Prostate Cancer Morphologies: Cribriform Pattern and Intraductal Carcinoma Relations to Adverse Pathological and Clinical Outcomes—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pathological Definition
2.2. Evidence Acquisition
2.3. Literature Search
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Assessment of Study Quality
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Evidence Synthesis
Characteristics of Included Studies
4. Results
4.1. Correlation between EPE and CP/IDC
4.2. Correlation between SVI and CP/IDC
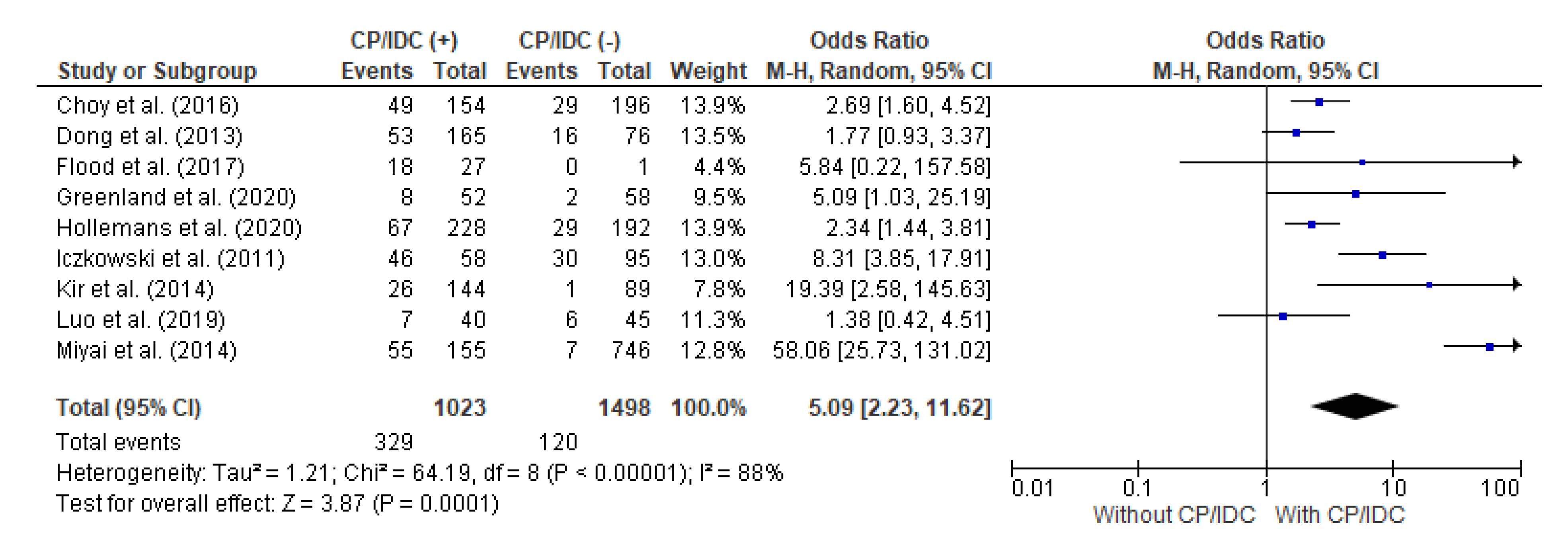
4.3. Correlation between LNs met and CP/IDC
4.4. Correlation between BCR and CP/IDC
4.5. Correlation between MET/DSD and CP/IDC
4.6. Publication Bias
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EAU Guidelines. In Proceedings of the EAU Annual Congress Amsterdam, Washington, DC, USA, 15–18 May 2022; ISBN 978-94-92671-16-5.
- Epstein, J.I.; Amin, M.; Boccon-Gibod, L.; Egevad, L.; Humphrey, P.A.; Mikuz, G.; Newling, D.; Nilsson, S.; Sakr, W.; Srigley, J.R.; et al. Prognostic factors and reporting of prostate carcinoma in radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy specimens. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. Suppl. 2005, 39, 34–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, G.P.; Basler, J.W. Prognostic Factors for Failure after Prostatectomy. J. Cancer 2011, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhmeida, A.; Pyrhönen, S.; Laato, M.; Collan, Y. Prognostic factors in prostate cancer. Diagn. Pathol. 2006, 1, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A.; Grading Committee. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.C.; Epstein, J.I. Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: Histologic features and clinical significance. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, P.A.; Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Ulbright, T.M.; Reuter, V.E. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part B: Prostate and Bladder Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyai, K.; Divatia, M.K.; Shen, S.S.; Miles, B.J.; Ayala, A.G.; Ro, J.Y. Clinicopathological analysis of intraductal proliferative lesions of prostate: Intraductal carcinoma of prostate, high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, and atypical cribriform lesion. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeal, J.E.; Yemoto, C.E.M. Spread of Adenocarcinoma Within Prostatic Ducts and Acini. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1996, 20, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Mori, K.; Mostafaei, H.; Quhal, F.; Motlagh, R.S.; Pradere, B.; Laukhtina, E.; D’Andrea, D.; Saika, T.; Shariat, S.F. The Prognostic Impact of Intraductal Carcinoma of the Prostate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Urol. 2020, 204, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinerman, B.F.; Khani, F.; Golan, R.; Bernstein, A.N.; Cosiano, M.F.; Margolis, D.J.; Hu, J.C. Population-based study of the incidence and survival for intraductal carcinoma of the prostate. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 673.e9–673.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, V.Q.; Sirois, J.; Benzerdjeb, N.; Mansoori, B.K.; Grosset, A.A.; Albadine, R.; Latour, M.; Mes-Masson, A.M.; Hovington, H.; Bergeron, A.; et al. The impact of intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on the site and timing of recurrence and cancer-specific survival. Prostate 2018, 78, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.D.; Epstein, J.I. Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate without invasive carcinoma on needle biopsy: Emphasis on radical prostatectomy findings. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, K.; Li, J.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Zhou, M. Incidence and clinicopathological characteristics of intraductal carcinoma detected in prostate biopsies: A prospective cohort study. Histopathology 2013, 63, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, M.; Hirakawa, A.; Kobayashi, Y.M.; Yamamoto, A.; Ishida, R.; Sano, T.; Kimura, T.; Majima, T.; Ishida, S.; Funahashi, Y.; et al. The influence of the presence of intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on the grade group system’s prognostic performance. Prostate 2019, 79, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweldam, C.F.; van der Kwast, T.; van Leenders, G.J. On cribriform prostate cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2018, 7, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweldam, C.; Kümmerlin, I.; Nieboer, D.; Verhoef, E.; Steyerberg, E.; van der Kwast, T.; Roobol, M.; van Leenders, G. Disease-specific survival of patients with invasive cribriform and intraductal prostate cancer at diagnostic biopsy. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Allsbrook, W.C., Jr.; Amin, M.B.; Egevad, L.L.; ISUP Grading Committee. The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweldam, C.F.; Nieboer, D.; Algaba, F.; Amin, M.B.; Berney, D.M.; Billis, A.; Bostwick, D.G.; Bubendorf, L.; Cheng, L.; Compérat, E.; et al. Gleason grade 4 prostate adenocarcinoma patterns: An interobserver agreement study among genitourinary pathologists. Histopathology 2016, 69, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kwast, T.H.; van Leenders, G.J.; Berney, D.M.; Delahunt, B.; Evans, A.J.; Iczkowski, K.A.; McKenney, J.K.; Ro, J.Y.; Samaratunga, H.; Srigley, J.R.; et al. ISUP Consensus Definition of Cribriform Pattern Prostate Cancer. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, M.C.; Weier, C.; Xu, M.M.; Vaghasia, A.; Gürel, B.; Gümüşkaya, B.; Esopi, D.M.; Fedor, H.; Tan, H.L.; Kulac, I.; et al. Molecular evidence that invasive adenocarcinoma can mimic prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) and intraductal carcinoma through retrograde glandular colonization. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.J.; Wheeler, T.M.; Bonkhoff, H.; Rubin, M.A. A proposal on the identification, histologic reporting, and implications of intraductal prostatic carcinoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryvenko, O.N.; Gupta, N.S.; Virani, N.; Schultz, D.; Gomez, J.; Amin, A.; Lane, Z.; Epstein, J.I. Gleason score 7 adenocarcinoma of the prostate with lymph node metastases: Analysis of 184 radical prostatectomy specimens. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trudel, D.; Downes, M.R.; Sykes, J.; Kron, K.J.; Trachtenberg, J.; van der Kwast, T.H. Prognostic impact of intraductal carcinoma and large cribriform carcinoma architecture after prostatectomy in a contemporary cohort. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Khurana, J.S.; Jhala, N.; Zhao, H.; Wang, H. The Association of Invasive Cribriform Lesions With Adverse Prostatic Adenocarcinoma Outcomes: An Institutional Experience, Systematic Review, and Meta-analysis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality if Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.htm (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Sarbay, B.C.; Kir, G.; Topal, C.S.; Gumus, E. Significance of the cribriform pattern in prostatic adenocarcinomas. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kir, G.; Sarbay, B.C.; Gümüş, E.; Topal, C.S. The association of the cribriform pattern with outcome for prostatic adenocarcinomas. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iczkowski, K.A.; Torkko, K.C.; Kotnis, G.R.; Wilson, R.S.; Huang, W.; Wheeler, T.M.; Abeyta, A.M.; La Rosa, F.G.; Cook, S.; Werahera, P.N.; et al. Digital quantification of five high-grade prostate cancer patterns, including the cribriform pattern, and their association with adverse outcome. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 136, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, N.Y.; Cowan, J.E.; Zhang, L.; Carroll, P.R.; Chan, E.; Stohr, B.A.; Simko, J.P. Expansile cribriform Gleason pattern 4 has histopathologic and molecular features of aggressiveness and greater risk of biochemical failure compared to glomerulation Gleason pattern 4. Prostate 2020, 80, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, B.; Pearce, S.M.; Anderson, B.B.; Shalhav, A.L.; Zagaja, G.; Eggener, S.E.; Paner, G.P. Prognostic Significance of Percentage and Architectural Types of Contemporary Gleason Pattern 4 Prostate Cancer in Radical Prostatectomy. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 1400–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, J.G.; Chen, J.R.; Liu, Z.H.; Sun, G.X.; Wang, Z.P.; Ni, Y.C.; Dai, J.D.; Shen, P.F.; Zeng, H. Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate in prostate biopsy samples: Correlation with aggressive pathological features after radical prostatectomy and prognostic value in high-risk prostate cancer. Asian J. Androl. 2020, 22, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweldam, C.F.; Wildhagen, M.F.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Bangma, C.H.; van der Kwast, T.H.; van Leenders, G.J. Cribriform growth is highly predictive for postoperative metastasis and disease-specific death in Gleason score 7 prostate cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollemans, E.; Verhoef, E.I.; Bangma, C.H.; Rietbergen, J.; Roobol, M.J.; Helleman, J.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H. Clinical outcome comparison of Grade Group 1 and Grade Group 2 prostate cancer with and without cribriform architecture at the time of radical prostatectomy. Histopathology 2020, 76, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, T.A.; Schieda, N.; Sim, J.; Breau, R.H.; Morash, C.; Belanger, E.C.; Robertson, S.J. Evaluation of tumor morphologies and association with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy in grade group 5 prostate cancer. Virchows Arch. 2018, 472, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Yang, P.; Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Xiao, Y.; McDougal, W.S.; Young, R.H.; Wu, C.L. Architectural heterogeneity and cribriform pattern predict adverse clinical outcome for Gleason grade 4 prostatic adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, J.; Epstein, J.I.; Ganzer, R.; Graefen, M.; Guazzoni, G.; Kaouk, J.; Menon, M.; Mottrie, A.; Myers, R.P.; Patel, V.; et al. A Critical Analysis of the Current Knowledge of Surgical Anatomy of the Prostate Related to Optimisation of Cancer Control and Preservation of Continence and Erection in Candidates for Radical Prostatectomy: An Update. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammia, S.; Frisenda, M.; Maggi, M.; Magliocca, F.; Ciardi, A.; Panebianco, V.; De Berardinis, E.; Salciccia, S.; Di Pierro, G.; Gentilucci, A.; et al. Cribriform pattern does not have a significant impact in Gleason Score ≥7/ISUP Grade ≥2 prostate cancers submitted to radical prostatectomy. Medicine 2020, 99, e22156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osiecki, R.; Kozikowski, M.; Pyzlak, M.; Dobruch, J. The presence of cribriform pattern in prostate biopsy is associated with increased risk of regional lymph node metastasis. In Proceedings of the the 51st Scientific Congress of the Polish Urological Association, Warsaw, Poland, 21–23 October 2021; Available online: https://kongres2021.pturol.org.pl/media/kongres2021/files/Book_of_Abstract_%202021.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2023).
- Moschini, M.; Sharma, V.; Zattoni, F.; Quevedo, J.F.; Davis, B.J.; Kwon, E.; Karnes, R.J. Natural History of Clinical Recurrence Patterns of Lymph Node-Positive Prostate Cancer After Radical Prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touijer, K.A.; Mazzola, C.R.; Sjoberg, D.D.; Scardino, P.T.; Eastham, J.A. Long-term outcomes of patients with lymph node metastasis treated with radical prostatectomy without adjuvant androgen-deprivation therapy. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boorjian, S.A.; Thompson, R.H.; Siddiqui, S.; Bagniewski, S.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Karnes, R.J.; Frank, I.; Blute, M.L. Long-term outcome after radical prostatectomy for patients with lymph node positive prostate cancer in the prostate specific antigen era. J. Urol. 2007, 178 Pt 1, 864–870; discussion 870–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zincke, H.; Blute, M.L.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Scherer, B.; Bostwick, D.G. Risk of prostate carcinoma death in patients with lymph node metastasis. Cancer 2001, 91, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehner, M.; Koch, R.; Farahzadi, S.; Heberling, U.; Borkowetz, A.; Twelker, L.; Baretton, G.B.; Wirth, M.P.; Thomas, C. Long-Term Mortality in Patients with Positive Lymph Nodes at the Time of Radical Prostatectomy. Urol. Int. 2019, 103, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, V.Q.; Benzerdjeb, N.; Chagnon-Monarque, S.; Dionne, N.; Delouya, G.; Kougioumoutzakis, A.; Sirois, J.; Albadine, R.; Latour, M.; Mes-Masson, A.; et al. Retrospective study on the benefit of adjuvant radiotherapy in men with intraductal carcinoma of prostate. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastham, J.A.; Auffenberg, G.B.; Barocas, D.A.; Chou, R.; Crispino, T.; Davis, J.W.; Eggener, S.; Horwitz, E.M.; Kane, C.J.; Kirkby, E.; et al. Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO Guideline, Part II: Principles of Active Surveillance, Principles of Surgery, and Follow-Up. J. Urol. 2022, 208, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.L.K.; Lo, W.; Pintilie, M.; Murgic, J.; Lalonde, E.; Bhandari, V.; Mahamud, O.; Gopalan, A.; Kweldam, C.F.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; et al. A Prostate Cancer “Nimbosus”: Genomic Instability and SChLAP1 Dysregulation Underpin Aggression of Intraductal and Cribriform Subpathologies. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Udager, A.M.; Ahearn, T.U.; Cao, X.; Feng, F.Y.; Loda, M.; Petimar, J.S.; Kantoff, P.; Mucci, L.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Overexpression of the Long Non-coding RNA SChLAP1 Independently Predicts Lethal Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, R.; Shi, Y.; Udager, A.M.; Prensner, J.R.; Sahu, A.; Iyer, M.K.; Siddiqui, J.; Cao, X.; Wei, J.; Jiang, H.; et al. A Novel RNA In Situ Hybridization Assay for the Long Noncoding RNA SChLAP1 Predicts Poor Clinical Outcome After Radical Prostatectomy in Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, R.; Kweldam, C.F.; Livingstone, J.; Lalonde, E.; Yamaguchi, T.N.; Huang, V.; Yousif, F.; Fraser, M.; Bristow, R.G.; van der Kwast, T.; et al. Cribriform and intraductal prostate cancer are associated with increased genomic instability and distinct genomic alterations. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; Siadat, F.; Kron, K.; Liu, L.; Savio, A.J.; Trachtenberg, J.; Fleshner, N.; van der Kwast, T.; Bapat, B. Distinct DNA methylation alterations are associated with cribriform architecture and intraductal carcinoma in Gleason pattern 4 prostate tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Kron, K.J.; Pethe, V.V.; Demetrashvili, N.; Nesbitt, M.E.; Trachtenberg, J.; Ozcelik, H.; Fleshner, N.E.; Briollais, L.; van der Kwast, T.H.; et al. Association of tissue promoter methylation levels of APC, TGFβ2, HOXD3 and RASSF1A with prostate cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2454–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.S.; Morgan, T.M.; Wallington, D.G.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Spratt, D.E.; Mehra, R. Correlation between cribriform/intraductal prostatic adenocarcinoma and percent Gleason pattern 4 to a 22-gene genomic classifier. Prostate 2020, 80, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risbridger, G.P.; Taylor, R.A.; Clouston, D.; Sliwinski, A.; Thorne, H.; Hunter, S.; Li, J.; Mitchell, G.; Murphy, D.; Frydenberg, M.; et al. Patient-derived xenografts reveal that intraductal carcinoma of the prostate is a prominent pathology in BRCA2 mutation carriers with prostate cancer and correlates with poor prognosis. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, R.; Salles, D.C.; Sandhu, S.; Aragón, I.M.; Thorne, H.; López-Campos, F.; Rubio-Briones, J.; Gutierrez-Pecharroman, A.M.; Maldonado, L.; di Domenico, T.; et al. Association between BRCA2 alterations and intraductal and cribriform histologies in prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 147, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osiecki, R.; Kozikowski, M.; Sarecka-Hujar, B.; Pyzlak, M.; Dobruch, J. Prostate Cancer Morphologies: Cribriform Pattern and Intraductal Carcinoma Relations to Adverse Pathological and Clinical Outcomes—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051372
Osiecki R, Kozikowski M, Sarecka-Hujar B, Pyzlak M, Dobruch J. Prostate Cancer Morphologies: Cribriform Pattern and Intraductal Carcinoma Relations to Adverse Pathological and Clinical Outcomes—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051372
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsiecki, Rafał, Mieszko Kozikowski, Beata Sarecka-Hujar, Michał Pyzlak, and Jakub Dobruch. 2023. "Prostate Cancer Morphologies: Cribriform Pattern and Intraductal Carcinoma Relations to Adverse Pathological and Clinical Outcomes—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051372
APA StyleOsiecki, R., Kozikowski, M., Sarecka-Hujar, B., Pyzlak, M., & Dobruch, J. (2023). Prostate Cancer Morphologies: Cribriform Pattern and Intraductal Carcinoma Relations to Adverse Pathological and Clinical Outcomes—Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 15(5), 1372. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051372







