CDK4/6 Inhibitors Overcome Endocrine ESR1 Mutation-Related Resistance in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Data Collection
2.2. Circulating Free DNA Extraction and ESR1 Mutational Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. ESR1 Mutation Is an Independent Predictive Biomarker of Clinical Recurrence after Adjuvant Therapy
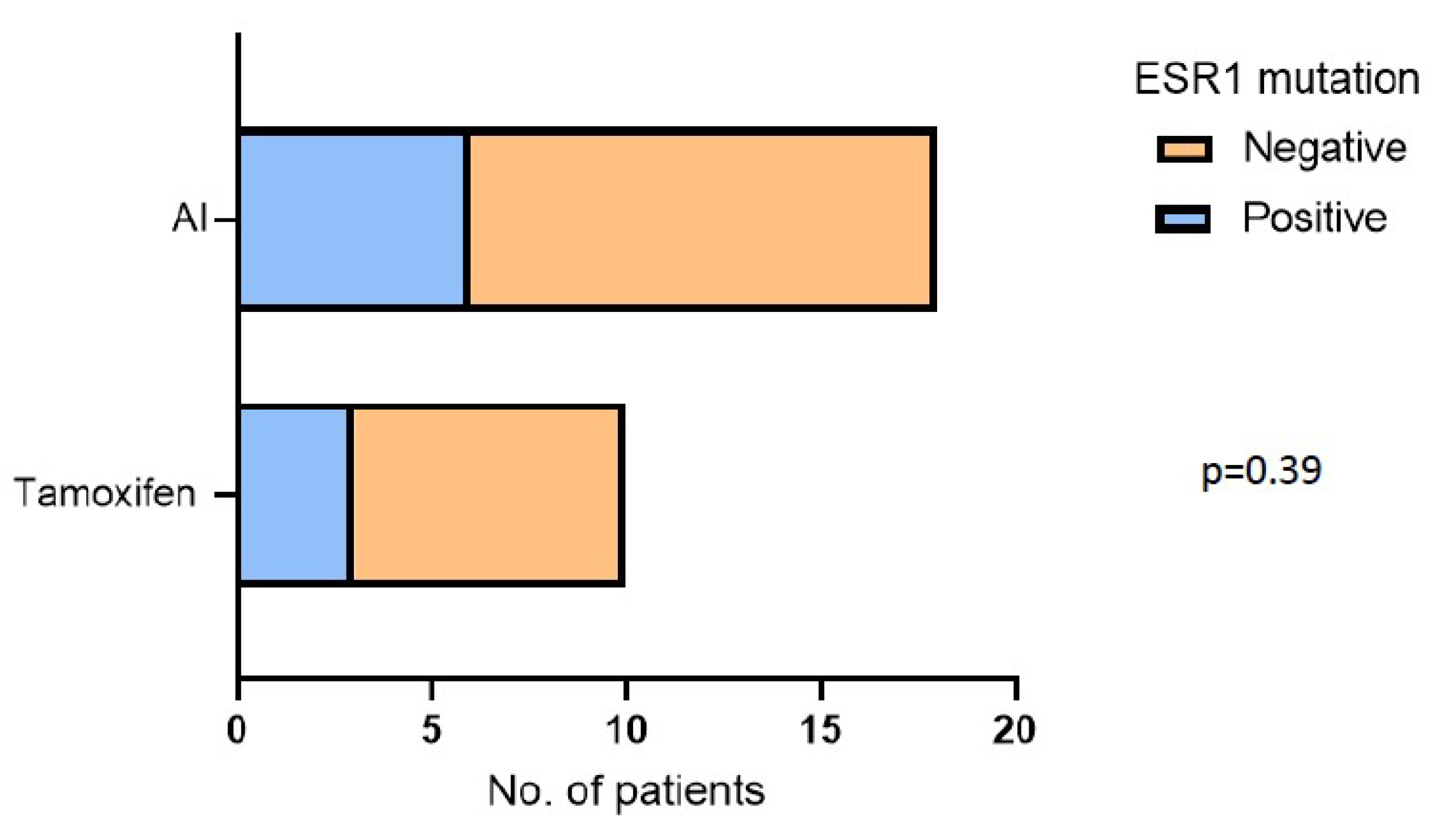
3.3. CDK4/6i Overcomes Hormone Therapy Resistance in ESR1 Mutant Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Breast Cancer: A Molecularly Heterogenous Disease Needing Subtype-Specific Treatments. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozeboom, B.; Dey, N.; De, P. ER+ metastatic breast cancer: Past, present, and a prescription for an apoptosis-targeted future. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2821–2831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeselsohn, R.; Buchwalter, G.; De Angelis, C.; Brown, M.; Schiff, R. ESR1 mutations-a mechanism for acquired endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dustin, D.; Gu, G.; Fuqua, S.A.W. ESR1 mutations in breast cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 3714–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toy, W.; Shen, Y.; Won, H.; Green, B.; Sakr, R.A.; Will, M.; Li, Z.; Gala, K.; Fanning, S.; King, T.A.; et al. ESR1 ligand-binding domain mutations in hormone-resistant breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanning, S.W.; Mayne, C.G.; Dharmarajan, V.; Carlson, K.E.; Martin, T.A.; Novick, S.J.; Toy, W.; Green, B.; Panchamukhi, S.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; et al. Estrogen receptor alpha somatic mutations Y537S and D538G confer breast cancer endocrine resistance by stabilizing the activating function-2 binding conformation. Elife 2016, 5, e12792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, J.O.; Spring, L.M.; Bardia, A.; Wander, S.A. ESR1 mutation as an emerging clinical biomarker in metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolillo, C.; Mu, Z.; Rossi, G.; Schiewer, M.J.; Nguyen, T.; Austin, L.; Capoluongo, E.; Knudsen, K.; Cristofanilli, M.; Fortina, P. Detection of Activating Estrogen Receptor Gene (ESR1) Mutations in Single Circulating Tumor Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6086–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segal, C.V.; Dowsett, M. Estrogen receptor mutations in breast cancer--new focus on an old target. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1724–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carausu, M.; Bidard, F.C.; Callens, C.; Melaabi, S.; Jeannot, E.; Pierga, J.Y.; Cabel, L. ESR1 mutations: A new biomarker in breast cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2019, 19, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Tomiguchi, M.; Sueta, A.; Murakami, K.; Omoto, Y.; Iwase, H. Comparison of ESR1 Mutations in Tumor Tissue and Matched Plasma Samples from Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandarlapaty, S.; Chen, D.; He, W.; Sung, P.; Samoila, A.; You, D.; Bhatt, T.; Patel, P.; Voi, M.; Gnant, M.; et al. Prevalence of ESR1 Mutations in Cell-Free DNA and Outcomes in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Secondary Analysis of the BOLERO-2 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bidard, F.C.; Callens, C.; Dalenc, F.; Pistilli, B.; Rouge, T.D.L.M.; Clatot, F.; D’hondt, V.; Teixeira, L.; Vegas, H.; Everhard, S.; et al. Prognostic impact of ESR1 mutations in ER+ HER2- MBC patients prior treated with first line AI and palbociclib: An exploratory analysis of the PADA-1 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, F.; Marce, M.; Delaloge, S.; Hardy-Bessard, A.C.; Bachelot, T.; Bieche, I.; Pradines, A.; De La Motte Rouge, T.; Canon, J.L.; Andre, F.; et al. Randomised, open-label, multicentric phase III trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of palbociclib in combination with endocrine therapy, guided by ESR1 mutation monitoring in oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients: Study design of PADA-1. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e055821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, M.; Bernat-Peguera, A.; Felip, E.; Margeli, M. Role of ctDNA in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Huang, W.; Pei, W.; Li, H. Detection of ESR1 Mutations Based on Liquid Biopsy in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: Clinical Impacts and Prospects. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 587671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Senkus, E.; Costa, A.; Papadopoulos, E.; Aapro, M.; André, F.; Harbeck, N.; Aguilar Lopez, B.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; et al. 4th ESO–ESMO International Consensus Guidelines for Advanced Breast Cancer (ABC 4). Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1634–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thurlimann, B.; Senn, H.J.; Panel, m. Strategies for subtypes--dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untch, M.; Gerber, B.; Harbeck, N.; Jackisch, C.; Marschner, N.; Mobus, V.; von Minckwitz, G.; Loibl, S.; Beckmann, M.W.; Blohmer, J.U.; et al. 13th st. Gallen international breast cancer conference 2013: Primary therapy of early breast cancer evidence, controversies, consensus—Opinion of a german team of experts (zurich 2013). Breast Care 2013, 8, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fribbens, C.; O’Leary, B.; Kilburn, L.; Hrebien, S.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Beaney, M.; Cristofanilli, M.; Andre, F.; Loi, S.; Loibl, S.; et al. Plasma ESR1 Mutations and the Treatment of Estrogen Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, B.; Cutts, R.J.; Liu, Y.; Hrebien, S.; Huang, X.; Fenwick, K.; Andre, F.; Loibl, S.; Loi, S.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; et al. The Genetic Landscape and Clonal Evolution of Breast Cancer Resistance to Palbociclib plus Fulvestrant in the PALOMA-3 Trial. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuang, Y.; Siddiqui, B.; Hu, J.; Pun, M.; Cornwell, M.; Buchwalter, G.; Hughes, M.E.; Wagle, N.; Kirschmeier, P.; Janne, P.A.; et al. Unraveling the clinicopathological features driving the emergence of ESR1 mutations in metastatic breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2018, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toy, W.; Weir, H.; Razavi, P.; Lawson, M.; Goeppert, A.U.; Mazzola, A.M.; Smith, A.; Wilson, J.; Morrow, C.; Wong, W.L.; et al. Activating ESR1 Mutations Differentially Affect the Efficacy of ER Antagonists. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gelsomino, L.; Gu, G.; Rechoum, Y.; Beyer, A.R.; Pejerrey, S.M.; Tsimelzon, A.; Wang, T.; Huffman, K.; Ludlow, A.; Ando, S.; et al. ESR1 mutations affect anti-proliferative responses to tamoxifen through enhanced cross-talk with IGF signaling. Breast Cancer Res. Treat 2016, 157, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Najim, O.; Huizing, M.; Papadimitriou, K.; Trinh, X.B.; Pauwels, P.; Goethals, S.; Zwaenepoel, K.; Peterson, K.; Weyler, J.; Altintas, S.; et al. The prevalence of estrogen receptor-1 mutation in advanced breast cancer: The estrogen receptor one study (EROS1). Cancer Treat Res. Commun. 2019, 19, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Knowles, E.; Pearson, A.; Schuster, G.; Gellert, P.; Ribas, R.; Yeo, B.; Cutts, R.; Buus, R.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Haynes, B.; et al. Molecular characterisation of aromatase inhibitor-resistant advanced breast cancer: The phenotypic effect of ESR1 mutations. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.V.; Ejlertsen, B.; Müller, S.; Møller, S.; Rasmussen, B.B.; Balslev, E.; Lænkholm, A.-V.; Christiansen, P.; Mouridsen, H.T. Amplification of ESR1 may predict resistance to adjuvant tamoxifen in postmenopausal patients with hormone receptor positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 127, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allouchery, V.; Beaussire, L.; Perdrix, A.; Sefrioui, D.; Augusto, L.; Guillemet, C.; Sarafan-Vasseur, N.; Di Fiore, F.; Clatot, F. Circulating ESR1 mutations at the end of aromatase inhibitor adjuvant treatment and after relapse in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muendlein, A.; Geiger, K.; Gaenger, S.; Dechow, T.; Nonnenbroich, C.; Leiherer, A.; Drexel, H.; Gaumann, A.; Jagla, W.; Winder, T.; et al. Significant impact of circulating tumour DNA mutations on survival in metastatic breast cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto-Ibusuki, M.; Tomiguchi, M.; Sueta, A.; Murakami, K.; Iwase, H. Clinical significance of plasma cell-free DNA mutations in PIK3CA, AKT1, and ESR1 gene according to treatment lines in ER-positive breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zundelevich, A.; Dadiani, M.; Kahana-Edwin, S.; Itay, A.; Sella, T.; Gadot, M.; Cesarkas, K.; Farage-Barhom, S.; Saar, E.G.; Eyal, E.; et al. ESR1 mutations are frequent in newly diagnosed metastatic and loco-regional recurrence of endocrine-treated breast cancer and carry worse prognosis. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caciolla, J.; Bisi, A.; Belluti, F.; Rampa, A.; Gobbi, S. Reconsidering Aromatase for Breast Cancer Treatment: New Roles for an Old Target. Molecules 2020, 25, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeselsohn, R.; Yelensky, R.; Buchwalter, G.; Frampton, G.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Ferrer-Lozano, J.; Perez-Fidalgo, J.A.; Cristofanilli, M.; Gomez, H.; et al. Emergence of constitutively active estrogen receptor-alpha mutations in pretreated advanced estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razavi, P.; Chang, M.T.; Xu, G.; Bandlamudi, C.; Ross, D.S.; Vasan, N.; Cai, Y.; Bielski, C.M.; Donoghue, M.T.A.; Jonsson, P.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Endocrine-Resistant Advanced Breast Cancers. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kingston, B.; Cutts, R.J.; Bye, H.; Beaney, M.; Walsh-Crestani, G.; Hrebien, S.; Swift, C.; Kilburn, L.S.; Kernaghan, S.; Moretti, L.; et al. Genomic profile of advanced breast cancer in circulating tumour DNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, S.; Jin, D.X.; Tukachinsky, H.; Murugesan, K.; McGregor, K.; Danziger, N.; Pavlick, D.; Gjoerup, O.; Ross, J.S.; Harmon, R.; et al. Tissue and liquid biopsy profiling reveal convergent tumor evolution and therapy evasion in breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, R.; Jeselsohn, R. Is ctDNA the Road Map to the Landscape of the Clonal Mutational Evolution in Drug Resistance? Lessons from the PALOMA-3 Study and Implications for Precision Medicine. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1352–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Im, S.A.; Slamon, D.J.; Harbeck, N.; Bondarenko, I.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Palbociclib and Fulvestrant in Women with HR+/HER2- ABC: Updated Exploratory Analyses of PALOMA-3, a Double-blind, Phase III Randomized Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3433–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, B.; Hrebien, S.; Morden, J.P.; Beaney, M.; Fribbens, C.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Bartlett, C.H.; Koehler, M.; Cristofanilli, M.; et al. Early circulating tumor DNA dynamics and clonal selection with palbociclib and fulvestrant for breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rani, A.; Stebbing, J.; Giamas, G.; Murphy, J. Endocrine Resistance in Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer-From Mechanism to Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osborne, C.K.; Schiff, R. Mechanisms of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2011, 62, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klinge, C.M. Estrogen receptor interaction with estrogen response elements. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2001, 29, 2905–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberto, M.; Astone, A.; Botticelli, A.; Carbognin, L.; Cassano, A.; D’Auria, G.; Fabbri, A.; Fabi, A.; Gamucci, T.; Krasniqi, E.; et al. CDK4/6 Inhibitor Treatments in Patients with Hormone Receptor Positive, Her2 Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: Potential Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Implications and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2021, 13, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, M.; Fanning, S.W.; Chang, Y.F.; Green, B.; Greene, M.E.; Komm, B.; Kurleto, J.D.; Phung, L.; Greene, G.L. Lasofoxifene as a potential treatment for therapy-resistant ER-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S.; Plourde, P.V.; Moore, H.C.F.; Anderson, I.C.; Portman, D.J. Open-label, phase 2, multicenter study of lasofoxifene (LAS) combined with abemaciclib (Abema) for treating pre- and postmenopausal women with locally advanced or metastatic ER+/HER2− breast cancer and an ESR1 mutation after progression on prior therapies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Neven, P.; Streich, G.; Montero, A.J.; Forget, F.; Mouret-Reynier, M.-A.; Sohn, J.H.; Vuylsteke, P.; Harnden, K.K.; Khong, H.; et al. Abstract GS2-02: Elacestrant, an oral selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), vs investigator’s choice of endocrine monotherapy for ER+/HER2- advanced/metastatic breast cancer (mBC) following progression on prior endocrine and CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy: Results of EMERALD phase 3 trial. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, GS2-02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.C.; Kaklamani, V.G.; Neven, P.; Streich, G.; Montero, A.J.; Forget, F.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Sohn, J.H.; Taylor, D.; Harnden, K.K.; et al. Elacestrant (oral selective estrogen receptor degrader) Versus Standard Endocrine Therapy for Estrogen Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: Results From the Randomized Phase III EMERALD Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3246–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, K.G.; Nangia, J.R.; Schiff, R.; Rimawi, M.F. Elacestrant and the Promise of Oral SERDs. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3227–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanning, S.W.; Jeselsohn, R.; Dharmarajan, V.; Mayne, C.G.; Karimi, M.; Buchwalter, G.; Houtman, R.; Toy, W.; Fowler, C.E.; Han, R.; et al. The SERM/SERD bazedoxifene disrupts ESR1 helix 12 to overcome acquired hormone resistance in breast cancer cells. Elife 2018, 7, e37161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardell, S.E.; Ellis, M.J.; Alley, H.M.; Eisele, K.; VanArsdale, T.; Dann, S.G.; Arndt, K.T.; Primeau, T.; Griffin, E.; Shao, J.; et al. Efficacy of SERD/SERM Hybrid-CDK4/6 Inhibitor Combinations in Models of Endocrine Therapy-Resistant Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5121–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bardia, A.; Cortes, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Delaloge, S.; Iwata, H.; Shao, Z.M.; Kanagavel, D.; Cohen, P.; Liu, Q.; Cartot-Cotton, S.; et al. AMEERA-5: A randomized, double-blind phase 3 study of amcenestrant plus palbociclib versus letrozole plus palbociclib for previously untreated ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2022, 14, 17588359221083956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.-A.; Hamilton, E.P.; Cussac, A.L.; Baird, R.D.; Ettl, J.; Goetz, M.P.; Iwata, H.; Joy, A.A.; Neven, P.; Haddad, V.; et al. SERENA-4: A phase 3 comparison of AZD9833 (camizestrant) plus palbociclib, versus anastrozole plus palbociclib, for patients with ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer who have not previously received systemic treatment for advanced disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, TPS1101-TPS1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Patients (n = 42) |
|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, median (range) | 55.1 ± 11.3 |
|
Stage at diagnosis, n (%) I II III IV (i.e., de novo M1) | 14 (33.3%) 11 (26.2%) 6 (14.3%) 11 (26.2%) |
|
ECOG PS, n (%) 0 1 | 38 (90.5%) 4 (9.5%) |
|
Pre/Post-menopause, n (%) Pre-menopause Post-menopause | 6 (14.3%) 36 (85.7%) |
|
HR receptor status in primitive lesions, n (%) ER+/PR+ ER+/PR− | 37 (88.1%) 5 (11.9%) |
|
Ki67 % in primitive lesions, n (%) <14%, n (%) 14–20%, n (%) >20%, n (%) | 17 (40.5%) 8 (19%) 17 (40.5%) |
|
Previous CT in neoadjuvant setting, n (%) No Yes | 36 (85.7%) 6 (14.3%) |
|
Previous CT in adjuvant setting, n (%) No Yes | 24 (57.1%) 18 (42.9%) |
|
Previous HT in adjuvant setting, n (%) No Yes | 14 (33.3%) 28 (66.7%) |
|
Previous RT in adjuvant setting, n (%) No Yes | 20 (47.6%) 22 (52.4%) |
|
Number of metastatic sites, n (%) ≤2 >2 | 28 (66.7%) 14 (33.3%) |
|
Disease site, n (%) Visceral Bone-only Nodes | 22 (52.4%) 6 (14.3%) 14 (33.3%) |
|
Endocrine-sensitive or resistant disease, n (%) Sensitive Resistant | 29 (69%) 13 (31%) |
|
CDK4/6i therapy, n (%) Palbociclib Ribociclib Abemaciclib | 15 (35.7%) 20 (47.6%) 7 (16.7%) |
|
CDK4/6i line of therapy, n (%) 1 2 | 35 (83.3%) 7 (16.7%) |
|
Type of HT associated to CDK4/6i, n (%) Letrozole Fulvestrant | 25 (59.5%) 17 (40.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crucitta, S.; Ruglioni, M.; Lorenzini, G.; Bargagna, I.; Luculli, G.I.; Albanese, I.; Bilancio, D.; Patanè, F.; Fontana, A.; Danesi, R.; et al. CDK4/6 Inhibitors Overcome Endocrine ESR1 Mutation-Related Resistance in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041306
Crucitta S, Ruglioni M, Lorenzini G, Bargagna I, Luculli GI, Albanese I, Bilancio D, Patanè F, Fontana A, Danesi R, et al. CDK4/6 Inhibitors Overcome Endocrine ESR1 Mutation-Related Resistance in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041306
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrucitta, Stefania, Martina Ruglioni, Giulia Lorenzini, Irene Bargagna, Giovanna Irene Luculli, Irene Albanese, Diana Bilancio, Francesca Patanè, Andrea Fontana, Romano Danesi, and et al. 2023. "CDK4/6 Inhibitors Overcome Endocrine ESR1 Mutation-Related Resistance in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041306
APA StyleCrucitta, S., Ruglioni, M., Lorenzini, G., Bargagna, I., Luculli, G. I., Albanese, I., Bilancio, D., Patanè, F., Fontana, A., Danesi, R., & Del Re, M. (2023). CDK4/6 Inhibitors Overcome Endocrine ESR1 Mutation-Related Resistance in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers, 15(4), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041306








