Mechanistic Studies and a Retrospective Cohort Study: The Interaction between PPAR Agonists and Immunomodulatory Agents in Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Methylation Specific PCR (MSP)
2.4. Protein Degradation Analysis (CHX Chase)
2.5. Reagents and Antibodies
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Metabolomics
2.8. Patient Population and Studies
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. High DNA Methylation at CpG Islands of the CRBN Promoter Region Was Associated with Acquisition of Resistance to Lenalidomide in MM Cell Lines
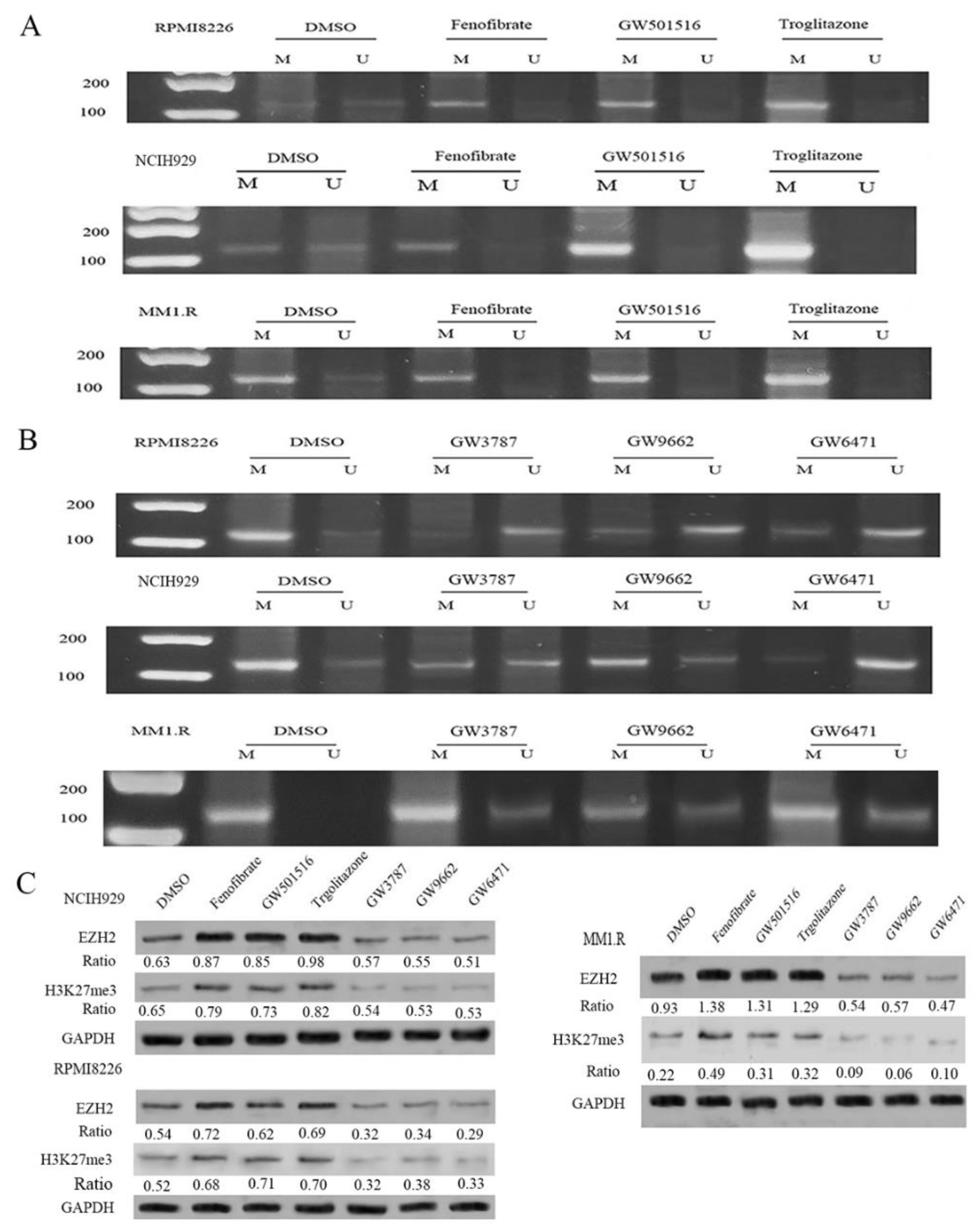
3.2. Exposure to PPAR Agonists Induced DNA Methylation in the CpG Islands of the CRBN Promoter Region in MM Cell Lines
3.3. CRBN Is Rapidly Degraded in the Presence of PPAR Agonists
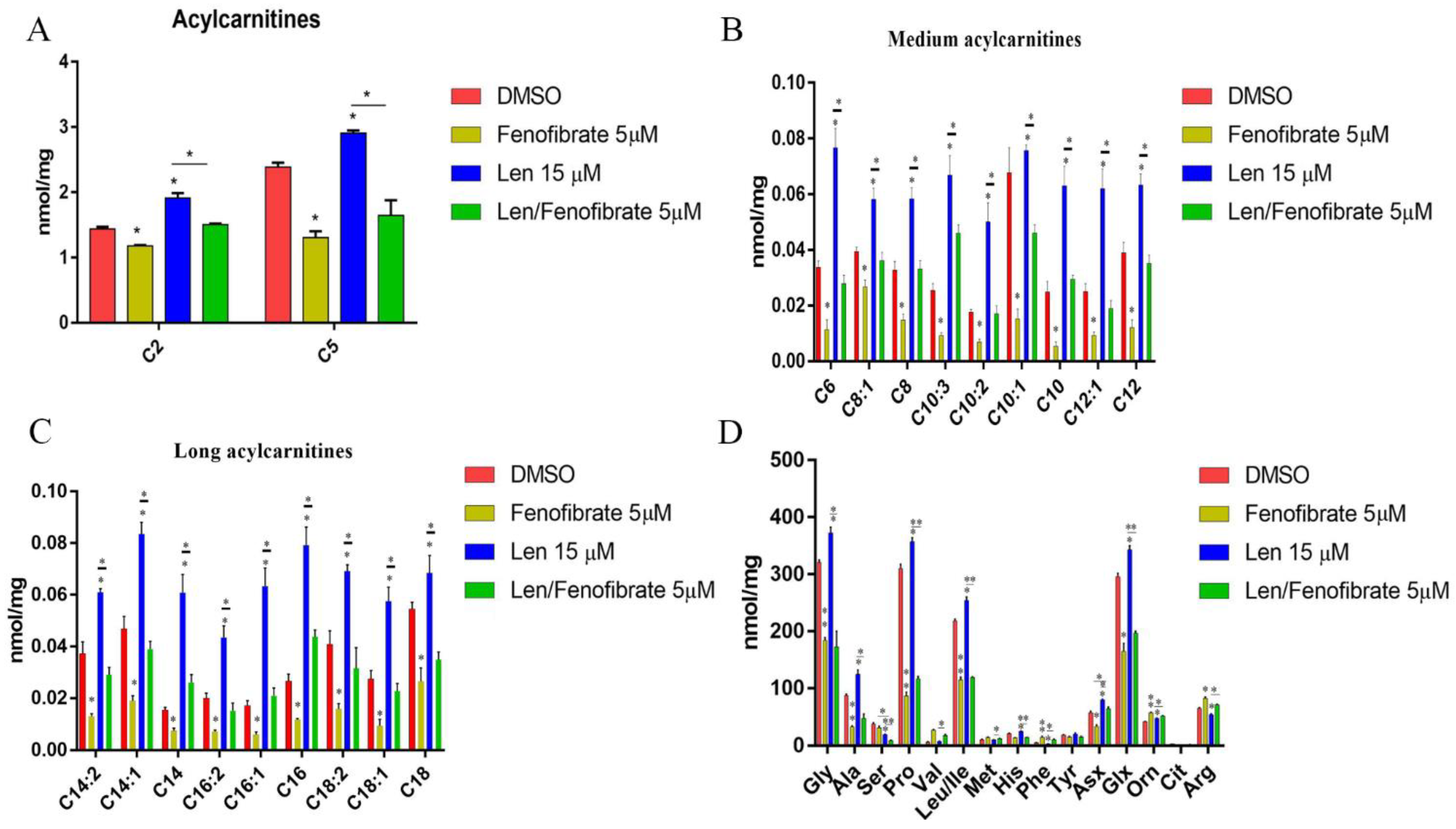
3.4. Fenofibrate and Lenalidomide Have Opposite Effects on Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolism
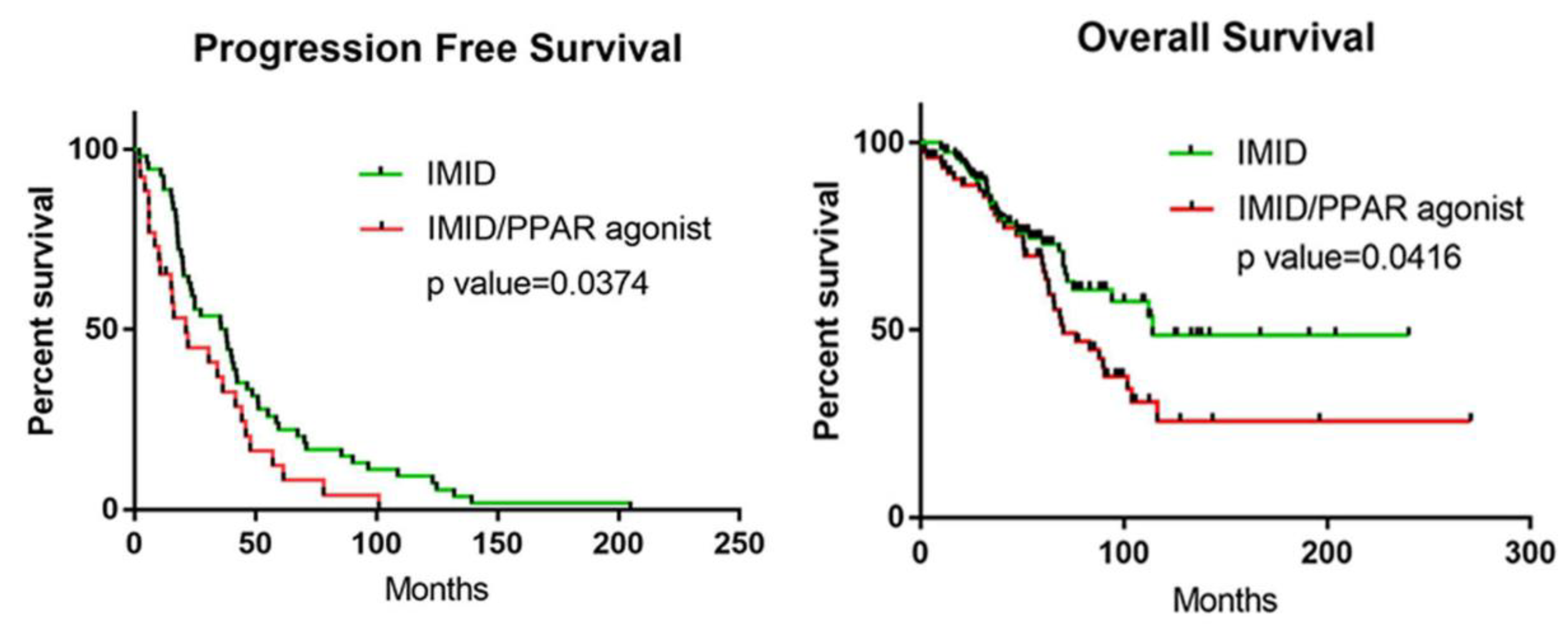
3.5. Retrospective Cohort Study: Co-Administration of PPAR Agonists with IMiDs Results in Worse PFS and OS in Patients with MM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianchi, G.; Kumar, S.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Roccaro, A.M. Cell Trafficking in Multiple Myeloma. Open J. Hematol. 2012, 3 (Suppl. 1), 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, Y.L.D.; Ramberger, E.; Bohl, S.R.; Dolnik, A.; Steinebach, C.; Conrad, T.; Muller, S.; Popp, O.; Kull, M.; Haji, M.; et al. Proteomic profiling reveals CDK6 upregulation as a targetable resistance mechanism for lenalidomide in multiple myeloma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, V.; Kyle, R.A.; van Duin, M.; Sonneveld, P.; Mateos, M.V.; Gay, F.; Anderson, K.C. Multiple myeloma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanamandra, U.; Sharma, R.; Shankar, S.; Yadav, S.; Kapoor, R.; Pramanik, S.; Ahuja, A.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.; Das, S.; et al. Survival Outcomes of Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma at a Tertiary Care Center in North India (IMAGe: 001A Study). JCO Glob. Oncol. 2021, 7, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringhen, S.; Milan, A.; Ferri, C.; Wasch, R.; Gay, F.; Larocca, A.; Salvini, M.; Terpos, E.; Goldschmidt, H.; Cavo, M.; et al. Cardiovascular adverse events in modern myeloma therapy—Incidence and risks. A review from the European Myeloma Network (EMN) and Italian Society of Arterial Hypertension (SIIA). Haematologica 2018, 103, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seedat, F.; Patel, M.; Phillip, V.; Mohamed, F.; Marais, A.D.; Blackhurst, D.M.; Solomon, G.; Currin, S.; Raal, F.J. Hyperlipidemic myeloma, a rare form of acquired dysbetalipoproteinemia, in an HIV seropositive African female. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 520, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, K.; Fadel, H.J.; Tande, A.J.; Pardi, D.S.; Khanna, S. Outcomes in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 and Clostridioides difficile Coinfection. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaigne, D.; Butruille, L.; Staels, B. PPAR control of metabolism and cardiovascular functions. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Guess, A.J.; Benndorf, R.; Smoyer, W.E. Comparison of direct action of thiazolidinediones and glucocorticoids on renal podocytes: Protection from injury and molecular effects. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IJpenberg, A.; Jeannin, E.; Wahli, W.; Desvergne, B. Polarity and specific sequence requirements of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)/retinoid X receptor heterodimer binding to DNA. A functional analysis of the malic enzyme gene PPAR response element. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20108–20117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinäniemi, M.; Carlberg, C. Screening for PPAR Responsive Regulatory Modules in Cancer. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 749073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalik, L.; Desvergne, B.; Dreyer, C.; Gavillet, M.; Laurini, R.N.; Wahli, W. PPAR expression and function during vertebrate development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2002, 46, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bookout, A.L.; Jeong, Y.; Downes, M.; Yu, R.T.; Evans, R.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Anatomical profiling of nuclear receptor expression reveals a hierarchical transcriptional network. Cell 2006, 126, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dreyer, C.; Krey, G.; Keller, H.; Givel, F.; Helftenbein, G.; Wahli, W. Control of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway by a novel family of nuclear hormone receptors. Cell 1992, 68, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugwood, J.D.; Issemann, I.; Anderson, R.G.; Bundell, K.R.; McPheat, W.L.; Green, S. The mouse peroxisome proliferator activated receptor recognizes a response element in the 5′ flanking sequence of the rat acyl CoA oxidase gene. Embo J. 1992, 11, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Umesono, K.; Noonan, D.J.; Heyman, R.A.; Evans, R.M. Convergence of 9-cis retinoic acid and peroxisome proliferator signalling pathways through heterodimer formation of their receptors. Nature 1992, 358, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, E.C.; Ebert, B.L. The novel mechanism of lenalidomide activity. Blood 2015, 126, 2366–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Ando, H.; Suzuki, T.; Ogura, T.; Hotta, K.; Imamura, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Handa, H. Identification of a primary target of thalidomide teratogenicity. Science 2010, 327, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tachita, T.; Kinoshita, S.; Ri, M.; Aoki, S.; Asano, A.; Kanamori, T.; Yoshida, T.; Totani, H.; Ito, A.; Kusumoto, S.; et al. Expression, mutation, and methylation of cereblon-pathway genes at pre- and post-lenalidomide treatment in multiple myeloma. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, X.; Sui, Y.; Yu, R.; Xu, G. Transcription factor IKZF1 is degraded during the apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells induced by kinase inhibition. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Song, Z.; Jian, H.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, S. Pyrotinib combined with thalidomide in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients harboring HER2 exon 20 insertions (PRIDE): Protocol of an open-label, single-arm phase II trial. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Braggio, E.; Shi, C.X.; Kortuem, K.M.; Bruins, L.A.; Schmidt, J.E.; Chang, X.B.; Langlais, P.; Luo, M.; Jedlowski, P.; et al. Identification of cereblon-binding proteins and relationship with response and survival after IMiDs in multiple myeloma. Blood 2014, 124, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Middleton, R.E.; Sun, H.; Naniong, M.; Ott, C.J.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Wong, K.K.; Bradner, J.E.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. The myeloma drug lenalidomide promotes the cereblon-dependent destruction of Ikaros proteins. Science 2014, 343, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kronke, J.; Udeshi, N.D.; Narla, A.; Grauman, P.; Hurst, S.N.; McConkey, M.; Svinkina, T.; Heckl, D.; Comer, E.; Li, X.; et al. Lenalidomide causes selective degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in multiple myeloma cells. Science 2014, 343, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, S.; Horiuchi, Y.; Matsuoka, S.; Kido, K.; Nishino, K.; Maeno, M.; Shibata, N.; Kosako, H.; Sawasaki, T. A proximity biotinylation-based approach to identify protein-E3 ligase interactions induced by PROTACs and molecular glues. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, K.; Ueda, Y.; Kanazawa, T.; Misawa, Y.; Jang, I.; Brenner, J.C.; Ogawa, T.; Takebayashi, S.; Grenman, R.A.; Herman, J.G.; et al. Epigenetic inactivation of galanin receptor 1 in head and neck cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7604–7613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.; Bai, P.; Ning, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, K.; He, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, R.; et al. The Monocot-Specific Receptor-like Kinase SDS2 Controls Cell Death and Immunity in Rice. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkata, J.K.; An, N.; Stuart, R.; Costa, L.J.; Cai, H.; Coker, W.; Song, J.H.; Gibbs, K.; Matson, T.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; et al. Inhibition of sphingosine kinase 2 downregulates the expression of c-Myc and Mcl-1 and induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma. Blood 2014, 124, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kadakia, R.; Scholtens, D.M.; Rouleau, G.W.; Talbot, O.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; George, T.; Josefson, J.L. Cord Blood Metabolites Associated with Newborn Adiposity and Hyperinsulinemia. J. Pediatr. 2018, 203, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Paiva, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Durie, B.; Landgren, O.; Moreau, P.; Munshi, N.; Lonial, S.; Blade, J.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Callander, N.S.; Hillengass, J.; Liedtke, M.; Baljevic, M.; Campagnaro, E.; Castillo, J.J.; Chandler, J.C.; Cornell, R.F.; Costello, C.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Multiple Myeloma, Version 1.2020. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prandi, F.R.; Lecis, D.; Illuminato, F.; Milite, M.; Celotto, R.; Lerakis, S.; Romeo, F.; Barilla, F. Epigenetic Modifications and Non-Coding RNA in Diabetes-Mellitus-Induced Coronary Artery Disease: Pathophysiological Link and New Therapeutic Frontiers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.C.; Dahiya, R. MethPrimer: Designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burke, L.J.; Baniahmad, A. Co-repressors 2000. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1876–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanim, F.L.; Gommersall, L.M.; Wood, V.H.; Smith, K.L.; Montalvo, L.; O’Neill, L.P.; Xu, Y.; Peehl, D.M.; Stewart, P.M.; Turner, B.M.; et al. Altered SMRT levels disrupt vitamin D3 receptor signalling in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6712–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molnár, F.; Matilainen, M.; Carlberg, C. Structural determinants of the agonist-independent association of human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors with coactivators. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26543–26556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perissi, V.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Controlling nuclear receptors: The circular logic of cofactor cycles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenuwein, T.; Allis, C.D. Translating the histone code. Science 2001, 293, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Liu, X.; Kumar, S.K.; Jin, F.; Dai, Y. Decoding DNA methylation in epigenetics of multiple myeloma. Blood Rev. 2022, 51, 100872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.Y.; Chim, C.S. DNA methylation of tumor suppressor protein-coding and non-coding genes in multiple myeloma. Epigenomics 2015, 7, 985–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, J.; Guerin-Charbonnel, C.; Gaborit, V.; Campion, L.; Devic, M.; Douillard, E.; Roi, N.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Decaux, O.; Facon, T.; et al. The DNA methylation landscape of multiple myeloma shows extensive inter- and intrapatient heterogeneity that fuels transcriptomic variability. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yu, C.; Zhuang, S. Histone Methyltransferase EZH2: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Kidney Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 640700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Moreau, F.; Chadee, K. PPARγ is an E3 ligase that induces the degradation of NFκB/p65. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, C. PPARγ E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates MUC1-C oncoprotein stability. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5619–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Attia, R.R.; Connaughton, S.; Niesen, M.I.; Ness, G.C.; Elam, M.B.; Hori, R.T.; Cook, G.A.; Park, E.A. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) and PPAR gamma coactivator (PGC-1alpha) induce carnitine palmitoyltransferase IA (CPT-1A) via independent gene elements. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2010, 325, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monsalve, F.A.; Pyarasani, R.D.; Delgado-Lopez, F.; Moore-Carrasco, R. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor targets for the treatment of metabolic diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 549627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Contreras, A.V.; Torres, N.; Tovar, A.R. PPAR-α as a key nutritional and environmental sensor for metabolic adaptation. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2013, 4, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korbecki, J.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M. Self-regulation of the inflammatory response by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, R.; Wang, J.; Hu, D.D.; Li, F. PPARalpha activation protects against cholestatic liver injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knapik-Czajka, M.; Gozdzialska, A.; Jaskiewicz, J. Adverse effect of fenofibrate on branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex in rat’s liver. Toxicology 2009, 266, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broyl, A.; Kuiper, R.; van Duin, M.; van der Holt, B.; el Jarari, L.; Bertsch, U.; Zweegman, S.; Buijs, A.; Hose, D.; Lokhorst, H.M.; et al. High cereblon expression is associated with better survival in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma treated with thalidomide maintenance. Blood 2013, 121, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuster, S.R.; Kortuem, K.M.; Zhu, Y.X.; Braggio, E.; Shi, C.X.; Bruins, L.A.; Schmidt, J.E.; Ahmann, G.; Kumar, S.; Rajkumar, S.V.; et al. The clinical significance of cereblon expression in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sha, Y.; Wu, J.; Paul, B.; Zhao, Y.; Mathews, P.; Li, Z.; Norris, J.; Wang, E.; McDonnell, D.P.; Kang, Y. PPAR agonists attenuate lenalidomide’s anti-myeloma activity in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2022, 545, 215832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haertle, L.; Barrio, S.; Munawar, U.; Han, S.; Zhou, X.; Vogt, C.; Fernandez, R.A.; Bittrich, M.; Ruiz-Heredia, Y.; da Via, M.; et al. Cereblon enhancer methylation and IMiD resistance in multiple myeloma. Blood 2021, 138, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, K.; Helbo, A.S.; Munch-Petersen, H.F.; Sjö, L.; Christensen, J.; Kristensen, L.S.; Asmar, F.; Hermansen, N.E.U.; O’Connel, C.; Gimsing, P.; et al. Dual inhibition of DNMTs and EZH2 can overcome both intrinsic and acquired resistance of myeloma cells to IMiDs in a cereblon-independent manner. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortum, K.M.; Mai, E.K.; Hanafiah, N.H.; Shi, C.X.; Zhu, Y.X.; Bruins, L.; Barrio, S.; Jedlowski, P.; Merz, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Targeted sequencing of refractory myeloma reveals a high incidence of mutations in CRBN and Ras pathway genes. Blood 2016, 128, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powell, C.E.; Du, G.; Bushman, J.W.; He, Z.; Zhang, T.; Fischer, E.S.; Gray, N.S. Selective degradation-inducing probes for studying cereblon (CRBN) biology. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, A.G.; Craigon, C.; Chan, K.H.; Testa, A.; Karapetsas, A.; Fasimoye, R.; Macartney, T.; Blow, J.J.; Alessi, D.R.; Ciulli, A. Development of BromoTag: A “Bump-and-Hole”-PROTAC System to Induce Potent, Rapid, and Selective Degradation of Tagged Target Proteins. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 15477–15502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.E.; Mayer, A.; Buckley, D.L.; Erb, M.A.; Roderick, J.E.; Vittori, S.; Reyes, J.M.; di Iulio, J.; Souza, A.; Ott, C.J.; et al. BET Bromodomain Proteins Function as Master Transcription Elongation Factors Independent of CDK9 Recruitment. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heim, C.; Pliatsika, D.; Mousavizadeh, F.; Bar, K.; Alvarez, B.H.; Giannis, A.; Hartmann, M.D. De-Novo Design of Cereblon (CRBN) Effectors Guided by Natural Hydrolysis Products of Thalidomide Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 6615–6629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, T.; Zhou, W.; Xing, L.; Wang, S.; Ho, M.; Peng, Z.; Tai, Y.T.; Hideshima, T.; Anderson, K.C.; et al. A genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screening in myeloma cells identifies regulators of immunomodulatory drug sensitivity. Leukemia 2019, 33, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Ciulli, A. E3 Ligase Ligands for PROTACs: How They Were Found and How to Discover New Ones. SLAS Discov. 2021, 26, 484–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaduri, U.; Merla, G. Ubiquitination, Biotech Startups, and the Future of TRIM Family Proteins: A TRIM-Endous Opportunity. Cells 2021, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.J.C.; Hnedzko, D.; Kim, B.K.; Aye, Y. Breaking the Fourth Wall: Modulating Quaternary Associations for Protein Regulation and Drug Discovery. Chembiochem 2019, 20, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helzer, K.T.; Hooper, C.; Miyamoto, S.; Alarid, E.T. Ubiquitylation of nuclear receptors: New linkages and therapeutic implications. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 54, R151–R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, M.C.; Nandi, G.; Donovan, K.A.; Cai, Q.; Berry, B.C.; Nowak, R.P.; Fischer, E.S.; Gray, N.S.; Ferguson, F.M.; Haggarty, S.J. Discovery and Optimization of Tau Targeted Protein Degraders Enabled by Patient Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells-Derived Neuronal Models of Tauopathy. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 801179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrowka, P.; Glodkowska-Mrowka, E. PPARgamma Agonists in Combination Cancer Therapies. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2020, 20, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungria, V.T.; Brandizzi, L.I.; Chiattone, C.S.; Bydlowski, S.P.; Maranhao, R.C. Metabolism of an artificial emulsion resembling chylomicrons in patients with multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. 1999, 23, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Huang, S.; Peng, J.; Gao, X.; Li, M.; Yu, S.; Liu, Z.; Qie, P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, S.; et al. Targeting lipid metabolism in multiple myeloma cells: Rational development of a synergistic strategy with proteasome inhibitors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 4741–4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Chu, E.; Paul, B.; Kang, Y. Mechanistic Studies and a Retrospective Cohort Study: The Interaction between PPAR Agonists and Immunomodulatory Agents in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2022, 14, 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215272
Wu J, Chu E, Paul B, Kang Y. Mechanistic Studies and a Retrospective Cohort Study: The Interaction between PPAR Agonists and Immunomodulatory Agents in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215272
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jian, Emily Chu, Barry Paul, and Yubin Kang. 2022. "Mechanistic Studies and a Retrospective Cohort Study: The Interaction between PPAR Agonists and Immunomodulatory Agents in Multiple Myeloma" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215272
APA StyleWu, J., Chu, E., Paul, B., & Kang, Y. (2022). Mechanistic Studies and a Retrospective Cohort Study: The Interaction between PPAR Agonists and Immunomodulatory Agents in Multiple Myeloma. Cancers, 14(21), 5272. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215272





