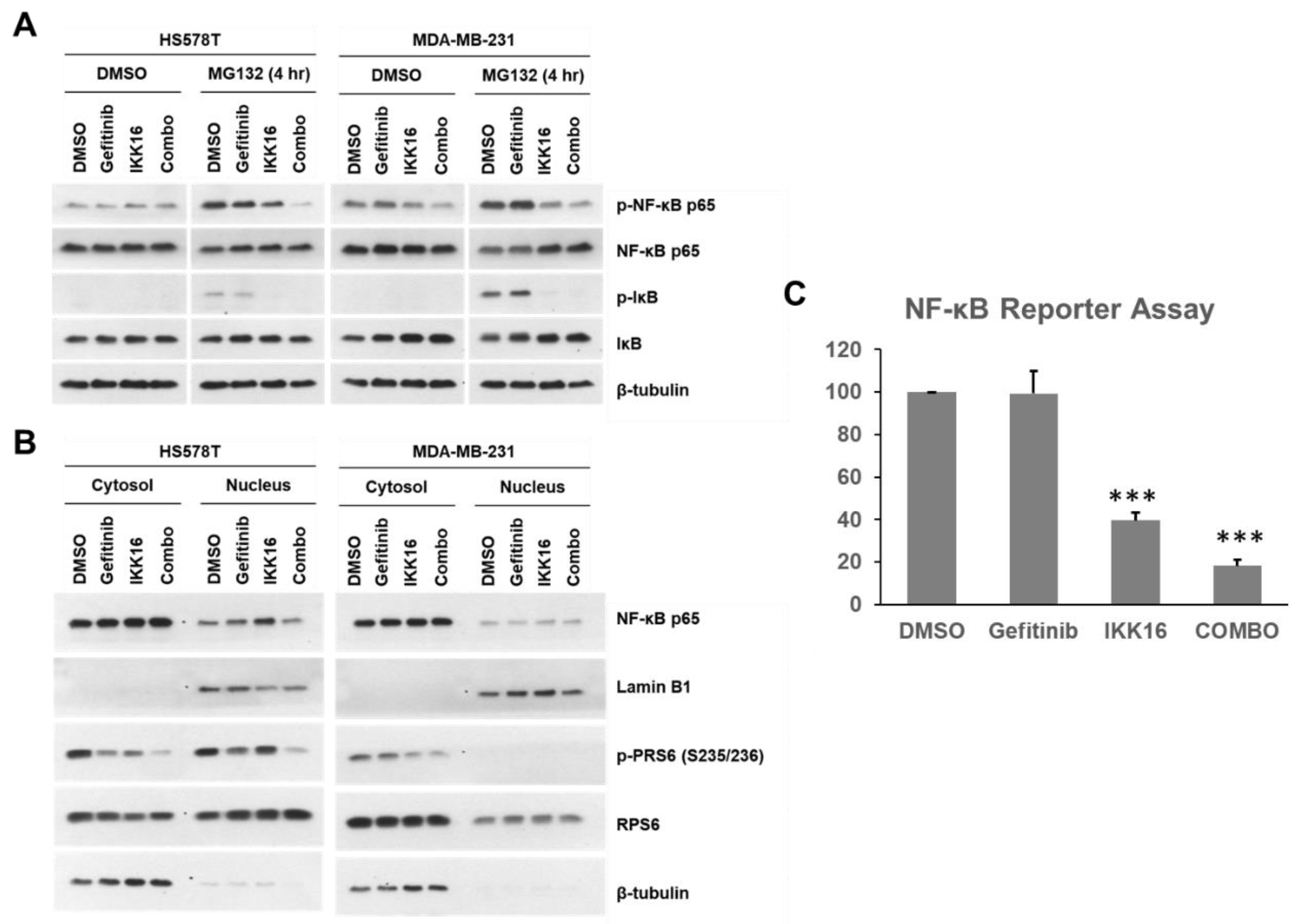
3.4. Regulation of NF-κB by the Gefitinib+IKK16 Treatment in TNBC Cells
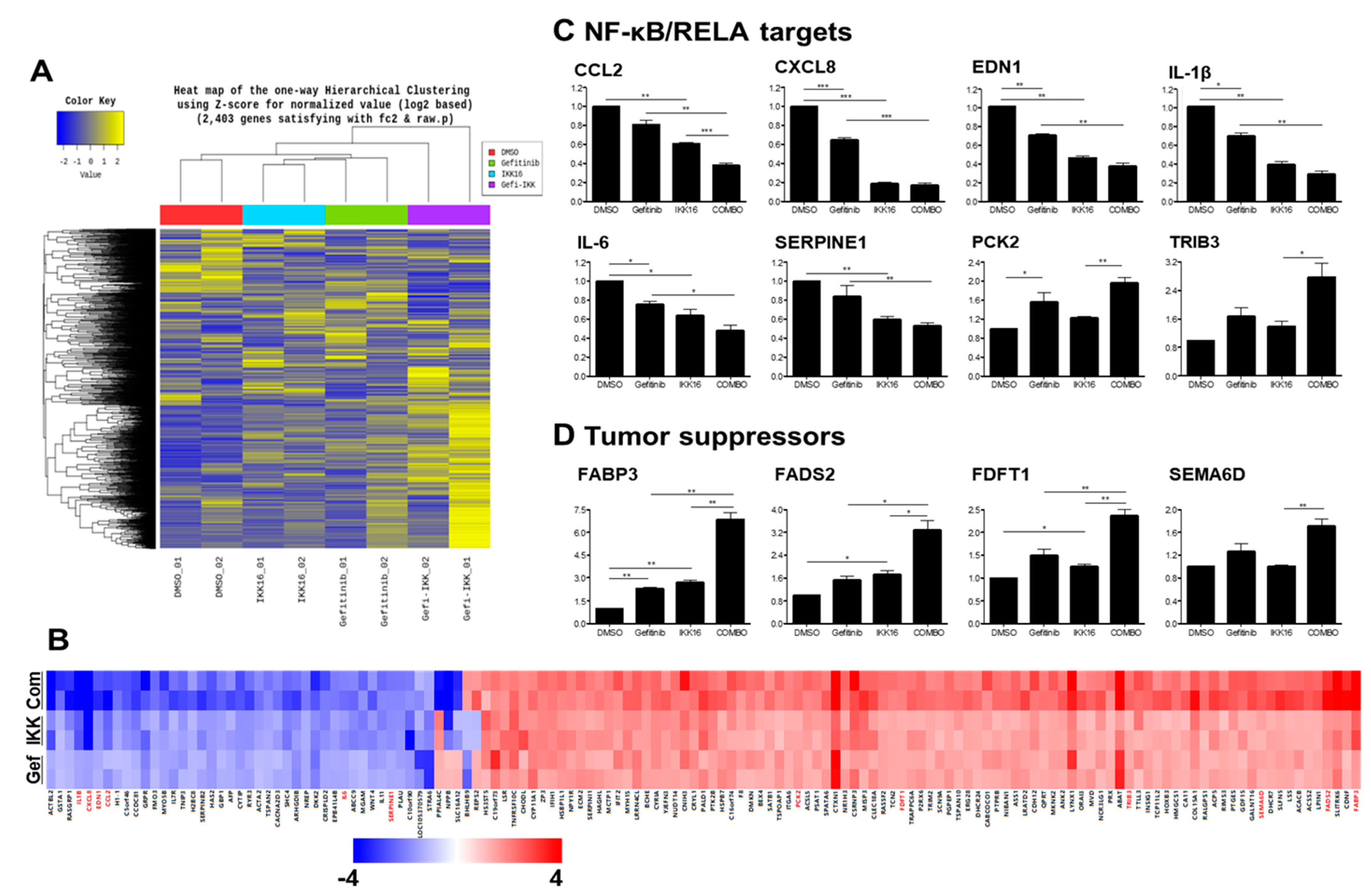
3.5. Transcriptomic Regulation by the Gefitinib+IKK16 Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz, L.K.; Cryns, V.L.; Symmans, W.F.; Sneige, N. Triple Negative Breast Carcinoma and the Basal Phenotype: From Expression Profiling to Clinical Practice. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2007, 14, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, M.; Pambid, M.R.; Jayanthan, A.; Dorr, A.; Los, G.; Dunn, S.E. The Dawn of Targeted Therapies for Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC): A Snapshot of Investigational Drugs in Phase I and II Trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, K.; Hung, M.-C.; Yamaguchi, H. A Perspective on Anti-EGFR Therapies Targeting Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Brenton, J.D.; Carey, L.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Caldas, C. Molecular Classification and Molecular Forecasting of Breast Cancer: Ready for Clinical Application? J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7350–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtypes and Preclinical Models for Selection of Targeted Therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification and Use of Biomarkers in Treatment Strategies for Triple-negative Breast Cancer Subtypes. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Premera Blue Cross. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Inhibitors. 2020. Available online: https://www.premera.com/medicalpolicies/5.01.603.pdf (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Solassol, I.; Pinguet, F.; Quantin, X. FDA- and EMA-Approved Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Safety, Tolerability, Plasma Concentration Monitoring, and Management. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, W.-Q.; Zeng, L.-S.; Wang, L.-F.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Cheng, J.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Z.-W.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, S.-L.; Wang, X.-W.; et al. The Latest Battles Between EGFR Monoclonal Antibodies and Resistant Tumor Cells. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S. Olmutinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2016, 76, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Hong, M.H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Park, C.W.; Kim, S.-Y.; Yun, M.R.; Kang, H.N.; Pyo, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Koh, J.S.; et al. YH25448, an Irreversible EGFR-TKI with Potent Intracranial Activity in EGFR Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, clincanres.2906.2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. Properties of FDA-Approved Small Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors: A 2021 Update. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 165, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, K.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Cho, J.; Park, J.-S.; Seong, Y.-S. Potentiating Therapeutic Effects of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignacio, R.M.C.; Gibbs, C.R.; Lee, E.-S.; Son, D.-S. The TGFα-EGFR-Akt Signaling Axis Plays a Role in Enhancing Proinflammatory Chemokines in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 29286–29303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Wang, A.; Bae, I. Inhibition of Constitutively Activated Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT Pathway Enhances Antitumor Activity of Chemotherapeutic Agents in Breast Cancer Susceptibility Gene 1-defective Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Bae, E.J.; Oh, S.; Seong, Y.-S.; Bae, I. β-TrCP1 Degradation Is a Novel Action Mechanism of PI3K/MTOR Inhibitors in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrab, A.E.; Bamdad, M.; Kwiatkowski, F.; Bignon, Y.-J.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Aubel, C. Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibodies and EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors as Combination Therapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 5, 73618–73637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.W.; Hong, W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, A.; Seong, Y.; Bae, I. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT Pathway Potentiates Cytotoxicity of EGFR Kinase Inhibitors in Triple-negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.W.; You, K.; Bae, E.J.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S.; Bae, I. Dual Inhibition of EGFR and MET Induces Synthetic Lethality in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Ribosomal Protein S6. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueno, N.T.; Zhang, D. Targeting EGFR in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2011, 2, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Inhibition of RPTOR Overcomes Resistance to EGFR Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; He, Q.; Williams, K.P.; Scott, J.E. Identification of a Triple Drug Combination That Is Synergistically Cytotoxic for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Using a Novel Combination Discovery Approach. Slas. Discov. 2020, 25, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveras-Ferraros, C.; Vazquez-Martin, A.; López-Bonet, E.; Martín-Castillo, B.; Barco, S.D.; Brunet, J.; Menendez, J.A. Growth and Molecular Interactions of the Anti-EGFR Antibody Cetuximab and the DNA Cross-Linking Agent Cisplatin in Gefitinib-Resistant MDA-MB-468 Cells: New Prospects in the Treatment of Triple-Negative/Basal-like Breast Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartholomeusz, C.; Yamasaki, F.; Saso, H.; Kurisu, K.; Horto-bagyi, G.N.; Ueno, N.T. Gemcitabine Overcomes Erlotinib Resistance in EGFR-Overexpressing Cancer Cells through Downregulation of Akt. J. Cancer 2011, 2c, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferraro, D.A.; Gaborit, N.; Maron, R.; Cohen-Dvashi, H.; Porat, Z.; Pareja, F.; Lavi, S.; Lindzen, M.; Ben-Chetrit, N.; Sela, M.; et al. Inhibition of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Models by Combinations of Antibodies to EGFR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1815–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, K.S.; Yi, Y.W.; Cho, J.; Seong, Y.-S. Dual Inhibition of AKT and MEK Pathways Potentiates the Anti-Cancer Effect of Gefitinib in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, M.M.; Sung, B.; Yadav, V.R.; Kannappan, R.; Aggarwal, B.B. NF-ΚB Addiction and Its Role in Cancer: ‘One Size Does Not Fit All’. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1615–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karin, M. The IκB Kinase–a Bridge between Inflammation and Cancer. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Cao, Y.; Greten, F.R.; Li, Z.-W. NF-ΚB in Cancer: From Innocent Bystander to Major Culprit. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llona-Minguez, S.; Baiget, J.; Mackay, S.P. Small-Molecule Inhibitors of IκB Kinase (IKK) and IKK-Related Kinases. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2013, 2, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descargues, P.; Sil, A.K.; Karin, M. IKKα, a Critical Regulator of Epidermal Differentiation and a Suppressor of Skin Cancer. Embo. J. 2008, 27, 2639–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.-C.; Ju, T.-K.; Hung, M.-C.; Chen, C.-C. Phosphorylation of CBP by IKKα Promotes Cell Growth by Switching the Binding Preference of CBP from P53 to NF-ΚB. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De, S.; Dermawan, J.K.T.; Stark, G.R. EGF Receptor Uses SOS1 to Drive Constitutive Activation of NFκB in Cancer Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11721–11726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) Activates Nuclear Factor-ΚB through IκBα Kinase-Independent but EGF Receptor-Kinase Dependent Tyrosine 42 Phosphorylation of IκBα. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7324–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Häussler, U.; von Wichert, G.; Schmid, R.M.; Keller, F.; Schneider, G. Epidermal Growth Factor Activates Nuclear Factor-κB in Human Proximal Tubule Cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. 2005, 289, F808–F815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alberti, C.; Pinciroli, P.; Valeri, B.; Ferri, R.; Ditto, A.; Umezawa, K.; Sensi, M.; Canevari, S.; Tomassetti, A. Ligand-Dependent EGFR Activation Induces the Co-Expression of IL-6 and PAI-1 via the NFkB Pathway in Advanced-Stage Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4139–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Carpenter, G. Epidermal Growth Factor Activation of NF-ΚB Is Mediated through IκBα Degradation and Intracellular Free Calcium. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, A.; Deyama, Y.; Deyama, A.; Okitsu, M.; Yoshimura, Y.; Suzuki, K. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mediated Expression of NF-ΚB Transcription Factor in Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells Cultured under a Low-Calcium Environment. Life Sci. 1998, 62, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, H.; Biro, S.; Arima, N.; Kaieda, H.; Kihara, T.; Eto, H.; Miyata, M.; Tanaka, H. NF-ΚB Is Induced in the Nuclei of Cultured Rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells by Stimulation of Various Growth Factors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 224, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, D.K.; Cruz, A.P.; Gansberger, E.; Pardee, A.B. Epidermal Growth Factor-Induced Nuclear Factor ΚB Activation: A Major Pathway of Cell-Cycle Progression in Estrogen-Receptor Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8542–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, S.; Mandal, G.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Purohit, S.; Payne, K.K.; Anadon, C.; Gupta, A.; Swanson, P.; Yu, X.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; et al. Exosomes Produced by Mesenchymal Stem Cells Drive Differentiation of Myeloid Cells into Immunosuppressive M2-Polarized Macrophages in Breast Cancer. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 3447–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardbower, D.M.; Singh, K.; Asim, M.; Verriere, T.G.; Olivares-Villagómez, D.; Barry, D.P.; Allaman, M.M.; Washington, M.K.; Peek, R.M.; Piazuelo, M.B.; et al. EGFR Regulates Macrophage Activation and Function in Bacterial Infection. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3296–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shostak, K.; Zhang, X.; Hubert, P.; Göktuna, S.I.; Jiang, Z.; Klevernic, I.; Hildebrand, J.; Roncarati, P.; Hennuy, B.; Ladang, A.; et al. NF-ΚB-Induced KIAA1199 Promotes Survival through EGFR Signalling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nottingham, L.K.; Yan, C.H.; Yang, X.; Si, H.; Coupar, J.; Bian, Y.; Cheng, T.-F.; Allen, C.; Arun, P.; Gius, D.; et al. Aberrant IKKα and IKKβ Cooperatively Activate NF-ΚB and Induce EGFR/AP1 Signaling to Promote Survival and Migration of Head and Neck Cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kung, C.-P.; Raab-Traub, N. Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 Modulates Distinctive NF-ΚB Pathways through C-Terminus-Activating Region 1 To Regulate Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6605–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Z.; Passaniti, A.; Lapidus, R.G.; Liu, X.; Cullen, K.J.; Dan, H.C. A Positive Feedback Loop Involving EGFR/Akt/MTORC1 and IKK/NF-KB Regulates Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Proliferation. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 31892–31906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makhov, P.; Naito, S.; Haifler, M.; Kutikov, A.; Boumber, Y.; Uzzo, R.G.; Kolenko, V.M. The Convergent Roles of NF-ΚB and ER Stress in Sunitinib-Mediated Expression of pro-Tumorigenic Cytokines and Refractory Phenotype in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Day, E.K.; Sosale, N.G.; Xiao, A.; Zhong, Q.; Purow, B.; Lazzara, M.J. Glioblastoma Cell Resistance to EGFR and MET Inhibition Can Be Overcome via Blockade of FGFR-SPRY2 Bypass Signaling. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3383–3396.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bivona, T.G.; Hieronymus, H.; Parker, J.; Chang, K.; Taron, M.; Rosell, R.; Moonsamy, P.; Dahlman, K.; Miller, V.A.; Costa, C.; et al. FAS and NF-ΚB Signalling Modulate Dependence of Lung Cancers on Mutant EGFR. Nature 2011, 471, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, R.; Li, Y.; Gao, M. Shikonin Causes Cell-Cycle Arrest and Induces Apoptosis by Regulating the EGFR–NF-ΚB Signalling Pathway in Human Epidermoid Carcinoma A431 Cells. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, e00189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvani, E.; Sun, J.; Leon, L.G.; Sciarrillo, R.; Narayan, R.S.; Sjin, R.T.T.; Lee, K.; Ohashi, K.; Heideman, D.A.M.; Alfieri, R.R.; et al. NF-ΚB Drives Acquired Resistance to a Novel Mutant-Selective EGFR Inhibitor. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42717–42732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraki, M.; Maeda, T.; Mehrotra, N.; Jin, C.; Alam, M.; Bouillez, A.; Hata, T.; Tagde, A.; Keating, A.; Kharbanda, S.; et al. Targeting MUC1-C Suppresses BCL2A1 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, R.; Raina, D.; Joshi, M.D.; Kawano, T.; Ren, J.; Kharbanda, S.; Kufe, D. MUC1-C Oncoprotein Functions as a Direct Activator of the Nuclear Factor-ΚB P65 Transcription Factor. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7013–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kufe, D.W. MUC1-C Oncoprotein as a Target in Breast Cancer: Activation of Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Approaches. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siroy, A.; Abdul-Karim, F.W.; Miedler, J.; Fong, N.; Fu, P.; Gilmore, H.; Baar, J. MUC1 Is Expressed at High Frequency in Early-Stage Basal-like Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wojtalla, A.; Fischer, B.; Kotelevets, N.; Mauri, F.A.; Sobek, J.; Rehrauer, H.; Wotzkow, C.; Tschan, M.P.; Seckl, M.J.; Zangemeister-Wittke, U.; et al. Targeting the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase P110-α Isoform Impairs Cell Proliferation, Survival, and Tumor Growth in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.I.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, K.; Hong, D.; Lim, H.; Cho, K.; Jung, N.; Yi, Y.W. Application of a Non-Hazardous Vital Dye for Cell Counting with Automated Cell Counters. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 492, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duong, H.-Q.; You, K.; Oh, S.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Silencing of NRF2 Reduces the Expression of ALDH1A1 and ALDH3A1 and Sensitizes to 5-FU in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2017, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Brown, M.M.; Bae, I. Targeting Mutant P53 by a SIRT1 Activator YK-3-237 Inhibits the Proliferation of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.-Y.; Lim, S.-L.; Jang, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Um, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Ahn, K.S.; Lee, S.-G. Embelin Induces Apoptosis in Human Glioma Cells Through Inactivating NF-ΚB. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 121, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D. Combination of SF1126 and Gefitinib Induces Apoptosis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells through the PI3K/AKT–MTOR Pathway. Anti-Cancer Drug 2015, 26, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecchin, D.; Moore, C.; Michailidis, F.; Horswell, S.; Rana, S.; Howell, M.; Downward, J. Combined Targeting of G Protein-coupled Receptor and EGF Receptor Signaling Overcomes Resistance to PI3K Pathway Inhibitors in PTEN-null Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Embo. Mol. Med. 2020, 12, e11987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Yacoub, R.; Taliaferro-Smith, L.D.; Sun, S.-Y.; Graham, T.R.; Dolan, R.; Lobo, C.; Tighiouart, M.; Yang, L.; Adams, A.; et al. Combinatorial Effects of Lapatinib and Rapamycin in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madden, J.M.; Mueller, K.L.; Bollig-Fischer, A.; Stemmer, P.; Mattingly, R.R.; Boerner, J.L. Abrogating Phosphorylation of EIF4B Is Required for EGFR and MTOR Inhibitor Synergy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; McLaughlin, R.P.; van der Noord, V.; Foekens, J.A.; Martens, J.W.M.; van Westen, G.; Zhang, Y.; van de Water, B. Multi-Targeted Kinase Inhibition Alleviates MTOR Inhibitor Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 178, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guerrab, A.E.; Bamdad, M.; Bignon, Y.-J.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Aubel, C. Co-Targeting EGFR and MTOR with Gefitinib and Everolimus in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep-UK 2020, 10, 6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, J.J.; Castel, P.; Radosevic-Robin, N.; Elkabets, M.; Auricchio, N.; Aceto, N.; Weitsman, G.; Barber, P.; Vojnovic, B.; Ellis, H.; et al. Antagonism of EGFR and HER3 Enhances the Response to Inhibitors of the PI3K-Akt Pathway in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Signal 2014, 7, ra29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cool, B.; Zinker, B.; Chiou, W.; Kifle, L.; Cao, N.; Perham, M.; Dickinson, R.; Adler, A.; Gagne, G.; Iyengar, R.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Small Molecule AMPK Activator That Treats Key Components of Type 2 Diabetes and the Metabolic Syndrome. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimshaw, K.M.; Hunter, L.-J.K.; Yap, T.A.; Heaton, S.P.; Walton, M.I.; Woodhead, S.J.; Fazal, L.; Reule, M.; Davies, T.G.; Seavers, L.C.; et al. AT7867 Is a Potent and Oral Inhibitor of AKT and P70 S6 Kinase That Induces Pharmacodynamic Changes and Inhibits Human Tumor Xenograft Growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Ikezoe, T.; Nishioka, C.; Tasaka, T.; Taniguchi, A.; Kuwayama, Y.; Komatsu, N.; Bandobashi, K.; Togitani, K.; Koeffler, H.P.; et al. AZD1152, a Novel and Selective Aurora B Kinase Inhibitor, Induces Growth Arrest, Apoptosis, and Sensitization for Tubulin Depolymerizing Agent or Topoisomerase II Inhibitor in Human Acute Leukemia Cells in Vitro and in Vivo. Blood 2007, 110, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derenzini, E.; Lemoine, M.; Buglio, D.; Katayama, H.; Ji, Y.; Davis, R.E.; Sen, S.; Younes, A. The JAK Inhibitor AZD1480 Regulates Proliferation and Immunity in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2011, 1, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boschelli, D.H.; Ye, F.; Wang, Y.D.; Dutia, M.; Johnson, S.L.; Wu, B.; Miller, K.; Powell, D.W.; Yaczko, D.; Young, M.; et al. Optimization of 4-Phenylamino-3-Quinolinecarbonitriles as Potent Inhibitors of Src Kinase Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 3965–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golas, J.M.; Arndt, K.; Etienne, C.; Lucas, J.; Nardin, D.; Gibbons, J.; Frost, P.; Ye, F.; Boschelli, D.H.; Boschelli, F. SKI-606, a 4-Anilino-3-Quinolinecarbonitrile Dual Inhibitor of Src and Abl Kinases, Is a Potent Antiproliferative Agent against Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Cells in Culture and Causes Regression of K562 Xenografts in Nude Mice. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.-L.; Lee, M.C.; Tan, K.O.; Yang, L.-K.; Lee, A.S.Y.; Flotow, H.; Fu, N.Y.; Butler, M.S.; Soejarto, D.D.; Buss, A.D.; et al. Identification of Chelerythrine as an Inhibitor of BclXL Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 20453–20456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carpinelli, P.; Ceruti, R.; Giorgini, M.L.; Cappella, P.; Gianellini, L.; Croci, V.; Degrassi, A.; Texido, G.; Rocchetti, M.; Vianello, P.; et al. PHA-739358, a Potent Inhibitor of Aurora Kinases with a Selective Target Inhibition Profile Relevant to Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 3158–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graff, J.R.; McNulty, A.M.; Hanna, K.R.; Konicek, B.W.; Lynch, R.L.; Bailey, S.N.; Banks, C.; Capen, A.; Goode, R.; Lewis, J.E.; et al. The Protein Kinase Cβ–Selective Inhibitor, Enzastaurin (LY317615.HCl), Suppresses Signaling through the AKT Pathway, Induces Apoptosis, and Suppresses Growth of Human Colon Cancer and Glioblastoma Xenografts. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7462–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waelchli, R.; Bollbuck, B.; Bruns, C.; Buhl, T.; Eder, J.; Feifel, R.; Hersperger, R.; Janser, P.; Revesz, L.; Zerwes, H.-G.; et al. Design and Preparation of 2-Benzamido-Pyrimidines as Inhibitors of IKK. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Griffith, D.J.; Druker, B.J.; Wait, C.L.; Ott, K.A.; Zigler, A.J. Inhibition of C-Kit Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activity by STI 571, a Selective Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. Blood 2000, 96, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mader, M.; de Dios, A.; Shih, C.; Bonjouklian, R.; Li, T.; White, W.; de Uralde, B.L.; Sánchez-Martinez, C.; del Prado, M.; Jaramillo, C.; et al. Imidazolyl Benzimidazoles and Imidazo [4,5-b]Pyridines as Potent P38α MAP Kinase Inhibitors with Excellent in Vivo Antiinflammatory Properties. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, J.J.J.; Golding, B.T.; Griffin, R.J.; Hardcastle, I.R.; Richardson, C.; Rigoreau, L.; Smith, G.C.M. Identification of a Highly Potent and Selective DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase (DNA-PK) Inhibitor (NU7441) by Screening of Chromenone Libraries. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 6083–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.E.; Parker, P.J.; Nixon, J.S. Isoenzyme Specificity of Bisindolylmaleimides, Selective Inhibitors of Protein Kinase C. Biochem. J. 1993, 294, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.D.; Bridges, A.J.; Dudley, D.T.; Saltiel, A.R.; Fergus, J.H.; Flamme, C.M.; Delaney, A.M.; Kaufman, M.; LePage, S.; Leopold, W.R.; et al. The Discovery of the Benzhydroxamate MEK Inhibitors CI-1040 and PD 0325901. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6501–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, L.R.; Alton, G.R.; Richter, D.T.; Kath, J.C.; Lingardo, L.; Chapman, J.; Hwang, C.; Alessi, D.R. Characterization of PF-4708671, a Novel and Highly Specific Inhibitor of P70 Ribosomal S6 Kinase (S6K1). Biochem. J. 2010, 431, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meijer, L.; Borgne, A.; Mulner, O.; Chong, J.P.J.; Blow, J.J.; Inagaki, N.; Inagaki, M.; Delcros, J.; Moulinoux, J. Biochemical and Cellular Effects of Roscovitine, a Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinases Cdc2, Cdk2 and Cdk5. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 243, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, A.; Stockett, D.E.; Walker, D.; Arkin, M.R.; Hoch, U.; Fox, J.A.; Hawtin, R.E. SNS-032 Is a Potent and Selective CDK 2, 7 and 9 Inhibitor That Drives Target Modulation in Patient Samples. Cancer Chemoth. Pharm. 2009, 64, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.; Zhu, J.; Johnson, M.D.; Chen, P.; Kornmann, J.; Chen, E.; Blasina, A.; Register, J.; Anderes, K.; Rogers, C.; et al. Structure-Based Design of (5-Arylamino-2 H -Pyrazol-3-Yl)-Biphenyl-2‘,4‘-Diols as Novel and Potent Human CHK1 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5253–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolin, P.L.; Callahan, J.F.; Bolognese, B.J.; Li, Y.H.; Carlson, K.; Davis, T.G.; Mellor, G.W.; Evans, C.; Roshak, A.K. Attenuation of Murine Collagen-Induced Arthritis by a Novel, Potent, Selective Small Molecule Inhibitor of IκB Kinase 2, TPCA-1 (2-[(Aminocarbonyl)amino]-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-thiophenecarboxamide), Occurs via Reduction of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Antigen-Induced T Cell Proliferation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cataldi, M.; Shah, N.R.; Felt, S.A.; Grdzelishvili, V.Z. Breaking Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cells to an Attenuated Vesicular Stomatitis Virus through a Novel Activity of IKK Inhibitor TPCA-1. Virology 2015, 485, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uehata, M.; Ishizaki, T.; Satoh, H.; Ono, T.; Kawahara, T.; Morishita, T.; Tamakawa, H.; Yamagami, K.; Inui, J.; Maekawa, M.; et al. Calcium Sensitization of Smooth Muscle Mediated by a Rho-Associated Protein Kinase in Hypertension. Nature 1997, 389, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, T.; Uehata, M.; Tamechika, I.; Keel, J.; Nonomura, K.; Maekawa, M.; Narumiya, S. Pharmacological Properties of Y-27632, a Specific Inhibitor of Rho-Associated Kinases. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 976–983. [Google Scholar]
- Ditchfield, C.; Johnson, V.L.; Tighe, A.; Ellston, R.; Haworth, C.; Johnson, T.; Mortlock, A.; Keen, N.; Taylor, S.S. Aurora B Couples Chromosome Alignment with Anaphase by Targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to Kinetochores. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Overstreet, A.-M.; Chen, M.-S.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.-J.; Ho, P.-C.; Smith, M.; Wang, S.-C. Combined Inhibition of EGFR and C-ABL Suppresses the Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth through Inhibition of HOTAIR. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11150–11161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburger, A.; Salmon, S. Primary Bioassay of Human Tumor Stem Cells. Science 1977, 197, 461–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, S.E.; Hamburger, A.W.; Soehnlen, B.; Durie, B.G.M.; Alberts, D.S.; Moon, T.E. Quantitation of Differential Sensitivity of Human-Tumor Stem Cells to Anticancer Drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 1978, 298, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, P.R.; Drewinko, B. Comparison of in Vitro Methods to Determine Drug-Induced Cell Lethality. Cancer Res. 1976, 36, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawada, K.; Yonei, T.; Ueoka, H.; Kiura, K.; Tabata, M.; Takigawa, N.; Harada, M.; Tanimoto, M. Comparison of Chemosensitivity Tests: Clonogenic Assay versus MTT Assay. Acta Med. Okayama 2002, 56, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, I.H.W.; Yeap, Y.Y.C.; Ong, L.S.R.; Jans, D.A.; Bogoyevitch, M.A. Oxidative Stress Impairs Multiple Regulatory Events to Drive Persistent Cytokine-Stimulated STAT3 Phosphorylation. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahn, Y.-I.; Saeidi, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Park, S.-Y.; Song, N.-Y.; Zheng, J.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, H.-B.; Han, W.; Noh, D.-Y.; et al. STAT3 Stabilizes IKKα Protein through Direct Interaction in Transformed and Cancerous Human Breast Epithelial Cells. Cancers 2020, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.W.; You, K.S.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, S.-G.; Seong, Y.-S. Ribosomal Protein S6: A Potental Therapeutic Target against Cancer? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-J.; Yeh, M.-H.; Yu, M.-C.; Wei, Y.-L.; Chen, W.-S.; Chen, J.-Y.; Shih, C.-Y.; Tu, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Hsia, T.-C.; et al. Lapatinib–Induced NF-KappaB Activation Sensitizes Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Proteasome Inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsubuki, S.; Saito, Y.; Tomioka, M.; Ito, H.; Kawashima, S. Differential Inhibition of Calpain and Proteasome Activities by Peptidyl Aldehydes of Di-Leucine and Tri-Leucine. J. Biochem. 1996, 119, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, D.E.; Ihekwaba, A.E.C.; Elliott, M.; Johnson, J.R.; Gibney, C.A.; Foreman, B.E.; Nelson, G.; See, V.; Horton, C.A.; Spiller, D.G.; et al. Oscillations in NF-ΚB Signaling Control the Dynamics of Gene Expression. Science 2004, 306, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, L.M.; Young, R.; Quick, L.; Riquelme, D.N.; Oliveira, A.M.; May, M.J.; Chou, M.M. Atypical Mechanism of NF-ΚB Activation by TRE17/Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 6 (USP6) Oncogene and Its Requirement in Tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3525–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herwig, R.; Hardt, C.; Lienhard, M.; Kamburov, A. Analyzing and Interpreting Genome Data at the Network Level with ConsensusPathDB. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1889–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.B.; Yao, M.; Brummer, G.; Acevedo, D.; Alhakamy, N.; Berkland, C.; Cheng, N. Targeted Gene Silencing of CCL2 Inhibits Triple Negative Breast Cancer Progression by Blocking Cancer Stem Cell Renewal and M2 Macrophage Recruitment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 49349–49367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, A.; Tian, Y.; Wu, J.D.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Wu, K. The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Pathways in Cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 31, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, N.-H.; Nair, V.S.; Reddy, D.N.S.; Mudvari, P.; Ohshiro, K.; Ghanta, K.S.; Pakala, S.B.; Li, D.-Q.; Costa, L.; Lipton, A.; et al. Lactoferrin–Endothelin-1 Axis Contributes to the Development and Invasiveness of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Phenotypes. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7259–7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, M.; Han, J.; Nam, S.J.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S. Elevated IL-1β Expression Induces Invasiveness of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells and Is Suppressed by Zerumbone. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2016, 258, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, Z.C.; Poage, G.M.; den Hollander, P.; Tsimelzon, A.; Hill, J.; Panupinthu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Mazumdar, A.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Mills, G.B.; et al. Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Relies upon Coordinate Autocrine Expression of the Proinflammatory Cytokines IL-6 and IL-8. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3470–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Lei, L.; Jing, D. Knockdown of SERPINE1 Reverses Resistance of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer to Paclitaxel via Suppression of VEGFA. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Yuan, C.; Shi, J.; Xiong, W.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Yang, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, X. Restoring the Epigenetically Silenced PCK2 Suppresses Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression and Increases Sensitivity to Sunitinib by Promoting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Theranostics 2020, 10, 11444–11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zhong, L.; Yu, L.; Xiong, L.; Dan, W.; Li, J.; Ye, J.; Chu, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, B. TRIB3 Destabilizes Tumor Suppressor PPARα Expression through Ubiquitin-Mediated Proteasome Degradation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, A.W.; Veerkamp, J.H. Members of the Fatty Acid-binding Protein Family Inhibit Cell-free Protein Synthesis. Febs. Lett. 1998, 437, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.X.; Shen, Y.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Sun, W.; Miao, L.P.; Zhou, L.J.; Liu, H.L.; Yang, R.; Kong, X.Q.; Cao, K.J.; et al. Overexpression of FABP3 Promotes Apoptosis through Inducing Mitochondrial Impairment in Embryonic Cancer Cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2012, 113, 3701–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, N.T.; Lee, C.H. Roles of Farnesyl-Diphosphate Farnesyltransferase 1 in Tumour and Tumour Microenvironments. Cells 2020, 9, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.J.; Kothapalli, K.S.D.; Lawrence, P.; Brenna, J.T. FADS2 Function Loss at the Cancer Hotspot 11q13 Locus Diverts Lipid Signaling Precursor Synthesis to Unusual Eicosanoid Fatty Acids. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, Y.-H.; Hsu, S.-H.; Hou, Y.-C.; Chu, P.-Y.; Su, Y.-Y.; Shan, Y.-S.; Hung, W.-C.; Chen, L.-T. Semaphorin 6C Suppresses Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells via Inhibition of the AKT/GSK3/β-Catenin/Cyclin D1 Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.J.; Yi, Y.W.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, Y.B.; Seong, Y.S.; Bae, I. BRCA1 Negatively Regulates IGF-1 Expression through an Estrogen-Responsive Element-like Site. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.; Yi, Y.W.; Kang, H.J.; Zhang, L.; Kim, H.J.; Kong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Kong, H.-S.; Grindrod, S.; et al. Novel Carbazole Inhibits Phospho-STAT3 through Induction of Protein–Tyrosine Phosphatase PTPN6. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6342–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.W.; Park, J.-S.; Kwak, S.-J.; Seong, Y.-S. Co-Treatment with BEZ235 Enhances Sensitivity of BRCA1-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Olaparib. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 3829–3838. [Google Scholar]
- DeFazio, A.; Chiew, Y.E.; McEvoy, M.; Watts, C.K.; Sutherland, R.L. Antisense Estrogen Receptor RNA Expression Increases Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Expression in Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Growth Differ. Mol. Biol. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1997, 8, 903–911. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.S.L.; deFazio, A.; Ormandy, C.J.; Sutherland, R.L. Inverse Regulation of Oestrogen Receptor and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Expression in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Phorbol Ester. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1996, 58, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.H.; Lu, Y.L.; Deng, F.; Ge, X.M.; Liu, S.; Tang, P.-H. EGFR Antisense RNA Blocks Expression of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Partially Reverse the Malignant Phenotype of Human Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Cell Res. 1998, 8, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newby, J.C.; Johnston, S.R.; Smith, I.E.; Dowsett, M. Expression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and C-ErbB2 during the Development of Tamoxifen Resistance in Human Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Ito, T.; Azuma, S.; Ito, E.; Honma, R.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Kawamura, M.; Imai, J.; Watanabe, S.; et al. Constitutive Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB Is Preferentially Involved in the Proliferation of Basal-like Subtype Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1668–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Ito, T.; Shimizu, T.; Ishida, T.; Semba, K.; Watanabe, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Inoue, J. Epigenetic Alteration of the NF-κB-inducing Kinase (NIK) Gene Is Involved in Enhanced NIK Expression in Basal-like Breast Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2391–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakely, C.M.; Pazarentzos, E.; Olivas, V.; Asthana, S.; Yan, J.J.; Tan, I.; Hrustanovic, G.; Chan, E.; Lin, L.; Neel, D.S.; et al. NF-ΚB-Activating Complex Engaged in Response to EGFR Oncogene Inhibition Drives Tumor Cell Survival and Residual Disease in Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buss, H.; Dörrie, A.; Schmitz, M.L.; Hoffmann, E.; Resch, K.; Kracht, M. Constitutive and Interleukin-1-Inducible Phosphorylation of P65 NF-ΚB at Serine 536 Is Mediated by Multiple Protein Kinases Including IκB Kinase (IKK)-α, IKKβ, IKKϵ, TRAF Family Member-Associated (TANK)-Binding Kinase 1 (TBK1), and an Unknown Kinase and Couples P65 to TATA-Binding Protein-Associated Factor II31-Mediated Interleukin-8 Transcription*. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 55633–55643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, T.; Bebien, M.; Liu, G.Y.; Nizet, V.; Karin, M. IKKα Limits Macrophage NF-ΚB Activation and Contributes to the Resolution of Inflammation. Nature 2005, 434, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, H.; Chiba, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Sugita, T.; Toriumi, W. IκB Kinases Phosphorylate NF-ΚB P65 Subunit on Serine 536 in the Transactivation Domain*. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30353–30356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sizemore, N.; Lerner, N.; Dombrowski, N.; Sakurai, H.; Stark, G.R. Distinct Roles of the IκB Kinase α and β Subunits in Liberating Nuclear Factor ΚB (NF-ΚB) from IκB and in Phosphorylating the P65 Subunit of NF-ΚB*. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3863–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattioli, I.; Sebald, A.; Bucher, C.; Charles, R.-P.; Nakano, H.; Doi, T.; Kracht, M.; Schmitz, M.L. Transient and Selective NF-ΚB P65 Serine 536 Phosphorylation Induced by T Cell Costimulation Is Mediated by IκB Kinase β and Controls the Kinetics of P65 Nuclear Import. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6336–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Tong, X.; Ye, X. Casein Kinase 1γ1 Inhibits the RIG-I/TLR Signaling Pathway through Phosphorylating P65 and Promoting Its Degradation. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sizemore, N.; Leung, S.; Stark, G.R. Activation of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase in Response to Interleukin-1 Leads to Phosphorylation and Activation of the NF-ΚB P65/RelA Subunit. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 4798–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madrid, L.V.; Wang, C.-Y.; Guttridge, D.C.; Schottelius, A.J.G.; Baldwin, A.S.; Mayo, M.W. Akt Suppresses Apoptosis by Stimulating the Transactivation Potential of the RelA/P65 Subunit of NF-ΚB. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 1626–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, L.V.; Mayo, M.W.; Reuther, J.Y.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt Stimulates the Transactivation Potential of the RelA/P65 Subunit of NF-ΚB through Utilization of the IκB Kinase and Activation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase P38*. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18934–18940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haller, D.; Russo, M.P.; Sartor, R.B.; Jobin, C. IKKβ and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Participate in Non-Pathogenic Gram-Negative Enteric Bacteria-Induced RelA Phosphorylation and NF-ΚB Activation in Both Primary and Intestinal Epithelial Cell Lines*. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 38168–38178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, A.; Das, K.; Lerner, N.; Sathe, S.; Cicek, M.; Casey, G.; Sizemore, N. The AKT/IκB Kinase Pathway Promotes Angiogenic/Metastatic Gene Expression in Colorectal Cancer by Activating Nuclear Factor-ΚB and β-Catenin. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, D.; Ueno, L.; Vogt, P.K. Akt-mediated Regulation of NFκB and the Essentialness of NFκB for the Oncogenicity of PI3K and Akt. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 2863–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dan, H.C.; Cooper, M.J.; Cogswell, P.C.; Duncan, J.A.; Ting, J.P.-Y.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt-Dependent Regulation of NF-ΚB Is Controlled by MTOR and Raptor in Association with IKK. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dan, H.C.; Ebbs, A.; Pasparakis, M.; Dyke, T.V.; Basseres, D.S.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt-Dependent Activation of MTORC1 Complex Involves Phosphorylation of MTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin) by IκB Kinase α (IKKα). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25227–25240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dan, H.C.; Antonia, R.J.; Baldwin, A.S. PI3K/Akt Promotes Feed Forward MTORC2 Activation through IKKα. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21064–21075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Shen, X.; Tang, P.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Q.; Li, M.; Xia, R.; Yang, X.; Feng, C.; et al. IL-36β Promotes CD8+ T Cell Activation and Antitumor Immune Responses by Activating MTORC1. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.-F.; Kuo, H.-P.; Chen, C.-T.; Hsu, J.-M.; Chou, C.-K.; Wei, Y.; Sun, H.-L.; Li, L.-Y.; Ping, B.; Huang, W.-C.; et al. IKKβ Suppression of TSC1 Links Inflammation and Tumor Angiogenesis via the MTOR Pathway. Cell 2007, 130, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dan, H.C.; Adli, M.; Baldwin, A.S. Regulation of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Activity in PTEN-Inactive Prostate Cancer Cells by IκB Kinase α. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6263–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, H.C.; Baldwin, A.S. Differential Involvement of IκB Kinases α and β in Cytokine- and Insulin-Induced Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Activation Determined by Akt. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 7582–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamberti, C.; Lin, K.-M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Verma, U.; Verma, I.M.; Byers, S.; Gaynor, R.B. Regulation of β-Catenin Function by the IκB Kinases*. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42276–42286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albanese, C.; Wu, K.; D’Amico, M.; Jarrett, C.; Joyce, D.; Hughes, J.; Hulit, J.; Sakamaki, T.; Fu, M.; Ben-Ze’ev, A.; et al. IKKα Regulates Mitogenic Signaling through Transcriptional Induction of Cyclin D1 via Tcf. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, F.; Sorrentino, C.; Ucar, D.A.; Peng, Y.; Matossian, M.; Wyczechowska, D.; Crabtree, J.; Zabaleta, J.; Morello, S.; Valle, L.D.; et al. Notch Signaling Regulates Mitochondrial Metabolism and NF-ΚB Activity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via IKKα-Dependent Non-Canonical Pathways. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PKI | Other Names | Known Targets (IC50 or EC50 Value in nM) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-769662 | AMPK (800) | [69] | |
| AT7867 | AKT2 (17), PKA (20), AKT1 (32), AKT3 (47), p70S6K (85) | [70] | |
| AZD1152 | Barasertib, AZD2811 | AURKB (0.37) | [71] |
| AZD1480 | JAK2 (0.26) | [72] | |
| Bosutinib | Bosulif®, SKI-606, DB8 | ABL1 (1), SRC (1.2) | [73,74] |
| Chelerythrine | - | PKC (660) | [75] |
| Danusertib | PHA-739358 | AURKA (13), ABL1 (25), RET (31), TRKA (31), FGFR1 (47), AURKC (61), AURKB (79) | [76] |
| Enzastaurin | LY317615 | PKCβ (6), PKCα (39), PKCγ (83), PKCε (110) | [77] |
| IKK 16 | IKK Inhibitor VII | IKKβ/IKK2 (40), IKK complex (70), IKKα/IKK1 (200) | [78] |
| Imatinib | Gleevec®, STI571, CGP057148B | PDGFR (100), KIT (100), v-ABL (600) | [79] |
| LY2228820 | Ralimetinib | P38α (7) | [80] |
| NU 7441 | KU-57788 | DNA-PK (14) | [81] |
| Ro-31-8220 | Bisindolylmaleimide IX | PKCα (5), PKCβ2 (14), PKCβ1 (24), PKCε (24), PKCγ (27) | [82] |
| PD-0325901 | Mirdametinib | MEK (0.33) | [83] |
| PF-4708671 | p70S6K1 (160) | [84] | |
| Roscovitine | Seliciclib, CYC202 | CDK5/P35 (160) | [85] |
| SNS-032 | BMS-387032 | CDK9/Cyclin T (4) | [86] |
| TCS 2312 | CHEK1 (60) | [87] | |
| TPCA-1 | GW683965 | IKK2 (17.9), JAK1 (43.78) | [88,89] |
| Y-27632 | ROCK1 (140; Ki); ROCK2 (300; Ki) | [90,91] | |
| ZM-447439 | AURKA (110), AURKB (130) | [92] |
| Gene Symbol | Description | Combo Effect | TF | Potential Roles in Cancer | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCL2 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 | ↓ | NF-κB/RelA [105] | CCL2 knockdown blocks the renewal of cancer stem cells, leading to the inhibition of the progression of TNBC in vivo | [106] |
| CXCL8 | CXC motif chemokine ligand 8 | ↓ | NF-κB/RelA [105] | CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathway mediates the tumorigenesis of multiple cancers, such as those of breast, prostate, lung, colon, and melanoma. | [107] |
| EDN1 | endothelin 1 | ↓ | NF-κB/RelA [105] | EDN1 receptor antagonist reduces migration of MCF7 breast cancer cells | [108] |
| IL1B | interleukin 1 beta | ↓ | NF-κB/RelA [105] | Upregulated in TNBC cells; Treatment of IL1 receptor antagonist decreases invasiveness of TNBC cells. | [109] |
| IL6 | interleukin 6 | ↓ | NF-κB/RelA [105] | Highly expressed in TNBC cellsTargeting IL6 and IL8 expression by shRNAs inhibits colony formation and survival of TNBC cells in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. | [110] |
| SERPINE1 | serpin family E member 1 | ↓ | NF-κB/RelA [105] | SERPINE1 knockdown reverse the paclitaxel resistance of TNBC cells by reducing vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) | [111] |
| PCK2 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 2, mitochondrial | ↑ | RelA [105] | A tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma | [112] |
| TRIB3 | tribbles pseudokinase 3 | ↑ | RelA [105] | A master oncogenic factor | [113] |
| FABP3 | fatty acid binding protein 3 | ↑ | A potential tumor suppressor in breast and embryonic cancers | [114,115] | |
| FDFT1 | farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase 1 | ↑ | A potential tumor suppressor | [116] | |
| FADS2 | fatty acid desaturase 2 | ↑ | A potential tumor suppressor | [117] | |
| SEMA6D | semaphorin 6D | ↑ | A tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer | [118] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, Y.W.; You, K.S.; Han, S.; Ha, I.J.; Park, J.-S.; Lee, S.-G.; Seong, Y.-S. Inhibition of IκB Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Circumvent Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215215
Yi YW, You KS, Han S, Ha IJ, Park J-S, Lee S-G, Seong Y-S. Inhibition of IκB Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Circumvent Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215215
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Yong Weon, Kyu Sic You, Sanghee Han, In Jin Ha, Jeong-Soo Park, Seok-Geun Lee, and Yeon-Sun Seong. 2022. "Inhibition of IκB Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Circumvent Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215215
APA StyleYi, Y. W., You, K. S., Han, S., Ha, I. J., Park, J.-S., Lee, S.-G., & Seong, Y.-S. (2022). Inhibition of IκB Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Circumvent Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers, 14(21), 5215. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215215








