The Next Paradigm Shift in the Management of Clear Cell Renal Cancer: Radiogenomics—Definition, Current Advances, and Future Directions
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. What Is Radiogenomics?
3. Associations between Image Features and Mutations in Single Genes Commonly Implicated in ccRCC
4. Beyond Mutations in Common Pathogenic Single Genes in Clear Cell Kidney Cancer: Establishing Image Biomarkers for Epigenetic, Regulatory, and Multiple Gene Expression Signatures
5. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmidt, L.S.; Linehan, W.M. Genetic predisposition to kidney cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latif, F.; Tory, K.; Gnarra, J.; Yao, M.; Duh, F.M.; Orcutt, M.L.; Stackhouse, T.; Kuzmin, I.; Modi, W.; Geil, L.; et al. Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 1993, 260, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandrino, F.; Shinagare, A.B.; Bossé, D.; Choueiri, T.K.; Krajewski, K.M. Radiogenomics in renal cell carcinoma. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamshidi, N.; Jonasch, E.; Zapala, M.; Korn, R.L.; Brooks, J.D.; Ljungberg, B.; Kuo, M.D. The radiogenomic risk score stratifies outcomes in a renal cell cancer phase 2 clinical trial. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 2798–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katabathina, V.S.; Marji, H.; Khanna, L.; Ramani, N.; Yedururi, S.; Dasyam, A.; Menias, C.O.; Prasad, S.R. Decoding genes: Current update on radiogenomics of select abdominal malignancies. RadioGraphics 2020, 40, 1600–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubner, M.G.; Smith, A.D.; Sandrasegaran, K.; Sahani, D.V.; Pickhard, P.J. CT texture analysis: Definitions, applications, biologic correlates, and challenges. Radiographics 2017, 37, 1483–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davnall, F.; Yip, C.S.; Ljungqvist, G.; Selmi, M.; Ng, F.; Sanghera, B.; Ganeshan, B.; Miles, K.A.; Cook, G.J.; Goh, V. Assessment of tumor heterogeneity: An emerging imaging tool for clinical practice? Insights Into. Imaging 2012, 3, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlo, C.A.; Di Paolo, P.L.; Chaim, J.; Hakimi, A.A.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Russo, P.; Hricak, H.; Motzer, R.; Hsieh, J.J.; Akin, O. Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Associations between CT imaging features and mutations. Radiology 2014, 270, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagare, A.B.; Vikram, R.; Jaffe, C.; Akin, O.; Kirby, J.; Huang, E.; Freymann, J.; Sainani, N.I.; Sadow, C.A.; Bathala, T.K.; et al. Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Preliminary findings of the cancer genome atlas–renal cell carcinoma (TCGA–RCC) imaging research group. Abdom. Imaging 2015, 40, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, F.; Mallio, C.A. Relationship between visceral adipose tissue and genetic mutations (VHL and KDM5C) in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. La Radiol. Med. 2021, 126, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Z.; Shen, Q.; Hu, Z.; Chen, F. Identifying BAP1 mutations in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma by CT radiomics: Preliminary findings. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, B.; Durmaz, E.S.; Kaya, O.K.; Kilickesmez, O. Machine learning-based unenhanced CT texture analysis for predicting BAP1 mutation status of clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Acta Radiol. 2020, 61, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, P.; Tamboli, P.; Vikram, R.; Rao, A. Imaging-genomic pipeline for identifying gene mutations using three-dimensional intra-tumor heterogeneity features. J. Med. Imaging 2015, 2, 041009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kocak, B.; Durmaz, E.S.; Ates, E.; Ulusan, M.B. Radiogenomics in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Machine learning–based high-dimensional quantitative CT texture analysis in predicting PBRM1 mutation status. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, W55–W63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Z.; Hannan, R.; Thomas, K.; Pedrosa, I.; Kapur, P.; Brugarolas, J.; Mou, X.; Wang, J. Reliable gene mutation prediction in clear cell renal cell carcinoma through multi-classifier multi-objective radiogenomics model. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 215008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigliano, C.; Badia, S.; Bellini, D.; Rengo, M.; Caruso, D.; Tito, C.; Miglietta, S.; Palleschi, G.; Pastore, A.L.; Carbone, A.; et al. Radiogenomics in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Correlations between advanced CT imaging (texture analysis) and microRNAs expression. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819878458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liang, B. Renal cell carcinoma: Predicting RUNX3 methylation level and its consequences on survival with CT features. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 5415–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Lin, C.; Li, X.; Quan, X. Renal Cell Carcinoma: Predicting DNA Methylation Subtyping and Its Consequences on Overall Survival With Computed Tomography Imaging Characteristics. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2020, 44, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, N.; Jonasch, E.; Zapala, M.; Korn, R.L.; Aganovic, L.; Zhao, H.; Tumkur Sitaram, R.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Banerjee, S.; Brooks, J.D.; et al. The radiogenomic risk score: Construction of a prognostic quantitative, noninvasive image-based molecular assay for renal cell carcinoma. Radiology 2015, 277, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowen, L.; Xiaojing, L. Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Associations between mRNA-based subtyping and CT imaging features. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, e32–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Q.; Hung, S.-C.; Rathmell, W.K.; Shen, L.; Wang, L.; Lin, W.; Fielding, J.R.; Khandani, A.H.; Woods, M.E.; Milowsky, M.I.; et al. Integrative radiomics expression predicts molecular subtypes of primary clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Cho, H.-H.; Joung, J.-G.; Jeon, H.G.; Jeong, B.C.; Jeon, S.S.; Lee, H.M.; Nam, D.H.; Park, W.Y.; Kim, C.K. Integrative radiogenomics approach for risk assessment of post-operative metastasis in pathological T1 renal cell carcinoma: A pilot retrospective cohort study. Cancers 2020, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, G.; Sun, Q.; Zhai, G.; Wu, G.; Li, Z.-C. Validation of CT radiomics for prediction of distant metastasis after surgical resection in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Exploring the underlying signaling pathways. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5032–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Lin, Y.-Q.; Gao, R.-Z.; Wen, R.; Qin, H.; He, Y.; Yang, H. Radiomic profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma reveals subtypes with distinct prognoses and molecular pathways. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Chen, L.; Luo, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y. Exploration of an Integrative Prognostic Model of Radiogenomics Features With Underlying Gene Expression Patterns in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Luo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ma, X. Integrative radiogenomics analysis for predicting molecular features and survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 9960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricketts, C.J.; De Cubas, A.A.; Fan, H.; Smith, C.C.; Lang, M.; Reznik, E.; Bowlby, R.; Gibb, E.A.; Akbani, R.; Beroukhim, R.; et al. The cancer genome atlas comprehensive molecular characterization of renal cell carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshizato, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Maekawa, S.; Okuno, Y.; Kamura, T.; Shimamura, T.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Nagae, G.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Integrated molecular analysis of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugarolas, J. Molecular genetics of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, R.W.; Kapur, P.; Serie, D.J.; Parasramka, M.; Ho, T.H.; Cheville, J.C.; Frenkel, E.; Parker, A.S.; Brugarolas, J. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma subtypes identified by BAP1 and PBRM1 expression. J. Urol. 2016, 195, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.I.; Marker, M.; Redzematovic, A.; Chen, Y.-B.; Selcuklu, S.D.; Weinhold, N.; Bouvier, N.; Huberman, K.H.; et al. Genomic biomarkers of a randomized trial comparing first-line everolimus and sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.-Z.; Xu, L.-W.; Zhou, C.-C.; Lu, T.-Z.; Yao, W.-T.; Wu, R.; Zhao, Y.C.; Xu, X.; Hu, Z.K.; Wang, M.A.; et al. BAP1 mutation-specific microRNA signature predicts clinical outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients with wild-type BAP1. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Fu, Q.; An, H.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, J. Decreased expression of SETD2 predicts unfavorable prognosis in patients with nonmetastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Medicine 2015, 94, e2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, B.J.; Reznik, E.; Ghanaat, M.; Kashan, M.; Becerra, M.F.; Casuscelli, J.; Tennenbaum, D.; Redzematovic, A.; Carlo, M.I.; Sato, Y.; et al. Characterizing recurrent and lethal small renal masses in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using recurrent somatic mutations. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2019, 37, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, A.; Ostrovnaya, I.; Reva, B.; Schultz, N.; Chen, Y.; Gonen, M.; Liu, H.; Takeda, S.; Voss, M.H.; Tickoo, S.K.; et al. ccRCC Cancer Genome Atlas (KIRC TCGA) Research Network investigators Adverse outcomes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma with mutations of 3p21 epigenetic regulators BAP1 and SETD2: A report by MSKCC and the KIRC TCGA research network. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3259–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Chang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Xu, J. Low expression of mucin-4 predicts poor prognosis in patients with clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Medicine 2016, 95, e3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gati, A.; Kouidhi, S.; Marrakchi, R.; El Gaaied, A.; Kourda, N.; Derouiche, A.; Chebil, M.; Caignard, A.; Perier, A. Obesity and renal cancer: Role of adipokines in the tumor-immune system conflict. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e27810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajandram, R.; Perumal, K.; Yap, N.Y. Prognostic biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma: Is there a relationship with obesity? Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Xu, H. Prognostic value of meta-signature miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: An integrated miRNA expression profiling analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Q.; Zhu, S.; Bai, J.; Zheng, J. RUNX3 regulates renal cell carcinoma metastasis via targeting miR-6780a-5p/E-cadherin/EMT signaling axis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Bai, J.; Li, W.; Mei, P.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Pan, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, J. RUNX3 suppresses migration, invasion and angiogenesis of human renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, C.; Kim, Y.W.; Ha, Y.S.; Kim, I.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Yun, S.J.; Moon, S.K.; Bae, S.C.; Kim, W.J. RUNX3 methylation as a predictor for disease progression in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 105, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richiardi, L.; Fiano, V.; Vizzini, L.; De Marco, L.; Delsedime, L.; Akre, O.; Tos, A.G.; Merletti, F. Promoter methylation in APC, RUNX3, and GSTP1 and mortality in prostate cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3161–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, K.; Hirata, H.; Majid, S.; Chen, Y.; Zaman, M.S.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; Hinoda, Y.; Dahiya, R. Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-3 (Dkk-3) induces apoptosis in human renal cell carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urakami, S.; Shiina, H.; Enokida, H.; Hirata, H.; Kawamoto, K.; Kawakami, T.; Kikuno, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Majid, S.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Wnt antagonist family genes as biomarkers for diagnosis, staging, and prognosis of renal cell carcinoma using tumor and serum DNA. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6989–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Ljungberg, B.; Grankvist, K.; Rasmuson, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Brooks, J.D. Gene expression profiling predicts survival in conventional renal cell carcinoma. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Network CGAR. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nature 2013, 499, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Velasco, G.; Culhane, A.C.; Fay, A.P.; Hakimi, A.A.; Voss, M.H.; Tannir, N.M.; Tamboli, P.; Appleman, L.J.; Bellmunt, J.; Kimryn Rathmell, W.; et al. Molecular subtypes improve prognostic value of international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium prognostic model. Oncologist 2017, 22, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brannon, A.R.; Reddy, A.; Seiler, M.; Arreola, A.; Moore, D.T.; Pruthi, R.S.; Wallen, E.M.; Nielsen, M.E.; Liu, H.; Nathanson, K.L.; et al. Molecular stratification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by consensus clustering reveals distinct subtypes and survival patterns. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, S.; Martinez, P.; Joshi, T.; Birkbak, N.J.; Santos, C.R.; Rowan, A.J.; Pickering, L.; Gore, M.; Larkin, J.; Szallasi, Z.; et al. Systematic evaluation of the prognostic impact and intratumour heterogeneity of clear cell renal cell carcinoma biomarkers. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricketts, C.J.; Hill, V.K.; Linehan, W.M. Tumor-specific hypermethylation of epigenetic biomarkers, including SFRP1, predicts for poorer survival in patients from the TCGA Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma (KIRC) project. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.R.; Ricketts, C.; Gentle, D.; McRonald, F.; Carli, N.; Khalili, H.; Brown, M.; Kishida, T.; Yao, M.; Banks, R.E.; et al. Genome-wide methylation analysis identifies epigenetically inactivated candidate tumour suppressor genes in renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kocak, B.; Durmaz, E.S.; Erdim, C.; Ates, E.; Kaya, O.K.; Kilickesmez, O. Radiomics of renal masses: Systematic review of reproducibility and validation strategies. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez, E.R.; Aerts, H.J.; Gu, Y.; Goldgof, D.B.; De Ruysscher, D.; Dekker, A.; Korn, R.; Gillies, R.J.; Lambin, P. A semiautomatic CT-based ensemble segmentation of lung tumors: Comparison with oncologists’ delineations and with the surgical specimen. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 105, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Dam, I.E.; de Koste, J.R.v.S.; Hanna, G.G.; Muirhead, R.; Slotman, B.J.; Senan, S. Improving target delineation on 4-dimensional CT scans in stage I NSCLC using a deformable registration tool. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 96, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Schieda, N.; James, N.; McInnes, M.D.; Wu, M.; Thornhill, R.E. Effect of phase of enhancement on texture analysis in renal masses evaluated with non-contrast-enhanced, corticomedullary, and nephrographic phase–enhanced CT images. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1676–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Ahmed, F.S.; Akin, O.; Luk, L.; Guo, X.; Yang, H.; Yoon, J.; Hakimi, A.A.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zhao, B. Uncontrolled Confounders May Lead to False or Overvalued Radiomics Signature: A Proof of Concept Using Survival Analysis in a Multicenter Cohort of Kidney Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, B.; Kaya, O.K.; Erdim, C.; Kus, E.A.; Kilickesmez, O. Artificial intelligence in renal mass characterization: A systematic review of methodologic items related to modeling, performance evaluation, clinical utility, and transparency. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhong, H.; Huang, C.; Huang, J.; Lin, Y.; Huang, J. Characterization of Molecular Heterogeneity Associated With Tumor Microenvironment in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma to Aid Immunotherapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 736540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullo, R.L.; Daimiel, I.; Morris, E.A.; Pinker, K. Combining molecular and imaging metrics in cancer: Radiogenomics. Insights Into. Imaging 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxi, V.; Edwards, R.; Montalto, M.; Saha, S. Digital pathology and artificial intelligence in translational medicine and clinical practice. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serie, D.J.; Joseph, R.W.; Cheville, J.C.; Ho, T.H.; Parasramka, M.; Hilton, T.; Thompson, R.H.; Leibovich, B.C.; Parker, A.S.; Eckel-Passow, J.E. Clear cell type A and B molecular subtypes in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Tumor heterogeneity and aggressiveness. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurowski, M.A. Radiogenomics: What it is and why it is important. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2015, 12, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
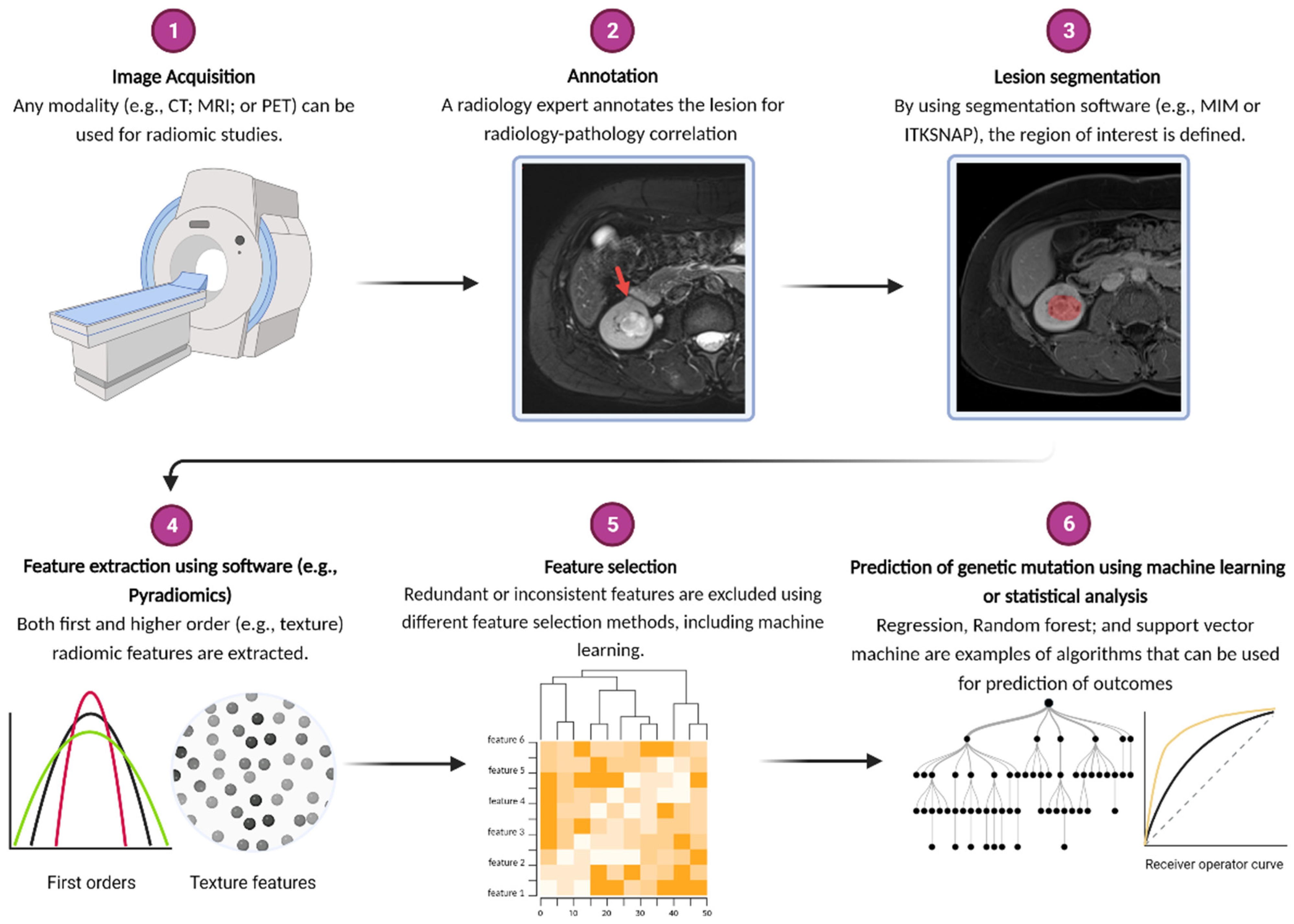
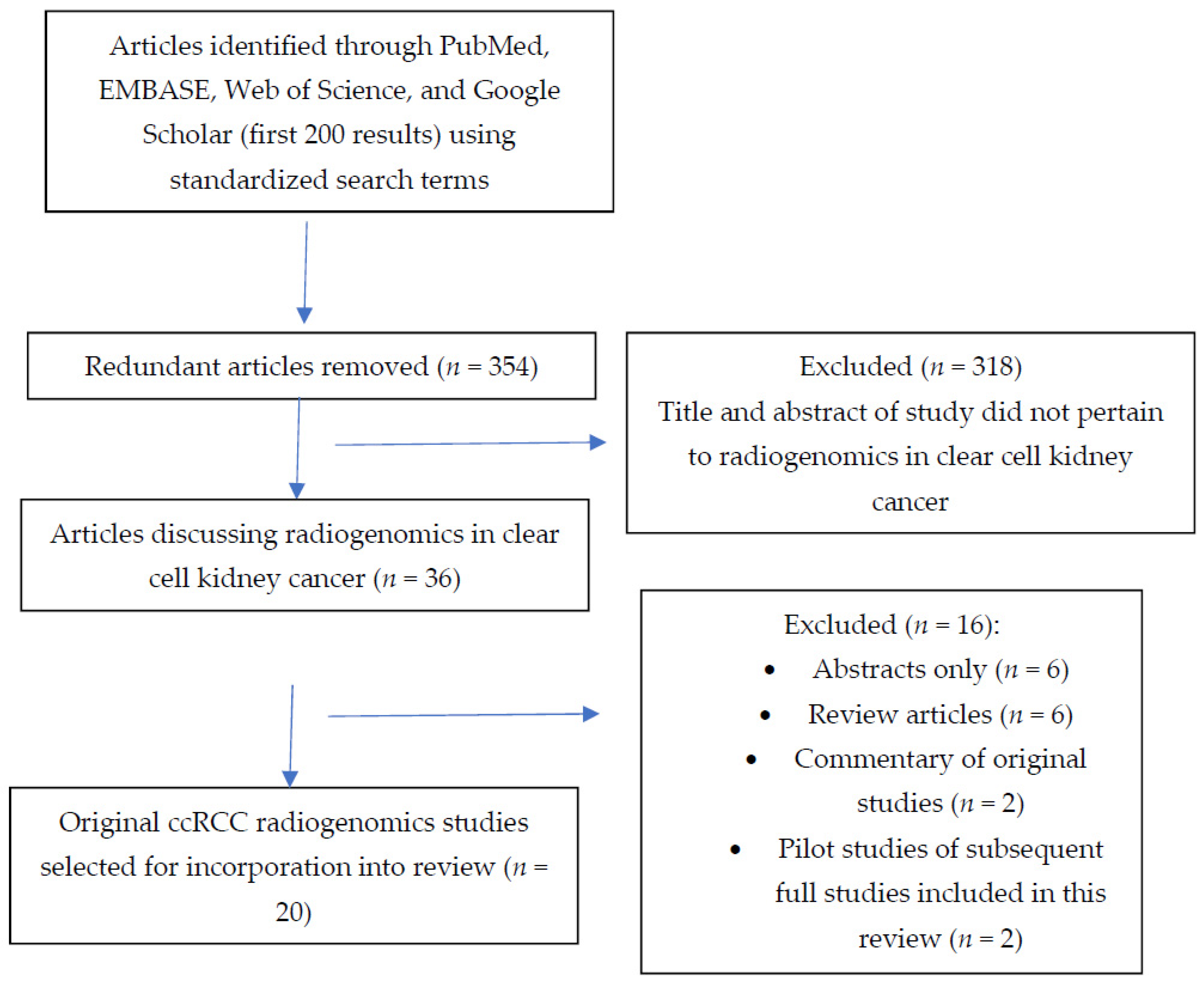
| Author | Title | Year of Publication | Patient # | Feature Extraction (Number) | ±Machine Learning | Image Phase Used | Genes Studied | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karlo et al. [9] | Radiogenomics of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Associations between CT Imaging Features and Mutations | 2014 | 233 | Radiologist (10) | − | CT | BAP1 VHL KD5MC | BAP1 and KD5MC: renal vein invasion (OR 3.50 and 3.89) VHL: ill-defined margin (OR 0.49), nodular enhancement (OR 2.33), intratumoral vasculature (OR 0.51) |
| Shinagare et al. [10] | Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Preliminary findings of the cancer genome atlas–renal cell carcinoma (TCGA–RCC) imaging research group | 2015 | 103 | Radiologist (6) | − | Contrast-enhanced CT | BAP1 MUC-4 | BAP1: Ill-defined margin and calcification MUC4: Exophytic growth |
| Greco et al. [11] | Relationship between visceral adipose tissue and genetic mutations (VHL and KDM5C) in clear cell renal cell carcinoma | 2021 | 97 | Computational (3) | − | CT | KDM5C vs. VHL | KDM5C higher TAT and VAT area than VHL |
| Feng et al. [12] | Identifying BAP1 Mutations in Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma by CT Radiomics: Preliminary Findings | 2020 | 54 | Computational (58) | + (Random Forest) | CT | BAP1 | AUC 0.77 |
| Kocak et al. [13] | Machine learning-based unenhanced CT texture analysis for predicting BAP1 mutation status of clear cell renal cell carcinomas | 2020 | 65 | Computational (6) | + (Random Forest) | CT | BAP1 | AUC 0.897 |
| Ghosh et al. [14] | Imaging-genomic pipeline for identifying gene mutations using three-dimensional intra-tumor heterogeneity features | 2015 | 78 | Computational (1636) | + (Random Forest) | CT nephrographic phase | BAP1 | AUC 0.71 |
| Kocak et al. [15] | Radiogenomics in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Machine Learning-Based High-Dimensional Quantitative CT Texture Analysis in Predicting PBRM1 Mutation Status | 2019 | 45 | Computational (10) | + (Random Forest) | CT | PBRM1 | AUC 0.987 |
| Chen et al. [16] | Reliable gene mutation prediction in clear cell renal cell carcinoma through multi-classifier multi-objective radiogenomics model | 2018 | 57 | Computational (43) | + (6 classifier composite) | CT | VHL PBRM1 BAP1 | AUC 0.88 0.86 0.93 Mutation status prediction |
| Marigliano et al. [17] | Radiogenomics in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: correlations between advanced CT imaging (texture analysis) and microRNAs expression | 2019 | 20 | Computational (6) | − | CT | miR-21-5p | R2 = 0.25 between entropy and change in miR-21-5p expression between tumor and surrounding parenchyma |
| Cen et al. [18] | Renal cell carcinoma: predicting RUNX3 methylation level and its consequences on survival with CT features | 2019 | 106 | Radiologist (9) | − | CT | RUNX3 methylation | High methylation: left side (OR 2.70), ill-defined margin (OR 2.69), intratumoral vascularity (OR 3.29)—AUC of 0.73 |
| Yu et al. [19] | Renal Cell Carcinoma: Predicting DNA Methylation Subtyping and Its Consequences on Overall Survival With Computed Tomography Imaging Characteristics | 2020 | 212 | Radiologist (12) | − | CT | Tumor methylation (M1-M3 subtype) | M1: >7 cm (OR 2.45), necrosis (OR 4.76) M2: necrosis (OR 0.047), enhancement (OR 0.083) M3: Long axis > median (OR 0.30), necrosis (OR 3.26) |
| Jamshidi et al. [20] | The radiogenomic risk score: construction of a prognostic quantitative, noninvasive image-based molecular assay for renal cell carcinoma | 2015 | 70 | Radiologist (4) | − | Contrast CT | SPC gene signature | RRS correlation with SPC (R = 0.45), HR 3.32 for CSS after surgery |
| Jamshidi et al. [4] | The radiogenomic risk score stratifies outcomes in a renal cell cancer phase 2 clinical trial | 2016 | 41 | Radiologist (4) | − | Contrast CT | SPC gene signature | PFS: 6 mo (high RRS) vs. >25 mo (low RRS)—After bevacizumab tx OS: 25 mo (high RRS) vs. >37 months (low RRS) |
| Bowen et al. [21] | Radiogenomics of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: associations between mRNA-based subtyping and CT imaging features | 2019 | 177 | Computational (8) | − | CT | mRNA subtyping (m1-m4) | M1: OR 2.1—well-defined margin M3: OR 0.42 (well-defined margin), OR 2.12 (renal vein involvement) |
| Yin et al. [22] | Integrative radiomics expression predicts molecular subtypes of primary clear cell renal cell carcinoma | 2018 | 8 | Computational (4) | + (Fisher’s linear discriminant analysis) | PET and MRI | Molecular subtype of ccRCC (ccA vs. ccB) | Accuracy of classification—86.96% |
| Lee et al. [23] | Integrative radiogenomics approach for risk assessment of post-operative metastasis in pathological T1 renal cell carcinoma: a pilot retrospective cohort study | 2020 | 58 | Computational (4) | + (Random Forest) | Contrast CT | Multiple gene-mediated pathways | AUC 0.955—Metastasis |
| Zhao et al. [24] | Validation of CT radiomics for prediction of distant metastasis after surgical resection in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma: exploring the underlying signaling pathways | 2021 | 547 | Computational (9) | + (Logistic regression) | CT | 19 gene pathway signatures | AUC 0.84—Metastasis |
| Lin et al. [25] | Radiomic profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma reveals subtypes with distinct prognoses and molecular pathways | 2021 | 160 | Computational (122) | + (Consensus clustering) | Unenhanced CT | VHL, MUC16, FBN2, and FLG Cell cycle related pathways | C1: Lower OS and PFS than C2 and C3 C1: Lower VHL expression C3: Higher FBN2 expression |
| Huang et al. [26] | Exploration of an integrated prognostic model of radiogenomics features with underlying gene expression patterns in clear cell renal cell carcinoma | 2021 | 205 | Computational (4) | + (LASSO/SVM for feature selection, random forest for classification) | Contrast CT | Gene modules | AUC 0.837, 0.806 and 0.751—1-, 3-, and 5-year OS (combined radiogenomic model) |
| Zeng et al. [27] | Integrative radiogenomics analysis for predicting molecular features and survival in clear cell renal cell carcinoma | 2021 | 207 | Computational (4) | + (Random Forest) | Contrast CT | VHL, BAP1, PBRM1, SETD2, molecular subtypes (m1–m4) | AUC 0.846—5-year OS (Combined radiogenomic model) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gopal, N.; Yazdian Anari, P.; Turkbey, E.; Jones, E.C.; Malayeri, A.A. The Next Paradigm Shift in the Management of Clear Cell Renal Cancer: Radiogenomics—Definition, Current Advances, and Future Directions. Cancers 2022, 14, 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030793
Gopal N, Yazdian Anari P, Turkbey E, Jones EC, Malayeri AA. The Next Paradigm Shift in the Management of Clear Cell Renal Cancer: Radiogenomics—Definition, Current Advances, and Future Directions. Cancers. 2022; 14(3):793. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030793
Chicago/Turabian StyleGopal, Nikhil, Pouria Yazdian Anari, Evrim Turkbey, Elizabeth C. Jones, and Ashkan A. Malayeri. 2022. "The Next Paradigm Shift in the Management of Clear Cell Renal Cancer: Radiogenomics—Definition, Current Advances, and Future Directions" Cancers 14, no. 3: 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030793
APA StyleGopal, N., Yazdian Anari, P., Turkbey, E., Jones, E. C., & Malayeri, A. A. (2022). The Next Paradigm Shift in the Management of Clear Cell Renal Cancer: Radiogenomics—Definition, Current Advances, and Future Directions. Cancers, 14(3), 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14030793






