MicroRNA-101-3p Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the USP47-Induced Deubiquitination of RPL11
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Drugs
2.2. Transient Transfection
2.3. Plasmids, siRNAs, and miRNA
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Immunoprecipitation
2.6. Ni-NTA Pull-Down Assay
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.8. Luciferase Assay
2.9. WST-1 Assay
2.10. Colony Formation Assay
2.11. Immunofluorescence
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
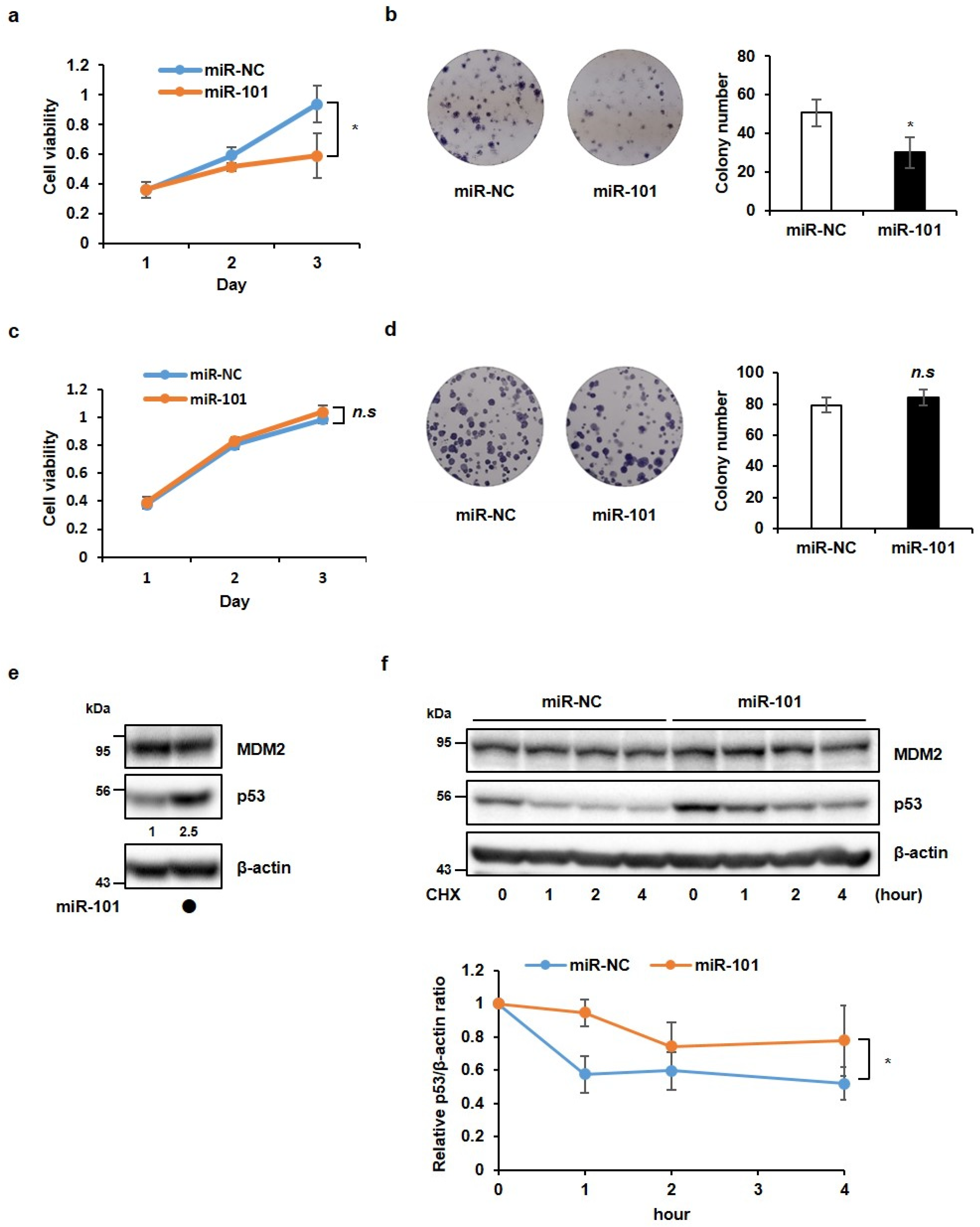
3.1. MiR-101-3p Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth in a p53-Dependent Manner
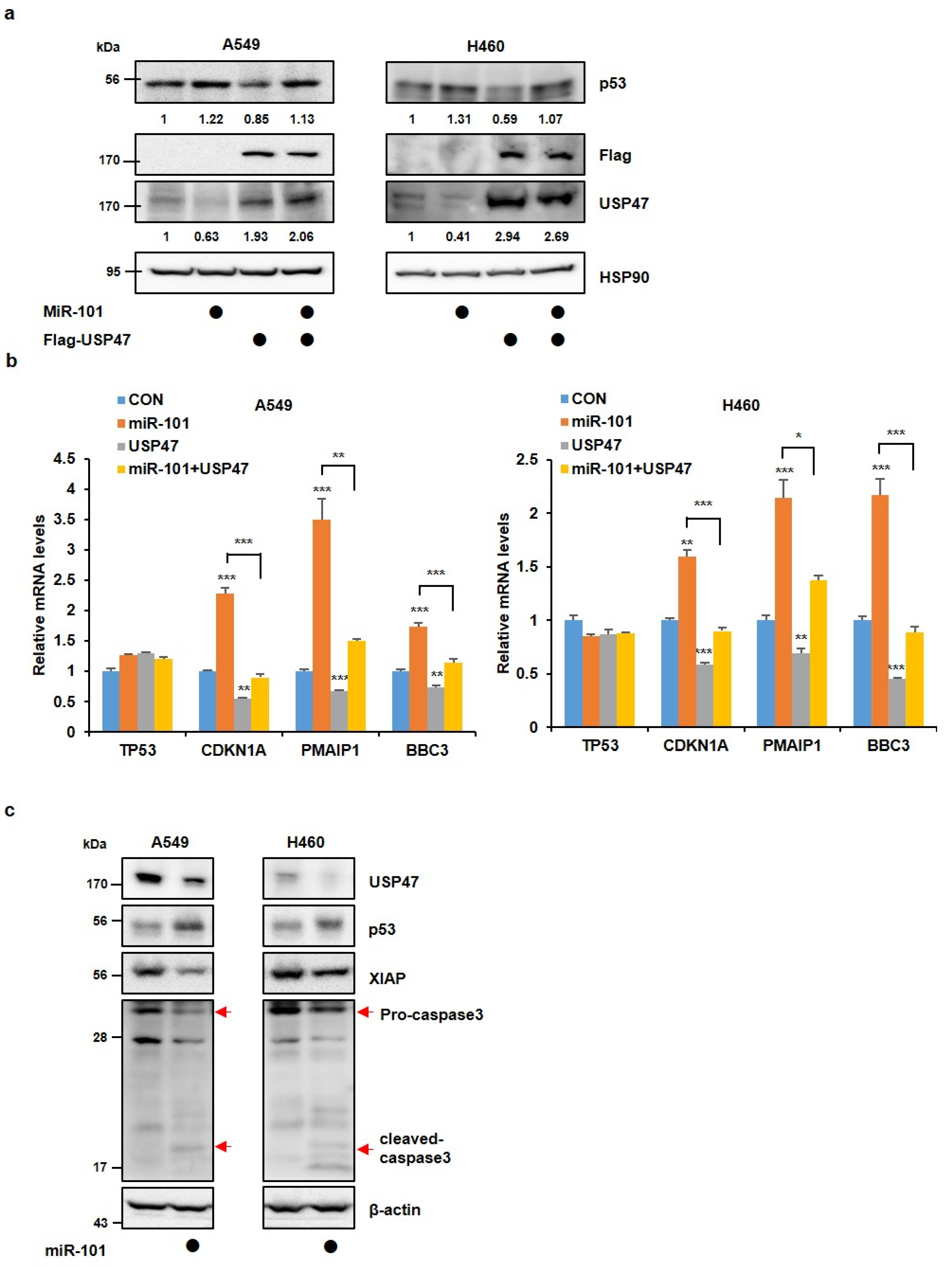
3.2. MiR-101-3p Maintains the Stability of p53 by Reducing USP47 Levels
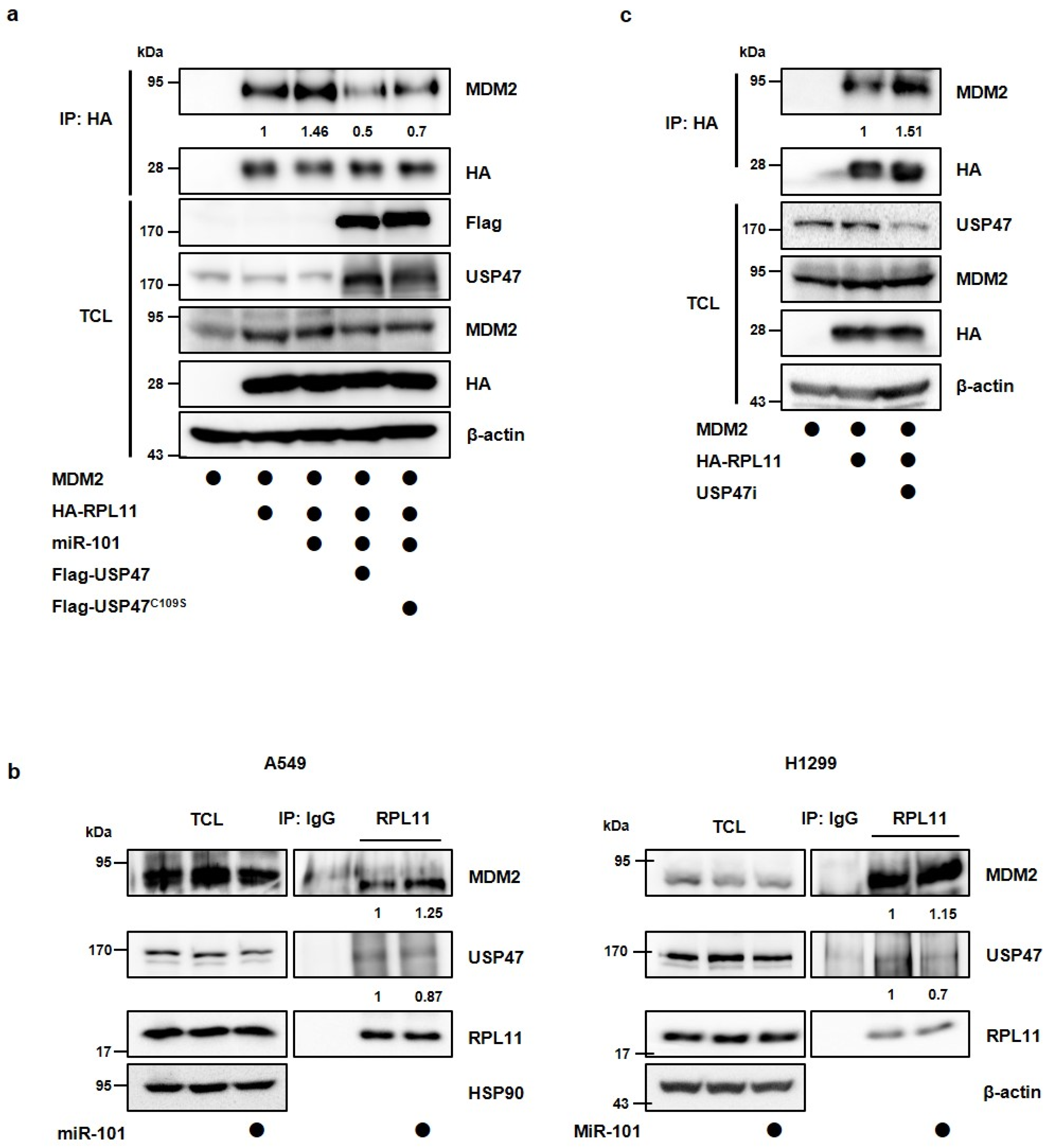
3.3. MiR-101-3p Regulates USP47-Induced Deubiquitination of RPL11
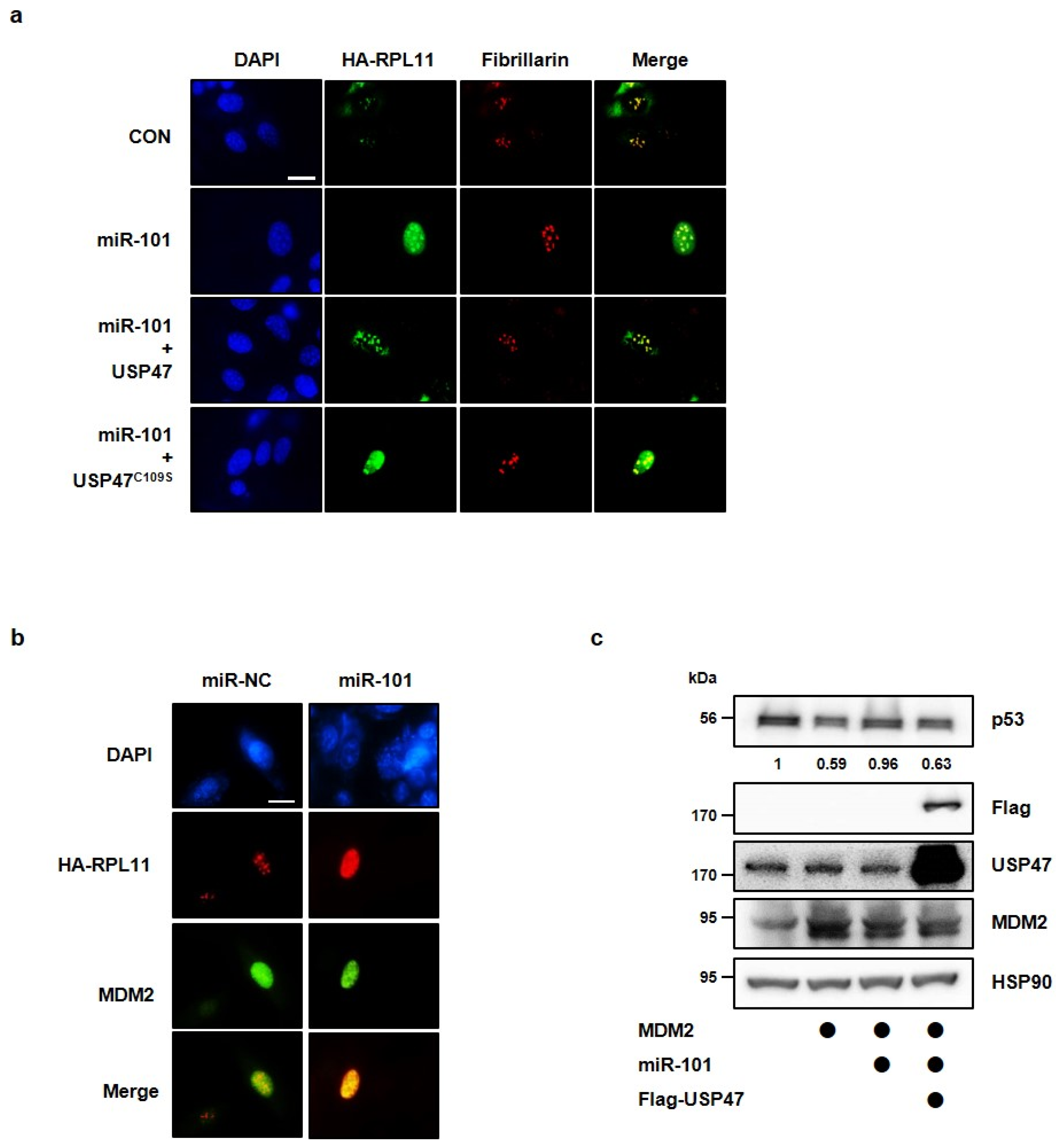
3.4. MiR-101-3p Regulates the Interaction between RPL11 and MDM2 by Translocation of RPL11
3.5. Aberrant Expression of miR-101-3p and USP47 in Lung Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.J.; Basson, M.; Pasquinelli, A.E.; Bettinger, J.C.; Rougvie, A.E.; Horvitz, H.R.; Ruvkun, G. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2000, 403, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquinelli, A.E.; Reinhart, B.J.; Slack, F.; Martindale, M.Q.; Kuroda, M.I.; Maller, B.; Hayward, D.C.; Ball, E.E.; Degnan, B.; Muller, P.; et al. Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 2000, 408, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doench, J.G.; Sharp, P.A. Specificity of microRNA target selection in translational repression. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inui, M.; Martello, G.; Piccolo, S. MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calin, G.A.; Cimmino, A.; Fabbri, M.; Ferracin, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Shimizu, M.; Taccioli, C.; Zanesi, N.; Garzon, R.; Aqeilan, R.I.; et al. MiR-15a and miR-16-1 cluster functions in human leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5166–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, M.; Paone, A.; Calore, F.; Galli, R.; Gaudio, E.; Santhanam, R.; Lovat, F.; Fadda, P.; Mao, C.; Nuovo, G.J.; et al. MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2110–E2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamakuchi, M.; Ferlito, M.; Lowenstein, C.J. miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13421–13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pichiorri, F.; Suh, S.S.; Rocci, A.; De Luca, L.; Taccioli, C.; Santhanam, R.; Zhou, W.; Benson, D.M., Jr.; Hofmainster, C.; Alder, H.; et al. Downregulation of p53-inducible microRNAs 192, 194, and 215 impairs the p53/MDM2 autoregulatory loop in multiple myeloma development. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Saito, M.; Robles, A.I.; Nishida, M.; Takeshita, F.; Watanabe, M.; Ochiya, T.; Yokota, J.; Kohno, T.; Harris, C.C.; et al. A Nucleolar Stress-Specific p53-miR-101 Molecular Circuit Functions as an Intrinsic Tumor-Suppressor Network. EBioMedicine 2018, 33, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rubbi, C.P.; Milner, J. Disruption of the nucleolus mediates stabilization of p53 in response to DNA damage and other stresses. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 6068–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lohrum, M.A.; Ludwig, R.L.; Kubbutat, M.H.; Hanlon, M.; Vousden, K.H. Regulation of HDM2 activity by the ribosomal protein L11. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wolf, G.W.; Bhat, K.; Jin, A.; Allio, T.; Burkhart, W.A.; Xiong, Y. Ribosomal protein L11 negatively regulates oncoprotein MDM2 and mediates a p53-dependent ribosomal-stress checkpoint pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 8902–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, M.S.; Lu, H. Inhibition of MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination and degradation by ribosomal protein L5. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 44475–44482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, A.; Itahana, K.; O’Keefe, K.; Zhang, Y. Inhibition of HDM2 and activation of p53 by ribosomal protein L23. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7669–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Poyurovsky, M.V.; Li, Y.; Biderman, L.; Stahl, J.; Jacq, X.; Prives, C. Ribosomal protein S7 is both a regulator and a substrate of MDM2. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, F.; Shen, N.; Pang, J.; Xie, D.; Deng, B.; Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Liu, S. Restoration of miR-101 suppresses lung tumorigenesis through inhibition of DNMT3a-dependent DNA methylation. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Guo, S.; Liang, Y. MiR-101-3p inhibits the growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through blocking PI3K/AKT signal pathway by targeting MALAT-1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varambally, S.; Cao, Q.; Mani, R.S.; Shankar, S.; Wang, X.; Ateeq, B.; Laxman, B.; Cao, X.; Jing, X.; Ramnarayanan, K.; et al. Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science 2008, 322, 1695–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Schulz, R.; Edmunds, S.; Kruger, E.; Markert, E.; Gaedcke, J.; Cormet-Boyaka, E.; Ghadimi, M.; Beissbarth, T.; Levine, A.J.; et al. MicroRNA-101 Suppresses Tumor Cell Proliferation by Acting as an Endogenous Proteasome Inhibitor via Targeting the Proteasome Assembly Factor POMP. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Chen, W.; Xia, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, H.; Jiang, T. MiR-101 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer by targeting zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ding, L.; Gao, F.; Fan, H. Long non-coding RNA DSCAM-AS1 upregulates USP47 expression through sponging miR-101-3p to accelerate osteosarcoma progression. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 98, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Park, J.; Shin, S.C.; Jang, M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.E.; Song, E.J. USP47 Promotes Tumorigenesis by Negative Regulation of p53 through Deubiquitinating Ribosomal Protein S2. Cancers 2020, 12, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonish-Rouach, E.; Resnitzky, D.; Lotem, J.; Sachs, L.; Kimchi, A.; Oren, M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature 1991, 352, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Bovey, R.; Tardy, S.; Sahli, R.; Sordat, B.; Costa, J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 4495–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahata, B.; Sundqvist, A.; Xirodimas, D.P. Recruitment of RPL11 at promoter sites of p53-regulated genes upon nucleolar stress through NEDD8 and in an Mdm2-dependent manner. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3060–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsons, J.L.; Dianova, I.I.; Khoronenkova, S.V.; Edelmann, M.J.; Kessler, B.M.; Dianov, G.L. USP47 is a deubiquitylating enzyme that regulates base excision repair by controlling steady-state levels of DNA polymerase beta. Mol. Cell 2011, 41, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Yu, T.; Jia, J.; Liu, C. Deubiquitinase USP47/UBP64E Regulates beta-Catenin Ubiquitination and Degradation and Plays a Positive Role in Wnt Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 3301–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peschiaroli, A.; Skaar, J.R.; Pagano, M.; Melino, G. The ubiquitin-specific protease USP47 is a novel beta-TRCP interactor regulating cell survival. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bian, Z.; Song, M.; Hua, D.; Huang, Z. MicroRNA-204-5p inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by downregulating USP47 and RAB22A. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golomb, L.; Volarevic, S.; Oren, M. p53 and ribosome biogenesis stress: The essentials. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundqvist, A.; Liu, G.; Mirsaliotis, A.; Xirodimas, D.P. Regulation of nucleolar signalling to p53 through NEDDylation of L11. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Motiam, A.; Vidal, S.; de la Cruz-Herrera, C.F.; Da Silva-Alvarez, S.; Baz-Martinez, M.; Seoane, R.; Vidal, A.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Xirodimas, D.P.; Carvalho, A.S.; et al. Interplay between SUMOylation and NEDDylation regulates RPL11 localization and function. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Cho, M.; Cho, J.; Kim, E.E.; Song, E.J. MicroRNA-101-3p Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the USP47-Induced Deubiquitination of RPL11. Cancers 2022, 14, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040964
Park J, Cho M, Cho J, Kim EE, Song EJ. MicroRNA-101-3p Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the USP47-Induced Deubiquitination of RPL11. Cancers. 2022; 14(4):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040964
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jinyoung, Moonsoo Cho, Jinhong Cho, Eunice EunKyeong Kim, and Eun Joo Song. 2022. "MicroRNA-101-3p Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the USP47-Induced Deubiquitination of RPL11" Cancers 14, no. 4: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040964
APA StylePark, J., Cho, M., Cho, J., Kim, E. E., & Song, E. J. (2022). MicroRNA-101-3p Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth by Inhibiting the USP47-Induced Deubiquitination of RPL11. Cancers, 14(4), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14040964





