Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Heterogeneity, Prognostic Impact, and Relationship with Immune Checkpoints
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
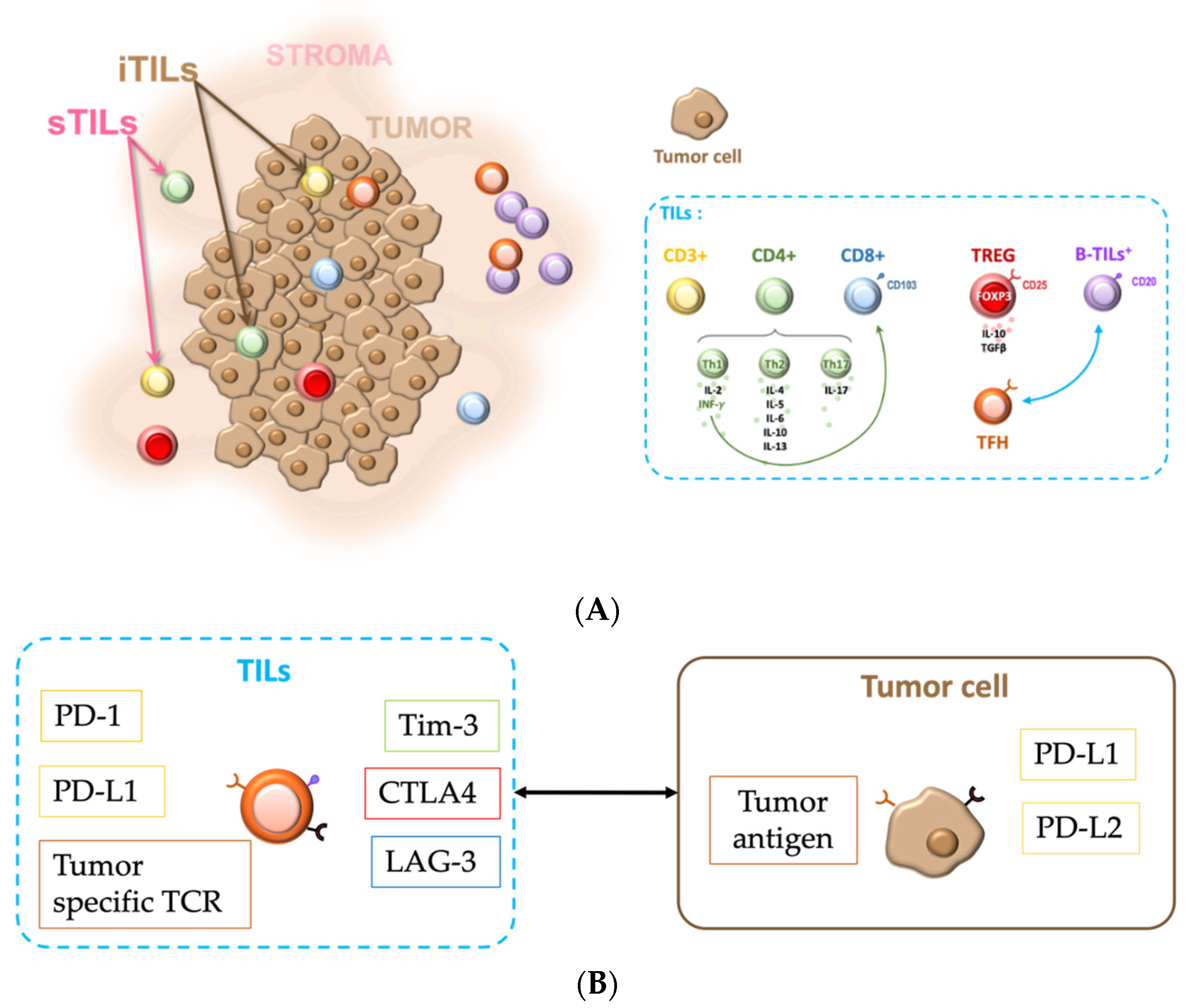
3.2. TIL Definition
- TILs in EOC are a subject that has gained a lot of interest in the last five years. In the published scientific data, TILs are evaluated using different methods, including genetic signature, count of TILs in hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) based pathological immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) [22]. The International Immuno-Oncology Biomarkers Working Group defined, in 2017, “intra-epithelial” (iTILs) as TILs present in the tumor and “stromal” (sTILs) as TILs that are present within 1 mm beneath the epithelial layer [23]. To evaluate the inflammatory infiltrate, sTILs and iTILs are expressed in percentages or median counts. In IHC, between three and 10 fields in stained slides are observed in x200 or x400 high-power fields (HPF). TILs in H&E, in IHC, or in IF with specific antibodies are analyzed with either an absolute count or a semi-quantitative cut-off. For example, Goode and al. divided iTILs CD8+ infiltration into four categories: 0, low: 1–2, median: 3–19, and high ≥ 20 [24]. Other authors concluded that TILs > 5 or 10 per HPF should define positive iTILs in EOC [25].
- Tumoral tissues and ascites from pCRS patients represent the main samples used in the studies [26]. The data showed variability in the immune infiltrate among the different tissue samples within the same patient (ovaries, omentum, and peritoneum) [27,28,29,30,31]. One study confirmed the feasibility of TIL evaluation in tumor samples that is performed using a 16-gauge needle biopsy [32]. Systematic tumor core biopsies can represent the immune microenvironment [33].
- The description of TILs in EOC uses various techniques, especially the cut-offs are extremely variable between the studies. To date, there is no consensus, apart from H&E which is not yet used in clinical routine, on the type of marker or the thresholds to identify TILs.
3.3. TIL Phenotypes
| Study Author (Publication Year) | Number of Cases n= | Tumor Stage | Moment | Subtype/ TIL Phenotype | Specimen Processing | Location | TIL Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hagemann (2011) [63] | 10 | IIIC | pCRS (n = 9) and recurrence (n = 1) | CD3, CD8, FoxP3 | primary tumor and two intraperitoneal metastases | iTILs and sTILs | heterogeneity in TIL density inter- and intra-patient (primary versus metastasis) |
| Murakami (2016) [57] | 132 | I to IV | at diagnosis: pCRS | CD8 | tumor samples | iTILs and sTILs | NEW PATHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION: mesenchymal transition, immunereactive, solid and proliferative, and papilloglandular |
| Ojalvo (2017) [64] | 52 | II to IV | pCRS (37) and recurrence (15) | CD8, FoxP3 | tumor samples | iTILs | median FOXP3 count recurrent > primary |
| Zhu (2017) [41] | 126 | I to IV | pCRS | CD4, IL17, FoxP3, CD31 | ovarian samples of the central areas of EOC | iTILs | % of Treg cells, Th17 cells, and ratio of Treg/Th17 cells: high in patients with EOC |
| Nakamura (2019) [65] | 839 | no data | no data | Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17, M1, and M2 macrophage | tumor samples | TILs | Higher intratumoral expressionmarkers may rescue or neutralize the negative associations of inflammation or angiogenesis |
| Jiménez (2020) [27] | 50 | IIIC and IV | 40 NACT and 10 pCRS | CD45, CD3, CD4, CD8, NK, FoxP3 | tumor samples | iTILs | transcriptomic heterogeneity in each patient |
| Dötzer (2019) [30] | 49 | IIIC and IV | pCRS (35 CC0, 8 CC1, 6 CC2) | CD45, CD3, CD8, PD-1, PD-L1 | tumor sample, peritoneum, and omentum | iTILs and sTILs | differences in the expression between primary cancer and omental and peritoneal lesions |
| Oberg (2020) [43] | 29 | III and IV | at diagnosis | CD45, CD8, CD56, CD3, IFN-𝛾, IL-4, IL-9, IL-10, IL-17, TNF-𝛼 | blood, ascites, and tumor samples | TILs | heterogeneity in TILs vs ascites |
| Gao (2020) [55] | 2086 | I to IV | no data | 22 immune cells | tumor samples | TILs | Heterogeneous immune microenvironment: infiltration varied between clinicopathological subgroups (stage, type, and survival) |
| Lakis (2020) [58] | 70 | III and IV | pCRS | H&E, morphological subtypes: IR, SD, PG, MT | tumor samples | iTILs and sTILs | higher sTIL density in implants than in ovarian tissue; heterogeneity between implants of the same patient |
| Zhou (2021) [54] | 379 | II to IV | no data | 22 immune cells | tumor samples | TILs | heterogeneity in CD8 and NK cells; TFH, monocyte, macrophage: proportion higher in OC than normal tissue |
| Zhu (2021) [62] | 41 | IIIB and IV | pCRS | CD8+, CD4+ | tumor samples | iTILs and sTILs | heterogeneity between stromal and tumoral tissues |
| Karakaya (2021) [38] | 66 | I to IV | at diagnosis | PD-1, CD8, CD4, CD3 | tumor samples | iTILs and sTILs | heterogeneity between stromal and tumoral tissues and between histologic types |
3.4. TILs and Patients’ Survival
| Study Author (Publication Year) | Number of Cases n= | Advanced Stage (%) | Serous Histology (%) | Moment | Median Follow-Up (Months) | Optimal Debulking (Residual Tumor <2.5 cm) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nielsen (2012) [89] | 264 | 92.5 | 100 | pCRS | 1.9 | 30 |
| Bachmayr-Heyda (2013) [93] | 203 | 95.5 | 88.2 | pCRS | 48 | 69.5 |
| Webb (2014) [101] | 497 | 58.9 | 44.3 | pCRS | no data | 100 |
| Hermans (2014) [90] | 210 | 100 | 77.1 | At diagnosis | no data | 30 |
| De Leeuw (2015) [91] | 187 | 34 | 100 | pCRS | no data | 100 |
| Murakami (2016) [57] | 132 | 82 | 100 | pCRS | no data | no data |
| Santoiemma (2016) [81] | 135 | 71 | 65.9 | no data | no data | 59.3 |
| Lundgren (2016) [100] | 154 | no data | 58.4 | pCRS | 87 | no data |
| Goode (2017) [24] | 5078 | 47.8 | 62.9 | pCRS | 48.9 | 42.4 |
| James (2017) [67] | 707 | 40 | 44.4 | pCRS | no data | no data |
| Pinto (2018) [87] | 128 | 80.5 | 100 | At diagnosis | no data | 80 |
| Hwang (2019) [68] | 256 | 62 | 56.6 | At diagnosis | no data | 91 |
| Martin de la Fuente (2020) [84] | 130 | 100 | 100 | At diagnosis | no data | 60 |
| Paijens (2021) [97] | 268 | 94.8 | 100 | pCRS (47%) or iCRS | no data | 75.7 (51.4 complete) |
| Wu (2021) [102] | 441 | 87 | no data | no data | no data | 62.4 |
| Li (2021) [103] | 308 | 88.9 | no data | no data | no data | 61.4 (18.2 complete) |
| Chen (2020) [104] | 189 | 59.3 | 12.7 | At diagnosis | 37 | no data |
3.5. Influence of DNA Repair Deficiency and TILs
3.6. TILs and Immune Checkpoints
3.7. Influence of First-Line Chemotherapy on TIL Landscape
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lheureux, S.; Gourley, C.; Vergote, I.; Oza, A.M. Epithelial ovarian cancer. Lancet 2019, 393, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Female Genital Tumours; World Health Organization Classification of Tumours: Lyon, France, 2020; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, D.K.; Alvarez, R.D.; Bakkum-Gamez, J.N.; Barroilhet, L.; Behbakht, K.; Berchuck, A.; Berek, J.S.; Chen, L.M.; Cristea, M.; DeRosa, M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Ovarian Cancer, Version 1.2019. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergote, I.; Tropé, C.G.; Amant, F.; Kristensen, G.B.; Ehlen, T.; Johnson, N.; Verheijen, R.H.; van der Burg, M.E.; Lacave, A.J.; Panici, P.B.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy or primary surgery in stage IIIC or IV ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kehoe, S.; Hook, J.; Nankivell, M.; Jayson, G.C.; Kitchener, H.; Lopes, T.; Luesley, D.; Perren, T.; Bannoo, S.; Mascarenhas, M.; et al. Primary chemotherapy versus primary surgery for newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer (CHORUS): An open-label, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagotti, A.; Ferrandina, M.G.; Vizzielli, G.; Pasciuto, T.; Fanfani, F.; Gallotta, V.; Margariti, P.A.; Chiantera, V.; Costantini, B.; Gueli Alletti, S.; et al. Randomized trial of primary debulking surgery versus neoadjuvant chemotherapy for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer (SCORPION-NCT01461850). Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2020, 30, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, F.; El Hajj, H.; Le Deley, M.-C.; Aissaoui, O.; Gachon, B.; Chevalier, A.; Abdeddaim, C.; Lemaire, A.-S.; Ben Haj Amor, M.; Sylla, D.; et al. A New Paradigm in Managing Advanced Ovarian Cancer: Differentiating Patients Requiring Neoadjuvant Treatment from Primary Cytoreduction. Cancers 2021, 13, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straubhar, A.M.; Filippova, O.T.; Cowan, R.A.; Lakhman, Y.; Sarasohn, D.M.; Nikolovski, I.; Torrisi, J.M.; Ma, W.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Gardner, G.J.; et al. A multimodality triage algorithm to improve cytoreductive outcomes in patients undergoing primary debulking surgery for advanced ovarian cancer: A Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center team ovary initiative. Gynecologic oncology 2020, 158, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagden, S.P.; Cook, A.D.; Poole, C.; Howells, L.; McNeish, I.A.; Dean, A.; Kim, J.W.; O’Donnell, D.M.; Hook, J.; James, E.C.; et al. Weekly platinum-based chemotherapy versus 3-weekly platinum-based chemotherapy for newly diagnosed ovarian cancer (ICON8): Quality-of-life results of a phase 3, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Driel, W.J.; Koole, S.N.; Sikorska, K.; Schagen van Leeuwen, J.H.; Schreuder, H.W.R.; Hermans, R.H.M.; de Hingh, I.; van der Velden, J.; Arts, H.J.; Massuger, L.; et al. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Tian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Luo, J.; Jia, M.; Tang, H.; et al. Evaluation of Cytoreductive Surgery with or without Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Stage III Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2013940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koole, S.; van Stein, R.; Sikorska, K.; Barton, D.; Perrin, L.; Brennan, D.; Zivanovic, O.; Mosgaard, B.J.; Fagotti, A.; Colombo, P.E.; et al. Primary cytoreductive surgery with or without hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for FIGO stage III epithelial ovarian cancer: OVHIPEC-2, a phase III randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2020, 30, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj, H.; Vanseymortier, M.; Hudry, D.; Bogart, E.; Abdeddaim, C.; Leblanc, E.; Le Deley, M.C.; Narducci, F. Rationale and study design of the CHIPPI-1808 trial: A phase III randomized clinical trial evaluating hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for stage III ovarian cancer patients treated with primary or interval cytoreductive surgery. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray-Coquard, I.; Pautier, P.; Pignata, S.; Perol, D.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Berger, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Vergote, I.; Colombo, N.; Maenpaa, J.; et al. Olaparib plus Bevacizumab as First-Line Maintenance in Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2416–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perren, T.J.; Swart, A.M.; Pfisterer, J.; Ledermann, J.A.; Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Kristensen, G.; Carey, M.S.; Beale, P.; Cervantes, A.; Kurzeder, C.; et al. A phase 3 trial of bevacizumab in ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2484–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, K.; Colombo, N.; Scambia, G.; Kim, B.G.; Oaknin, A.; Friedlander, M.; Lisyanskaya, A.; Floquet, A.; Leary, A.; Sonke, G.S.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSilvestro, P.; Colombo, N.; Scambia, G.; Kim, B.G.; Oaknin, A.; Friedlander, M.; Lisyanskaya, A.; Floquet, A.; Leary, A.; Sonke, G.S.; et al. Efficacy of Maintenance Olaparib for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer with a BRCA Mutation: Subgroup Analysis Findings From the SOLO1 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3528–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P.-P. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendry, S.; Salgado, R.; Gevaert, T.; Russell, P.A.; John, T.; Thapa, B.; Christie, M.; van de Vijver, K.; Estrada, M.V.; Gonzalez-Ericsson, P.I.; et al. Assessing Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Solid Tumors: A Practical Review for Pathologists and Proposal for a Standardized Method from the International Immunooncology Biomarkers Working Group: Part 1: Assessing the Host Immune Response, TILs in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Ductal Carcinoma In Situ, Metastatic Tumor Deposits and Areas for Further Research. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2017, 24, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hendry, S.; Salgado, R.; Gevaert, T.; Russell, P.A.; John, T.; Thapa, B.; Christie, M.; van de Vijver, K.; Estrada, M.V.; Gonzalez-Ericsson, P.I.; et al. Assessing Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Solid Tumors: A Practical Review for Pathologists and Proposal for a Standardized Method from the International Immuno-Oncology Biomarkers Working Group: Part 2: TILs in Melanoma, Gastrointestinal Tract Carcinomas, Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma and Mesothelioma, Endometrial and Ovarian Carcinomas, Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck, Genitourinary Carcinomas, and Primary Brain Tumors. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2017, 24, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goode, E.L.; Block, M.S.; Kalli, K.R.; Vierkant, R.A.; Chen, W.; Fogarty, Z.C.; Gentry-Maharaj, A.; Tołoczko, A.; Hein, A.; Bouligny, A.L.; et al. Dose-Response Association of CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Survival Time in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, e173290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, W.T.; Adams, S.F.; Tahirovic, E.; Hagemann, I.S.; Coukos, G. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T cells in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2012, 124, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.; Yew, P.Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Fujiwara, K.; Fleming, G.F.; Nakamura, Y.; Park, J.H. TCR profiling of T lymphocytes in ovarian tumors and malignant ascites using next-generation sequencing. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Sánchez, A.; Cybulska, P.; Mager, K.L.V.; Koplev, S.; Cast, O.; Couturier, D.L.; Memon, D.; Selenica, P.; Nikolovski, I.; Mazaheri, Y.; et al. Unraveling tumor–immune heterogeneity in advanced ovarian cancer uncovers immunogenic effect of chemotherapy. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foord, E.; Arruda, L.C.M.; Gaballa, A.; Klynning, C.; Uhlin, M. Characterization of ascites- and tumor-infiltrating γδ T cells reveals distinct repertoires and a beneficial role in ovarian cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb0192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cândido, E.B.; Silva, L.M.; Carvalho, A.T.; Lamaita, R.M.; Filho, R.M.P.; Cota, B.D.C.V.; Da Silva-Filho, A.L. Immune response evaluation through determination of type 1, type 2, and type 17 patterns in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 20, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dötzer, K.; Schlüter, F.; Bo Schoenberg, M.; Bazhin, A.V.; von Koch, F.E.; Schnelzer, A.; Anthuber, S.; Grab, D.; Czogalla, B.; Burges, A.; et al. Immune heterogeneity between primary tumors and corresponding metastatic lesions and response to platinum therapy in primary ovarian cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, E.; Nielsen, J.S.; Wick, D.A.; Ng, A.V.; Johnson, L.D.S.; Nesslinger, N.J.; McMurtrie, E.; Webb, J.R.; Nelson, B.H. Polyfunctional t-cell responses are disrupted by the ovarian cancer ascites environment and only partially restored by clinically relevant cytokines. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, A.R.; Cadungog, M.; Hagemann, I.S.; Hammond, R.; Adams, S.F.; Chu, C.S.; Rubin, S.C.; Zhang, L.; Addya, K.; Birrer, M.J.; et al. Tissue-based immune monitoring I: Tumor core needle biopsies allow in-depth interrogation of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lara, O.D.; Krishnan, S.; Wang, Z.; Corvigno, S.; Zhong, Y.; Lyons, Y.; Dood, R.; Hu, W.; Qi, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Tumor core biopsies adequately represent immune microenvironment of high-grade serous carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasby, E.A. Weapons ovarian epithelial tumors may use in immune escape: An immunohistochemical correlational study. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2012, 18, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, J.; Cohen, B. An overview of the immune system. Lancet 2001, 357, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pages, F.; Sautes-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The immune contexture in human tumours: Impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, P.; Katayama, H.; Ostrin, E.J.; Hanash, S.M. The Emerging Role of B Cells in Tumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5597–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arman Karakaya, Y.; Atıgan, A.; Güler, Ö.; Demiray, A.G.; Bir, F. The relation of CD3, CD4, CD8 and PD-1 expression with tumor type and prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancers. Ginekol. Pol. 2021, 92, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, S.; Bachmayr-Heyda, A.; Pils, D.; Zhao, L.; Tong, W.; Berger, A.; Fogel, M.; Thalhammer, T.; Sehouli, J.; Horvat, R.; et al. Determination of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ lymphocytes in human ovarian cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2013, 32, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska, M.; Pawłowska, A.; Zakrzewska, E.; Chudzik, A.; Suszczyk, D.; Gogacz, M.; Wertel, I. Th17 Cells and IL-17 as Novel Immune Targets in Ovarian Cancer Therapy. J. Oncol. 2020, 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Q.; Wu, X.; Wang, X. Differential distribution of tumor-associated macrophages and Treg/Th17 cells in the progression of malignant and benign epithelial ovarian tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.R.; Wick, D.A.; Nielsen, J.S.; Tran, E.; Milne, K.; McMurtrie, E.; Nelson, B.H. Profound elevation of CD8+ T cells expressing the intraepithelial lymphocyte marker CD103 (αE/β7 Integrin) in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 118, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberg, H.H.; Janitschke, L.; Sulaj, V.; Weimer, J.; Gonnermann, D.; Hedemann, N.; Arnold, N.; Kabelitz, D.; Peipp, M.; Bauerschlag, D.; et al. Bispecific antibodies enhance tumor-infiltrating T cell cytotoxicity against autologous HER-2-expressing high-grade ovarian tumors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robins, H.S.; Ericson, N.G.; Guenthoer, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Tewari, M.; Drescher, C.W.; Bielas, J.H. Digital genomic quantification of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 214ra169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mhawech-Fauceglia, P.; Wang, D.; Ali, L.; Lele, S.; Huba, M.A.; Liu, S.; Odunsi, K. Intraepithelial T cells and tumor-associated macrophages in ovarian cancer patients. Cancer Immun. 2013, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Westergaard, M.C.W.; Andersen, R.; Chong, C.; Kjeldsen, J.W.; Pedersen, M.; Friese, C.; Hasselager, T.; Lajer, H.; Coukos, G.; Bassani-Sternberg, M.; et al. Tumour-reactive T cell subsets in the microenvironment of ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landskron, J.; Helland, Ø.; Torgersen, K.M.; Aandahl, E.M.; Gjertsen, B.T.; Bjørge, L.; Taskén, K. Activated regulatory and memory T-cells accumulate in malignant ascites from ovarian carcinoma patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacsovics-Bankowski, M.; Chisholm, L.; Vercellini, J.; Tucker, C.G.; Montler, R.; Haley, D.; Newell, P.; Ma, J.; Tseng, P.; Wolf, R.; et al. Detailed characterization of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in two distinct human solid malignancies show phenotypic similarities. J. ImmunoTherapy Cancer 2014, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.C.; Bean, S.M.; Whitaker, R.S.; Kondoh, E.; Baba, T.; Fujii, S.; Marks, J.R.; Dressman, H.K.; Murphy, S.K.; Berchuck, A. Ovarian cancer tumor infiltrating T-regulatory (Treg) cells are associated with a metastatic phenotype. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 116, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeger, D.R.; Milne, K.; Nelson, B.H. Tumor-infiltrating plasma cells are associated with tertiary lymphoid structures, cytolytic T-cell responses, and superior prognosis in ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3005–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 2011, 474, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martínez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Treviño, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ling, Z.J.; Yang, B. Profiles of immune infiltration in ovarian cancer and their clinical significance: A gene expression-based study. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2021, 42, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Cai, G.; Xiong, X.; Wu, Y.; Ma, D.; Li, S.C.; Gao, Q. Heterogeneity of immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer and its clinical significance: A retrospective study. OncoImmunology 2020, 9, 1760067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, X.; Zuo, Y.; Hao, D. Clinical significance of the immune microenvironment in ovarian cancer patients. Mol. Omics 2018, 14, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, R.; Matsumura, N.; Mandai, M.; Yoshihara, K.; Tanabe, H.; Nakai, H.; Yamanoi, K.; Abiko, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Hamanishi, J.; et al. Establishment of a Novel Histopathological Classification of High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma Correlated with Prognostically Distinct Gene Expression Subtypes. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lakis, S.; Kotoula, V.; Koliou, G.A.; Efstratiou, I.; Chrisafi, S.; Papanikolaou, A.; Zebekakis, P.; Fountzilas, G. Multisite Tumor Sampling Reveals Extensive Heterogeneity of Tumor and Host Immune Response in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2020, 17, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzinger, C.; Geroldinger, A.; Smeets, D.; Braicu, E.I.; Sehouli, J.; Koller, J.; Wolf, A.; Darb-Esfahani, S.; Joehrens, K.; Vergote, I.; et al. A complex network of tumor microenvironment in human high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7621–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojalvo, L.S.; Thompson, E.D.; Wang, T.L.; Meeker, A.K.; Shih, I.M.; Fader, A.N.; Cimino-Mathews, A.; Emens, L.A. Tumor-associated macrophages and the tumor immune microenvironment of primary and recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 74, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olalekan, S.; Xie, B.; Back, R.; Eckart, H.; Basu, A. Characterizing the tumor microenvironment of metastatic ovarian cancer by single-cell transcriptomics. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ferri-Borgogno, S.; Sheng, J.; Yeung, T.L.; Burks, J.K.; Cappello, P.; Jazaeri, A.A.; Kim, J.H.; Han, G.H.; Birrer, M.J.; et al. Sio: A spatioimageomics pipeline to identify prognostic biomarkers associated with the ovarian tumor microenvironment. Cancers 2021, 13, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, A.R.; Hagemann, I.S.; Cadungog, M.; Hwang, W.T.; Patel, P.; Lal, P.; Hammond, R.; Gimotty, P.A.; Chu, C.S.; Rubin, S.C.; et al. Tissue-based immune monitoring II: Multiple tumor sites reveal immunologic homogeneity in serous ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ojalvo, L.S.; Thompson, E.D.; Wang, T.L.; Meeker, A.K.; Shih, I.M.; Fader, A.N.; Cimino-Mathews, A.; Emens, L.A. Profiling the immune tumor microenvironment in primary and recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, M.; Bax, H.J.; Scotto, D.; Souri, E.A.; Sollie, S.; Harris, R.J.; Hammar, N.; Walldius, G.; Winship, A.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Immune mediator expression signatures are associated with improved outcome in ovarian carcinoma. OncoImmunology 2019, 8, e1593811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; Katsaros, D.; Gimotty, P.A.; Massobrio, M.; Regnani, G.; Makrigiannakis, A.; Gray, H.; Schlienger, K.; Liebman, M.N.; et al. Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- James, F.R.; Jiminez-Linan, M.; Alsop, J.; Mack, M.; Song, H.; Brenton, J.D.; Pharoah, P.D.P.; Ali, H.R. Association between tumour infiltrating lymphocytes, histotype and clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Suh, D.S.; Kwon, B.S.; Choi, K.U. Stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes evaluated on H&E-stained slides are an independent prognostic factor in epithelial ovarian cancer and ovarian serous carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 4557–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bansal, A.; Srinivasan, R.; Rohilla, M.; Rai, B.; Rajwanshi, A.; Suri, V.; Chandra Saha, S. Immunotyping in tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma by PD-L1 and CD8+ T-lymphocytes predicts disease-free survival. APMIS 2021, 129, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, E.; Olson, S.H.; Ahn, J.; Bundy, B.; Nishikawa, H.; Qian, F.; Jungbluth, A.A.; Frosina, D.; Gnjatic, S.; Ambrosone, C.; et al. Intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8+/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 18538–18543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamanishi, J.; Mandai, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Okazaki, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Higuchi, T.; Yagi, H.; Takakura, K.; Minato, N.; et al. Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1 and Tumor-Infiltrating CD8⁺ T Lymphocytes Are Prognostic Factors of Human Ovarian Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3360–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryczek, I.; Banerjee, M.; Cheng, P.; Vatan, L.; Szeliga, W.; Wei, S.; Huang, E.; Finlayson, E.; Simeone, D.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Phenotype, distribution, generation, and functional and clinical relevance of Th17 cells in the human tumor environments. Blood 2009, 114, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curiel, T.J.; Coukos, G.; Zou, L.; Alvarez, X.; Cheng, P.; Mottram, P.; Evdemon-Hogan, M.; Conejo-Garcia, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Burow, M.; et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leffers, N.; Gooden, M.J.M.; de Jong, R.A.; Hoogeboom, B.-N.; ten Hoor, K.A.; Hollema, H.; Boezen, H.M.; van der Zee, A.G.J.; Daemen, T.; Nijman, H.W. Prognostic significance of tumor-infiltrating T-lymphocytes in primary and metastatic lesions of advanced stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milne, K.; Köbel, M.; Kalloger, S.E.; Barnes, R.O.; Gao, D.; Gilks, C.B.; Watson, P.H.; Nelson, B.H. Systematic analysis of immune infiltrates in high-grade serous ovarian cancer reveals CD20, FoxP3 and TIA-1 as positive prognostic factors. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuji, T.; Eng, K.H.; Matsuzaki, J.; Battaglia, S.; Brian Szender, J.; Miliotto, A.; Gnjatic, S.; Bshara, W.; Morrison, C.D.; Lele, S.; et al. Clonality and antigen-specific responses shape the prognostic effects of tumor-infiltrating T cells in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 2669–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; He, M.; Lu, J.; Liu, H. Spatial cytotoxic and memory T cells in tumor predict superior survival outcomes in patients with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 3905–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.H.; Hwang, I.; Cho, H.; Ylaya, K.; Choi, J.A.; Kwon, H.; Chung, J.Y.; Hewitt, S.M.; Kim, J.H. Clinical Significance of Tumor Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Association with Hormone Receptor Expression Patterns in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Motte Rouge, T.; Corné, J.; Cauchois, A.; Le Boulch, M.; Poupon, C.; Henno, S.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Le Pabic, E.; Laviolle, B.; Catros, V.; et al. Serum CD95L level correlates with tumor immune infiltration and is a positive prognostic marker for advanced high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preston, C.; Maurer, M.; Oberg, A.; Hartmann, L.; Kalli, K.; Goode, E.; Knutson, K. CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and association with survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Santoiemma, P.P.; Reyes, C.; Wang, L.P.; McLane, M.W.; Feldman, M.D.; Tanyi, J.L.; Powell, D.J. Systematic evaluation of multiple immune markers reveals prognostic factors in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 143, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, N.; Akman, L.; Acar, K.; Demir, S.; Ozkan, S.; Alan, N.; Zekioglu, O.; Terek, M.C.; Ozdemir, N.; Ozsaran, A. Do tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes really indicate favorable prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer? EJOG 2017, 215, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinchcliff, E.M.; Paquette, C.; Roszik, J.; Kelting, S.; Stoler, M.H.; Mok, S.C.; Yeung, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yates, M.; Peng, W.; et al. Lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase expression predicts survival in ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 154, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin de la Fuente, L.; Westbom-Fremer, S.; Arildsen, N.S.; Hartman, L.; Malander, S.; Kannisto, P.; Måsbäck, A.; Hedenfalk, I. PD-1/PD-L1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are prognostically favorable in advanced high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Virchows Arch. 2020, 477, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanske, M.; Wienert, S.; Castillo-Tong, D.C.; Kreuzinger, C.; Vergote, I.; Lambrechts, S.; Gabra, H.; Gourley, C.; Ganapathi, R.N.; Kolaschinski, I.; et al. Dynamics of the Intratumoral Immune Response during Progression of High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, O.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, B. Prognostic value of immune-related cells and genes in the tumor microenvironment of ovarian cancer, especially CST4. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.P.; Balmaceda, C.; Bravo, M.L.; Kato, S.; Villarroel, A.; Owen, G.I.; Roa, J.C.; Cuello, M.A.; Ibañez, C. Patient inflammatory status and CD4+/CD8+ intraepithelial tumor lymphocyte infiltration are predictors of outcomes in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 151, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinchcliff, E.; Paquette, C.; Roszik, J.; Kelting, S.; Stoler, M.H.; Mok, S.C.; Yeung, T.L.; Zhang, Q.; Yates, M.; Peng, W.; et al. Lymphocyte-specific kinase expression is a prognostic indicator in ovarian cancer and correlates with a prominent B cell transcriptional signature. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.S.; Sahota, R.A.; Milne, K.; Kost, S.E.; Nesslinger, N.J.; Watson, P.H.; Nelson, B.H. CD20+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes have an atypical CD27—Memory phenotype and together with CD8+ T cells promote favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3281–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermans, C.; Anz, D.; Engel, J.; Kirchner, T.; Endres, S.; Mayr, D. Analysis of FoxP3+ T-regulatory cells and CD8+T-Cells in ovarian carcinoma: Location and tumor infiltration patterns are key prognostic markers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Leeuw, R.J.; Kroeger, D.R.; Kost, S.E.; Chang, P.P.; Webb, J.R.; Nelson, B.H. CD25 identifies a subset of CD4 FoxP3 TIL that are exhausted yet prognostically favorable in Human Ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farrag, M.S.; Abdelwahab, K.; Farrag, N.S.; Elrefaie, W.E.; Emarah, Z. Programmed death ligand-1 and CD8 tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) as prognostic predictors in ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma (HGSC). J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 33, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmayr-Heyda, A.; Aust, S.; Heinze, G.; Polterauer, S.; Grimm, C.; Braicu, E.I.; Sehouli, J.; Lambrechts, S.; Vergote, I.; Mahner, S.; et al. Prognostic impact of tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells in association with cell proliferation in ovarian cancer patients—A study of the OVCAD consortium. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Preston, C.C.; Maurer, M.J.; Oberg, A.L.; Visscher, D.W.; Kalli, K.R.; Hartmann, L.C.; Goode, E.L.; Knutson, K.L. The ratios of CD8+ T cells to CD4+CD25+ FOXP3+ and FOXP3- T cells correlate with poor clinical outcome in human serous ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laumont, C.M.; Wouters, M.C.A.; Smazynski, J.; Gierc, N.S.; Chavez, E.A.; Chong, L.C.; Thornton, S.; Milne, K.; Webb, J.R.; Steidl, C.; et al. Single-cell profiles and prognostic impact of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes coexpressing CD39, CD103, and PD-1 in ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4089–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, J.R.; Milne, K.; Watson, P.; DeLeeuw, R.J.; Nelson, B.H. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes expressing the tissue resident memory marker cd103 are associated with increased survival in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paijens, S.T.; Vledder, A.; Loiero, D.; Duiker, E.W.; Bart, J.; Hendriks, A.M.; Jalving, M.; Workel, H.H.; Hollema, H.; Werner, N.; et al. Prognostic image-based quantification of CD8CD103 T cell subsets in high-grade serous ovarian cancer patients. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1935104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalique, S.; Nash, S.; Mansfield, D.; Wampfler, J.; Attygale, A.; Vroobel, K.; Kemp, H.; Buus, R.; Cottom, H.; Roxanis, I.; et al. Quantitative Assessment and Prognostic Associations of the Immune Landscape in Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesia, M.D.; Vincent, B.G.; Parker, J.S.; Hoadley, K.A.; Carey, L.A.; Perou, C.M.; Serody, J.S. Prognostic B-cell signatures using mRNA-seq in patients with subtype-specific breast and ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3818–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundgren, S.; Berntsson, J.; Nodin, B.; Micke, P.; Jirström, K. Prognostic impact of tumour-associated B cells and plasma cells in epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2016, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webb, J.R.; Milne, K.; Nelson, B.H. Location, location, location: CD103 demarcates intraepithelial, prognostically favorable CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in ovarian cancer. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e27668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, L.; Jin, X.; Chen, P.; Mo, Q. Prognostic implications of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes for recurrence in epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 206, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Li, B.; Zhan, X. Comprehensive Analysis of Tumor Microenvironment Identified Prognostic Immune-Related Gene Signature in Ovarian Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 616073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Molberg, K.; Strickland, A.L.; Castrillon, D.H.; Carrick, K.; Jiang, Q.; Niu, S.; Rivera-Colon, G.; Gwin, K.; Hinson, S.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and CD8+ Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Different Types of Tubo-ovarian Carcinoma and Their Prognostic Value in High-grade Serous Carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Dong, D.; He, W.; Song, L.; Wang, Q.; Yue, J.; Xie, L. Mismatch repair deficiency is associated with MSI phenotype, increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and PD-L1 expression in immune cells in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 149, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Petrucci, E.; Pasquini, L.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Ovarian Cancers: Genetic Abnormalities, Tumor Heterogeneity and Progression, Clonal Evolution and Cancer Stem Cells. Medicines 2018, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Z.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yan, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhang, L.; Su, P.; Bi, J.; et al. lncRNA-Xist/miR-101-3p/KLF6/C/EBPα axis promotes TAM polarization to regulate cancer cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Ther.—Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Oda, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Asada, K.; Karasaki, T.; Yabuno, A.; Nishijima, A.; Nejo, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Neoantigen load and HLA-class i expression identify a subgroup of tumors with a T-cell-inflamed phenotype and favorable prognosis in homologous recombination-proficient high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, K.C.; Howitt, B.E.; Shukla, S.A.; Rodig, S.; Ritterhouse, L.L.; Liu, J.F.; Garber, J.E.; Chowdhury, D.; Wu, C.J.; D’Andrea, A.D.; et al. Association and prognostic significance of BRCA1/2-mutation status with neoantigen load, number of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and expression of PD-1/PD-L1 in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13587–13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, G. Comprehensive genomic analysis of microenvironment phenotypes in ovarian cancer. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, C.B.; Toukatly, M.N.; Kilgore, M.R.; Agnew, K.J.; Bernards, S.S.; Norquist, B.M.; Pennington, K.P.; Garcia, R.L.; Liao, J.B.; Swisher, E.M. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and homologous recombination deficiency are independently associated with improved survival in ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 153, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ou, T.; Lu, Y.; Wu, G.; Long, Y.; Pan, X.; Yao, D. Classification of ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 mutations, immune checkpoints, and tumor microenvironment based on immunogenomic profiling. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.; Lim, K.; Rambech, E.; Andersen, M.H.; Svane, I.M.; Andersen, O.; Jensen, L.H.; Nilbert, M.; Therkildsen, C. Lynch syndrome-associated epithelial ovarian cancer and its immunological profile. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 162, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehair, R.; Peres, L.C.; Mills, A.M. Expression of the Immune Checkpoints LAG-3 and PD-L1 in High-grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma: Relationship to Tumor-associated Lymphocytes and Germline BRCA Status. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2020, 39, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindl, A.; Khan, A.M.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Eason, K.; Sadanandam, A.; Orbegoso, C.; Punta, M.; Sottoriva, A.; Lise, S.; Banerjee, S.; et al. Microenvironmental niche divergence shapes BRCA1-dysregulated ovarian cancer morphological plasticity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coukos, G.; Tanyi, J.; Kandalaft, L.E. Opportunities in immunotherapy of ovarian cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, i11–i15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, E.; Pelosof, L.; Lemery, S.; Gong, Y.; Goldberg, K.B.; Farrell, A.T.; Keegan, P.; Veeraraghavan, J.; Wei, G.; Blumenthal, G.M.; et al. Systematic Review of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Oncology: From Personalized Medicine to Public Health. Oncologist 2021, 26, e1786–e1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.A.; Patel, V.G. The role of PD-L1 expression as a predictive biomarker: An analysis of all US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approvals of immune checkpoint inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.R.; Milne, K.; Nelson, B.H. PD-1 and CD103 are widely coexpressed on prognostically favorable intraepithelial CD8 T cells in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webb, J.R.; Milne, K.; Kroeger, D.R.; Nelson, B.H. PD-L1 expression is associated with tumor-infiltrating T cells and favorable prognosis in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 141, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darb-Esfahani, S.; Kunze, C.A.; Kulbe, H.; Sehouli, J.; Wienert, S.; Lindner, J.; Budczies, J.; Bockmayr, M.; Dietel, M.; Denkert, C.; et al. Prognostic impact of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in cancer cells and tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes in ovarian high grade serous carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucikova, J.; Rakova, J.; Hensler, M.; Kasikova, L.; Belicova, L.; Hladikova, K.; Truxova, I.; Skapa, P.; Laco, J.; Pecen, L.; et al. TIM-3 dictates functional orientation of the immune infiltrate in ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4820–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Lou, W.; Di, W.; Wu, X. Prognostic value of tumor PD-L1 expression combined with CD8(+) tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in high grade serous ovarian cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 52, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Choi, K.U.; Kim, A.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.H.; Suh, D.S.; Kwon, B.S.; Hwang, C. PD-L1 expression on stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is a favorable prognostic factor in ovarian serous carcinoma. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, M.; Goto, K.; Morimoto-Okazawa, A.; Haruna, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Hiramatsu, K.; Matsuzaki, S.; Kobayashi, E.; et al. PD-1+Tim3+tumor-infiltrating CD8 T cells sustain the potential for IFN-γproduction, but lose cytotoxic activity in ovarian cancer. Int. Immunol. 2020, 32, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekos, C.; Pils, D.; Dekan, S.; Hofstetter, G.; Horak, P.; Reinthaller, A.; Polterauer, S.; Schwameis, R.; Aust, S. PD-1 and PD-L1 expression on TILs in peritoneal metastases compared to ovarian tumor tissues and its associations with clinical outcome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, Y.; Anderson, A.C.; Kuchroo, V.K. TIM3 comes of age as an inhibitory receptor. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakellariou-Thompson, D.; Forget, M.A.; Hinchcliff, E.; Celestino, J.; Hwu, P.; Jazaeri, A.A.; Haymaker, C.; Bernatchez, C. Potential clinical application of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy for ovarian epithelial cancer prior or post-resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, S.; Montfort, A.; Pearce, O.M.T.; Topping, J.; Chakravarty, P.; Everitt, G.L.A.; Clear, A.; McDermott, J.R.; Ennis, D.; Dowe, T.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy modulates the immune microenvironment in metastases of tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3025–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Baal, J.O.A.M.; Lok, C.A.R.; Jordanova, E.S.; Horlings, H.; van Driel, W.J.; Amant, F.C.; Van de Vijver, K.K. The effect of the peritoneal tumor microenvironment on invasion of peritoneal metastases of high-grade serous ovarian cancer and the impact of NEOADJUVANT chemotherapy. Virchows Arch. 2020, 477, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pölcher, M.; Braun, M.; Friedrichs, N.; Rudlowski, C.; Bercht, E.; Fimmers, R.; Sauerwald, A.; Keyver-Paik, M.D.; Kübler, K.; Büttner, R.; et al. Foxp3+ cell infiltration and granzyme B+/Foxp3 + cell ratio are associated with outcome in neoadjuvant chemotherapy-treated ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2010, 59, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, S.; Le, N.; Lockley, M.; Brockbank, E.; Faruqi, A.; Said, I.; Jeyarajah, A.; Wuntakal, R.; Gilks, B.; Singh, N. Histopathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy as a prognostic biomarker in tubo-ovarian high-grade serous carcinoma: Updated Chemotherapy Response Score (CRS) results. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2019, 29, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesnage, S.J.L.; Auguste, A.; Genestie, C.; Dunant, A.; Pain, E.; Drusch, F.; Gouy, S.; Morice, P.; Bentivegna, E.; Lhomme, C.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) increases immune infiltration and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, R.A.; Robinson, B.W. Immunotherapy and chemotherapy—A practical partnership. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiringhelli, F.; Larmonier, N.; Schmitt, E.; Parcellier, A.; Cathelin, D.; Garrido, C.; Chauffert, B.; Solary, E.; Bonnotte, B.; Martin, F. CD4⁺CD25⁺ regulatory T cells suppress tumor immunity but are sensitive to cyclophosphamide which allows immunotherapy of established tumors to be curative. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, A.; Genestie, C.; Blanc-Durand, F.; Gouy, S.; Dunant, A.; Maulard, A.; Drusch, F.; Cheaib, B.; Michels, J.; Bentivegna, E.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy alters the balance of effector to suppressor immune cells in advanced ovarian cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobisse, S.; Genolet, R.; Roberti, A.; Tanyi, J.L.; Racle, J.; Stevenson, B.J.; Iseli, C.; Michel, A.; Le Bitoux, M.A.; Guillaume, P.; et al. Sensitive and frequent identification of high avidity neo-epitope specific CD8+ T cells in immunotherapy-naive ovarian cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandalaft, L.E.; Odunsi, K.; Coukos, G. Immune Therapy Opportunities in Ovarian Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2020, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarivalasis, A.; Morotti, M.; Mulvey, A.; Imbimbo, M.; Coukos, G. Cell therapies in ovarian cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211008399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, S.; Schwameis, R.; Gagic, T.; Müllauer, L.; Langthaler, E.; Prager, G.; Grech, C.; Reinthaller, A.; Krainer, M.; Pils, D.; et al. Precision Medicine Tumor Boards: Clinical Applicability of Personalized Treatment Concepts in Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, F.G.; Irving, M.; Kandalaft, L.E.; Coukos, G. Rational combinations of immunotherapy with radiotherapy in ovarian cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e417–e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study Author (Publication Year) | Number of Cases n= | PD-1 | PD-L1 | Definition of Positive TILs | Scoring PD-1 | Scoring PD-L1 | Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Webb (2015) [120] | 489 | PD-1+ cells: positive factor DFS in HGSOC, and not in other EOCs | Not studied | CD3 and CD8 >5 and < 5 | absolute numbers of PD-1+ and CD103+ | Not studied | immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry |
| Webb (2016) [121] | 490 | Not studied | PD-L1 expression: positive factor OS in HGSOC, and no difference in other EOCs | CD8 quantitative pathology imaging system | Not studied | PD-L1 scored as positive or negative, using a threshold of ≥1 positive cells | immunohistochemistry, TCGA |
| Darb Esfahni (2016) [122] | 215 | PD-1 on cancer cells and TILs: positive factor OS | PD-L1 on cancer cells and TILs: positive factor DFS and OS | i and sCD3 cut-off: > 65/mm2 | cancer cells PD-1+ > 11/mm2 | cancer cells PD-L1+ > 20/mm2 | Tissue microarrays + MRNA expression + MA |
| Wang (2017) [124] | 107 | Not studied | tumor PD-L1 expression: negative factor for OS; TILs-PD-L1+: no difference for OS | sTILs: score 1 (≤5/HPF), 2 (6–20/HPF), and 3 (≥20/HPF); iTILs: score 1 (≤5/HPF) and 2 (>5/HPF) | Not studied | PD-L1 staining in tumor cells scored: 0, negative; 1, weak expression; 2, moderate expression but weaker than placenta; and 3, equivalent or stronger expression than placenta. | immunohistochemistry |
| Fucikova (2019) [123] | 80 | PD-1 high: positive factor OS | PD-L1 (positive vs negative): positive factor OS | CD8: entire TME: absolute number of positive cells/mm2; CD20: cell surface/tumor section surface | PD-1, CTLA4, LAG-3: stroma and tumor of whole tumor | PD-L1 intratumoral and stromal, categorized as 1 (0%), 2 (1–4%), 4 (5–9%), and 4 (>10%); cut-off 5% to survival analysis | immunohistochemistry + flow cytometry + TCGA |
| Kim (2019) [125] | 248 | Not studied | sTILs-PD-L1+: positive factor OS | stromal sTILs, and iTILs: graded on a semiquantitative scale of 0 (none), 1+ (mild), 2+ (moderate), and 3+ (marked) | Not studied | intensities of PD-L1: intraepithelial (staining in tumor cells) | immunohistochemistry |
| Martin de la Fuente (2020) [84] | 130 | high PD-1 expression: better OS | high PD-L1 expression: better OS | grading CD3: 0%, < 1%, 1%, 2–4%, and ≥ 5% (high expression = ≥ 50% cores with ≥ 2% lymphocyte) | PD-1 expression ≥ 1% in ≤50% cores considered high expression | grading PD-L1 and PD-L1: 0%, <1%, 1–4%, ≥5%; iTILs PD-1 | Tissue microarray construction and immunohistochemistry |
| Chen (2020) [104] | 189 | Not studied | in HGSOC TPS: better DFS and OS (CPS: no difference) | Not studied | TPS and CPS; TPS and CPS ranged from 0 to 100; cutoff score ≥1% for TPS and ≥1 for CPS used to define PD-L1 positivity; for CPS intratumoral and peritumoral, stromal immune cells excluded | immunohistochemistry | |
| Bekos (2021) [127] | 111 | PD-1 in TILs in peritoneal metastases: positive factor OS | PD-L1 in TILs in peritoneal metastases: negative factor OS | CD8+: % (cut-off 44.3%) | PD-1 % in TILs (cut-off 40%) | PD-L1 % in TILs: ovarian tissue and peritoneal samples (cut-off 15%) | immunohistochemistry |
| Bansal (2021) [69] | 100 | Not studied | CPS or TCS PD-L1: no correlation with DFS | sTILs and iTILs: quantified in 5 different (400×) HPF on 3 sections/cases, 0: no lymphoid cells, 1: mild, 2: moderate, and 3: numerous numbers | Not studied | CPS | immunohistochemistry |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hudry, D.; Le Guellec, S.; Meignan, S.; Bécourt, S.; Pasquesoone, C.; El Hajj, H.; Martínez-Gómez, C.; Leblanc, É.; Narducci, F.; Ladoire, S. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Heterogeneity, Prognostic Impact, and Relationship with Immune Checkpoints. Cancers 2022, 14, 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215332
Hudry D, Le Guellec S, Meignan S, Bécourt S, Pasquesoone C, El Hajj H, Martínez-Gómez C, Leblanc É, Narducci F, Ladoire S. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Heterogeneity, Prognostic Impact, and Relationship with Immune Checkpoints. Cancers. 2022; 14(21):5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215332
Chicago/Turabian StyleHudry, Delphine, Solenn Le Guellec, Samuel Meignan, Stéphanie Bécourt, Camille Pasquesoone, Houssein El Hajj, Carlos Martínez-Gómez, Éric Leblanc, Fabrice Narducci, and Sylvain Ladoire. 2022. "Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Heterogeneity, Prognostic Impact, and Relationship with Immune Checkpoints" Cancers 14, no. 21: 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215332
APA StyleHudry, D., Le Guellec, S., Meignan, S., Bécourt, S., Pasquesoone, C., El Hajj, H., Martínez-Gómez, C., Leblanc, É., Narducci, F., & Ladoire, S. (2022). Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Heterogeneity, Prognostic Impact, and Relationship with Immune Checkpoints. Cancers, 14(21), 5332. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14215332







