The Impact of Clonal Hierarchy and Heterogeneity on Phenotypic Manifestations of Myelodysplastic Neoplasms
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Clonal Heterogeneity in MDS
3. Recurrent Cytogenetic and Molecular Alterations in MDS
4. Events Influencing Mutational Order
5. Clonal-Rank vs. Burden: Hierarchy Matters
6. Ancestral Versus Secondary, Random Versus Pre-Determined Clones
7. Impact of Mutation Combination on Phenotype and Response to Therapy
8. Updates to MDS Classification Incorporating Additional Genetic Factors: WHO vs. ICC
9. Prognostic Scoring Systems: From IPSS to IPSS-R and IPSS-M
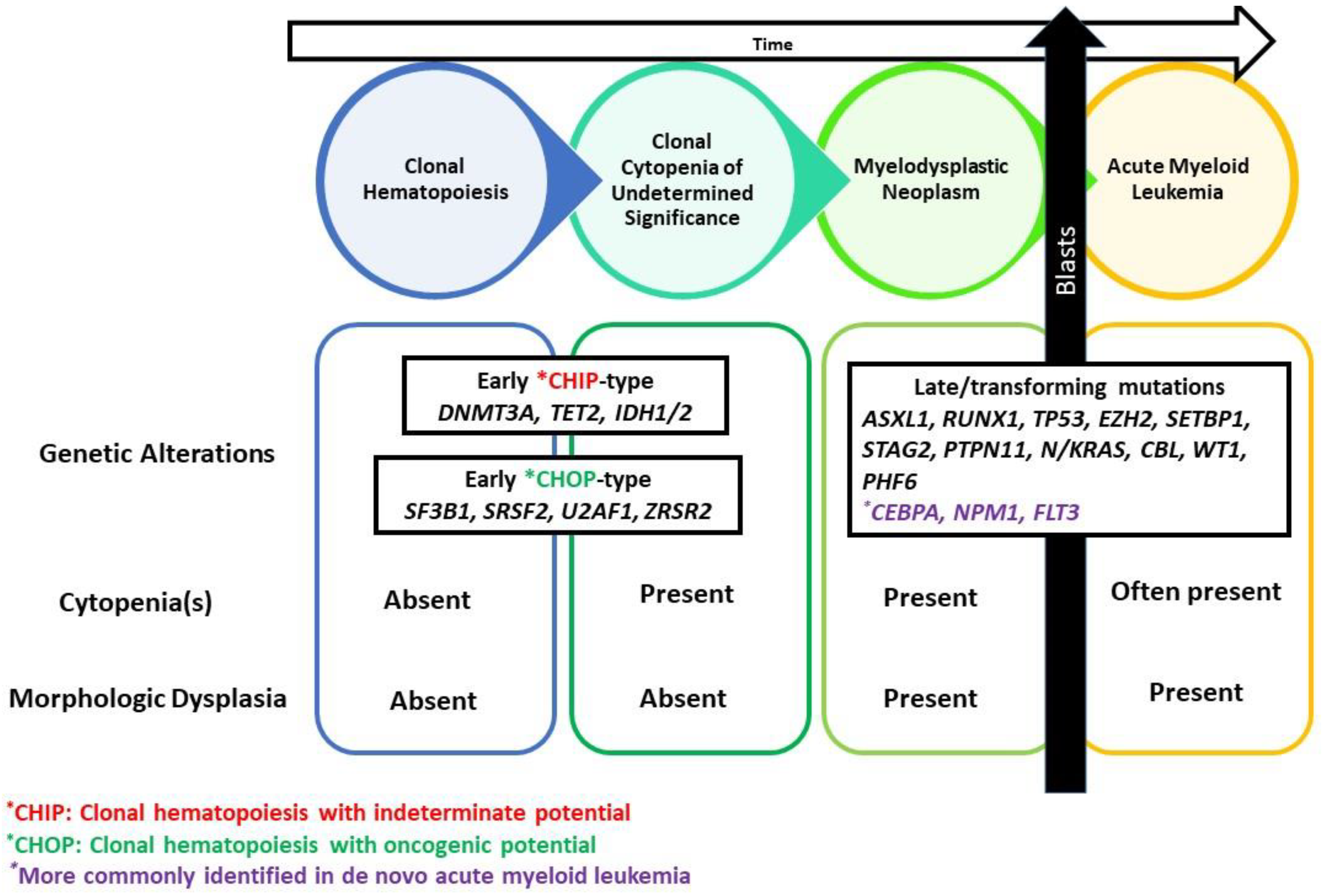
10. Clonal Hematopoiesis Ancestral Relationship to MDS
11. Transcriptomic Data & the Road to Improving MDS Stratification
12. The Role of Flow Cytometry Analysis in MDS Follow-Up
13. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.J.; Shen, D.; Shao, J.; Ding, L.; White, B.S.; Kandoth, C.; Miller, C.A.; Niu, B.; McLellan, M.D.; Dees, N.D.; et al. Clonal diversity of recurrently mutated genes in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walter, M.J.; Shen, D.; Ding, L.; Shao, J.; Koboldt, D.C.; Chen, K.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Dooling, D.; Abbott, R.; et al. Clonal architecture of secondary acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Kao, Y.R.; Sun, D.; Todorova, T.I.; Reynolds, D.; Narayanagari, S.R.; Montagna, C.; Will, B.; Verma, A.; Steidl, U. Myelodysplastic syndrome progression to acute myeloid leukemia at the stem cell level. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.; Khattra, J.; Yap, D.; Wan, A.; Laks, E.; Biele, J.; Ha, G.; Aparicio, S.; Bouchard-Cote, A.; Shah, S.P. PyClone: Statistical inference of clonal population structure in cancer. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 396–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, R.C.; Mar, B.G.; Mazzola, E.; Grauman, P.V.; Shareef, S.; Allen, S.L.; Pigneux, A.; Wetzler, M.; Stuart, R.K.; Erba, H.P.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia ontogeny is defined by distinct somatic mutations. Blood 2015, 125, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haferlach, T.; Nagata, Y.; Grossmann, V.; Okuno, Y.; Bacher, U.; Nagae, G.; Schnittger, S.; Sanada, M.; Kon, A.; Alpermann, T.; et al. Landscape of genetic lesions in 944 patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Leukemia 2014, 28, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Malcovati, L.; Tauro, S.; Gundem, G.; Van Loo, P.; Yoon, C.J.; Ellis, P.; Wedge, D.C.; Pellagatti, A.; et al. Chronic Myeloid Disorders Working Group of the International Cancer Genome C: Clinical and biological implications of driver mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2013, 122, 3616–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makishima, H.; Yoshizato, T.; Yoshida, K.; Sekeres, M.A.; Radivoyevitch, T.; Suzuki, H.; Przychodzen, B.; Nagata, Y.; Meggendorfer, M.; Sanada, M.; et al. Dynamics of clonal evolution in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Tuechler, H.; Greenberg, P.L.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Ossa, J.E.A.; Nannya, Y.; Devlin, S.M.; Creignou, M.; Pinel, P.; Monnier, L.; et al. Molecular International Prognostic Scoring System for Myelodysplastic Syndromes. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MDS Response Criteria. Available online: https://www.cibmtr.org/manuals/fim/1/en/topic/mds-mpn-response-criteria (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- McGranahan, N.; Swanton, C. Clonal Heterogeneity and Tumor Evolution: Past, Present, and the Future. Cell 2017, 168, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, M.J.; Werner, B.; Barnes, C.P.; Graham, T.A.; Sottoriva, A. Identification of neutral tumor evolution across cancer types. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Beau, M.M.; Espinosa, R., 3rd; Davis, E.M.; Eisenbart, J.D.; Larson, R.A.; Green, E.D. Cytogenetic and molecular delineation of a region of chromosome 7 commonly deleted in malignant myeloid diseases. Blood 1996, 88, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haase, D.; Germing, U.; Schanz, J.; Pfeilstocker, M.; Nosslinger, T.; Hildebrandt, B.; Kundgen, A.; Lubbert, M.; Kunzmann, R.; Giagounidis, A.A.; et al. New insights into the prognostic impact of the karyotype in MDS and correlation with subtypes: Evidence from a core dataset of 2124 patients. Blood 2007, 110, 4385–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadersten, M.; Saft, L.; Smith, A.; Kulasekararaj, A.; Pomplun, S.; Gohring, G.; Hedlund, A.; Hast, R.; Schlegelberger, B.; Porwit, A.; et al. TP53 mutations in low-risk myelodysplastic syndromes with del(5q) predict disease progression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soenen, V.; Preudhomme, C.; Roumier, C.; Daudignon, A.; Lai, J.L.; Fenaux, P. 17p Deletion in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Analysis of breakpoints and deleted segments by fluorescence in situ. Blood 1998, 91, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshizato, T.; Nannya, Y.; Atsuta, Y.; Shiozawa, Y.; Iijima-Yamashita, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Shiraishi, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Nagata, Y.; Sato, Y.; et al. Genetic abnormalities in myelodysplasia and secondary acute myeloid leukemia: Impact on outcome of stem cell transplantation. Blood 2017, 129, 2347–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernard, E.; Nannya, Y.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Devlin, S.M.; Tuechler, H.; Medina-Martinez, J.S.; Yoshizato, T.; Shiozawa, Y.; Saiki, R.; Malcovati, L.; et al. Implications of TP53 allelic state for genome stability, clinical presentation and outcomes in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemia: Integrating Morphological, Clinical, and Genomic Data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Sanada, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Nowak, D.; Nagata, Y.; Yamamoto, R.; Sato, Y.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Kon, A.; Nagasaki, M.; et al. Frequent pathway mutations of splicing machinery in myelodysplasia. Nature 2011, 478, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhommeau, F.; Dupont, S.; Della Valle, V.; James, C.; Trannoy, S.; Masse, A.; Kosmider, O.; Le Couedic, J.P.; Robert, F.; Alberdi, A.; et al. Mutation in TET2 in myeloid cancers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, T.J.; Ding, L.; Walter, M.J.; McLellan, M.D.; Lamprecht, T.; Larson, D.E.; Kandoth, C.; Payton, J.E.; Baty, J.; Welch, J.; et al. DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Dooling, D.J.; Larson, D.E.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; Delehaunty, K.D.; McGrath, S.D.; et al. Recurring mutations found by sequencing an acute myeloid leukemia genome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikoloski, G.; Langemeijer, S.M.; Kuiper, R.P.; Knops, R.; Massop, M.; Tonnissen, E.R.; van der Heijden, A.; Scheele, T.N.; Vandenberghe, P.; de Witte, T.; et al. Somatic mutations of the histone methyltransferase gene EZH2 in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Hosono, N.; Nakazawa, H.; Przychodzen, B.; Polprasert, C.; Carraway, H.E.; Sekeres, M.A.; Radivoyevitch, T.; Yoshida, K.; Sanada, M.; et al. A novel genetic and morphologic phenotype of ARID2-mediated myelodysplasia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Cazzola, M.; Boultwood, J.; Malcovati, L.; Vyas, P.; Bowen, D.; Pellagatti, A.; Wainscoat, J.S.; Hellstrom-Lindberg, E.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; et al. Chronic Myeloid Disorders Working Group of the International Cancer Genome C: Somatic SF3B1 mutation in myelodysplasia with ring sideroblasts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1384–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Graubert, T.A.; Shen, D.; Ding, L.; Okeyo-Owuor, T.; Lunn, C.L.; Shao, J.; Krysiak, K.; Harris, C.C.; Koboldt, D.C.; Larson, D.E.; et al. Recurrent mutations in the U2AF1 splicing factor in myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat. Genet. 2011, 44, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kon, A.; Shih, L.Y.; Minamino, M.; Sanada, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Okuno, Y.; Bando, M.; Nakato, R.; et al. Recurrent mutations in multiple components of the cohesin complex in myeloid neoplasms. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, M.; Suzuki, T.; Shih, L.Y.; Otsu, M.; Kato, M.; Yamazaki, S.; Tamura, A.; Honda, H.; Sakata-Yanagimoto, M.; Kumano, K.; et al. Gain-of-function of mutated C-CBL tumour suppressor in myeloid neoplasms. Nature 2009, 460, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortmann, C.A.; Kent, D.G.; Nangalia, J.; Silber, Y.; Wedge, D.C.; Grinfeld, J.; Baxter, E.J.; Massie, C.E.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Menon, S.; et al. Effect of mutation order on myeloproliferative neoplasms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaszar, E.; Kirouac, D.C.; Yu, M.; Wang, W.; Qiao, W.; Cooke, M.P.; Boitano, A.E.; Ito, C.; Zandstra, P.W. Rapid expansion of human hematopoietic stem cells by automated control of inhibitory feedback signaling. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mossner, M.; Jann, J.C.; Wittig, J.; Nolte, F.; Fey, S.; Nowak, V.; Oblander, J.; Pressler, J.; Palme, I.; Xanthopoulos, C.; et al. Mutational hierarchies in myelodysplastic syndromes dynamically adapt and evolve upon therapy response and failure. Blood 2016, 128, 1246–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woll, P.S.; Kjallquist, U.; Chowdhury, O.; Doolittle, H.; Wedge, D.C.; Thongjuea, S.; Erlandsson, R.; Ngara, M.; Anderson, K.; Deng, Q.; et al. Myelodysplastic syndromes are propagated by rare and distinct human cancer stem cells in vivo. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 794–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awada, H.; Kerr, C.M.; Durmaz, A.; Adema, V.; Gurnari, C.; Pagliuca, S.; Zawit, M.; Kongkiatkamon, S.; Rogers, H.J.; Saunthararajah, Y.; et al. Clonal trajectories and cellular dynamics of myeloid neoplasms with SF3B1 mutations. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3324–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, Y.; Makishima, H.; Kerr, C.M.; Przychodzen, B.P.; Aly, M.; Goyal, A.; Awada, H.; Asad, M.F.; Kuzmanovic, T.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Invariant patterns of clonal succession determine specific clinical features of myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, S. Genetics of MDS. Blood 2019, 133, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenberg, P.; Cox, C.; LeBeau, M.M.; Fenaux, P.; Morel, P.; Sanz, G.; Sanz, M.; Vallespi, T.; Hamblin, T.; Oscier, D.; et al. International scoring system for evaluating prognosis in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 1997, 89, 2079–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, P.L.; Tuechler, H.; Schanz, J.; Sanz, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Sole, F.; Bennett, J.M.; Bowen, D.; Fenaux, P.; Dreyfus, F.; et al. Revised international prognostic scoring system for myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2012, 120, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schanz, J.; Tuchler, H.; Sole, F.; Mallo, M.; Luno, E.; Cervera, J.; Granada, I.; Hildebrandt, B.; Slovak, M.L.; Ohyashiki, K.; et al. New comprehensive cytogenetic scoring system for primary myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and oligoblastic acute myeloid leukemia after MDS derived from an international database merge. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangat, N.; Patnaik, M.M.; Tefferi, A. Myelodysplastic syndromes: Contemporary review and how we treat. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalban-Bravo, G.; Garcia-Manero, G. Myelodysplastic syndromes: 2018 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos, F.; Robledo, C.; Pereira, A.; Pedro, C.; Benito, R.; de Paz, R.; Del Rey, M.; Insunza, A.; Tormo, M.; Diez-Campelo, M.; et al. Multidimensional assessment of patient condition and mutational analysis in peripheral blood, as tools to improve outcome prediction in myelodysplastic syndromes: A prospective study of the Spanish MDS group. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, E534–E541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, K.B.; Yeager, M.; Zhou, W.; Wacholder, S.; Wang, Z.; Rodriguez-Santiago, B.; Hutchinson, A.; Deng, X.; Liu, C.; Horner, M.J.; et al. Detectable clonal mosaicism and its relationship to aging and cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurie, C.C.; Laurie, C.A.; Rice, K.; Doheny, K.F.; Zelnick, L.R.; McHugh, C.P.; Ling, H.; Hetrick, K.N.; Pugh, E.W.; Amos, C.; et al. Detectable clonal mosaicism from birth to old age and its relationship to cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loh, P.R.; Genovese, G.; Handsaker, R.E.; Finucane, H.K.; Reshef, Y.A.; Palamara, P.F.; Birmann, B.M.; Talkowski, M.E.; Bakhoum, S.F.; McCarroll, S.A.; et al. Insights into clonal haematopoiesis from 8342 mosaic chromosomal alterations. Nature 2018, 559, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, G.; Kahler, A.K.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lindberg, J.; Rose, S.A.; Bakhoum, S.F.; Chambert, K.; Mick, E.; Neale, B.M.; Fromer, M.; et al. Clonal hematopoiesis and blood-cancer risk inferred from blood DNA sequence. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, S.; Fontanillas, P.; Flannick, J.; Manning, A.; Grauman, P.V.; Mar, B.G.; Lindsley, R.C.; Mermel, C.H.; Burtt, N.; Chavez, A.; et al. Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2488–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malcovati, L.; Galli, A.; Travaglino, E.; Ambaglio, I.; Rizzo, E.; Molteni, E.; Elena, C.; Ferretti, V.V.; Catricala, S.; Bono, E.; et al. Clinical significance of somatic mutation in unexplained blood cytopenia. Blood 2017, 129, 3371–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlush, L.I.; Minden, M.D. Preleukemia: The normal side of cancer. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valent, P.; Kern, W.; Hoermann, G.; Milosevic Feenstra, J.D.; Sotlar, K.; Pfeilstöcker, M.; Germing, U.; Sperr, W.R.; Reiter, A.; Wolf, D.; et al. Clonal Hematopoiesis with Oncogenic Potential (CHOP): Separation from CHIP and Roads to AML. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelson, S.; Collord, G.; Ng, S.W.K.; Weissbrod, O.; Mendelson Cohen, N.; Niemeyer, E.; Barda, N.; Zuzarte, P.C.; Heisler, L.; Sundaravadanam, Y.; et al. Prediction of acute myeloid leukaemia risk in healthy individuals. Nature 2018, 559, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.; Mencia-Trinchant, N.; Savenkov, O.; Simon, M.S.; Cheang, G.; Lee, S.; Samuel, M.; Ritchie, E.K.; Guzman, M.L.; Ballman, K.V.; et al. Somatic mutations precede acute myeloid leukemia years before diagnosis. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, A.S.; Gibson, C.J.; Ebert, B.L. The genetics of myelodysplastic syndrome: From clonal haematopoiesis to secondary leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coelho-Silva, J.L.; Silveira, D.R.A.; Pereira-Martins, D.A.; Rojas, C.A.O.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Rego, E.M.; Machado-Neto, J.A.; Bendit, I.; Rocha, V.; Traina, F. Molecular-Based Score inspired on metabolic signature improves prognostic stratification for myelodysplastic syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thol, F.; Yun, H.; Sonntag, A.K.; Damm, F.; Weissinger, E.M.; Krauter, J.; Wagner, K.; Morgan, M.; Wichmann, M.; Gohring, G.; et al. Prognostic significance of combined MN1, ERG, BAALC, and EVI1 (MEBE) expression in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Ann. Hematol. 2012, 91, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Huang, H.H.; Hou, H.A.; Lin, C.C.; Tseng, M.H.; Kao, C.J.; Lu, T.P.; Chou, W.C.; Tien, H.F. A 4-lncRNA scoring system for prognostication of adult myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loken, M.R.; van de Loosdrecht, A.; Ogata, K.; Orfao, A.; Wells, D.A. Flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndromes: Report from a working conference. Leuk. Res. 2008, 32, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, K.; Kishikawa, Y.; Satoh, C.; Tamura, H.; Dan, K.; Hayashi, A. Diagnostic application of flow cytometric characteristics of CD34+ cells in low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 2006, 108, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Della Porta, M.G.; Picone, C.; Pascutto, C.; Malcovati, L.; Tamura, H.; Handa, H.; Czader, M.; Freeman, S.; Vyas, P.; Porwit, A.; et al. Multicenter validation of a reproducible flow cytometric score for the diagnosis of low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes: Results of a European LeukemiaNET study. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogata, K.; Della Porta, M.G.; Malcovati, L.; Picone, C.; Yokose, N.; Matsuda, A.; Yamashita, T.; Tamura, H.; Tsukada, J.; Dan, K. Diagnostic utility of flow cytometry in low-grade myelodysplastic syndromes: A prospective validation study. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.C.; Wang, T.F.; Li, C.C.; Kao, R.H.; Li, D.K.; Su, Y.C.; Wells, D.A.; Loken, M.R. Flow cytometric scoring system as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk. Res. 2011, 35, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, D.A.; Benesch, M.; Loken, M.R.; Vallejo, C.; Myerson, D.; Leisenring, W.M.; Deeg, H.J. Myeloid and monocytic dyspoiesis as determined by flow cytometric scoring in myelodysplastic syndrome correlates with the IPSS and with outcome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2003, 102, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porwit, A.; van de Loosdrecht, A.A.; Bettelheim, P.; Brodersen, L.E.; Burbury, K.; Cremers, E.; Della Porta, M.G.; Ireland, R.; Johansson, U.; Matarraz, S.; et al. Revisiting guidelines for integration of flow cytometry results in the WHO classification of myelodysplastic syndromes-proposal from the International/European LeukemiaNet Working Group for Flow Cytometry in MDS. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Westers, T.M.; Ireland, R.; Kern, W.; Alhan, C.; Balleisen, J.S.; Bettelheim, P.; Burbury, K.; Cullen, M.; Cutler, J.A.; Della Porta, M.G.; et al. Standardization of flow cytometry in myelodysplastic syndromes: A report from an international consortium and the European LeukemiaNet Working Group. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Clonal Hierarchy | The order in which mutations are acquired. “Founder” (ancestral) mutations, typically involving epigenetic modifiers and splicing factors in MDS, occur early and are followed by “successor” alterations, which typically involve the signaling cascades, transcription factors, and copy number alterations |
| Clonal Burden | Size of a population with a specific genetic aberrancy (for mutations, typically inferred using variant allele frequency “VAF” by next-generation sequencing analysis) |
| Clonal Sweeping | The process by which a neoplastic population develops new advantageous genetic lesions, allowing it to expand and dominate the neoplasm (“selective sweeps” or “positive selection”) |
| Neutral Growth | Egalitarian propagation of neoplastic populations harboring genetic aberrations that do not affect cellular fitness |
| Clonal Heterogeneity | Genetic diversity among neoplastic populations resulting from an interplay between clonal sweeping and/or neutral growth |
| Mutational Combination | Pre-determined (in contrast to random) co-occurrence of certain mutations resulting in a specific disease phenotype |
| Epistasis | The conditional relationship between two genes that can determine a single phenotype (an allele of one gene hides or masks the phenotype of another gene) |
| Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities |
|---|
| Most common: del(7q), del(5q) & + 8 |
| Others: dup(1q), del(20q), del(11q), del(12p)/t(12p), del(17p)/ i(17q), del(18q), 12q gains, del(13q), der(1;7)(q10;p10) |
| Recurrent Mutations |
| DNA methylation:TET2, DNMT3A & IDH1/IDH2 |
| Chromatin/histone modification:KMT2D, EZH2, ARID2 & ASXL1 |
| RNA splicing:SF3B1, SRSF2, U2AF1, U2AF2 & ZXRSR2 |
| Cohesin complex:STAG2, RAD21, SMC1A, SMC3, NIPBL, PDS5b & CTCF |
| Transcription:RUNX1, ETV6, GATA2 & IRF1 |
| RAS pathway:NRAS, KRAS, PTPN11, NF1 & CBL |
| DNA repair machinery:TP53, PPM1D, BRCC3, FANCL & ATM |
| Signaling molecules:JAK2, KIT, MPL, GNB1 & FLT3 |
| Early CHIP (clonal hematopoiesis with indeterminate potential)-type |
| DNMT3A, TET2, ASXL1, IDH2 |
| CHOP (clonal hematopoiesis with oncogenic potential)-type |
| U2AF1, SRSF2, ZRSR2, SF3B1 |
| Late/ Transforming mutations |
| ASXL1, RUNX1, TP53, EZH2, SETBP1, STAG2, NPM1, FLT3, PTPN11, N/KRAS, CBL, WT1, PHF6 |
| MDS-Defining Genetic Abnormalities Per WHO & ICC |
| Isolated del(5q), SF3B1, Multi-hit/bi-allelic TP53 mutations |
| IPSS-M Top Predictors of Adverse Outcomes |
| Multi-hit TP53 alterations, FLT3 mutation, KMT2A partial tandem duplication |
| Evolution of Prognostic Scoring Systems in Myelodysplastic Neoplasms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables in the International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS)-1997 | ||||
| Blast Percentage <5% 5–10% 11–20% 21–29% | Cytopenia(s) -Hemoglobin <10 g/dL -Platelets <100 × 109/L -Leukocyte count <1.8 × 109/L) | Cytogenetic Groups -Good (diploid karyotype, -Y, del(20q), del(5q) -Poor (chromosome 7 anomalies or complex karyotype with 3 abnormalities) -Intermediate (all other abnormalities) | ||
| Variables in the Revised International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-R)-2012 | ||||
| Blast Percentage ≤2% >2 and <5% 5–10% >10% and <20% | Cytopenia(s) -Hemoglobin <8 vs. >8 and <10 vs. 10 g/dL -Platelet count <50 vs. >50 and <100 vs. 100 × 109/L -Absolute neutrophil count 0.8 vs. <0.8 × 109/L | Cytogenetic Categories -Very good (-Y, del(11q) -Good (normal, del(20q), del(5q)del(12p)- or two abnormalities including del(5q) -Intermediate (+8, del(7q), i(17q), +19, +21, other single abnormalities, independent clones, two abnormalities not including del( 5q) or -7/del(7q) -Poor (-7, inv(3), del(3q), two abnormalities including del(7q), complex karyotype with 3 abnormalities) -Very poor (complex karyotype with >3abnormalities) | ||
| Variables in the Molecular International Prognostic Scoring System (IPSS-M)-2022 | ||||
| Blast Percentage | Hemoglobin level | Platelet Count | IPSS-R Cytogenetic Category | Top Molecular Predictors of Adverse Outcome among 31 genes -Multi-hit TP53 alterations -FLT3 mutation(s) -KMT2A partial tandem duplication |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Hussein, S.; Loghavi, S. The Impact of Clonal Hierarchy and Heterogeneity on Phenotypic Manifestations of Myelodysplastic Neoplasms. Cancers 2022, 14, 5690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225690
El Hussein S, Loghavi S. The Impact of Clonal Hierarchy and Heterogeneity on Phenotypic Manifestations of Myelodysplastic Neoplasms. Cancers. 2022; 14(22):5690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225690
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Hussein, Siba, and Sanam Loghavi. 2022. "The Impact of Clonal Hierarchy and Heterogeneity on Phenotypic Manifestations of Myelodysplastic Neoplasms" Cancers 14, no. 22: 5690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225690
APA StyleEl Hussein, S., & Loghavi, S. (2022). The Impact of Clonal Hierarchy and Heterogeneity on Phenotypic Manifestations of Myelodysplastic Neoplasms. Cancers, 14(22), 5690. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14225690







