Therapeutic Targeting of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CAF Biomarkers and Heterogeneity in NSCLC
2.1. Biomarkers for CAFs in NSCLC
2.2. Heterogeneity of CAFs in NSCLC
3. CAF-Related Signaling Pathways in NSCLC
3.1. Signaling Pathways between CAFs and NSCLC
3.2. Role of CAFs in Resistance to Antitumor Therapy
3.3. Role of CAFs in Oncogene Addicted NSCLC
3.4. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Communication between CAFs and NSCLC
4. Role of CAFs in the Immune Environment in NSCLC
4.1. Impact of CAFs on Immunosuppressive Activity in NSCLC
4.2. ECM Production and CAF Barrier Function in NSCLC
5. Tumor-Suppressing CAF Phenotypes
6. CAF-Mediated Anticancer Therapies
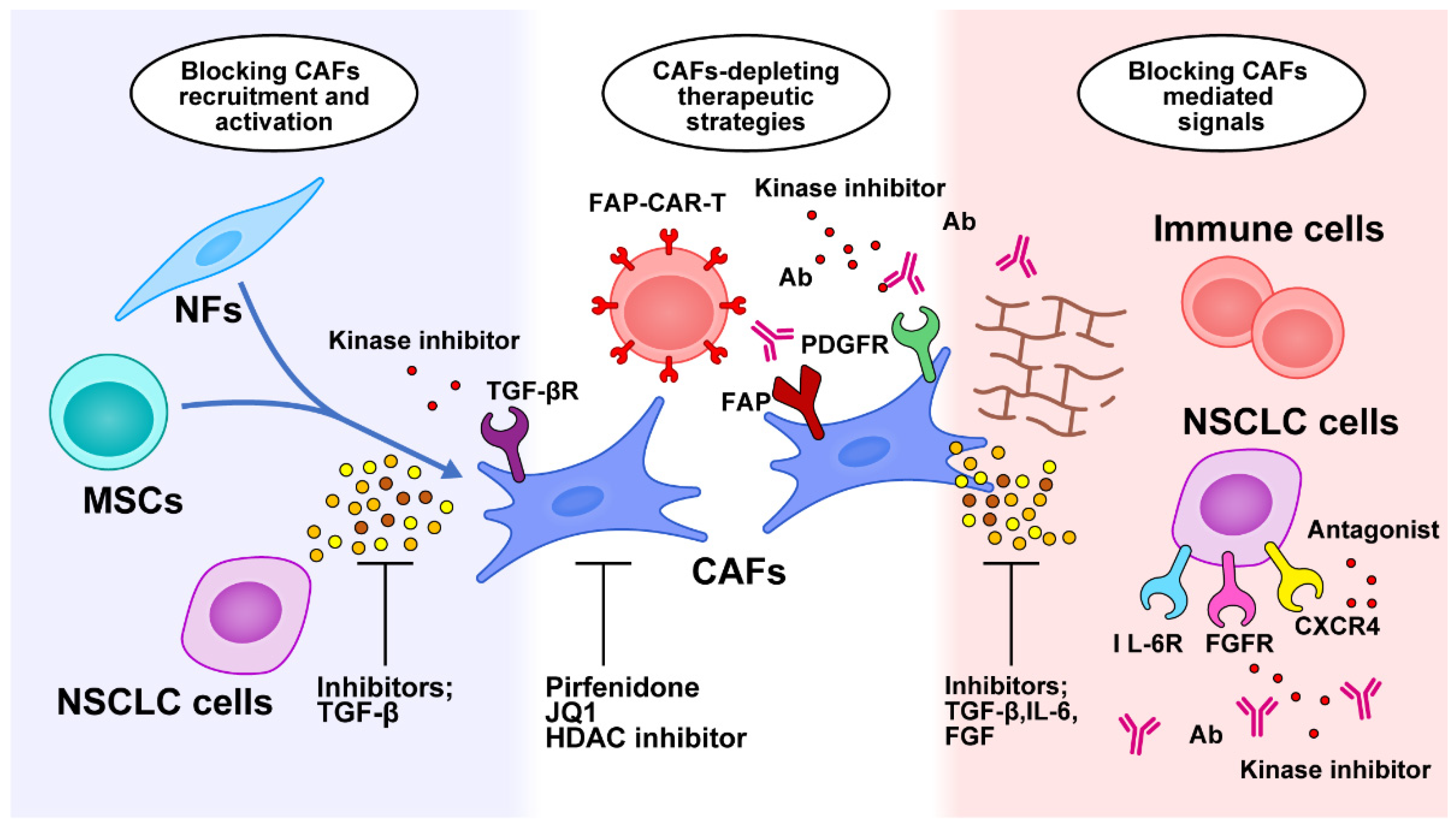
6.1. Targeting CAFs
6.2. Targeting the Signaling Pathways of CAFs
6.3. Antifibrotic Therapy to Normalize the Tumor Microenvironment
6.4. Targeting Immunomodulation of CAFs
6.5. New Concepts for Targeted Therapies Using CAFs
6.6. Clinical Trials Targeting CAFs in NSCLC
7. Future Perspectives and Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howlader, N.; Forjaz, G.; Mooradian, M.J.; Meza, R.; Kong, C.Y.; Cronin, K.A.; Mariotto, A.B.; Lowy, D.R.; Feuer, E.J. The Effect of Advances in Lung-Cancer Treatment on Population Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbour, K.C.; Riely, G.J. Systemic Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Huang, L.L.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, J.; Xu, Q. The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erez, N.; Truitt, M.; Olson, P.; Arron, S.T.; Hanahan, D. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Are Activated in Incipient Neoplasia to Orchestrate Tumor-Promoting Inflammation in an NF-kappaB-Dependent Manner. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmouliere, A.; Guyot, C.; Gabbiani, G. The stroma reaction myofibroblast: A key player in the control of tumor cell behavior. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2004, 48, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyden, B. The myofibroblast: Phenotypic characterization as a prerequisite to understanding its functions in translational medicine. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, E.; Astsaturov, I.; Cukierman, E.; DeNardo, D.G.; Egeblad, M.; Evans, R.M.; Fearon, D.; Greten, F.R.; Hingorani, S.R.; Hunter, T.; et al. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nature reviews. Cancer 2020, 20, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mu, J.; Zeng, Q.; Deng, S.; Zhou, H. Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts and targeted therapy for cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteran, L.; Erez, N. The Dark Side of Fibroblasts: Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts as Mediators of Immunosuppression in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Yamada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Matsumoto, I.; Oda, M.; Watanabe, G.; Kayano, Y.; Nishioka, Y.; Sone, S.; et al. Crosstalk to stromal fibroblasts induces resistance of lung cancer to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6630–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.J.; Ho, C.C.; Chang, Y.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, C.A.; Ling, T.Y.; Yu, S.L.; Yuan, S.S.; Chen, Y.J.; Lin, C.Y.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts regulate the plasticity of lung cancer stemness via paracrine signalling. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Ishii, G.; Goto, K.; Neri, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Niho, S.; Umemura, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Ohmatsu, H.; et al. Podoplanin-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts in the tumor microenvironment induce primary resistance to EGFR-TKIs in lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, Y.; Fujiwara, A.; Kimura, T.; Kawamura, T.; Funaki, S.; Minami, M.; Okumura, M. IL-6 Secreted from Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Mediates Chemoresistance in NSCLC by Increasing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Signaling. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2016, 11, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Liu, T.; Yin, R. Biomarkers for cancer-associated fibroblasts. Biomark. Res. 2020, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurmik, M.; Ullmann, P.; Rodriguez, F.; Haan, S.; Letellier, E. In search of definitions: Cancer-associated fibroblasts and their markers. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R. Fibroblast Activation Protein-alpha as a Target in the Bench-to-Bedside Diagnosis and Treatment of Tumors: A Narrative Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 648187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domen, A.; Quatannens, D.; Zanivan, S.; Deben, C.; Van Audenaerde, J.; Smits, E.; Wouters, A.; Lardon, F.; Roeyen, G.; Verhoeven, Y.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts as a Common Orchestrator of Therapy Resistance in Lung and Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieniec, K.A.; Butler, L.M.; Worthley, D.L.; Woods, S.L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-heroes or villains? Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Dedhia, P.H.; Jin, S.; Ruiz-Vega, R.; Ma, D.; Liu, Y.; Yamaga, K.; Shestova, O.; Gay, D.L.; Yang, Z.; et al. Single-cell analysis reveals fibroblast heterogeneity and myeloid-derived adipocyte progenitors in murine skin wounds. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieffer, Y.; Hocine, H.R.; Gentric, G.; Pelon, F.; Bernard, C.; Bourachot, B.; Lameiras, S.; Albergante, L.; Bonneau, C.; Guyard, A.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis Reveals Fibroblast Clusters Linked to Immunotherapy Resistance in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1330–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nature reviews. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, Y.; Abulaiti, A.; Kimura, T.; Funaki, S.; Nakagiri, T.; Inoue, M.; Sawabata, N.; Minami, M.; Morii, E.; Okumura, M. Pulmonary fibroblasts induce epithelial mesenchymal transition and some characteristics of stem cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 96, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paauwe, M.; Schoonderwoerd, M.J.A.; Helderman, R.; Harryvan, T.J.; Groenewoud, A.; van Pelt, G.W.; Bor, R.; Hemmer, D.M.; Versteeg, H.H.; Snaar-Jagalska, B.E.; et al. Endoglin Expression on Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Regulates Invasion and Stimulates Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6331–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugai, M.; Yanagawa, N.; Shikanai, S.; Hashimoto, M.; Saikawa, H.; Osakabe, M.; Saito, H.; Maemondo, M.; Sugai, T. Correlation of tumor microenvironment-related markers with clinical outcomes in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harryvan, T.J.; Verdegaal, E.M.E.; Hardwick, J.C.H.; Hawinkels, L.; van der Burg, S.H. Targeting of the Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-T-Cell Axis in Solid Malignancies. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, A.V.; Humeres, C.; Frangogiannis, N.G. The role of alpha-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix contraction and remodeling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strutz, F.; Okada, H.; Lo, C.W.; Danoff, T.; Carone, R.L.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Neilson, E.G. Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 130, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, R. Functional roles of S100 proteins, calcium-binding proteins of the EF-hand type. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1450, 191–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, W.E.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Zoia, O.; Stathopoulos, G.T.; Han, W.; Plieth, D.; Loyd, J.E.; Neilson, E.G.; Blackwell, T.S. Characterization of fibroblast-specific protein 1 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, A.A.; Weiner, L.M. The role of fibroblast activation protein in health and malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, R.; Pietras, K. Heterogeneity of cancer-associated fibroblasts: Opportunities for precision medicine. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvine, A.F.; Waise, S.; Green, E.W.; Stuart, B.; Thomas, G.J. Characterising cancer-associated fibroblast heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.; Calle, A.S.; Zahra, M.H.; Prieto-Vila, M.; Oo, A.K.K.; Hurley, L.; Vaidyanath, A.; Seno, A.; Masuda, J.; Iwasaki, Y.; et al. A cancer stem cell model as the point of origin of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, A.L.; Pei, D.T.; Hurst, C.G.; Gimble, J.M.; Burow, M.E.; Bunnell, B.A. Obesity Enhances the Conversion of Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells into Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblast Leading to Cancer Cell Proliferation and Progression to an Invasive Phenotype. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 9216502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoto, K.; Ito, K.; Aoki, S. Complex formation between platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta and transforming growth factor beta receptor regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34090–34102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoschek, M.; Oskolkov, N.; Bocci, M.; Lovrot, J.; Larsson, C.; Sommarin, M.; Madsen, C.D.; Lindgren, D.; Pekar, G.; Karlsson, G.; et al. Spatially and functionally distinct subclasses of breast cancer-associated fibroblasts revealed by single cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyada, E.; Bolisetty, M.; Laise, P.; Flynn, W.F.; Courtois, E.T.; Burkhart, R.A.; Teinor, J.A.; Belleau, P.; Biffi, G.; Lucito, M.S.; et al. Cross-Species Single-Cell Analysis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Reveals Antigen-Presenting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1102–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, D.; Wauters, E.; Boeckx, B.; Aibar, S.; Nittner, D.; Burton, O.; Bassez, A.; Decaluwe, H.; Pircher, A.; Van den Eynde, K.; et al. Phenotype molding of stromal cells in the lung tumor microenvironment. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Courtois, E.T.; Sengupta, D.; Tan, Y.; Chen, K.H.; Goh, J.J.L.; Kong, S.L.; Chua, C.; Hon, L.K.; Tan, W.S.; et al. Reference component analysis of single-cell transcriptomes elucidates cellular heterogeneity in human colorectal tumors. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Olbrecht, S.; Boeckx, B.; Vos, H.; Laoui, D.; Etlioglu, E.; Wauters, E.; Pomella, V.; Verbandt, S.; Busschaert, P.; et al. A pan-cancer blueprint of the heterogeneous tumor microenvironment revealed by single-cell profiling. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Piotrowska, Z.; Hare, P.J.; Chen, H.; Mulvey, H.E.; Mayfield, A.; Noeen, S.; Kattermann, K.; Greenberg, M.; Williams, A.; et al. Three subtypes of lung cancer fibroblasts define distinct therapeutic paradigms. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1531–1547.e1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.S.; Cheon, I.; Kim, S.R.; Chun, S.H.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, S.; Yoon, J.S.; Hong, S.A.; Won, H.S.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Subpopulations in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Chen, J.; Yao, H.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Lao, L.; Wang, M.; Luo, M.; Xing, Y.; Chen, F.; et al. CD10(+)GPR77(+) Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Cancer Formation and Chemoresistance by Sustaining Cancer Stemness. Cell 2018, 172, 841–856.e816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denys, H.; Derycke, L.; Hendrix, A.; Westbroek, W.; Gheldof, A.; Narine, K.; Pauwels, P.; Gespach, C.; Bracke, M.; De Wever, O. Differential impact of TGF-beta and EGF on fibroblast differentiation and invasion reciprocally promotes colon cancer cell invasion. Cancer Lett. 2008, 266, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, T.; Yashiro, M.; Nishii, T.; Matsuoka, J.; Fuyuhiro, Y.; Morisaki, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Shimizu, K.; Shimizu, T.; Miwa, A.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts might sustain the stemness of scirrhous gastric cancer cells via transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guan, J.; Long, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, X. mir-1-mediated paracrine effect of cancer-associated fibroblasts on lung cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulaiti, A.; Shintani, Y.; Funaki, S.; Nakagiri, T.; Inoue, M.; Sawabata, N.; Minami, M.; Okumura, M. Interaction between non-small-cell lung cancer cells and fibroblasts via enhancement of TGF-beta signaling by IL-6. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, N.; Glanz, S.; Raz, Y.; Avivi, C.; Barshack, I. Cancer associated fibroblasts express pro-inflammatory factors in human breast and ovarian tumors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts enhance metastatic potential of lung cancer cells through IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 76116–76128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, M.; Tulafu, M.; Togo, S.; Kawaji, H.; Kadoya, K.; Namba, Y.; Jin, J.; Watanabe, J.; Okabe, T.; Hidayat, M.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast migration in non-small cell lung cancers is modulated by increased integrin alpha11 expression. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1507–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Okimura, A.; Sato, K.; Nakagiri, T.; Kadota, Y.; Inoue, M.; Sawabata, N.; Minami, M.; Ikeda, N.; Kawahara, K.; et al. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a determinant of sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 1794–1804; discussion 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Huang, G.; Wang, R.; Pan, Y.; He, Z.; Chu, X.; Song, H.; Chen, L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts treated with cisplatin facilitates chemoresistance of lung adenocarcinoma through IL-11/IL-11R/STAT3 signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, R.; Naito, H.; Kise, K.; Takara, K.; Eino, D.; Minami, M.; Shintani, Y.; Funaki, S.; Kawamura, T.; Kimura, T.; et al. Gas6 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes migration of Axl-expressing lung cancer cells during chemotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, J.; Huang, R.Y. AXL-Driven EMT State as a Targetable Conduit in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3725–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Geng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, L.; Meng, Z.; Wu, X.; Xu, M.; Xu, K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute to cisplatin resistance by modulating ANXA3 in lung cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Bai, J.; Ren, J. Reverse of non-small cell lung cancer drug resistance induced by cancer-associated fibroblasts via a paracrine pathway. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Aske, J.; Sulaiman, R.; Dey, N. Bete Noire of Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy: CAF-Mediated Resistance. Cancers 2022, 14, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.G.; Di Noia, V.; D’Argento, E.; Vita, E.; Damiano, P.; Cannella, A.; Ribelli, M.; Pilotto, S.; Milella, M.; Tortora, G.; et al. Oncogene-Addicted Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Treatment Opportunities and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2020, 12, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellinen, T.; Paavolainen, L.; Martin-Bernabe, A.; Papatella Araujo, R.; Strell, C.; Mezheyeuski, A.; Backman, M.; La Fleur, L.; Bruck, O.; Sjolund, J.; et al. Fibroblast subsets in non-small cell lung cancer: Associations with survival, mutations, and immune features. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, djac178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, C.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, C.; Choi, S.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, Y.B.; Kim, J. Crosstalk with cancer-associated fibroblasts induces resistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 3665–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Ma, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition and EGFR-TKI resistance of non-small cell lung cancers via HGF/IGF-1/ANXA2 signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shien, K.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Ruder, D.; Behrens, C.; Shen, L.; Kalhor, N.; Song, J.; Lee, J.J.; Wang, J.; Tang, X.; et al. JAK1/STAT3 Activation through a Proinflammatory Cytokine Pathway Leads to Resistance to Molecularly Targeted Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2234–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Wang, K.; Sun, S.Y. MET inhibitors for targeted therapy of EGFR TKI-resistant lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apicella, M.; Giannoni, E.; Fiore, S.; Ferrari, K.J.; Fernandez-Perez, D.; Isella, C.; Granchi, C.; Minutolo, F.; Sottile, A.; Comoglio, P.M.; et al. Increased Lactate Secretion by Cancer Cells Sustains Non-cell-autonomous Adaptive Resistance to MET and EGFR Targeted Therapies. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 848–865.e846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yu, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, J.; Sun, J.; Choksi, S.; Jitkaew, S.; Shu, Y. Reprogramming of Normal Fibroblasts into Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts by miRNAs-Mediated CCL2/VEGFA Signaling. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Z.; Qin, X.; Yan, M.; Li, R.R.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, W.T. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote cancer cell growth through a miR-7-RASSF2-PAR-4 axis in the tumor microenvironment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1290–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hong, X.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z.; Liu, B.; Ye, L. MiR-210 in exosomes derived from CAFs promotes non-small cell lung cancer migration and invasion through PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway. Cell. Signal. 2020, 73, 109675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Zhang, B.; Ke, B. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-20a suppresses the PTEN/PI3K-AKT pathway to promote the progression and chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunita, A.; Morita, S.; Irisa, T.U.; Goto, A.; Niki, T.; Takai, D.; Nakajima, J.; Fukayama, M. MicroRNA-21 in cancer-associated fibroblasts supports lung adenocarcinoma progression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Hong, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, J.S.; Chun, S.H.; Hong, S.A.; Kim, E.J.; Kang, K.; Lee Kang, J.; Ko, Y.H.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts activated by miR-196a promote the migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2021, 508, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ti, W.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y. The Interaction Between Long Non-Coding RNAs and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Lung Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 714125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Han, C.; Fang, P.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Meng, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, E.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblast-specific lncRNA LINC01614 enhances glutamine uptake in lung adenocarcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, R.L.; Pure, E. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and their influence on tumor immunity and immunotherapy. eLife 2020, 9, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhaidly, R.; Mechta-Grigoriou, F. Role of cancer-associated fibroblast subpopulations in immune infiltration, as a new means of treatment in cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2021, 302, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazareth, M.R.; Broderick, L.; Simpson-Abelson, M.R.; Kelleher, R.J., Jr.; Yokota, S.J.; Bankert, R.B. Characterization of human lung tumor-associated fibroblasts and their ability to modulate the activation of tumor-associated T cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5552–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, M.; Santiago, B.; Rivero, M.; Rullas, J.; Alcami, J.; Pablos, J.L. Chemokine expression by systemic sclerosis fibroblasts: Abnormal regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 expression. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1382–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbervliet, B.; Homey, B.; Durand, I.; Massacrier, C.; Ait-Yahia, S.; de Bouteiller, O.; Vicari, A.; Caux, C. Sequential involvement of CCR2 and CCR6 ligands for immature dendritic cell recruitment: Possible role at inflamed epithelial surfaces. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Ramil, C.P.; Hai, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Watkins, A.A.; Afshar, R.; Georgiev, P.; Sze, M.A.; Song, X.S.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promote Immunosuppression by Inducing ROS-Generating Monocytic MDSCs in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Ishii, G.; Hiraoka, N.; Hirayama, S.; Yamauchi, C.; Aokage, K.; Hishida, T.; Yoshida, J.; Nagai, K.; Ochiai, A. Forkhead box P3 regulatory T cells coexisting with cancer associated fibroblasts are correlated with a poor outcome in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshio, Y.; Teramoto, K.; Hanaoka, J.; Tezuka, N.; Itoh, Y.; Asai, T.; Daigo, Y.; Ogasawara, K. Cancer-associated fibroblast-targeted strategy enhances antitumor immune responses in dendritic cell-based vaccine. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.T.; Abuwarwar, M.H.; Poly, L.; Wilkins, S.; Fletcher, A.L. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and T Cells: From Mechanisms to Outcomes. J. Immunol. 2021, 206, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, C.; Miki, Y.; Saito, R.; Hata, S.; Abe, J.; Sato, I.; Okada, Y.; Sasano, H. PD-L1 Induction by Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Derived Factors in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, K.; Igarashi, T.; Kataoka, Y.; Ishida, M.; Hanaoka, J.; Sumimoto, H.; Daigo, Y. Clinical significance of PD-L1-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts in pN0M0 non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 137, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakins, M.A.; Ghorani, E.; Munir, H.; Martins, C.P.; Shields, J.D. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce antigen-specific deletion of CD8 (+) T Cells to protect tumour cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarthy, A.; Khan, L.; Bensler, N.P.; Bose, P.; De Carvalho, D.D. TGF-beta-associated extracellular matrix genes link cancer-associated fibroblasts to immune evasion and immunotherapy failure. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhabib, I.; Zaghdoudi, S.; Lac, C.; Bousquet, C.; Jean, C. Extracellular Matrices and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Targets for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy? Cancers 2021, 13, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glentis, A.; Oertle, P.; Mariani, P.; Chikina, A.; El Marjou, F.; Attieh, Y.; Zaccarini, F.; Lae, M.; Loew, D.; Dingli, F.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce metalloprotease-independent cancer cell invasion of the basement membrane. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, H.; Franciszkiewicz, K.; Damotte, D.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.C.; Validire, P.; Trautmann, A.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Donnadieu, E. Matrix architecture defines the preferential localization and migration of T cells into the stroma of human lung tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraman, M.; Bambrough, P.J.; Arnold, J.N.; Roberts, E.W.; Magiera, L.; Jones, J.O.; Gopinathan, A.; Tuveson, D.A.; Fearon, D.T. Suppression of antitumor immunity by stromal cells expressing fibroblast activation protein-alpha. Science 2010, 330, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Wu, J.; Shen, B.; Jiang, F.; Feng, J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts and resistance to anticancer therapies: Status, mechanisms, and countermeasures. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ye, J.; Yuan, B.; Yu, W. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Suppress Cancer Development: The Other Side of the Coin. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 613534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, B.C.; Pentcheva-Hoang, T.; Carstens, J.L.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C.C.; Simpson, T.R.; Laklai, H.; Sugimoto, H.; Kahlert, C.; Novitskiy, S.V.; et al. Depletion of carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and fibrosis induces immunosuppression and accelerates pancreas cancer with reduced survival. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remsing Rix, L.L.; Sumi, N.J.; Hu, Q.; Desai, B.; Bryant, A.T.; Li, X.; Welsh, E.A.; Fang, B.; Kinose, F.; Kuenzi, B.M.; et al. IGF-binding proteins secreted by cancer-associated fibroblasts induce context-dependent drug sensitization of lung cancer cells. Sci. Signal. 2022, 15, eabj5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.M.; Jung, J.; Aziz, N.; Kissil, J.L.; Pure, E. Targeting fibroblast activation protein inhibits tumor stromagenesis and growth in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3613–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ruiz, P.; Corvigno, S.; Te Grootenhuis, N.C.; La Fleur, L.; Backman, M.; Strell, C.; Mezheyeuski, A.; Hoelzlwimmer, G.; Klein, C.; Botling, J.; et al. Stromal FAP is an independent poor prognosis marker in non-small cell lung adenocarcinoma and associated with p53 mutation. Lung Cancer 2021, 155, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.M.; Wiseman, G.; Welt, S.; Adjei, A.; Lee, F.T.; Hopkins, W.; Divgi, C.R.; Hanson, L.H.; Mitchell, P.; Gansen, D.N.; et al. A Phase I dose-escalation study of sibrotuzumab in patients with advanced or metastatic fibroblast activation protein-positive cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar]
- Eager, R.M.; Cunningham, C.C.; Senzer, N.; Richards, D.A.; Raju, R.N.; Jones, B.; Uprichard, M.; Nemunaitis, J. Phase II trial of talabostat and docetaxel in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.) 2009, 21, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, M.; Kruger, J.A.; Niethammer, A.G.; Reisfeld, R.A. Targeting tumor-associated fibroblasts improves cancer chemotherapy by increasing intratumoral drug uptake. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duperret, E.K.; Trautz, A.; Ammons, D.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; Wise, M.C.; Yan, J.; Reed, C.; Weiner, D.B. Alteration of the Tumor Stroma Using a Consensus DNA Vaccine Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) Synergizes with Antitumor Vaccine Therapy in Mice. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1190–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Yuan, S.; Peng, L.; Li, H.; Niu, L.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Yang, M.; Duan, F. Antitumor immunity targeting fibroblast activation protein-alpha in a mouse Lewis lung carcinoma model. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakarla, S.; Chow, K.K.; Mata, M.; Shaffer, D.R.; Song, X.T.; Wu, M.F.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.L.; Rowley, D.R.; Pfizenmaier, K.; et al. Antitumor effects of chimeric receptor engineered human T cells directed to tumor stroma. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2013, 21, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.C.; Lo, A.; Scholler, J.; Sun, J.; Majumdar, R.S.; Kapoor, V.; Antzis, M.; Cotner, C.E.; Johnson, L.A.; Durham, A.C.; et al. Targeting fibroblast activation protein in tumor stroma with chimeric antigen receptor T cells can inhibit tumor growth and augment host immunity without severe toxicity. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, E.; Chinnasamy, D.; Yu, Z.; Morgan, R.A.; Lee, C.C.; Restifo, N.P.; Rosenberg, S.A. Immune targeting of fibroblast activation protein triggers recognition of multipotent bone marrow stromal cells and cachexia. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltbrunner, S.; Britschgi, C.; Schuberth, P.; Bankel, L.; Nguyen-Kim, T.D.L.; Gulati, P.; Weder, W.; Opitz, I.; Lauk, O.; Caviezel, C.; et al. Local delivery of CAR T cells targeting fibroblast activation protein is safe in patients with pleural mesothelioma: First report of FAPME, a phase I clinical trial. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 120–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.F.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhu, Y.G.; Cui, X.R.; Lu, Z.M.; Yu, B.T.; Wu, N. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy in Lung Cancer: Potential and Challenges. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 782775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, P.E.; Chen, J.; Song, E. Targeting CAFs to overcome anticancer therapeutic resistance. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 527–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Fu, M.; Wang, M.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting TGF-beta signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Smith, M.A.; Doshi, P.; Sasser, K.; Fulp, W.; Altiok, S.; Haura, E.B. Antitumor efficacy of the anti-interleukin-6 (IL-6) antibody siltuximab in mouse xenograft models of lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2014, 9, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, T.J.; Smith, J.T.; Schuster, M.; Dragnev, K.H.; Rigas, J.R. A humanized anti-IL-6 antibody (ALD518) in non-small cell lung cancer. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Zhang, L.; Dai, Y. The role of IL-6 in immunotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Thorac. Cancer 2020, 11, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, A.E.; Ozaki, M.; Kameyama, N.; Gao, J.; Kagawa, S.; Yasuda, H.; Soejima, K.; Yin, Y.; Guzy, R.D.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Effect of FGF/FGFR pathway blocking on lung adenocarcinoma and its cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Pathol. 2019, 249, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, O.; Izhar, U.; Amir, G.; Kirshberg, S.; Shlomai, Z.; Zamir, G.; Peled, A.; Shapira, O.M. Interaction between neoplastic cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts through the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis: Role in non-small cell lung cancer tumor proliferation. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2011, 141, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ramjiawan, R.R.; Reiberger, T.; Ng, M.R.; Hato, T.; Huang, Y.; Ochiai, H.; Kitahara, S.; Unan, E.C.; Reddy, T.P.; et al. CXCR4 inhibition in tumor microenvironment facilitates anti-programmed death receptor-1 immunotherapy in sorafenib-treated hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.S.; Chang, C.C.; Wu, C.H.; Dinh, T.K.; Jan, J.J.; Huang, K.W.; Chou, M.C.; Shiue, T.Y.; Yeh, K.C.; Ke, Y.Y.; et al. A highly selective and potent CXCR4 antagonist for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, N.; Yu, M.; Tu, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, M.; Xie, B.; Fu, J.; Han, L. AMD3100 inhibits brain-specific metastasis in lung cancer via suppressing the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis and protecting blood-brain barrier. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 5259–5274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Tateishi, K.; Kudo, Y.; Hoshikawa, M.; Tanaka, M.; Nakatsuka, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Miyabayashi, K.; Takahashi, R.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Stromal remodeling by the BET bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 suppresses the progression of human pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61469–61484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.L.; Yuan, L.W.; Jiang, X.M.; Su, M.X.; Huang, M.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Lu, J.J. Glutathione peroxidase 8 expression on cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts facilitates lung cancer metastasis. MedComm 2022, 3, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamdani, H.; Jalal, S.I. Histone Deacetylase Inhibition in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Hype or Hope? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 582370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, T.; Schmull, S.; Han, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Dual inhibition of HDAC and tyrosine kinase signaling pathways with CUDC-907 attenuates TGFbeta1 induced lung and tumor fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Lung Cancer: Mechanisms and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Liang, C.; Hua, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B.; Meng, Q.; Yu, X.; Shi, S. Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment: New findings and future perspectives. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, A.; Taguchi, Y.; Ogura, T.; Ebina, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Suga, M.; Takahashi, H.; Nakata, K.; Sato, A.; et al. Exploratory analysis of a phase III trial of pirfenidone identifies a subpopulation of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as benefiting from treatment. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, E.; Gili, E.; Fagone, E.; Fruciano, M.; Iemmolo, M.; Vancheri, C. Effect of pirfenidone on proliferation, TGF-beta-induced myofibroblast differentiation and fibrogenic activity of primary human lung fibroblasts. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. Off. J. Eur. Fed. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 58, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, A.; Funaki, S.; Fukui, E.; Kimura, K.; Kanou, T.; Ose, N.; Minami, M.; Shintani, Y. Effects of pirfenidone targeting the tumor microenvironment and tumor-stroma interaction as a novel treatment for non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dwyer, D.N.; Moore, B.B. The role of periostin in lung fibrosis and airway remodeling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2017, 74, 4305–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak-Wielgomas, K.; Kmiecik, A.; Grzegrzolka, J.; Piotrowska, A.; Gomulkiewicz, A.; Partynska, A.; Pawelczyk, K.; Nowinska, K.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Dziegiel, P. Prognostic Significance of Stromal Periostin Expression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamato, H.; Kimura, K.; Fukui, E.; Kanou, T.; Ose, N.; Funaki, S.; Minami, M.; Shintani, Y. Periostin secreted by activated fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis promotes tumorigenesis of non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.F.; Chen, X.J.; Liang, L.J.; Yu, L.; Wu, X.G.; Zhou, C.F.; Wang, Z.C.; Fan, L.S.; Hu, Z.; Liang, L.; et al. Periostin(+) cancer-associated fibroblasts promote lymph node metastasis by impairing the lymphatic endothelial barriers in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Taniyama, Y.; Sanada, F.; Morishita, R.; Nakamori, S.; Morimoto, K.; Yeung, K.T.; Yang, J. Periostin blockade overcomes chemoresistance via restricting the expansion of mesenchymal tumor subpopulations in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Kaiser, R.; Mellemgaard, A.; Douillard, J.Y.; Orlov, S.; Krzakowski, M.; von Pawel, J.; Gottfried, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Liao, M.; et al. Docetaxel plus nintedanib versus docetaxel plus placebo in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (LUME-Lung 1): A phase 3, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richeldi, L.; du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, R.; Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Sakai, K.; Sakai, H.; Kawakami, H.; Tanaka, K.; Takeda, M.; Yonesaka, K.; Nishio, K.; et al. Nintedanib promotes antitumour immunity and shows antitumour activity in combination with PD-1 blockade in mice: Potential role of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noman, M.Z.; Parpal, S.; Van Moer, K.; Xiao, M.; Yu, Y.; Viklund, J.; De Milito, A.; Hasmim, M.; Andersson, M.; Amaravadi, R.K.; et al. Inhibition of Vps34 reprograms cold into hot inflamed tumors and improves anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax7881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, L.; Jungwirth, U.; Avgustinova, A.; Iravani, M.; Mills, A.; Haider, S.; Harper, J.; Isacke, C.M. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Suppress CD8+ T-cell Infiltration and Confer Resistance to Immune-Checkpoint Blockade. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2904–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pure, E.; Lo, A. Can Targeting Stroma Pave the Way to Enhanced Antitumor Immunity and Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors? Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.W.; Tanlimco, S.G.; Hickson, J.; Fox, M.; Sho, M.; Durkin, L.; Uziel, T.; Powers, R.; Foster, K.; McGonigal, T.; et al. LRRC15 Is a Novel Mesenchymal Protein and Stromal Target for Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4059–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, T.J.; Lee, J.P.; Bourne, C.M.; Wijewarnasuriya, D.; Kinarivala, N.; Kurtz, K.G.; Corless, B.C.; Dacek, M.M.; Chang, A.Y.; Mo, G.; et al. Engineering CAR-T cells to activate small-molecule drugs in situ. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankeu Fonkoua, L.A.; Sirpilla, O.; Sakemura, R.; Siegler, E.L.; Kenderian, S.S. CAR T cell therapy and the tumor microenvironment: Current challenges and opportunities. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 25, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, T.; Fu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Deng, Y.; Chen, G.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Cancer-associated Fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Transglutaminase 2-dependent IL-6/IL6R/STAT3 axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Biol.Sci. 2020, 16, 2542–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Moreno, V.; Gaggioli, C.; Yeo, M.; Albrengues, J.; Wallberg, F.; Viros, A.; Hooper, S.; Mitter, R.; Feral, C.C.; Cook, M.; et al. ROCK and JAK1 signaling cooperate to control actomyosin contractility in tumor cells and stroma. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bughda, R.; Dimou, P.; D’Souza, R.R.; Klampatsa, A. Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP)-Targeted CAR-T Cells: Launching an Attack on Tumor Stroma. Immunotargets Ther. 2021, 10, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardi, L.; Airo Farulla, L.S.; Demirci, E.; Clerici, I.; Omodeo Sale, E.; Ceci, F. Imaging Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) with FAPi PET. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, S.; Baars, M.J.D.; Vercoulen, Y. Multiplex Tissue Imaging: Spatial Revelations in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2022, 14, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glabman, R.A.; Choyke, P.L.; Sato, N. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Tumorigenicity and Targeting for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CAF Marker | Description | Function | Effect on Tumor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vimentin | Type III intermediate filament protein | Cell structure, integrity | Tumor invasion, metastasis (when expressed in cancer cells) |
| α-SMA | Actin isoform | Cell structure, integrity, contractility | Tumor proliferation |
| S100A4/FSP-1 | Ca2+-dependent S100 family | Cell motility, tissue fibrosis | Tumor invasion, metastasis (when expressed in cancer cells) |
| FAP | Serine protease | ECM remodeling | Tumor invasion, metastasis |
| PDGFR-α/β | Tyrosine kinase receptor | Tyrosine kinase activity | Angiogenesis, immunomodulation |
| Tenascin-C | ECM glycoprotein | Cell proliferation, migration | Angiogenesis |
| Periostin | ECM protein | Cell proliferation, migration | Tumor proliferation, fibrosis |
| Podoplanin | Mucin-type transmembrane protein | Cell proliferation, migration | Tumor invasion, metastasis, immunosuppression |
| Thy-1 | Heavily N-glycosylated cell surface protein | Cell–cell interaction | Tumor proliferation, metastasis |
| Integrin-β1 | Transmembrane receptor | Cell–matrix adhesion | Tumor proliferation, metastasis |
| Caveolin-1 | Scaffolding protein within caveolar membranes | Cell signaling, transport | Tumor proliferation, invasion |
| AEBP | Transcriptional repressor | Gene expression regulation | Tumorigenesis, tumor proliferation |
| Endoglin | TGF-β co-receptor | Modulation of cellular responses to TGF-β | Angiogenesis |
| Author | Subtype | Biomarkers | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lambrechts | Cluster 1 | COL10A1 | EMT signaling |
| Cluster 2 | ACTA2 | Myogenesis, angiogenesis | |
| Cluster 3 | - | ECM | |
| Cluster 4 | PLA2GA2 | Similar to Cluster 1; enriched in leading edge of tumor | |
| Cluster 5 | MMP3 | Low myogenesis, high mTOR expression | |
| Cluster 6 | FIGF | Non-malignant fibroblasts | |
| Cluster 7 | - | Similar to Cluster 4 but differing in glycolysis pathway | |
| Hu | Subtype I | HGF High, FGF High/Low, p-SMAD2 Low | Protects cancer cells, strong TKI rescuer |
| Subtype II | HGF Low, FGF High, p-SMAD2 Low | Protects cancer cells, intermediate rescuer | |
| Subtype III | HGF Low, FGF Low, p-SMAD2 High | Immune cell migration, better clinical response | |
| Kim | Branch 1 | IGFBP6, IFITM3, LGALS3 | Immunosuppressive CAF, immunomodulation |
| Branch 2 | UBE2T, TK1, CXCL12, KPNA2, HMGB3 | Neoantigen-presenting CAF, antigen processing and presentation | |
| Branch 4 | - | Myofibroblastic CAF, secretion of cytokines such as CCL2 and TGF-β, leading to fibrosis, immunomodulation, metastasis | |
| Branch 5 | PRC1, AURKA | Proliferative CAFs, majority of total CAFs | |
| Su | CD10 + GPR77+ | Sustaining cancer stemness |
| NCT Number | Drug | Mechanism | Title | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05386888 | GFH018 | TGF-βRI kinase inhibitor | A phase 2 Trial of GFH018 in Combination toripalimab given concurrently with platinum-based chemoradiotherapy for participants with unresectable, locally advanced stage III NSCLC | Not yet recruiting |
| 04691817 | Tocilizumab | Human anti-IL-6R mAb | A phase Ib-II trial of tocilizumab and atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer refractory to first-line immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-based therapy | Not yet recruiting |
| 04940299 | Tocilizumab | Human anti-IL-6R mAb | A phase II study to assess the safety and efficacy of tocilizumab in combination with ipilimumab and nivolumab in patients with advanced melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, or urothelial carcinoma | Recruiting |
| 03762122 | Rogaratinib | FGFR inhibitor | FGFR inhibitor rogaratinib in patients with advanced pretreated squamous cell non-small cell lung cancer (SQCLC) Overexpressing FGFR mRNA. A multicenter, single-arm phase II trial | Active, not recruiting |
| 03827850 | Erdafitinib | FGFR inhibitor | A phase II trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of erdafitinib in patients with advanced squamous NSCLC harboring FGFR genetic alterations after relapse of standard therapy | Recruiting |
| 05210946 | Pemigatinib | FGFR inhibitor | A single-arm clinical study of pemigatinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with FGFR gene alterations who had failed standard therapy | Recruiting |
| 04619563 | Anlotinib | Multitarget receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor | A single-arm exploratory clinical study of anlotinib hydrochloride combined with docetaxel in EGFR mutations and advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients who had progressed after targeted therapy and chemotherapy | Recruiting |
| 05460481 | Anlotinib | Multitarget receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor | Anlotinib plus penpulimab in advanced non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: a multicenter, single-arm, explorative trial | Recruiting |
| 05465590 | MB1707 | CXCR4 peptide antagonist | A phase 1 study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and safety of MB1707 in patients with advanced cancer | Not yet recruiting |
| 01928576 | Entinostat | HDAC inhibitor | A phase II Study of epigenetic therapy with azacitidine and entinostat with concurrent nivolumab in subjects with metastatic NSCLC | Active, not recruiting |
| 05141357 | HBI-8000 | HDAC inhibitor | A phase 2 study to assess the safety and efficacy of hbi-8000 in combination with pembrolizumab for advanced or metastatic NSCLC | Not yet recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shintani, Y.; Kimura, T.; Funaki, S.; Ose, N.; Kanou, T.; Fukui, E. Therapeutic Targeting of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2023, 15, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020335
Shintani Y, Kimura T, Funaki S, Ose N, Kanou T, Fukui E. Therapeutic Targeting of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020335
Chicago/Turabian StyleShintani, Yasushi, Toru Kimura, Soichiro Funaki, Naoko Ose, Takashi Kanou, and Eriko Fukui. 2023. "Therapeutic Targeting of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Microenvironment" Cancers 15, no. 2: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020335
APA StyleShintani, Y., Kimura, T., Funaki, S., Ose, N., Kanou, T., & Fukui, E. (2023). Therapeutic Targeting of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers, 15(2), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020335






