Endothelial Dysfunction Syndromes after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
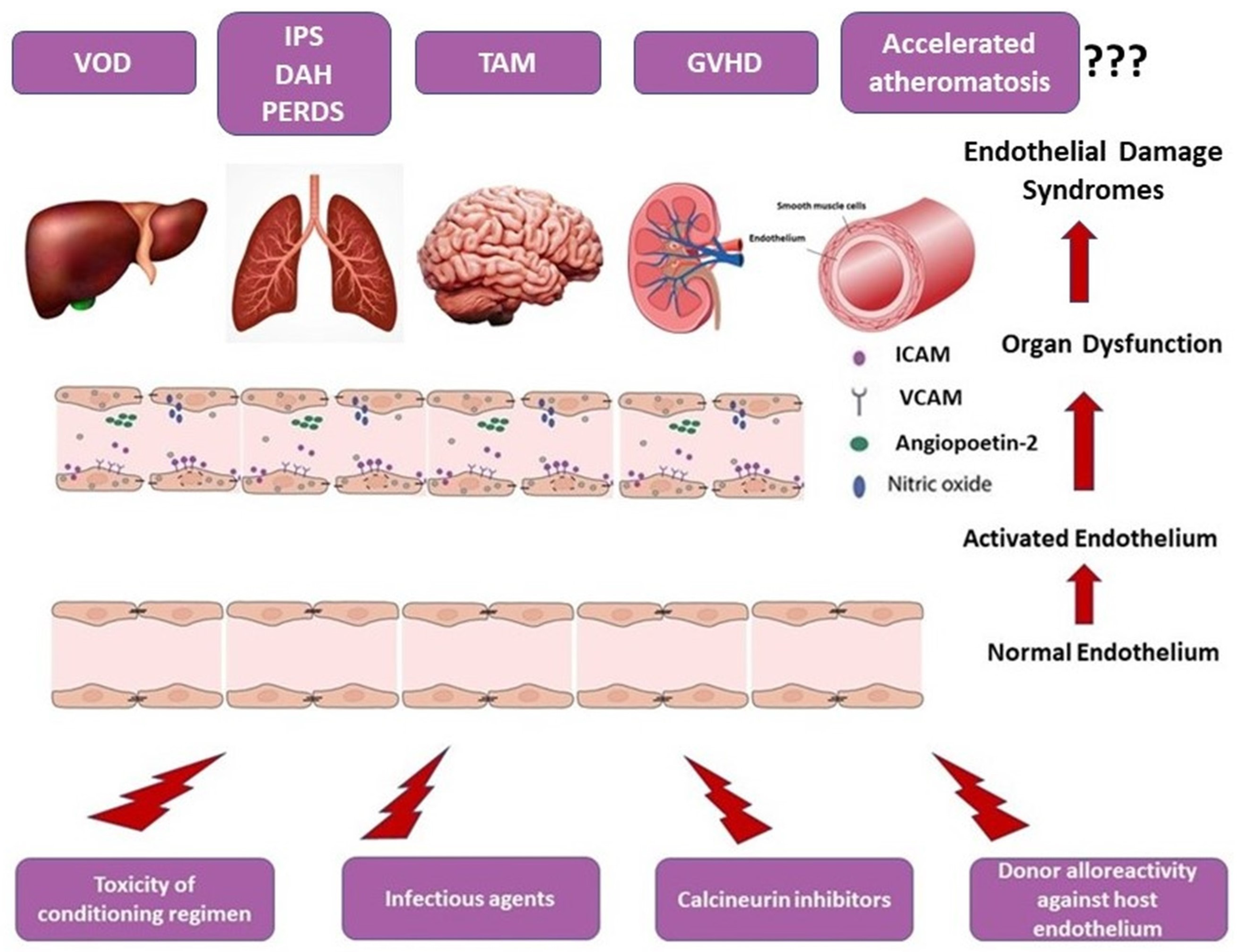
2. Pathophysiology of Endothelial Dysfunction in allo-HSCT
3. Endothelial Dysfunction-Related Post-Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
3.1. Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TA-TMA)
3.2. Sinusoidal Obstructive Syndrome (SOS)/Veno-Occlusive Disease (VOD)
3.3. Lung Injury Syndromes
3.3.1. Idiopathic Pneumonia Syndrome
3.3.2. Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
3.3.3. Peri-Engraftment Respiratory Distress Syndrome
4. Vascular Endothelium: A Target of Graft-Versus-Host Disease
5. Atheromatosis: A Late GVHD Manifestation
6. Soluble Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction
6.1. Von Willebrand Factor
6.2. Cellular Adhesion Molecules
6.3. Thrombomodulin and Plasminogen Activation Inhibitor-1
6.4. Circulating Angiogenic Factors
6.5. Proinflammatory Cytokines
6.6. GVHD Biomarkers Discovered by Proteomics
6.7. Endothelial Activation and Stress Index (EASIX)
7. Cellular Biomarkers of Endothelial Dysfunction
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Luft, T.; Dreger, P.; Radujkovic, A. Endothelial cell dysfunction: A key determinant for the outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 2326–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Rondon, G.; Srour, S.A.; Chen, J.; Ledesma, C.; Champlin, R.E.; Ciurea, S.O.; Saliba, R.M. Endothelial Activation and Stress Index (EASIX) at Admission Predicts Fluid Overload in Recipients of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrandt, G.C.; Chao, N. Endothelial cell function and endothelial-related disorders following haematopoietic cell transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vion, A.-C.; Durand, F.; Boulanger, C.M.; Valla, D.C.; Rautou, P.-E. Interplay of Inflammation and Endothelial Dysfunction in Bone Marrow Transplantation: Focus on Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennings, I.; Luddington, R.J.; Harper, P.L. Changes in endothelial-related coagulation proteins in response to venous occlusion. Thromb. Haemost. 1991, 65, 374–376. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, C.L.; Ordonez, N.G.; Schaefer, R.; Cook, C.D.; Xie, S.S.; Granger, J.; Hsu, P.L.; Fink, L.; Hsu, S.M. Thrombomodulin ex-pression in malignant pleural mesothelioma and pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 1992, 141, 827–833. [Google Scholar]
- Palomo, M.; Diaz-Ricart, M.; Carbo, C.; Rovira, M.; Fernandez-Aviles, F.; Escolar, G.; Eissner, G.; Holler, E.; Carreras, E. The Release of Soluble Factors Contributing to Endothelial Activation and Damage after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Is Not Limited to the Allogeneic Setting and Involves Several Pathogenic Mechanisms. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009, 15, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kasai, K. Globular adiponectin upregulates nitric oxide production in vascular endothelial cells. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleve, L. Decreased hepatic nitric oxide production contributes to the development of rat sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Hepatology 2003, 38, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Yamasaki, M.; Hirai, K.; Matsubara, T.; Nomura, T.; Sato, F.; Mimata, H. Angiopoietin-like protein 2 induces androgen-independent and malignant behavior in human prostate cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 33, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, H.F.; Chavakis, T. Leukocyte—Endothelial interactions in inflammation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Salinero, J.M.; Rafii, S. Endothelial cell adaptation in regeneration. Science 2018, 362, 1116–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebaschi, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Wada, S.; Cong, G.-T.; Rodeo, S.A. Tissue-specific endothelial cells: A promising approach for augmentation of soft tissue repair in orthopedics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1410, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakellari, I.; Gavriilaki, E.; Boussiou, Z.; Batsis, I.; Mallouri, D.; Constantinou, V.; Kaloyannidis, K.; Yannaki, E.; Bamihas, G.; Anagnostopoulos, A. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: An unresolved complication of unrelated allogeneic transplant for hematologic diseases. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 35, 932–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postalcioglu, M.; Kim, H.T.; Obut, F.; Yilmam, O.A.; Yang, J.; Byun, B.C.; Kupiec-Weglinski, S.; Soiffer, R.; Ritz, J.; Antin, J.H.; et al. Impact of Thrombotic Microangiopathy on Renal Outcomes and Survival after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, S.; Bollinger, N.; Bodenmann, B.; Heim, D.; Bucher, C.; Lengerke, C.; Kleber, M.; Tsakiris, D.A.; Passweg, J.R.; Tzankov, A.; et al. High mortality in hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy with and without concomitant acute graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018, 54, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliuca, S.; Michonneau, D.; de Fontbrune, F.S.; del Galy, A.S.; Xhaard, A.; Robin, M.; de Latour, R.P.; Socie, G. Allogeneic reactivity–mediated endothelial cell complications after HSCT: A plea for consensual definitions. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2424–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.A.; Pallas, C.R.; Knovich, M.A. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: Theoretical considerations and a practical approach to an unrefined diagnosis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Laskin, B.L.; Dandoy, C.E.; Myers, K.C.; El-Bietar, J.; Davies, S.M.; Goebel, J.; Dixon, B.P. A new paradigm: Diagnosis and management of HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy as multi-system endothelial injury. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Davies, S.M.; Lane, A.; Khoury, J.; Dandoy, C.; Goebel, J.; Myers, K.; Grimley, M.; Bleesing, J.; El-Bietar, J.; et al. Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: A study in children and young adults. Blood 2014, 124, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Sakellari, I.; Batsis, I.; Mallouri, D.; Bousiou, Z.; Vardi, A.; Yannaki, E.; Constantinou, V.; Tsompanakou, A.; Vadikoliou, C.; et al. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: Incidence, prognostic factors, morbidity, and mortality in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2018, 32, e13371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhunia, N.; Abu-Arja, R.; Bajwa, R.P.; Auletta, J.J.; Rangarajan, H.G. Successful treatment with eculizumab for posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome due to underlying transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in patients transplanted for sickle cell disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Bietar, J.; Warren, M.; Dandoy, C.; Myers, K.C.; Lane, A.; Wallace, G.; Davies, S.M.; Jodele, S. Histologic Features of Intestinal Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 1994–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, R.; Nemoto, T.; Ohashi, K.; Tonooka, A.; Horiguchi, S.-I.; Motoi, T.; Hishima, T. Distribution of Transplantation-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TA-TMA) and Comparison between Renal TA-TMA and Intestinal TA-TMA: Autopsy Study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 26, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandoy, C.E.; Hirsch, R.; Chima, R.; Davies, S.M.; Jodele, S. Pulmonary Hypertension after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 19, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galie, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 67–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heybeli, C.; Sridharan, M.; Alkhateeb, H.B.; Bisneto, J.C.V.; Buadi, F.K.; Chen, D.; Dingli, D.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Go, R.S.; et al. Characteristics of late transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in patients who underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Sakellari, I.; Anagnostopoulos, A.; Brodsky, R.A. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: Opening Pandora’s box. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, V.T.; Cutler, C.; Carter, S.; Martin, P.; Adams, R.; Horowitz, M.; Ferrara, J.; Soiffer, R.; Giralt, S. Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network Toxicity Committee Consensus Summary: Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005, 11, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruutu, T.; Barosi, G.; Benjamin, R.J.; Clark, R.E.; George, J.N.; Gratwohl, A.; Holler, E.; Iacobelli, M.; Kentouche, K.; Lämmle, B.; et al. Diagnostic criteria for hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated microangiopathy: Results of a consensus process by an International Working Group. Haematologica 2007, 92, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.-S.; Yahng, S.-A.; Lee, S.-E.; Eom, K.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Min, C.-K.; Cho, S.-G.; Kim, D.-W.; et al. Validation of Recently Proposed Consensus Criteria for Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation. Transplantation 2010, 90, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayani, S.; Palmer, J.; Stiller, T.; Liu, X.; Thomas, S.H.; Khuu, T.; Parker, P.M.; Khaled, S.K.; Forman, S.J.; Nakamura, R. Thrombotic Microangiopathy Associated with Sirolimus Level after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation with Tacrolimus/Sirolimus-Based Graft-versus-Host Disease Prophylaxis. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 19, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, R.; Clink, H.; Spence, D.; Morgenstern, G.; Watson, J.; Selby, P.; Woods, M.; Barrett, A.; Jameson, B.; Sloane, J.; et al. Cyclosporin a to prevent graft-versus-host disease in man after allogeneic bone-marrow transplantation. Lancet 1980, 315, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Wu, Q.; Davis, C.; Kirtane, K.S.; Pham, P.D.; Sorror, M.L.; Lee, S.J.; Gopal, A.K.; Dong, J.-F.; Garcia, D.A.; et al. Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy Is a Multifactorial Disease Unresponsive to Immunosuppressant Withdrawal. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 25, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruutu, T.; Juvonen, E.; Remberger, M.; Remes, K.; Volin, L.; Mattsson, J.; Nihtinen, A.; Hägglund, H.; Ringdén, O. Improved Survival with Ursodeoxycholic Acid Prophylaxis in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: Long-Term Follow-up of a Randomized Study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 20, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, T.; Benner, A.; Terzer, T.; Jodele, S.; Dandoy, C.E.; Storb, R.; Kordelas, L.; Beelen, D.; Gooley, T.; Sandmaier, B.M.; et al. EASIX and mortality after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 55, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meri, S.; Bunjes, D.; Cofiell, R.; Jodele, S. The Role of Complement in HSCT-TMA: Basic Science to Clinical Practice. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 3896–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Sabulski, A. Transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: Elucidating prevention strategies and identifying high-risk patients. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2021, 14, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, V.; Rizvi, M.; Vesely, S.; George, J. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-like syndromes following bone marrow transplantation: An analysis of associated conditions and clinical outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001, 27, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuge, R.; Bird, J.M.; Fraser, A.; Hart, D.; Hunt, L.; Cornish, J.M.; Goulden, N.; Oakhill, A.; Pamphilon, D.H.; Steward, C.; et al. The clinical features, risk factors and outcome of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura occurring after bone marrow transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2001, 113, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uderzo, C.; Bonanomi, S.; Busca, A.; Renoldi, M.; Ferrari, P.; Iacobelli, M.; Morreale, G.; Lanino, E.; Annaloro, C.; Della Volpe, A.; et al. Risk Factors and Severe Outcome in Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Transplantation 2006, 82, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeates, L.; Slatter, M.A.; Bonanomi, S.; Lim, F.L.W.I.; Ong, S.Y.; Dalissier, A.; Barberi, W.; Shulz, A.; Duval, M.; Heilmann, C.; et al. Use of defibrotide to treat transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: A retrospective study of the Paediatric Diseases and Inborn Errors Working Parties of the European Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohl, S.R.; Kuchenbauer, F.; von Harsdorf, S.; Kloevekorn, N.; Schönsteiner, S.S.; Rouhi, A.; Schwarzwälder, P.; Döhner, H.; Bunjes, D.; Bommer, M. Thrombotic Microangiopathy after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Comparison of Eculizumab Therapy and Conventional Therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higham, C.S.; Shimano, K.A.; Melton, A.; Kharbanda, S.; Chu, J.; Dara, J.; Winestone, L.E.; Hermiston, M.L.; Huang, J.N.; Dvorak, C.C. A pilot trial of prophylactic defibrotide to prevent serious thrombotic microangiopathy in high-risk pediatric patients. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2022, 69, e29641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.S.; Hosing, C.; Aung, F.; Yeh, J. Approaching treatment of transplant-associated thrombotic Microangiopathy from two directions with Eculizumab and transitioning from Tacrolimus to Sirolimus. Transfusion 2019, 59, 3519–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontbrune, F.S.; Galambrun, C.; Sirvent, A.; Huynh, A.; Faguer, S.; Nguyen, S.; Bay, J.O.; Neven, B.; Moussi, J.; Simon, L.; et al. Use of Eculizumab in Patients with Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Study from the SFGM-TC. Transplantation 2015, 99, 1953–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodele, S.; Fukuda, T.; Vinks, A.; Mizuno, K.; Laskin, B.L.; Goebel, J.; Dixon, B.P.; Teusink, A.; Pluthero, F.G.; Lu, L.; et al. Eculizumab Therapy in Children with Severe Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation–Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 20, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodele, S.; Dandoy, C.E.; Lane, A.; Laskin, B.L.; Teusink-Cross, A.; Myers, K.C.; Wallace, G.H.; Nelson, A.; Bleesing, J.; Chima, R.S.; et al. Complement blockade for TA-TMA: Lessons learned from large pediatric cohort treated with eculizumab. Blood 2020, 135, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearman, S.I. The syndrome of hepatic veno-occlusive disease after marrow transplantation. Blood 1995, 85, 3005–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Deleve, L.D.; Kamath, P.S.; Tefferi, A. Hepatic Veno-occlusive Disease (Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome) after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2003, 78, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, L.F.; Colby, T.V. Pathogenesis of veno-occlusive liver disease after radiation. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1980, 104, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takamura, H.; Nakanuma, S.; Hayashi, H.; Tajima, H.; Kakinoki, K.; Kitahara, M.; Sakai, S.; Makino, I.; Nakagawara, H.; Miyashita, T.; et al. Severe Veno-occlusive Disease/Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome after Deceased-donor and Living-donor Liver Transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 3523–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valla, D.; Cazals-Hatem, D. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2016, 40, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLeve, L.D.; Shulman, H.M.; McDonald, G.B. Toxic Injury to Hepatic Sinusoids: Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome (Veno-Occlusive Disease). Semin. Liver Dis. 2002, 22, 027–042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.Q.; Crawford, J.M. Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome (Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease). J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2014, 4, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifazi, F.; Barbato, F.; Ravaioli, F.; Sessa, M.; DeFrancesco, I.; Arpinati, M.; Cavo, M.; Colecchia, A. Diagnosis and Treatment of VOD/SOS after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppell, J.A.; Richardson, P.G.; Soiffer, R.; Martin, P.L.; Kernan, N.A.; Chen, A.; Guinan, E.; Vogelsang, G.; Krishnan, A.; Giralt, S.; et al. Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease following Stem Cell Transplantation: Incidence, Clinical Course, and Outcome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle, J.-H.; Giralt, S.A. Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Risk Factors and Stratification, Prophylaxis, and Treatment. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 22, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohty, M.; Malard, F.; Abecasis, M.; Aerts, E.; Alaskar, A.S.; Aljurf, M.; Arat, M.; Bader, P.; Baron, F.; Basak, G.; et al. Prophylactic, preemptive, and curative treatment for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in adult patients: A position statement from an international expert group. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 55, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Advani, A.S.; Stelljes, M.; Kebriaei, P.; Cassaday, R.D.; Merchant, A.A.; Fujishima, N.; Uchida, T.; Calbacho, M.; et al. Hepatic adverse event profile of inotuzumab ozogamicin in adult patients with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: Results from the open-label, randomised, phase 3 INO-VATE study. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e387–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarjian, H.M.; Vandendries, E.; Bangdiwala, A.S. Advani notuzumab Ozogamicin for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2100–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, M.; Strasser, S.I.; Shulman, H.M.; McDonald, S.J.; Schoch, H.G.; McDonald, G.B. Severe hepatocellular injury after hematopoietic cell transplant: Incidence, etiology and outcome. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 44, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.L.; Gooley, T.; Bensinger, W.; Schiffman, K.; McDonald, G.B. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver after busulfan, melphalan, and thiotepa conditioning therapy: Incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 1999, 5, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.J.; Lee, K.S.K.; Beschorner, W.E.; Vogel, V.G.; Grochow, L.B.; Braine, H.G.; Vogelsang, G.B.; Sensenbrenner, L.L.; Santos, G.W.; Saral, R. Venoocclusive disease of the liver following bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 1987, 44, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, G.B.; Sharma, P.; Matthews, D.E.; Shulman, H.M.; Thomas, E.D. Venocclusive Disease of the Liver after Bone Marrow Transplantation: Diagnosis, Incidence, and Predisposing Factors. Hepatology 1984, 4, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbacioglu, S.; Cesaro, S.; Faraci, M.; Valteau-Couanet, D.; Gruhn, B.; Rovelli, A.; Boelens, J.J.; Hewitt, A.; Schrum, J.; Schulz, A.S.; et al. Defibrotide for prophylaxis of hepatic veno-occlusive disease in paediatric haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation: An open-label, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakushijin, K.; Atsuta, Y.; Doki, N.; Yokota, A.; Kanamori, H.; Miyamoto, T.; Ohwada, C.; Miyamura, K.; Nawa, Y.; Kurokawa, M.; et al. Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Incidence, risk factors and outcomes. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015, 51, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Riches, M.L.; Kernan, N.A.; Brochstein, J.A.; Mineishi, S.; Termuhlen, A.M.; Arai, S.; Grupp, S.A.; Guinan, E.C.; Martin, P.L.; et al. Phase 3 trial of defibrotide for the treatment of severe veno-occlusive disease and multi-organ failure. Blood 2016, 127, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohty, M.; Malard, F.; Abecassis, M.; Aerts, E.; Alaskar, A.; Aljurf, M.; Arat, M.; Bader, P.; Baron, F.; Bazarbachi, A.; et al. Revised diagnosis and severity criteria for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in adult patients: A new classification from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Yoo, K.H.; Sung, K.W.; Jung, C.W.; Kim, J.S.; Hahn, S.M.; Kang, H.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Im, H.J.; Ahn, J.-S.; et al. Validation of treatment outcomes according to revised severity criteria from European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease (SOS/VOD). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Corbacioglu, S.; Ho, V.T.-V.; Kernan, N.; Lehmann, L.; Maguire, C.; Maglio, M.; Hoyle, M.; Sardella, M.; Giralt, S.; et al. Drug safety evaluation of defibrotide. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2012, 12, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbacioglu, S.; Carreras, E.; Mohty, M.; Pagliuca, A.; Boelens, J.J.; Damaj, G.; Iacobelli, M.; Niederwieser, D.; Olavarría, E.; Suarez, F.; et al. Defibrotide for the Treatment of Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease: Final Results from the International Compassionate-Use Program. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kernan, N.A.; Grupp, S.; Smith, A.R.; Arai, S.; Triplett, B.; Antin, J.H.; Lehmann, L.; Shore, T.; Ho, V.T.; Bunin, N.; et al. Final results from a defibrotide treatment-IND study for patients with hepatic veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 181, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Smith, A.R.; Triplett, B.M.; Kernan, N.A.; Grupp, S.A.; Antin, J.H.; Lehmann, L.; Miloslavsky, M.; Hume, R.; Hannah, A.L.; et al. Earlier defibrotide initiation post-diagnosis of veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome improves Day +100 survival following haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 178, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essell, J.H.; Schroeder, M.T.; Harman, G.S.; Halvorson, R.; Lew, V.; Callander, N.; Snyder, M.; Lewis, S.K.; Allerton, J.P.; Thompson, J.M. Ursodiol Prophylaxis against Hepatic Complications of Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1998, 128, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, K.; Tanabe, J.; Watanabe, R.; Tanaka, T.; Sakamaki, H.; Maruta, A.; Okamoto, S.; Aotsuka, N.; Saito, K.; Nishimura, M.; et al. The Japanese multicenter open randomized trial of ursodeoxycholic acid prophylaxis for hepatic veno-occlusive disease after stem cell transplantation. Am. J. Hematol. 2000, 64, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruutu, T.; Eriksson, B.; Remes, K.; Juvonen, E.; Volin, L.; Remberger, M.; Parkkali, T.; Hägglund, H.; Ringdén, O. Ursodeoxycholic acid for the prevention of hepatic complications in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2002, 100, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbacioglu, S.; Topaloglu, O.; Aggarwal, S. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies of Defibrotide Prophylaxis for Veno-Occlusive Disease/Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome. Clin. Drug Investig. 2022, 42, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H. Defibrotide for the prevention of hepatic veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A systematic review. Clin. Transplant. 2012, 26, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Griese, M.; Madtes, D.K.; Belperio, J.A.; Haddad, I.Y.; Folz, R.J.; Cooke, K.R. An Official American Thoracic Society Research Statement: Noninfectious Lung Injury after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Idiopathic Pneumonia Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afessa, B.; Peters, S.G. Noninfectious pneumonitis after blood and marrow transplant. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2008, 20, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, T.R.; Chien, J.W.; Crawford, S.W. Graft versus Host-Associated Pulmonary Disease and other Idiopathic Pulmonary Complications after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 26, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, G.; Cohen, D.A. Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after bone marrow transplantation: The role of pre-transplant radiation conditioning and local cytokine dysregulation in promoting lung inflammation and fibrosis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2001, 82, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, K.R.; Kobzik, L.; Martin, T.R.; Brewer, J.; Delmonte, J., Jr.; Crawford, J.M.; Ferrara, J.L. An experimental model of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after bone marrow transplantation: I. The roles of minor H antigens and endotoxin. Blood 1996, 88, 3230–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keates-Baleeiro, J.; Moore, P.; Koyama, T.; Manes, B.; Calder, C.; Frangoul, H. Incidence and outcome of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome in pediatric stem cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006, 38, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huisman, C.; van der Straaten, H.M.; Dijk, M.R.C.-V.; Fijnheer, R.; Verdonck, L.F. Pulmonary complications after T-cell-depleted allogeneic stem cell transplantation: Low incidence and strong association with acute graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006, 38, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Hackman, R.C.; Guthrie, K.A.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Boeckh, M.; Maris, M.B.; Maloney, D.G.; Deeg, H.J.; Martin, P.J.; Storb, R.F.; et al. Risks and outcomes of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after nonmyeloablative and conventional conditioning regimens for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2003, 102, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.G.; Hansen, J.A.; Hertz, M.I.; Parkman, R.; Jensen, L.; Peavy, H.H. Idiopathic Pneumonia Syndrome after Bone Marrow Transplantation. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, S.W.; Hackman, R.C. Clinical Course of Idiopathic Pneumonia after Bone Marrow Transplantation. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, R.S.; Bortin, M.M.; Gale, R.P.; Gluckman, E.; Kay, H.E.M.; Kolb, H.-J.; Hartz, A.J.; Rimm, A.A. Interstitial Pneumonitis after Bone Marrow Transplantation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1986, 104, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantrow, S.P.; Hackman, R.C.; Boeckh, M.; Myerson, D.; Crawford, S.W. Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome. Transplantation 1997, 63, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.A.; Hill, M.E.; Milan, S.; O’Brien, M.; Cunningham, D. Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after high-dose chemotherapy for relapsed Hodgkin’s disease. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, S.; Schultheiss, T.; Wong, J. Dose response and factors related to interstitial pneumonitis after bone marrow transplant. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2005, 63, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.G.; Madtes, D.K.; Martin, T.R.; Hackman, R.C.; Farrand, A.L.; Crawford, S.W. Idiopathic pneumonia after bone marrow transplantation: Cytokine activation and lipopolysaccharide amplification in the bronchoalveolar compartment. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 27, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Yin, Z.; D’Souza, A.; Fenske, T.; Hamadani, M.; Hari, P.; Rizzo, J.D.; Pasquini, M.; Saber, W.; Shah, N.; et al. Etanercept and Corticosteroid Therapy for the Treatment of Late-Onset Idiopathic Pneumonia Syndrome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 1955–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanik, G.A.; Ho, V.T.; Levine, J.E.; White, E.S.; Braun, T.; Antin, J.H.; Whitfield, J.; Custer, J.; Jones, D.; Ferrara, J.L.M.; et al. The impact of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor etanercept on the treatment of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2008, 112, 3073–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, T.S.; Johnstone, I.C.; Pearce, M.S.; Fulton, B.; Cant, A.J.; Gennery, A.R.; Slatter, M.A. Outcome of children requiring intensive care following haematopoietic SCT for primary immunodeficiency and other non-malignant disorders. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011, 47, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, C.; Ramirez, J.; Picado, C.; Xaubet, A.; Carreras, E.; Ballester, E.; Torres, A.; Battochia, C.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplantation: A Postmortem Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahya, V.N. Noninfectious Acute Lung Injury Syndromes Early after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Clin. Chest Med. 2017, 38, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keklik, F.; Alrawi, E.B.; Cao, Q.; Bejanyan, N.; Rashidi, A.; Lazaryan, A.; Arndt, P.; Dincer, E.H.; Bachanova, V.; Warlick, E.D.; et al. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage is most often fatal and is affected by graft source, conditioning regimen toxicity, and engraftment kinetics. Haematologica 2018, 103, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.K.; Hyland, R.H.; Hutcheon, M.A. Pulmonary Complications Following Bone Marrow Transplantation. Clin. Chest Med. 1990, 11, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, R.A.; Linder, J.; Stahl, M.G.; Thompson, A.B.; Haire, W.; Kessinger, A.; Armitage, J.O.; Arneson, M.; Woods, G.; Vaughan, W.P.; et al. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in autologous bone marrow transplant recipients. Am. J. Med. 1989, 87, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afessa, B.; Abdulai, R.M.; Kremers, W.K.; Hogan, W.J.; Litzow, M.R.; Peters, S.G. Risk Factors and Outcome of Pulmonary Complications after Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Chest 2012, 141, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolben, Y.; Darawshy, F.; Barhoum, B.; Abutbul, A.; Kuint, R. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage in a healthy stem cell donor following administration of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 108019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, K.R. Acute lung injury after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: From the clinic, to the bench and back again. Pediatr. Transplant. 2005, 9, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piguet, P.F.; Grau, G.E.; Collart, M.A.; Vassalli, P.; Kapanci, Y. Pneumopathies of the graft-versus-host reaction. Alveolitis associated with an increased level of tumor necrosis factor mRNA and chronic interstitial pneumonitis. Lab. Investig. 1989, 61, 37–45, PMID: 2747216. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf, J.P.; Rennard, S.I.; Reed, E.C.; Haire, W.D.; Sisson, J.H.; Walter, T.; Robbins, R.A. Corticosteroids as adjunctive therapy for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage associated with bone marrow transplantation. Am. J. Med. 1994, 96, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, N.K.; Tanner, A.R.; Dinh, A.; Dong, W.; Feng, L.; Ensor, J.; Wallace, S.K.; Haque, S.A.; Rondon, G.; Price, K.J.; et al. Low-, medium- and high-dose steroids with or without aminocaproic acid in adult hematopoietic SCT patients with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014, 50, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afessa, B.; Tefferi, A.; Litzow, M.R.; Peters, S.G. Outcome of Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojno, K.J.; Vogelsang, G.B.; Bescnorner, W.E.; Santos, G.W. Pulmonary hemorrhage as a cause of death in allogeneic bone marrow recipients with severe acute graft-versus-host disease. Transplantation 1994, 57, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselton, D.J.; Klekamp, J.G.; Christman, B.W.; Barr, F.E. Use of high-dose corticosteroids and high-frequency oscillatory ventilation for treatment of a child with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage after bone marrow transplantation: Case report and review of the literature. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, R.F.; Hari, P.; Drobyski, W.R. Engraftment Syndrome after Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation: An Update Unifying the Definition and Management Approach. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 2061–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spitzer, T.R. Engraftment syndrome: Double-edged sword of hematopoietic cell transplants. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015, 50, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiolino, A.; Biasoli, I.; Lima, J.; Portugal, A.C.; Pulcheri, W.; Nucci, M. Engraftment syndrome following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Definition of diagnostic criteria. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003, 31, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, I.; Stachel, D.; Pagel, P.; Albert, M.H. Incidence, Predisposing Factors, and Outcome of Engraftment Syndrome in Pediatric Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008, 14, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinezcibrian, N.; Magnano, L.; Gutiérrez-García, G.; Andrade, X.; Correa, J.G.; Suárez-Lledó, M.; Martinez, C.E.; Rovira, M.; Carreras, E.; Rosinol, L.; et al. At-home autologous stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma with and without G-CSF administration: A comparative study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015, 51, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasheh, M.; Eastwood, D.; Vesole, D.H. Engraftment syndrome after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant supported by granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) versus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003, 31, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-García, G.; Rovira, M.; Magnano, L.; Rosiñol, L.; Bataller, A.; Suárez-Lledó, M.; Cibeira, M.T.; de Larrea, C.F.; Garrote, M.; Jorge, S.; et al. Innovative strategies minimize engraftment syndrome in multiple myeloma patients with novel induction therapy following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018, 53, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, E.; Fernández-Avilés, F.; Silva, L.; Guerrero, M.; de Larrea, F.; Martínez, C.; Rosiñol, L.; Lozano, M. Engraftment syndrome after auto-SCT: Analysis of diagnostic criteria and risk factors in a large series from a single center. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010, 45, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capizzi, S.; Kumar, S.; Huneke, N.; Gertz, M.; Inwards, D.; Litzow, M.R.; Lacy, M.; Gastineau, D.; Prakash, U.; Tefferi, A. Peri-engraftment respiratory distress syndrome during autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001, 27, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nürnberger, W.; Willers, R.; Burdach, S.; Göbel, U. Risk factors for capillary leakage syndrome after bone marrow transplantation. Ann. Hematol. 1997, 74, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Frame, D.; Braun, T.; Gatza, E.; Hanauer, D.A.; Zhao, S.; Magenau, J.M.; Schultz, K.; Tokala, H.; Ferrara, J.L.; et al. Engraftment Syndrome after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Predicts Poor Outcomes. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, B.C. Vascular endothelium and graft-versus-host disease. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2008, 21, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichelli, A.; Gratwohl, A. Vascular endothelium as ‘novel’ target of graft-versus-host disease. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2008, 21, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, S.; Ishii, K.; Fujita, S.; Nakaya, A.; Satake, A.; Ito, T. Associations between acute GVHD-related biomarkers and endothelial cell activation after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl. Immunol. 2017, 43–44, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, B.C.; Sahner, S.; Gregor, M.; Tsakiris, D.A.; Jeanneret, C.; Pober, J.S.; Gratwohl, A. Endothelial injury mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and loss of microvessels in chronic graft versus host disease. Lancet 2002, 359, 2078–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagai, R.; Valujskikh, A.; Canaday, D.H.; Bailey, E.; Lalli, P.N.; Harding, C.V.; Heeger, P.S. Mouse Endothelial Cells Cross-Present Lymphocyte-Derived Antigen on Class I MHC via a TAP1- and Proteasome-Dependent Pathway. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 7711–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.S.; Ness, K.K.; Steinberger, J.; Carter, A.; Francisco, L.; Burns, L.J.; Sklar, C.; Forman, S.; Weisdorf, D.; Gurney, J.G.; et al. Diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular events in survivors of hematopoietic cell transplantation: A report from the bone marrow transplantation survivor study. Blood 2006, 109, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couriel, D.R.; Saliba, R.; Escalon, M.P.; Hsu, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Ippoliti, C.; Hicks, K.; Donato, M.; Giralt, S.; Khouri, I.F.; et al. Sirolimus in combination with tacrolimus and corticosteroids for the treatment of resistant chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2005, 130, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichelli, A.; Bucher, C.; Rovó, A.; Stussi, G.; Stern, M.; Paulussen, M.; Halter, J.; Meyer-Monard, S.; Heim, D.; Tsakiris, D.A.; et al. Premature cardiovascular disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Blood 2007, 110, 3463–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, S.R. Intravascular ultrasound imaging after cardiac transplantation: Advantage of multi-vessel imaging. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2000, 19, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, M.; Cruz, R.P.; Granville, D.J.; McManus, B.M. Allograft Vasculopathy Versus Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailhier, J.-F.; Laplante, P.; Hébert, M.-J. Endothelial Apoptosis and Chronic Transplant Vasculopathy: Recent Results, Novel Mechanisms. Am. J. Transplant. 2006, 6, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chung, D.W. Inflammation, von Willebrand factor, and ADAMTS13. Blood 2018, 132, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, T.; Gliddon, A.; Doré, C.J.; Maddison, P.; Moots, R.J. Baseline vWF factor predicts the development of elevated pulmonary artery pressure in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1606–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürol, G.; Ciftci, I.H.; Harman, H.; Karakece, E.; Kamanl, A.; Tekeoglu, I. Roles of Claudin-5 and Von Willebrand Factor in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 1979–1984. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, P.; Kavi, J.; Chant, I.; Taylor, C.; Struthers, G.; Robertson, M. Factor VIII von Willebrand protein in haemolytic uraemic syndrome and systemic vasculitides. Lancet 1990, 335, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, E.; Palomo, M.; Rovira, M.; Pereira, A.; Escolar, G.; Penack, O.; Holler, E.; Carreras, E.; Diaz-Ricart, M. Endothelial damage is aggravated in acute GvHD and could predict its development. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedermann, B.C.; Tsakiris, D.A.; Gregor, M.; Pober, J.S.; Gratwohl, A. Combining altered levels of effector transcripts in circulating T cells with a marker of endothelial injury is specific for active graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003, 32, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulanic, D.; Samardzic, A.; Desnica, L.; Zadro, R.; Milosevic, M.; Serventi Seiwerth, R.; Durakovic, N.; Peric, Z.; Coen Herak, D.; Milos, M.; et al. High Levels of FVIII and Von Willebrand Factor in Chronic Graft versus- Host Disease. The 45th Annual Meeting of the European Society for Blood and Marrow transplantation: Physicians–Poster Session. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019, 54, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito-Habe, N.; Wada, H.; Matsumoto, T.; Ohishi, K.; Toyoda, H.; Ishikawa, E.; Nomura, S.; Komada, Y.; Ito, M.; Nobori, T.; et al. Elevated Von Willebrand factor propeptide for the diagnosis of thrombotic microangiopathy and for predicting a poor outcome. Int. J. Hematol. 2010, 93, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Luo, C.; Lai, P.; Ling, W.; Wu, S.; Huang, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G.; Du, X.; Weng, J. von Willebrand Factor as a Predictor for Transplant-Associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2020, 26, 1076029619892684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonneveld, R.; Martinelli, R.; Shapiro, N.I.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Plötz, F.B.; Carman, C.V. Soluble adhesion molecules as markers for sepsis and the potential pathophysiological discrepancy in neonates, children and adults. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, Y.; Hara, J.; Osugi, Y.; Tokimasa, S.; Fujisaki, H.; Takai, K.; Ohta, H.; Kawa-Ha, K.; Okada, S. Serum levels of soluble adhesion molecules in stem cell transplantation-related complications. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2001, 27, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, C.; Kim, H.T.; Ayanian, S.; Bradwin, G.; Revta, C.; Aldridge, J.; Ho, V.; Alyea, E.; Koreth, J.; Armand, P.; et al. Prediction of Veno-Occlusive Disease using Biomarkers of Endothelial Injury. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Hatano, E.; Miyagawa-Hayashino, A.; Okuno, M.; Koyama, Y.; Narita, M.; Seo, S.; Taura, K.; Uemoto, S. Soluble thrombomodulin attenuates sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in rat through suppression of high mobility group box 1. Liver Int. 2013, 34, 1473–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, Z.R.; Rosenfeld, C.S.; Andrews, D.F.; Nemunaitis, J.; Raymond, J.M.; Shadduck, R.K.; Kramer, R.E.; Gryn, J.F.; Rintels, P.B.; Besa, E.C.; et al. Plasma von Willebrand factor antigen (vWF:AG) and thrombomodulin (TM) levels in adult thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndromes (TTP/HUS) and bone marrow transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (BMT-TM). Am. J. Hematol. 1996, 53, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, M.; Diaz-Ricart, M.; Carbo, C.; Rovira, M.; Fernandez-Aviles, F.; Martine, C.; Ghita, G.; Escolar, G.; Carreras, E. Endothelial Dysfunction after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Role of the Conditioning Regimen and the Type of Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.G.; Soiffer, R.J.; Antin, J.H.; Uno, H.; Jin, Z.; Kurtzberg, J.; Martin, P.L.; Steinbach, G.; Murray, K.F.; Vogelsang, G.B.; et al. Defibrotide for the Treatment of Severe Hepatic Veno-Occlusive Disease and Multiorgan Failure after Stem Cell Transplantation: A Multicenter, Randomized, Dose-Finding Trial. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010, 16, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatekawa, S.; Kohno, A.; Ozeki, K.; Watamoto, K.; Ueda, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Yokota, I.; Teramukai, S.; Taniwaki, M.; et al. A Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker Panel for Endothelial Cell Damage–Related Complications in Allogeneic Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Chihara, D.; Kohno, A.; Tatekawa, S.; Ozeki, K.; Watamoto, K.; Morishita, Y. Predictive Value of Circulating Angiopoietin-2 for Endothelial Damage–Related Complications in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, S.; Falk, C.S.; Benner, A.; Karamustafa, S.; Hahn, E.; Andrulis, M.; Hegenbart, U.; Ho, A.D.; Dreger, P.; Luft, T. Endothelial Vulnerability and Endothelial Damage Are Associated with Risk of Graft-versus-Host Disease and Response to Steroid Treatment. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012, 19, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseev, I.S.; Lapin, S.V.; Surkova, E.A.; Lerner, M.Y.; Vavilov, V.N.; Afanasyev, B.V. Level of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Predicts Both Relapse and Nonrelapse Mortality after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 19, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, R.A.; Sumar, N.; Bansal, A.S.; Treleaven, J. Cytokine profiles in stem cell transplantation: Possible use as a predictor of graft-versus-host disease. Hematology 2005, 10, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiser, R.; Blazar, B.R. Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease—Biologic Process, Prevention, and Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2167–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; DiPersio, J.F.; Schroeder, M.A. The Role of Biomarkers in the Diagnosis and Risk Stratification of Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease: A Systematic Review. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 1552–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-B.; Cutler, C.S. Biomarkers for acute GVHD: Can we predict the unpredictable. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012, 48, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Kitko, C.L.; Braun, T.; Paczesny, S.; Yanik, G.; Mineishi, S.; Krijanovski, O.; Jones, D.; Whitfield, J.; Cooke, K.; et al. Change in plasma tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 levels in the first week after myeloablative allogeneic transplantation correlates with severity and incidence of GVHD and survival. Blood 2008, 112, 1539–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Sugiyama, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Tokunaga, Y.; Yujiri, T.; Tanizawa, Y. Soluble interleukin-2 receptor index predicts the development of acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 103, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, R.; Couban, S.; Walker, I.; Greene, K.; Chen, C.; Messner, H.; Gauldie, J. Monitoring soluble interleukin-2 receptor levels in related and unrelated donor allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1998, 21, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenauer, B.; Paczesny, S. The ST2/IL-33 Axis in Immune Cells during Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinagesh, H.K.; Özbek, U.; Kapoor, U.; Ayuk, F.; Aziz, M.; Ben-David, K.; Choe, H.K.; DeFilipp, Z.; Etra, A.; Grupp, S.A.; et al. The MAGIC algorithm probability is a validated response biomarker of treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 4034–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebghati, Z.J.; Abbasi, S.; Abhyankar, S.; Ganguly, S.; Shune, L.; McGuirk, J.P.; Singh, A.K. Endothelial Activation and Stress Index (EASIX) Score at 100 Days Post-allo HCT in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Predicts Overall Survival. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilaki, E.; Sakellari, I.; Chatziconstantinou, T.; Mallouri, D.; Batsis, I.; Vardi, A.; Bousiou, Z.; Koravou, E.; Masmanidou, M.; Touloumenidou, T.; et al. Easix Is Strongly Associated with Complement Activation and Overall Survival in Adult Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Recipients. Blood 2019, 134, 4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, T.; Benner, A.; Jodele, S.; Dandoy, C.E.; Storb, R.; Gooley, T.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Becker, N.; Radujkovic, A.; Dreger, P.; et al. EASIX in patients with acute graft-versus-host disease: A retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e414–e423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Penack, O.; Terzer, T.; Schult, D.; Majer-Lauterbach, J.; Radujkovic, A.; Blau, I.W.; Bullinger, L.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Dreger, P.; et al. Predicting sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after allogeneic stem cell transplantation with the EASIX biomarker panel. Haematologica 2020, 106, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubitz, M.; Woywodt, A. Circulating Endothelial Cells and Vasculitis. Intern. Med. 2004, 43, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdbruegger, U.; Haubitz, M.; Woywodt, A. Circulating endothelial cells: A novel marker of endothelial damage. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 373, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Nascimento, M.C.; Alessio, A.M.; Orsi, F.L.D.A.; Annichino-Bizzacchi, J.M. CD144, CD146 and VEGFR-2 properly identify circulating endothelial cell. Rev. Bras. Hematol. Hemoter. 2015, 37, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignat-George, F.; Sampol, J. Circulating endothelial cells in vascular disorders: New insights into an old concept. Eur. J. Haematol. 2000, 65, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Barros, M.; Paris, F.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Lyden, D.; Rafii, S.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Fuks, Z.; Kolesnick, R. Tumor Response to Radiotherapy Regulated by Endothelial Cell Apoptosis. Science 2003, 300, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touzot, F.; Moshous, D.; Cros, G.; Frange, P.; Chomton, M.; Frémond, M.-L.; Neven, B.; Cavazzana, M.; Fischer, A.; Blanche, S.; et al. Circulating endothelial cells as markers of endothelial dysfunction during hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for pediatric primary immunodeficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almici, C.; Skert, C.; Bruno, B.; Bianchetti, A.; Verardi, R.; Di Palma, A.; Neva, A.; Braga, S.; Piccinelli, G.; Piovani, G.; et al. Circulating endothelial cell count: A reliable marker of endothelial damage in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 52, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Malik, A.B.; Rehman, J. Reprogramming Fibroblasts to Endothelial Cells. Circulation 2014, 130, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, D.; Touyz, R.M. Cellular biomarkers of endothelial health: Microparticles, endothelial progenitor cells, and circulating endothelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2012, 6, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, N.; Nickenig, G. Endothelial progenitor cells in health and atherosclerotic disease. Ann. Med. 2007, 39, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pytlík, R.; Kideryová, L.; Benesová, K.; Cechová, H.; Veselá, R.; Rychtrmocová, H.; Trnený, M. Circulating endothelial pre-cursor cells (EPC) in patients undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation. Folia Biol. 2010, 56, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Lazana, I.; Vassilopoulos, G. A ‘waste product’ to save the day in the field of transplantation: The evolving potential of extracellular vesicles. Immunology 2022, 167, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazana, I. Extracellular Vesicles in Haematological Disorders: A Friend or a Foe. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccin, A.; Sartori, M.T.; Bisogno, G.; van Schilfgaarde, M.; Saggiorato, G.; Pierro, A.M.D.; Corvetta, D.; Marcheselli, L.; Mega, A.; Gastl, G.; et al. New insights into sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Criteria | BMT-CTN, 2005 | IWG, 2007 | Jodele, 2014 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | All Criteria Present | All Criteria Present | ≥4 of 7 Criteria Present in ≥2 Occasions in 14 Days |
| Anemia or increasing RBC transfusion requirements | YES | YES | YES |
| New-onset thrombocytopenia, >50% decrease in PLT count, increase in PLT transfusion requirements | YES | YES | YES |
| Presence of schistocytes | YES (≥2 per HPF) | YES (>4%) | YES |
| Elevated LDH | YES | YES | YES |
| Decreased haptoglobin | ----- | YES | ----- |
| Hypertension | ----- | ----- | YES |
| Proteinuria | ----- | ----- | YES |
| Elevated sC5b-9 | ----- | ----- | YES |
| Renal dysfunction | YES | ----- | ----- |
| Characteristic | Idiopathic Pneumonia Syndrome | Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage | Peri-Engraftment Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epidemiology | More common after allo-SCT | Equal incidence after Auto and allo-SCT | More common after auto-SCT |
| Median time of onset | 30–40 days after allo-SCT | 20–25 days after SCT | From 3 days before to 7 days after engraftment |
| Relation to engraftment | No relation | No relation | Occurs during the peri-engraftment phase |
| Clinical features | Rapid progression to respiratory failure | Progressively bloodier aliquots of bronchoalveolar lavage | Systemic manifestations such as fever, rash |
| Pathology | Diffuse alveolar damage | Diffuse alveolar damage | Diffuse alveolar damage |
| Pathogenetic drivers * | TNFα | Various cytokines | GM-CSF, G-CSF |
| Response to corticosteroids | Poor, some response after anti-TNF agents | Moderate response to high dose steroids | Excellent response |
| Prognosis | Very poor | Moderate to Poor | Favorable |
| Marker | VOD/SOS | TAM | IPS/DAH | GVHD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coagulation factors | ||||
| VWF | ↑ | ↑ | ----- | ↑ |
| TM | ↑ | ↑ | ----- | ↑ |
| PAI1 | ↑ | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| Cell adhesion molecules | ||||
| ICAM | ↑ | ----- | ↑ | ↑ |
| VCAM | ----- | ↑ | ↑ | ----- |
| E-selectin | ↑ | ↑ | ----- | ↑ |
| P-selectin | ↑ | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| Proinflammatory cytokines | ||||
| TNFa | ↑ | ----- | ↑ | ↑ |
| IL6 | ----- | ----- | ----- | ↑ |
| sIL2R | ↑ | ----- | ----- | ↑ |
| Angiogenetic factors | ||||
| CEC | ----- | ----- | ----- | ↑ |
| VEGF | ↑ | ----- | ----- | ----- |
| Ang2 | ----- | ----- | ↑ | ↑ |
| Panels | ||||
| EASIX | ↑ | ↑ | ----- | ↑ |
| MAGIC (ST2, REG3a) | ----- | ----- | ----- | ↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vythoulkas, D.; Tsirigotis, P.; Griniezaki, M.; Konstantellos, I.; Lazana, I. Endothelial Dysfunction Syndromes after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Cancers 2023, 15, 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030680
Vythoulkas D, Tsirigotis P, Griniezaki M, Konstantellos I, Lazana I. Endothelial Dysfunction Syndromes after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):680. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030680
Chicago/Turabian StyleVythoulkas, Dionysios, Panagiotis Tsirigotis, Marianna Griniezaki, Ioannis Konstantellos, and Ioanna Lazana. 2023. "Endothelial Dysfunction Syndromes after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation" Cancers 15, no. 3: 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030680
APA StyleVythoulkas, D., Tsirigotis, P., Griniezaki, M., Konstantellos, I., & Lazana, I. (2023). Endothelial Dysfunction Syndromes after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Cancers, 15(3), 680. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030680






