Image-Guided Precision Medicine in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology, Genetics, and Molecular Background: How to Stratify Risk
2.1. Epidemiology and Embryology
2.2. An Endocrine Functional Status
2.3. Genetic Background: A Prerequisite to Understand Pathology
2.4. A Potentially Malignant Tumor with Common Sites of Metastases
2.5. Prognosis and Prognostic Markers
3. Anatomical Imaging Techniques in Initial Diagnosis
3.1. How to Explore an Indeterminate Adrenal Mass?
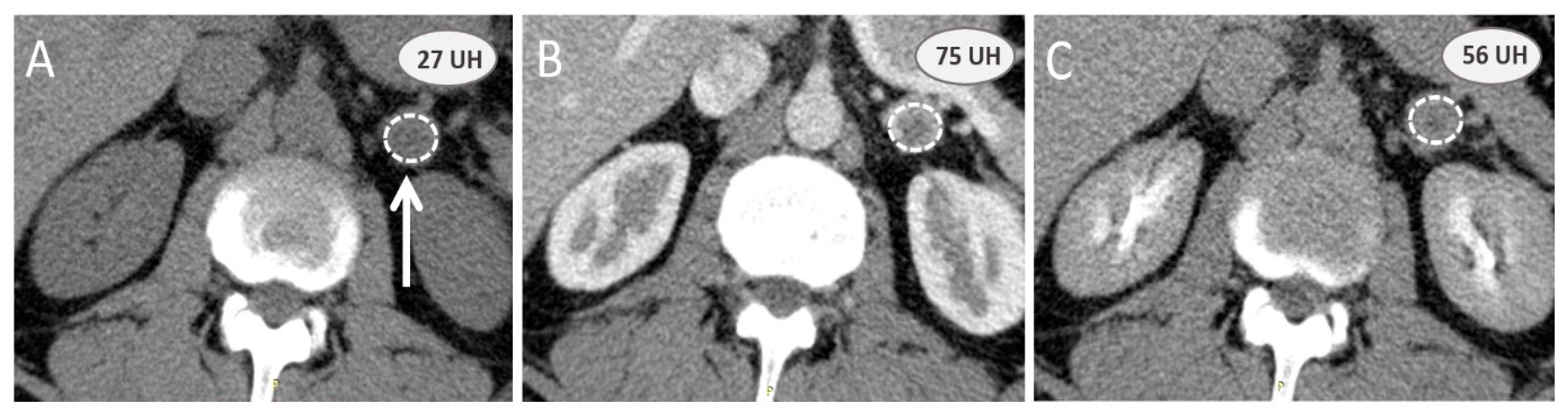
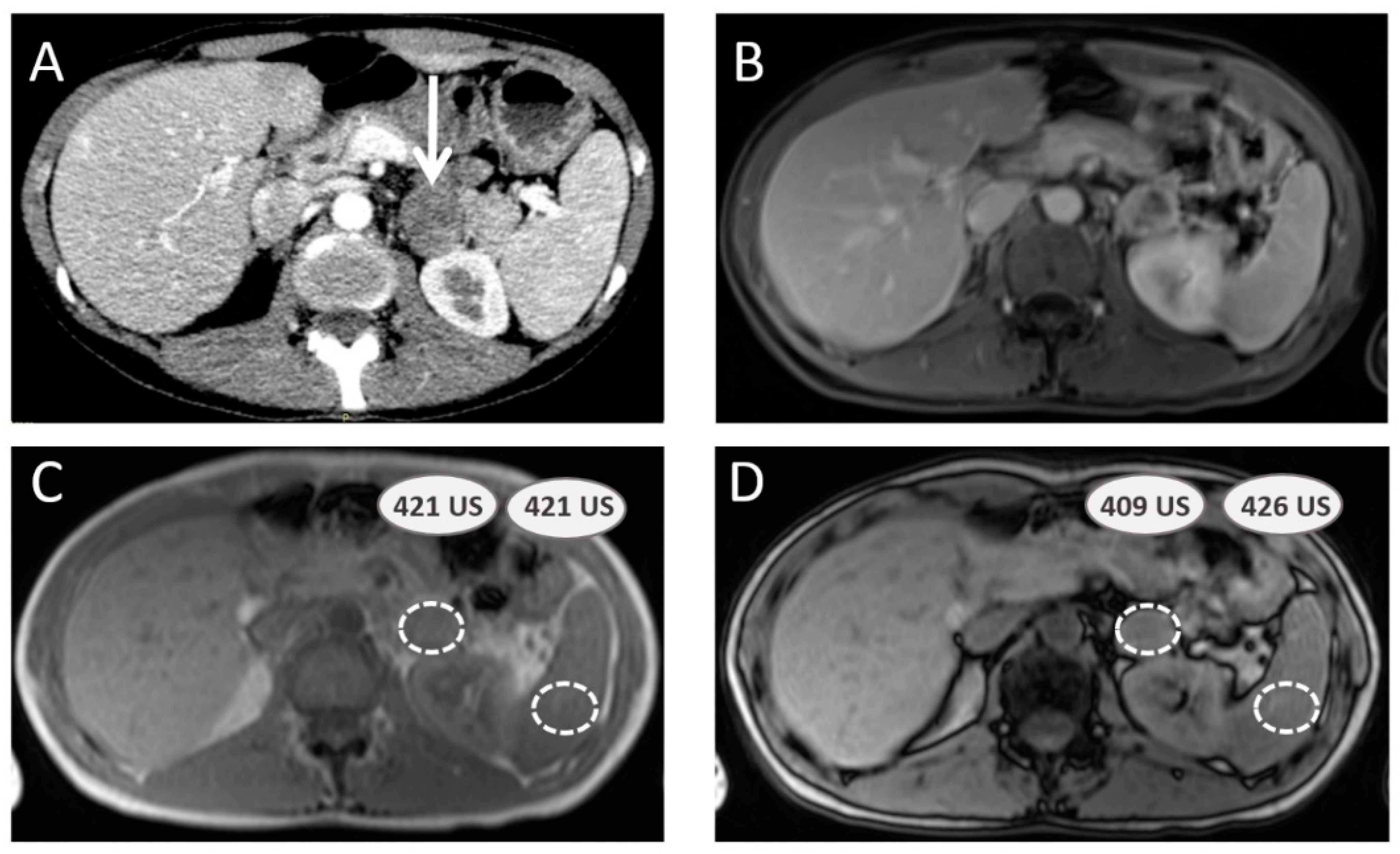
3.2. Additional Value of Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Scan
3.3. Additional Value of Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Chemical Shift Imaging
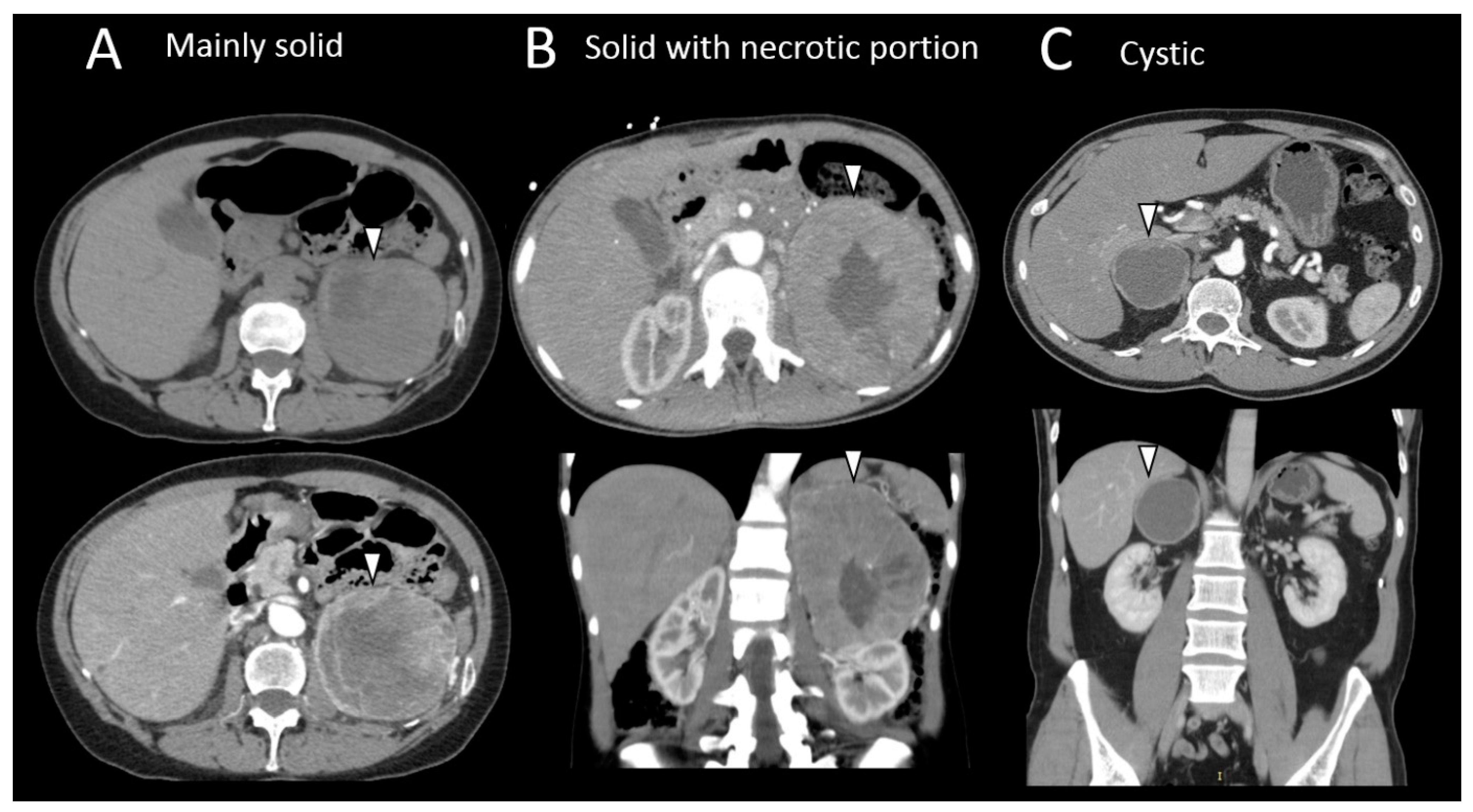
3.4. Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas: Variable Morphological Characteristics Using Anatomical Imaging
3.5. Head and Neck Parangangliomas: Specific Concerns
3.6. Specific Concern: How to Manage Asymptomatic SDHx Mutation Carriers?
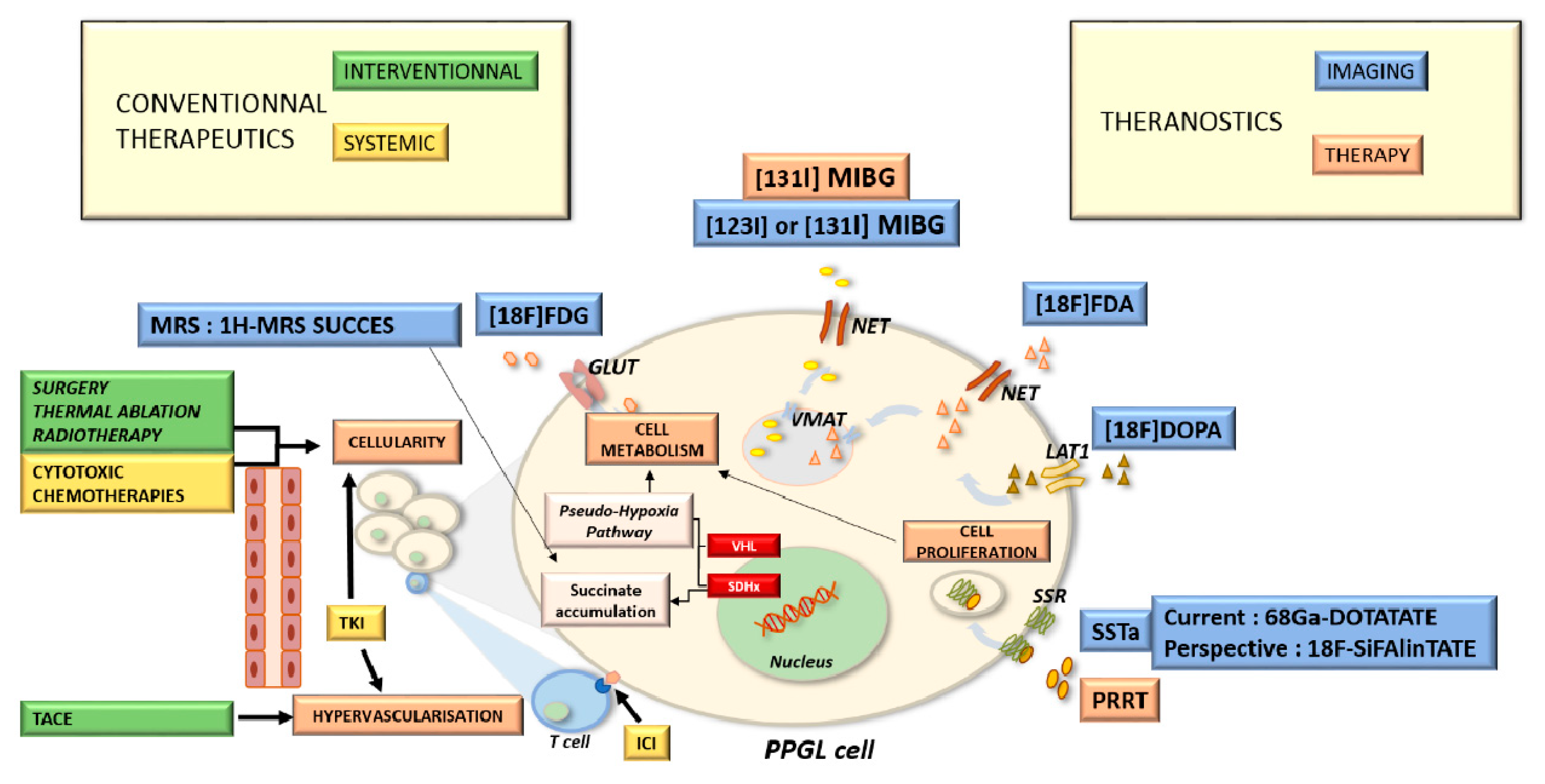
4. Molecular Imaging Techniques in Precise Diagnosis and Follow-Up
4.1. Metaiodobenzylguanidine: About the Historical Tracer
4.2. Contributions of Computed Tomography Using Dopamine and Glucose Analogues
4.3. Positron Emission Tomography with Computed Tomography Using Somatostatin Analogues
4.4. Current Guidelines for Molecular Imaging in Diagnosis and Staging of PPGLs
4.5. Future Perspectives in Metabolic Imaging
5. Planning a Surgical Treatment: The Role of Imaging
5.1. Reminder on Biopsy and PPGLs
5.2. Curative Surgical Management: How to Prepare a Surgery?
5.3. Palliative Surgery: The Debulking Strategy Concept
6. Imaging Guided Therapeutic Options
6.1. Thermal Ablation Techniques for Percutaneous Tumor Destruction
6.2. Transarterial Chemoembolization for Liver Metastases
6.3. Transarterial Embolization with Polyvinyl or Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol (Onyx)
6.4. Percutaneous Ethanol Injection
6.5. External Radiotherapy: Local Control and Symptoms Improvement
7. Systemic Therapies: Impact of New Therapeutics in Imaging Management
7.1. Cytotoxic Therapies
7.2. Targeted Therapies
7.3. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
8. Targeted Radionuclide Therapies in Palliative Treatments
8.1. Rationale
8.2. Iobenguane
8.3. Peptide Receptor Radiotherapy
9. Tumor Response Management: New Concepts and Pitfalls
9.1. RECIST 1.1 Limitations
9.2. Molecular Imaging Reporting and Data System: The SSTR-RADS
10. Current and Future Perspectives in the Era of Artificial Intelligence
10.1. Imaging, Radiomics, and Biomarkers as Predictors of Tumor Type and Progression
10.2. Metabolomics
10.3. Genomic and Methylomic
11. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | apparent diffusion coefficient |
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| ASII | adrenal signal intensity index |
| CEUS | contrast enhanced ultrasound examination |
| CE-MRA | contrast-enhanced MR angiography |
| CT | computed tomography |
| CgA | plasma chromogranin A |
| CSI | chemical shift imaging |
| DCE | dynamic contrast enhanced |
| DOPA | dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| DOTATOC | DOTA0-Phe1-Tyr3 octreotide |
| DWI | diffusion-weighted imaging |
| ECL | enterochromaffin-like |
| ENETs | European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society |
| 18F-FDG | 18Fluoro-Fluorodeoxyglucose |
| 68Ga | 68Gallium |
| GEP | gastroenteropancreatic |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide 1 |
| HaN PGL | head and neck paraganglioma |
| IACIG | intra-arterial injection of calcium |
| Ifα | Interferon α |
| IOUS | intra operative ultrasound examination |
| 177Lu | 177Lutetium |
| MEN2A | multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 |
| M/NM | metanephrine/normetanephrine |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NANETS | North American Neuroendocrine Tumor Society |
| NETs | neuroendocrine tumors |
| NF1 | neurofibromatosis type 1 |
| OS | overall survival |
| PCC | pheochromocytoma |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PERCIST | PET Response Criteria in Solid Tumors |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| pNET | pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor |
| PPGLs | pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas, if metastatic: MPPGLS |
| PR | partial response |
| PRRT | peptide receptor radionuclide therapy |
| RECIST | Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors |
| SD | stable disease |
| SDHx | Succinate DeHydrogenase genetic alterations |
| SPECT | single photon emission computed tomography |
| SSA | somatostatin analogs |
| SSTR | somatostatin receptor |
| SSTR-PET | somatostatin receptor PET |
| SSTR scintigraphy | somatostatin receptor scintigraphy |
| SUV | standardized uptake value |
| T1-w or T2-w | T1-weighted or T2-weighted (MRI sequence) |
| TACE | transarterial chemo-embolization |
| TAE | transarterial embolization |
| US | ultrasound examination |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| 90Y | 90Yttrium |
Appendix A

References
- Kim, J.H.; Moon, H.; Noh, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.G. Epidemiology and Prognosis of Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma in Korea: A Nationwide Study Based on the National Health Insurance Service. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 35, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacak, K.; Linehan, W.M.; Eisenhofer, G.; Walther, M.M.; Goldstein, D.S. Recent Advances in Genetics, Diagnosis, Localization, and Treatment of Pheochromocytoma. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001, 134, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berends, A.M.A.; Buitenwerf, E.; de Krijger, R.R.; Veeger, N.J.G.M.; van der Horst-Schrivers, A.N.A.; Links, T.P.; Kerstens, M.N. Incidence of Pheochromocytoma and Sympathetic Paraganglioma in the Netherlands: A Nationwide Study and Systematic Review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 51, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currás-Freixes, M.; Inglada-Pérez, L.; Mancikova, V.; Montero-Conde, C.; Letón, R.; Comino-Méndez, I.; Apellániz-Ruiz, M.; Sánchez-Barroso, L.; Aguirre Sánchez-Covisa, M.; Alcázar, V.; et al. Recommendations for Somatic and Germline Genetic Testing of Single Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Based on Findings from a Series of 329 Patients. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Baracco, R.; Kapur, G. Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma—An Update on Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 35, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenders, J.W.; Eisenhofer, G.; Mannelli, M.; Pacak, K. Phaeochromocytoma. Lancet 2005, 366, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Kozupa, A.; Eisenhofer, G.; Raygada, M.; Adams, K.T.; Solis, D.; Lenders, J.W.M.; Pacak, K. Clinical Presentations, Biochemical Phenotypes, and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in Patients with Succinate Dehydrogenase Subunit B -Associated Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokomoto-Umakoshi, M.; Umakoshi, H.; Fukumoto, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Nagata, H.; Ogata, M.; Kawate, H.; Miyazawa, T.; Sakamoto, R.; Ogawa, Y. Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: An Emerging Cause of Secondary Osteoporosis. Bone 2020, 133, 115221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderveen, K.A.; Thompson, S.M.; Callstrom, M.R.; Young, W.F.; Grant, C.S.; Farley, D.R.; Richards, M.L.; Thompson, G.B. Biopsy of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas: Potential for Disaster. Surgery 2009, 146, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhofer, G.; Goldstein, D.S.; Walther, M.M.; Friberg, P.; Lenders, J.W.M.; Keiser, H.R.; Pacak, K. Biochemical Diagnosis of Pheochromocytoma: How to Distinguish True- from False-Positive Test Results. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 2656–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bílek, R.; Vlček, P.; Šafařík, L.; Michalský, D.; Novák, K.; Dušková, J.; Václavíková, E.; Widimský, J., Jr.; Zelinka, T. Zelinka Chromogranin A in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Cancers 2019, 11, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouin, P.F.; Amar, L.; Dekkers, O.M.; Fassnacht, M.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.P.; Lenders, J.W.M.; Lussey-Lepoutre, C.; Steichen, O. European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline for Long-Term Follow-up of Patients Operated on for a Phaeochromocytoma or a Paraganglioma. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, G1–G10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benn, D.E.; Robinson, B.G. Genetic Basis of Phaeochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 20, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, L.M.; Lairmore, T.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Quasebarth, M.A.; DeBenedetti, M.; Moley, J.F. Adrenalectomy for Familial Pheochromocytoma in the Laparoscopic Era. Ann. Surg. 2002, 235, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, P.J.; El-Bahrawy, M.; Poulsom, R.; Elia, G.; Killick, P.; Kelly, G.; Hunt, T.; Jeffery, R.; Seedhar, P.; Barwell, J.; et al. Expression of HIF-1α, HIF-2α (EPAS1), and Their Target Genes in Paraganglioma and Pheochromocytoma with VHL and SDH Mutations. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 4593–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, J.; Langer, P.; Habbe, N.; Fendrich, V.; Ramaswamy, A.; Rothmund, M.; Bartsch, D.K.; Slater, E.P. Mutations and Polymorphisms in the SDHB, SDHD, VHL, and RET Genes in Sporadic and Familial Pheochromocytomas. Endocrine 2009, 35, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dluhy, R.G. Pheochromocytoma—Death of an Axiom. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1486–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yao, L.; King, E.E.; Buddavarapu, K.; Lenci, R.E.; Chocron, E.S.; Lechleiter, J.D.; Sass, M.; Aronin, N.; Schiavi, F.; et al. Germline Mutations in TMEM127 Confer Susceptibility to Pheochromocytoma. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbein, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Walter, V.; Danilova, L.; Robertson, A.G.; Johnson, A.R.; Lichtenberg, T.M.; Murray, B.A.; Ghayee, H.K.; Else, T.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, D.; Latif, F.; Dallol, A.; Dahia, P.L.M.; Douglas, F.; George, E.; Sköldberg, F.; Husebye, E.S.; Eng, C.; Maher, E.R. Gene Mutations in the Succinate Dehydrogenase Subunit SDHB Cause Susceptibility to Familial Pheochromocytoma and to Familial Paraganglioma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.-P.; Favier, J.; Rustin, P.; Rieubland, C.; Crespin, M.; Nau, V.; Khau Van Kien, P.; Corvol, P.; Plouin, P.-F.; Jeunemaitre, X.; et al. Mutations in the SDHB Gene Are Associated with Extra-Adrenal and/or Malignant Phaeochromocytomas. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5615–5621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricketts, C.J.; Forman, J.R.; Rattenberry, E.; Bradshaw, N.; Lalloo, F.; Izatt, L.; Cole, T.R.; Armstrong, R.; Kumar, V.K.A.; Morrison, P.J.; et al. Tumor Risks and Genotype–Phenotype–Proteotype Analysis in 358 Patients with Germline Mutations in SDHB and SDHD. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, O.; Young, W.F.; Gruber, L.; Smestad, J.; Yan, Q.; Ponce, O.J.; Prokop, L.; Murad, M.H.; Bancos, I. Outcomes of Patients with Metastatic Phaeochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 87, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelinka, T.; Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Kozupa, A.; Chen, C.C.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Reynolds, J.C.; Ling, A.; Eisenhofer, G.; Lazurova, I.; Adams, K.T.; et al. Role of Positron Emission Tomography and Bone Scintigraphy in the Evaluation of Bone Involvement in Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: Specific Implications for Succinate Dehydrogenase Enzyme Subunit B Gene Mutations. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, L.; Baudin, E.; Burnichon, N.; Peyrard, S.; Silvera, S.; Bertherat, J.; Bertagna, X.; Schlumberger, M.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.-P.; et al. Succinate Dehydrogenase B Gene Mutations Predict Survival in Patients with Malignant Pheochromocytomas or Paragangliomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3822–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nederveen, F.H.; Gaal, J.; Favier, J.; Korpershoek, E.; Oldenburg, R.A.; de Bruyn, E.M.; Sleddens, H.F.; Derkx, P.; Rivière, J.; Dannenberg, H.; et al. An Immunohistochemical Procedure to Detect Patients with Paraganglioma and Phaeochromocytoma with Germline SDHB, SDHC, or SDHD Gene Mutations: A Retrospective and Prospective Analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menara, M.; Oudijk, L.; Badoual, C.; Bertherat, J.; Lepoutre-Lussey, C.; Amar, L.; Iturrioz, X.; Sibony, M.; Zinzindohoué, F.; de Krijger, R.; et al. SDHD Immunohistochemistry: A New Tool to Validate SDHx Mutations in Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E287–E291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The NGS in PPGL (NGSnPPGL) Study Group; Toledo, R.A.; Burnichon, N.; Cascon, A.; Benn, D.E.; Bayley, J.-P.; Welander, J.; Tops, C.M.; Firth, H.; Dwight, T.; et al. Consensus Statement on Next-Generation-Sequencing-Based Diagnostic Testing of Hereditary Phaeochromocytomas and Paragangliomas. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.K. Update on Adrenal Tumours in 2017 World Health Organization (WHO) of Endocrine Tumours. Endocr. Pathol. 2017, 28, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Tavangar, S.; Shojaee, A.; Moradi Tabriz, H.; Haghpanah, V.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R.; Lashkari, A.; Azimi, S. Immunohistochemical Expression of Ki67, c-ErbB-2, and c-Kit Antigens in Benign and Malignant Pheochromocytoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2010, 206, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenman, A.; Zedenius, J.; Juhlin, C. The Value of Histological Algorithms to Predict the Malignancy Potential of Pheochromocytomas and Abdominal Paragangliomas—A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of the Literature. Cancers 2019, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Gonzalez, A.; Jimenez, C. Malignant Pheochromocytoma–Paraganglioma: Pathogenesis, TNM Staging, and Current Clinical Trials. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2017, 24, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenman, A.; Zedenius, J.; Juhlin, C.C. Retrospective Application of the Pathologic Tumor-Node-Metastasis Classification System for Pheochromocytoma and Abdominal Paraganglioma in a Well Characterized Cohort with Long-Term Follow-Up. Surgery 2019, 166, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turchini, J.; Cheung, V.K.Y.; Tischler, A.S.; De Krijger, R.R.; Gill, A.J. Pathology and Genetics of Phaeochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Histopathology 2018, 72, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, O.; Young, W.F.; Iñiguez-Ariza, N.M.; Kittah, N.E.; Gruber, L.; Bancos, C.; Tamhane, S.; Bancos, I. Malignant Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: 272 Patients Over 55 Years. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 3296–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.-H.; Chung, S.-D.; Chen, S.-C.; Chueh, S.-C.; Pu, Y.-S.; Lai, M.-K.; Lin, W.-C. Clinical and Pathological Data of 10 Malignant Pheochromocytomas: Long-Term Follow up in a Single Institute: Long-Term Follow up of Malignant Pheochromocytoma. Int. J. Urol. 2007, 14, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Barich, F.; Karnell, L.H.; Robinson, R.A.; Zhen, W.K.; Gantz, B.J.; Hoffman, H.T. American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer and the American Cancer Society National Cancer Data Base Report on Malignant Paragangliomas of the Head and Neck. Cancer 2002, 94, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Ramirez, M.; Palmer, J.L.; Hofmann, M.-C.; de la Cruz, M.; Moon, B.S.; Waguespack, S.G.; Habra, M.A.; Jimenez, C. Bone Metastases and Skeletal-Related Events in Patients With Malignant Pheochromocytoma and Sympathetic Paraganglioma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Ramirez, M.; Feng, L.; Johnson, M.M.; Ejaz, S.; Habra, M.A.; Rich, T.; Busaidy, N.; Cote, G.J.; Perrier, N.; Phan, A.; et al. Clinical Risk Factors for Malignancy and Overall Survival in Patients with Pheochromocytomas and Sympathetic Paragangliomas: Primary Tumor Size and Primary Tumor Location as Prognostic Indicators. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.T.; Sturgeon, C.; Clark, O.H.; Duh, Q.-Y.; Kebebew, E. Should Pheochromocytoma Size Influence Surgical Approach? A Comparison of 90 Malignant and 60 Benign Pheochromocytomas. Surgery 2004, 136, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasiliti-Caprino, M.; Lucatello, B.; Lopez, C.; Burrello, J.; Maletta, F.; Mistrangelo, M.; Migliore, E.; Tassone, F.; La Grotta, A.; Pia, A.; et al. Predictors of Recurrence of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Multicenter Study in Piedmont, Italy. Hypertens. Res. 2019, 43, 500–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hescot, S.; Curras-Freixes, M.; Deutschbein, T.; van Berkel, A.; Vezzosi, D.; Amar, L.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Valdes, N.; Riccardi, F.; Do Cao, C.; et al. Prognosis of Malignant Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma (MAPP-Prono Study): A European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 2367–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards-Taylor, S.; Ewings, S.M.; Jaynes, E.; Tilley, C.; Ellis, S.G.; Armstrong, T.; Pearce, N.; Cave, J. The Assessment of Ki-67 as a Prognostic Marker in Neuroendocrine Tumours: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 69, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, P.L.; Reidy-Lagunes, D.; Anthony, L.B.; Bertino, E.M.; Brendtro, K.; Chan, J.A.; Chen, H.; Jensen, R.T.; Kim, M.K.; Klimstra, D.S.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for the Management and Treatment of Neuroendocrine Tumors. Pancreas 2013, 42, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, E.E.; Xu, D.; Höög, A.; Enberg, U.; Hou, M.; Pisa, P.; Gruber, A.; Larsson, C.; Bäckdahl, M. KI-67 AND HTERT Expression Can Aid in the Distinction between Malignant and Benign Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Mod. Pathol. 2003, 16, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, E.; D’Avella, E.; Cappabianca, P.; Colao, A.; Del Basso De Caro, M. Ki67 in Endocrine Neoplasms: To Count or Not to Count, This Is the Question! A Systematic Review from the English Language Literature. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 1429–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moog, S.; Castinetti, F.; DoCao, C.; Amar, L.; Hadoux, J.; Lussey-Lepoutre, C.; Borson-Chazot, F.; Vezzosi, D.; Drui, D.; Laboureau, S.; et al. Recurrence-Free Survival Analysis in Locally Advanced Pheochromocytoma: First Appraisal. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 2726–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, H.M.; Komorowski, R.A.; Wilson, S.D.; Demeure, M.J.; Zhu, Y.R. Predicting Metastasis of Pheochromocytomas Using DNA Flow Cytometry and Immunohistochemical Markers of Cell Proliferation: A Positive Correlation between MIB-1 Staining and Malignant Tumor Behavior. Cancer 1999, 86, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, N.; Takekoshi, K.; Naruse, M. Risk Stratification on Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma from Laboratory and Clinical Medicine. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.-M.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.-J.; Sung, T.-Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Hong, S.J.; Song, D.E.; Lee, S.H. Validation of Pathological Grading Systems for Predicting Metastatic Potential in Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.Y.; Kwak, M.K.; Lee, S.-E.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, H.; Suh, S.; Kim, B.-J.; Song, K.-H.; Koh, J.-M.; Kim, J.H.; et al. A Clinical Prediction Model to Estimate the Metastatic Potential of Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma: ASES Score. Surgery 2018, 164, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Mehrotra, P.K.; Jain, M.; Gupta, S.K.; Mishra, A.; Chand, G.; Agarwal, G.; Verma, A.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, U. Size of the Tumor and Pheochromocytoma of the Adrenal Gland Scaled Score (PASS): Can They Predict Malignancy? World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 3022–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taïeb, D.; Rubello, D.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Calzada, M.; Marzola, M.C.; Hindié, E. Modern PET Imaging for Paragangliomas: Relation to Genetic Mutations. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. EJSO 2011, 37, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, Q. Differentiation of Malignant From Benign Pheochromocytomas With Diffusion-Weighted and Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance at 3.0 T. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2012, 36, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torresan, F.; Beber, A.; Schiavone, D.; Zovato, S.; Galuppini, F.; Crimì, F.; Ceccato, F.; Iacobone, M. Long-Term Outcomes after Surgery for Pheochromocytoma and Sympathetic Paraganglioma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogowski-Lehmann, N.; Geroula, A.; Prejbisz, A.; Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Megerle, F.; Robledo, M.; Fassnacht, M.; Fliedner, S.M.J.; Reincke, M.; Stell, A.; et al. Missed Clinical Clues in Patients with Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma Discovered by Imaging. Endocr. Connect. 2018, 7, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta-Ramirez, G.A.; Remer, E.M.; Herts, B.R.; Gill, I.S.; Hamrahian, A.H. Comparison of CT Findings in Symptomatic and Incidentally Discovered Pheochromocytomas. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 185, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahdev, A.; Reznek, R. Imaging Evaluation of the Non-Functioning Indeterminate Adrenal Mass. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 15, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, M.; Arlt, W.; Bancos, I.; Dralle, H.; Newell-Price, J.; Sahdev, A.; Tabarin, A.; Terzolo, M.; Tsagarakis, S.; Dekkers, O.M. Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas: European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline in Collaboration with the European Network for the Study of Adrenal Tumors. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 175, G1–G34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, M.A.; Krishnamoorthy, S.K.; Boland, G.W.; Sweeney, A.T.; Pitman, M.B.; Harisinghani, M.; Mueller, P.R.; Hahn, P.F. Low-Density Pheochromocytoma on CT: A Mimicker of Adrenal Adenoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caoili, E.M.; Korobkin, M.; Francis, I.R.; Cohan, R.H.; Platt, J.F.; Dunnick, N.R.; Raghupathi, K.I. Adrenal Masses: Characterization with Combined Unenhanced and Delayed Enhanced CT. Radiology 2002, 222, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Park, B.K.; Kim, C.K. Adrenal Imaging for Adenoma Characterization: Imaging Features, Diagnostic Accuracies and Differential Diagnoses. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20151018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, S.Z.; Nikolaidis, P.; Horowitz, J.M.; Gabriel, H.; Hammond, N.A.; Patel, T.; Yaghmai, V.; Miller, F.H. Chemical Shift MR Imaging of the Adrenal Gland: Principles, Pitfalls, and Applications. RadioGraphics 2016, 36, 414–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffel, M.; Haji-Momenian, S.; Nikolaidis, P.; Miller, F.H. Adrenal Imaging: A Comprehensive Review. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 50, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, J.; Bhatt, A.A. Multimodality Imaging of Paragangliomas of the Head and Neck. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.-P.; Caumont-Prim, A.; Houzard, C.; Hignette, C.; Hernigou, A.; Halimi, P.; Niccoli, P.; Leboulleux, S.; Amar, L.; Borson-Chazot, F.; et al. Imaging Work-Up for Screening of Paraganglioma and Pheochromocytoma in SDHx Mutation Carriers: A Multicenter Prospective Study from the PGL.EVA Investigators. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E162–E173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Shi, H.; Tao, X. Head and Neck Paragangliomas: Diffusion Weighted and Dynamic Contrast Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Characteristics. BMC Med. Imaging 2016, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, F.; Huwart, L.; Jourdan, G.; Reizine, D.; Herman, P.; Vicaut, E.; Guichard, J.P. Head and Neck Paragangliomas: Value of Contrast-Enhanced 3D MR Angiography. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsovic, E.; Montava, M.; Fakhry, N.; Lavieille, J.-P.; Pacak, K.; Taïeb, D.; Varoquaux, A. Quantitative Biomarkers Allow the Diagnosis of Head and Neck Paraganglioma on Multiparametric MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 143, 109911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, J.-P.; Fakhry, N.; Franc, J.; Herman, P.; Righini, C.-A.; Taieb, D. Morphological and Functional Imaging of Neck Paragangliomas. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2017, 134, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amar, L.; Pacak, K.; Steichen, O.; Akker, S.A.; Aylwin, S.J.B.; Baudin, E.; Buffet, A.; Burnichon, N.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Dahia, P.L.M.; et al. International Consensus on Initial Screening and Follow-up of Asymptomatic SDHx Mutation Carriers. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegerle, S.; Nitzsche, E.; Altehoefer, C.; Ghanem, N.; Manz, T.; Brink, I.; Reincke, M.; Moser, E.; Neumann, H.P.H. Pheochromocytomas: Detection with 18 F DOPA Whole-Body PET—Initial Results. Radiology 2002, 222, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fottner, C.; Helisch, A.; Anlauf, M.; Rossmann, H.; Musholt, T.J.; Kreft, A.; Schadmand-Fischer, S.; Bartenstein, P.; Lackner, K.J.; Klöppel, G.; et al. 6-18F-Fluoro-L-Dihydroxyphenylalanine Positron Emission Tomography Is Superior to 123I-Metaiodobenzyl-Guanidine Scintigraphy in the Detection of Extraadrenal and Hereditary Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas: Correlation with Vesicular Monoamine Transporter Expression. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 2800–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taïeb, D.; Sebag, F.; Hubbard, J.G.; Mundler, O.; Henry, J.F.; Conte-Devolx, B. Does Iodine-131 Meta-Iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) Scintigraphy Have an Impact on the Management of Sporadic and Familial Phaeochromocytoma? Clin. Endocrinol. 2004, 61, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Harst, E.; de Herder, W.W.; Bruining, H.A.; Bonjer, H.J.; de Krijger, R.R.; Lamberts, S.W.; van de Meiracker, A.H.; Boomsma, F.; Stijnen, T.; Krenning, E.P.; et al. [123I]Metaiodobenzylguanidine and [111In]Octreotide Uptake in Begnign and Malignant Pheochromocytomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupilli, C.; Lanzillotti, R.; Fiorelli, G.; Selli, C.; Gomez, R.A.; Carey, R.M.; Serio, M.; Mannelli, M. Dopamine D2 Receptor Gene Expression and Binding Sites in Adrenal Medulla and Pheochromocytoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1994, 79, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Hadi, M.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Chen, C.C.; Martiniova, L.; Whatley, M.; Ling, A.; Eisenhofer, G.; Adams, K.T.; Pacak, K. The Effects of Carbidopa on Uptake of 6-18F-Fluoro-L-DOPA in PET of Pheochromocytoma and Extraadrenal Abdominal Paraganglioma. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1599–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ilias, I.; Chen, C.C.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Whatley, M.; Ling, A.; Lazurova, I.; Adams, K.T.; Perera, S.; Pacak, K. Comparison of 6-[18F]-Fluorodopamine PET with [123I]-Metaiodobenzylguanidine and [111In]-Pentetreotide Scintigraphy in Localization of Nonmetastatic and Metastatic Pheochromocytoma. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Eisenhofer, G.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Chen, C.C.; Whatley, M.; Ling, A.; Adams, K.T.; Pacak, K. Use of 6-[18F]-Fluorodopamine Positron Emission Tomography (PET) as First-Line Investigation for the Diagnosis and Localization of Non-Metastatic and Metastatic Phaeochromocytoma (PHEO). Clin. Endocrinol. 2009, 71, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, I.; Yu, J.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Chen, C.C.; Eisenhofer, G.; Whatley, M.; McElroy, B.; Pacak, K. Superiority of 6-[18F]-Fluorodopamine Positron Emission Tomography Versus [131I]-Metaiodobenzylguanidine Scintigraphy in the Localization of Metastatic Pheochromocytoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4083–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.S.; Chen, C.C.; Alexopoulos, D.K.; Whatley, M.A.; Reynolds, J.C.; Patronas, N.; Ling, A.; Adams, K.T.; Xekouki, P.; Lando, H.; et al. Functional Imaging of SDHx-Related Head and Neck Paragangliomas: Comparison of 18F-Fluorodihydroxyphenylalanine, 18F-Fluorodopamine, 18F-Fluoro-2-Deoxy-d-Glucose PET, 123I-Metaiodobenzylguanidine Scintigraphy, and 111In-Pentetreotide Scintigraphy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 2779–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacak, K.; Eisenhofer, G.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Chen, C.C.; Li, S.-T.; Goldstein, D.S. 6-[18F]Fluorodopamine Positron Emission Tomographic (PET) Scanning for Diagnostic Localization of Pheochromocytoma. Hypertension 2001, 38, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordzij, W.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Schaafsma, M.; van der Horst-Schrivers, A.N.A.; Slart, R.H.J.A.; van Beek, A.P.; Kerstens, M.N. Adrenal Tracer Uptake by 18F-FDOPA PET/CT in Patients with Pheochromocytoma and Controls. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1560–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufini, V.; Treglia, G.; Castaldi, P.; Perotti, G.; Calcagni, M.L.; Corsello, S.M.; Galli, G.; Fanti, S.; Giordano, A. Comparison of 123I-MIBG SPECT-CT and 18F-DOPA PET-CT in the Evaluation of Patients with Known or Suspected Recurrent Paraganglioma. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2011, 32, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebrich, H.-B.; Brouwers, A.H.; Kerstens, M.N.; Pijl, M.E.J.; Kema, I.P.; de Jong, J.R.; Jager, P.L.; Elsinga, P.H.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; van der Wal, J.E.; et al. 6-[F-18]Fluoro-L-Dihydroxyphenylalanine Positron Emission Tomography Is Superior to Conventional Imaging with 123I-Metaiodobenzylguanidine Scintigraphy, Computer Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Localizing Tumors Causing Catecholamine Excess. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 3922–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luster, M.; Karges, W.; Zeich, K.; Pauls, S.; Verburg, F.A.; Dralle, H.; Glatting, G.; Buck, A.K.; Solbach, C.; Neumaier, B.; et al. Clinical Value of 18F-Fluorodihydroxyphenylalanine Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (18F-DOPA PET/CT) for Detecting Pheochromocytoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imani, F.; Agopian, V.G.; Auerbach, M.S.; Walter, M.A.; Imani, F.; Benz, M.R.; Dumont, R.A.; Lai, C.K.; Czernin, J.G.; Yeh, M.W. 18F-FDOPA PET and PET/CT Accurately Localize Pheochromocytomas. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taïeb, D.; Hicks, R.J.; Hindié, E.; Guillet, B.A.; Avram, A.; Ghedini, P.; Timmers, H.J.; Scott, A.T.; Elojeimy, S.; Rubello, D.; et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine Practice Guideline/Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Procedure Standard 2019 for Radionuclide Imaging of Phaeochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2112–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taieb, D.; Sebag, F.; Barlier, A.; Tessonnier, L.; Palazzo, F.F.; Morange, I.; Niccoli-Sire, P.; Fakhry, N.; De Micco, C.; Cammilleri, S.; et al. 18F-FDG Avidity of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas: A New Molecular Imaging Signature? J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favier, J.; Brière, J.-J.; Burnichon, N.; Rivière, J.; Vescovo, L.; Benit, P.; Giscos-Douriez, I.; De Reyniès, A.; Bertherat, J.; Badoual, C.; et al. The Warburg Effect Is Genetically Determined in Inherited Pheochromocytomas. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Berkel, A.; Vriens, D.; Visser, E.P.; Janssen, M.J.R.; Gotthardt, M.; Hermus, A.R.M.M.; de Geus-Oei, L.-F.; Timmers, H.J.L.M. Metabolic Subtyping of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma by 18F-FDG Pharmacokinetics Using Dynamic PET/CT Scanning. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulkin, B.L.; Thompson, N.W.; Shapiro, B.; Francis, I.R.; Sisson, J.C. Pheochromocytomas: Imaging with 2-[Fluorine-18]Fluoro-2-Deoxy-d-Glucose PET. Radiology 1999, 212, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Chen, C.C.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Whatley, M.; Ling, A.; Eisenhofer, G.; King, K.S.; Rao, J.U.; Wesley, R.A.; Adams, K.T.; et al. Staging and Functional Characterization of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma by 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) Positron Emission Tomography. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Chen, C.C.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Whatley, M.; Ling, A.; Havekes, B.; Eisenhofer, G.; Martiniova, L.; Adams, K.T.; Pacak, K. Comparison of 18F-Fluoro-L-DOPA, 18F-Fluoro-Deoxyglucose, and 18F-Fluorodopamine PET and 123I-MIBG Scintigraphy in the Localization of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 4757–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Kozupa, A.; Chen, C.C.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Ling, A.; Eisenhofer, G.; Adams, K.T.; Solis, D.; Lenders, J.W.M.; Pacak, K. Superiority of Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography to Other Functional Imaging Techniques in the Evaluation of Metastatic SDHB-Associated Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueberberg, B.; Tourne, H.; Redmann, A.; Redman, A.; Walz, M.K.; Schmid, K.W.; Mann, K.; Petersenn, S. Differential Expression of the Human Somatostatin Receptor Subtypes Sst1 to Sst5 in Various Adrenal Tumors and Normal Adrenal Gland. Horm. Metab. Res. Horm. Stoffwechselforschung Horm. Metab. 2005, 37, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Laissue, J.; Krenning, E.; Lamberts, S.W. Somatostatin Receptors in Human Cancer: Incidence, Characteristics, Functional Correlates and Clinical Implications. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 43, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustillo, A.; Telischi, F.; Weed, D.; Civantos, F.; Angeli, S.; Serafini, A.; Whiteman, M. Octreotide Scintigraphy in the Head and Neck. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Fischer, E.; Dietlein, M.; Michel, O.; Weber, K.; Moka, D.; Stennert, E.; Schicha, H. Clinical Value of Somatostatin Receptor Imaging in Patients with Suspected Head and Neck Paragangliomas. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopmans, K.P.; Jager, P.L.; Kema, I.P.; Kerstens, M.N.; Albers, F.; Dullaart, R.P.F. 111In-Octreotide Is Superior to 123I-Metaiodobenzylguanidine for Scintigraphic Detection of Head and Neck Paragangliomas. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1232–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteman, M.L.; Serafini, A.N.; Telischi, F.F.; Civantos, F.J.; Falcone, S. 111In Octreotide Scintigraphy in the Evaluation of Head and Neck Lesions. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1997, 18, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duet, M.; Sauvaget, E.; Pételle, B.; Rizzo, N.; Guichard, J.-P.; Wassef, M.; Le Cloirec, J.; Herman, P.; Tran Ba Huy, P. Clinical Impact of Somatostatin Receptor Scintigraphy in the Management of Paragangliomas of the Head and Neck. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muros, M.A.; Llamas-Elvira, J.M.; Rodríguez, A.; Ramírez, A.; Gómez, M.; Arráez, M.A.; Valéncia, E.; Vílchez, R. 111In-Pentetreotide Scintigraphy Is Superior to 123I-MIBG Scintigraphy in the Diagnosis and Location of Chemodectoma. Nucl. Med. Commun. 1998, 19, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Blanchet, E.M.; Adams, K.; Chen, C.C.; Millo, C.M.; Herscovitch, P.; Taieb, D.; Kebebew, E.; Lehnert, H.; Fojo, A.T.; et al. Superiority of [68Ga]-DOTATATE PET/CT to Other Functional Imaging Modalities in the Localization of SDHB-Associated Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3888–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrokhi, P.; Emami-Ardekani, A.; Harsini, S.; Eftekhari, M.; Fard Esfehani, A.; Fallahi, B.; Karamzade Ziarati, N.; Akhlaghi, M.; Farzanefar, S.; Beiki, D.; et al. 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT Compared with 131I-MIBG SPECT/CT in the Evaluation of Neural Crest Tumors. Asia Ocean. J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2019, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, M.; Zhao, C.; Welsh, S.J.; Meades, R.; Win, Z.; Ferrarese, A.; Tan, T.; Rubello, D.; Al-Nahhas, A. 68Ga-DOTA-TATE PET vs. 123I-MIBG in Identifying Malignant Neural Crest Tumours. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2011, 13, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, V.; Kunikowska, J.; Baudin, E.; Bodei, L.; Bouvier, C.; Capdevila, J.; Cremonesi, M.; de Herder, W.W.; Dromain, C.; Falconi, M.; et al. Consensus on Molecular Imaging and Theranostics in Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 146, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, H.; Todica, A.; Lindner, S.; Boening, G.; Gosewisch, A.; Wängler, C.; Wängler, B.; Schirrmacher, R.; Bartenstein, P. First-in-Human 18F-SiFAlin-TATE PET/CT for NET Imaging and Theranostics. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2400–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fani, M.; Nicolas, G.P.; Wild, D. Somatostatin Receptor Antagonists for Imaging and Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 61S–66S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, S.; Jimenez, C. Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: Management of Endocrine Manifestations, Surgery and Ablative Procedures, and Systemic Therapies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 34, 101354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamblin, W.R.; ReMine, W.H.; Sheps, S.G.; Harrison, E.G. Carotid Body Tumor (Chemodectoma). Am. J. Surg. 1971, 122, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasper, A.; Mammen, S.; Gowri, M.S.; Keshava, S.N.; Selvaraj, D. Department of Vascular Surgery, Christian Medical College, Vellore, India Imaging Criteria to Predict Shamblin Group in Carotid Body Tumors—Revisited. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2021, 27, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, S.; Rao, V.; Juvekar, S.; Dcruz, A.K. Carotid Body Tumors: Objective Criteria to Predict the Shamblin Group on MR Imaging. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, P.; Ramachandran, R.; Tandon, N.; Kumar, R. Open Surgery for Pheochromocytoma: Current Indications and Outcomes from a Retrospective Cohort. Indian J. Urol. IJU J. Urol. Soc. India 2020, 36, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, L.; Lussey, C.; Lenders, J.W.M.; Pratt, J.D.; Plouin, P.-F.; Steichen, O. Recurrence or New Tumors after Complete Resection of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, e269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.M.; Violette, P.D.; Tran, C.; Tomiak, E.; Izard, J.; Bathini, V.; Rowe, N.E. Canadian Urological Association Best Practice Report on the Long-Term Followup for Patients with Pheochromocytomas. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2019, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nölting, S.; Ullrich, M.; Pietzsch, J.; Ziegler, C.G.; Eisenhofer, G.; Grossman, A.; Pacak, K. Pacak Current Management of Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma: A Guide for the Practicing Clinician in the Era of Precision Medicine. Cancers 2019, 11, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrisoulidou, A.; Kaltsas, G.; Ilias, I.; Grossman, A.B. The Diagnosis and Management of Malignant Phaeochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Gonzalez, A.; Zhou, S.; Ayala-Ramirez, M.; Shen, C.; Waguespack, S.G.; Habra, M.A.; Karam, J.A.; Perrier, N.; Wood, C.G.; Jimenez, C. Impact of Surgical Resection of the Primary Tumor on Overall Survival in Patients With Metastatic Pheochromocytoma or Sympathetic Paraganglioma. Ann. Surg. 2018, 268, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.M.; Locklin, J.; Dupuy, D.E.; Wood, B.J. Percutaneous Ablation of Adrenal Tumors. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 13, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-H.; Tyan, Y.-S.; Ueng, K.-C. Immediate Results and Long-Term Outcomes Following Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation of Unilateral Aldosterone-Producing Adenoma. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2020, 36, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlenberg, J.; Welch, B.; Hamidi, O.; Callstrom, M.; Morris, J.; Sprung, J.; Bancos, I.; Young, W. Efficacy and Safety of Ablative Therapy in the Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Cancers 2019, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, J.F.; Atwell, T.D.; Charboneau, W.J.; Young, W.F.; Wass, T.C.; Callstrom, M.R. Minimally Invasive Treatment of Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation and Cryoablation Therapy. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravel, G.; Leboulleux, S.; Tselikas, L.; Fassio, F.; Berraf, M.; Berdelou, A.; Ba, B.; Hescot, S.; Hadoux, J.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Prevention of Serious Skeletal-Related Events by Interventional Radiology Techniques in Patients with Malignant Paraganglioma and Pheochromocytoma. Endocrine 2018, 59, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J.; Stålberg, P.; Nilsson, A.; Krause, J.; Lundberg, C.; Skogseid, B.; Granberg, D.; Eriksson, B.; Åkerström, G.; Hellman, P. Surgery and Radiofrequency Ablation for Treatment of Liver Metastases from Midgut and Foregut Carcinoids and Endocrine Pancreatic Tumors. World J. Surg. 2008, 32, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Baère, T.; Aupérin, A.; Deschamps, F.; Chevallier, P.; Gaubert, Y.; Boige, V.; Fonck, M.; Escudier, B.; Palussiére, J. Radiofrequency Ablation Is a Valid Treatment Option for Lung Metastases: Experience in 566 Patients with 1037 Metastases. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacak, K.; Fojo, T.; Goldstein, D.S.; Eisenhofer, G.; Walther, M.M.; Linehan, W.M.; Bachenheimer, L.; Abraham, J.; Wood, B.J. Radiofrequency Ablation: A Novel Approach for Treatment of Metastatic Pheochromocytoma. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 648–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orditura, M.; Petrillo, A.; Ventriglia, J.; Diana, A.; Laterza, M.M.; Fabozzi, A.; Savastano, B.; Franzese, E.; Conzo, G.; Santini, L.; et al. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Nosography, Management and Treatment. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 28, S156–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Baère, T.; Palussière, J.; Aupérin, A.; Hakime, A.; Abdel-Rehim, M.; Kind, M.; Dromain, C.; Ravaud, A.; Tebboune, N.; Boige, V.; et al. Midterm Local Efficacy and Survival after Radiofrequency Ablation of Lung Tumors with Minimum Follow-up of 1 Year: Prospective Evaluation. Radiology 2006, 240, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dromain, C.; de Baere, T.; Lumbroso, J.; Caillet, H.; Laplanche, A.; Boige, V.; Ducreux, M.; Duvillard, P.; Elias, D.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Detection of Liver Metastases From Endocrine Tumors: A Prospective Comparison of Somatostatin Receptor Scintigraphy, Computed Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellman, P.; Ladjevardi, S.; Skogseid, B.; Åkerström, G.; Elvin, A. Radiofrequency Tissue Ablation Using Cooled Tip for Liver Metastases of Endocrine Tumors. World J. Surg. 2002, 26, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, A.M.; Locklin, J.; Lai, E.W.; Adams, K.T.; Fojo, A.T.; Pacak, K.; Wood, B.J. Radiofrequency Ablation of Metastatic Pheochromocytoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2009, 20, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Leon Pachter, H.; Sarpel, U. Hepatic Arterial Embolization for the Treatment of Metastatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 471203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Ashizawa, N.; Minami, T.; Suzuki, S.; Sakamoto, I.; Hayashi, K.; Tomiyasu, S.; Sumikawa, K.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; et al. Malignant Pheochromocytoma with Multiple Hepatic Metastases Treated by Chemotherapy and Transcatheter Arterial Embolization. Intern. Med. 1999, 38, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Watanabe, D.; Tanabe, A.; Naruse, M.; Tsuiki, M.; Torii, N.; Noshiro, T.; Takano, K. Transcatheter Arterial Embolization for the Treatment of Liver Metastases in a Patient with Malignant Pheochromocytoma. Endocr. J. 2006, 53, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, S.; Hiraoka, A.; Ochi, H.; Uehara, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hasebe, A.; Tanihira, T.; Tanabe, A.; Ichiryu, M.; et al. Malignant Pheochromocytoma with Liver Metastasis Treated by Transcatheter Arterial Chemo-Embolization (TACE). Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mora, J.; Cruz, O.; Parareda, A.; Sola, T.; de Torres, C. Treatment of Disseminated Paraganglioma with Gemcitabine and Docetaxel. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.B.; Link, M.J.; Cloft, H.J. Endovascular Embolization of Paragangliomas: A Safe Adjuvant to Treatment. J. Vasc. Interv. Neurol. 2008, 1, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Michelozzi, C.; Januel, A.C.; Cuvinciuc, V.; Tall, P.; Bonneville, F.; Fraysse, B.; Deguine, O.; Serrano, E.; Cognard, C. Arterial Embolization with Onyx of Head and Neck Paragangliomas. J. NeuroInterv. Surg. 2016, 8, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.S.; Myhill, J.A.; Padhya, T.A.; McCaffrey, J.C.; McCaffrey, T.V.; Mhaskar, R.S. The Effects of Preoperative Embolization on Carotid Body Paraganglioma Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2015, 153, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zuo, C.; Qian, Z.; Tian, J.; Ren, F.; Zhou, D. Computerized Tomography Guided Percutaneous Ethanol Injection for the Treatment of Hyperfunctioning Pheochromocytoma. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 1132–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, C.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Bödeker, C.C.; Llorente, J.L.; Silver, C.E.; Jansen, J.C.; Takes, R.P.; Strojan, P.; Pellitteri, P.K.; Rinaldo, A.; et al. Jugular and Vagal Paragangliomas: Systematic Study of Management with Surgery and Radiotherapy. Head Neck 2013, 35, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinerman, R.W.; Amdur, R.J.; Morris, C.G.; Kirwan, J.; Mendenhall, W.M. Definitive Radiotherapy in the Management of Paragangliomas Arising in the Head and Neck: A 35-Year Experience. Head Neck 2008, 30, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.; Atanacio, A.S.; Prodanov, T.; Turkbey, B.I.; Adams, K.; Martucci, V.; Camphausen, K.; Fojo, A.T.; Pacak, K.; Kaushal, A. External Beam Radiation Therapy in Treatment of Malignant Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, W.; Bancos, I.; Young, W.F.; Bible, K.C.; Laack, N.N.; Foote, R.L.; Hallemeier, C.L. External Beam Radiation Therapy for Advanced/Unresectable Malignant Paraganglioma and Pheochromocytoma. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 3, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C. Treatment for Patients With Malignant Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas: A Perspective From the Hallmarks of Cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, K.; Kimura, H.; Shimizu, S.; Kodama, H.; Okamoto, T.; Obara, T.; Takano, K. Survival of Patients with Metastatic Malignant Pheochromocytoma and Efficacy of Combined Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, and Dacarbazine Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2850–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Abraham, J.; Hung, E.; Averbuch, S.; Merino, M.; Steinberg, S.M.; Pacak, K.; Fojo, T. Treatment of Malignant Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma with Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, and Dacarbazine: Recommendation From a 22-Year Follow-up of 18 Patients. Cancer 2008, 113, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeijer, N.D.; Alblas, G.; van Hulsteijn, L.T.; Dekkers, O.M.; Corssmit, E.P.M. Chemotherapy with Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine and Dacarbazine for Malignant Paraganglioma and Pheochromocytoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 81, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averbuch, S.D. Malignant Pheochromocytoma: Effective Treatment with a Combination of Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, and Dacarbazine. Ann. Intern. Med. 1988, 109, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadoux, J.; Favier, J.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; Leboulleux, S.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Caramella, C.; Déandreis, D.; Borget, I.; Loriot, C.; Chougnet, C.; et al. SDHB Mutations Are Associated with Response to Temozolomide in Patients with Metastatic Pheochromocytoma or Paraganglioma: Temozolomide for Malignant Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On behalf of the Spanish Cooperative Group of Neuroendocrine Tumors (GETNE); Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Garcia-Figueiras, R.; Carmona-Bayonas, A.; Sevilla, I.; Teule, A.; Quindos, M.; Grande, E.; Capdevila, J.; Aller, J.; et al. Imaging Approaches to Assess the Therapeutic Response of Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (GEP-NETs): Current Perspectives and Future Trends of an Exciting Field in Development. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundin, A.; Garske, U.; Örlefors, H. Nuclear Imaging of Neuroendocrine Tumours. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 21, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IEO ENETS Center of Excellence for GEP NETs; Martins, D.; Spada, F.; Lambrescu, I.; Rubino, M.; Cella, C.; Gibelli, B.; Grana, C.; Ribero, D.; Bertani, E.; et al. Predictive Markers of Response to Everolimus and Sunitinib in Neuroendocrine Tumors. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dercle, L.; Ma, J.; Xie, C.; Chen, A.-P.; Wang, D.; Luk, L.; Revel-Mouroz, P.; Otal, P.; Peron, J.-M.; Rousseau, H.; et al. Using a Single Abdominal Computed Tomography Image to Differentiate Five Contrast-Enhancement Phases: A Machine-Learning Algorithm for Radiomics-Based Precision Medicine. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 125, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiris, A.; Mellott, A.; Spies, S. PET Scan Assessment of Chemotherapy Response in Metastatic Paraganglioma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 26, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadoux, J.; Terroir, M.; Leboulleux, S.; Deschamps, F.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Hescot, S.; Tselikas, L.; Borget, I.; Caramella, C.; Déandréis, D.; et al. Interferon-Alpha Treatment for Disease Control in Metastatic Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma Patients. Horm. Cancer 2017, 8, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, A.M.; Ezzat, S.; Asa, S.L.; Evans, A.; Broom, R.; Freeman, M.; Knox, J.J. Rationale and Evidence for Sunitinib in the Treatment of Malignant Paraganglioma/Pheochromocytoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Ramirez, M.; Chougnet, C.N.; Habra, M.A.; Palmer, J.L.; Leboulleux, S.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Caramella, C.; Anderson, P.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Waguespack, S.G.; et al. Treatment with Sunitinib for Patients with Progressive Metastatic Pheochromocytomas and Sympathetic Paragangliomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 4040–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudin, E.; Goichot, B.; Berruti, A.; Hadoux, J.; Moalla, S.; Laboureau, S.; Noelting, S.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Kienitz, T.; Deutschbein, T.; et al. 567O First International Randomized Study in Malignant Progressive Pheochromocytoma and Paragangliomas (FIRSTMAPPP): An Academic Double-Blind Trial Investigating Sunitinib. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Richard, M.; Massutí, B.; Pineda, E.; Alonso, V.; Marmol, M.; Castellano, D.; Fonseca, E.; Galán, A.; Llanos, M.; Sala, M.A.; et al. Antiproliferative Effects of Lanreotide Autogel in Patients with Progressive, Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumours: A Spanish, Multicentre, Open-Label, Single Arm Phase II Study. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wymenga, A.N.M.; Eriksson, B.; Salmela, P.I.; Jacobsen, M.B.; Van Cutsem, E.J.D.G.; Fiasse, R.H.; Välimäki, M.J.; Renstrup, J.; de Vries, E.G.E.; Öberg, K.E. Efficacy and Safety of Prolonged-Release Lanreotide in Patients With Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors and Hormone-Related Symptoms. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Santarpia, L.; Jonasch, E.; Kyle, K.L.; Lano, E.A.; Matin, S.F.; Nunez, R.F.; Perrier, N.D.; Phan, A.; et al. Use of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Sunitinib in a Patient with von Hippel-Lindau Disease: Targeting Angiogenic Factors in Pheochromocytoma and Other von Hippel-Lindau Disease-Related Tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naing, A.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Stephen, B.; Karp, D.D.; Hajjar, J.; Rodon Ahnert, J.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Colen, R.R.; Jimenez, C.; Raghav, K.P.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Advanced Rare Cancers. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dercle, L.; Mokrane, F.-Z.; Schiano de Colella, J.M.; Stamatoullas, A.; Morschhauser, F.; Brice, P.; Ghesquières, H.; Casasnovas, O.; Chen, A.; Manson, G.; et al. Unconventional Immune-Related Phenomena Observed Using 18F-FDG PET/CT in Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated with Anti PD-1 Monoclonal Antibodies. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1391–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dercle, L.; Seban, R.-D.; Lazarovici, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Houot, R.; Ammari, S.; Danu, A.; Edeline, V.; Marabelle, A.; Ribrag, V.; et al. 18F-FDG PET and CT Scans Detect New Imaging Patterns of Response and Progression in Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma Treated by Anti–Programmed Death 1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dercle, L.; Ammari, S.; Seban, R.-D.; Schwartz, L.H.; Houot, R.; Labaied, N.; Mokrane, F.-Z.; Lazarovici, J.; Danu, A.; Marabelle, A.; et al. Kinetics and Nadir of Responses to Immune Checkpoint Blockade by Anti-PD1 in Patients with Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 91, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champiat, S.; Dercle, L.; Ammari, S.; Massard, C.; Hollebecque, A.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Chaput, N.; Eggermont, A.; Marabelle, A.; Soria, J.-C.; et al. Hyperprogressive Disease Is a New Pattern of Progression in Cancer Patients Treated by Anti-PD-1/PD-L1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dercle, L.; Chisin, R.; Ammari, S.; Gillebert, Q.; Ouali, M.; Jaudet, C.; Delord, J.-P.; Dierickx, L.; Zerdoud, S.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. Nonsurgical Giant Cell Tumour of the Tendon Sheath or of the Diffuse Type: Are MRI or 18F-FDG PET/CT Able to Provide an Accurate Prediction of Long-Term Outcome? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Callahan, M.K.; Flores-Chávez, A.; Keegan, N.; Khamashta, M.A.; Lambotte, O.; Mariette, X.; Prat, A.; Suárez-Almazor, M.E. Immune-Related Adverse Events of Checkpoint Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Zang, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-C.; Huang, S.-S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, P. Diagnosis and Management of Immune Related Adverse Events (IrAEs) in Cancer Immunotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, A.; Dercle, L.; Lichtenstein, P.; Marabelle, A.; Michot, J.-M.; Lambotte, O.; Le Pavec, J.; De Martin, E.; Balleyguier, C.; Champiat, S.; et al. Detection of Immune-Related Adverse Events by Medical Imaging in Patients Treated with Anti-Programmed Cell Death 1. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 96, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfarb, L.; Duchemann, B.; Chouahnia, K.; Zelek, L.; Soussan, M. Monitoring Anti-PD-1-Based Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with FDG PET: Introduction of IPERCIST. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hulsteijn, L.T.; Niemeijer, N.D.; Dekkers, O.M.; Corssmit, E.P.M. 131 I-MIBG Therapy for Malignant Paraganglioma and Phaeochromocytoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2014, 80, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryma, D.A.; Chin, B.B.; Noto, R.B.; Dillon, J.S.; Perkins, S.; Solnes, L.; Kostakoglu, L.; Serafini, A.N.; Pampaloni, M.H.; Jensen, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of High-Specific-Activity 131 I-MIBG Therapy in Patients with Advanced Pheochromocytoma or Paraganglioma. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.; Erwin, W.; Chasen, B. Targeted Radionuclide Therapy for Patients with Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: From Low-Specific-Activity to High-Specific-Activity Iodine-131 Metaiodobenzylguanidine. Cancers 2019, 11, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonias, S.; Goldsby, R.; Matthay, K.K.; Hawkins, R.; Price, D.; Huberty, J.; Damon, L.; Linker, C.; Sznewajs, A.; Shiboski, S.; et al. Phase II Study of High-Dose [131I]Metaiodobenzylguanidine Therapy for Patients With Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4162–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Essen, M.; Krenning, E.P.; De Jong, M.; Valkema, R.; Kwekkeboom, D.J. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy with Radiolabelled Somatostatin Analogues in Patients with Somatostatin Receptor Positive Tumours. Acta Oncol. 2007, 46, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taïeb, D.; Pacak, K. Molecular Imaging and Theranostic Approaches in Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 372, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, T.A.; Abbott, A.; Colucci, K.; Bushnell, D.L.; Gardner, L.; Graham, W.S.; Lindsay, S.; Metz, D.C.; Pryma, D.A.; Stabin, M.G.; et al. NANETS/SNMMI Procedure Standard for Somatostatin Receptor–Based Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, A.; Brunner, P.; Marincek, N.; Briel, M.; Schindler, C.; Rasch, H.; Mäcke, H.R.; Rochlitz, C.; Müller-Brand, J.; Walter, M.A. Response, Survival, and Long-Term Toxicity After Therapy With the Radiolabeled Somatostatin Analogue [90Y-DOTA]-TOC in Metastasized Neuroendocrine Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2416–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldherr, C.; Pless, M.; Maecke, H.R.; Haldemann, A.; Mueller-Brand, J. The Clinical Value of [90Y-DOTA]-D-Phe1-Tyr3-Octreotide (90Y-DOTATOC) in the Treatment of Neuroendocrine Tumours: A Clinical Phase II Study. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, G.; Bodei, L.; Handkiewicz Junak, D.; Rocca, P.; Papi, S.; Lopera Sierra, M.; Gatti, M.; Chinol, M.; Bartolomei, M.; Fiorenza, M.; et al. 90Y-DOTA-D-Phe1-Try3-Octreotide in Therapy of Neuroendocrine Malignancies. Biopolymers 2002, 66, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, J.P.; Krenning, E.P.; Teunissen, J.J.M.; Kooij, P.P.M.; van Gameren, A.L.H.; Bakker, W.H.; Kwekkeboom, D.J. Comparison of [177Lu-DOTA0,Tyr3]Octreotate and [177Lu-DOTA0,Tyr3]Octreotide: Which Peptide Is Preferable for PRRT? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2006, 33, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; Srirajaskanthan, R.; Toumpanakis, C.; Grana, C.M.; Baldari, S.; Shah, T.; Lamarca, A.; Courbon, F.; Scheidhauer, K.; Baudin, E.; et al. Lessons from a Multicentre Retrospective Study of Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy Combined with Lanreotide for Neuroendocrine Tumours: A Need for Standardised Practice. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 2358–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosberg, J.; El-Haddad, G.; Wolin, E.; Hendifar, A.; Yao, J.; Chasen, B.; Mittra, E.; Kunz, P.L.; Kulke, M.H.; Jacene, H.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of 177 Lu-Dotatate for Midgut Neuroendocrine Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zovato, S.; Kumanova, A.; Demattè, S.; Sansovini, M.; Bodei, L.; Di Sarra, D.; Casagranda, E.; Severi, S.; Ambrosetti, A.; Schiavi, F.; et al. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) with 177Lu-DOTATATE in Individuals with Neck or Mediastinal Paraganglioma (PGL). Horm. Metab. Res. 2012, 44, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.; Taïeb, D.; Carrasquillo, J.A.; Pryma, D.A.; Patel, M.; Millo, C.; de Herder, W.W.; Del Rivero, J.; Crona, J.; Shulkin, B.L.; et al. High-Specific-Activity-131I-MIBG versus 177Lu-DOTATATE Targeted Radionuclide Therapy for Metastatic Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 2989–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hescot, S.; Leboulleux, S.; Amar, L.; Vezzosi, D.; Borget, I.; Bournaud-Salinas, C.; de la Fouchardiere, C.; Libé, R.; Do Cao, C.; Niccoli, P.; et al. One-Year Progression-Free Survival of Therapy-Naive Patients With Malignant Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4006–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, S.; Terroir, M.; Caramella, C. Advances in Oncological Treatment: Limitations of RECIST 1.1 Criteria. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 62, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinker, K.; Riedl, C.; Weber, W.A. Evaluating Tumor Response with FDG PET: Updates on PERCIST, Comparison with EORTC Criteria and Clues to Future Developments. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, R.A.; Bundschuh, R.A.; Bundschuh, L.; Javadi, M.S.; Higuchi, T.; Weich, A.; Sheikhbahaei, S.; Pienta, K.J.; Buck, A.K.; Pomper, M.G.; et al. Molecular Imaging Reporting and Data Systems (MI-RADS): A Generalizable Framework for Targeted Radiotracers with Theranostic Implications. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2018, 32, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, R.A.; Solnes, L.B.; Javadi, M.S.; Weich, A.; Gorin, M.A.; Pienta, K.J.; Higuchi, T.; Buck, A.K.; Pomper, M.G.; Rowe, S.P.; et al. SSTR-RADS Version 1.0 as a Reporting System for SSTR PET Imaging and Selection of Potential PRRT Candidates: A Proposed Standardization Framework. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedraza-Arévalo, S.; Gahete, M.D.; Alors-Pérez, E.; Luque, R.M.; Castaño, J.P. Multilayered Heterogeneity as an Intrinsic Hallmark of Neuroendocrine Tumors. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2018, 19, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasquillo, J.A.; Chen, C.C.; Jha, A.; Ling, A.; Lin, F.I.; Pryma, D.A.; Pacak, K. Imaging of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresan, F.; Crimì, F.; Ceccato, F.; Zavan, F.; Barbot, M.; Lacognata, C.; Motta, R.; Armellin, C.; Scaroni, C.; Quaia, E.; et al. Radiomics: A New Tool to Differentiate Adrenocortical Adenoma from Carcinoma. BJS Open 2021, 5, zraa061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ctvrtlik, F.; Tudos, Z.; Szasz, P.; Sedlackova, Z.; Hartmann, I.; Schovanek, J.; Frysak, Z.; Macova, I.; Zelinka, T.; Hora, M.; et al. Characteristic CT Features of Pheochromocytomas—Probability Model Calculation Tool Based on a Multicentric Study. Biomed. Pap. 2019, 163, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Guan, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, P.; Yu, A.; Long, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Adrenal Incidentaloma: Machine Learning-Based Quantitative Texture Analysis of Unenhanced CT Can Effectively Differentiate SPHEO from Lipid-Poor Adrenal Adenoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3577–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Guan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Long, X.; Yin, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Liao, W.; Chen, B.T.; et al. Radiomics Improves Efficiency for Differentiating Subclinical Pheochromocytoma from Lipid-Poor Adenoma: A Predictive, Preventive and Personalized Medical Approach in Adrenal Incidentalomas. EPMA J. 2018, 9, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimì, F.; Agostini, E.; Toniolo, A.; Torresan, F.; Iacobone, M.; Tizianel, I.; Scaroni, C.; Quaia, E.; Campi, C.; Ceccato, F. CT Texture Analysis of Adrenal Pheochromocytomas: A Pilot Study. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2169–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aide, N.; De Pontdeville, M.; Lopci, E. Evaluating Response to Immunotherapy with 18F-FDG PET/CT: Where Do We Stand? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1019–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozley, P.D.; Bendtsen, C.; Zhao, B.; Schwartz, L.H.; Thorn, M.; Rong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Perrone, A.; Korn, R.; Buckler, A.J. Measurement of Tumor Volumes Improves RECIST-Based Response Assessments in Advanced Lung Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 5, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarca, A.; Crona, J.; Ronot, M.; Opalinska, M.; Lopez Lopez, C.; Pezzutti, D.; Najran, P.; Carvhalo, L.; Franca Bezerra, R.O.; Borg, P.; et al. Value of Tumor Growth Rate (TGR) as an Early Biomarker Predictor of Patients’ Outcome in Neuroendocrine Tumors (NET)—The GREPONET Study. Oncologist 2019, 24, e1082–e1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- On Behalf of the CLARINET Study Group; Dromain, C.; Pavel, M.E.; Ruszniewski, P.; Langley, A.; Massien, C.; Baudin, E.; Caplin, M.E. Tumor Growth Rate as a Metric of Progression, Response, and Prognosis in Pancreatic and Intestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toriihara, A.; Baratto, L.; Nobashi, T.; Park, S.; Hatami, N.; Davidzon, G.; Kunz, P.L.; Iagaru, A. Prognostic Value of Somatostatin Receptor Expressing Tumor Volume Calculated from 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT in Patients with Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, R.A.; Ilhan, H.; Lehner, S.; Papp, L.; Zsótér, N.; Schatka, I.; Muegge, D.O.; Javadi, M.S.; Higuchi, T.; Buck, A.K.; et al. Pre-Therapy Somatostatin Receptor-Based Heterogeneity Predicts Overall Survival in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Patients Undergoing Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haug, A.R.; Auernhammer, C.J.; Wängler, B.; Schmidt, G.P.; Uebleis, C.; Göke, B.; Cumming, P.; Bartenstein, P.; Tiling, R.; Hacker, M. 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT for the Early Prediction of Response to Somatostatin Receptor–Mediated Radionuclide Therapy in Patients with Well-Differentiated Neuroendocrine Tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussey-Lepoutre, C.; Bellucci, A.; Burnichon, N.; Amar, L.; Buffet, A.; Drossart, T.; Fontaine, S.; Clement, O.; Benit, P.; Rustin, P.; et al. Succinate Detection Using in Vivo 1H-MR Spectroscopy Identifies Germline and Somatic SDHx Mutations in Paragangliomas. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussey-Lepoutre, C.; Bellucci, A.; Morin, A.; Buffet, A.; Amar, L.; Janin, M.; Ottolenghi, C.; Zinzindohoue, F.; Autret, G.; Burnichon, N.; et al. In Vivo Detection of Succinate by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy as a Hallmark of SDHx Mutations in Paraganglioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoquaux, A.; le Fur, Y.; Imperiale, A.; Reyre, A.; Montava, M.; Fakhry, N.; Namer, I.-J.; Moulin, G.; Pacak, K.; Guye, M.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Paragangliomas: New Insights into in Vivo Metabolomics. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, M1–M8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.; Peitzsch, M.; Rapizzi, E.; Lenders, J.W.; Qin, N.; de Cubas, A.A.; Schiavi, F.; Rao, J.U.; Beuschlein, F.; Quinkler, M.; et al. Krebs Cycle Metabolite Profiling for Identification and Stratification of Pheochromocytomas/Paragangliomas Due to Succinate Dehydrogenase Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 3903–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letouzé, E.; Martinelli, C.; Loriot, C.; Burnichon, N.; Abermil, N.; Ottolenghi, C.; Janin, M.; Menara, M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Benit, P.; et al. SDH Mutations Establish a Hypermethylator Phenotype in Paraganglioma. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćwikła, J.B.; Bodei, L.; Kolasinska-Ćwikła, A.; Sankowski, A.; Modlin, I.M.; Kidd, M. Circulating Transcript Analysis (NETest) in GEP-NETs Treated With Somatostatin Analogs Defines Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1437–E1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, M.; Jann, H.; Prasad, V.; Drozdov, I.; Modlin, I.M.; Kidd, M. NET Blood Transcript Analysis Defines the Crossing of the Clinical Rubicon: When Stable Disease Becomes Progressive. Neuroendocrinology 2017, 104, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pęczkowska, M.; Cwikla, J.; Kidd, M.; Lewczuk, A.; Kolasinska-Ćwikła, A.; Niec, D.; Michałowska, I.; Prejbisz, A.; Januszewicz, A.; Chiarelli, J.; et al. The Clinical Utility of Circulating Neuroendocrine Gene Transcript Analysis in Well-Differentiated Paragangliomas and Pheochromocytomas. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacak, K.; Kidd, M.; Meuter, L.; Modlin, I.M. A Novel Liquid Biopsy (NETest) Identifies Paragangliomas and Pheochromocytomas with High Accuracy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Lai, P.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y. The Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes Showing Aberrant Methylation Patterns in Pheochromocytoma by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, F.; Beuschlein, F. Disease Monitoring of Patients with Pheochromocytoma or Paraganglioma by Biomarkers and Imaging Studies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 34, 101347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calsina, B.; Castro-Vega, L.J.; Torres-Pérez, R.; Inglada-Pérez, L.; Currás-Freixes, M.; Roldán-Romero, J.M.; Mancikova, V.; Letón, R.; Remacha, L.; Santos, M.; et al. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Identifies a Prognostic MiRNA Signature and a Targetable MiR-21-3p/TSC2/MTOR Axis in Metastatic Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4946–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, Z.; Rahman, L.; Murrell, J.; Todd, J.; Al-Nahhas, A. The Possible Role of 68Ga-DOTATATE PET in Malignant Abdominal Paraganglioma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2006, 33, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, Z.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Towey, D.; Todd, J.F.; Rubello, D.; Lewington, V.; Gishen, P. 68Ga-DOTATATE PET in Neuroectodermal Tumours: First Experience. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2007, 28, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosini, V.; Tomassetti, P.; Castellucci, P.; Campana, D.; Montini, G.; Rubello, D.; Nanni, C.; Rizzello, A.; Franchi, R.; Fanti, S. Comparison between 68Ga-DOTA-NOC and 18F-DOPA PET for the Detection of Gastro-Entero-Pancreatic and Lung Neuro-Endocrine Tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wild, D.; Schmitt, J.S.; Ginj, M.; Mäcke, H.R.; Bernard, B.F.; Krenning, E.; de Jong, M.; Wenger, S.; Reubi, J.-C. DOTA-NOC, a High-Affinity Ligand of Somatostatin Receptor Subtypes 2, 3 and 5 for Labelling with Various Radiometals. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, V.; Nanni, C.; Zompatori, M.; Campana, D.; Tomassetti, P.; Castellucci, P.; Allegri, V.; Rubello, D.; Montini, G.; Franchi, R.; et al. 68Ga-DOTA-NOC PET/CT in Comparison with CT for the Detection of Bone Metastasis in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putzer, D.; Gabriel, M.; Henninger, B.; Kendler, D.; Uprimny, C.; Dobrozemsky, G.; Decristoforo, C.; Bale, R.J.; Jaschke, W.; Virgolini, I.J. Bone Metastases in Patients with Neuroendocrine Tumor: 68Ga-DOTA-Tyr3-Octreotide PET in Comparison to CT and Bone Scintigraphy. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroiss, A.; Putzer, D.; Uprimny, C.; Decristoforo, C.; Gabriel, M.; Santner, W.; Kranewitter, C.; Warwitz, B.; Waitz, D.; Kendler, D.; et al. Functional Imaging in Phaeochromocytoma and Neuroblastoma with 68Ga-DOTA-Tyr3-Octreotide Positron Emission Tomography and 123I-Metaiodobenzylguanidine. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Tripathi, M.; Roesch, F.; Bal, C. Evaluation of [68Ga]Ga-DATA-TOC for Imaging of Neuroendocrine Tumours: Comparison with [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-NOC PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, T.A.; Bodei, L.; Chan, J.A.; El-Haddad, G.; Fidelman, N.; Kunz, P.L.; Mailman, J.; Menda, Y.; Metz, D.C.; Mittra, E.S.; et al. NANETS/SNMMI Consensus Statement on Patient Selection and Appropriate Use of 177Lu-DOTATATE Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochwil, C.; Stefanova, M.; Mavriopoulou, E.; Holland-Letz, T.; Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss, A.; Afshar-Oromieh, A.; Mier, W.; Haberkorn, U.; Giesel, F.L. SUV of [68Ga]DOTATOC-PET/CT Predicts Response Probability of PRRT in Neuroendocrine Tumors. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2015, 17, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, K.; Toyokawa, G.; Yoneshima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, I.; Shimokawa, M.; Wakasu, S.; Haro, A.; Osoegawa, A.; Tagawa, T.; et al. 18F-FDG Uptake in PET/CT Is a Potential Predictive Biomarker of Response to Anti-PD-1 Antibody Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, D.W.; Lim, H.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, S.P.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, B.-T. Prognostic Value of Volume-Based Metabolic Parameters Measured by (18)F-FDG PET/CT of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 48, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Seban, R.-D.; Nemer, J.S.; Marabelle, A.; Yeh, R.; Deutsch, E.; Ammari, S.; Moya-Plana, A.; Mokrane, F.-Z.; Gartrell, R.D.; Finkel, G.; et al. Prognostic and Theranostic 18F-FDG PET Biomarkers for Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy in Metastatic Melanoma: Association with Outcome and Transcriptomics. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2298–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seban, R.-D.; Mezquita, L.; Berenbaum, A.; Dercle, L.; Botticella, A.; Le Pechoux, C.; Caramella, C.; Deutsch, E.; Grimaldi, S.; Adam, J.; et al. Baseline Metabolic Tumor Burden on FDG PET/CT Scans Predicts Outcome in Advanced NSCLC Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetz, C.; Apostolova, I.; Steffen, I.G.; Hofheinz, F.; Furth, C.; Kupitz, D.; Ruf, J.; Venerito, M.; Klose, S.; Amthauer, H. Predictive Value of Asphericity in Pretherapeutic [111In]DTPA-Octreotide SPECT/CT for Response to Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy with [177Lu]DOTATATE. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
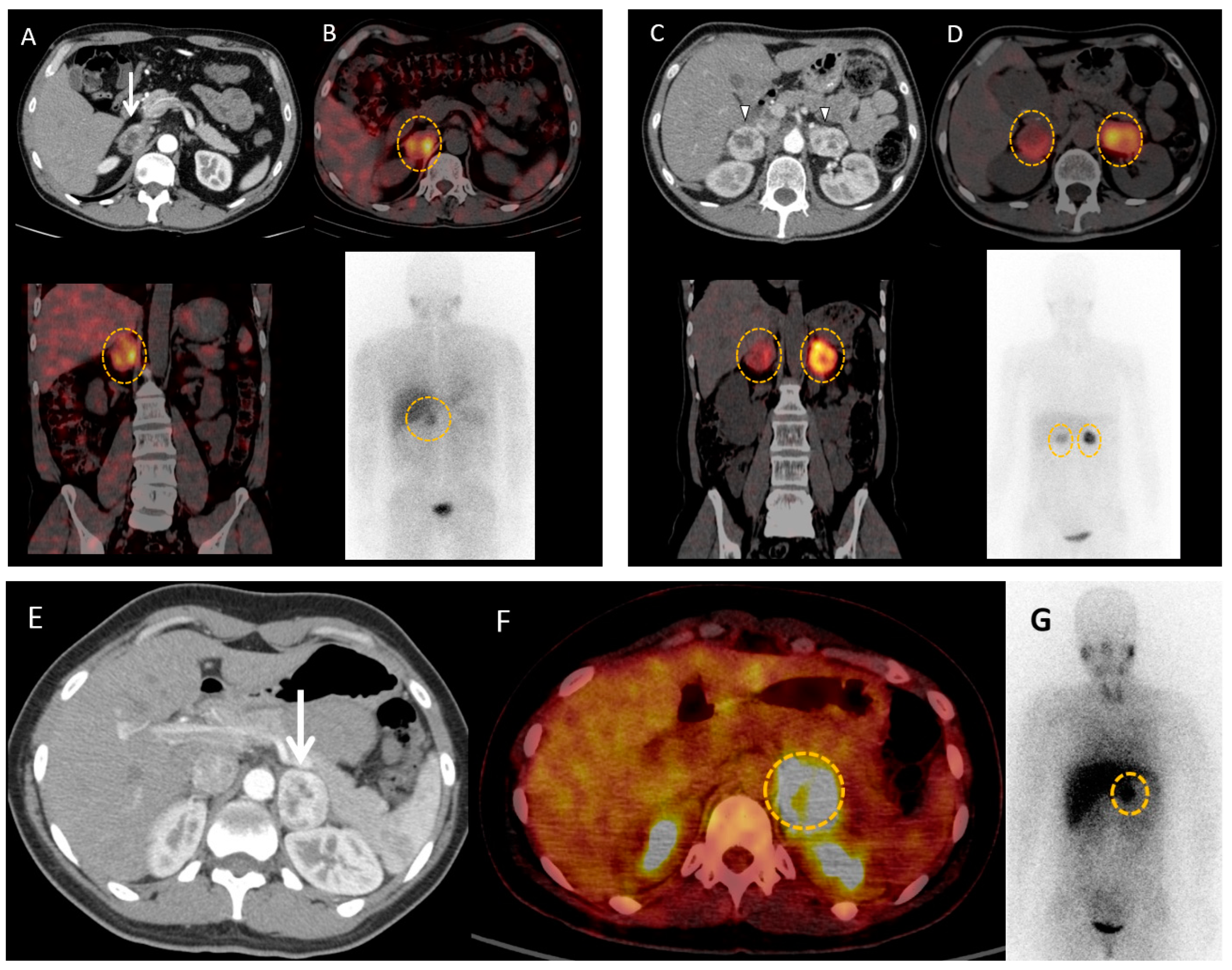

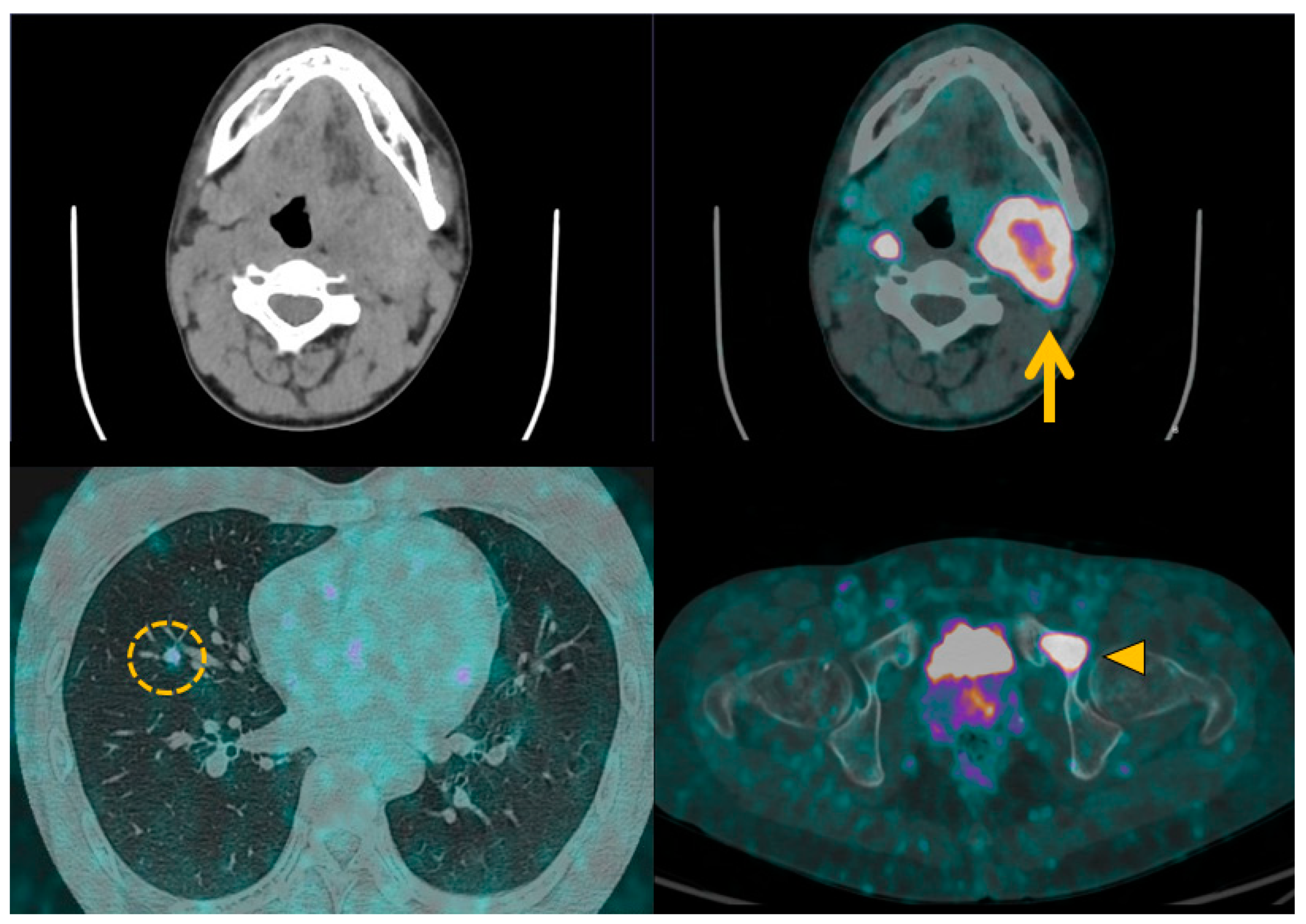
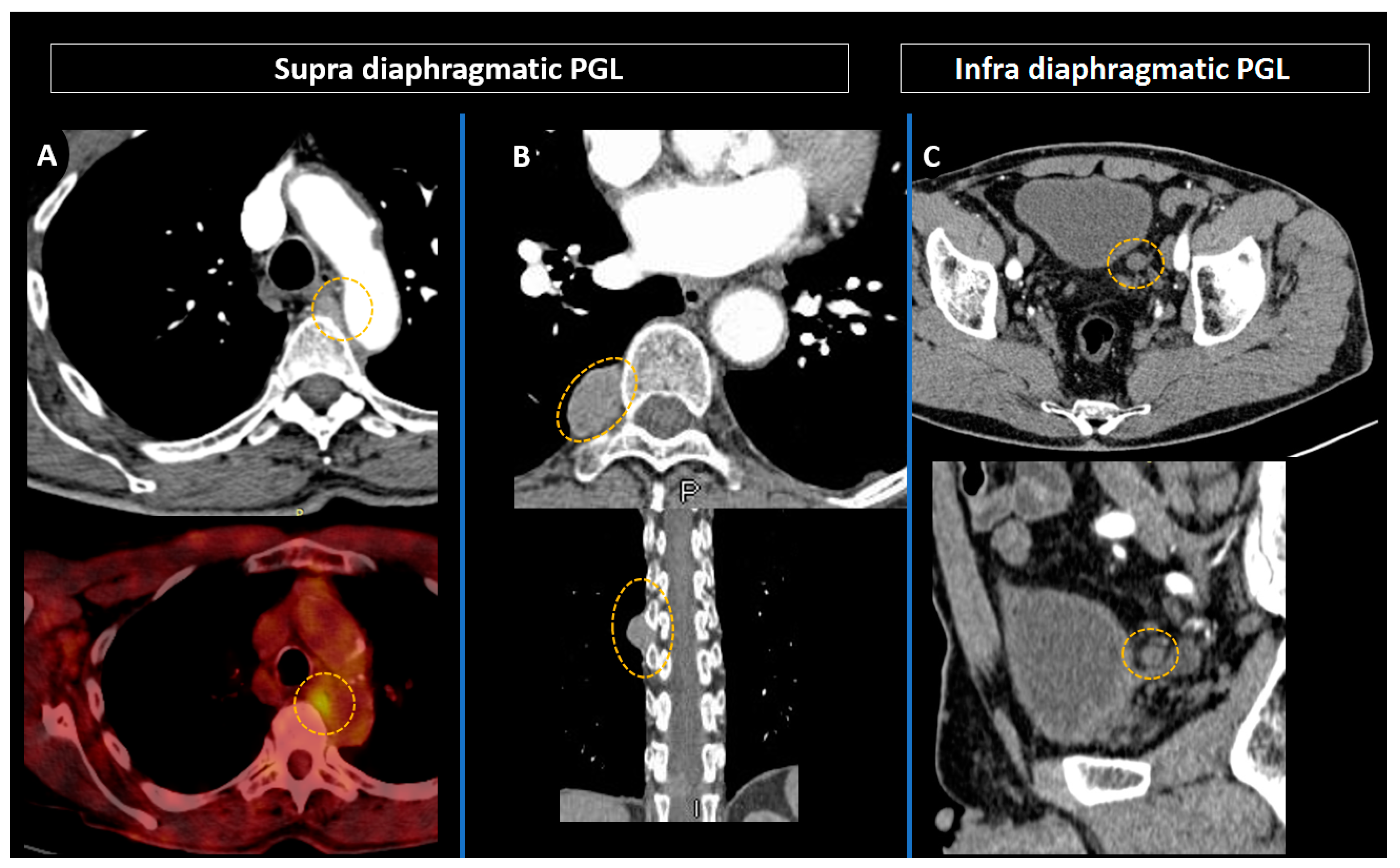
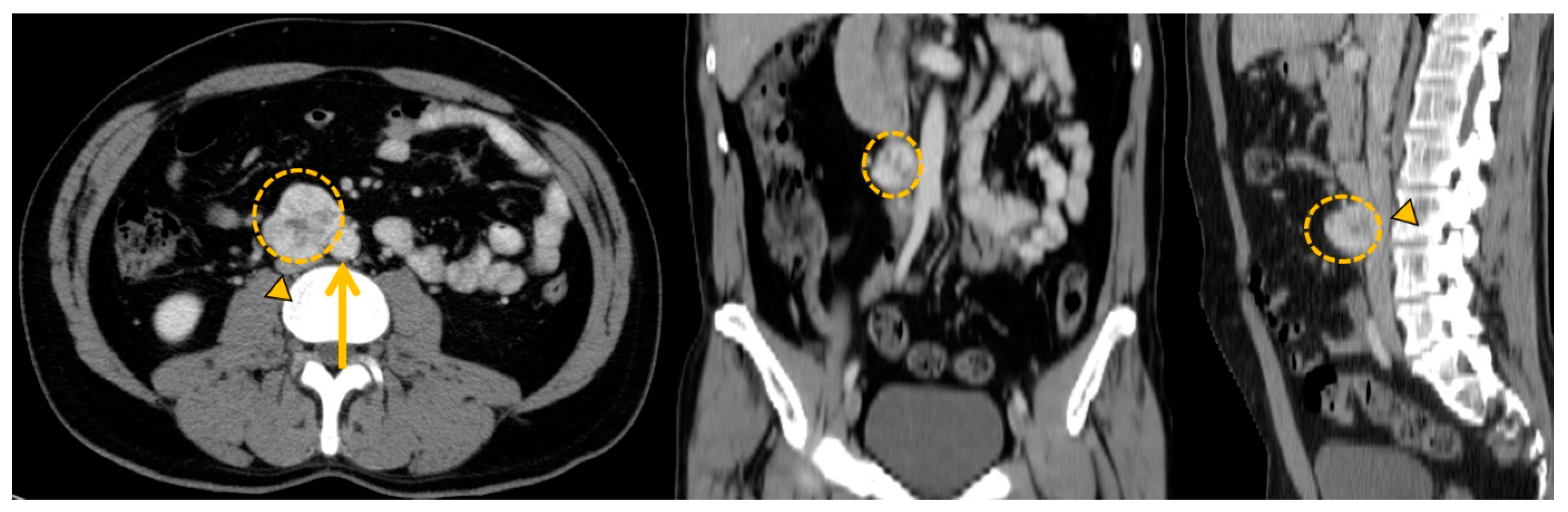

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gabiache, G.; Zadro, C.; Rozenblum, L.; Vezzosi, D.; Mouly, C.; Thoulouzan, M.; Guimbaud, R.; Otal, P.; Dierickx, L.; Rousseau, H.; et al. Image-Guided Precision Medicine in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas. Cancers 2023, 15, 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184666
Gabiache G, Zadro C, Rozenblum L, Vezzosi D, Mouly C, Thoulouzan M, Guimbaud R, Otal P, Dierickx L, Rousseau H, et al. Image-Guided Precision Medicine in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184666
Chicago/Turabian StyleGabiache, Gildas, Charline Zadro, Laura Rozenblum, Delphine Vezzosi, Céline Mouly, Matthieu Thoulouzan, Rosine Guimbaud, Philippe Otal, Lawrence Dierickx, Hervé Rousseau, and et al. 2023. "Image-Guided Precision Medicine in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184666
APA StyleGabiache, G., Zadro, C., Rozenblum, L., Vezzosi, D., Mouly, C., Thoulouzan, M., Guimbaud, R., Otal, P., Dierickx, L., Rousseau, H., Trepanier, C., Dercle, L., & Mokrane, F.-Z. (2023). Image-Guided Precision Medicine in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas. Cancers, 15(18), 4666. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184666





