Venetoclax in Relapse/Refractory AL Amyloidosis—A Multicenter International Retrospective Real-World Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Treatment and Response
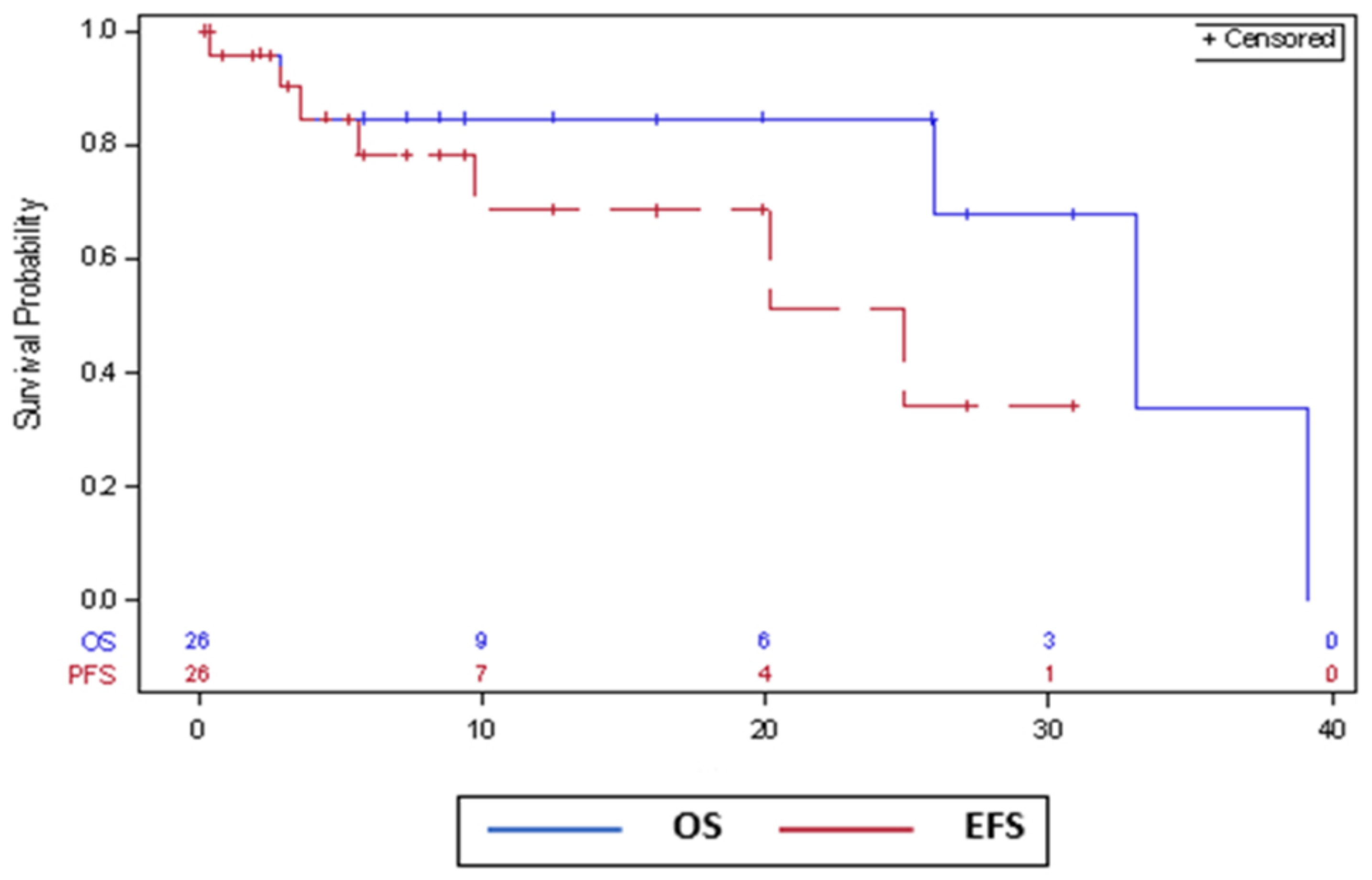
3.3. Survival Outcomes
3.4. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gertz, M.A. Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis: 2022 update on diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastritis, E.; Palladini, G.; Minnema, M.C.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Jaccard, A.; Lee, H.C.; Sanchorawala, V.; Gibbs, S.; Mollee, P.; Venner, C.P.; et al. Daratumumab-Based Treatment for Immunoglobulin Light-Chain Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palladini, G.; Milani, P.; Merlini, G. Management of AL amyloidosis in 2020. Blood 2020, 136, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Hamed, R.; Bazarbachi, A.H.; Bazarbachi, A.; Malard, F.; Harousseau, J.L.; Mohty, M. Comprehensive Review of AL amyloidosis: Some practical recommendations. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, V.A.; DiNardo, C.; Konopleva, M. Venetoclax-based therapies for acute myeloid leukemia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2019, 32, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Anderson, M.A.; Pott, C.; Agarwal, R.; Handunnetti, S.; Hicks, R.J.; Burbury, K.; Turner, G.; Di Iulio, J.; Bressel, M.; et al. Ibrutinib plus Venetoclax for the Treatment of Mantle-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaxman, I.; Sidiqi, M.H.; Gertz, M. Venetoclax for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2018, 11, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce, A.H.; Ketterling, R.P.; Gertz, M.A.; Lacy, M.; Knudson, R.A.; Zeldenrust, S.; Kumar, S.; Hayman, S.; Buadi, F.; Kyle, R.A.; et al. Translocation t(11;14) and survival of patients with light chain (AL) amyloidosis. Haematologica 2009, 94, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.S.; Spetz, J.K.E.; Qin, X.; Presser, A.; Choiniere, J.; Li, C.; Yu, S.; Blevins, F.; Hata, A.N.; Miller, J.W.; et al. Exploiting endogenous and therapy-induced apoptotic vulnerabilities in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis with BH3 mimetics. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiqi, M.H.; Al Saleh, A.S.; Leung, N.; Jevremovic, D.; Aljama, M.A.; Gonsalves, W.I.; Buadi, F.K.; Kourelis, T.V.; Warsame, R.; Muchtar, E.; et al. Venetoclax for the treatment of translocation (11;14) AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquer, H.; Belhadj, K.; Dupuis, J.; Oghina, S.; Galat, A.; Ladaique, A.; Maarek, A.; Roulin, L.; Gounot, R.; Poulot, E.; et al. Venetoclax induces profound and sustained responses in patients with relapsed/refractory light-chain amyloidosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahi, H.; Kashif, M.; Klimkowska, M.; Karvouni, M.; Wallblom, A.; Gran, C.; Hauenstein, J.; Frengen, N.; Gustafsson, C.; Afram, G.; et al. Low dose venetoclax as a single agent treatment of plasma cell malignancies harboring t(11;14). Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, V.J.; Lentzsch, S.; Pan, S.; Bhutani, D.; Richter, J.; Jagannath, S.; Liedtke, M.; Jaccard, A.; Wechalekar, A.D.; Comenzo, R.; et al. Venetoclax induces deep hematologic remissions in t(11;14) relapsed/refractory AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Palumbo, A.; Blade, J.; Merlini, G.; Mateos, M.-V.; Kumar, S.; Hillengass, J.; Kastritis, E.; Richardson, P.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e538–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Dispenzieri, A.; Gertz, M.A.; Kumar, S.; Wechalekar, A.; Hawkins, P.N.; Schonland, S.; Hegenbart, U.; Comenzo, R.; Kast, E.; et al. New criteria for response to treatment in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis based on free light chain measurement and cardiac biomarkers: Impact on survival outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4541–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladini, G.; Schönland, S.O.; Sanchorawala, V.; Kumar, S.; Wechalekar, A.; Hegenbart, U.; Milani, P.; Ando, Y.; Westermark, P.; Dispenzieri, A.; et al. Clarification on the definition of complete haematologic response in light-chain (AL) amyloidosis. Amyloid 2021, 28, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiqi, M.H.; Al Saleh, A.S.; Kumar, S.K.; Leung, N.; Jevremovic, D.; Muchtar, E.; Gonsalves, W.I.; Kourelis, T.V.; Warsame, R.; Buadi, F.K.; et al. Venetoclax for the treatment of multiple myeloma: Outcomes outside of clinical trials. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1131–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kaufman, J.L.; Gasparetto, C.; Mikhael, J.; Vij, R.; Pegourie, B.; Benboubker, L.; Facon, T.; Amiot, M.; Moreau, P.; et al. Efficacy of venetoclax as targeted therapy for relapsed/refractory t(11;14) multiple myeloma. Blood 2017, 130, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccon-Gibod, C.; Talbot, A.; Le Bras, F.; Frenzel, L.; Royer, B.; Harel, S.; Lombion, N.; Belhadj, K.; Cuccuini, W.; Arnulf, B. Carfilzomib, venetoclax and dexamethasone for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, e73–e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.K.; Harrison, S.J.; Cavo, M.; de la Rubia, J.; Popat, R.; Gasparetto, C.; Hungria, V.; Salwender, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kim, I.; et al. Venetoclax or placebo in combination with bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (BELLINI): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, J.L.; Gasparetto, C.; Schjesvold, F.H.; Moreau, P.; Touzeau, C.; Facon, T.; Boise, L.H.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, X.; Dunbar, F.; et al. Targeting BCL-2 with venetoclax and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed/refractory t(11;14) multiple myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Cohort (n = 26) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age at venetoclax initiation, median (range) years | 65 (50–88) | |
| Males (n)/Females (n) | 15/11 | |
| Median bone marrow plasma cells at diagnosis, % (IQR) | 20 (13–30) | |
| Involved light chain- Kappa, n (%) | 9 (35) | |
| Lambda, n (%) | 17 (65) | |
| Median dFLC at diagnosis, mg/L (IQR) | 348 (120–551) | |
| Involved organs—n (%) | Heart | 20 (77) |
| Kidneys | 15 (58) | |
| PNS | 6 (23) | |
| GI | 7 (27) | |
| Soft tissue | 10 (38) | |
| Liver | 4 (15) | |
| Cardiac stage—n (%) | 1 | 6 (23) |
| 2 | 9 (35) | |
| 3a | 8 (31) | |
| 3b | 2 (8) | |
| missing | 1 (4) | |
| t(11;14) translocation— n (%) | 22/25 (88) | |
| Concurrent clinical MM— n (%) | 8 (31) | |
| Performance status at venetoclax initiation *, n (%) | ||
| 0–1 | 12 (46) | |
| 2 | 10 (38) | |
| 3–4 | 4 (15) | |
| No. of prior lines of therapy, median (range) | 3.5 (1–7) | |
| Prior therapies **—n (%) | Bortezomib | 26 (100) |
| Lenalidomide | 17 (65) | |
| Pomalidomide | 13 (50) | |
| Daratumumab | 22 (85) | |
| Alkylators | 23 (88) | |
| ASCT | 5 (19) | |
| Time from Diagnosis to venetoclax, month (IQR) | 12 (5–41) | |
| Hemoglobin at venetoclax initiation, g/dL (IQR) | 11.6 (10.6–12.1) | |
| Platelets at venetoclax initiation, ×109/L (IQR) | 198 (166–235) | |
| ANC at venetoclax initiation, ×109/L (IQR) | 4.1 (2.2–6.5) | |
| Creatinine at venetoclax initiation, mg/dL (IQR) | 1.13 (0.8–2) | |
| Variable | Cohort (n = 26) | |
|---|---|---|
| Venetoclax maximum daily dose *—median (range) | 400 mg (200–800) | |
| Venetoclax combination—n (%) | single agent | 9 (35) |
| with DEX | 9 (35) | |
| with DARA (±DEX) | 7 (27) | |
| with DARA + BOR + DEX | 1 (4) | |
| Overall response rate—n (%) | 23 (88) | |
| Quality of response, n (%) | CR | 9 (35) |
| VGPR | 9 (35) | |
| PR | 5 (19) | |
| NR | 3 (12) | |
| Time to any response—median (range) months | 1 (0.3–12) | |
| Time to best response—median (range) months | 2 (0.3–11) | |
| Infections | Hematological Toxicities | TLS | GI Toxicities | Dose Reductions | Treatment Discontinuation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venetoclax monotherapy | 1 G2 | 1 G4 TCP 2 G1-2 anemia 1 G1 neutropenia | 0 | 0 | 2 patients | two discontinued due to PD |
| Venetoclax + DEX | 2 G3 infections, 1 G5 infection | 1 G1 TCP 1 G3 TCP 1 G3 anemia 1 G2 anemia 1 G4 neutropenia 1 G1 neutropenia | 0 | 1 G1 diarrhea; 1 G3 diarrhea | 4 patients | two discontinued due to toxicity |
| Venetoclax + DARA) ±DEX, +BOR in 1 patient) | 2 G1-2 | 3 G1-2 TCP 2 G1 anemia 1 G3 neutropenia 2 G1-2 neutropenia | 0 | 0 | 4 patients | two discontinued due to PD and one due to toxicity |
| Sidiqi 2020 BCJ [11] | Pasquer 2021 BJH [12] | Nahi * 2021 AJH [13] | Premkumar 2021 BCJ [14] | Current Cohort | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 12 | 10 | 8 | 43 | 26 |
| % t(11;14) | 92% | 70% | 100% | 72% | 88% |
| Median prior lines | 2 (range 1–4) | Not reported (70% 3 + pervious lines) | Not reported | 3 | 3.5 (range 1–7) |
| Daily doses | 7–800 mg; 5–400 mg | 5–400 mg; 4–200 mg; 1–100 mg | 400 mg | 100–800 mg | Median 400 mg, range 200–800 |
| ORR % | 88% | 66.6% | 71% | 68% | 88% |
| Infections | in 2 patients | Not reported | Not reported | 7% grade 3+ | 11% G3-5 |
| TLS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| G3+ cytopenias | Not reported | 1 patient (10%) with anemia and grade 3 thrombocytopenia | Not reported | 9% | 11% G3-4 |
| Treatment discontinuation due to toxicity | 16% | 30% | Not reported | 19% | 8% |
| Death on therapy | 0 | 5 patients (50%) died: 3 from heart failure not attributed to venetoclax, 1 from infection and 1 from an unknown cause | 0 | 1 patient died due to sepsis and 1 due to heart failure not attributed to venetoclax | 1 patient died due to infection |
| mDOR | Not reported | 241 days | Not reported | Not reported | 25 months |
| mPFS | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | 31 months ‡ | 25 months ‡ |
| mOS | Not reported | 10.5 months | Not reported | Not reached | 33 months |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lebel, E.; Kastritis, E.; Palladini, G.; Milani, P.; Theodorakakou, F.; Aumann, S.; Lavi, N.; Shargian, L.; Magen, H.; Cohen, Y.; et al. Venetoclax in Relapse/Refractory AL Amyloidosis—A Multicenter International Retrospective Real-World Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061710
Lebel E, Kastritis E, Palladini G, Milani P, Theodorakakou F, Aumann S, Lavi N, Shargian L, Magen H, Cohen Y, et al. Venetoclax in Relapse/Refractory AL Amyloidosis—A Multicenter International Retrospective Real-World Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061710
Chicago/Turabian StyleLebel, Eyal, Efstathios Kastritis, Giovanni Palladini, Paolo Milani, Foteini Theodorakakou, Shlomzion Aumann, Noa Lavi, Liat Shargian, Hila Magen, Yael Cohen, and et al. 2023. "Venetoclax in Relapse/Refractory AL Amyloidosis—A Multicenter International Retrospective Real-World Study" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061710
APA StyleLebel, E., Kastritis, E., Palladini, G., Milani, P., Theodorakakou, F., Aumann, S., Lavi, N., Shargian, L., Magen, H., Cohen, Y., Gatt, M. E., & Vaxman, I. (2023). Venetoclax in Relapse/Refractory AL Amyloidosis—A Multicenter International Retrospective Real-World Study. Cancers, 15(6), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061710








