E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4 Affects Estrogen Receptor α Expression and the Prognosis of Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
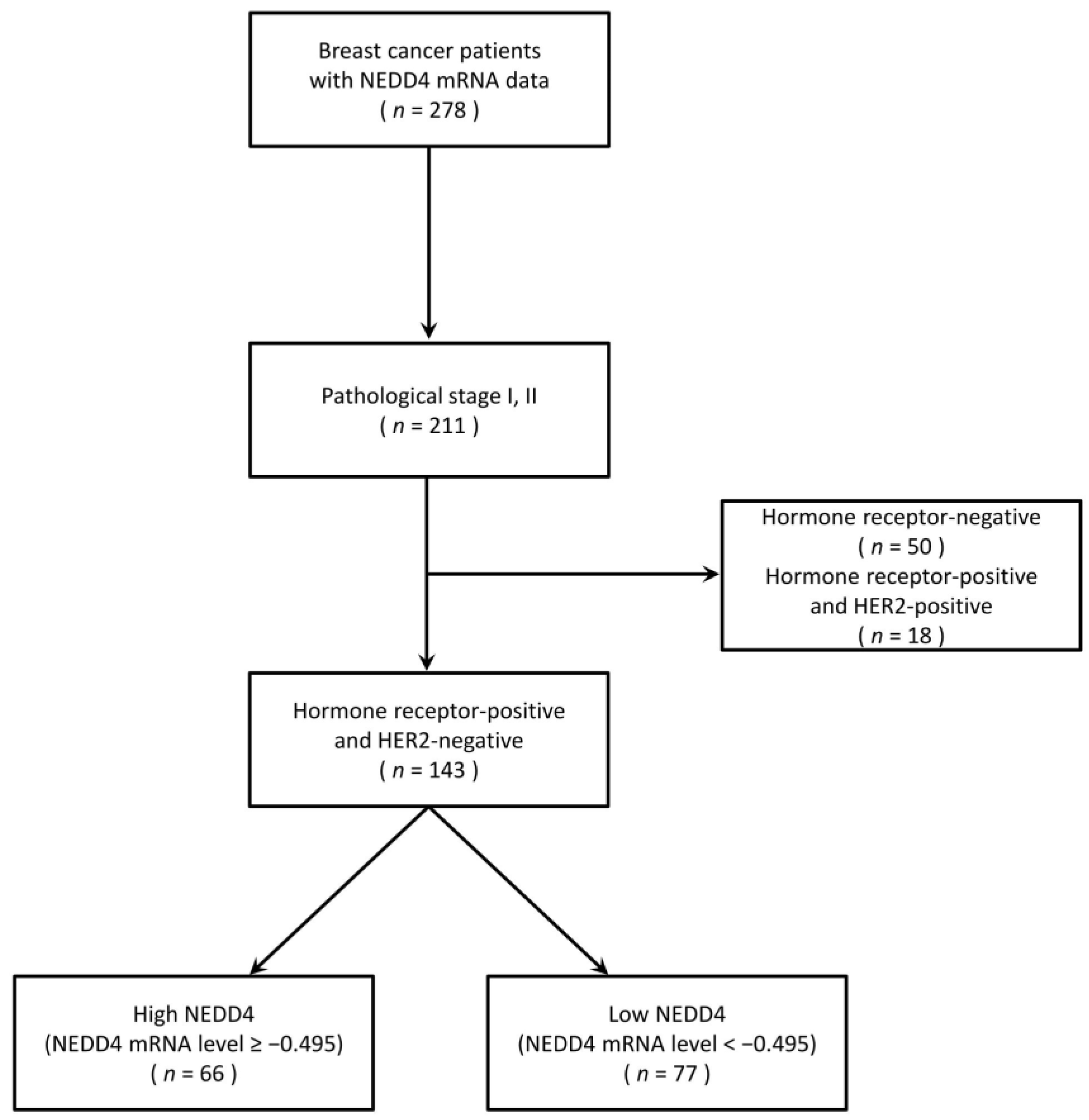
2.1. Clinical Sample Material
2.2. NEDD4 mRNA Expression Analysis
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Small Hairpin RNA (shRNA)-Mediated Knockdown
2.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.6. Western Blots
2.7. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
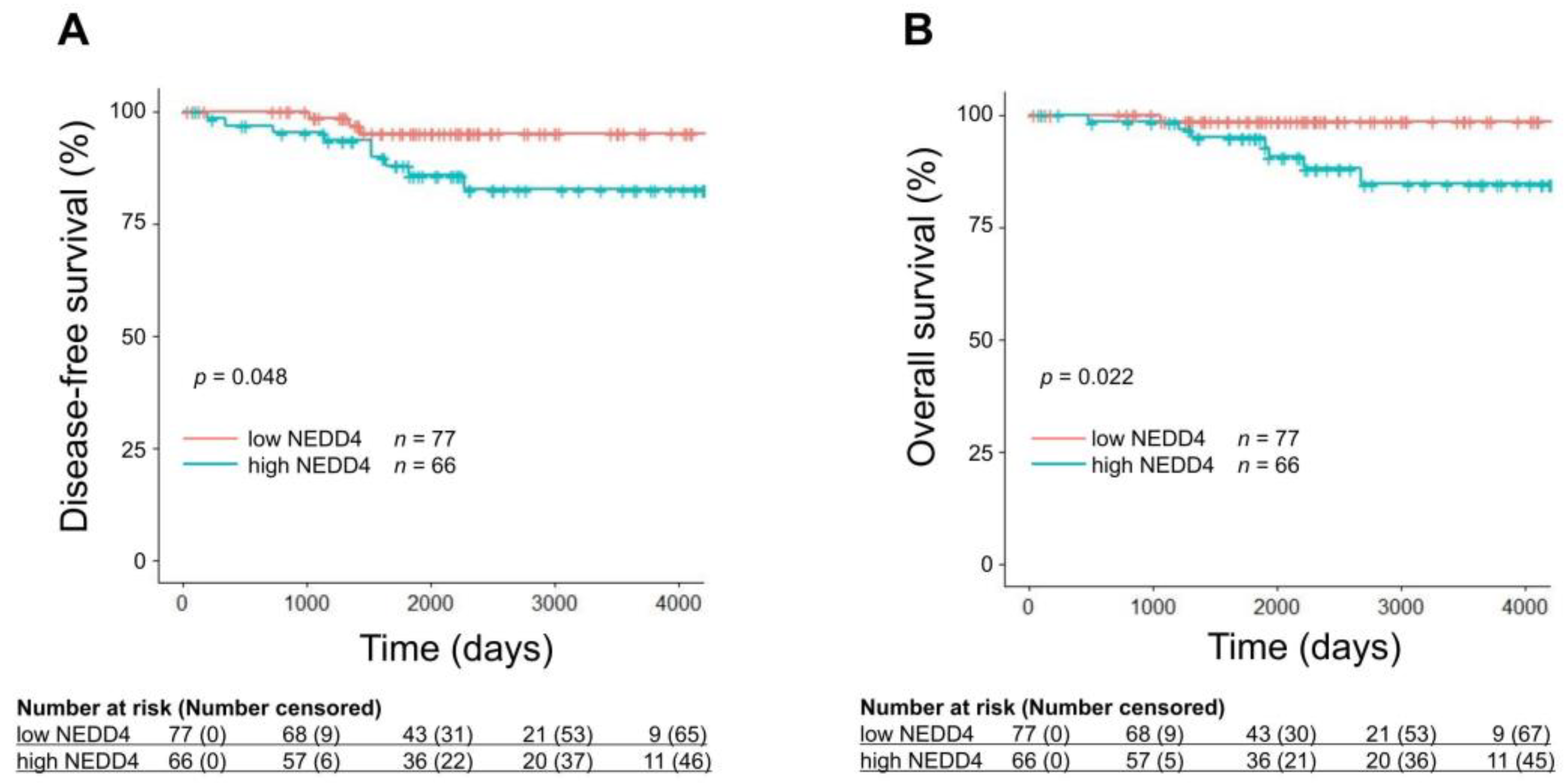
3.1. A Low NEDD4 mRNA Level Is Associated with a Favorable Prognosis in HR-Positive Breast Cancer
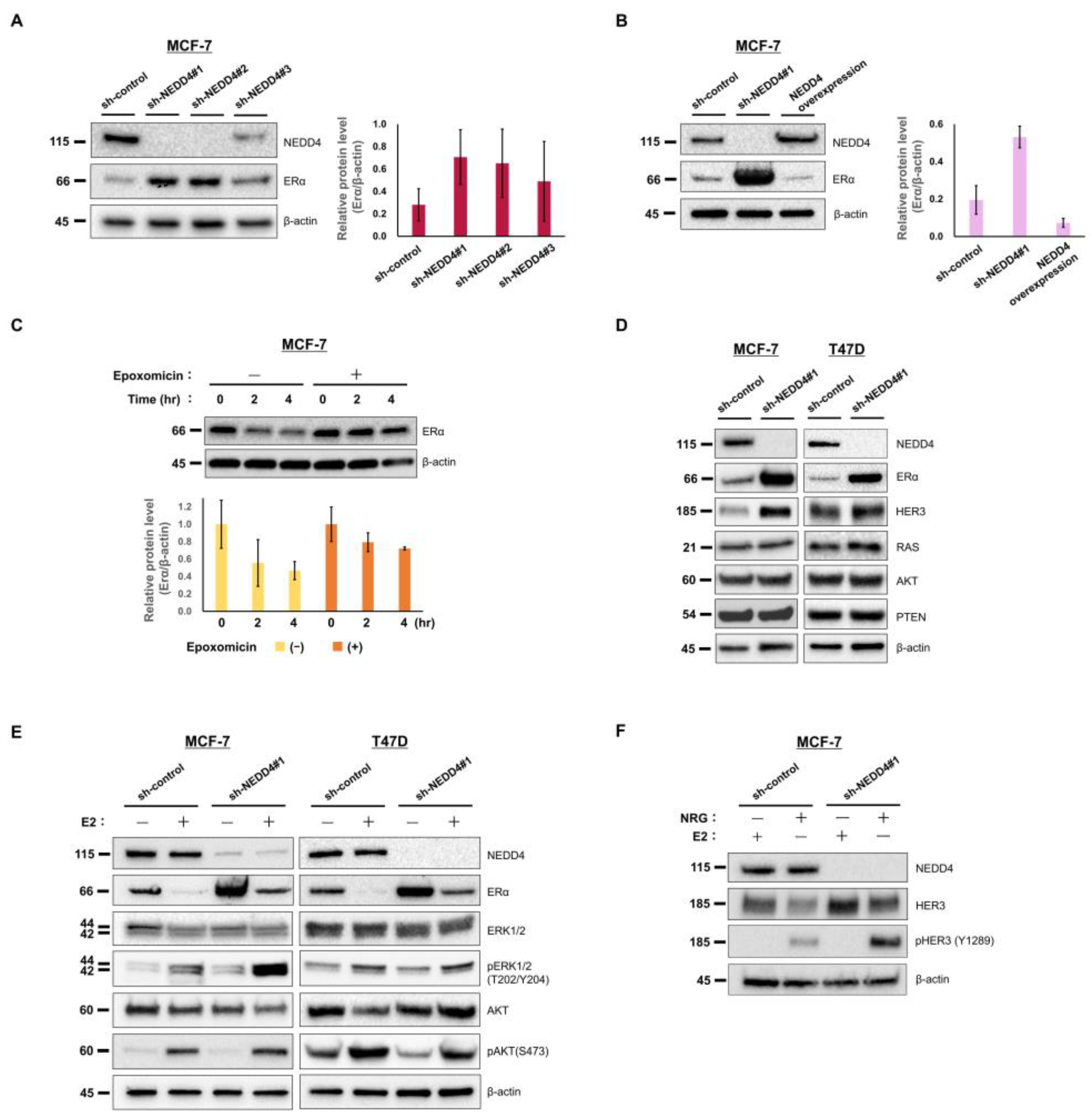
3.2. NEDD4 Knockdown Increases the ERα Protein Level and E2-Stimulated ERK Signaling
3.3. NEDD4 Knockdown Enhances the Suppression of Cell Growth by Hormone Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Cao, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, Q.; He, J.; Yi, Q.; Huang, H.; Zhang, E.; Cai, Z. The Many Substrates and Functions of NEDD4–1. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boase, N.; Kumar, S. NEDD4: The Founding Member of a Family of Ubiquitin-Protein Ligases. Gene 2015, 557, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Wang, Q.; Fu, J.; Lin, Q.; Bi, J.; Ding, W.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.; Lin, H.; et al. Impeded Nedd4–1-Mediated Ras Degradation Underlies Ras-Driven Tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.D.; Lum, M.A.; Xu, C.; Black, J.D.; Wang, X. Ubiquitin-Dependent Regulation of Phospho-AKT Dynamics by the Ubiquitin E3 LIGASE, NEDD4–1, in the Insulin-like Growth Factor−1 Response. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1674–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Trotman, L.C.; Koppie, T.; Alimonti, A.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Z.; Wang, J.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; et al. NEDD4–1 Is a Proto-Oncogenic Ubiquitin Ligase for PTEN. Cell 2007, 128, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Gal, L.-C.; Michael, B. Molecular Functions of NEDD4 E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1856, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.; Li, C.; Jeong, D.; Lee, S.; Ohk, J.; Park, M.; Han, S.; Duan, J.; Kim, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. Oncogenic Function of P34SEI–1 via NEDD4–1-Mediated PTEN Ubiquitination/Degradation and Activation of the PI3K/AKT Pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amodio, N.; Scrima, M.; Palaia, L.; Salman, A.N.; Quintiero, A.; Franco, R.; Botti, G.; Pirozzi, P.; Rocco, G.; de Rosa, N.; et al. Oncogenic Role of the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4–1, a PTEN Negative Regulator, in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinomas. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2622–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Choi, B.K.; Mujoo, K.; Fan, X.; Fa, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Owiti, N.; Zhang, N.; An, Z. The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4 Negatively Regulates HER3/ErbB3 Level and Signaling. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luhtala, S.; Staff, S.; Kallioniemi, A.; Tanner, M.; Isola, J. Clinicopathological and Prognostic Correlations of HER3 Expression and Its Degradation Regulators, NEDD4–1 and NRDP1, in Primary Breast Cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Liu, T.; Hong, Z.; Pan, Y.; Sizemore, S.T.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z. NEDD4 Expression Is Associated with Breast Cancer Progression and Is Predictive of a Poor Prognosis. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.A.; Kim, D.W.; bin Lee, D.; Cho, J.Y. NEDD4 Plays Roles in the Maintenance of Breast Cancer Stem Cell Characteristics. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J. Strategies for Subtypes-Dealing with the Diversity of Breast Cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Winer, E.P.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J.; Albain, K.S.; André, F.; Bergh, J.; et al. Personalizing the Treatment of Women with Early Breast Cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2013. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2206–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, A.S.; Winer, E.P.; Goldhirsch, A.; Gelber, R.D.; Gnant, M.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; Thürlimann, B.; Senn, H.J.; André, F.; Baselga, J.; et al. Tailoring Therapies-Improving the Management of Early Breast Cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1533–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C.; Neven, P.; Loibl, S.; Andre, F. Advances in the Treatment of Advanced Oestrogen-Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 2403–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Gianni, L. HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 2415–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkert, C.; Liedtke, C.; Tutt, A.; von Minckwitz, G. Molecular Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—The Road to New Treatment Strategies. Lancet 2017, 389, 2430–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfakeeh, A.; Brezden-Masley, C. Overcoming Endocrine Resistance in Hormone Receptor–Positive Breast Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, S18–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, J.; Izumiyama, K.; Tanaka, N.; Saji, S. Estradiol Promotes Rapid Degradation of HER3 in ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF–7. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 16, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Honma, R.; Imai, J.I.; Saze, Z.; Kogure, M.; Marubashi, S.; Tasaki, K.; Unakami, M.; Ezaki, J.; Tamura, H.; et al. A Novel Gene Expression Scoring System for Accurate Diagnosis of Basaloid Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCCN Guidelines Breast Cancer. 2021. Available online: https://Www.Nccn.Org/Guidelines/Guidelines-Detail?Category=1&id=1419 (accessed on 18 June 2021).
- Burstein, H.J.; Lacchetti, C.; Anderson, H.; Buchholz, T.A.; Davidson, N.E.; Gelmon, K.A.; Giordano, S.H.; Hudis, C.A.; Solky, A.J.; Stearns, V.; et al. Adjuvant Endocrine Therapy for Women With Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer: ASCO Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Hibshoosh, H.; Parsons, R.; Saal, L.H. PTEN and NEDD4 in Human Breast Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2016, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, Z.; Lonard, D.M.; Dennis, A.P.; Smith, C.L.; O’Malley, B.W. Proteasome-Dependent Degradation of the Human Estrogen Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1858–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Slingerland, J.M. Links between Oestrogen Receptor Activation and Proteolysis: Relevance to Hormone-Regulated Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Fan, C.D.; Wang, X. Regulation of Mdm2 Protein Stability and the P53 Response by NEDD4–1 E3 Ligase. Oncogene 2015, 34, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladkou, F.; Landry, T.; Kawabe, H.; Neeb, A.; Lu, C.; Brose, N.; Stambolic, V.; Rotin, D. The Ubiquitin Ligase Nedd4–1 Is Dispensable for the Regulation of PTEN Stability and Localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8585–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Goodfellow, R.; Li, Y.; Yanga, S.; Winters, C.J.; Thiel, K.W.; Leslie, K.K.; Yanga, B. NEDD4 Ubiquitin Ligase Is a Putative Oncogene in Endometrial Cancer That Activates IGF–1R/PI3K/Akt Signaling. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 139, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wan, L.; Liu, P.; Inuzuka, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, W. SCF β-TRCP-Mediated Degradation of NEDD4 Inhibits Tumorigenesis through Modulating the PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | High NEDD4 (n = 66) | Low NEDD4 (n = 77) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) median (range) | 54 (30–85) | 61 (29–85) |
| Female (%) | 66 (100) | 77 (100) |
| Stage (%) | ||
| I | 26 (39.4) | 35 (45.5) |
| II | 40 (60.6) | 42 (54.5) |
| Lymph node metastasis (%) | 23 (34.8) | 26 (33.8) |
| Estrogen receptor (+) (%) | 66 (100) | 77 (100) |
| Progesterone receptor (+) (%) | 47 (71.2) | 67 (87.0) |
| HER2 (+) (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
| Surgery (%) | 66 (100) | 77 (100) |
| Chemotherapy (%) | 27 (40.9) | 21 (27.3) |
| Neoadjuvant | 2 (3.0) | 3 (3.9) |
| Adjuvant | 25 (37.9) | 18 (23.4) |
| Radiotherapy (%) | 41 (62.1) | 37 (48.1) |
| Neoadjuvant/adjuvant hormone therapy (%) | 65 (98.4) | 74 (96.1) |
| Aromatase inhibitors | 36 (54.5) | 54 (70.1) |
| Tamoxifen | 29 (43.9) | 20 (26.0) |
| NEDD4 mRNA (range) | −0.258 (−0.494 to –1.105) | −0.775 (−1.681 to −0.496) |
| p-Value (Univariate Analysis) | ||
|---|---|---|
| DFS | OS | |
| Age ≥ 50 vs. <50 (years) | 0.862 | 0.643 |
| Age ≥ 60 vs. <40 (years) | 0.724 | 0.567 |
| Lymph node metastasis (+) vs. (−) | 0.609 | 0.959 |
| Stage I vs. II | 0.062 | 0.779 |
| Chemotherapy (+) vs. (−) | 0.628 | 0.949 |
| Radiotherapy (+) vs. (−) | 0.991 | 0.580 |
| High NEDD4 vs. Low NEDD4 | 0.048 * | 0.022 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Natori, Y.; Suga, J.; Tokuda, E.; Tachibana, K.; Imai, J.-i.; Honma, R.; Azami, Y.; Noda, M.; Sasaki, E.; Watanabe, S.; et al. E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4 Affects Estrogen Receptor α Expression and the Prognosis of Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020539
Natori Y, Suga J, Tokuda E, Tachibana K, Imai J-i, Honma R, Azami Y, Noda M, Sasaki E, Watanabe S, et al. E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4 Affects Estrogen Receptor α Expression and the Prognosis of Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020539
Chicago/Turabian StyleNatori, Yutaka, Junko Suga, Emi Tokuda, Kazunoshin Tachibana, Jun-ichi Imai, Reiko Honma, Yusuke Azami, Masaru Noda, Eisaku Sasaki, Shinya Watanabe, and et al. 2023. "E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4 Affects Estrogen Receptor α Expression and the Prognosis of Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 2: 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020539
APA StyleNatori, Y., Suga, J., Tokuda, E., Tachibana, K., Imai, J.-i., Honma, R., Azami, Y., Noda, M., Sasaki, E., Watanabe, S., Ohtake, T., & Saji, S. (2023). E3 Ubiquitin Ligase NEDD4 Affects Estrogen Receptor α Expression and the Prognosis of Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers, 15(2), 539. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020539






