PD-L1 Expression in Paired Samples of Rectal Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. PD-L1 Expression in Diagnostic Biopsies and Surgical Specimens
3.3. Changes in PD-L1 Expression in Paired Specimens
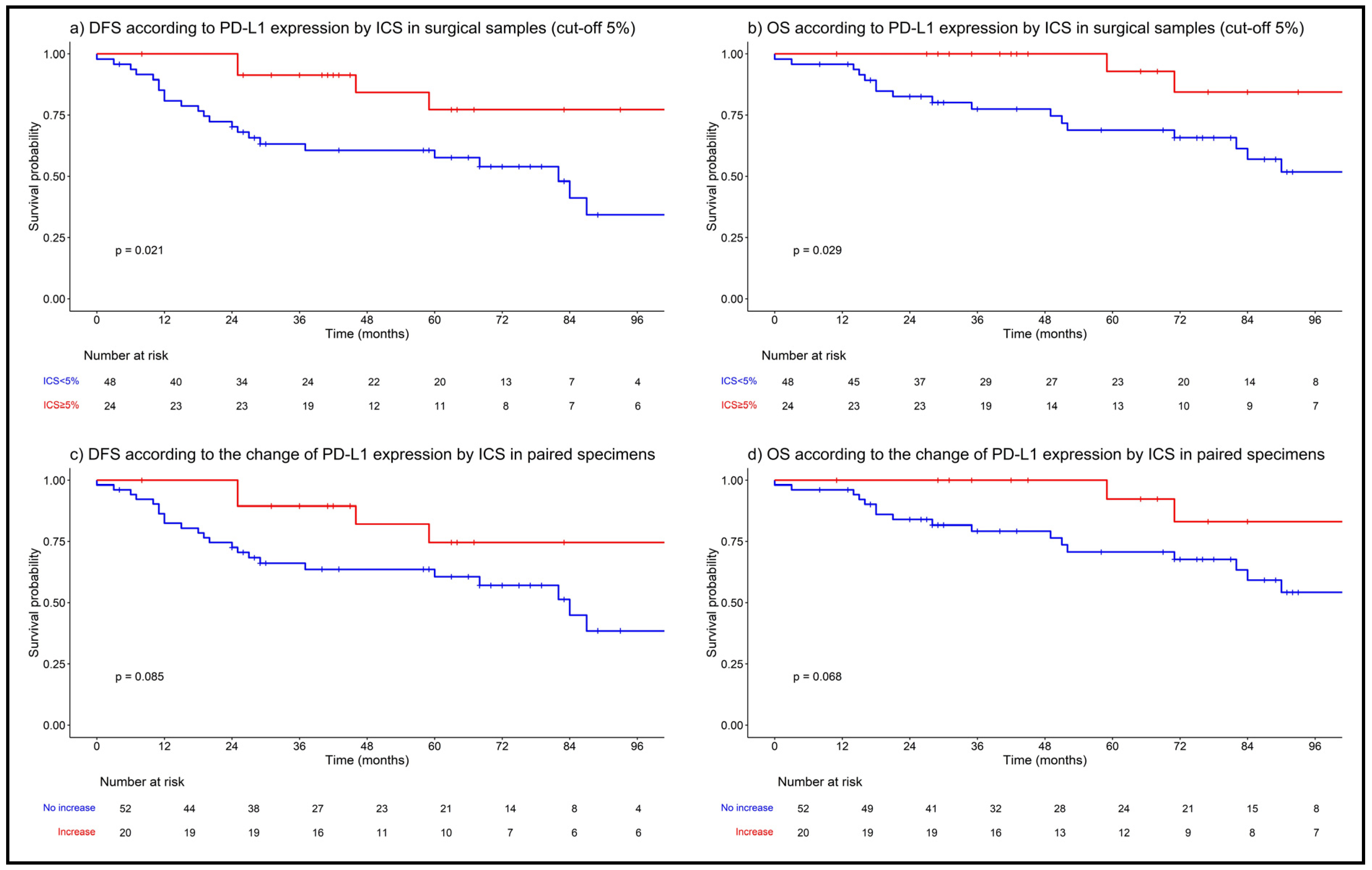
3.4. PD-L1 Expression/Change and Survival Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Wagle, N.S.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, E.A.; Nilsson, P.J.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Bahadoer, R.R.; Meershoek-Klein Kranenbarg, E.; Roodvoets, A.G.H.; Putter, H.; Berglund, Å.; Cervantes, A.; Crolla, R.M.P.H.; et al. Locoregional Failure during and after Short-course Radiotherapy followed by Chemotherapy and Surgery Compared with Long-course Chemoradiotherapy and Surgery: A 5-Year Follow-up of the RAPIDO Trial. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, e766–e772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, T.; Etienne, P.-L.; Rio, E.; Evesque, L.; Mesgouez-Nebout, N.; Vendrely, V.; Artignan, X.; Bouche, O.; Boileve, A.; Delaye, M.; et al. Total neoadjuvant therapy with mFOLFIRINOX versus preoperative chemoradiation in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer: 7-year results of PRODIGE 23 phase III trial, a UNICANCER GI trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S17), LBA3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheij, F.S.; Omer, D.M.R.; Williams, H.; Buckley, J.T.; Lin, S.T.; Qin, L.-X.; Thompson, H.M.; Yuval, J.B.; Gollub, M.J.; Wu, A.J.-C.; et al. Sustained organ preservation in patients with rectal cancer treated with total neoadjuvant therapy: Long-term results of the OPRA trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S16), 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, D.; Shi, Q.; Weiser, M.R.; Gollub, M.J.; Saltz, L.B.; Musher, B.L.; Goldberg, J.; Al Baghdadi, T.; Goodman, K.A.; McWilliams, R.R.; et al. Preoperative Treatment of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chi, P.; Lan, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Cui, L.; Chen, D.; Cao, J.; Wei, H.; Peng, X.; et al. Neoadjuvant Modified FOLFOX6 with or without Radiation versus Fluorouracil Plus Radiation for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: Final Results of the Chinese FOWARC Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3223–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, J.-P.; Barbet, N.; Schiappa, R.; Magné, N.; Martel, I.; Mineur, L.; Deberne, M.; Zilli, T.; Dhadda, A.; Myint, A.S.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with radiation dose escalation with contact x-ray brachytherapy boost or external beam radiotherapy boost for organ preservation in early cT2-cT3 rectal adenocarcinoma (OPERA): A phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, R.; Junginger, T.; Kube, R.; Strassburg, J.; Lewin, A.; Baral, J.; Maurer, C.A.; Sauer, J.; Lauscher, J.; Winde, G.; et al. Risk-Adapted Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Rectal Cancer: Final Report of the OCUM Study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4025–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynne-Jones, R.; Wyrwicz, L.; Tiret, E.; Brown, G.; Rödel, C.; Cervantes, A.; Arnold, D. Rectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv22–iv40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.B.; Venook, A.P.; Adam, M.; Chen, Y.J.; Ciombor, K.K.; Cohen, S.; Cooper, H.S.; Deming, D.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Grem, J.L.; et al. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®), Rectal Cancer, Version 3. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/rectal.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2024).
- Cercek, A.; Lumish, M.; Sinopoli, J.; Weiss, J.; Shia, J.; Lamendola-Essel, M.; El Dika, I.H.; Segal, N.; Shcherba, M.; Sugarman, R.; et al. PD-1 Blockade in Mismatch Repair–Deficient, Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2363–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Kang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Huang, M.; Lan, P.; Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Cao, W.; et al. Neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade with toripalimab, with or without celecoxib, in mismatch repair-deficient or microsatellite instability-high, locally advanced, colorectal cancer (PICC): A single-centre, parallel-group, non-comparative, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoor, Y.L.; Van Den Berg, J.; Beets, G.; Sikorska, K.; Aalbers, A.; Van Lent, A.; Grootscholten, C.; Huibregtse, I.; Marsman, H.; Oosterling, S.; et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab, ipilimumab, and celecoxib in MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient colon cancers: Final clinical analysis of the NICHE study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalabi, M.; Verschoor, Y.L.; Van Den Berg, J.; Sikorska, K.; Beets, G.; Lent, A.V.; Grootscholten, M.C.; Aalbers, A.; Buller, N.; Marsman, H.; et al. LBA7 Neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibition in locally advanced MMR-deficient colon cancer: The NICHE-2 study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschoor, Y.L.; Van Den Berg, J.; Balduzzi, S.; Van Blijderveen, J.C.; Oosterling, S.; Burger, P.; Aukema, T.; Vogten, T.; Dokter, S.; Beets-Tan, R.; et al. LBA31 Neoadjuvant nivolumab plus relatlimab (anti-LAG3) in locally advanced MMR-deficient colon cancers: The NICHE-3 study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Jin, Y.; Guan, W.-L.; Zhang, R.-X.; Xiao, W.-W.; Cai, P.-Q.; Liu, M.; Lin, J.-Z.; Wang, F.-L.; Li, C.; et al. Neoadjuvant PD-1 blockade with sintilimab in mismatch-repair deficient, locally advanced rectal cancer: An open-label, single-centre phase 2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludford, K.; Ho, W.J.; Thomas, J.V.; Raghav, K.P.S.; Murphy, M.B.; Fleming, N.D.; Lee, M.S.; Smaglo, B.G.; You, Y.N.; Tillman, M.M.; et al. Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab in Localized Microsatellite Instability High/Deficient Mismatch Repair Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2181–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasi, P.M.; Jafari, M.D.; Yeo, H.; Lowenfeld, L.; Khan, U.; Nguyen, A.; Siolas, D.; Swed, B.; Khan, S.; Wood, M.; et al. Neoadjuvant botensilimab plus balstilimab in resectable mismatch repair proficient and deficient colorectal cancer: NEST-1 clinical trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S3), 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papke, D.J.; Yurgelun, M.B.; Noffsinger, A.E.; Turner, K.O.; Genta, R.M.; Redston, M. Prevalence of Mismatch-Repair Deficiency in Rectal Adenocarcinomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1714–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchini, C.; Bibeau, F.; Ligtenberg, M.J.L.; Singh, N.; Nottegar, A.; Bosse, T.; Miller, R.; Riaz, N.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Andre, F.; et al. ESMO recommendations on microsatellite instability testing for immunotherapy in cancer, and its relationship with PD-1/PD-L1 expression and tumour mutational burden: A systematic review-based approach. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1232–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalabi, M.; Fanchi, L.F.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Van Den Berg, J.G.; Aalbers, A.G.; Sikorska, K.; Lopez-Yurda, M.; Grootscholten, C.; Beets, G.L.; Snaebjornsson, P.; et al. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy leads to pathological responses in MMR-proficient and MMR-deficient early-stage colon cancers. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, H.; Tsukada, Y.; Ito, M.; Yoshino, T. Novel Immunological Approaches in the Treatment of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2022, 21, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Luo, H.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, R.; Chen, G. Total neoadjuvant treatment and PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitor in locally advanced rectal cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1149122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev-Kumar, G.; Pitroda, S.P. Synergizing radiotherapy and immunotherapy: Current challenges and strategies for optimization. Neoplasia 2023, 36, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, G.-A.; Weickhardt, A.; Azad, A.A.; Solomon, B.; Siva, S. Radiotherapy and immunotherapy: A synergistic effect in cancer care. Med. J. Aust. 2019, 210, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derer, A.; Frey, B.; Fietkau, R.; Gaipl, U.S. Immune-modulating properties of ionizing radiation: Rationale for the treatment of cancer by combination radiotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Kurata, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; De Wit, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtness, B.; Harrington, K.J.; Greil, R.; Soulières, D.; Tahara, M.; De Castro, G.; Psyrri, A.; Basté, N.; Neupane, P.; Bratland, Å.; et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2019, 394, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes with Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with PD-L1 Tumor Proportion Score ≥ 50%. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-M.; Shen, L.; Shah, M.A.; Enzinger, P.; Adenis, A.; Doi, T.; Kojima, T.; Metges, J.-P.; Li, Z.; Kim, S.-B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 2021, 398, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Shitara, K.; Moehler, M.; Garrido, M.; Salman, P.; Shen, L.; Wyrwicz, L.; Yamaguchi, K.; Skoczylas, T.; Campos Bragagnoli, A.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, P.G.; McMillan, D.C.; Park, J.H. A meta-analysis of CD274 (PD-L1) assessment and prognosis in colorectal cancer and its role in predicting response to anti-PD-1 therapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Meng, X.; Kong, L.; Mu, D.; Zhu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, forkhead box P3, programmed death ligand-1, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte–associated antigen-4 expressions before and after neoadjuvant chemoradiation in rectal cancer. Transl. Res. 2015, 166, 721–732.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigusa, S.; Toiyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Mori, K.; Ide, S.; Imaoka, H.; Kawamura, M.; Mohri, Y.; Kusunoki, M. Implication of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in tumor recurrence and prognosis in rectal cancer with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 21, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, M.; Büttner-Herold, M.; Erlenbach-Wünsch, K.; Haderlein, M.; Croner, R.; Grützmann, R.; Hartmann, A.; Fietkau, R.; Distel, L.V. PD-L1 is upregulated by radiochemotherapy in rectal adenocarcinoma patients and associated with a favourable prognosis. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 65, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomrich, G.; Silberhumer, G.R.; Marian, B.; Beer, A.; Müllauer, L. Programmed death-ligand 1 expression in rectal cancer. Eur. Surg. 2016, 48, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Richter, I.; Jirasek, T.; Dvorak, J.; Cermakova, E.; Rehakova, P.; Bartos, J. The prognostic effect of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy on the change of PD-L1 expression in patients with locally advanced rectal adenocarcinoma. J. BUON Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2017, 22, 875–881. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Peng, Q.; Du, K.; He, J.; Dong, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, J.; Wu, J. Tumor cell PD-L1 predicts poor local control for rectal cancer patients following neoadjuvant radiotherapy. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Chiang, S.F.; Chen, T.L.W.; Ke, T.W.; Chen, T.W.; You, Y.S.; Chao, K.S.C. Upregulation of Tumor PD-L1 by NeoCRT May Hold the Key to Successes in Patients with pN + Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 99, S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Koh, J.; Kim, S.; Jeon, S.-R.; Chie, E.K.; Kim, K.; Kang, G.H.; Han, S.-W.; Kim, T.-Y.; Jeong, S.-Y.; et al. Chemoradiation-Induced Alteration of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 and CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Identified Patients with Poor Prognosis in Rectal Cancer: A Matched Comparison Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 99, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, A.; Akiyoshi, T.; Yamamoto, N.; Kawachi, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Mori, S.; Oba, K.; Nagino, M.; Fukunaga, Y.; Ueno, M. Pattern of programmed cell death-ligand 1 expression and CD8-positive T-cell infiltration before and after chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 91, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Nakagawa, A.; Tanaka, T.; Arimoto, A.; Fukuoka, E.; Sugita, Y.; Mukohyama, J.; Dalerba, P.; Hasegawa, H.; Matsuda, T.; et al. Abstract 4572: The induction of PD-L1 positive immune cells and CD8-positive T lymphocytes by neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78 (Suppl. S13), 4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.-F.; Huang, C.-Y.; Ke, T.-W.; Chen, T.-W.; Lan, Y.-C.; You, Y.-S.; Chen, W.T.-L.; Chao, K.S.C. Upregulation of tumor PD-L1 by neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (neoCRT) confers improved survival in patients with lymph node metastasis of locally advanced rectal cancers. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.U.; Jeong, W.K.; Baek, S.K. Impact of microsatellite instability status and programmed deathligand 1 expression on tumor response after neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Society of Surgical Oncology 72nd Annual Cancer Symposium, 2019. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26 (Suppl. S1, Abstract GPP17), S207–S208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustani, J.; Derangère, V.; Bertaut, A.; Adotevi, O.; Morgand, V.; Charon-Barra, C.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Mirjolet, C. Radiotherapy Scheme Effect on PD-L1 Expression for Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, F.; Klieser, E.; Neureiter, D.; Schlintl, V.; Rinnerthaler, G.; Pagès, F.; Kirilovsky, A.; El Sissy, C.; Iglseder, W.; Singhartinger, F.; et al. Impact of PD-L1 Scores and Changes on Clinical Outcome in Rectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, G.; Zheng, L.; Liu, L. Programmed death-ligand 1 and mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in locally advanced rectal cancer. Discov. Oncol. 2022, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Hashimura, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Yokoi, A.; Nakagawa, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Ito, T.; Ohhigata, K.; Saegusa, M. A combination of stromal PD-L1 and tumoral nuclear β-catenin expression as an indicator of colorectal carcinoma progression and resistance to chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal carcinoma. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2022, 8, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Koh, J.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.; Chie, E.K. Prognostic stratification based on the levels of tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells and PD-1/PD-L1 axis in locally advanced rectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1018700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baretti, M.; Zhu, Q.; Fu, W.; Meyer, J.; Wang, H.; Anders, R.A.; Azad, N.S. Chemoradiation-induced alteration of programmed death-ligand 1, CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and mucin expression in rectal cancer. Oncotarget 2022, 13, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, C.; Zhang, N.; Corigliano, E.; Jansson, M.; Toland, G.; Ponto, G.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Emancipator, K.; Stanforth, D.; Kulangara, K. Development of a Companion Diagnostic PD-L1 Immunohistochemistry Assay for Pembrolizumab Therapy in Non–Small-cell Lung Cancer. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2016, 24, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennapusa, B.; Baker, B.; Kowanetz, M.; Boone, J.; Menzl, I.; Bruey, J.-M.; Fine, G.; Mariathasan, S.; McCaffery, I.; Mocci, S.; et al. Development of a PD-L1 Complementary Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry Assay (SP142) for Atezolizumab. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2019, 27, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulangara, K.; Zhang, N.; Corigliano, E.; Guerrero, L.; Waldroup, S.; Jaiswal, D.; Ms, M.J.; Shah, S.; Hanks, D.; Wang, J.; et al. Clinical Utility of the Combined Positive Score for Programmed Death Ligand-1 Expression and the Approval of Pembrolizumab for Treatment of Gastric Cancer. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K.; Stadler, Z.K.; Cercek, A.; Mendelsohn, R.B.; Shia, J.; Segal, N.H.; Diaz, L.A. Immunotherapy in colorectal cancer: Rationale, challenges and potential. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.-S.; Liao, I.-C.; Lin, P.-C.; Wu, S.-Y.; Kang, J.-W.; Lin, B.-W.; Chen, P.-C.; Chan, R.-H.; Lee, C.-T.; Shen, M.-R.; et al. PD-L1 Expression in High-Risk Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer—Its Clinical and Biological Significance in Immune Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, D.; Zaharia, C.; Søreide, K. Programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) clone 22C3 expression in resected colorectal cancer as companion diagnostics for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A comparison study and inter-rater agreement evaluation across proposed cut-offs and predictive (TPS, CPS and IC) scores. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2024, 38, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, S.-J.; Chen, J.; Lu, S.-X.; Fan, X.-J.; Tong, J.H.-M.; Chow, C.; Tin, E.K.-Y.; Chan, S.L.; Chong, C.C.-N.; et al. A comparability study of immunohistochemical assays for PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1646–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, E.A.; Sanzari, J.K.; Pandya, D.; Huron, D.; Edwards, R. Analytical Concordance of PD-L1 Assays Utilizing Antibodies from FDA-Approved Diagnostics in Advanced Cancers: A Systematic Literature Review. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 953–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shilo, K.; Hopkins, C.; Joy, W.; Margerrison, A.; Wharton, K.; Parwani, A. Comparison of different monoclonal antibodies for detection of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in breast, colorectal and liver carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 1669. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-C.; Wu, M.-L.; Huang, K.-C.; Huang, I.-P.; Chung, Y.-L. The Effects of Neoadjuvant Treatment on the Tumor Microenvironment in Rectal Cancer: Implications for Immune Activation and Therapy Response. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2020, 19, e164–e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovedi, S.; Adlard, A.; Lipowska-Bhalla, G.; McKenna, C.; Jones, S.; Cheadle, E.; Stratford, I.; Poon, E.; Morrow, M.; Stewart, R.; et al. The anti-tumor immune response generated by radiation therapy may be limited by tumor cell adaptive resistance and can be circumvented by PD-L1 blockade. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2 (Suppl. S3), O9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- George, T.J.; Yothers, G.; Lee, J.J.; Jacobs, S.A.; Deutsch, M.; Allegra, C.J.; Wolmark, N. NSABP FR-2: Phase II study of durvalumab following neoadjuvant chemoRT in stage II-IV rectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S4), TPS727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, L.; Bensi, M.; Corallo, S.; Bergamo, F.; Pellegrini, I.; Rasola, C.; Borelli, B.; Tamburini, E.; Randon, G.; Galuppo, S.; et al. Phase II study of preoperative (PREOP) chemoradiotherapy (CTRT) plus avelumab (AVE) in patients (PTS) with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC): The AVANA study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S15), 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, H.; Tsukada, Y.; Inamori, K.; Togashi, Y.; Koyama, S.; Kotani, D.; Fukuoka, S.; Yuki, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Homma, S.; et al. Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy plus Nivolumab before Surgery in Patients with Microsatellite Stable and Microsatellite Instability–High Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseddine, A.; Zeidan, Y.H.; El Husseini, Z.; Kreidieh, M.; Al Darazi, M.; Turfa, R.; Kattan, J.; Khalifeh, I.; Mukherji, D.; Temraz, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety-in analysis of short-course radiation followed by mFOLFOX-6 plus avelumab for locally advanced rectal adenocarcinoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, P.; Li, G.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; Cai, K.; Nie, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; et al. Phase II, single-arm trial of preoperative short-course radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy and camrelizumab in locally advanced rectal cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, E.; Zingaretti, C.; Petracci, E.; Corbelli, J.; Papiani, G.; Banchelli, I.; Valli, I.; Frassineti, G.L.; Passardi, A.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; et al. Phase II study of capecitabine-based concomitant chemoradiation followed by durvalumab as a neoadjuvant strategy in locally advanced rectal cancer: The PANDORA trial. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 101824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.J.; Yothers, G.; Rahma, O.E.; Hong, T.S.; Russell, M.M.; You, Y.N.; Parker, W.; Jacobs, S.A.; Lucas, P.C.; Colangelo, L.H.; et al. Long-term results from NRG-GI002: A phase II clinical trial platform using total neoadjuvant therapy (TNT) in locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S4), 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Yang, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, G.; Wei, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Xu, R.; et al. Safety and efficacy evaluation of long course neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus tislelizumab followed by total mesorectal excision for locally advanced rectal cancer: Short-term results of a multicenter, phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), e15599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, Y.; Bando, H.; Inamori, K.; Wakabayashi, M.; Togashi, Y.; Koyama, S.; Kotani, D.; Yuki, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Homma, S.; et al. Survival outcomes and functional results of VOLTAGE-A: Preoperative chemoradiotherapy (CRT) and consolidation nivolumab (nivo) in patients (pts) with both microsatellite stable (MSS) and microsatellite instability–high (MSI-H) locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S4), 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tao, K.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Yin, Y.; Chi, P.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xu, X.; et al. LBA25 Neoadjuvant short-course radiotherapy followed by camrelizumab plus chemotherapy versus long-course chemoradiotherapy followed by chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer: A randomized phase III trial (UNION). Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1266–S1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Montalvo-Ortiz, W.; Yu, L.; Krasco, A.; Ebstein, S.; Cortez, C.; Lowy, I.; Murphy, A.J.; Sleeman, M.A.; Skokos, D. Sequence of αPD-1 relative to local tumor irradiation determines the induction of abscopal antitumor immune responses. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabg0117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Kim, J.E.; Hong, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Ryu, Y.-M.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, T.W. Comprehensive evaluation of the tumor immune microenvironment and its dynamic changes in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer treated with preoperative chemoradiotherapy: From the phase II ADORE study. OncoImmunology 2022, 11, 2148374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abstracts from the 47th Sir Peter Freyer Surgical Symposium 2022. Ir. J. Med. Sci. (1971-) 2022, 191, 187–237. [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.-L.; Chou, T.-Y.; Yang, S.-H.; Jiang, J.-K.; Chen, W.-S.; Chao, Y.; Teng, H.-W. PD-L1 is a double-edged sword in colorectal cancer: The prognostic value of PD-L1 depends on the cell type expressing PD-L1. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.B.; Yao, H.; Li, C.S.; Liang, L.X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.-Y.; Xu, J. Rise of PD-L1 expression during metastasis of colorectal cancer: Implications for immunotherapy. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 18, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayshetye, P.; Friday, A.J.; Omstead, A.N.; Verma, T.; Miller, S.; Zheng, P.; Jani, P.; Zaidi, A.; Finley, G. Tumor Microenvironment before and after Chemoradiation in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer: Beyond PD-L1. Cancers 2022, 15, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patients | 100% (83) | Patients | 100% (83) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Preoperative treatment | ||
| Male | 50.6% (42) | No | 12% (10) |
| Female | 49.4% (41) | Yes | 88% (73) |
| Age | Type of preoperative treatment | ||
| Median | 63 (30–98) | Radiotherapy | 66.3% (55) |
| <70 | 68.7% (57) | TNT | 19.3% (16) |
| ≥70 | 31.3% (26) | Chemotherapy | 2.4% (2) |
| cT stage | Type of radiotherapy | ||
| Ct1 | 1.2% (1) | SCRT | 16.9% (14) |
| cT2 | 10.8% (9) | LC-CRT | 65.1% (54) |
| cT3 | 72.3% (60) | LC-RT | 3.6% (3) |
| cT4 | 10.8% (9) | NA | 14.5% (12) |
| NA | 4.8% (4) | Type of chemotherapy (for TNT-treated pts) | |
| cN stage | Induction | 4.8% (4) | |
| cN0 | 19.3% (16) | Consolidation | 14.5% (12) |
| cN1 | 75.9% (63) | ||
| NA | 4.8% (4) | ||
| cM stage | |||
| cM0 | 86.7% (72) | ||
| cM1 | 13.3% (11) | ||
| Tumour differentiation | |||
| G1 | 22.9% (19) | ||
| G2 | 56.6% (47) | ||
| G3 | 3.6% (3) | ||
| NA | 16.9% (14) | ||
| Tumour location | |||
| Low | 37.3% (31) | ||
| Mid | 42.2% (35) | ||
| High | 20.5% (17) | ||
| PD-L1 Expression from Biopsy to Resection Specimens | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPS | ICS | CPS | |||||||
| Decreased | Stable | Increased | Decreased | Stable | Increased | Decreased | Stable | Increased | |
| Neoadjuvant treatment | |||||||||
| No | 22.2% (2) | 77.8% (7) | 0% (0) | 40% (4) | 40% (4) | 20% (2) | 55.6% (5) | 33.3% (3) | 11.1% (1) |
| Yes | 14.8% (8) | 79.6% (43) | 5.6% (3) | 41.1% (30) | 28.8% (21) | 30.1% (22) | 31.5% (17) | 40.7% (22) | 27.8% (15) |
| p value * | 0.63 | - | 1.00 | 1.00 | - | 0.72 | 0.26 | - | 0.43 |
| Type of neoadjuvant treatment | |||||||||
| TNT | 11.1% (1) | 88.9% (8) | 0% (0) | 31.2% (5) | 37.5% (6) | 31.2% (5) | 22.2% (2) | 33.4% (3) | 44.4% (4) |
| LC-CRT/LC-RT | 15.6% (7) | 77.8% (35) | 6.6% (3) | 45.5% (25) | 25.4% (14) | 29.1% (16) | 32.6% (14) | 44.2% (19) | 23.2% (10) |
| p value * | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | 0.39 | - | 1.00 | 0.70 | - | 0.23 |
| Type of radiotherapy | |||||||||
| SCRT | 11.1% (1) | 88.9% (8) | 0% (0) | 14.3% (2) | 50% (7) | 35.7% (5) | 11.1% (1) | 66.7% (6) | 22.2% (2) |
| LC-CRT/LC-RT | 16.3% (7) | 76.7% (33) | 7% (3) | 49.1% (28) | 22.8% (13) | 28.1% (16) | 34.9% (15) | 37.2% (16) | 27.9% (12) |
| p value * | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | 0.03 | - | 0.74 | 0.24 | - | 1.00 |
| Dose of radiotherapy | |||||||||
| <50 Gy | 25% (5) | 75% (15) | 0% (0) | 48.2% (13) | 25.9% (7) | 25.9% (7) | 45% (9) | 40% (8) | 15% (3) |
| ≥50 Gy | 8.7% (2) | 78.3% (18) | 13% (3) | 50% (15) | 20% (6) | 30% (9) | 26.1% (6) | 34.8% (8) | 39.1% (9) |
| p value * | 0.22 | - | 0.24 | 1.00 | - | 0.78 | 0.22 | - | 0.10 |
| Radiotherapy-to-surgery interval | |||||||||
| <2 months | 10% (2) | 80% (16) | 10% (2) | 37% (10) | 29.7% (8) | 33.3% (9) | 25% (5) | 55% (11) | 20% (4) |
| ≥2 months | 18.8% (6) | 78.1% (25) | 3.1% (1) | 45.4% (20) | 27.3% (12) | 27.3 (12) | 34.4% (11) | 34.4% (11) | 31.2% (10) |
| p value * | 0.46 | - | 0.55 | 0.62 | - | 0.60 | 0.55 | - | 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coussement, M.; Fazio, R.; Audisio, A.; El Khoury, R.; Abbassi, F.-Z.; Assaf, I.; Conti, C.; Gallio, C.; Benhima, N.; Bregni, G.; et al. PD-L1 Expression in Paired Samples of Rectal Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142606
Coussement M, Fazio R, Audisio A, El Khoury R, Abbassi F-Z, Assaf I, Conti C, Gallio C, Benhima N, Bregni G, et al. PD-L1 Expression in Paired Samples of Rectal Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(14):2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142606
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoussement, Mina, Roberta Fazio, Alessandro Audisio, Reem El Khoury, Fatima-Zahra Abbassi, Irene Assaf, Chiara Conti, Chiara Gallio, Nada Benhima, Giacomo Bregni, and et al. 2024. "PD-L1 Expression in Paired Samples of Rectal Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 14: 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142606
APA StyleCoussement, M., Fazio, R., Audisio, A., El Khoury, R., Abbassi, F.-Z., Assaf, I., Conti, C., Gallio, C., Benhima, N., Bregni, G., Gkolfakis, P., Spagnolo, V., Anthoine, G., Liberale, G., Moretti, L., Martinive, P., Hendlisz, A., Demetter, P., & Sclafani, F. (2024). PD-L1 Expression in Paired Samples of Rectal Cancer. Cancers, 16(14), 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16142606






