Vascular Biomarkers for Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy: Arteries vs. Veins
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. Differentiation and Quantification of Macro-Vascular Arteries and Veins
2.3. Nodule Features
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Integrative Prediction Modeling
2.6. Feature Importance Analysis
3. Results
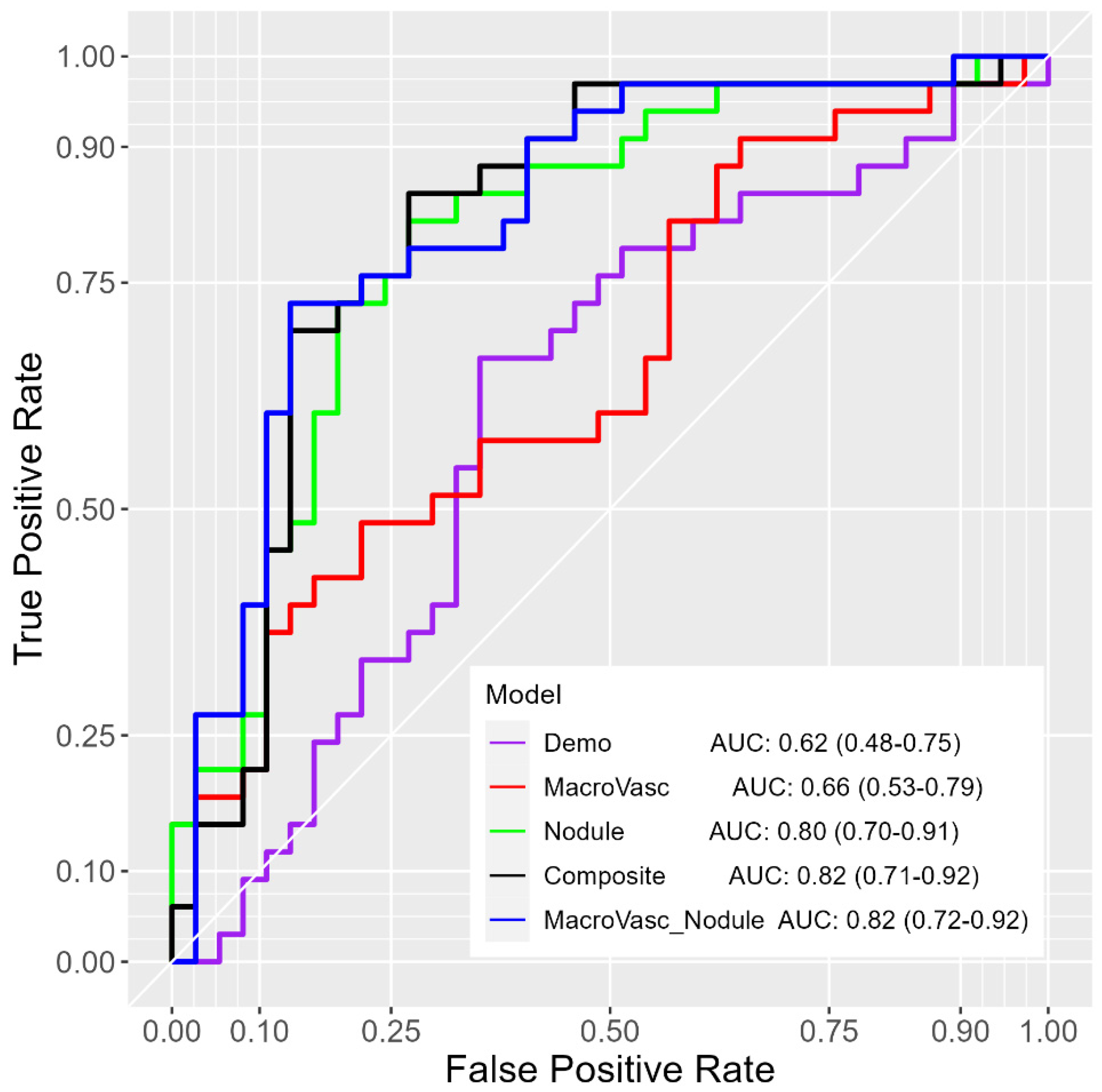
3.1. Performance on the All Nodule-Size Dataset
3.2. Performance on the 8–20 mm Nodule-Size Dataset
3.3. Feature Importance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| CI | confidence interval |
| LDCT | low-dose computed tomography |
| LASSO | least absolute shrinkage and selection operator |
| LR | logistic regression |
| PI | permutation importance |
| ROC-AUC | the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve |
| RF | random forest |
| VIF | variance inflation factor |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Low-Dose Computed Tomographic Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. The National Lung Screening Trial: Overview and Study Design. Radiology 2011, 258, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chudgar, N.P.; Bucciarelli, P.R.; Jeffries, E.M.; Rizk, N.P.; Park, B.J.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Jones, D.R. Results of the National Lung Cancer Screening Trial. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2015, 25, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thalanayar, P.M.; Altintas, N.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Fuhrman, C.R.; Wilson, D.O. Indolent Potentially Inconsequential Lung Cancers in the Pittsburgh Lung Screening Study (PLuSS). Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wei, Z.; Nie, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, F.; Chen, K. Comprehensive Analysis of Clinical Logistic and Machine Learning-Based Models for the Evaluation of Pulmonary Nodules. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 100299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loverdos, K.; Fotiadis, A.; Kontogianni, C.; Iliopoulou, M.; Gaga, M. Lung nodules: A comprehensive review on current approach and management. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2019, 14, 226. [Google Scholar]
- Way, T.W.; Sahiner, B.; Chan, H.P.; Hadjiiski, L.; Cascade, P.N.; Chughtai, A.; Bogot, N.; Kazerooni, E. Computer-aided diagnosis of pulmonary nodules on CT scans: Improvement of classification performance with nodule surface features. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 3086–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alilou, M.; Beig, N.; Orooji, M.; Rajiah, P.; Velcheti, V.; Rakshit, S.; Reddy, N.; Yang, M.; Jacono, F.; Gilkeson, R.C.; et al. An integrated segmentation and shape-based classification scheme for distinguishing adenocarcinomas from granulomas on lung CT. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 3556–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, A.P.; Xie, Y.; Jirapatnakul, A. Automated pulmonary nodule CT image characterization in lung cancer screening. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2016, 11, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perandini, S.; Soardi, G.A.; Motton, M.; Rossi, A.; Signorini, M.; Montemezzi, S. Solid pulmonary nodule risk assessment and decision analysis: Comparison of four prediction models in 285 cases. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3071–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gierada, D.S.; Politte, D.G.; Zheng, J.; Schechtman, K.B.; Whiting, B.R.; Smith, K.E.; Crabtree, T.; Kreisel, D.; Krupnick, A.S.; Patterson, G.A.; et al. Quantitative Computed Tomography Classification of Lung Nodules. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2016, 40, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armato III, S.G.; Drukker, K.; Li, F.; Hadjiiski, L.; Tourassi, G.D.; Engelmann, R.M.; Giger, M.L.; Redmond, G.; Farahani, K.; Kirby, J.S. LUNGx Challenge for computerized lung nodule classification. J. Med. Imaging 2016, 3, 044506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Hua, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J. Feature Selection and Performance Evaluation of Support Vector Machine (SVM)-Based Classifier for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Pulmonary Nodules by Computed Tomography. J. Digit. Imaging 2010, 23, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Litjens, G.; Gerke, P.; Jacobs, C.; Van Riel, S.J.; Wille, M.M.W.; Naqibullah, M.; Sanchez, C.I.; Van Ginneken, B. Pulmonary Nodule Detection in CT Images: False Positive Reduction Using Multi-View Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibali, A.; He, Z.; Wollersheim, D. Pulmonary nodule classification with deep residual networks. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, P.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J. Pulmonary Nodule Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks on Computed Tomography Images. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2016, 2016, 6215085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, Y.; Teramoto, A.; Tsujimoto, M.; Tsukamoto, T.; Saito, K.; Toyama, H.; Imaizumi, K.; Fujita, H. Automated Pulmonary Nodule Classification in Computed Tomography Images Using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network Trained by Generative Adversarial Networks. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6051939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Sugiyama, O.; Yakami, M.; Ueno, S.; Kubo, T.; Kuroda, T.; Togashi, K. Computer-aided diagnosis of lung nodule classification between benign nodule, primary lung cancer, and metastatic lung cancer at different image size using deep convolutional neural network with transfer learning. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Leader, J.K.; Wang, R.; Wilson, D.; Herman, J.; Yuan, J.-M.; Pu, J. Vasculature surrounding a nodule: A novel lung cancer biomarker. Lung Cancer 2017, 114, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, H.; Leader, J.K.; Wilson, D.; Meng, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.A.; Pu, J. Computerized identification of the vasculature surrounding a pulmonary nodule. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2019, 74, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Leader, J.K.; Sechrist, J.; Beeche, C.A.; Singh, J.P.; Ocak, I.K.; Risbano, M.G. Automated identification of pulmonary arteries and veins depicted in non-contrast chest CT scans. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 77, 102367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, J.; Paik, D.S.; Meng, X.; Roos, J.E.; Rubin, G.D. Shape “break-and-repair” strategy and its application to automated medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2011, 17, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, S.F.; Yin, K.; Meng, C.X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Pu, J.; Dhupar, R. Predicting benign, preinvasive, and invasive lung nodules on computed tomography scans using machine learning. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 163, 1496–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman Professor, D.A.; Freedman Professor, D.A. A Note on Screening Regression Equations. Am. Stat. 1983, 37, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, A.; Toloşi, L.; Sander, O.; Lengauer, T. Permutation importance: A corrected feature importance measure. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Joachims, T. Making Large-Scale SVM Learning Practical; Technical Report; Universität Dortmund: Dortmund, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatt, U.; Xiang, A.; Sharma, S.; Weller, A.; Taly, A.; Jia, Y.; Ghosh, J.; Puri, R.; Moura, J.M.F.; Eckersley, P. Explainable machine learning in deployment. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparen, Barcelona, Spain, 27–30 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Saarela, M.; Jauhiainen, S. Comparison of feature importance measures as explanations for classification models. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, L.; Wagner, E.M. Angiogenesis in the lung. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelkel, N.F.; Gomez-Arroyo, J. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in pulmonary arterial hypertension. The angiogenesis paradox. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeckx, A.; Reyntiens, P.; Desbuquoit, D.; Spinhoven, M.J.; Van Schil, P.E.; Van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Parizel, P.M. Evaluation of the solitary pulmonary nodule: Size matters, but do not ignore the power of morphology. Insights Into Imaging 2018, 9, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larici, A.R.; Farchione, A.; Franchi, P.; Ciliberto, M.; Cicchetti, G.; Calandriello, L.; Del Ciello, A.; Bonomo, L. Lung nodules: Size still matters. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, H.J.; Ravenel, J.G.; Shaftman, S.R.; Tanner, N.T.; Paoletti, L.; Taylor, K.K.; Tammemagi, M.C.; Gomez, M.; Nietert, P.J.; Gould, M.K.; et al. The Utility of Nodule Volume in the Context of Malignancy Prediction for Small Pulmonary Nodules. Chest 2014, 145, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Benegas, M.; Vollmer, I. Management of incidental lung nodules <8 mm in diameter. J. Thorac. Dis. 2611. [Google Scholar]
- Gould, M.K.; Donington, J.; Lynch, W.R.; Mazzone, P.J.; Midthun, D.E.; Naidich, D.P.; Wiener, R.S. Evaluation of Individuals With Pulmonary Nodules: When Is It Lung Cancer? Chest 2013, 143, e93S–e120S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, N.T.; Aggarwal, J.; Gould, M.K.; Kearney, P.; Diette, G.; Vachani, A.; Fang, K.C.; Silvestri, G.A. Management of Pulmonary Nodules by Community Pulmonologists. Chest 2015, 148, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dong, J.; Sun, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, F.; Wang, L.; Jiao, Y. Obesity and incidence of lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, H.; Zhou, S.; Wang, D.; Zhu, L.; Hou, J.; Tang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, S. Body mass index and mortality in lung cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, L.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Cheruvu, K.; Krabak, C.; Rachala, R.; Ratnakaram, K.; Sharma, P.; Singh, M.; Yendamuri, S. Exploring the Impact of the Obesity Paradox on Lung Cancer and Other Malignancies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | Malignant (n = 67) | Benign (n = 79) | Coefficient (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age (year) | 63.13 (5.97) | 66.11 (4.65) | −0.12 (−1.20, −0.04) | 0.003 | |
| gender | |||||
| Male | 36 | 48 | −0.29 (−0.95, 0.36) | 0.382 | |
| Female | 31 | 31 | |||
| smoking status | |||||
| Former | 43 | 51 | −0.03 (−0.71, 0.65) | 0.933 | |
| Current | 24 | 28 | |||
| pack (year) | 45.62 (24.58) | 50.33 (21.56) | −0.01 (−0.03, 0.01) | 0.145 | |
| BMI | 26.58 (4.14) | 28.57 (4.71) | −0.10 (−0.19, −0.02) | 0.011 | |
| Variable | Malignant | Benign | Coefficient (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artery | ||||
| artery5_count | 5.39 (4.35) | 1.67 (2.18) | 0.38 (0.24, 0.53) | 0.000 |
| artery5_volume | 0.34 (0.61) | 0.08 (0.13) | 4.38 (2.16, 6.61) | <0.001 |
| artery5_tortuosity | 1.06 (0.08) | 1.04 (0.16) | 1.88 (−1.22, 4.99) | 0.234 |
| artery10_count | 10.68 (9.67) | 4.86 (4.61) | 0.12 (0.06, 0.18) | <0.0001 |
| artery10_volume | 0.85 (1.21) | 0.28 (0.36) | 1.51 (0.71, 2.32) | <0.001 |
| artery10_tortuosity | 1.07 (0.07) | 1.06 (0.15) | 0.67 (−2.13, 3.47) | 0.640 |
| artery15_count | 18.70 (18.26) | 11.51 (10.78) | 0.04 (0.01, 0.06) | 0.006 |
| artery15_volume | 1.68 (2.14) | 0.74 (0.89) | 0.55 (0.20, 0.89) | 0.002 |
| artery15_tortuosity | 1.08(0.07) | 1.06 (0.14) | 1.58 (−2.02, 5.17) | 0.390 |
| Vein | ||||
| vein5_count | 5.38 (4.08) | 2.17 (3.24) | 0.27 (0.15, 0.39) | <0.0001 |
| vein5_volume | 0.33 (0.40) | 0.09 (0.14) | 4.46 (2.29, 6.64) | <0.0001 |
| vein5_tortuosity | 1.06 (0.08) | 1.04 (0.14) | 2.66 (−1.23, 6.55) | 0.181 |
| vein10_count | 10.09 (9.10) | 4.85 (5.75) | 0.11 (0.05, 0.17) | <0.001 |
| vein10_volume | 0.80 (0.78) | 0.27 (0.32) | 1.96 (1.07, 2.85) | <0.0001 |
| vein10_tortuosity | 1.06 (0.05) | 1.04 (0.14) | 2.60 (−2.09, 7.28) | 0.277 |
| vein10_count | 16.77 (16.01) | 9.63 (8.91) | 0.05 (0.02, 0.08) | 0.003 |
| vein10_volume | 1.51 (1.35) | 0.62 (0.62) | 1.02 (0.55, 1.49) | <0.0001 |
| vein10_tortuosity | 1.06 (0.04) | 1.05 (0.14) | 1.54 (−2.45, 5.54) | 0.449 |
| 5 mm distance | |||
| Variable | Artery5 | Vein5 | Vessel5 |
| artery5_count | 1.47 | 1.47 | |
| vein5_count | 0.60 | ||
| vein5_volume | 0.70 | ||
| AUC | 0.78 (0.71–0.86) | 0.77 (0.69–0.85) | 0.78 (0.71–0.86) |
| Accuracy | 0.70 (0.62, 0.77) | 0.68 (0.59, 0.75) | 0.70 (0.62, 0.77) |
| 10 mm distance | |||
| Variable | Artery10 | Vein10 | Vessel10 |
| artery10_count | 0.54 | ||
| artery5_volume | 0.67 | ||
| vein10_count | 1.24 | 1.24 | |
| AUC | 0.68 (0.60–0.77) | 0.71 (0.62–0.80) | 0.71 (0.62–0.80) |
| Accuracy | 0.67 (0.59, 0.74) | 0.68 (0.60, 0.76) | 0.68 (0.60, 0.76) |
| 15 mm distance | |||
| Variable | Artery15 | Vein15 | Vessel15 |
| artery15_volume | 0.91 | ||
| vein15_volume | 1.13 | 1.13 | |
| AUC | 0.67 (0.58–0.76) | 0.71 (0.63–0.80) | 0.71 (0.63–0.80) |
| Accuracy | 0.64 (0.56, 0.72) | 0.71 (0.63, 0.78) | 0.71 (0.63, 0.78) |
| All distances (5, 10, 15 mm) | |||
| Variable | Artery | Vein | Vessel |
| artery5_count | 1.47 | 1.47 | |
| vein5_count | 0.60 | ||
| vein5_volume | 0.70 | ||
| AUC | 0.78 (0.71–0.86) | 0.77 (0.69–0.85) | 0.78 (0.71–0.86) |
| Accuracy | 0.70 (0.62, 0.77) | 0.68 (0.59, 0.75) | 0.70 (0.62, 0.77) |
| Model | Variables Included | Coefficient | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | age | −0.59 | 0.64 (0.55, 0.71) | |
| BMI | −0.40 | |||
| Macro-vasculature | artery5_count | 1.47 | 0.70 (0.62, 0.77) | |
| CT-derived nodule | tumor_surface_area | 3.20 | 0.80 (0.73, 0.86) | |
| tumor_ground_glass_ratio | 0.22 | |||
| tumor_cavitiy_ratio | −0.48 | |||
| tumor_fat_ratio | −0.04 | |||
| tumor_cal_volume | −0.07 | |||
| Macro-vasculature + demographics | Demographics | pack/year | −0.72 | 0.78 (0.70, 0.84) |
| Macro-vasculature | artery5_count | 3.39 | ||
| artery15_count | −1.39 | |||
| vein15_count | −0.36 | |||
| Macro-vasculature + CT-derived nodule | Macro-vasculature | artery5_count | 1.42 | 0.84 (0.78, 0.90) |
| artery15_count | −1.01 | |||
| CT-derived nodule | tumor_cavitiy_ratio | −0.59 | ||
| tumor_density | −0.35 | |||
| tumor_irregularity | 0.03 | |||
| tumor_mean_diameter | 2.63 | |||
| Composite | Demographics | age | −0.41 | 0.87 (0.81, 0.92) |
| pack/year | −0.49 | |||
| BMI | −0.27 | |||
| Macro-vasculature | artery5_count | 0.86 | ||
| CT-derived nodule | tumor_cavitiy_ratio | −0.61 | ||
| tumor_mean_diameter | 2.17 | |||
| Variable | Artery | Vessel | Vessel5/Artery5 |
|---|---|---|---|
| artery5_count | 1.60 | 1.45 | 0.50 |
| artery15_count | −1.31 | −1.41 | |
| vein10_volume | 0.32 | ||
| AUC | 0.67 (0.54, 0.80) | 0.66 (0.53, 0.79) | 0.57 (0.43, 0.71) |
| Accuracy | 0.59 (0.46, 0.70) | 0.60 (0.48, 0.72) | 0.56 (0.43, 0.68) |
| Model | Variables Included | Coefficient | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | age | −0.33 | 0.60 (0.48, 0.72) | |
| pack/year | −0.42 | |||
| BMI | −0.34 | |||
| Macro-vasculature | artery5_count | 1.45 | 0.60 (0.48, 0.72) | |
| artery15_count | −1.41 | |||
| vein10_count | 0.32 | |||
| CT-derived nodule | tumor_mean_diameter | 1.35 | 0.76 (0.64, 0.85) | |
| tumor_AgatstonCal | −0.54 | |||
| tumor_cavitiy_ratio | −0.67 | |||
| Macro-vasculature + demographics | Demographics | / | / | 0.60 (0.48, 0.72) |
| Macro-vasculature | artery5_count | 1.45 | ||
| artery15_count | −1.41 | |||
| vein10_count | 0.32 | |||
| Macro-vasculature + CT-derived nodule | Macro-vasculature | artery15_count | −0.81 | 0.77 (0.66, 0.86) |
| vein10_volume | 0.71 | |||
| CT-derived nodule | tumor_mean_diameter | 1.46 | ||
| tumor_cavitiy_ratio | −0.57 | |||
| Composite | Demographics | pack/year | −0.65 | 0.76 (0.64, 0.85) |
| Macro-vasculature | artery5_count | 0.62 | ||
| CT-derived nodule | tumor_mean_diameter | 1.02 | ||
| tumor_cavitiy_ratio | −0.79 | |||
| Nodule Size | Model | Features | PI Score | SHAP Score | Average Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | SVM | MLP | LR | SVM | MLP | ||||
| All-nodule-size | Macro-vasculature (3) | artery5_count | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| artery15_volume | 0.54 | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.90 | 0.31 | 0.39 | 0.56 | ||
| artery15_count | 0.34 | 0.23 | 0.43 | 0.68 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 0.42 | ||
| Composite | tumor_mean_diameter | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| artery5_count | 0.40 | 0.58 | 0.11 | 0.55 | 0.80 | 0.43 | 0.41 | ||
| tumor_cavitiy_ratio | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.17 | ||
| pack-years | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 0.51 | 0.10 | 0.15 | ||
| age | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.08 | ||
| BMI | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.03 | ||
| 8-20 mm-nodule-size | Macro-vasculature (3) | artery5_count | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.95 |
| vein5_volume | 0.67 | 0.82 | 0.86 | 0.29 | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.66 | ||
| artery5_volume | 0.85 | 0.45 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.66 | ||
| Composite | tumor_mean_diameter | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| pack-years | 0.28 | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.01 | 0.28 | ||
| artery5_count | 0.38 | 0.48 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.98 | 0.43 | 0.24 | ||
| tumor_cavitiy_ratio | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, T.; Zhao, X.; Leader, J.K.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Herman, J.; Wilson, D.; Pu, J. Vascular Biomarkers for Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy: Arteries vs. Veins. Cancers 2024, 16, 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193274
Yu T, Zhao X, Leader JK, Wang J, Meng X, Herman J, Wilson D, Pu J. Vascular Biomarkers for Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy: Arteries vs. Veins. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193274
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Tong, Xiaoyan Zhao, Joseph K. Leader, Jing Wang, Xin Meng, James Herman, David Wilson, and Jiantao Pu. 2024. "Vascular Biomarkers for Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy: Arteries vs. Veins" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193274
APA StyleYu, T., Zhao, X., Leader, J. K., Wang, J., Meng, X., Herman, J., Wilson, D., & Pu, J. (2024). Vascular Biomarkers for Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy: Arteries vs. Veins. Cancers, 16(19), 3274. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193274






