Platelet and Cancer-Cell Interactions Modulate Cancer-Associated Thrombosis Risk in Different Cancer Types
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
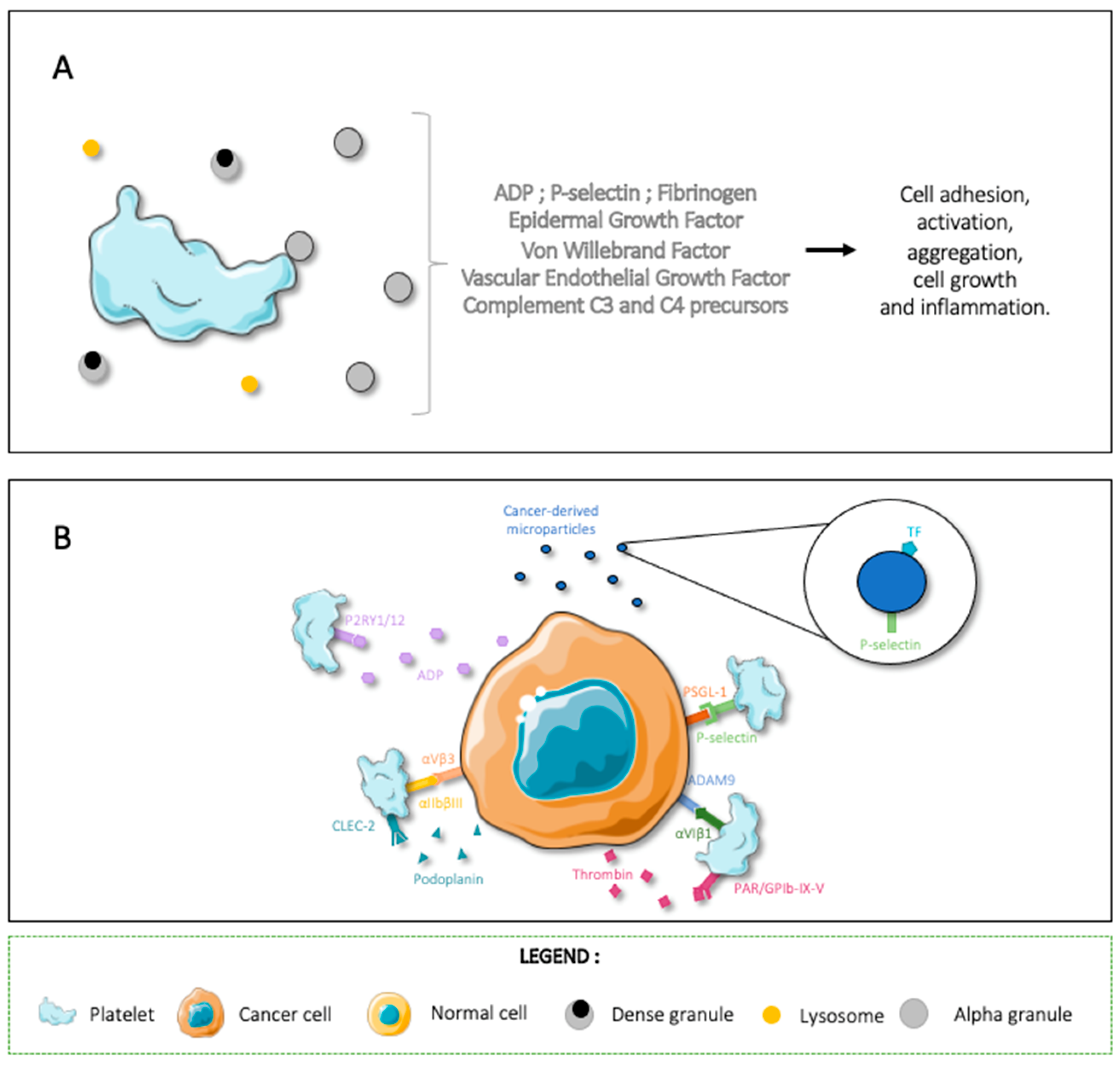
2. Platelet and Cancer-Cell Interactions
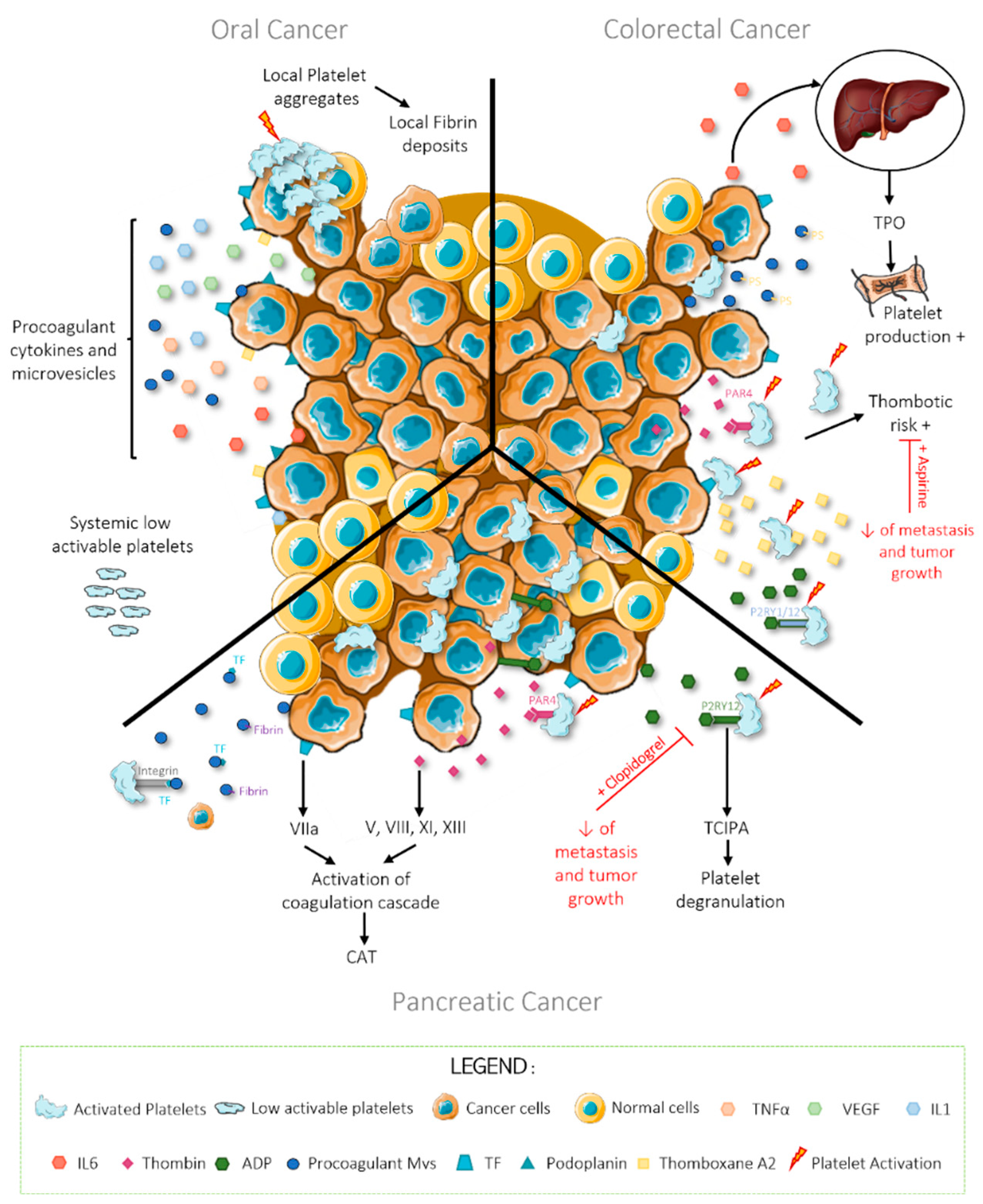
3. Oral Cancer
4. Colorectal Cancer
5. Pancreatic Cancer
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAM9 | ADAM Metallopeptidase Domain 9 |
| ADP | Adenosine Diphosphate |
| ALK | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase |
| ANXA1/5 | Annexin A1/5 |
| BRCA2 | Breast cancer type 2 susceptibility protein |
| CAT | Cancer-associated thrombosis |
| CDKN2B | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitor B |
| CLEC-2 | C-type lectin-like type II transmembrane receptor |
| COX-1/2 | Cyclooxygenase 1/2 |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| CTNNB1 | Catenin beta-1 |
| GPIbα | Glycoprotein Ib alpha |
| GPIV | Glycoprotein IV |
| HNC | Head-and-neck cancer |
| HPGD | 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (NAD(+)) |
| ICAM1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| IDH1/2 | Isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP) cytoplasmic or mitochondrial |
| IL1/6 | Interleukin 1/6 |
| ITGB1 | Integrin beta-1 |
| KEAP1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| KRAS | Proto-Ongene GTPase |
| MET | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor |
| MPV | Mean platelet volume |
| MVs | Microvesicles |
| NFKB1 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit |
| OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| P2RY1/P2RY12 | Purinergic Receptor P2Y1/P2Y12 |
| PAR | Protease-Activated Receptors |
| PDAC | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma |
| PLF4 | Platelet factor 4 |
| PSGL-1 | P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 |
| ROS | Proto-Ongene 1, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase |
| STK11 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STK11 |
| TCIPA | Tumor-cell-induced-platelet-aggregation |
| TF | Tissue Factor |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor α |
| TPO | Thrombopoietin |
| TXA2 | Thromboxan A2 |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| VTE | Venous thromboembolism |
| vWF | Von Willebrand Factor |
References
- Metharom, P.; Falasca, M.; Berndt, M.C. The history of armand trousseau and cancer-associated thrombosis. Cancers 2019, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plantureux, L.; Crescence, L.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Effects of platelets on cancer progression. Thromb. Res. 2018, 164, S40–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timp, J.F.; Braekkan, S.K.; Versteeg, H.H.; Cannegieter, S.C. Epidemiology of cancer-associated venous thrombosis. Blood 2013, 122, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falanga, A.; Marchetti, M.; Vignoli, A. Coagulation and cancer: Biological and clinical aspects. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisada, Y.; Mackman, N. Cancer-associated pathways and biomarkers of venous thrombosis. Blood 2017, 130, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Culakova, E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Lyman, G.H. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevestre, M.A.; Soudet, S. Epidemiology and risk factors for cancer-associated thrombosis. J. Med. Vasc. 2020, 45, 6S3–6S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiva, O.; Newcomb, R.; Connors, J.M.; Al-Samkari, H. Cancer and thrombosis: New insights to an old problem. J. Med. Vasc. 2020, 45, 6S8–6S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Culakova, E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Lyman, G.H. Frequency, risk factors, and trends for venous thromboembolism among hospitalized cancer patients. Cancer 2007, 110, 2339–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiari, R.; Ricciuti, B.; Landi, L.; Morelli, A.M.; Delmonte, A.; Spitaleri, G.; Cortinovis, D.L.; Lamberti, G.; Facchinetti, F.; Pilotto, S.; et al. ROS1-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer is associated with a high rate of venous thromboembolism: Analysis from a phase II, prospective, multicenter, two-Arms trial (METROS). Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ades, S.; Kumar, S.; Alam, M.; Goodwin, A.; Weckstein, D.; Dugan, M.; Ashikaga, T.; Evans, M.; Verschraegen, C.; Holmes, C.E. Tumor oncogene (KRAS) status and risk of venous thrombosis in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2015, 13, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunbar, A.; Bolton, K.L.; Devlin, S.M.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Gao, J.; Mones, J.V.; Wills, J.; Kelly, D.; Farina, M.; Cordner, K.B.; et al. Genomic profiling identifies somatic mutations predicting thromboembolic risk in patients with solid tumors. Blood 2021, 137, 2103–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.H.; Melloni, G.E.M.; Gulhan, D.C.; Park, P.J.; Haigis, K.M. The origins and genetic interactions of KRAS mutations are allele- and tissue-specific. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granado-Martínez, P.; Garcia-Ortega, S.; González-Sánchez, E.; McGrail, K.; Selgas, R.; Grueso, J.; Gil, R.; Naldaiz-Gastesi, N.; Rhodes, A.C.; Hernandez-Losa, J.; et al. STK11 (LKB1) missense somatic mutant isoforms promote tumor growth, motility and inflammation. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, S. Mutation Hotspots in the β-catenin gene: Lessons from the human cancer genome databases. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.M.; Scheffler, M.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Scheel, A.H.; Ulmer, B.; Wolf, J.; Buettner, R. Comprehensive analysis of TP53 and KEAP1 mutations and their impact on survival in localized- and advanced-stage NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Zhou, X.; Yin, J.; Lei, J.; Jiang, H.Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Chan, T.; Hannon, G.J.; Mergner, W.J.; Abraham, J.M. Intragenic mutations of CDKN2B and CDKN2A in primary human esophageal cancers. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1995, 4, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaccio, C.; Sabatino, G.; Medico, E.; Girolami, F.; Follenzi, A.; Reato, G.; Sottile, A.; Naldini, L.; Comoglio, P.M. The MET oncogene drives a genetic programme linking cancer to haemostasis. Nature 2005, 434, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Segura, P.; Zamorano-León, J.J.; Acosta, D.; Santos-Sancho, J.M.; Modrego, J.; Caldés, T.; de la Hoya, M.; Díaz-Rubio, E.; Díaz-Millán, I.; de Las Heras, N.; et al. BRCA2 gene mutations and coagulation-associated biomarkers. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawil, N.; Bassawon, R.; Meehan, B.; Nehme, A.; Montermini, L.; Gayden, T.; De Jay, N.; Spinelli, C.; Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Choi, D.; et al. Glioblastoma cell populations with distinct oncogenic programs release podoplanin as procoagulant extracellular vesicles. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1682–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, B.; Versteeg, H.H. Cancer-associated thrombosis: The search for the holy grail continues. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palacios-Acedo, A.L.; Mège, D.; Crescence, L.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Platelets, thrombo-inflammation, and cancer: Collaborating with the enemy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, A.S.; Khorana, A.A.; McCrae, K.R. Mechanisms and biomarkers of cancer-associated thrombosis. Transl. Res. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2020, 225, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.M.; Brill, A.; Mezouar, S.; Crescence, L.; Gallant, M.; Dubois, C.; Wagner, D.D. Tissue factor expressed by circulating cancer cell-derived microparticles drastically increases the incidence of deep vein thrombosis in mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erpenbeck, L.; Schön, M.P. Neutrophil extracellular traps: Protagonists of cancer progression? Oncogene 2017, 36, 2483–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools-Lartigue, J.; Spicer, J.; McDonald, B.; Gowing, S.; Chow, S.; Giannias, B.; Bourdeau, F.; Kubes, P.; Ferri, L. Neutrophil extracellular traps sequester circulating tumor cells and promote metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3446–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.B.; Hajal, C.; Benjamin, D.C.; Yu, C.; Azizgolshani, H.; Hynes, R.O.; Kamm, R.D. Inflamed neutrophils sequestered at entrapped tumor cells via chemotactic confinement promote tumor cell extravasation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7022–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Chen, J.; Huang, D.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Chen, F.; et al. DNA of neutrophil extracellular traps promotes cancer metastasis via CCDC25. Nature 2020, 583, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridlender, Z.G.; Sun, J.; Kim, S.; Kapoor, V.; Cheng, G.; Ling, L.; Worthen, G.S.; Albelda, S.M. Polarization of tumor-associated neutrophil (TAN) phenotype by TGF-β: “N1” versus “N2” TAN. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darbousset, R.; Thomas, G.M.; Mezouar, S.; Frère, C.; Bonier, R.; Mackman, N.; Renné, T.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Tissue factor-positive neutrophils bind to injured endothelial wall and initiate thrombus formation. Blood 2012, 120, 2133–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egorina, E.M.; Sovershaev, M.A.; Olsen, J.O.; Østerud, B. Granulocytes do not express but acquire monocyte-derived tissue factor in whole blood: Evidence for a direct transfer. Blood 2008, 111, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, N.; Brambilla, M.; Camera, M.; Carbone, A.; Tremoli, E.; Donati, M.B.; De Gaetano, G.; Cerletti, C. Human polymorphonuclear leukocytes produce and express functional tissue factor upon stimulation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritis, K.; Doumas, M.; Mastellos, D.; Micheli, A.; Giaglis, S.; Magotti, P.; Rafail, S.; Kartalis, G.; Sideras, P.; Lambris, J.D. A novel C5a receptor-tissue factor cross-talk in neutrophils links innate immunity to coagulation pathways. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4794–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.A.; Brill, A.; Duerschmied, D.; Schatzberg, D.; Monestier, M.; Myers, D.D.; Wrobleski, S.K.; Wakefield, T.W.; Hartwig, J.H.; Wagner, D.D. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15880–15885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longstaff, C.; Varjú, I.; Sótonyi, P.; Szabó, L.; Krumrey, M.; Hoell, A.; Bóta, A.; Varga, Z.; Komorowicz, E.; Kolev, K. Mechanical stability and fibrinolytic resistance of clots containing fibrin, DNA, and histones. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 6946–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plantureux, L.; Mège, D.; Crescence, L.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Impacts of cancer on platelet production, activation and education and mechanisms of cancer-associated thrombosis. Cancers 2018, 10, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nuyttens, B.P.; Thijs, T.; Deckmyn, H.; Broos, K. Platelet adhesion to collagen. Thromb. Res. 2011, 127, S26–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, J.N.; Italiano, J.E. Platelets: Production, morphology and ultrastructure. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iba, T.; Levy, J.H. Inflammation and thrombosis: Roles of neutrophils, platelets and endothelial cells and their interactions in thrombus formation during sepsis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plantureux, L.; Mege, D.; Crescence, L.; Carminita, E.; Robert, S.; Cointe, S.; Brouilly, N.; Ezzedine, W.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; et al. The interaction of platelets with colorectal cancer cells inhibits tumor growth but promotes metastasis. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.R.; Zhang, D.; Oswald, B.E.; Carrim, N.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lavalle, C.; McKeown, T.; Marshall, A.H.; et al. Platelets are versatile cells: New discoveries in hemostasis, thrombosis, immune responses, tumor metastasis and beyond. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpatkin, S.; Ambrogio, C.; Pearlstein, E. The Role of Tumor-Induced Platelet Aggregation, Platelet Adhesion and Adhesive Proteins in Tumor Metastasis. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1988, 283, 585–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Sierko, E.; Hempel, D.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Platelets and cancer angiogenesis nexus. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsopanoglou, N.E.; Maragoudakis, M.E. Role of thrombin in angiogenesis and tumor progression. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2004, 30, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammadova-Bach, E.; Zigrino, P.; Brucker, C.; Bourdon, C.; Freund, M.; De Arcangelis, A.; Abrams, S.I.; Orend, G.; Gachet, C.; Mangin, P.H. Platelet integrin A6β1 controls lung metastasis through direct binding to cancer cell–derived ADAM9. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e88245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaker, H.; Bundred, N.J.; Landberg, G.; Pritchard, S.A.; Albadry, H.; Nicholson, S.L.; Harries, L.J.; Heah, J.Y.E.; Castle, J.; Kirwan, C.C. Breast cancer stromal clotting activation (tissue factor and thrombin): A pre-invasive phenomena that is prognostic in invasion. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omarova, F.; Rosing, J.; Bertina, R.M.; Castoldi, E. Negatively charged phospholipids stimulate factor XI activation by thrombin. Thromb. Update 2021, 2, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.; Miller, W.; Rosenfeldt, L.; Kombrinck, K.; Flick, M.J.; Steinbrecher, K.A.; Harmel-Laws, E.; Mullins, E.S.; Shaw, M.; Witte, D.P.; et al. Thrombin drives tumorigenesis in colitis-associated colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3020–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Bae, J.-S. Tumor-associated macrophages and neutrophils in tumor microenvironment. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 6058147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Lan, H. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor metastasis: Biological roles and clinical therapeutic applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Acedo, A.L.; Mezouar, S.; Mège, D.; Crescence, L.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. P2RY12-Inhibitors reduce cancer-associated thrombosis and tumor growth in pancreatic cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Wysoczynski, M.; Kijowski, J.; Marquez-Curtis, L.; Machalinski, B.; Ratajczak, J.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowska-Wieczorek, A.; Marquez-Curtis, L.A.; Wysoczynski, M.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Enhancing effect of platelet-derived microvesicles on the invasive potential of breast cancer cells. Transfusion 2006, 46, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mege, D.; Crescence, L.; Ouaissi, M.; Sielezneff, I.; Guieu, R.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Fibrin-bearing microparticles: Marker of thrombo-embolic events in pancreatic and colorectal cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97394–97406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mezouar, S.; Frère, C.; Darbousset, R.; Mege, D.; Crescence, L.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Role of platelets in cancer and cancer-associated thrombosis: Experimental and clinical evidences. Thromb. Res. 2016, 139, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mezouar, S.; Darbousset, R.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Inhibition of platelet activation prevents the P-selectin and integrin-dependent accumulation of cancer cell microparticles and reduces tumor growth and metastasis in Vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palacios-Acedo, A.L.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Platelet-educated cancer cells and tumor-educated platelets: An egg-and-chicken debate. ICTHIC Magazine, 17 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ercan, H.; Mauracher, L.-M.; Grilz, E.; Hell, L.; Hellinger, R.; Schmid, J.A.; Moik, F.; Ay, C.; Pabinger, I.; Zellner, M. Alterations of the platelet proteome in lung cancer: Accelerated F13A1 and ER processing as new actors in hypercoagulability. Cancers 2021, 13, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F13A1 Coagulation Factor XIII A Chain [Homo Sapiens (Human)]—Gene—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/2162 (accessed on 24 January 2022).
- Sundermann, B.V.; Uhlmann, L.; Hoffmann, J.; Freier, K.; Thiele, O.C. The localization and risk factors of squamous cell carcinoma in the oral cavity: A retrospective study of 1501 cases. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haen, P.; Mege, D.; Crescence, L.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Thrombosis risk associated with head and neck cancer: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haen, P.; Crescence, L.; Mege, D.; Altié, A.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Oral squamous cell carcinoma is associated with a low thrombosis risk due to storage pool deficiency in platelets. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, N.; Fedewa, S.; Chen, A.Y. Epidemiology and demographics of the head and neck cancer population. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 30, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Nanavati, R.; Modi, T.; Dobariya, C. Oral cancer: Etiology and risk Factors: A review. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Dong, Y. Human papillomavirus and oral squamous cell carcinoma: A review of HPV-positive oral squamous cell carcinoma and possible strategies for future. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2017, 41, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, R.R.; Yan, S.-D.; Huang, C.-C. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope 1994, 104, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.G.; Man, Q.W.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Xiong, X.P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, W.M.; Sun, Z.J.; Jia, J.; Zhang, W.F.; et al. Elevated level of circulating platelet-derived microparticles in oral cancer. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, M.-C.; Chan, C.-P.; Ho, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-J.; Lin, P.-S.; Lin, B.-R.; Huang, Y.-L.; Hahn, L.-J.; Yeh, H.-W.; Wang, Y.-J.; et al. Signaling pathways for induction of platelet aggregation by SAS tongue cancer cells—A mechanism of hematogenous metastasis. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2008, 38, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.; Kiss, K.; Lelkaitis, G.; Juhl, K.; Persson, M.; Charabi, B.W.; Mortensen, J.; Forman, J.L.; Sørensen, A.L.; Jensen, D.H.; et al. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (UPAR), tissue factor (TF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR): Tumor expression patterns and prognostic value in oral cancer. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jagielska, B.; Symonides, M.; Stachurska, E.; Kawecky, A.; Kraszewska, E. Coagulation disorders in patients with locally advanced head and neck cancer—Should they really be disregarded? Neoplasma 2011, 58, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosugi, T.; Takagi, I.; Ariga, Y.; Okada, S.; Morimitsu, T.; Mihara, H. Fibrinolysis-coagulation system in patients with cancer of the head and neck. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 1982, 236, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langiu, M.; Palacios-Acedo, A.-L.; Crescence, L.; Mege, D.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Neutrophils, cancer and thrombosis: The new bermuda triangle in cancer research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbousset, R.; Delierneux, C.; Mezouar, S.; Hego, A.; Lecut, C.; Guillaumat, I.; Riederer, M.A.; Evans, R.J.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; et al. P2X1 expressed on polymorphonuclear neutrophils and platelets is required for thrombosis in mice. Blood 2014, 124, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Abate, D.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdel-Rahman, O.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdoli, A.; Abdollahpour, I.; Abdulle, A.S.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawicki, T.; Ruszkowska, M.; Danielewicz, A.; Niedźwiedzka, E.; Arłlukowicz, T.; Przybyłlowicz, K.E. A review of colorectal cancer in terms of epidemiology, risk factors, development, symptoms and diagnosis. Cancers 2021, 13, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaiher, J.; Ravipati, A.; Grams, B.; Chowdhury, S.; Alatise, O.; Are, C. Colorectal cancer-global burden, trends, and geographical variations. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 115, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, J.; Luo, Q.; Kuang, M.; Mao, M.; Dai, S.; Wang, X. Prediction of poor outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer: Elevated preoperative prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT). Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.Y.; Qin, J.Q.; Lin, F.Q. Mean platelet volume/platelet count ratio in colorectal cancer: A retrospective clinical study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braun, A.; Anders, H.J.; Gudermann, T.; Mammadova-Bach, E. Platelet-cancer interplay: Molecular mechanisms and new therapeutic avenues. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 665534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretis, C.; Youssef, H.; Chapman, M. Hypercoagulation in colorectal cancer: What can platelet indices tell us? Platelets 2015, 26, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, R.T.; Wang, X.S. Elevated mean platelet volume is associated with presence of colon cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2014, 15, 10501–10504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrugno, A.; Yunga, S.T.; Sylman, J.L.; Zilberman-Rudenko, J.; Shirai, T.; Hebert, J.F.; Kayton, R.; Zhang, Y.; Nan, X.; Shatzel, J.J.; et al. The role of coagulation and platelets in colon cancer-associated thrombosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillem-Llobat, P.; Dovizio, M.; Bruno, A.; Ricciotti, E.; Cufino, V.; Sacco, A.; Grande, R.; Alberti, S.; Arena, V.; Cirillo, M.; et al. Aspirin prevents colorectal cancer metastasis in mice by splitting the crosstalk between platelets and tumor cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, J.A.; Cole, B.F.; Sandler, R.S.; Haile, R.W.; Ahnen, D.; Bresalier, R.; McKeown-Eyssen, G.; Summers, R.W.; Rothstein, R.; Burke, C.A.; et al. A randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal adenomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandler, R.S.; Halabi, S.; Baron, J.A.; Budinger, S.; Paskett, E.; Keresztes, R.; Petrelli, N.; Pipas, J.M.; Karp, D.D.; Loprinzi, C.L.; et al. A randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal adenomas in patients with previous colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornelas, A.; Zacharias-Millward, N.; Menter, D.G.; Davis, J.S.; Lichtenberger, L.; Hawke, D.; Hawk, E.; Vilar, E.; Bhattacharya, P.; Millward, S. Beyond COX-1: The effects of aspirin on platelet biology and potential mechanisms of chemoprevention. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and cancer: Triggers, mechanisms and consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mege, D.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Ouaissi, M.; Robert, S.; Sielezneff, I.; Sastre, B.; Dignat-George, F.; Dubois, C. The origin and concentration of circulating microparticles differ according to cancer type and evolution: A prospective single-center study. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mege, D.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Tumor-derived microparticles to monitor colorectal cancer evolution. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1765, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Bi, Y.; Kou, J.; Shi, J.; Piao, D. Phosphatidylserine exposing-platelets and microparticles promote procoagulant activity in colon cancer patients. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2016, 35, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aier, I.; Semwal, R.; Sharma, A.; Varadwaj, P.K. A systematic assessment of statistics, risk factors, and underlying features involved in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2019, 58, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Candia, E. Mechanisms of platelet activation by thrombin: A short history. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mege, D.; Mezouar, S.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Microparticles and cancer thrombosis in animal models. Thromb. Res. 2016, 140, S21–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.M.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Lacroix, R.; Dignat-George, F.; Lombardo, D.; Dubois, C. Cancer cell-derived microparticles bearing P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 accelerate thrombus formation in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1913–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mezouar, S.; Mege, D.; Darbousset, R.; Farge, D.; Debourdeau, P.; Dignat-George, F.; Panicot-Dubois, L.; Dubois, C. Involvement of platelet-derived microparticles in tumor progression and thrombosis. Semin. Oncol. 2014, 41, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniuchi, K.; Furihata, M.; Naganuma, S.; Sakaguchi, M.; Saibara, T. Overexpression of PODXL/ITGB1 and BCL7B/ITGB1 accurately predicts unfavorable prognosis compared to the TNM staging system in postoperative pancreatic cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In ‘T Veld, S.G.J.G.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-educated platelets. Blood 2019, 133, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palacios-Acedo, A.-L.; Langiu, M.; Crescence, L.; Mège, D.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Platelet and Cancer-Cell Interactions Modulate Cancer-Associated Thrombosis Risk in Different Cancer Types. Cancers 2022, 14, 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030730
Palacios-Acedo A-L, Langiu M, Crescence L, Mège D, Dubois C, Panicot-Dubois L. Platelet and Cancer-Cell Interactions Modulate Cancer-Associated Thrombosis Risk in Different Cancer Types. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):730. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030730
Chicago/Turabian StylePalacios-Acedo, Ana-Luisa, Mélanie Langiu, Lydie Crescence, Diane Mège, Christophe Dubois, and Laurence Panicot-Dubois. 2022. "Platelet and Cancer-Cell Interactions Modulate Cancer-Associated Thrombosis Risk in Different Cancer Types" Cancers 14, no. 3: 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030730
APA StylePalacios-Acedo, A.-L., Langiu, M., Crescence, L., Mège, D., Dubois, C., & Panicot-Dubois, L. (2022). Platelet and Cancer-Cell Interactions Modulate Cancer-Associated Thrombosis Risk in Different Cancer Types. Cancers, 14(3), 730. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030730






