Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as an Efficient Nanocarrier to Deliver siRNA or Drug to Pancreatic Cancer Cells
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Samples and Culture of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Phenotypic Analysis of WJ-MSCs
2.4. EV Isolation and Characterization
2.5. Uptake of EVs by Cell Lines
2.6. Loading of EVs with siRNA
2.7. Drug Encapsulation in EVs
2.8. Real-Time PCR Analyses
2.9. Biological Assays
2.9.1. Cell Viability
2.9.2. Clonogenic Growth Assay (CFU-F)
2.9.3. Transwell Migration
2.9.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Apoptosis
2.9.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.9.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Isolation of MSCs from Umbilical Cord (hUC-MSCs)
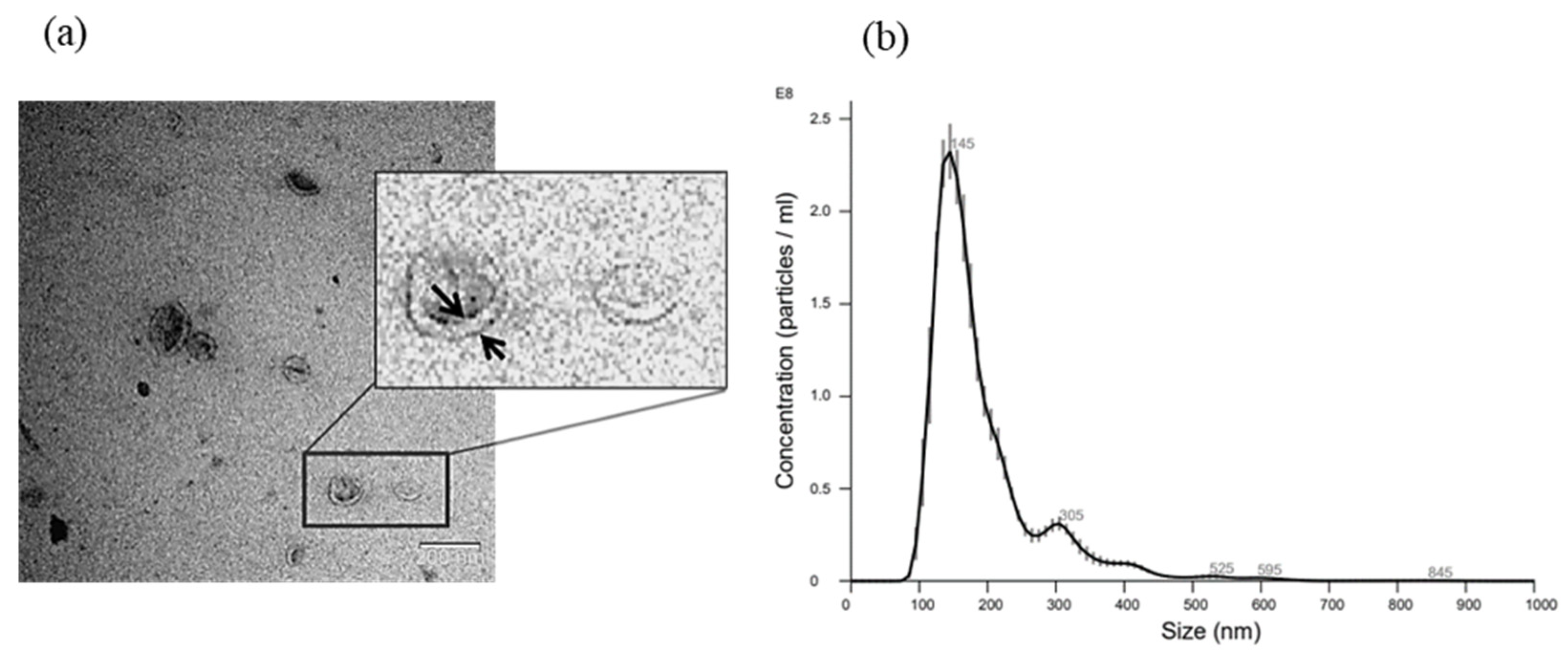
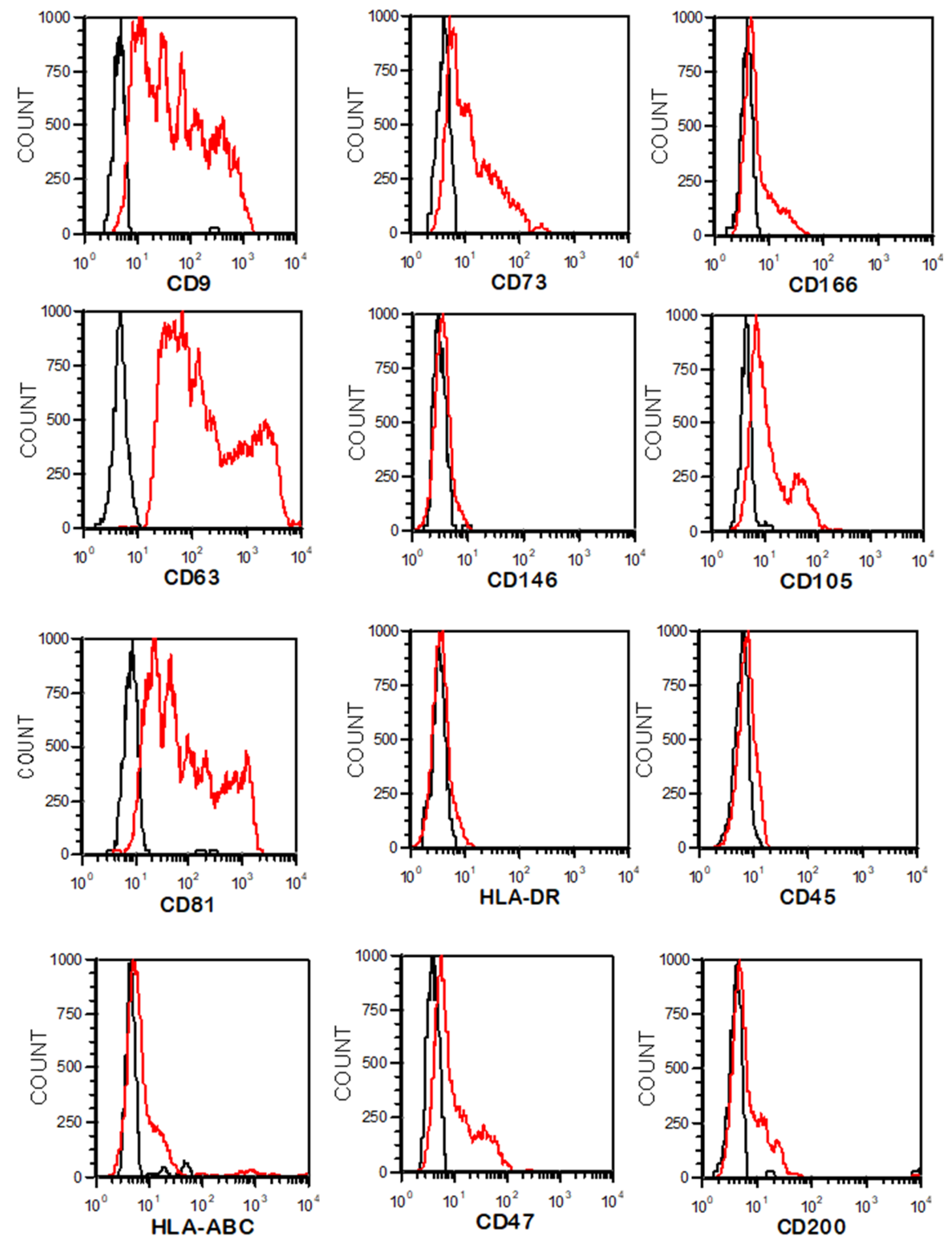
3.2. EV Isolation by Differential Centrifugation and Characterization
3.3. EV Electroporation Leads to siRNA Incorporation
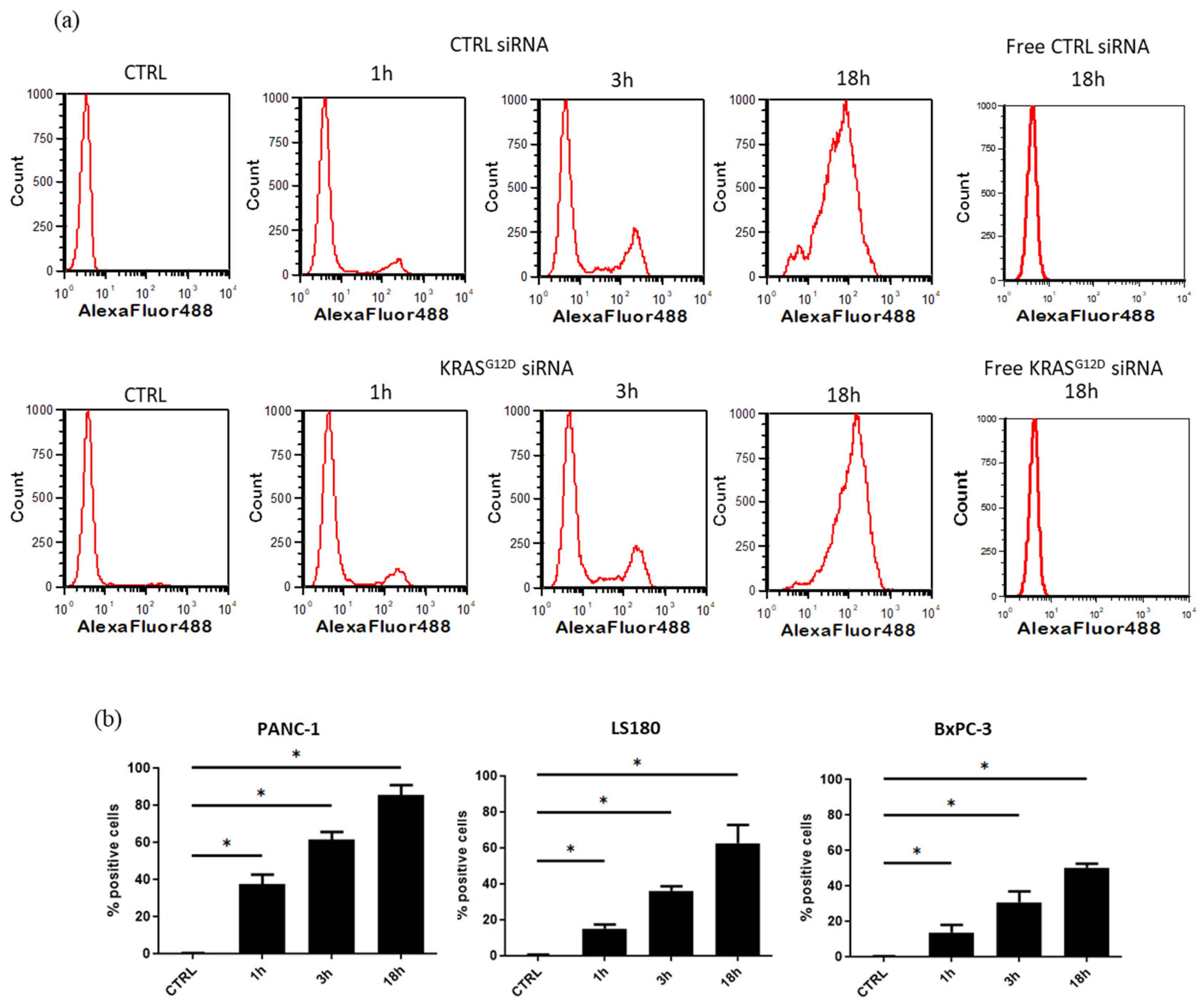
3.4. Cellular Uptake of EVs
3.5. EVs Loaded with KRASG12D siRNA Reduce the Expression Level of KRASG12D
3.6. The Clonogenicity of PANC-1 Cells Decreases after Treatment with siKRASG12D EVs
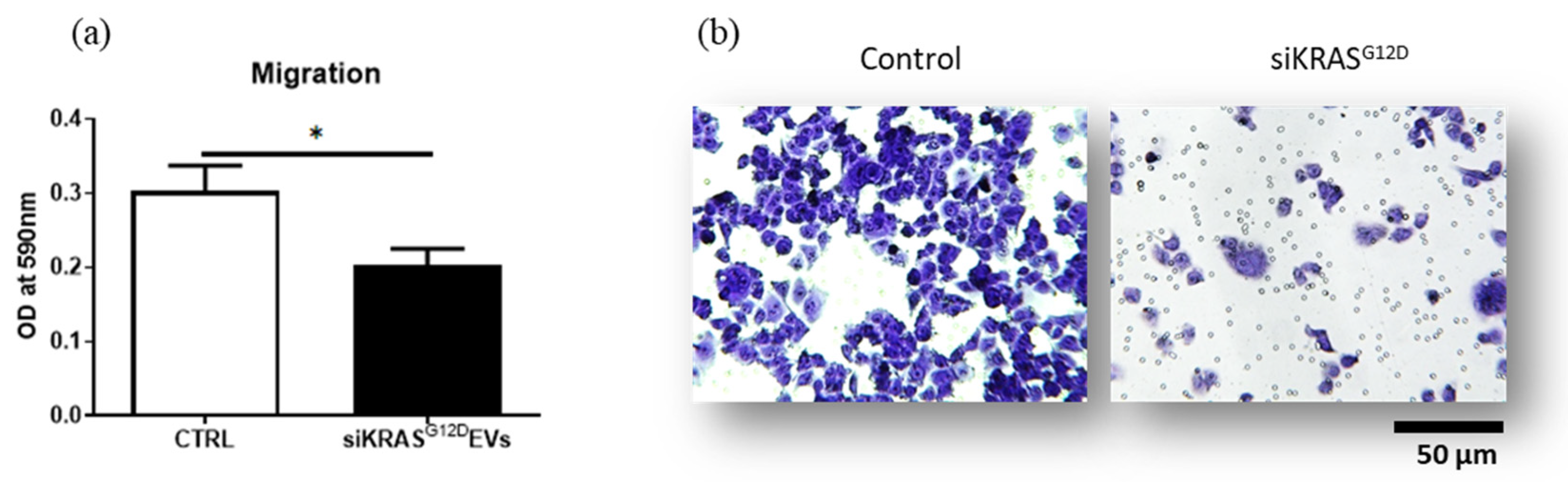
3.7. siKRASG12D EVs Decrease the Migration Potential of PANC-1 Cells
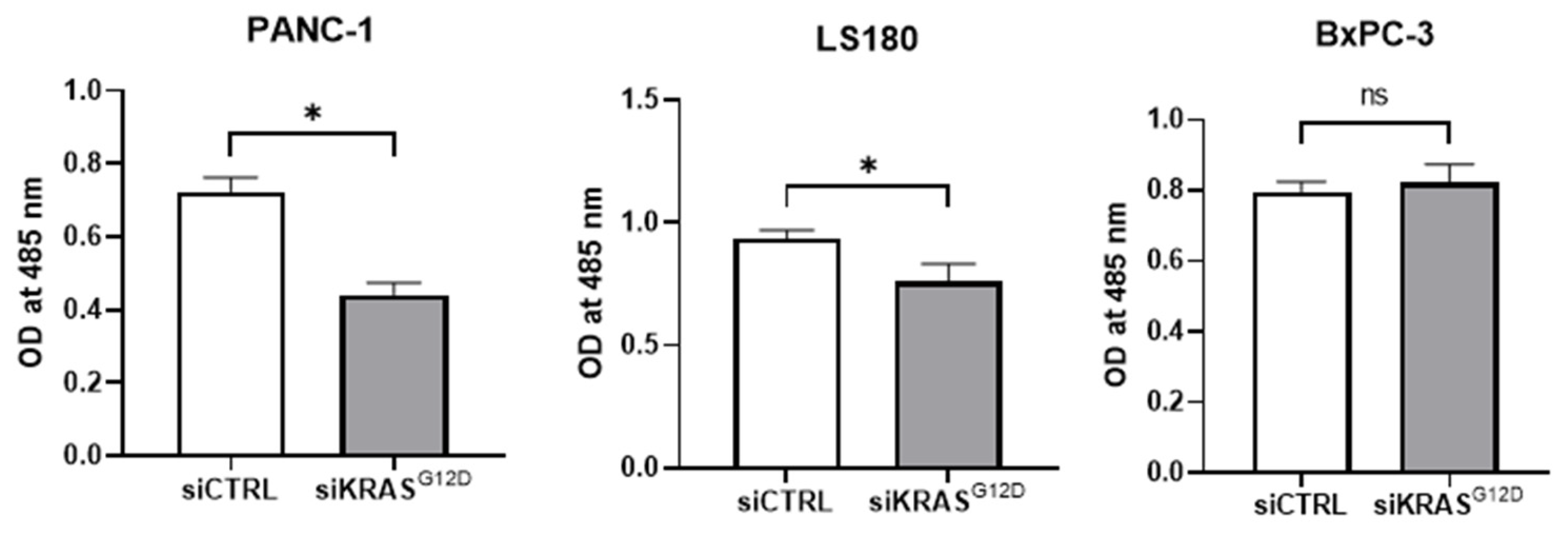
3.8. siKRASG12D EVs Decrease Cell Viability
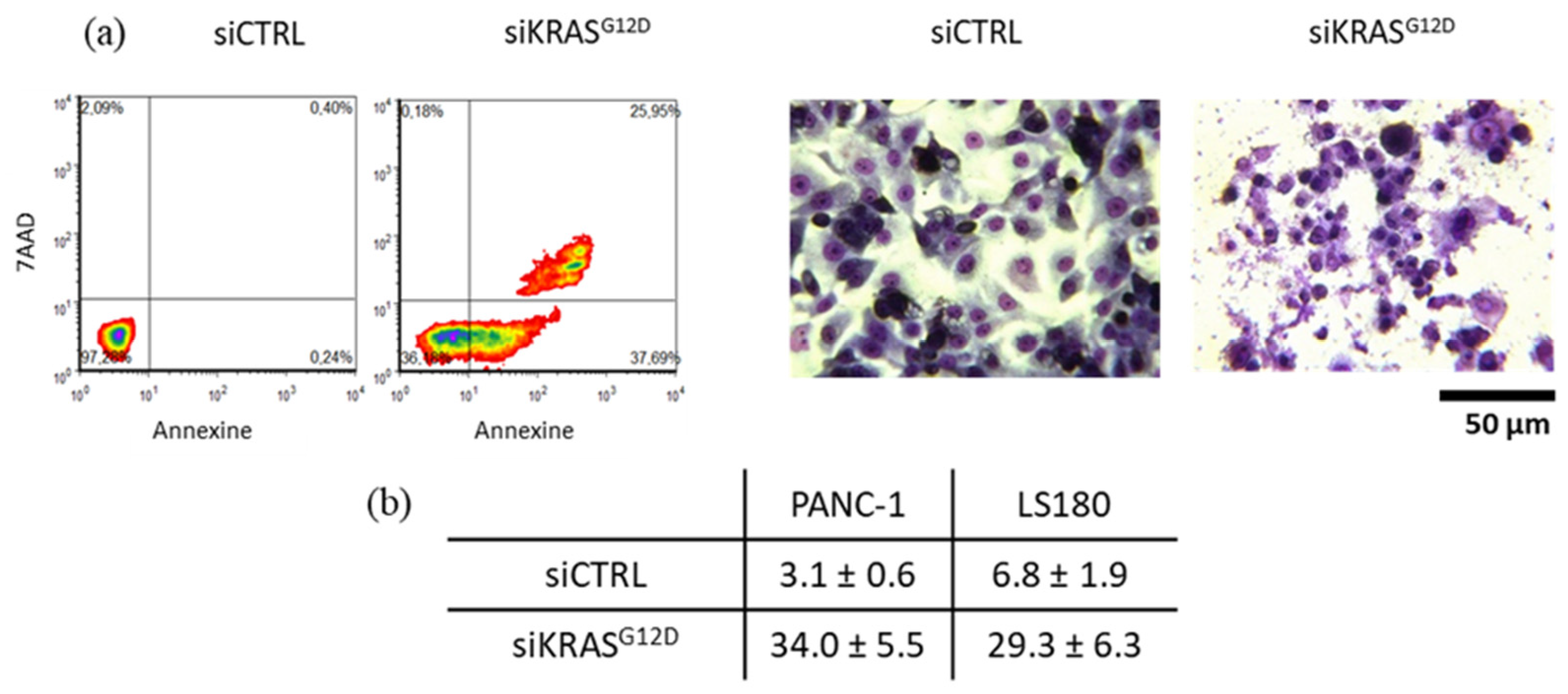
3.9. siKRASG12D EVs Induce Apoptosis in KRAS-Mutant Cells
3.10. Arrest of the Cell Cycle and Accumulation of Cells in the S Phase
3.11. UC-MSC-Derived EVs as Natural Drug Delivery Vehicles
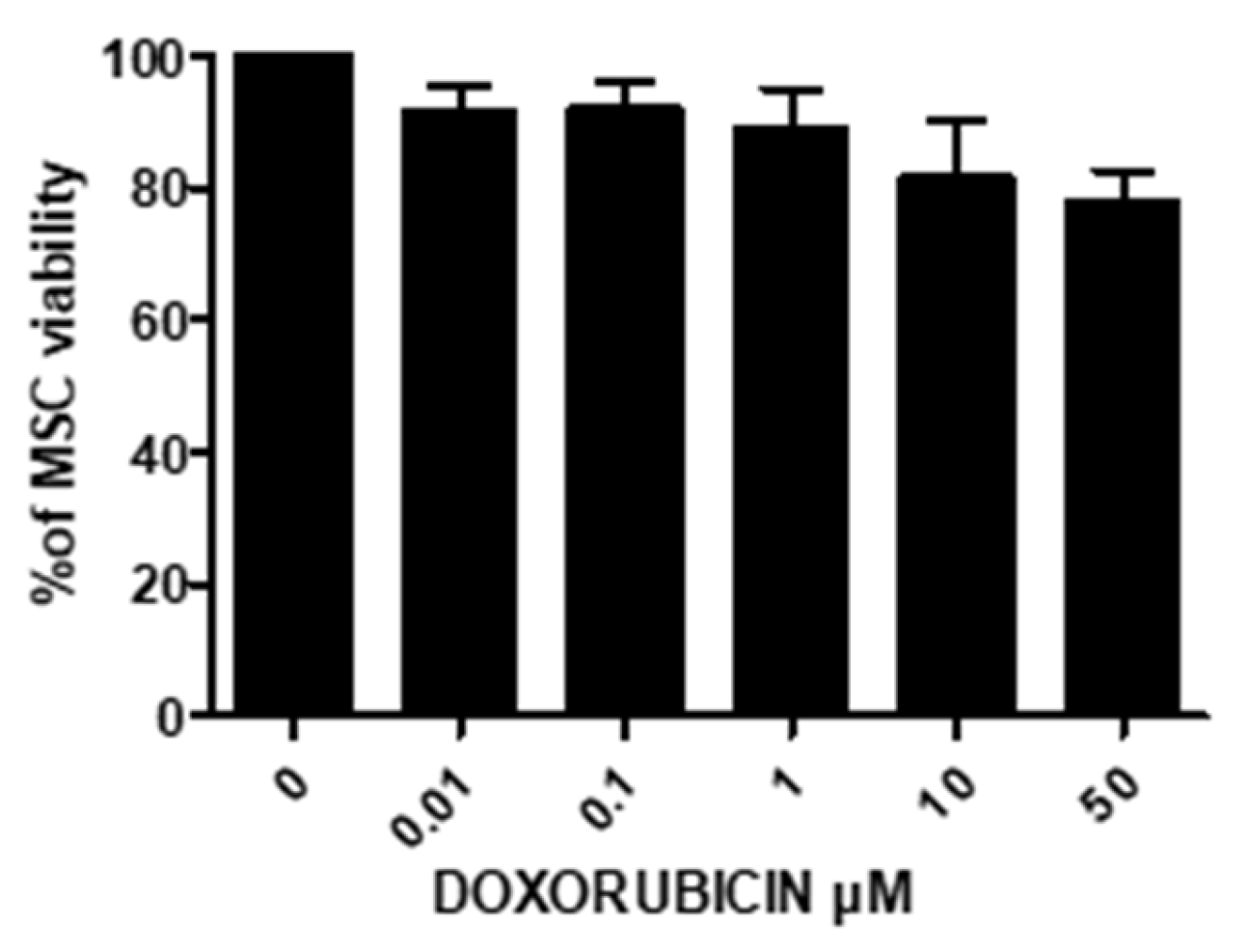
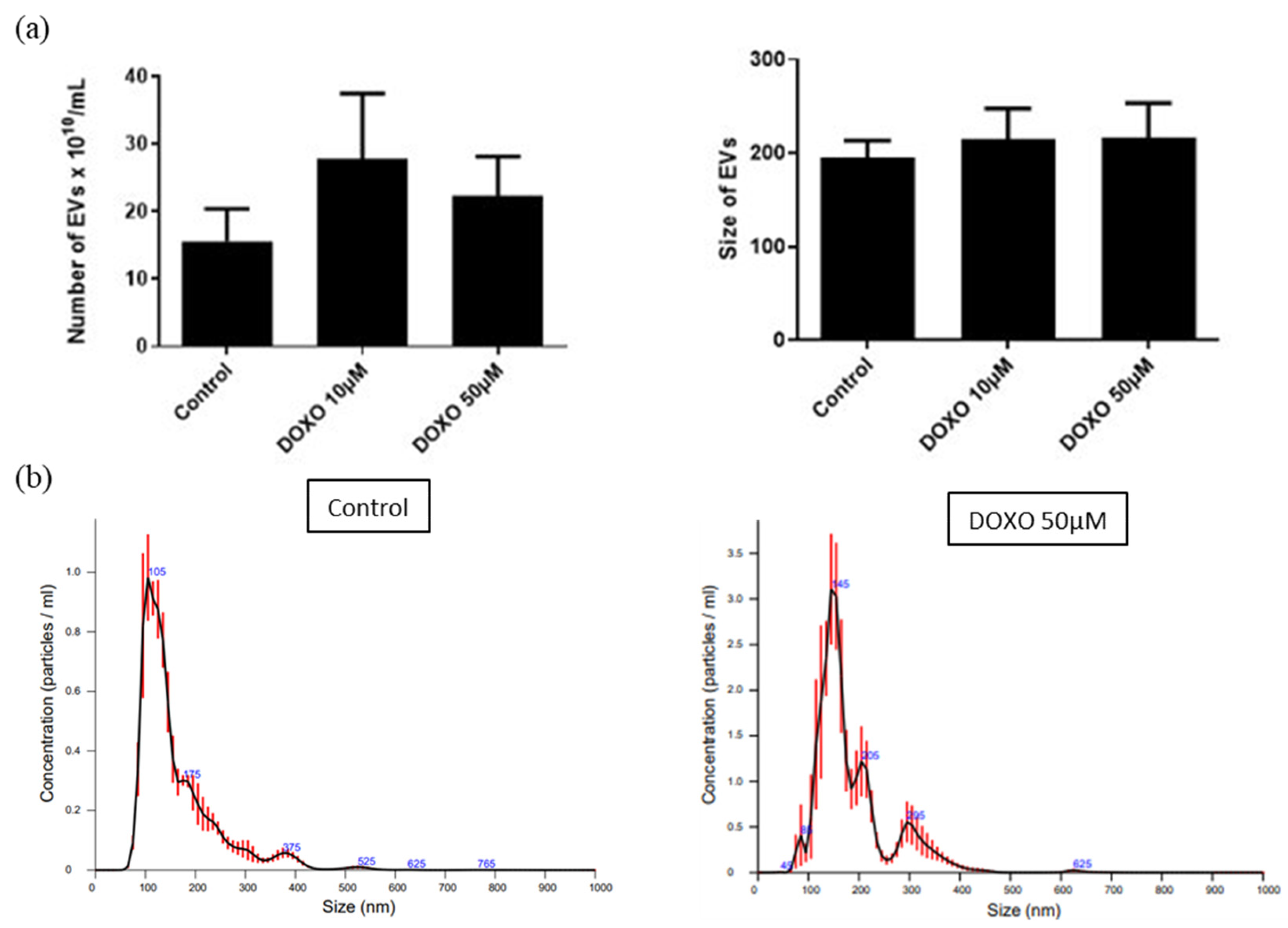
3.11.1. Treatment of UC-MSCs with DOXO
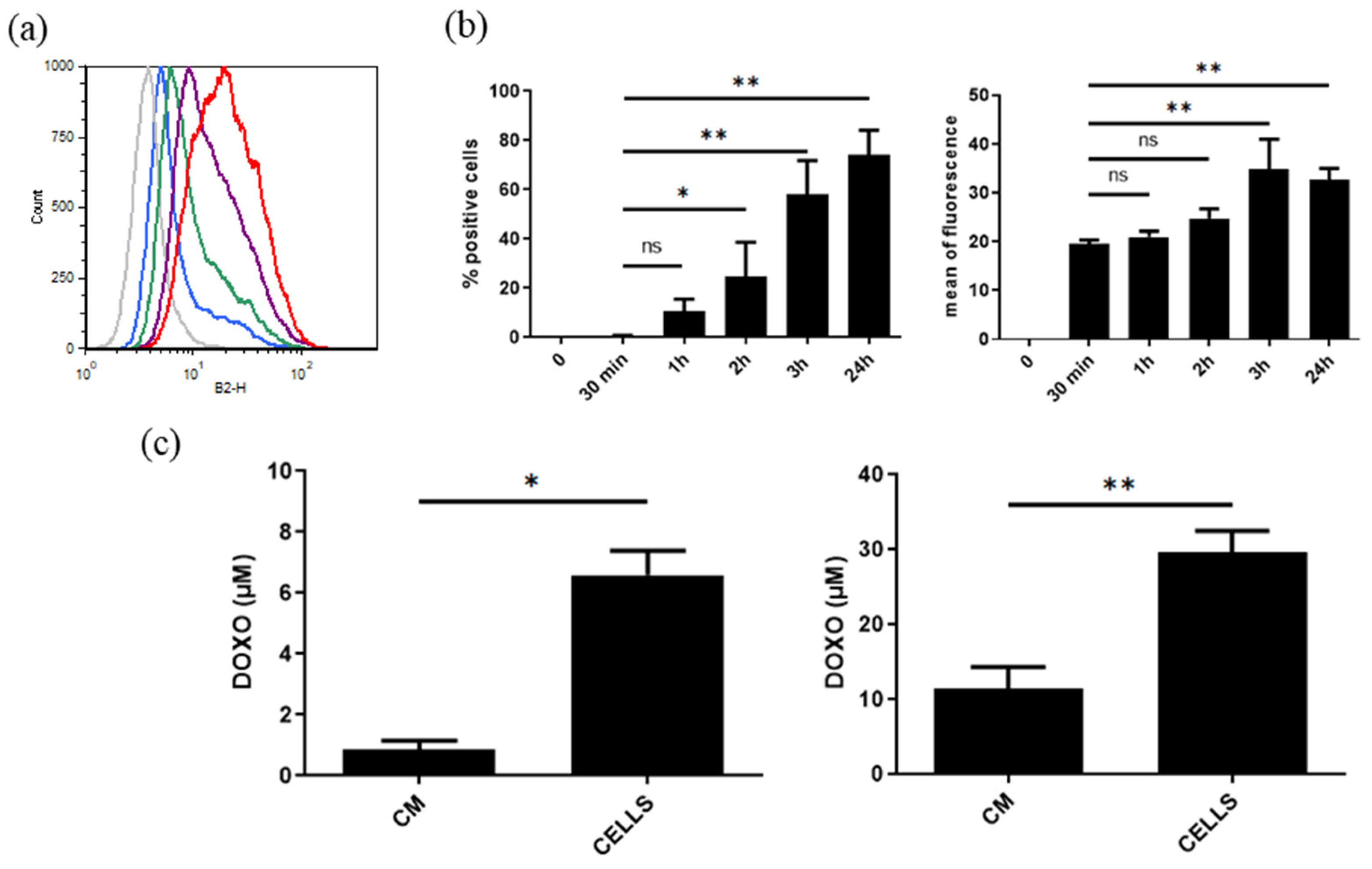
3.11.2. Characterization of DOXO-Loaded EVs
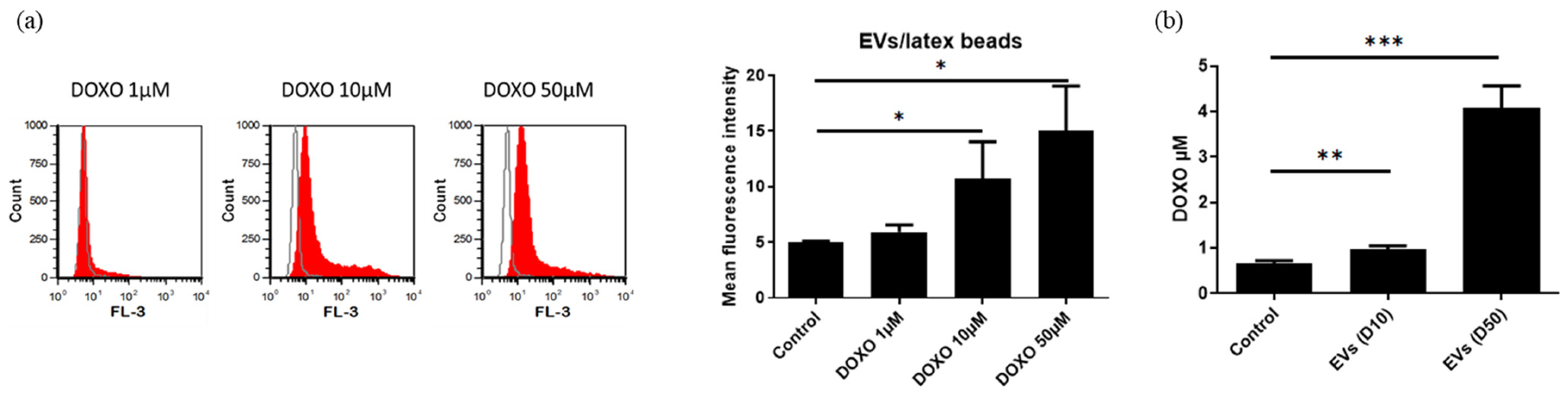
3.11.3. Uptake of DOXO EVs by PANC-1 Cells and Their Anticancer Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Lundy, J.; Strickland, A.H.; Harris, M.; Swan, M.; Desmond, C.; Jenkins, B.J.; Croagh, D. KRAS G12D Mutation Subtype in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Does It Influence Prognosis or Stage of Disease at Presentation? Cells 2022, 11, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfredini, S.; Thapa, A.; O’Neill, E. RAS in pancreatic cancer. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 961–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Bien, H.; Mofunanya, A.; Powers, S. Challenges in Ras therapeutics in pancreatic cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 54, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, E.J. Pancreatic cancer inhibition by specific knockdown of K-ras mutant allele expression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2007, 6, 293–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslan, M.; Shahbazi, R.; Ulubayram, K.; Ozpolat, B. Targeted Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer and Hurdles Ahead. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6591–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, M.S.; Krasnick, B.A.; Pan, H.; Zhang, X.; Bi, Y.; Brooks, C.; Wetzel, C.; Sankpal, N.; Fleming, T.; Goedegebuure, S.P.; et al. Precision delivery of RAS-inhibiting siRNA to KRAS driven cancer via peptide-based nanoparticles. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4761–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comandatore, A.; Immordino, B.; Balsano, R.; Capula, M.; Garajovà, I.; Ciccolini, J.; Giovannetti, E.; Morelli, L. Potential Role of Exosomes in the Chemoresistance to Gemcitabine and Nab-Paclitaxel in Pancreatic Cancer. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterman, C.J.D.; Lynch, J.C.; Leaf, P.; Gonda, A.; Ferguson Bennit, H.R.; Griffiths, D.; Wall, N.R. Curcumin Modulates Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell-Derived Exosomal Function. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspe, J.R.; Diaz Osterman, C.J.; Jutzy, J.M.S.; Deshields, S.; Whang, S.; Wall, N.R. Enhancement of Gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by novel exosome-mediated delivery of the Survivin-T34A mutant. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2014, 3, 23244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Ehata, S.; Koinuma, D.; Morishita, Y.; Soda, M.; Mano, H.; Miyazono, K. Pancreatic tumor microenvironment confers highly malignant properties on pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2757–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, D.; Wei, A.; Ke, N.; Wang, Y.; Tang, J.; He, S.; Hu, W.; Liu, X. MicroRNA-410-3p attenuates gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by inhibiting HMGB1-mediated autophagy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 107500–107512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamerkar, S.; Lebleu, V.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Ruivo, C.F.; Melo, S.A.; Lee, J.J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crivelli, B.; Chlapanidas, T.; Perteghella, S.; Lucarelli, E.; Pascucci, L.; Brini, A.T.; Ferrero, I.; Marazzi, M.; Pessina, A.; Torre, M.L.; et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell extracellular vesicles: From active principle to next generation drug delivery system. J. Control. Release 2017, 262, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, N.; Dutt Arya, B.; Jain, N.; Yadav, P.; Wajid, S.; Singh, S.P.; Choudhury, S. Biophysical Characterization and Drug Delivery Potential of Exosomes from Human Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 13143–13152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, C.; Najar, M.; Raicevic, G.; Meuleman, N.; Pieters, K.; Stamatopoulos, B.; Delforge, A.; Bron, D.; Lagneaux, L. A rapid, simple, and reproducible method for the isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells from Wharton’s jelly without enzymatic treatment. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raicevic, G.; Najar, M.; Stamatopoulos, B.; De Bruyn, C.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Toungouz, M.; Lagneaux, L. The source of human mesenchymal stromal cells influences their TLR profile as well as their functional properties. Cell Immunol. 2011, 270, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompot, E.; van Damme, M.; Pieters, K.; Vermeersch, M.; Perez-Morga, D.; Mineur, P.; Maerevoet, M.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Lagneaux, L.; et al. Extracellular vesicles of bone marrow stromal cells rescue chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells from apoptosis, enhance their migration and induce gene expression modifications. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najar, M.; Raicevic, G.; Jebbawi, F.; De Bruyn, C.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Toungouz, M.; Lagneaux, L. Characterization and functionality of the CD200-CD200R system during mesenchymal stromal cell interactions with T-lymphocytes. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 146, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liang, Z.Y.; Ren, X.Y.; Liu, T.H. Small interfering RNAs targeting mutant K-ras inhibit human pancreatic carcinoma cells growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berebichez-Fridman, R.; Montero-Olvera, P.R. Sources and Clinical Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: State-of-the-art review. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2018, 18, e264-77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappa, K.I.; Anagnou, N.P. Novel sources of fetal stem cells: Where do they fit on the developmental continuum? Regen Med. 2009, 4, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Shyu, W.C.; Lin, S.Z. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: A new era for stem cell therapy. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Rhim, W.K.; Cha, S.G.; Woo, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, C.G.; Han, D.K. Bolstering the secretion and bioactivities of umbilical cord MSC-derived extracellular vesicles with 3D culture and priming in chemically defined media. Nano Converg. 2022, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraszti, R.A.; Miller, R.; Stoppato, M.; Sere, Y.Y.; Coles, A.; Didiot, M.C.; Wollacott, R.; Sapp, E.; Dubuke, M.L.; Li, X.; et al. Exosomes Produced from 3D Cultures of MSCs by Tangential Flow Filtration Show Higher Yield and Improved Activity. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2838–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.L.; Harada, T.; Christian, D.A.; Pantano, D.A.; Tsai, R.K.; Discher, D.E. Minimal “Self” peptides that inhibit phagocytic clearance and enhance delivery of nanoparticles. Science 2013, 339, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shan, Z.; Fan, J. Extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow stem cells inhibit acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell growth by inhibiting MAPK pathway via the miR-29b-3p/GDF15 axis. Acta Haematol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, H.; Wu, Y. Extracellular vesicles extracted from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells carrying MicroRNA-342-3p inhibit the INHBA/IL13Rα2 axis to suppress the growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 18, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wu, M.; Lv, S.; Hu, Q.; Xu, W.; Zeng, A.; Huang, K.; Zhu, X. Exosomes derived from microRNA-512-5p-transfected bone mesenchymal stem cells inhibit glioblastoma progression by targeting JAG1. Aging 2021, 13, 9911–9926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendt, M.; Kamerkar, S.; Sugimoto, H.; McAndrews, K.M.; Wu, C.C.; Gagea, M.; Yang, S.; Rodriges Blanko, E.V.; Peng, Q.; Ma, X.; et al. Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic cancer. JCI Insight 2018, 3, 99263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, S.; Hu, R.; Lin, G.; Tian, J.; Hu, S.; Lan, R.F.; Yoon, H.S.; et al. A Light-Driven Therapy of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Using Gold Nanorods-Based Nanocarriers for Co-Delivery of Doxorubicin and siRNA. Theranostics 2015, 5, 818–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Sun, M.; Liu, Z.; Kong, C.; Kong, W.; Ye, J.; Gong, J.; Huang, D.C.S.; Qian, F. KRAS-enhanced macropinocytosis and reduced FcRn-mediated recycling sensitize pancreatic cancer to albumin-conjugated drugs. J. Control. Release 2019, 296, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanapally, R.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Chavva, S.R.; Tyagi, N.; Srivastava, S.K.; Patel, G.K.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, S. Drug-loaded exosomal preparations from different cell types exhibit distinctive loading capability, yield, and antitumor efficacies: A comparative analysis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrutkar, M.; Gladhaug, I.P. Pancreatic Cancer Chemoresistance to Gemcitabine. Cancers 2017, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karukstis, K.K.; Thompson, E.H.; Whiles, J.A.; Rosenfeld, R.J. Deciphering the fluorescence signature of daunomycin and doxorubicin. Biophys. Chem. 1998, 73, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib Hasan Khan, M.; Shankar Hazra, R.; Nair, G.; Mohammad, J.; Jiang, L.; Reindl, K.; Jawed, M.K.; Ganai, S.; Quadir, M. Cellulose nanofibers as Scaffold-forming materials for thin film drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 627, 122189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, W.; Li, F.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Weng, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, L. Amplification of anticancer efficacy by co-delivery of doxorubicin and lonidamine with extracellular vesicles. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.; Roy, I. Doxorubicin-loaded casein nanoparticles for drug delivery: Preparation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babajani, A.; Soltani, P.; Jamshidi, E.; Farjoo, M.H.; Niknejad, H. Recent Advances on Drug-Loaded Mesenchymal Stem Cells With Anti-neoplastic Agents for Targeted Treatment of Cancer. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Hou, M. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor rescues mesenchymal stem cells from doxorubicin-induced senescence though the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, E.; Abnous, K.; Farzad, S.A.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Targeted doxorubicin-loaded mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes as a versatile platform for fighting against colorectal cancer. Life Sci. 2020, 261, 118369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Fu, F.; Zhu, X.; Wu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Lin, J. A Nanodrug Consisting of Doxorubicin and Exosome Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteosarcoma Treatment In Vitro. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8603–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Jin, L.; Guo, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhanghuang, C.; Tan, X.; Mi, T.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Exosome mimetics derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells deliver doxorubicin to osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhat, W.; Yeung, V.; Kahale, F.; Parekh, M.; Cortinas, J.; Chen, L.; Ross, A.E.; Ciolino, J.B. Doxorubicin-Loaded Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Tumor Cell Death in Retinoblastoma. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Guan, Z.; Pang, X.; Tan, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Guan, F. Desialylated Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Loaded with Doxorubicin for Targeted Inhibition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, C.; Collinson, A.; Matthews, C.; Pointon, A.; Jenkinson, L.; Minter, R.R.; Vaughan, T.J.; Tigue, N.J. Exosomal delivery of doxorubicin enables rapid cell entry and enhanced in vitro potency. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Haney, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Mahajan, V.; Deygen, I.; Klyachko, N.L.; Inskoe, E.; Piroyan, A.; Sokolsky, M.; Okolie, O.; et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccè, V.; Franzè, S.; Brini, A.T.; Giannì, A.B.; Pascucci, L.; Ciusani, E.; Alessandri, G.; Farronato, G.; Cavicchini, L.; Sordi, V.; et al. In Vitro Anticancer Activity of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) Secreted by Gingival Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Primed with Paclitaxel. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, B.I.; Demirbolat, G.M.; Cevik, O. Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cell exosomes induce apoptosis and suppress EMT signaling in cervical cancer cells as an effective drug carrier system of paclitaxel. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimova, D.; Jakubechova, J.; Altanerova, U.; Nicodemou, A.; Styk, J.; Szemes, T.; Repiska, V.; Altaner, C. Extracellular vesicles derived from dental mesenchymal stem/stromal cells with gemcitabine as a cargo have an inhibitory effect on the growth of pancreatic carcinoma cell lines in vitro. Mol. Cell. Probes. 2023, 67, 101894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ding, X.; Jiang, C. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for penetrating and targeted chemotherapy of pancreatic cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, J.; Liao, Y.P.; Tang, I.; Zheng, E.; Qiu, W.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Ji, Y.; Mei, K.C.; et al. Combination Chemo-Immunotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer Using the Immunogenic Effects of an Irinotecan Silicasome Nanocarrier Plus Anti-PD-1. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draguet, F.; Bouland, C.; Dubois, N.; Bron, D.; Meuleman, N.; Stamatopoulos, B.; Lagneaux, L. Potential of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Natural Nanocarriers: Concise Review. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pincela Lins, P.M.; Pirlet, E.; Szymonik, M.; Bronckaers, A.; Nelissen, I. Manufacture of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stromal cells. Trends Biotechnol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Reverse | Forward | |
|---|---|---|
| KRASWT | TGTAGGAATCCTCTATTGTTGGATCA | AAGAGTGCCTTGACGATACAGCTA |
| KRASG12D | TTGGATCATATTCGTCCACAA | ACTTGTGGTAGTTGGEGCAGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Draguet, F.; Dubois, N.; Bouland, C.; Pieters, K.; Bron, D.; Meuleman, N.; Stamatopoulos, B.; Lagneaux, L. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as an Efficient Nanocarrier to Deliver siRNA or Drug to Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancers 2023, 15, 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15112901
Draguet F, Dubois N, Bouland C, Pieters K, Bron D, Meuleman N, Stamatopoulos B, Lagneaux L. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as an Efficient Nanocarrier to Deliver siRNA or Drug to Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2023; 15(11):2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15112901
Chicago/Turabian StyleDraguet, Florian, Nathan Dubois, Cyril Bouland, Karlien Pieters, Dominique Bron, Nathalie Meuleman, Basile Stamatopoulos, and Laurence Lagneaux. 2023. "Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as an Efficient Nanocarrier to Deliver siRNA or Drug to Pancreatic Cancer Cells" Cancers 15, no. 11: 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15112901
APA StyleDraguet, F., Dubois, N., Bouland, C., Pieters, K., Bron, D., Meuleman, N., Stamatopoulos, B., & Lagneaux, L. (2023). Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as an Efficient Nanocarrier to Deliver siRNA or Drug to Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancers, 15(11), 2901. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15112901






