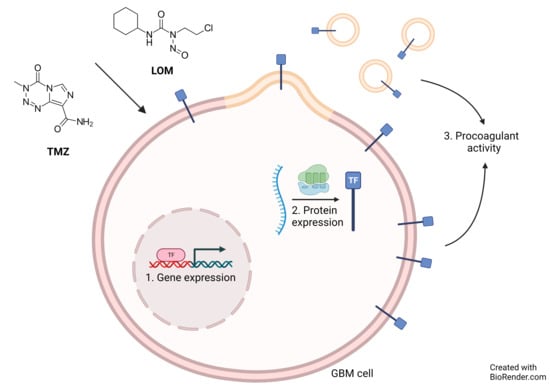
Temozolomide and Lomustine Induce Tissue Factor Expression and Procoagulant Activity in Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. FXa Generation
2.3. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemotherapeutic Agents TMZ and LOM Induce Procoagulant Activity in GBM Cells
3.2. Treatment with TMZ or LOM Induces TF Gene and Protein Expression in GBM Cells
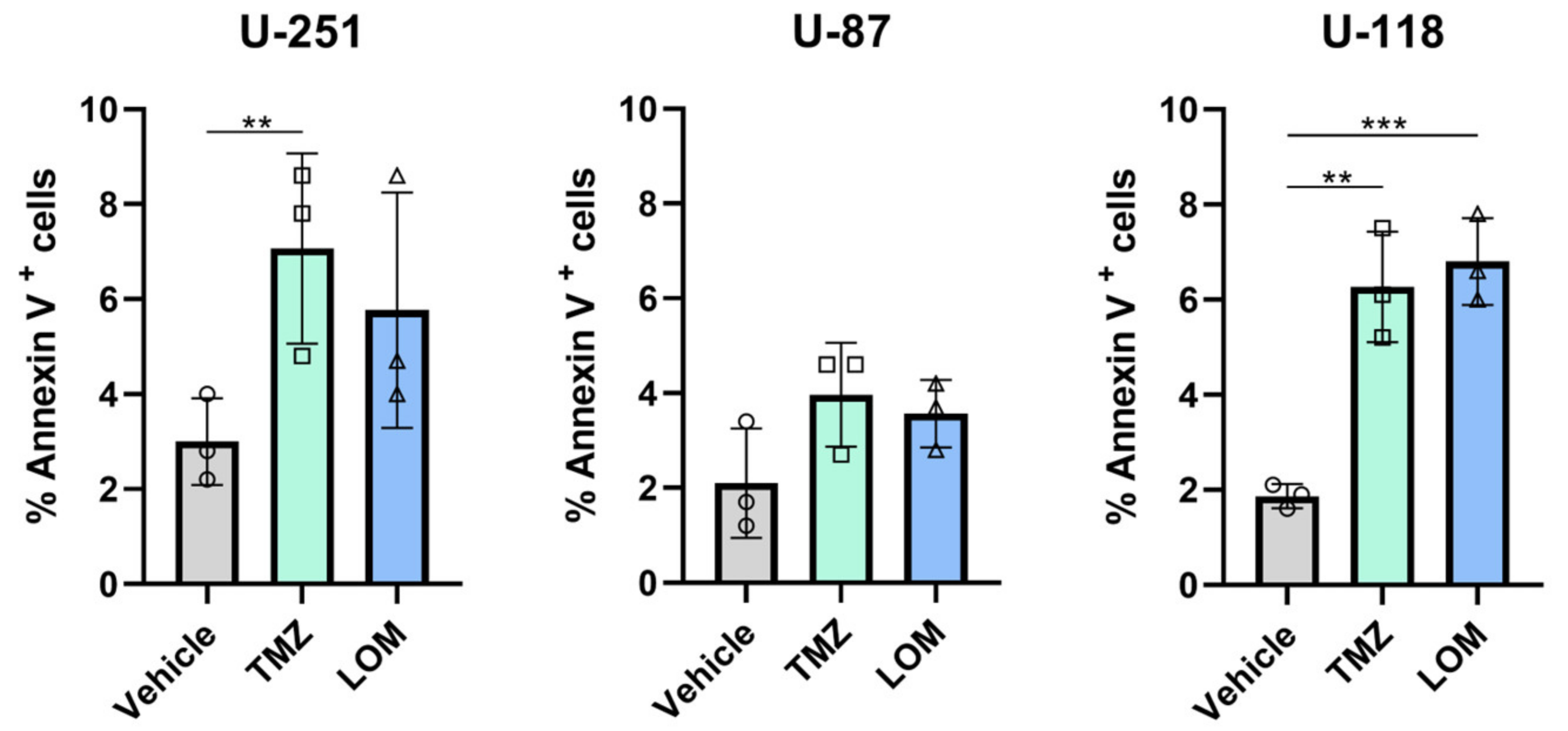
3.3. Treatment with TMZ or LOM Increases the Percentage of Annexin V-Positive GBM Cells
3.4. TMZ- and LOM-Induced TF Activity Is Fully Prevented by TF Blocking Antibody mAb 5G9 and Reduced by PS-Binding Annexin V
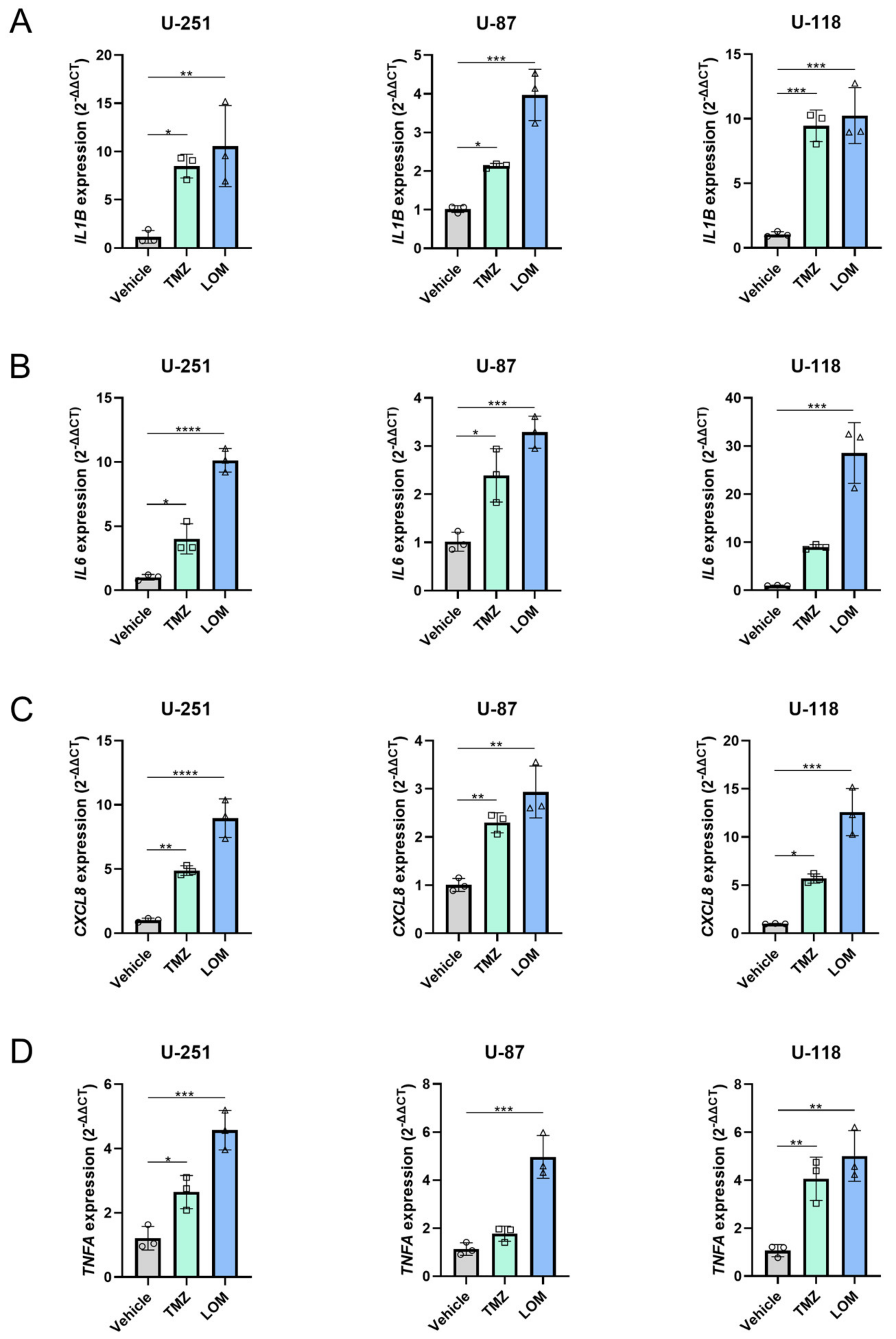
3.5. Treatment with TMZ or LOM Induces Expression of Several Proinflammatory Genes in GBM Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yust-Katz, S.; Mandel, J.J.; Wu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Webre, C.; Pawar, T.A.; Lhadha, H.S.; Gilbert, M.R.; Armstrong, T.S. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) and glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaptein, F.H.J.; Stals, M.A.M.; Kapteijn, M.Y.; Cannegieter, S.C.; Dirven, L.; van Duinen, S.G.; van Eijk, R.; Huisman, M.V.; Klaase, E.E.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; et al. Incidence and determinants of thrombotic and bleeding complications in patients with glioblastoma. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 20, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, J.; Ay, C. Venous Thromboembolism in Brain Tumors: Risk Factors, Molecular Mechanisms, and Clinical Challenges. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2019, 45, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Culakova, E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Lyman, G.H. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, F.I.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; van Es, N.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Pedersen, L.; Moik, F.; Ay, C.; Büller, H.R.; Sørensen, H.T. Venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: A population-based cohort study. Blood 2021, 137, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, J.; Bensaid, B.; Elkacemi, H.; Afif, M.; Bensaid, Y.; Kebdani, T.; Benjaafar, N. Venous thromboembolism in cancer patients: An underestimated major health problem. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; Kuderer, N.M.; Culakova, E.; Lyman, G.H.; Francis, C.W. Development and validation of a predictive model for chemotherapy-associated thrombosis. Blood 2008, 111, 4902–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppelt, P.; Betbadal, A.; Nayak, L. Approach to chemotherapy-associated thrombosis. Vasc. Med. 2015, 20, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, T.C.; Greeno, E.W. Chemotherapy-induced thrombosis. Thromb. Res. 2006, 118, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.P.; Hisada, Y.M.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Reeves, B.N.; Mackman, N. Cancer Therapy-Associated Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, R.R. Tissue factor encryption. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.A.; Pendurthi, U.R.; Rao, L.V.M. Role of Cell Surface Lipids and Thiol-Disulphide Exchange Pathways in Regulating the Encryption and Decryption of Tissue Factor. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swystun, L.L.; Shin, L.Y.; Beaudin, S.; Liaw, P.C. Chemotherapeutic agents doxorubicin and epirubicin induce a procoagulant phenotype on endothelial cells and blood monocytes. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewirtz, D.A.; Holt, S.E.; Elmore, L.W. Accelerated senescence: An emerging role in tumor cell response to chemotherapy and radiation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, P.J.; Parker, B.; Jones, V.; Adler, K.A.; Perez, C.J.; Johnson, S.; Cohen-Zion, M.; Marler, M.; Sadler, G.R.; Dimsdale, J.E.; et al. The effects of standard anthracycline-based chemotherapy on soluble ICAM-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor levels in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4998–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.; Oechsle, K.; Hauschild, J.; Steinemann, G.; Spath, B.; Bokemeyer, C.; Ruf, W.; Honecker, F.; Langer, F. Regulation of tissue factor in NT2 germ cell tumor cells by cisplatin chemotherapy. Thromb. Res. 2015, 136, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysov, Z.; Swystun, L.L.; Kuruvilla, S.; Arnold, A.; Liaw, P.C. Lung cancer chemotherapy agents increase procoagulant activity via protein disulfide isomerase-dependent tissue factor decryption. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2015, 26, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, N.; Xu, L.; Berry, L.R.; Chan, A.K. The effects of chemotherapeutic agents on the regulation of thrombin on cell surfaces. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 120, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, A.; Sabbah, A.R.; Issman, L.; Berkovich, H.; Copty, R.; Talmon, Y.; Brenner, B. Effects of Low- and High-Dose Chemotherapy Agents on Thrombogenic Properties of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, M.T.; Della Puppa, A.; Ballin, A.; Campello, E.; Radu, C.M.; Saggiorato, G.; d’Avella, D.; Scienza, R.; Cella, G.; Simioni, P. Circulating microparticles of glial origin and tissue factor bearing in high-grade glioma: A potential prothrombotic role. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 110, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekman, M.L.; Maas, S.L.N.; Abels, E.R.; Mempel, T.R.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Multidimensional communication in the microenvirons of glioblastoma. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Peng, C.; Li, D. Epigenetic Underpinnings of Inflammation: A Key to Unlock the Tumor Microenvironment in Glioblastoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Hambardzumyan, D. Immune Microenvironment in Glioblastoma Subtypes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.C.; Ashley, D.M.; López, G.Y.; Malinzak, M.; Friedman, H.S.; Khasraw, M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Le Rhun, E. How did lomustine become standard of care in recurrent glioblastoma? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 87, 102029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syro, L.V.; Rotondo, F.; Camargo, M.; Ortiz, L.D.; Serna, C.A.; Kovacs, K. Temozolomide and Pituitary Tumors: Current Understanding, Unresolved Issues, and Future Directions. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y. Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Genes Dis. 2016, 3, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stritzelberger, J.; Distel, L.; Buslei, R.; Fietkau, R.; Putz, F. Acquired temozolomide resistance in human glioblastoma cell line U251 is caused by mismatch repair deficiency and can be overcome by lomustine. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mégalizzi, V.; Mathieu, V.; Mijatovic, T.; Gailly, P.; Debeir, O.; De Neve, N.; Van Damme, M.; Bontempi, G.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Decaestecker, C.; et al. 4-IBP, a sigma1 receptor agonist, decreases the migration of human cancer cells, including glioblastoma cells, in vitro and sensitizes them in vitro and in vivo to cytotoxic insults of proapoptotic and proautophagic drugs. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, S.; Takahashi, M.; Satomi, K.; Sasaki, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Uchida, E.; Kawauchi, D.; Nakano, T.; Fujii, T.; Narita, Y.; et al. Lomustine and nimustine exert efficient antitumor effects against glioblastoma models with acquired temozolomide resistance. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 4736–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, H.H.; Schaffner, F.; Kerver, M.; Petersen, H.H.; Ahamed, J.; Felding-Habermann, B.; Takada, Y.; Mueller, B.M.; Ruf, W. Inhibition of tissue factor signaling suppresses tumor growth. Blood 2008, 111, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boles, J.C.; Williams, J.C.; Hollingsworth, R.M.; Wang, J.G.; Glover, S.L.; Owens, A.P., 3rd; Barcel, D.A.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Key, N.S.; Mackman, N. Anthracycline treatment of the human monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1 increases phosphatidylserine exposure and tissue factor activity. Thromb. Res. 2012, 129, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Francia, G.; Viloria-Petit, A.; Hicklin, D.J.; du Manoir, J.; Rak, J.; Kerbel, R.S. In vitro procoagulant activity induced in endothelial cells by chemotherapy and antiangiogenic drug combinations: Modulation by lower-dose chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5365–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, P.; Van Dreden, P.; Rousseau, A.; Kassim, Y.; Legrand, E.; Vannier, J.P.; Vasse, M. Increased levels of tissue factor activity and procoagulant phospholipids during treatment of children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.; Pongor, L.; Su, Y.T.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Quezado, M.; Trepel, J.; Aldape, K.; Pommier, Y.; Wu, J. MGMT Status as a Clinical Biomarker in Glioblastoma. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.K.; Shen, D.; Chen, Y.S.; Yang, Q.Y.; Guo, C.C.; Feng, B.H.; Chen, Z.P. Enhanced MGMT expression contributes to temozolomide resistance in glioma stem-like cells. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, A.; Mueller, W.; Urdangarín, E.; Lázcoz, P.; von Deimling, A.; Castresana, J.S. Detection of methylation in promoter sequences by melting curve analysis-based semiquantitative real time PCR. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taal, W.; Bromberg, J.E.; van den Bent, M.J. Chemotherapy in glioma. CNS Oncol. 2015, 4, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrlinger, U.; Tzaridis, T.; Mack, F.; Steinbach, J.P.; Schlegel, U.; Sabel, M.; Hau, P.; Kortmann, R.D.; Krex, D.; Grauer, O.; et al. Lomustine-temozolomide combination therapy versus standard temozolomide therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated MGMT promoter (CeTeG/NOA-09): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, N.; Maier, D.; Merlo, A.; Tada, M.; Sawamura, Y.; Diserens, A.C.; Van Meir, E.G. Frequent co-alterations of TP53, p16/CDKN2A, p14ARF, PTEN tumor suppressor genes in human glioma cell lines. Brain Pathol. 1999, 9, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blough, M.D.; Beauchamp, D.C.; Westgate, M.R.; Kelly, J.J.; Cairncross, J.G. Effect of aberrant p53 function on temozolomide sensitivity of glioma cell lines and brain tumor initiating cells from glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 102, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesselaar, M.E.; Romijn, F.P.; van der Linden, I.K.; Bertina, R.M.; Osanto, S. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity in cancer patients with and without thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1421–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Hengel, L.G.; van Steijn-van Tol, A.Q.; Bertina, R.M.; Versteeg, H.H.; Osanto, S. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity in plasma is unaffected by cytolytic chemotherapy treatment in metastatic testicular cancer patients. Thromb. Res. 2013, 131, 187–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auwerda, J.J.; Yuana, Y.; Osanto, S.; de Maat, M.P.; Sonneveld, P.; Bertina, R.M.; Leebeek, F.W. Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity and venous thrombosis in multiple myeloma. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 105, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasthuri, R.S.; Hisada, Y.; Ilich, A.; Key, N.S.; Mackman, N. Effect of chemotherapy and longitudinal analysis of circulating extracellular vesicle tissue factor activity in patients with pancreatic and colorectal cancer. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 4, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuenschwander, P.F.; Bianco-Fisher, E.; Rezaie, A.R.; Morrissey, J.H. Phosphatidylethanolamine augments factor VIIa-tissue factor activity: Enhancement of sensitivity to phosphatidylserine. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 13988–13993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.D.; Blanco, V.M.; Sulaiman, M.K.; Vallabhapurapu, S.L.; Chu, Z.; Franco, R.S.; Qi, X. Variation in human cancer cell external phosphatidylserine is regulated by flippase activity and intracellular calcium. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34375–34388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Kanwar, S.S. Phosphatidylserine: A cancer cell targeting biomarker. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Guessan, K.F.; Patel, P.H.; Qi, X. SapC-DOPS-a Phosphatidylserine-targeted Nanovesicle for selective Cancer therapy. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Hou, J.; Cao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Rasmussen, J.T.; Heegaard, C.W.; Gilbert, G.E. Phosphatidylserine exposure and procoagulant activity in acute promyelocytic leukemia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, D.; Laput, G.; Vyas, A.K. Chemotherapy-enhanced inflammation may lead to the failure of therapy and metastasis. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2014, 7, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, R.M.; Stringer, A.M.; Bowen, J.M.; Gibson, R.J.; Sonis, S.T.; Keefe, D.M. Serum levels of NFkappaB and pro-inflammatory cytokines following administration of mucotoxic drugs. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevilacqua, M.P.; Pober, J.S.; Majeau, G.R.; Fiers, W.; Cotran, R.S.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor induces procoagulant activity in cultured human vascular endothelium: Characterization and comparison with the actions of interleukin 1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4533–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, M.; Ichikawa, J.; Ando, T.; Schoenecker, J.G.; Ohba, T.; Koyama, K.; Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Haro, H. Platelet-Derived TGF-β Induces Tissue Factor Expression via the Smad3 Pathway in Osteosarcoma Cells. J. Bone. Miner. Res. 2018, 33, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unruh, D.; Horbinski, C. Beyond thrombosis: The impact of tissue factor signaling in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kapteijn, M.Y.; Zwaan, S.; ter Linden, E.; Laghmani, E.H.; van den Akker, R.F.P.; Rondon, A.M.R.; van der Zanden, S.Y.; Neefjes, J.; Versteeg, H.H.; Buijs, J.T. Temozolomide and Lomustine Induce Tissue Factor Expression and Procoagulant Activity in Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro. Cancers 2023, 15, 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082347
Kapteijn MY, Zwaan S, ter Linden E, Laghmani EH, van den Akker RFP, Rondon AMR, van der Zanden SY, Neefjes J, Versteeg HH, Buijs JT. Temozolomide and Lomustine Induce Tissue Factor Expression and Procoagulant Activity in Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro. Cancers. 2023; 15(8):2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082347
Chicago/Turabian StyleKapteijn, Maaike Y., Shanna Zwaan, Esther ter Linden, El Houari Laghmani, Rob F. P. van den Akker, Araci M. R. Rondon, Sabina Y. van der Zanden, Jacques Neefjes, Henri H. Versteeg, and Jeroen T. Buijs. 2023. "Temozolomide and Lomustine Induce Tissue Factor Expression and Procoagulant Activity in Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro" Cancers 15, no. 8: 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082347
APA StyleKapteijn, M. Y., Zwaan, S., ter Linden, E., Laghmani, E. H., van den Akker, R. F. P., Rondon, A. M. R., van der Zanden, S. Y., Neefjes, J., Versteeg, H. H., & Buijs, J. T. (2023). Temozolomide and Lomustine Induce Tissue Factor Expression and Procoagulant Activity in Glioblastoma Cells In Vitro. Cancers, 15(8), 2347. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082347