Efficacy of Liver Chemoembolization after Prior Cetuximab Monotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedure
2.2. Feasibility of Chemoembolization
2.3. Imaging and Tumor Response
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
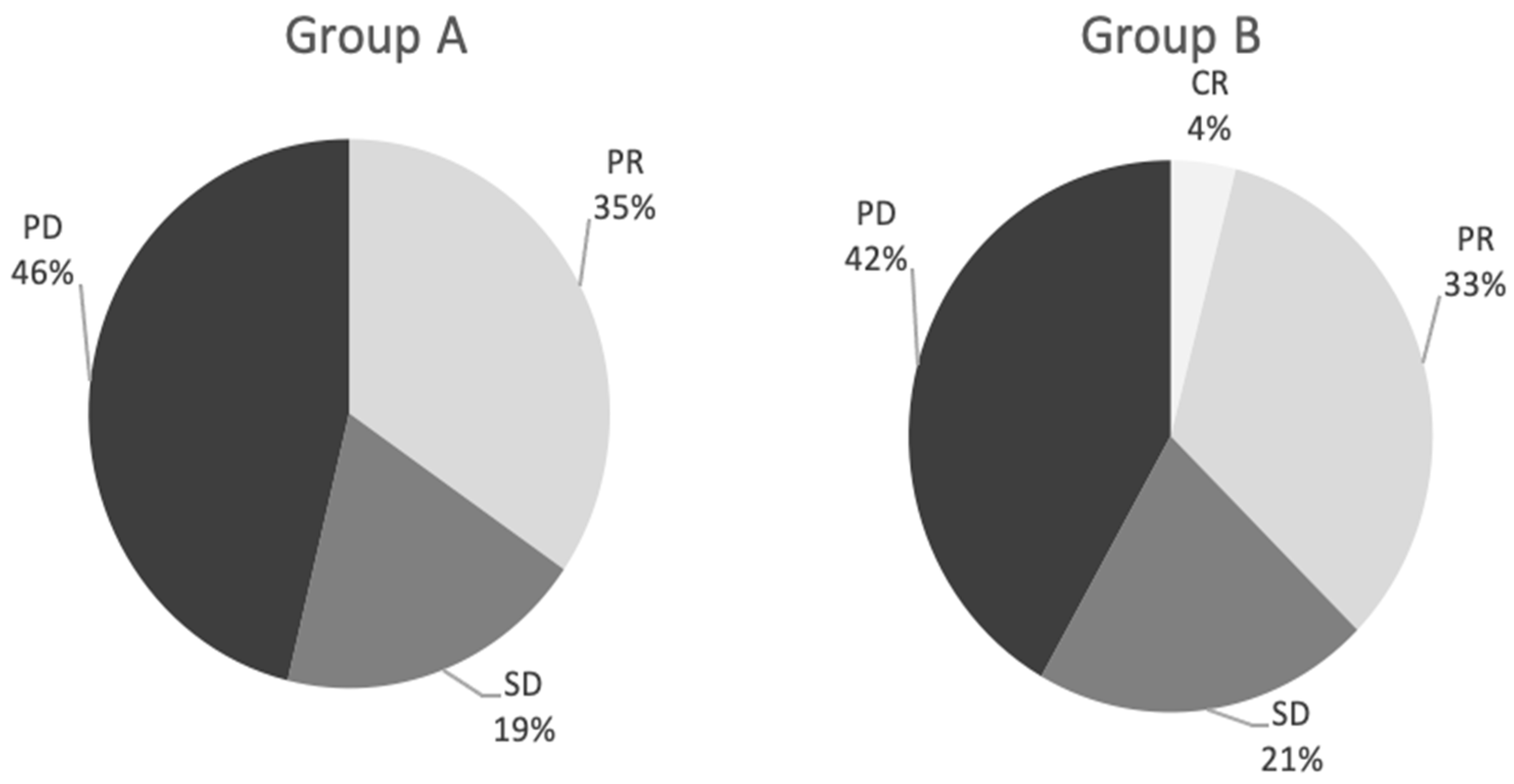
3.2. Response
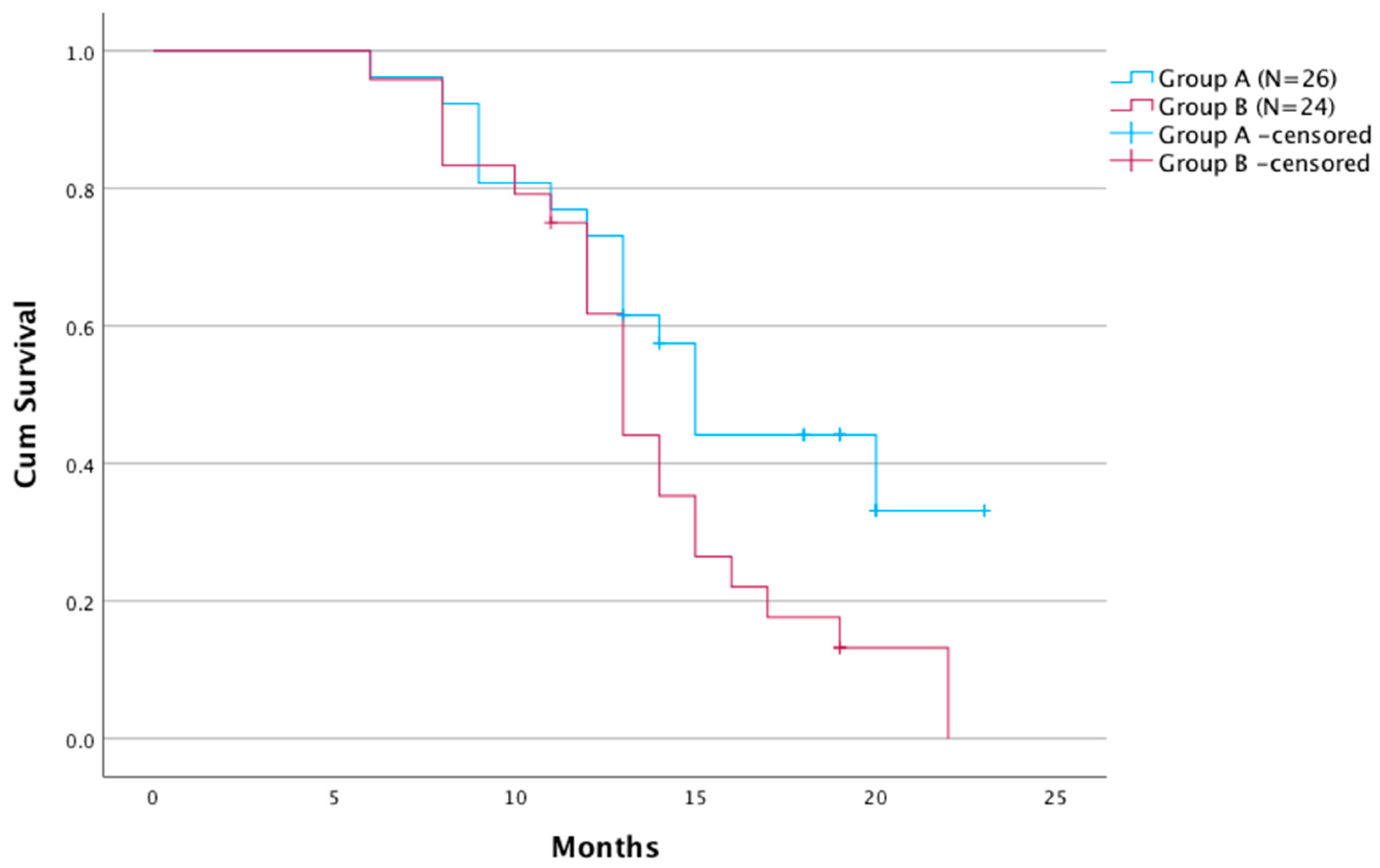
3.3. Survival Analysis
3.4. Adverse Events
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruers, T.; Bleichrodt, R.P. Treatment of liver metastases, an update on the possibilities and results. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baidoun, F.; Elshiwy, K.; Elkeraie, Y.; Merjaneh, Z.; Khoudari, G.; Sarmini, M.T.; Gad, M.; Al-Husseini, M.; Saad, A. Colorectal Cancer Epidemiology: Recent Trends and Impact on Outcomes. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentsch, M.; Schiergens, T.; Khandoga, A.; Werner, J. Surgery for Colorectal Cancer—Trends, Developments, and Future Perspectives. Visc. Med. 2016, 32, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.K.; Pawlik, T.M.; Zorzi, D.; Gleisner, A.L.; Ribero, D.; Assumpcao, L.; Barbas, A.S.; Abdalla, E.K.; Choti, M.A.; Vauthey, J.N.; et al. Simultaneous resections of colorectal cancer and synchronous liver metastases: A multi-institutional analysis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 3481–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismaili, N. Treatment of colorectal liver metastases. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogl, T.J.; Zangos, S.; Eichler, K.; Yakoub, D.; Nabil, M. Colorectal liver metastases: Regional chemotherapy via transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and hepatic chemoperfusion: An update. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentini, G.; Aliberti, C.; Tilli, M.; Mulazzani, L.; Graziano, F.; Giordani, P.; Mambrini, A.; Montagnani, F.; Alessandroni, P.; Catalano, V.; et al. Intra-arterial infusion of irinotecan-loaded drug eluting beads (DEBIRI) versus intravenous therapy (FOLFIRI) for hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: Final results of a phase III study. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann, V.; von Weikersthal, L.F.; Decker, T.; Kiani, A.; Kaiser, F.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; Heintges, T.; Lerchenmüller, C.; Kahl, C.; Seipelt, G.; et al. FOLFIRI plus cetuximab or bevacizumab for advanced colorectal cancer: Final survival and per-protocol analysis of FIRE-3, a randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, R.; Halama, N. FOLFOX plus cetuximab in first-line therapy of advanced colorectal cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6 (Suppl. S2), S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaii-Saab, T.; Kim, R.; Kim, T.W.; O’Connor, J.M.; Strickler, J.H.; Malka, D.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Bi, F.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Third- or Later-line Therapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Reviewing Best Practice. Clin. Color. Cancer 2019, 18, e117–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentini, G.; Sarti, D.; Nani, R.; Aliberti, C.; Fiorentini, C.; Guadagni, S. Updates of colorectal cancer liver metastases therapy: Review on DEBIRI. Hepat Oncol. 2020, 7, HEP16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scevola, G.; Loreni, G.; Rastelli, M.; Sposato, S.; Ramponi, S.; Miele, V. Third-line treatment of colorectal liver metastases using DEBIRI chemoembolization. Med. Oncol. 2017, 34, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.; Zuckerman, J.; Garfinkle, R.; Acuna, S.A.; Touchette, J.; Vanounou, T.; Pelletier, J.S. Intra-arterial therapies for unresectable and chemorefractory colorectal cancer liver metastases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. HPB 2018, 20, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, S.; Miura, T.; Terashima, J.; Habano, W. Cellular irinotecan resistance in colorectal cancer and overcoming irinotecan refractoriness through various combination trials including DNA methyltransferase inhibitors: A review. Cancer Drug Resist. 2021, 4, 946–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saletti, P.; Molinari, F.; De Dosso, S.; Frattini, M. EGFR signaling in colorectal cancer: A clinical perspective. Gastrointest. Cancer Targets Ther. 2015, 5, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J.; Laurence, J.M.; Lam, V.W. Transarterial chemoembolization with irinotecan beads in the treatment of colorectal liver metastases: Systematic review. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Suyama, K.; Baba, H. Recent Advances in Targeting the EGFR Signaling Pathway for the Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Patel, H.; Bo, L.; Lin, L.; Chen, Z.S. Establishment and Characterization of an Irinotecan-Resistant Human Colon Cancer Cell Line. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 624954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitprez, A.; Larsen, A.K. Irinotecan resistance is accompanied by upregulation of EGFR and Src signaling in human cancer models. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, A.; Caine, M.; Press, C.; Macfarlane, W.; Phillips, G.; Lloyd, A.; Czuczman, P.; Kilpatrick, H.; Bascal, Z.; Tang, Y.; et al. Predicting pharmacokinetic behaviour of drug release from drug-eluting embolization beads using in vitro elution methods. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 136, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.J.; Hammond, J.S.; Girling, K.; Beckingham, I.J. The effect of hepatic vascular inflow occlusion on liver tissue pH, carbon dioxide, and oxygen partial pressures: Defining the optimal clamp/release regime for intermittent portal clamping. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 141, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modest, D.P.; Stintzing, S.; von Weikersthal, L.F.; Decker, T.; Kiani, A.; Vehling-Kaiser, U.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; Heintges, T.; Lerchenmüller, C.; Kahl, C.; et al. Impact of subsequent therapies on outcome of the FIRE-3/AIO KRK0306 trial: First-line therapy with FOLFIRI plus Cetuximab or bevacizumab in patients with KRAS wild-type tumors in metastatic colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3718–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakih, M.M. KRAS mutation screening in colorectal cancer: From paper to practice. Clin. Color. Cancer 2010, 9, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardelli, A.; Siena, S. Molecular mechanisms of resistance to cetuximab and panitumumab in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ji, Q.; Li, Q. Resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer: Underlying mechanisms and reversal strategies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Guo, W.J.; Zhang, X.W.; Cai, X.; Tian, S.; Li, J. Cetuximab enhances the activities of irinotecan on gastric cancer cell lines through downregulating the EGFR pathway upregulated by irinotecan. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 68, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentini, G.; Aliberti, C.; Sarti, D.; Coschiera, P.; Tilli, M.; Mulazzani, L.; Giordani, P.; Graziano, F.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Marcos, R.G.; et al. Locoregional therapy and systemic cetuximab to treat colorectal liver metastases. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 7, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Heo, J.S.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, M.Y.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, W.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.A.; Cho, Y.B.; et al. The impact of KRAS mutations on prognosis in surgically resected colorectal cancer patients with liver and lung metastases: A retrospective analysis. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Group A (n = 26) | Group B (n = 24) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range) | 65.3 (32–74) | 66.5(38–77) | 0.426 |
| Gender, female/male (n) | 15/11 | 12/12 | 0.667 |
| ECOG status (n): | 0.323 | ||
| 0 | 10 | 8 | - |
| 1 | 12 | 13 | - |
| 2 | 4 | 3 | - |
| Tumor location (n): | 0.178 | ||
| Bilobar | 24 | 22 | |
| Unilobar | 2 | 2 | |
| Number of liver metastases, median (range) | 4.4 (1–10) | 4.1(1–9) | 0.139 |
| Largest nodule size diameter, cm (median) | 9.8 | 8.9 | 0.297 |
| Extent of liver involvement (n, <25%/>25%) | 21/5 | 19/5 | 0.401 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis (n, %) | 8 | 8 | 0.278 |
| Site of primary tumor (n): | 0.409 | ||
| Left colon | 15 | 14 | |
| Right colon | 11 | 10 | |
| Prior liver surgery/ablation (n) | 5/0 | 4/0 | 0.502 |
| Prior locoregional therapy (n) | 0 | 0 | - |
| TACE procedure performed for patient (n): | 0.178 | ||
| 4 procedures | 24 | 22 | |
| 4 procedures | 2 | 2 | |
| CEA level (n): | |||
| <10 ng/mL | 12 | 11 | 0.578 |
| >10 ng/mL | 14 | 13 | 0.451 |
| CRC somatic mutation (n) | |||
| KRAS (Exon2) | - | 21 | |
| KRAS(non-Exon2) | - | 1 | |
| BRAS (V600E) | - | 2 |
| Factor | Univariate Cox’s Regression HR (95% Cl) p-Value | Multivariate Cox’s Regression HR (95% Cl) p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age (>65 vs. ≤65) | 2.760 (0.371–20.50), p = 0.321 | |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 1.959 (0.262–14.662), p = 0.512 | |
| ECOG status: (0 vs. 1 and 2) | 0.155 (0.057–0.421), p <0.001 | 0.108 (0.024–0.477), p <0.003 |
| Largest nodule size diameter (<5 cm vs. >5 cm) | 1.846 (0.821–4.232), p = 0.136 | |
| Extent of liver involvement (<25%/>25%) | 0.375 (0.173–0.816), p = 0.013 | 0.185 (0.051–0.676), p = 0.011 |
| Previous cetuximab (yes vs. no) | 1.906 (0.977–3.716), p = 0.058 | |
| CEA (>10 ng/mL vs. < 10 ng/mL) | 2.374 (1.043–5.406), p = 0.039 | 3.330 (1.036–10.702), p = 0.043 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis (yes vs. no) | 0.769 (0.090–6.600), p = 0.811 | |
| Primary tumor resection (yes vs. no) | 1.485 (0.674–3.271), p = 0.32 | |
| Site of primary tumor (left colon vs. right) | 1.452 (0.573–3.495), p = 0.452 | |
| TACE procedure performed for patient (4 vs. 2) | 6.132 (0.799–47.053), p = 0.081 |
| Adverse Event | Group A | Group B |
|---|---|---|
| Liver failure/ascites | 2 | 1 |
| Inflammation of the gallbladder | 2 | 1 |
| Occlusion of the main branch of the hepatic artery | 0 | 2 |
| Leukopenia < 2000/mm3 | 2 | 2 |
| Liver abscesses | 0 | 1 |
| Anaphylactic reaction | 2 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szemitko, M.; Golubinska-Szemitko, E.; Sienko, J.; Falkowski, A.; Wiernicki, I. Efficacy of Liver Chemoembolization after Prior Cetuximab Monotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020541
Szemitko M, Golubinska-Szemitko E, Sienko J, Falkowski A, Wiernicki I. Efficacy of Liver Chemoembolization after Prior Cetuximab Monotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020541
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzemitko, Marcin, Elzbieta Golubinska-Szemitko, Jerzy Sienko, Aleksander Falkowski, and Ireneusz Wiernicki. 2023. "Efficacy of Liver Chemoembolization after Prior Cetuximab Monotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 2: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020541
APA StyleSzemitko, M., Golubinska-Szemitko, E., Sienko, J., Falkowski, A., & Wiernicki, I. (2023). Efficacy of Liver Chemoembolization after Prior Cetuximab Monotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancers, 15(2), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020541





